cdad6f9d2b851884783b67dbfe2cf884.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 50
 A Hierarchical System Design for detection of Glaucoma from Color Fundus Images Madhulika Jain, Jayanthi Sivaswamy IIIT Hyderabad CVIT, IIIT Hyderabad, India
A Hierarchical System Design for detection of Glaucoma from Color Fundus Images Madhulika Jain, Jayanthi Sivaswamy IIIT Hyderabad CVIT, IIIT Hyderabad, India
 What is glaucoma? Glaucoma is an eye disorder that causes irreversible loss of vision IIIT Hyderabad It affects the Optic Nerve in retina
What is glaucoma? Glaucoma is an eye disorder that causes irreversible loss of vision IIIT Hyderabad It affects the Optic Nerve in retina
 Why glaucoma detection needed? – Leading cause of blindness worldwide • In India – 2 nd leading cause of blindness • It is estimated to affect 79 million people in the world by the year 2020 – Prevalent in aging population § India alone hosts 20% of glaucoma cases – Irreversible loss of vision • Thus timely detection required – lack of manpower in terms of skilled technicians IIIT Hyderabad • Thus computer aided solutions for screening
Why glaucoma detection needed? – Leading cause of blindness worldwide • In India – 2 nd leading cause of blindness • It is estimated to affect 79 million people in the world by the year 2020 – Prevalent in aging population § India alone hosts 20% of glaucoma cases – Irreversible loss of vision • Thus timely detection required – lack of manpower in terms of skilled technicians IIIT Hyderabad • Thus computer aided solutions for screening
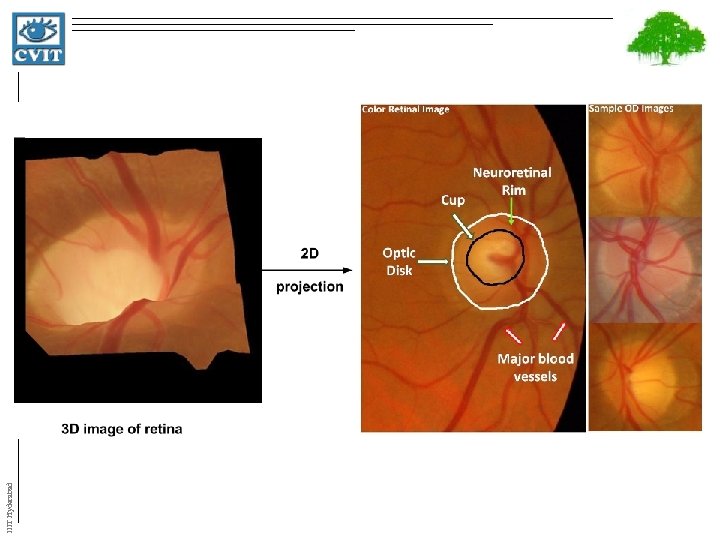
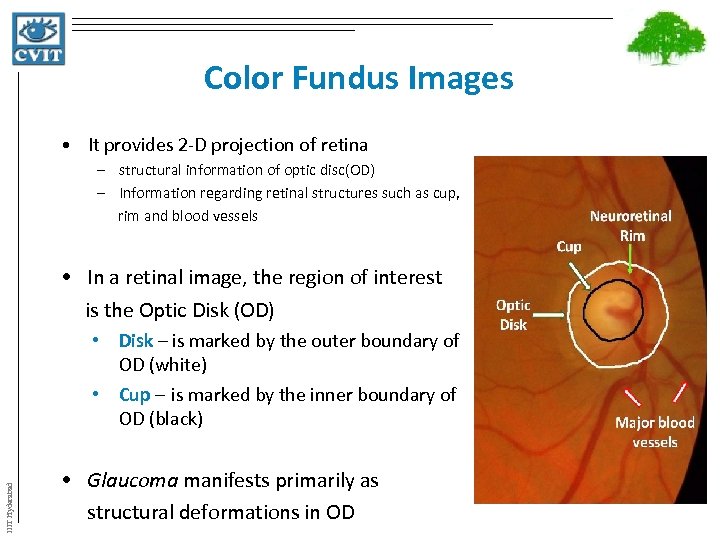 Color Fundus Images • It provides 2 -D projection of retina – structural information of optic disc(OD) – Information regarding retinal structures such as cup, rim and blood vessels • In a retinal image, the region of interest is the Optic Disk (OD) IIIT Hyderabad • Disk – is marked by the outer boundary of OD (white) • Cup – is marked by the inner boundary of OD (black) • Glaucoma manifests primarily as structural deformations in OD
Color Fundus Images • It provides 2 -D projection of retina – structural information of optic disc(OD) – Information regarding retinal structures such as cup, rim and blood vessels • In a retinal image, the region of interest is the Optic Disk (OD) IIIT Hyderabad • Disk – is marked by the outer boundary of OD (white) • Cup – is marked by the inner boundary of OD (black) • Glaucoma manifests primarily as structural deformations in OD
 Why color fundus images are used? IIIT Hyderabad low cost non-invasiveness ease of use higher penetrability to every section of society
Why color fundus images are used? IIIT Hyderabad low cost non-invasiveness ease of use higher penetrability to every section of society
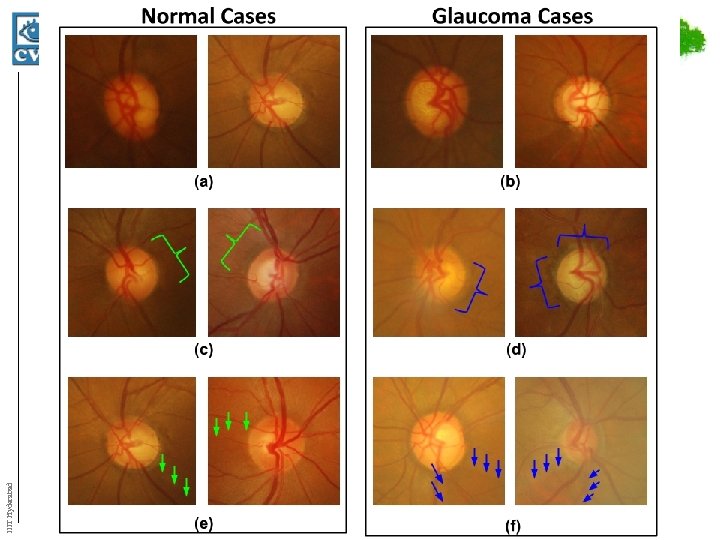
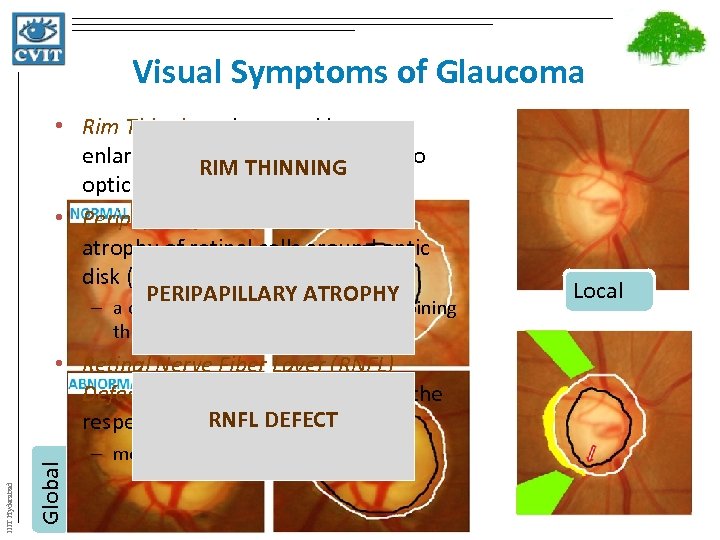 Visual Symptoms of Glaucoma • Rim Thinning – is caused by enlargement of cup with respect to RIM THINNING optic disk (arrow) • Peripapillary Atrophy (PPA) – is atrophy of retinal cells around optic disk (yellow) PERIPAPILLARY ATROPHY – a change in intensity is observed adjoining the disk boundary Global IIIT Hyderabad • Retinal Nerve Fiber Layer (RNFL) Defect – occurs due to the loss of the RNFL DEFECT respective layer in retina (green) – most subtle indicator of glaucoma Local
Visual Symptoms of Glaucoma • Rim Thinning – is caused by enlargement of cup with respect to RIM THINNING optic disk (arrow) • Peripapillary Atrophy (PPA) – is atrophy of retinal cells around optic disk (yellow) PERIPAPILLARY ATROPHY – a change in intensity is observed adjoining the disk boundary Global IIIT Hyderabad • Retinal Nerve Fiber Layer (RNFL) Defect – occurs due to the loss of the RNFL DEFECT respective layer in retina (green) – most subtle indicator of glaucoma Local
