a2111826aef7d992182f4c17f3ac3838.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 51
 A+ Guide to Managing and Maintaining Your PC Fifth Edition Chapter 6 Managing Memory
A+ Guide to Managing and Maintaining Your PC Fifth Edition Chapter 6 Managing Memory
 You Will Learn… l About the different kinds of physical memory and how they work l How to upgrade and troubleshoot memory l About Windows memory management A+ Guide to Managing and Maintaining Your PC, Fifth Edition 2
You Will Learn… l About the different kinds of physical memory and how they work l How to upgrade and troubleshoot memory l About Windows memory management A+ Guide to Managing and Maintaining Your PC, Fifth Edition 2
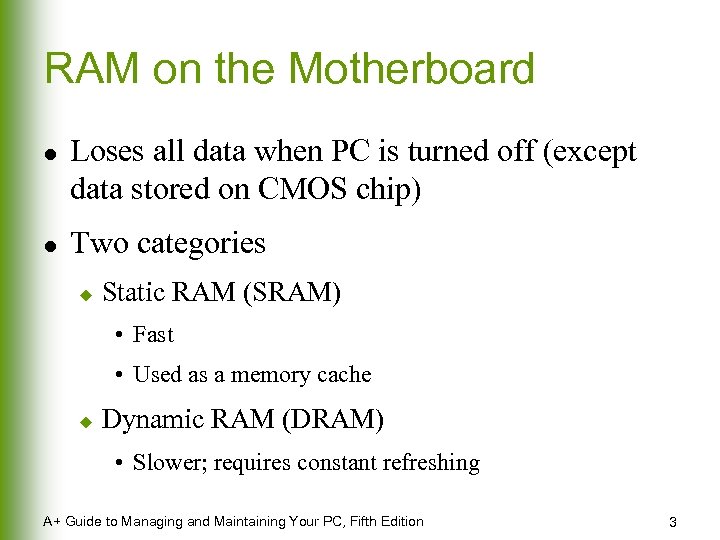 RAM on the Motherboard l l Loses all data when PC is turned off (except data stored on CMOS chip) Two categories u Static RAM (SRAM) • Fast • Used as a memory cache u Dynamic RAM (DRAM) • Slower; requires constant refreshing A+ Guide to Managing and Maintaining Your PC, Fifth Edition 3
RAM on the Motherboard l l Loses all data when PC is turned off (except data stored on CMOS chip) Two categories u Static RAM (SRAM) • Fast • Used as a memory cache u Dynamic RAM (DRAM) • Slower; requires constant refreshing A+ Guide to Managing and Maintaining Your PC, Fifth Edition 3
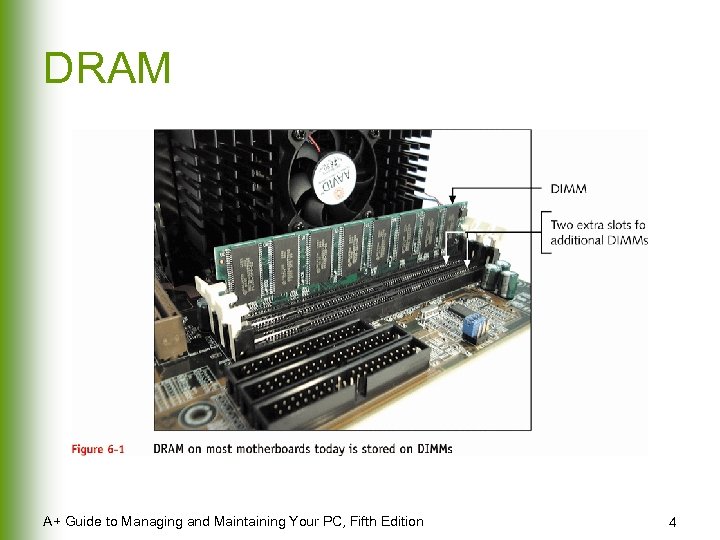 DRAM A+ Guide to Managing and Maintaining Your PC, Fifth Edition 4
DRAM A+ Guide to Managing and Maintaining Your PC, Fifth Edition 4
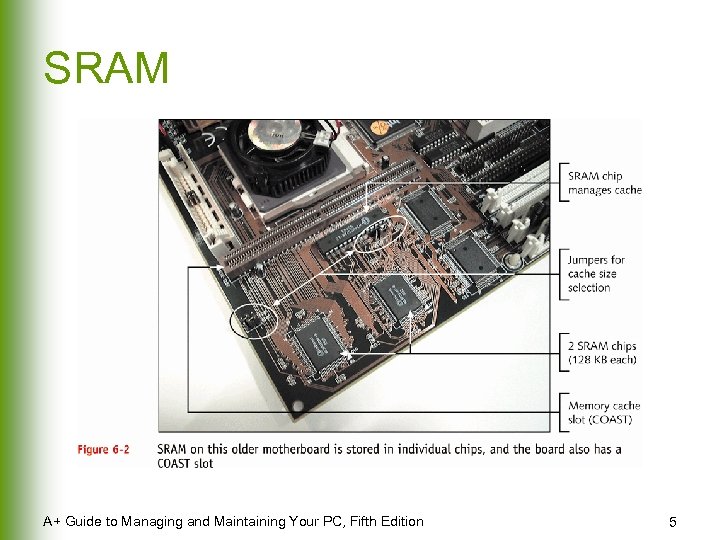 SRAM A+ Guide to Managing and Maintaining Your PC, Fifth Edition 5
SRAM A+ Guide to Managing and Maintaining Your PC, Fifth Edition 5
 COAST, an acronym for Cache On A STick, is a packaging standard ST for modules containing SRAM used as an L 2 cache in a computer. COAST modules look like somewhat oversided SIMM modules. COAST modules were somewhat popular in the early 1990 s, but as of 2004, most cache is build-in to either the CPU or the motherboard. COAST modules decoupled the motherboard from its cache, allowing varying configurations to be created. A+ Guide to Managing and Maintaining Your PC, Fifth Edition 6
COAST, an acronym for Cache On A STick, is a packaging standard ST for modules containing SRAM used as an L 2 cache in a computer. COAST modules look like somewhat oversided SIMM modules. COAST modules were somewhat popular in the early 1990 s, but as of 2004, most cache is build-in to either the CPU or the motherboard. COAST modules decoupled the motherboard from its cache, allowing varying configurations to be created. A+ Guide to Managing and Maintaining Your PC, Fifth Edition 6