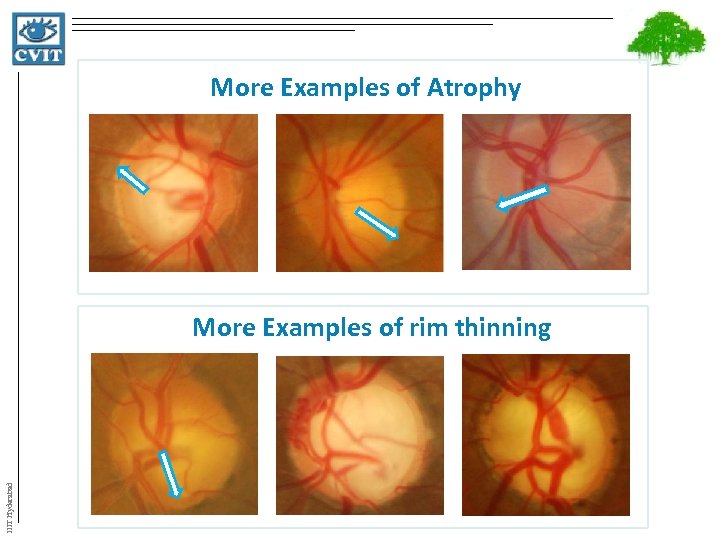 More Examples of Atrophy IIIT Hyderabad More Examples of rim thinning
More Examples of Atrophy IIIT Hyderabad More Examples of rim thinning
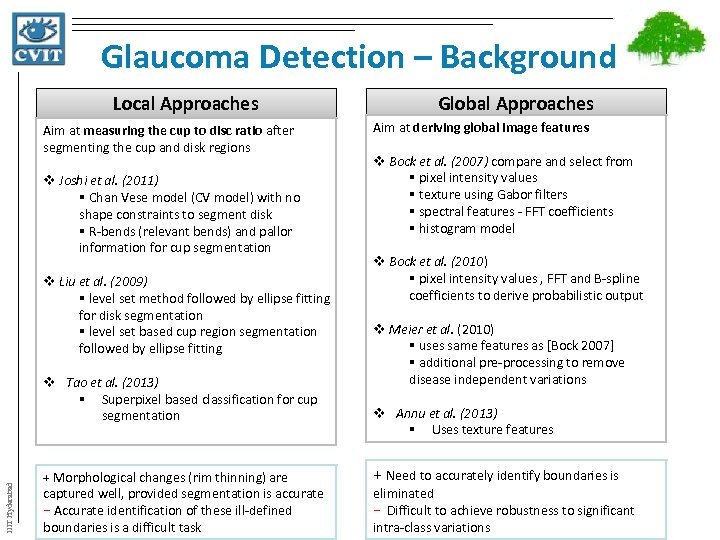 Glaucoma Detection – Background Local Approaches Aim at measuring the cup to disc ratio after segmenting the cup and disk regions v Joshi et al. (2011) § Chan Vese model (CV model) with no shape constraints to segment disk § R-bends (relevant bends) and pallor information for cup segmentation v Liu et al. (2009) § level set method followed by ellipse fitting for disk segmentation § level set based cup region segmentation followed by ellipse fitting IIIT Hyderabad v Tao et al. (2013) § Superpixel based classification for cup segmentation + Morphological changes (rim thinning) are captured well, provided segmentation is accurate − Accurate identification of these ill-defined boundaries is a difficult task Global Approaches Aim at deriving global image features v Bock et al. (2007) compare and select from § pixel intensity values § texture using Gabor filters § spectral features - FFT coefficients § histogram model v Bock et al. (2010) § pixel intensity values , FFT and B-spline coefficients to derive probabilistic output v Meier et al. (2010) § uses same features as [Bock 2007] § additional pre-processing to remove disease independent variations v Annu et al. (2013) § Uses texture features + Need to accurately identify boundaries is eliminated − Difficult to achieve robustness to significant intra-class variations
Glaucoma Detection – Background Local Approaches Aim at measuring the cup to disc ratio after segmenting the cup and disk regions v Joshi et al. (2011) § Chan Vese model (CV model) with no shape constraints to segment disk § R-bends (relevant bends) and pallor information for cup segmentation v Liu et al. (2009) § level set method followed by ellipse fitting for disk segmentation § level set based cup region segmentation followed by ellipse fitting IIIT Hyderabad v Tao et al. (2013) § Superpixel based classification for cup segmentation + Morphological changes (rim thinning) are captured well, provided segmentation is accurate − Accurate identification of these ill-defined boundaries is a difficult task Global Approaches Aim at deriving global image features v Bock et al. (2007) compare and select from § pixel intensity values § texture using Gabor filters § spectral features - FFT coefficients § histogram model v Bock et al. (2010) § pixel intensity values , FFT and B-spline coefficients to derive probabilistic output v Meier et al. (2010) § uses same features as [Bock 2007] § additional pre-processing to remove disease independent variations v Annu et al. (2013) § Uses texture features + Need to accurately identify boundaries is eliminated − Difficult to achieve robustness to significant intra-class variations
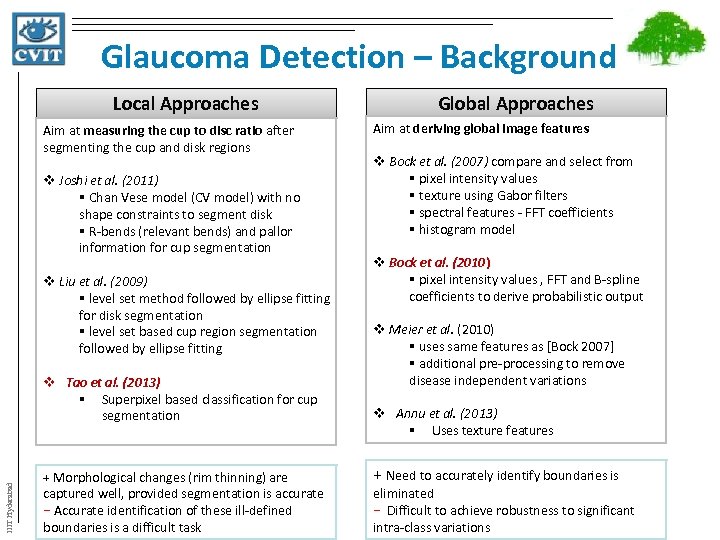 Glaucoma Detection – Background Local Approaches Aim at measuring the cup to disc ratio after segmenting the cup and disk regions v Joshi et al. (2011) § Chan Vese model (CV model) with no shape constraints to segment disk § R-bends (relevant bends) and pallor information for cup segmentation v Liu et al. (2009) § level set method followed by ellipse fitting for disk segmentation § level set based cup region segmentation followed by ellipse fitting IIIT Hyderabad v Tao et al. (2013) § Superpixel based classification for cup segmentation + Morphological changes (rim thinning) are captured well, provided segmentation is accurate − Accurate identification of