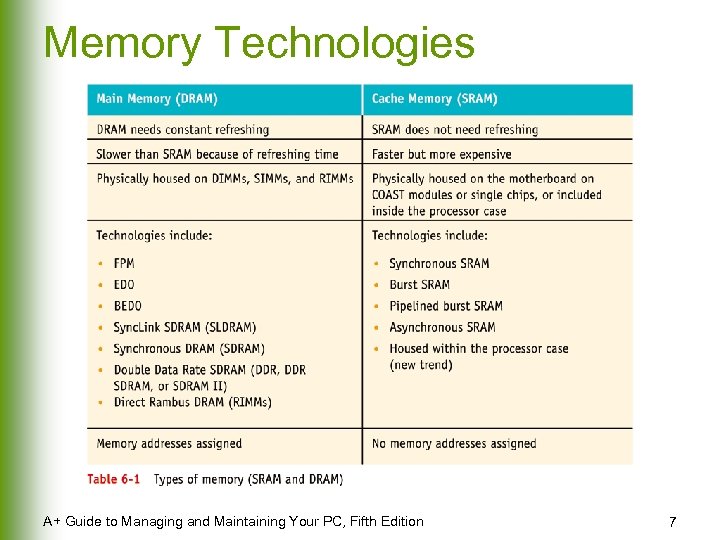 Memory Technologies A+ Guide to Managing and Maintaining Your PC, Fifth Edition 7
Memory Technologies A+ Guide to Managing and Maintaining Your PC, Fifth Edition 7
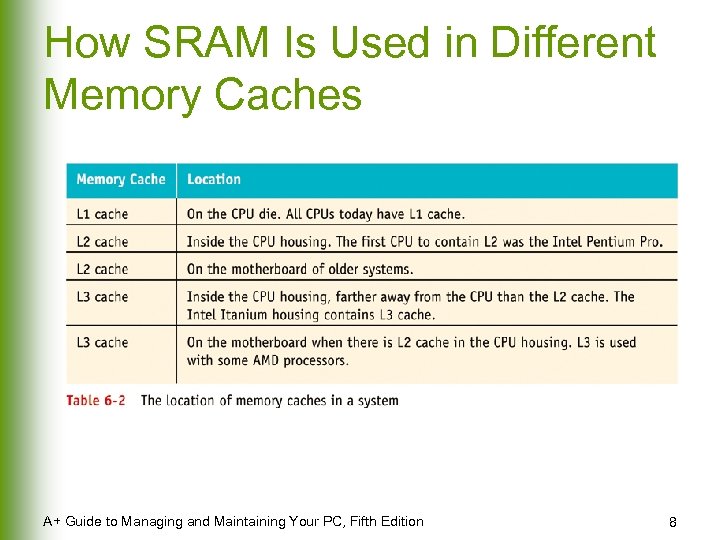 How SRAM Is Used in Different Memory Caches A+ Guide to Managing and Maintaining Your PC, Fifth Edition 8
How SRAM Is Used in Different Memory Caches A+ Guide to Managing and Maintaining Your PC, Fifth Edition 8
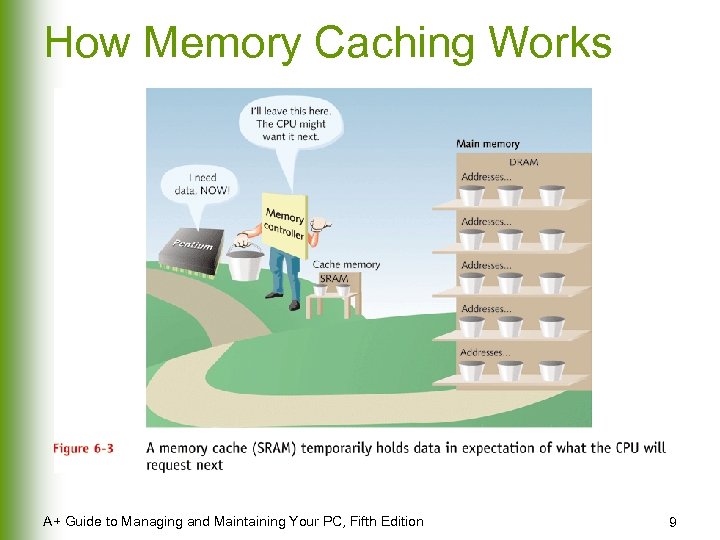 How Memory Caching Works A+ Guide to Managing and Maintaining Your PC, Fifth Edition 9
How Memory Caching Works A+ Guide to Managing and Maintaining Your PC, Fifth Edition 9
 Dynamic RAM Technologies l l Stored on DIMM, RIMM, or SIMM modules (plug directly into motherboard) Differences among these modules: u Width of data path that each type accommodates u The way data moves from system bus to module A+ Guide to Managing and Maintaining Your PC, Fifth Edition 10
Dynamic RAM Technologies l l Stored on DIMM, RIMM, or SIMM modules (plug directly into motherboard) Differences among these modules: u Width of data path that each type accommodates u The way data moves from system bus to module A+ Guide to Managing and Maintaining Your PC, Fifth Edition 10
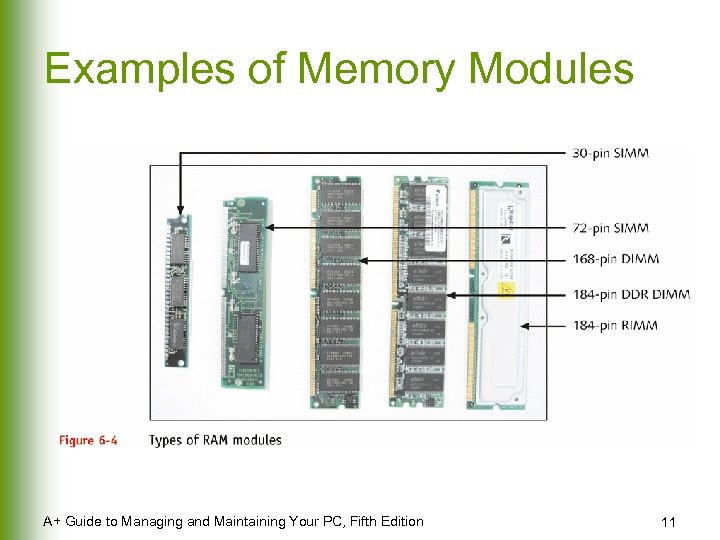 Examples of Memory Modules A+ Guide to Managing and Maintaining Your PC, Fifth Edition 11
Examples of Memory Modules A+ Guide to Managing and Maintaining Your PC, Fifth Edition 11
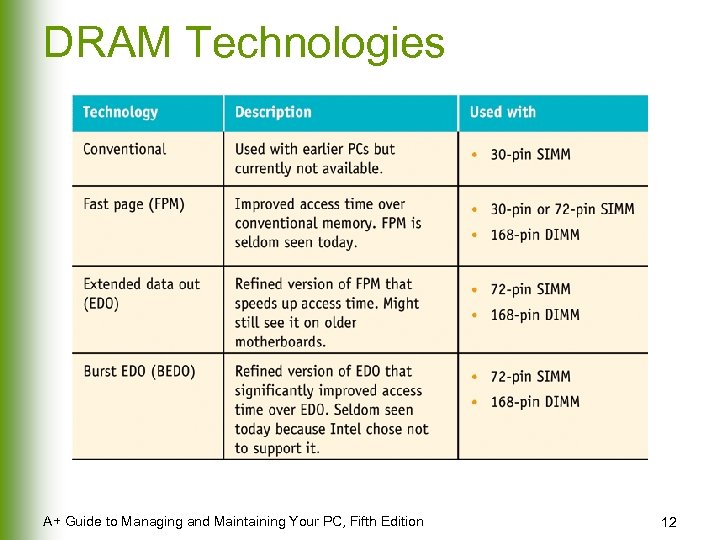 DRAM Technologies A+ Guide to Managing and Maintaining Your PC, Fifth Edition 12
DRAM Technologies A+ Guide to Managing and Maintaining Your PC, Fifth Edition 12
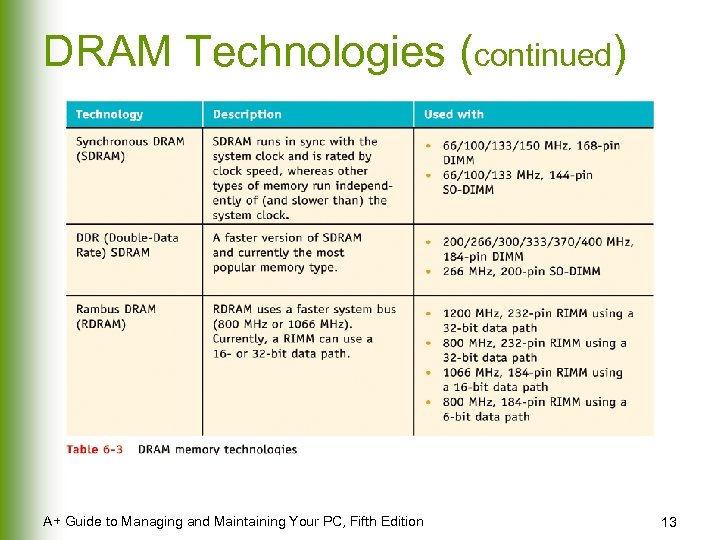 DRAM Technologies (continued) A+ Guide to Managing and Maintaining Your PC, Fifth Edition 13
DRAM Technologies (continued) A+ Guide to Managing and Maintaining Your PC, Fifth Edition 13
 DRAM l SIMM technologies u l DIMM technologies u l Can use either EDO or FPM technology Can use either BEDO (burst EDO) or synchronous RAM (SDRAM) RIMM technologies u Each socket must be filled to maintain continuity A+ Guide to Managing and Maintaining Your PC, Fifth Edition 14
DRAM l SIMM technologies u l DIMM technologies u l Can use either EDO or FPM technology Can use either BEDO (burst EDO) or synchronous RAM (SDRAM) RIMM technologies u Each socket must be filled to maintain continuity A+ Guide to Managing and Maintaining Your PC, Fifth Edition 14
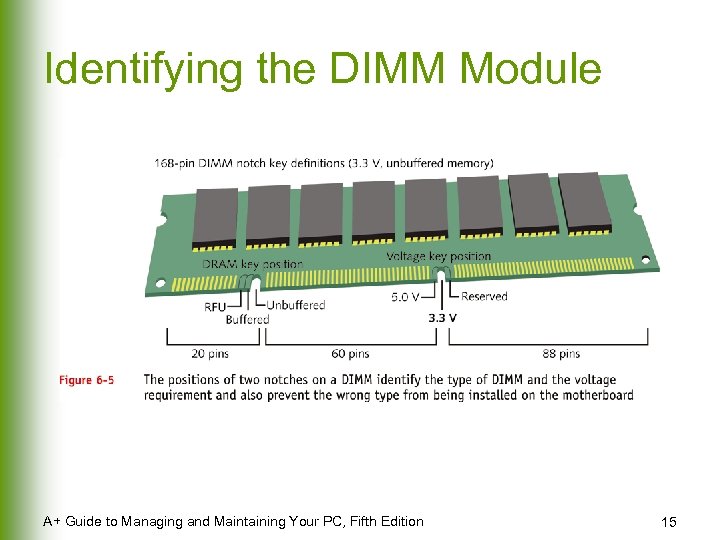 Identifying the DIMM Module A+ Guide to Managing and Maintaining Your PC, Fifth Edition 15
Identifying the DIMM Module A+ Guide to Managing and Maintaining Your PC, Fifth Edition 15
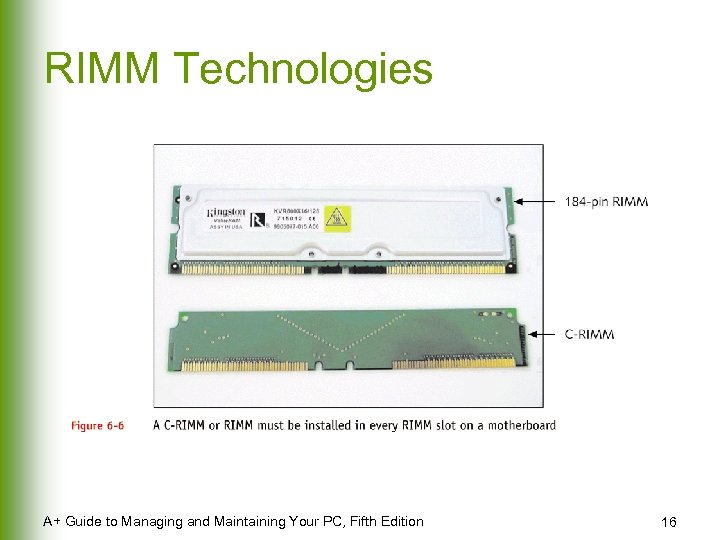 RIMM Technologies A+ Guide to Managing and Maintaining Your PC, Fifth Edition 16