these ill-defined boundaries is a difficult task Global Approaches Aim at deriving global image features v Bock et al. (2007) compare and select from § pixel intensity values § texture using Gabor filters § spectral features - FFT coefficients § histogram model v Bock et al. (2010) § pixel intensity values , FFT and B-spline coefficients to derive probabilistic output v Meier et al. (2010) § uses same features as [Bock 2007] § additional pre-processing to remove disease independent variations v Annu et al. (2013) § Uses texture features + Need to accurately identify boundaries is eliminated − Difficult to achieve robustness to significant intra-class variations
Glaucoma Detection – Background Local Approaches Aim at measuring the cup to disc ratio after segmenting the cup and disk regions v Joshi et al. (2011) § Chan Vese model (CV model) with no shape constraints to segment disk § R-bends (relevant bends) and pallor information for cup segmentation v Liu et al. (2009) § level set method followed by ellipse fitting for disk segmentation § level set based cup region segmentation followed by ellipse fitting IIIT Hyderabad v Tao et al. (2013) § Superpixel based classification for cup segmentation + Morphological changes (rim thinning) are captured well, provided segmentation is accurate − Accurate identification of these ill-defined boundaries is a difficult task Global Approaches Aim at deriving global image features v Bock et al. (2007) compare and select from § pixel intensity values § texture using Gabor filters § spectral features - FFT coefficients § histogram model v Bock et al. (2010) § pixel intensity values , FFT and B-spline coefficients to derive probabilistic output v Meier et al. (2010) § uses same features as [Bock 2007] § additional pre-processing to remove disease independent variations v Annu et al. (2013) § Uses texture features + Need to accurately identify boundaries is eliminated − Difficult to achieve robustness to significant intra-class variations
 Proposals Extending this global approach to the detection of atrophy Hierarchical system design using global analysis only IIIT Hyderabad Exploring global motion pattern based features for glaucoma detection Hierarchical system design using both global and local analysis
Proposals Extending this global approach to the detection of atrophy Hierarchical system design using global analysis only IIIT Hyderabad Exploring global motion pattern based features for glaucoma detection Hierarchical system design using both global and local analysis
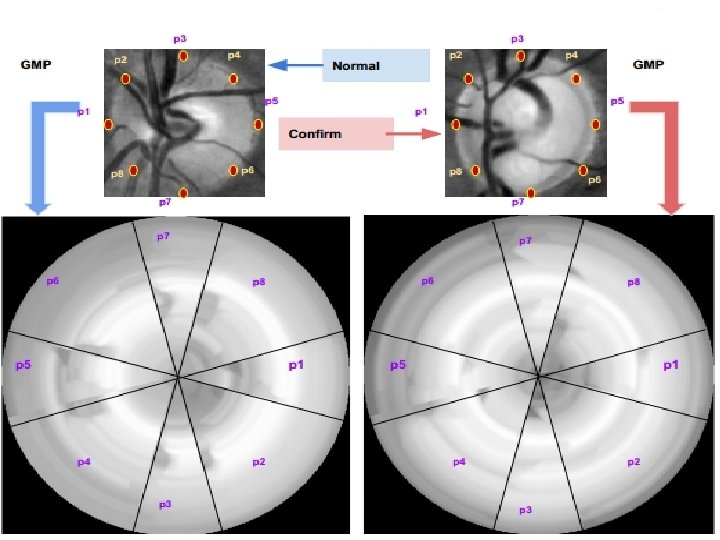
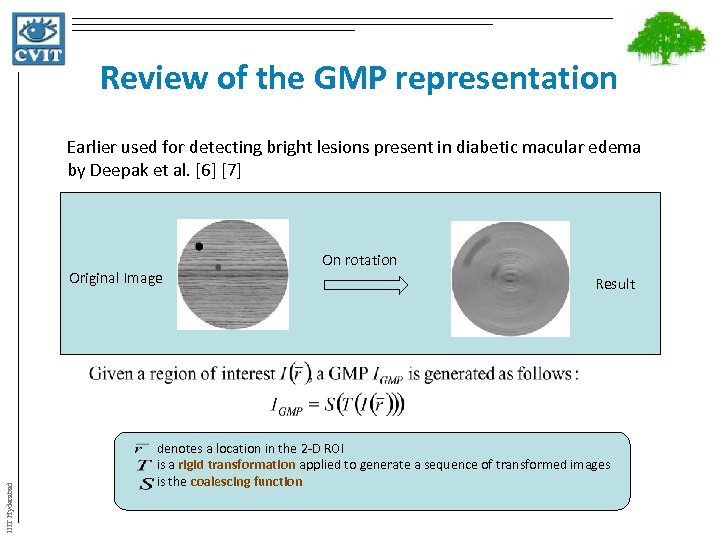 Review of the GMP representation Earlier used for detecting bright lesions present in diabetic macular edema by Deepak et al. [6] [7] IIIT Hyderabad Original Image On rotation Result denotes a location in the 2 -D ROI is a rigid transformation applied to generate a sequence of transformed images is the coalescing function
Review of the GMP representation Earlier used for detecting bright lesions present in diabetic macular edema by Deepak et al. [6] [7] IIIT Hyderabad Original Image On rotation Result denotes a location in the 2 -D ROI is a rigid transformation applied to generate a sequence of transformed images is the coalescing function
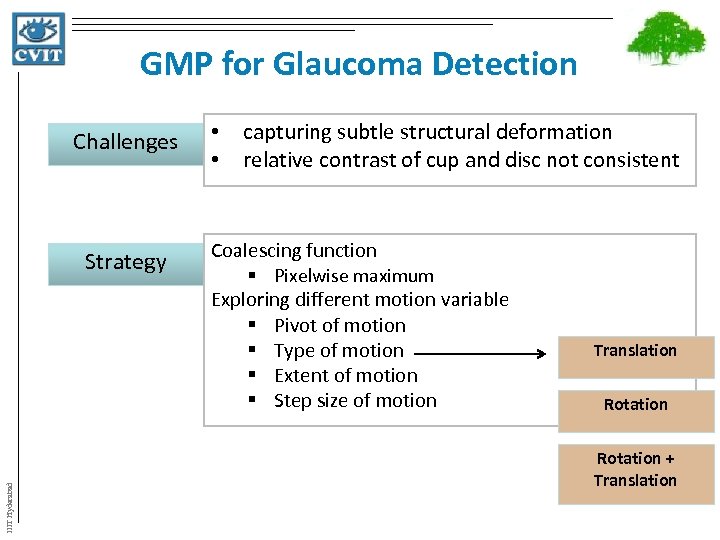 GMP for Glaucoma Detection Challenges IIIT Hyderabad Strategy • capturing subtle structural deformation • relative contrast of cup and disc not consistent Coalescing function § Pixelwise maximum Exploring different motion variable § Pivot of motion § Type of motion § Extent of motion § Step size of motion Translation Rotation + Translation
GMP for Glaucoma Detection Challenges IIIT Hyderabad Strategy • capturing subtle structural deformation • relative contrast of cup and disc not consistent Coalescing function § Pixelwise maximum Exploring different motion variable § Pivot of motion § Type of motion § Extent of motion § Step size of motion Translation Rotation + Translation
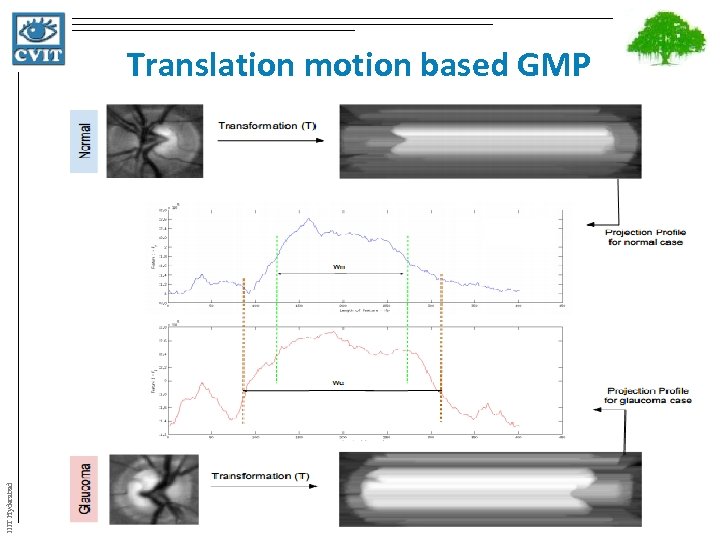
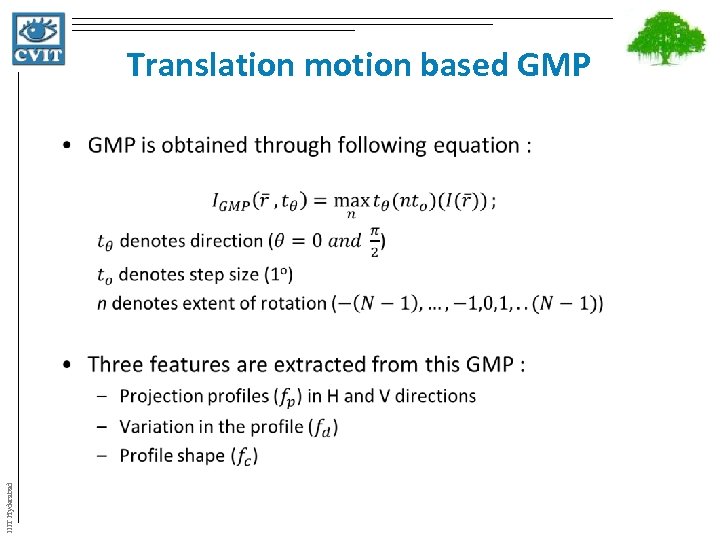
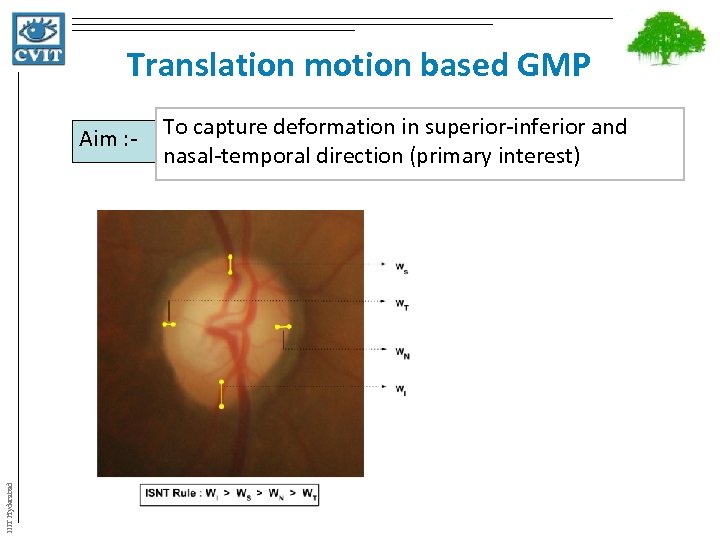 Translation motion based GMP IIIT Hyderabad Aim : - To capture deformation in superior-inferior and nasal-temporal direction (primary interest)
Translation motion based GMP IIIT Hyderabad Aim : - To capture deformation in superior-inferior and nasal-temporal direction (primary interest)
 IIIT Hyderabad Translation motion based GMP
IIIT Hyderabad Translation motion based GMP
 Translation motion based GMP IIIT Hyderabad •
Translation motion based GMP IIIT Hyderabad •
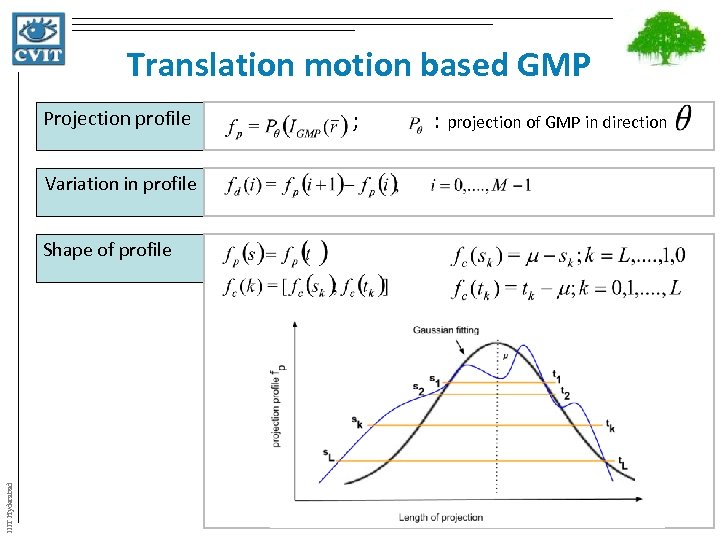 Translation motion based GMP Projection profile ; : projection of GMP in direction Shape of profile IIIT Hyderabad Variation in profile
Translation motion based GMP Projection profile ; : projection of GMP in direction Shape of profile IIIT Hyderabad Variation in profile
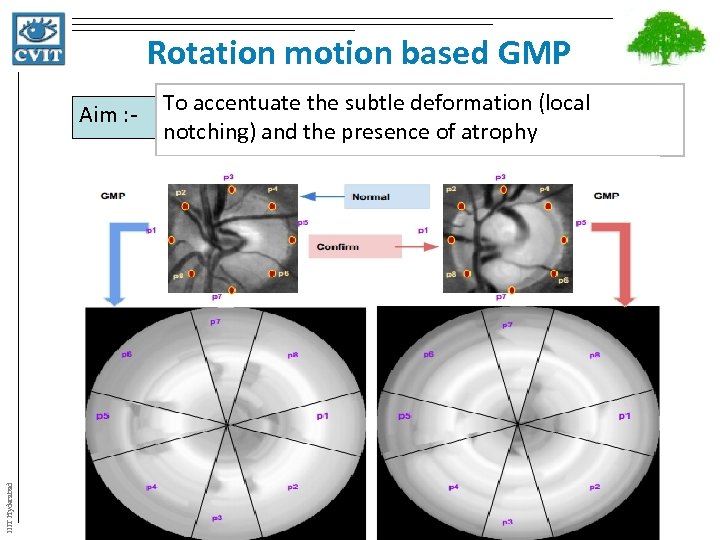 Rotation motion based GMP IIIT Hyderabad Aim : - To accentuate the subtle deformation (local notching) and the presence of atrophy
Rotation motion based GMP IIIT Hyderabad Aim : - To accentuate the subtle deformation (local notching) and the presence of atrophy
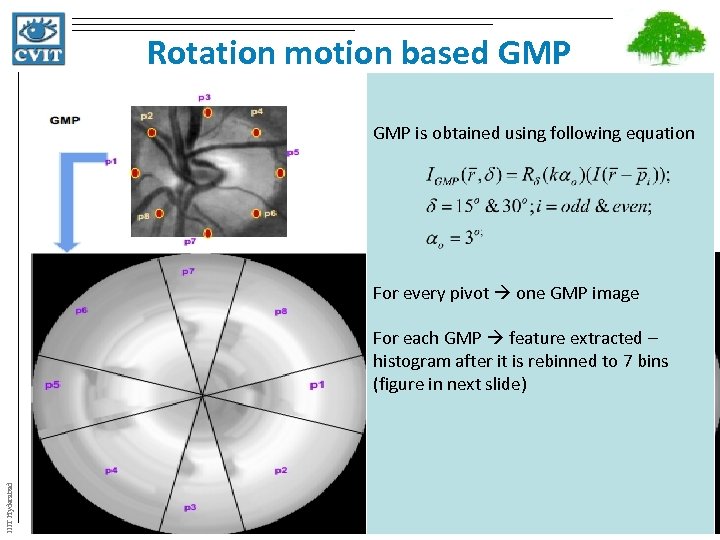 Rotation motion based GMP is obtained using following equation For every pivot one GMP image IIIT Hyderabad For each GMP feature extracted – histogram after it is rebinned to 7 bins (figure in next slide)
Rotation motion based GMP is obtained using following equation For every pivot one GMP image IIIT Hyderabad For each GMP feature extracted – histogram after it is rebinned to 7 bins (figure in next slide)
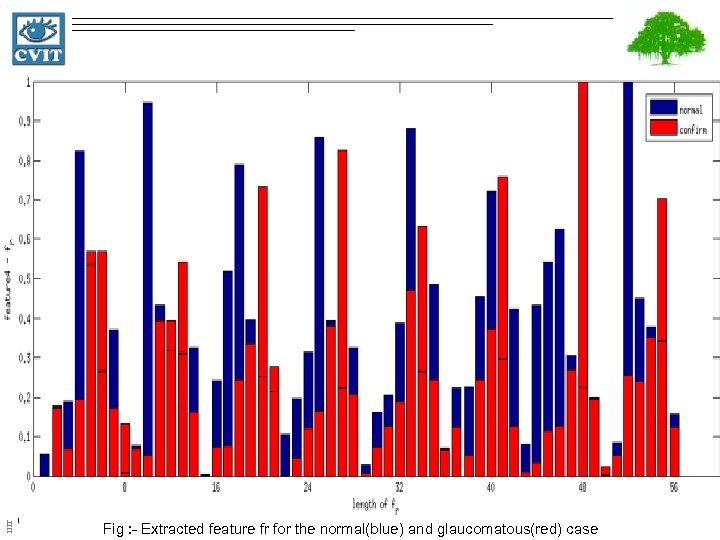 IIIT Hyderabad Fig : - Extracted feature fr for the normal(blue) and glaucomatous(red) case
IIIT Hyderabad Fig : - Extracted feature fr for the normal(blue) and glaucomatous(red) case
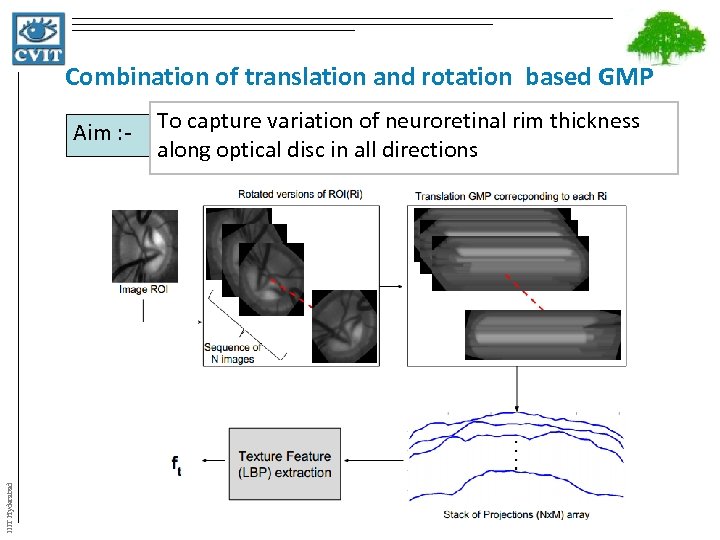 Combination of translation and rotation based GMP IIIT Hyderabad Aim : - To capture variation of neuroretinal rim thickness along optical disc in all directions
Combination of translation and rotation based GMP IIIT Hyderabad Aim : - To capture variation of neuroretinal rim thickness along optical disc in all directions
 Combination of translation and rotation based GMP IIIT Hyderabad •
Combination of translation and rotation based GMP IIIT Hyderabad •
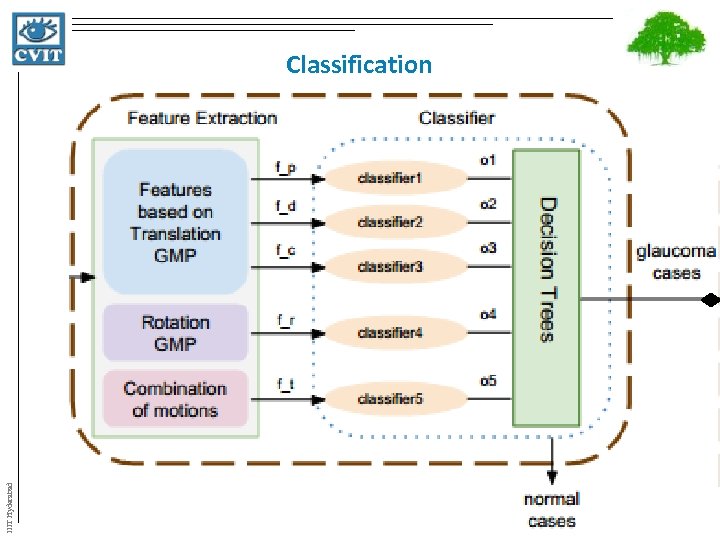 IIIT Hyderabad Classification
IIIT Hyderabad Classification
 Experiments and Results Dataset details • Total test set -1845 images : 1272 normal & 573 glaucomatous cases • Training images – 800 images : 400 normal & 400 glaucomatous cases • Groundtruth : opinion of 3 glaucoma experts as normal, suspect and confirm case (gold standard – majority) • Size of original image = 1494 * 1996 • ROI = 401*401 (all processing with a circular mask of radius 200 pixels) IIIT Hyderabad Evaluation Scheme • using ROC curve -- area under ROC curve
Experiments and Results Dataset details • Total test set -1845 images : 1272 normal & 573 glaucomatous cases • Training images – 800 images : 400 normal & 400 glaucomatous cases • Groundtruth : opinion of 3 glaucoma experts as normal, suspect and confirm case (gold standard – majority) • Size of original image = 1494 * 1996 • ROI = 401*401 (all processing with a circular mask of radius 200 pixels) IIIT Hyderabad Evaluation Scheme • using ROC curve -- area under ROC curve