RIMM Technologies A+ Guide to Managing and Maintaining Your PC, Fifth Edition 16
 Error Checking and Parity l Parity Error-checking procedure in which every byte has an even number of ones or an odd number of ones u Older method of testing integrity of bits u • Stored in RAM or secondary medium • Sent over a communications device l Error-correcting code (ECC) u Current method of error checking that can detect and correct an error in a single bit A+ Guide to Managing and Maintaining Your PC, Fifth Edition 17
Error Checking and Parity l Parity Error-checking procedure in which every byte has an even number of ones or an odd number of ones u Older method of testing integrity of bits u • Stored in RAM or secondary medium • Sent over a communications device l Error-correcting code (ECC) u Current method of error checking that can detect and correct an error in a single bit A+ Guide to Managing and Maintaining Your PC, Fifth Edition 17
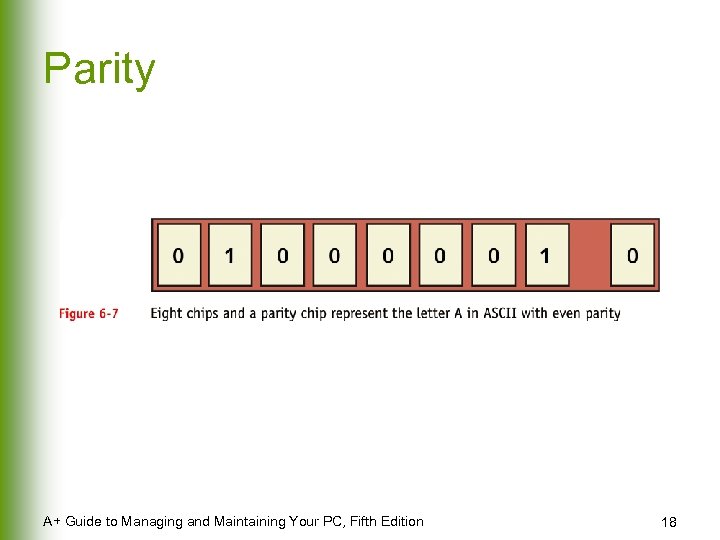 Parity A+ Guide to Managing and Maintaining Your PC, Fifth Edition 18
Parity A+ Guide to Managing and Maintaining Your PC, Fifth Edition 18
 Other Memory Features l CAS (column access strobe) latency l RAS (row access strobe) latency l Both CAS and RAS refer to the number of clock cycles it takes to write or read a column or row of data A+ Guide to Managing and Maintaining Your PC, Fifth Edition 19
Other Memory Features l CAS (column access strobe) latency l RAS (row access strobe) latency l Both CAS and RAS refer to the number of clock cycles it takes to write or read a column or row of data A+ Guide to Managing and Maintaining Your PC, Fifth Edition 19
 Memory Speeds: Factors to Consider l Speed of memory in ns, MHz, or PC rating l How much memory is installed l Memory technology used l CL (CAS Latency) rating CL- the number of clock cycles between the time a read command is sent and the data is available l ECC/parity or non-ECC/nonparity A+ Guide to Managing and Maintaining Your PC, Fifth Edition 20
Memory Speeds: Factors to Consider l Speed of memory in ns, MHz, or PC rating l How much memory is installed l Memory technology used l CL (CAS Latency) rating CL- the number of clock cycles between the time a read command is sent and the data is available l ECC/parity or non-ECC/nonparity A+ Guide to Managing and Maintaining Your PC, Fifth Edition 20
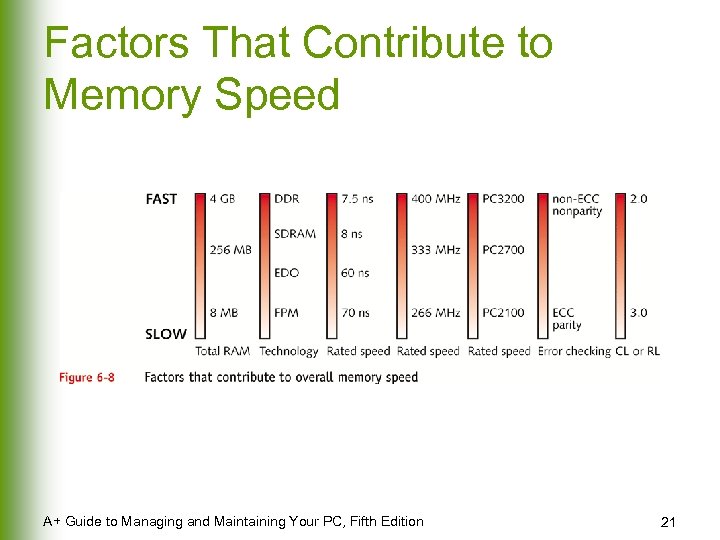 Factors That Contribute to Memory Speed A+ Guide to Managing and Maintaining Your PC, Fifth Edition 21
Factors That Contribute to Memory Speed A+ Guide to Managing and Maintaining Your PC, Fifth Edition 21
 PC RATINGS It is the rating standard that involves Data-transfer speed on the Memory BUS between the CPU and Memory when running any application. The rating refers directly to the maximum bandwidth obtainable and indirectly to the memory clock rate. PC 2100, for example, has a 2. 1 GB/S maximum transfer rate, and a clock rate of 133 MHz. PC 4000, as another example, has a 4 GB/S ideal transfer rate and a 250 MHz clock. To obtain the clock rate from the PCXXXX rating, divide the rating by 16. Multiply the MHz rating by 16 to obtain the bandwidth rating. The DDRXXX is just two times the actual clock speed; i. e. DDR 400 is clocked at 200 MHz. if you want know the PC-XXXX speed of the DDRXXX speed, times it by 8 DDR-I PC 1600 = DDR 200 MHz Data-rate (100 Clk x 2) 1. 6 Gb/Sec PC 2100 = DDR 266 MHz Data-rate (133 Clk x 2) 2. 1 Gb/Sec PC 2400 = DDR 300 MHz Date-rate (150 Clk x 2) 2. 4 Gb/Sec PC 2700 = DDR 333 MHz Data-rate (166 Clk x 2) 2. 7 Gb/Sec PC 3000 = DDR 366 MHz Data-rate (183 Clk x 2) 3. 0 Gb/Sec PC 3200 = DDR 400 MHz Data-rate (200 Clk x 2) 3. 2 Gb/Sec DDR-II PC 4300 = DDR 533 MHz Data-rate (266 Clk x 2) 4. 3 Gb/Sec A+ Guide to Managing and Maintaining Your PC, Fifth Edition 22
PC RATINGS It is the rating standard that involves Data-transfer speed on the Memory BUS between the CPU and Memory when running any application. The rating refers directly to the maximum bandwidth obtainable and indirectly to the memory clock rate. PC 2100, for example, has a 2. 1 GB/S maximum transfer rate, and a clock rate of 133 MHz. PC 4000, as another example, has a 4 GB/S ideal transfer rate and a 250 MHz clock. To obtain the clock rate from the PCXXXX rating, divide the rating by 16. Multiply the MHz rating by 16 to obtain the bandwidth rating. The DDRXXX is just two times the actual clock speed; i. e. DDR 400 is clocked at 200 MHz. if you want know the PC-XXXX speed of the DDRXXX speed, times it by 8 DDR-I PC 1600 = DDR 200 MHz Data-rate (100 Clk x 2) 1. 6 Gb/Sec PC 2100 = DDR 266 MHz Data-rate (133 Clk x 2) 2. 1 Gb/Sec PC 2400 = DDR 300 MHz Date-rate (150 Clk x 2) 2. 4 Gb/Sec PC 2700 = DDR 333 MHz Data-rate (166 Clk x 2) 2. 7 Gb/Sec PC 3000 = DDR 366 MHz Data-rate (183 Clk x 2) 3. 0 Gb/Sec PC 3200 = DDR 400 MHz Data-rate (200 Clk x 2) 3. 2 Gb/Sec DDR-II PC 4300 = DDR 533 MHz Data-rate (266 Clk x 2) 4. 3 Gb/Sec A+ Guide to Managing and Maintaining Your PC, Fifth Edition 22
 Upgrading Memory l What to look for when buying memory chips and modules l How much and what kind of memory to buy l Reading ads about memory modules l Installing memory A+ Guide to Managing and Maintaining Your PC, Fifth Edition 23