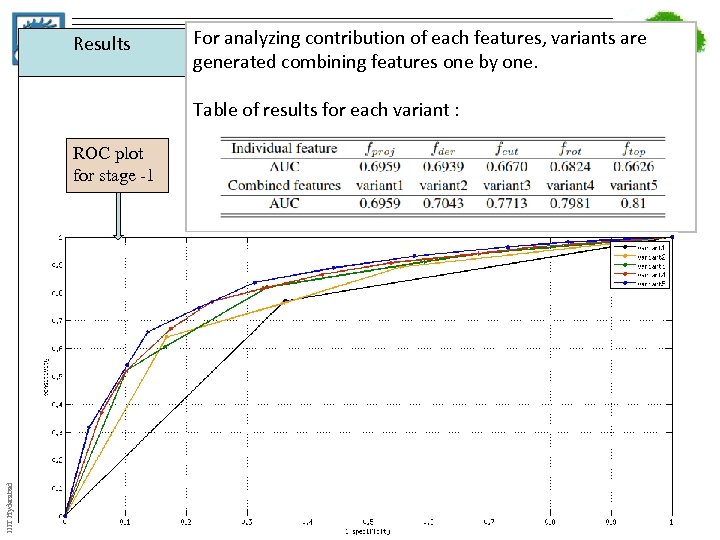 Results For analyzing contribution of each features, variants are generated combining features one by one. Table of results for each variant : IIIT Hyderabad ROC plot for stage -1
Results For analyzing contribution of each features, variants are generated combining features one by one. Table of results for each variant : IIIT Hyderabad ROC plot for stage -1
 Proposals Extending this global approach to the detection of atrophy Hierarchical system design using global analysis only IIIT Hyderabad Exploring global motion pattern based features for glaucoma detection Hierarchical system design using both global and local analysis
Proposals Extending this global approach to the detection of atrophy Hierarchical system design using global analysis only IIIT Hyderabad Exploring global motion pattern based features for glaucoma detection Hierarchical system design using both global and local analysis
 Atrophy detection - Background • Kolar et al. : Using active contours in Heidelberg retinal angiography images • Joshi et al. (2011) : Using dissimilarity measure of regions adjoining disc • Cheng et al. : Using biologically inspired feature • Muramatsu et al. : Using texture analysis (only on 26 images) IIIT Hyderabad Previous work largely based on local feature based detection Our strategy : - GMP based global features approach
Atrophy detection - Background • Kolar et al. : Using active contours in Heidelberg retinal angiography images • Joshi et al. (2011) : Using dissimilarity measure of regions adjoining disc • Cheng et al. : Using biologically inspired feature • Muramatsu et al. : Using texture analysis (only on 26 images) IIIT Hyderabad Previous work largely based on local feature based detection Our strategy : - GMP based global features approach
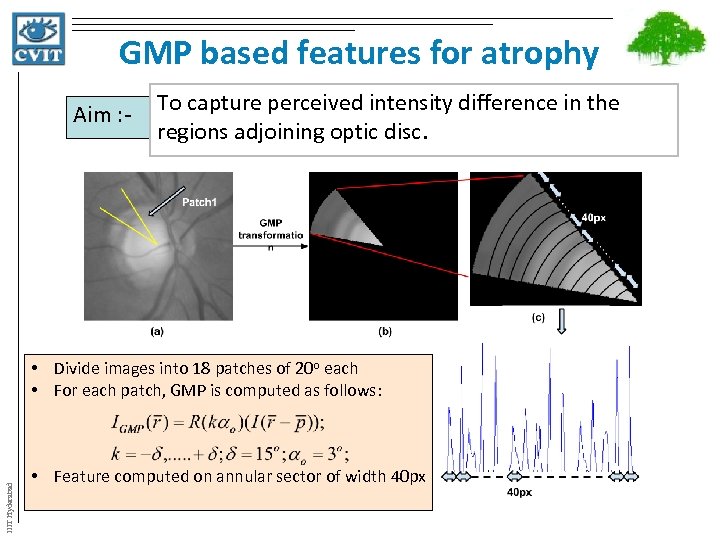 GMP based features for atrophy Aim : - To capture perceived intensity difference in the regions adjoining optic disc. IIIT Hyderabad • Divide images into 18 patches of 20 o each • For each patch, GMP is computed as follows: • Feature computed on annular sector of width 40 px
GMP based features for atrophy Aim : - To capture perceived intensity difference in the regions adjoining optic disc. IIIT Hyderabad • Divide images into 18 patches of 20 o each • For each patch, GMP is computed as follows: • Feature computed on annular sector of width 40 px
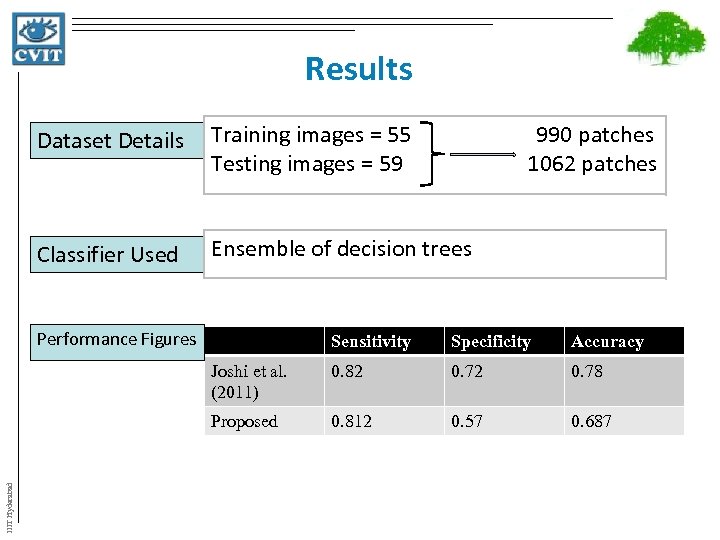 Results Dataset Details Training images = 55 990 patches Testing images = 59 1062 patches Classifier Used Ensemble of decision trees Performance Figures Specificity Accuracy Joshi et al. (2011) 0. 82 0. 78 Proposed IIIT Hyderabad Sensitivity 0. 812 0. 57 0. 687
Results Dataset Details Training images = 55 990 patches Testing images = 59 1062 patches Classifier Used Ensemble of decision trees Performance Figures Specificity Accuracy Joshi et al. (2011) 0. 82 0. 78 Proposed IIIT Hyderabad Sensitivity 0. 812 0. 57 0. 687
 Proposals Extending this global approach to the detection of atrophy Hierarchical system design using global analysis only IIIT Hyderabad Exploring global motion pattern based features for glaucoma detection Hierarchical system design using both global and local analysis
Proposals Extending this global approach to the detection of atrophy Hierarchical system design using global analysis only IIIT Hyderabad Exploring global motion pattern based features for glaucoma detection Hierarchical system design using both global and local analysis
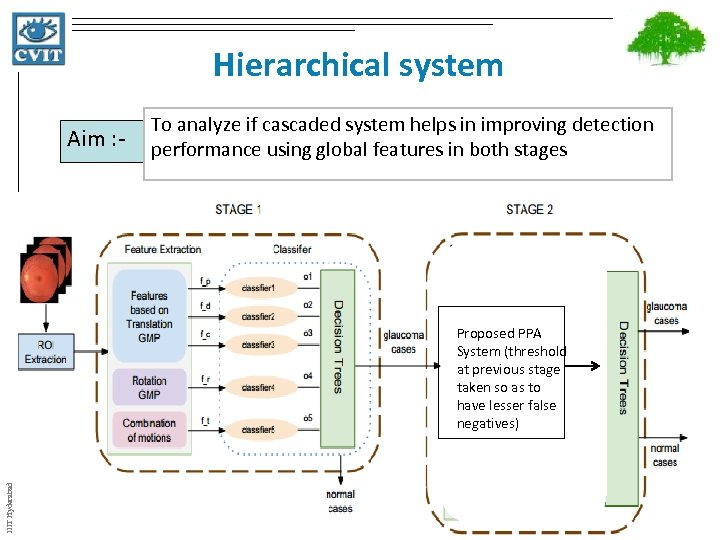 Hierarchical system Aim : - To analyze if cascaded system helps in improving detection performance using global features in both stages IIIT Hyderabad Proposed PPA System (threshold at previous stage taken so as to have lesser false negatives)
Hierarchical system Aim : - To analyze if cascaded system helps in improving detection performance using global features in both stages IIIT Hyderabad Proposed PPA System (threshold at previous stage taken so as to have lesser false negatives)
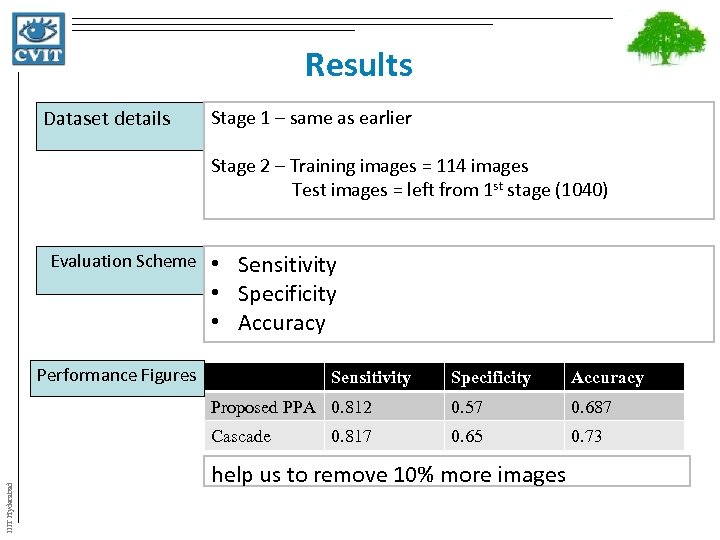 Results Dataset details Stage 1 – same as earlier Stage 2 – Training images = 114 images Test images = left from 1 st stage (1040) Evaluation Scheme Performance Figures • Sensitivity • Specificity • Accuracy Specificity Accuracy Proposed PPA 0. 812 0. 57 0. 687 Cascade IIIT Hyderabad Sensitivity 0. 65 0. 73 0. 817 help us to remove 10% more images
Results Dataset details Stage 1 – same as earlier Stage 2 – Training images = 114 images Test images = left from 1 st stage (1040) Evaluation Scheme Performance Figures • Sensitivity • Specificity • Accuracy Specificity Accuracy Proposed PPA 0. 812 0. 57 0. 687 Cascade IIIT Hyderabad Sensitivity 0. 65 0. 73 0. 817 help us to remove 10% more images
 Proposals Extending this global approach to the detection of atrophy Hierarchical system design using global analysis only IIIT Hyderabad Exploring global motion pattern based features for glaucoma detection Hierarchical system design using both global and local analysis
Proposals Extending this global approach to the detection of atrophy Hierarchical system design using global analysis only IIIT Hyderabad Exploring global motion pattern based features for glaucoma detection Hierarchical system design using both global and local analysis
 Hierarchical System • This uses Stage 1 same as used in previous system ( global feature based) – Aim – to remove as many as true negatives – Enables tuning second stage for higher specificity without compromising sensitivity • Stage 2 is borrowed from a work within our group (local feature based) IIIT Hyderabad – A clinical paper of this work is under review – Explained next • So far no attempts to assess glaucoma using capabilities of both
Hierarchical System • This uses Stage 1 same as used in previous system ( global feature based) – Aim – to remove as many as true negatives – Enables tuning second stage for higher specificity without compromising sensitivity • Stage 2 is borrowed from a work within our group (local feature based) IIIT Hyderabad – A clinical paper of this work is under review – Explained next • So far no attempts to assess glaucoma using capabilities of both
 Stage - 2 IIIT Hyderabad • Local features used in this stage are : – Cup-to-disk vertical diameter ratio (CDR) – Cup-to-disk area ratio (CAR) – Atrophy presence decision in the inferior and superior directions – RNFL presence decision in the inferior and superior directions – Relative distributions of image structures using structural clustering
Stage - 2 IIIT Hyderabad • Local features used in this stage are : – Cup-to-disk vertical diameter ratio (CDR) – Cup-to-disk area ratio (CAR) – Atrophy presence decision in the inferior and superior directions – RNFL presence decision in the inferior and superior directions – Relative distributions of image structures using structural clustering
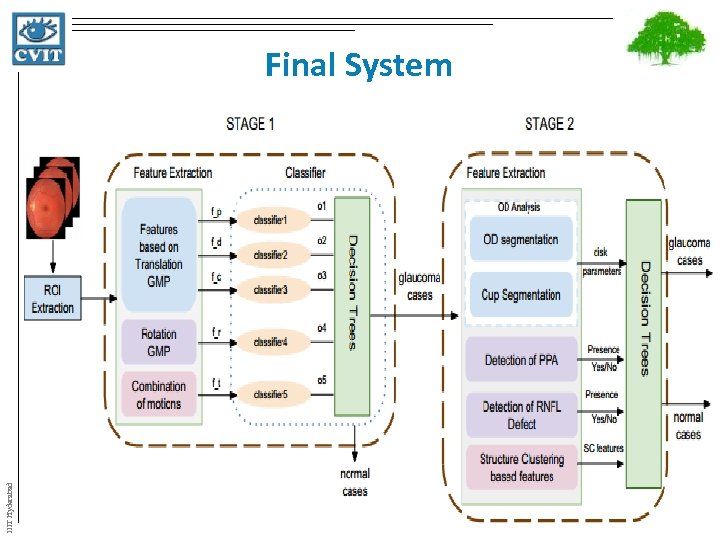 IIIT Hyderabad Final System
IIIT Hyderabad Final System
 Experiments & Results • Two experiments are done – Using same training set of 800 images (as used earlier) in both the stages (Expt 1) – Using the left over images from stage 1 to train the stage 2 (Expt 2) • 1040 (from stage 1) IIIT Hyderabad • Dataset details – In Expt 1 – testing set similar as used before – In Expt 2 – 800 new images (added to 1040) 652 normal and 148 glaucomatous • Evaluation scheme – AUC – Sensitivity – Specificity