Upgrading Memory l What to look for when buying memory chips and modules l How much and what kind of memory to buy l Reading ads about memory modules l Installing memory A+ Guide to Managing and Maintaining Your PC, Fifth Edition 23
 What to Look for When Buying Memory Chips and Modules l l l Use type, size, density, and fastest speed supported by the motherboard Match tin leads to tin connectors and gold leads to gold connectors Beware of remanufactured and re-marked memory chips A+ Guide to Managing and Maintaining Your PC, Fifth Edition 24
What to Look for When Buying Memory Chips and Modules l l l Use type, size, density, and fastest speed supported by the motherboard Match tin leads to tin connectors and gold leads to gold connectors Beware of remanufactured and re-marked memory chips A+ Guide to Managing and Maintaining Your PC, Fifth Edition 24
 How Much and What Kind of Memory to Buy l l Determine how much memory you have and need Identify the number, type, and size of memory modules supported by your motherboard l Determine how much memory can you afford l Match memory modules to the motherboard A+ Guide to Managing and Maintaining Your PC, Fifth Edition 25
How Much and What Kind of Memory to Buy l l Determine how much memory you have and need Identify the number, type, and size of memory modules supported by your motherboard l Determine how much memory can you afford l Match memory modules to the motherboard A+ Guide to Managing and Maintaining Your PC, Fifth Edition 25
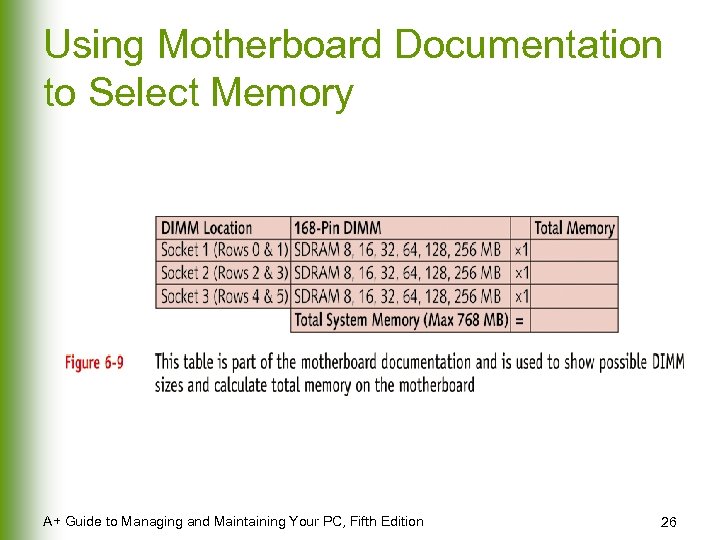 Using Motherboard Documentation to Select Memory A+ Guide to Managing and Maintaining Your PC, Fifth Edition 26
Using Motherboard Documentation to Select Memory A+ Guide to Managing and Maintaining Your PC, Fifth Edition 26
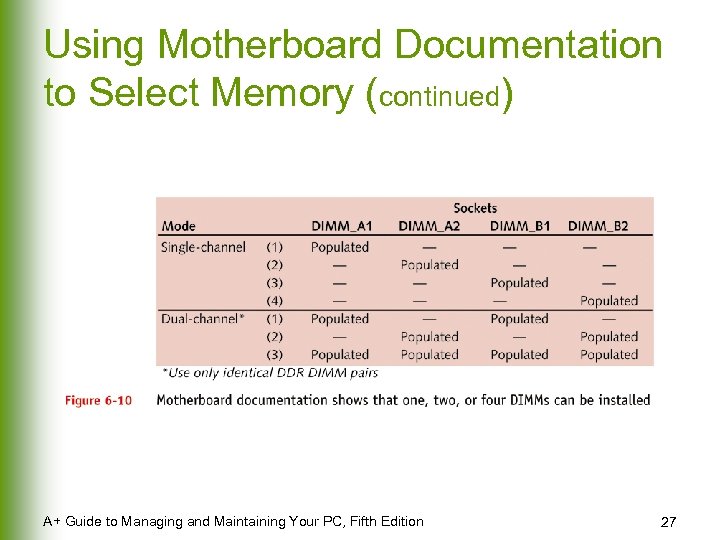 Using Motherboard Documentation to Select Memory (continued) A+ Guide to Managing and Maintaining Your PC, Fifth Edition 27
Using Motherboard Documentation to Select Memory (continued) A+ Guide to Managing and Maintaining Your PC, Fifth Edition 27
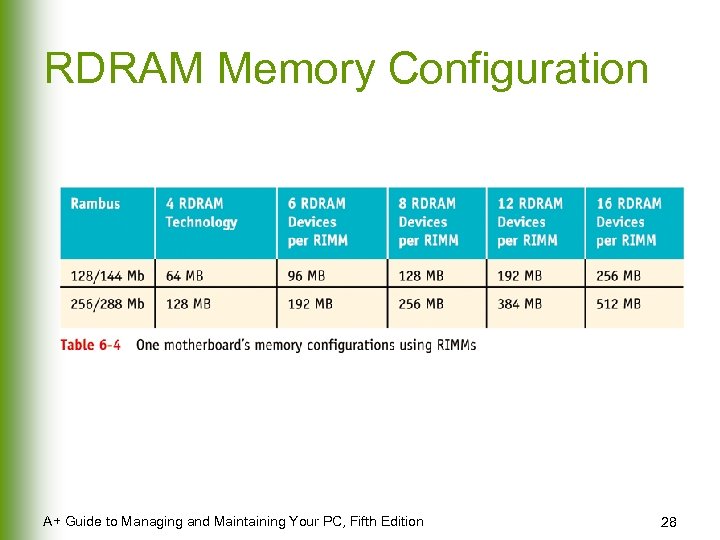 RDRAM Memory Configuration A+ Guide to Managing and Maintaining Your PC, Fifth Edition 28
RDRAM Memory Configuration A+ Guide to Managing and Maintaining Your PC, Fifth Edition 28
 Installing Memory l l Protect chips against static electricity Usually modules pop into place easily and are secured by spring catches on both ends A+ Guide to Managing and Maintaining Your PC, Fifth Edition 29
Installing Memory l l Protect chips against static electricity Usually modules pop into place easily and are secured by spring catches on both ends A+ Guide to Managing and Maintaining Your PC, Fifth Edition 29
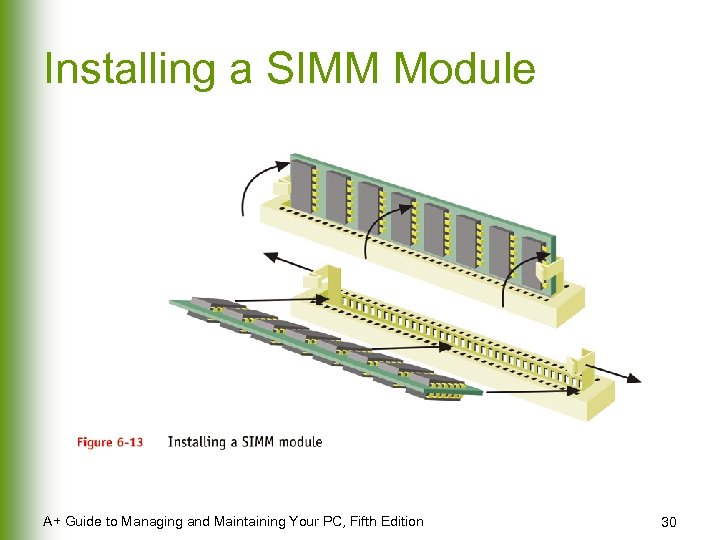 Installing a SIMM Module A+ Guide to Managing and Maintaining Your PC, Fifth Edition 30
Installing a SIMM Module A+ Guide to Managing and Maintaining Your PC, Fifth Edition 30
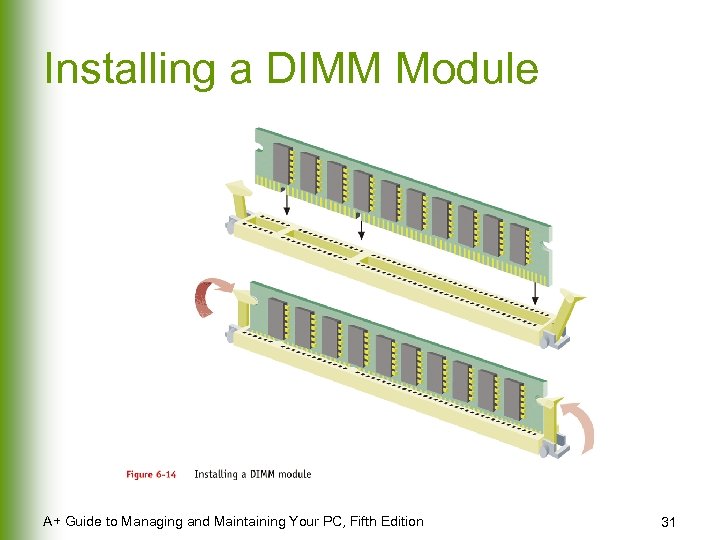 Installing a DIMM Module A+ Guide to Managing and Maintaining Your PC, Fifth Edition 31
Installing a DIMM Module A+ Guide to Managing and Maintaining Your PC, Fifth Edition 31
 Installing a DIMM Module (continued) A+ Guide to Managing and Maintaining Your PC, Fifth Edition 32
Installing a DIMM Module (continued) A+ Guide to Managing and Maintaining Your PC, Fifth Edition 32
 Installing a RIMM Module A+ Guide to Managing and Maintaining Your PC, Fifth Edition 33
Installing a RIMM Module A+ Guide to Managing and Maintaining Your PC, Fifth Edition 33
 Troubleshooting Memory l l What to do if the computer does not recognize new SIMMs, DIMMs, or RIMMs, or memory error messages appear Recurring errors during normal operations can mean unreliable memory A+ Guide to Managing and Maintaining Your PC, Fifth Edition 34
Troubleshooting Memory l l What to do if the computer does not recognize new SIMMs, DIMMs, or RIMMs, or memory error messages appear Recurring errors during normal operations can mean unreliable memory A+ Guide to Managing and Maintaining Your PC, Fifth Edition 34
 Windows Memory Management l Evolution of OS memory management l Windows 9 x memory management l Windows NT/2000/XP memory management A+ Guide to Managing and Maintaining Your PC, Fifth Edition 35
Windows Memory Management l Evolution of OS memory management l Windows 9 x memory management l Windows NT/2000/XP memory management A+ Guide to Managing and Maintaining Your PC, Fifth Edition 35
 Evolution of OS Memory Management l DOS and Windows 9 x u l Complicated; must deal with conventional, upper, and extended memory for backward compatibility Windows NT/2000/XP u u Eliminates complexity; memory is simply memory; all memory addresses are used the same way Causes loss of backward compatibility A+ Guide to Managing and Maintaining Your PC, Fifth Edition 36
Evolution of OS Memory Management l DOS and Windows 9 x u l Complicated; must deal with conventional, upper, and extended memory for backward compatibility Windows NT/2000/XP u u Eliminates complexity; memory is simply memory; all memory addresses are used the same way Causes loss of backward compatibility A+ Guide to Managing and Maintaining Your PC, Fifth Edition 36
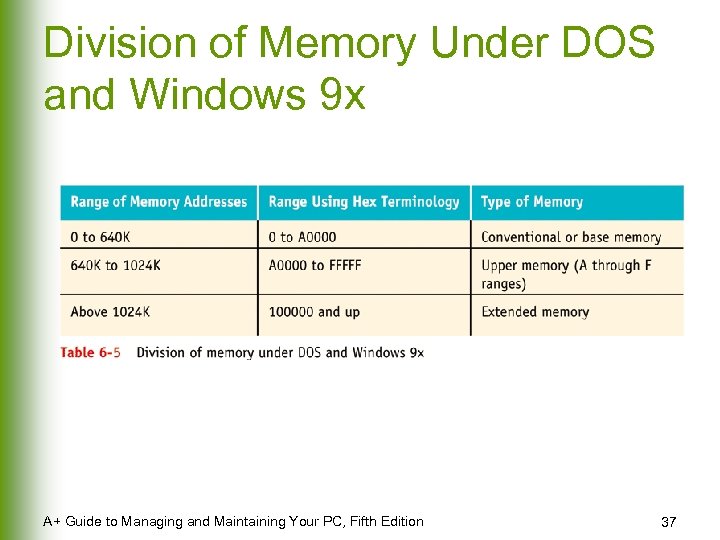 Division of Memory Under DOS and Windows 9 x A+ Guide to Managing and Maintaining Your PC, Fifth Edition 37
Division of Memory Under DOS and Windows 9 x A+ Guide to Managing and Maintaining Your PC, Fifth Edition 37