Experiments & Results • Two experiments are done – Using same training set of 800 images (as used earlier) in both the stages (Expt 1) – Using the left over images from stage 1 to train the stage 2 (Expt 2) • 1040 (from stage 1) IIIT Hyderabad • Dataset details – In Expt 1 – testing set similar as used before – In Expt 2 – 800 new images (added to 1040) 652 normal and 148 glaucomatous • Evaluation scheme – AUC – Sensitivity – Specificity
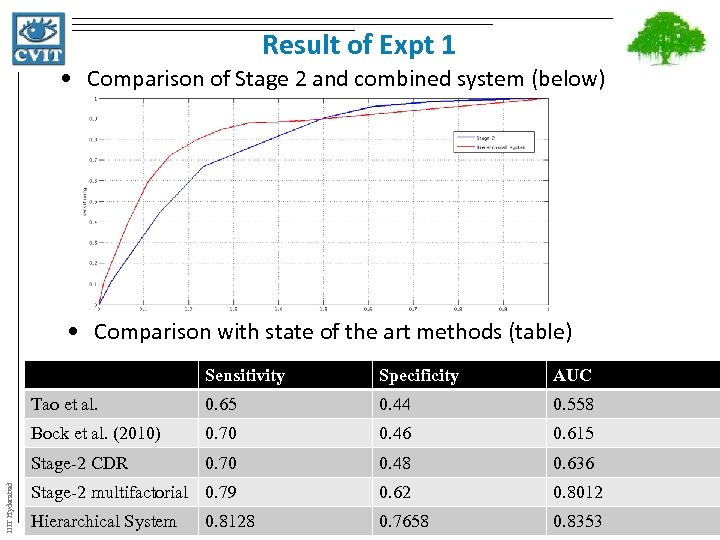 Result of Expt 1 • Comparison of Stage 2 and combined system (below) • Comparison with state of the art methods (table) Sensitivity Specificity AUC Tao et al. 0. 65 0. 44 0. 558 Bock et al. (2010) 0. 70 0. 46 0. 615 Stage-2 CDR 0. 70 0. 48 0. 636 Stage-2 multifactorial 0. 79 0. 62 0. 8012 Hierarchical System 0. 7658 0. 8353 IIIT Hyderabad 0. 8128
Result of Expt 1 • Comparison of Stage 2 and combined system (below) • Comparison with state of the art methods (table) Sensitivity Specificity AUC Tao et al. 0. 65 0. 44 0. 558 Bock et al. (2010) 0. 70 0. 46 0. 615 Stage-2 CDR 0. 70 0. 48 0. 636 Stage-2 multifactorial 0. 79 0. 62 0. 8012 Hierarchical System 0. 7658 0. 8353 IIIT Hyderabad 0. 8128
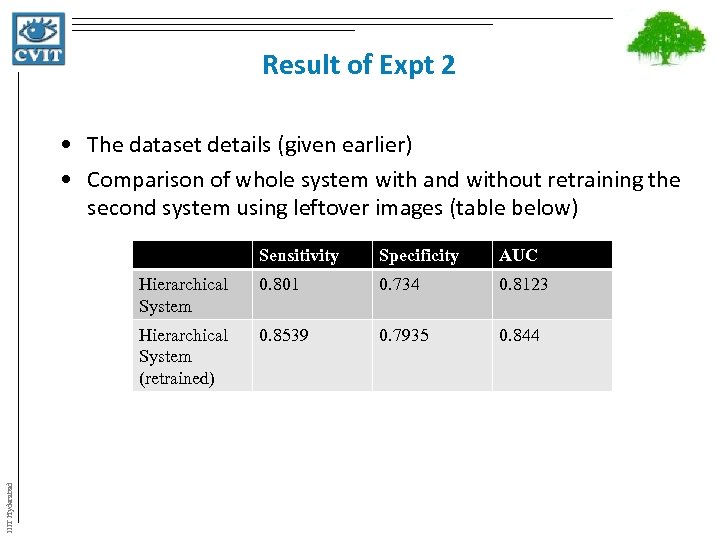 Result of Expt 2 • The dataset details (given earlier) • Comparison of whole system with and without retraining the second system using leftover images (table below) Specificity AUC Hierarchical System 0. 801 0. 734 0. 8123 Hierarchical System (retrained) IIIT Hyderabad Sensitivity 0. 8539 0. 7935 0. 844
Result of Expt 2 • The dataset details (given earlier) • Comparison of whole system with and without retraining the second system using leftover images (table below) Specificity AUC Hierarchical System 0. 801 0. 734 0. 8123 Hierarchical System (retrained) IIIT Hyderabad Sensitivity 0. 8539 0. 7935 0. 844
 Conclusion Ø A global feature based approach for glaucoma detection from retinal images was proposed Ø The Generalized Moment Pattern representation is extended for detecting structural distortions in Optic Disk Ø Hierarchical design (using both global and local analysis) posited to be best to avoid a trade off between sensitivity and specificity IIIT Hyderabad Ø Evaluation of glaucoma detection is performed on a large retinal image dataset
Conclusion Ø A global feature based approach for glaucoma detection from retinal images was proposed Ø The Generalized Moment Pattern representation is extended for detecting structural distortions in Optic Disk Ø Hierarchical design (using both global and local analysis) posited to be best to avoid a trade off between sensitivity and specificity IIIT Hyderabad Ø Evaluation of glaucoma detection is performed on a large retinal image dataset
 Note IIIT Hyderabad • Computing cost may be an issue but alternative ways can be explored for that (especially for Stage-2) • Given the variabilities that occur in screening scenarios, the parameters may need to be retrained for desired results
Note IIIT Hyderabad • Computing cost may be an issue but alternative ways can be explored for that (especially for Stage-2) • Given the variabilities that occur in screening scenarios, the parameters may need to be retrained for desired results
 Possible Future Directions • Exploring more efficient global feature for RNFL detection. – Performance presented in literature not great – Due to subtleness – Adding this as new stage or in the stage-1 of the proposed system will boost performance • Automatic detection of parameters of GMP – will be a major step forward in generalization of detection system using GMP – Can be trained automatically as and when new data arrives IIIT Hyderabad • Optimizing the computational cost.