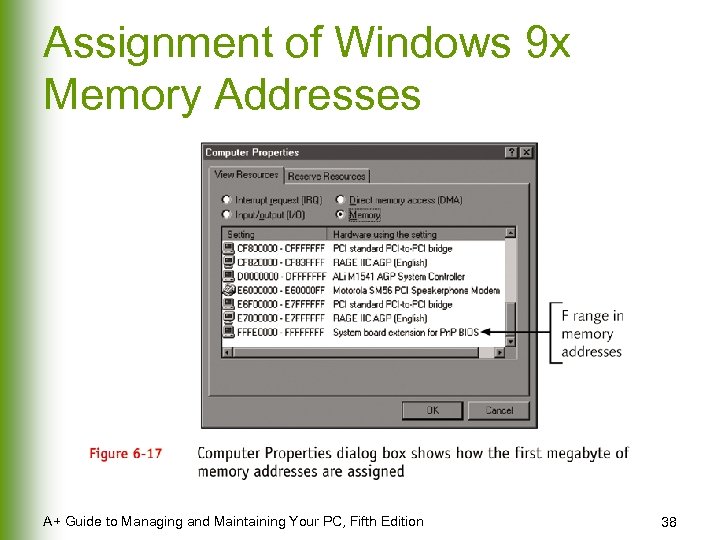 Assignment of Windows 9 x Memory Addresses A+ Guide to Managing and Maintaining Your PC, Fifth Edition 38
Assignment of Windows 9 x Memory Addresses A+ Guide to Managing and Maintaining Your PC, Fifth Edition 38
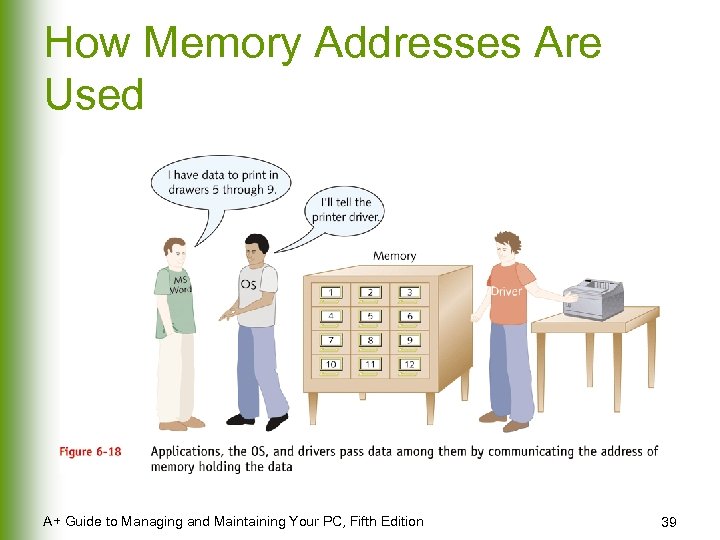 How Memory Addresses Are Used A+ Guide to Managing and Maintaining Your PC, Fifth Edition 39
How Memory Addresses Are Used A+ Guide to Managing and Maintaining Your PC, Fifth Edition 39
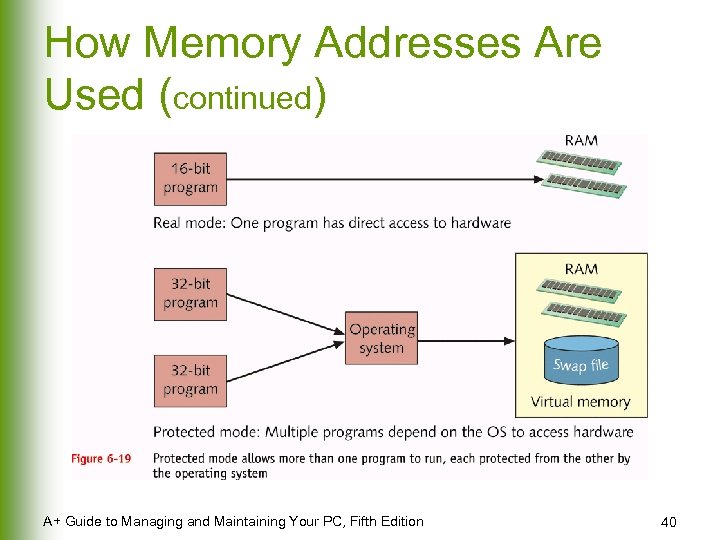 How Memory Addresses Are Used (continued) A+ Guide to Managing and Maintaining Your PC, Fifth Edition 40
How Memory Addresses Are Used (continued) A+ Guide to Managing and Maintaining Your PC, Fifth Edition 40
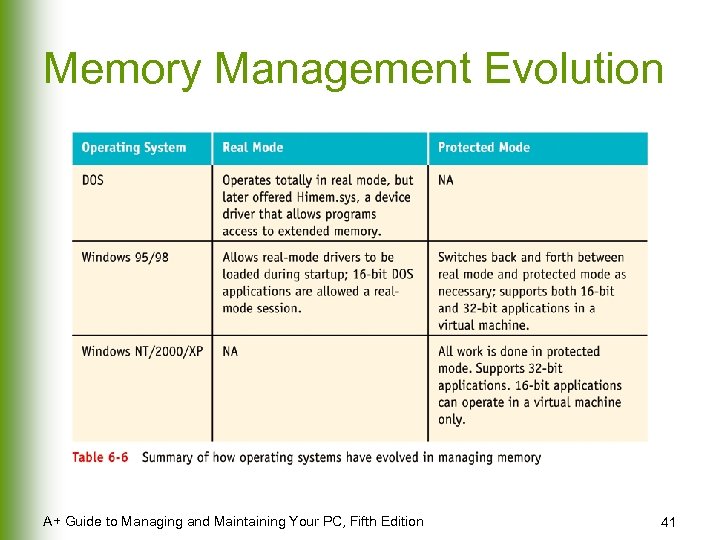 Memory Management Evolution A+ Guide to Managing and Maintaining Your PC, Fifth Edition 41
Memory Management Evolution A+ Guide to Managing and Maintaining Your PC, Fifth Edition 41
 Windows 9 x Memory Management l l Views and manages memory addresses as DOS did Runs in protected mode and uses virtual memory; does a better job managing extended memory than DOS A+ Guide to Managing and Maintaining Your PC, Fifth Edition 42
Windows 9 x Memory Management l l Views and manages memory addresses as DOS did Runs in protected mode and uses virtual memory; does a better job managing extended memory than DOS A+ Guide to Managing and Maintaining Your PC, Fifth Edition 42
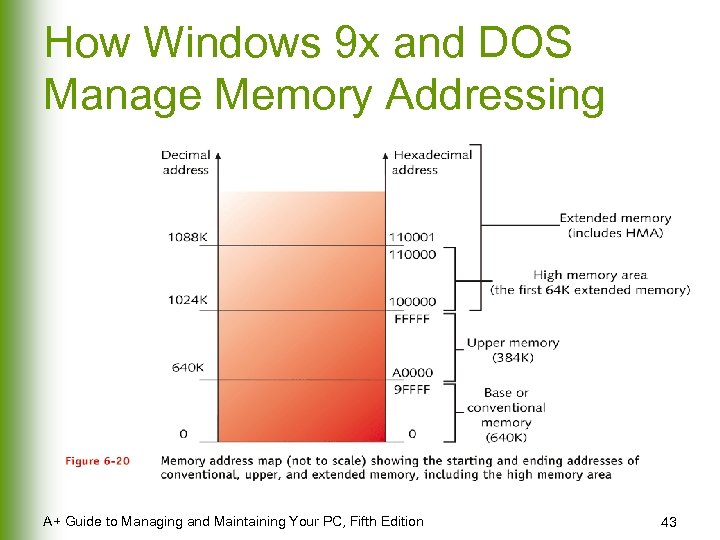 How Windows 9 x and DOS Manage Memory Addressing A+ Guide to Managing and Maintaining Your PC, Fifth Edition 43
How Windows 9 x and DOS Manage Memory Addressing A+ Guide to Managing and Maintaining Your PC, Fifth Edition 43
 Windows 9 x and DOS Utilities That Manage Memory l Himem. sys u l Device driver for all memory above 640 K Emm 386. exe u Contains software that loads device drivers and other programs into upper memory A+ Guide to Managing and Maintaining Your PC, Fifth Edition 44
Windows 9 x and DOS Utilities That Manage Memory l Himem. sys u l Device driver for all memory above 640 K Emm 386. exe u Contains software that loads device drivers and other programs into upper memory A+ Guide to Managing and Maintaining Your PC, Fifth Edition 44
 Using Himem. sys A+ Guide to Managing and Maintaining Your PC, Fifth Edition 45
Using Himem. sys A+ Guide to Managing and Maintaining Your PC, Fifth Edition 45
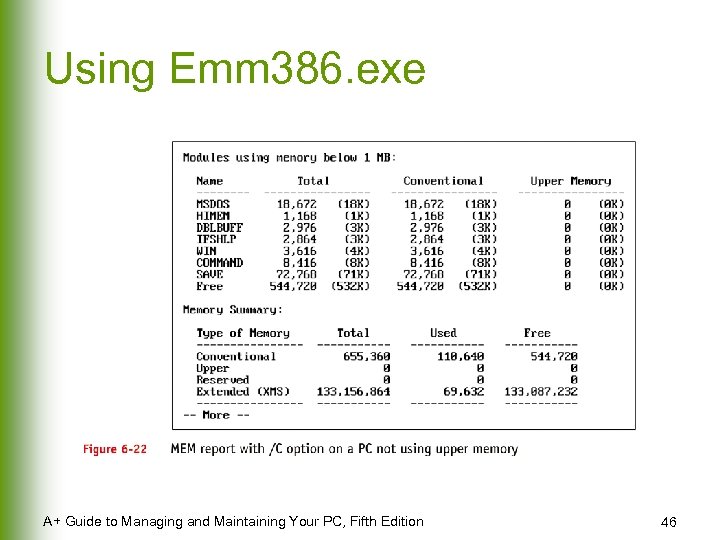 Using Emm 386. exe A+ Guide to Managing and Maintaining Your PC, Fifth Edition 46
Using Emm 386. exe A+ Guide to Managing and Maintaining Your PC, Fifth Edition 46
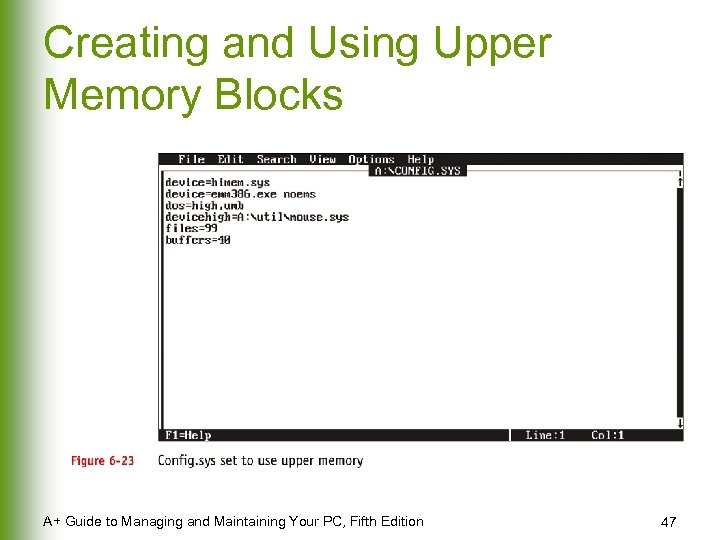 Creating and Using Upper Memory Blocks A+ Guide to Managing and Maintaining Your PC, Fifth Edition 47