Possible Future Directions • Exploring more efficient global feature for RNFL detection. – Performance presented in literature not great – Due to subtleness – Adding this as new stage or in the stage-1 of the proposed system will boost performance • Automatic detection of parameters of GMP – will be a major step forward in generalization of detection system using GMP – Can be trained automatically as and when new data arrives IIIT Hyderabad • Optimizing the computational cost.
![IIIT Hyderabad References [1] G. D. Joshi, J. Sivaswamy, and S. R. Krishnadas. Optic IIIT Hyderabad References [1] G. D. Joshi, J. Sivaswamy, and S. R. Krishnadas. Optic](https://present5.com/presentation/cdad6f9d2b851884783b67dbfe2cf884/image-42.jpg) IIIT Hyderabad References [1] G. D. Joshi, J. Sivaswamy, and S. R. Krishnadas. Optic disk and cup segmentation from monocular colour retinal images for glaucoma assessment. IEEE Trans on Medical Imaging, 30(6): 1192 -1205, 2011. [2] J. Liu, D. Wong, J. Lim, H. Li, N. Tan, and T. Wong. Argali- an automatic cup-to-disc ratio measurement system for glaucoma detection and analysis framework. In Proc. SPIE, Medical Imaging, pages 72 603 k-8, 2009. [3] R. Bock, J. Meier, G. Michelson, L. Nyul, and J. Hornegger. Classifying glaucoma with image-based features from fundus photographs. Proc. DAGM, pages 355 -364, 2007. [4] R. Bock, J. Meier, L. Nyul, and G. Michelson. Glaucoma risk index: automated glaucoma detection from color fundus images. Medical Image Analysis, 14(3): 471 -481, 2010. [5] J. Meier, R. Bock, G. Michelson, L. Nyul, and J. Hornegger. Effects of preprocessing eye fundus images on appearance based glaucoma classification. Proc. CAIP, pages 165 -172, 2007. [6] K. S. Deepak, N. K. Medathati, and J. Sivaswamy. Detection and discrimination of disease-related abnormalities based on learning normal cases. Pattern Recogn. , 45(10): 3707 -3716, Oct. 2012. [7] K. S. Deepak and J. Sivaswamy. Automatic assessment of macular edema from color retinal images. Medical Imaging, IEEE Trans on, 31(3): 766 -776, march 2012. [8] D. Tao, F. Yin, D. Kee, Y. Xu, T. Yin, J. Cheng, and J. Liu. Superpixel classification based optic cup segmentation. Medical Image Computing and Computer-assisted Intervention (MICCAI), 8151: 421– 428, 2013. [9] N. Annu and J. Justin. Automated classification of glaucoma images by wavelet energy features. International Journal of Engineering and Technology, 2013. [10] R. Kolar, J. Jan, R. Laemmer, and R. Jirik. Semiautomatic detection and evaluation of autofluorescent areas in retinal images. Proc. EMBS, pages 3327– 3330, 2007
IIIT Hyderabad References [1] G. D. Joshi, J. Sivaswamy, and S. R. Krishnadas. Optic disk and cup segmentation from monocular colour retinal images for glaucoma assessment. IEEE Trans on Medical Imaging, 30(6): 1192 -1205, 2011. [2] J. Liu, D. Wong, J. Lim, H. Li, N. Tan, and T. Wong. Argali- an automatic cup-to-disc ratio measurement system for glaucoma detection and analysis framework. In Proc. SPIE, Medical Imaging, pages 72 603 k-8, 2009. [3] R. Bock, J. Meier, G. Michelson, L. Nyul, and J. Hornegger. Classifying glaucoma with image-based features from fundus photographs. Proc. DAGM, pages 355 -364, 2007. [4] R. Bock, J. Meier, L. Nyul, and G. Michelson. Glaucoma risk index: automated glaucoma detection from color fundus images. Medical Image Analysis, 14(3): 471 -481, 2010. [5] J. Meier, R. Bock, G. Michelson, L. Nyul, and J. Hornegger. Effects of preprocessing eye fundus images on appearance based glaucoma classification. Proc. CAIP, pages 165 -172, 2007. [6] K. S. Deepak, N. K. Medathati, and J. Sivaswamy. Detection and discrimination of disease-related abnormalities based on learning normal cases. Pattern Recogn. , 45(10): 3707 -3716, Oct. 2012. [7] K. S. Deepak and J. Sivaswamy. Automatic assessment of macular edema from color retinal images. Medical Imaging, IEEE Trans on, 31(3): 766 -776, march 2012. [8] D. Tao, F. Yin, D. Kee, Y. Xu, T. Yin, J. Cheng, and J. Liu. Superpixel classification based optic cup segmentation. Medical Image Computing and Computer-assisted Intervention (MICCAI), 8151: 421– 428, 2013. [9] N. Annu and J. Justin. Automated classification of glaucoma images by wavelet energy features. International Journal of Engineering and Technology, 2013. [10] R. Kolar, J. Jan, R. Laemmer, and R. Jirik. Semiautomatic detection and evaluation of autofluorescent areas in retinal images. Proc. EMBS, pages 3327– 3330, 2007
![References IIIT Hyderabad [11] G. D. Joshi, J. Sivaswamy, R. Prashanth, and S. R. References IIIT Hyderabad [11] G. D. Joshi, J. Sivaswamy, R. Prashanth, and S. R.](https://present5.com/presentation/cdad6f9d2b851884783b67dbfe2cf884/image-43.jpg) References IIIT Hyderabad [11] G. D. Joshi, J. Sivaswamy, R. Prashanth, and S. R. Krishnadas. Detection of peri-papillary atrophy and rnfl defect from retinal images. ICIAR, 2011. [12] C. Muramatsu, Y. Hatanaka, A. Sawada, T. Yamamoto, and H. Fujita. Computerized detection of peripapillary chorioretinal atrophy by texture analysis. 33 rd Annual International Conference of the IEEE EMBS Boston, Massachusetts USA, 2011. [13] J. Cheng*, D. Tao, J. Liu, D. W. K. Wong, N. -M. Tan, T. Y. Wong, and S. M. Saw. Peripapillary atrophy detection by sparse biologically inspired feature manifold. IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON MEDICAL IMAGING, 2012.
References IIIT Hyderabad [11] G. D. Joshi, J. Sivaswamy, R. Prashanth, and S. R. Krishnadas. Detection of peri-papillary atrophy and rnfl defect from retinal images. ICIAR, 2011. [12] C. Muramatsu, Y. Hatanaka, A. Sawada, T. Yamamoto, and H. Fujita. Computerized detection of peripapillary chorioretinal atrophy by texture analysis. 33 rd Annual International Conference of the IEEE EMBS Boston, Massachusetts USA, 2011. [13] J. Cheng*, D. Tao, J. Liu, D. W. K. Wong, N. -M. Tan, T. Y. Wong, and S. M. Saw. Peripapillary atrophy detection by sparse biologically inspired feature manifold. IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON MEDICAL IMAGING, 2012.
 We gratefully acknowledge Aravind Eye Hospital, Madurai (for data and expert diagnosis) IIIT Hyderabad
We gratefully acknowledge Aravind Eye Hospital, Madurai (for data and expert diagnosis) IIIT Hyderabad
 IIIT Hyderabad THANK YOU
IIIT Hyderabad THANK YOU
 IIIT Hyderabad
IIIT Hyderabad
 IIIT Hyderabad
IIIT Hyderabad
 IIIT Hyderabad
IIIT Hyderabad
 IIIT Hyderabad
IIIT Hyderabad
 IIIT Hyderabad
IIIT Hyderabad