Creating and Using Upper Memory Blocks A+ Guide to Managing and Maintaining Your PC, Fifth Edition 47
 How Windows 9 x Manages Virtual Memory l l Automates virtual memory management Stores virtual memory in swap file and manages that memory for application programs Controlled by the VMM (memory paging) Symptoms of excessive memory paging Very high CPU use u Very slow system response u Constant hard drive use u A+ Guide to Managing and Maintaining Your PC, Fifth Edition 48
How Windows 9 x Manages Virtual Memory l l Automates virtual memory management Stores virtual memory in swap file and manages that memory for application programs Controlled by the VMM (memory paging) Symptoms of excessive memory paging Very high CPU use u Very slow system response u Constant hard drive use u A+ Guide to Managing and Maintaining Your PC, Fifth Edition 48
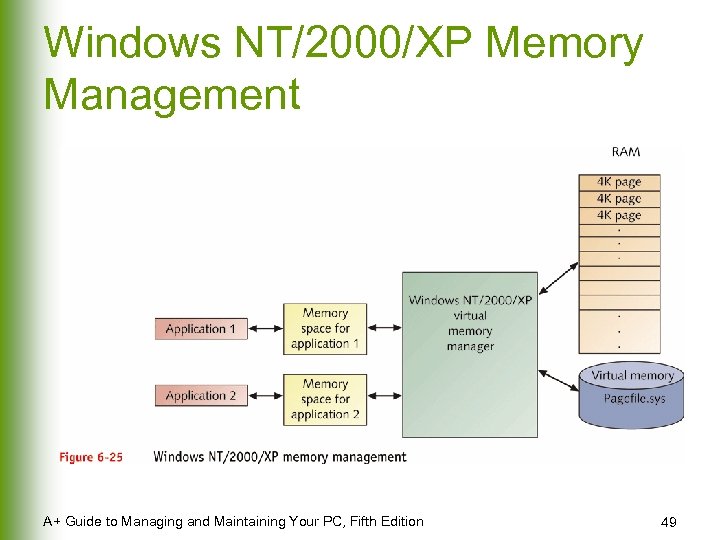 Windows NT/2000/XP Memory Management A+ Guide to Managing and Maintaining Your PC, Fifth Edition 49
Windows NT/2000/XP Memory Management A+ Guide to Managing and Maintaining Your PC, Fifth Edition 49
 How Windows 2000/XP Manages Virtual Memory l l Default size of paging file is set to 1. 5 times amount of RAM installed Guidelines for managing paging files Set initial and maximum size of file to same value u Balance file size with disk space usage u Move paging file to a volume other than boot volume u Remember that memory dumps cannot be captured if the paging file is on a different physical disk from the OS u A+ Guide to Managing and Maintaining Your PC, Fifth Edition 50
How Windows 2000/XP Manages Virtual Memory l l Default size of paging file is set to 1. 5 times amount of RAM installed Guidelines for managing paging files Set initial and maximum size of file to same value u Balance file size with disk space usage u Move paging file to a volume other than boot volume u Remember that memory dumps cannot be captured if the paging file is on a different physical disk from the OS u A+ Guide to Managing and Maintaining Your PC, Fifth Edition 50
 Summary l Memory u u u l Required in order for a system to work Stored on microchips, which are often stored on memory modules (SIMMs, DIMMS, RIMMs) Adding more memory can improve system performance How DOS, Windows 9 x, and Windows NT/2000/XP manage memory A+ Guide to Managing and Maintaining Your PC, Fifth Edition 51
Summary l Memory u u u l Required in order for a system to work Stored on microchips, which are often stored on memory modules (SIMMs, DIMMS, RIMMs) Adding more memory can improve system performance How DOS, Windows 9 x, and Windows NT/2000/XP manage memory A+ Guide to Managing and Maintaining Your PC, Fifth Edition 51


