9a9fda6b6a6f804c050a71789022c608.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 55
 A GOVERNMENT IS FORMED 1783 -1791
A GOVERNMENT IS FORMED 1783 -1791
 To Be Free, One Must Be Chained
To Be Free, One Must Be Chained
 • What are your duties & responsibilities as a citizen of the United States? • What is the role you play in government? • What makes a perfect society?
• What are your duties & responsibilities as a citizen of the United States? • What is the role you play in government? • What makes a perfect society?
 Powers of the National Government • To declare war and make peace. • To coin and borrow money. • To deal with foreign countries and sign treaties. • To operate post offices.
Powers of the National Government • To declare war and make peace. • To coin and borrow money. • To deal with foreign countries and sign treaties. • To operate post offices.
 Weaknesses of the Confederation • The national government could not force the states to obey its laws. • It did not have the power to tax. • Congress lacked strong and steady leadership.
Weaknesses of the Confederation • The national government could not force the states to obey its laws. • It did not have the power to tax. • Congress lacked strong and steady leadership.
 Weaknesses • • There was no national army or navy. There was no national system of courts. Each state could issue its own money. Each state could put tariffs on trade between states.
Weaknesses • • There was no national army or navy. There was no national system of courts. Each state could issue its own money. Each state could put tariffs on trade between states.
 A New Nation Faces Problems Land Ownership Problems 1. Pioneers ignored the fact that the land belonged to the American Indians. Trading Problems 1. Great Britain closed its ports to American shippers. Problems with the Spanish 1. Spain would not allow Americans to ship goods from New Orleans.
A New Nation Faces Problems Land Ownership Problems 1. Pioneers ignored the fact that the land belonged to the American Indians. Trading Problems 1. Great Britain closed its ports to American shippers. Problems with the Spanish 1. Spain would not allow Americans to ship goods from New Orleans.
 Problems with Congress 1. 2. 3. 4. Each state had only one vote. Congress had no power to tax imports. Each state was printing its own money. Congress lacked the power to regulate trade among the states. 5. No national courts existed, only state courts.
Problems with Congress 1. 2. 3. 4. Each state had only one vote. Congress had no power to tax imports. Each state was printing its own money. Congress lacked the power to regulate trade among the states. 5. No national courts existed, only state courts.
 Demand for Change Business Owners, Merchants, Shippers, Manufacturers, and Bankers 1. Wanted a stronger government. Annapolis Convention of 1786 1. Proposed by James Madison. 2. Only five states sent delegates.
Demand for Change Business Owners, Merchants, Shippers, Manufacturers, and Bankers 1. Wanted a stronger government. Annapolis Convention of 1786 1. Proposed by James Madison. 2. Only five states sent delegates.
 James Madison
James Madison
 Shay’s Rebellion 1. Proved the need for a strong central government. 2. Farmers were upset by low farm prices and high state taxes.
Shay’s Rebellion 1. Proved the need for a strong central government. 2. Farmers were upset by low farm prices and high state taxes.
 Shay’s Rebellion • In 1786, The American economy was in trouble. Many people could not pay their debts. Farmers in Massachusetts started an armed rebellion against the state. Their leader was Daniel Shay, a Revolutionary War Captain. He asked the Massachusetts government to ease up on debtors. When it did not, his troops conducted raids all over the state.
Shay’s Rebellion • In 1786, The American economy was in trouble. Many people could not pay their debts. Farmers in Massachusetts started an armed rebellion against the state. Their leader was Daniel Shay, a Revolutionary War Captain. He asked the Massachusetts government to ease up on debtors. When it did not, his troops conducted raids all over the state.
 Shays’s Rebellion • Since there was no national army, the Massachusetts state government had to put down the rebellion alone. Shay’s Rebellion showed the leaders of the new states that they needed a stronger national government than was provided by the Articles of Confederation.
Shays’s Rebellion • Since there was no national army, the Massachusetts state government had to put down the rebellion alone. Shay’s Rebellion showed the leaders of the new states that they needed a stronger national government than was provided by the Articles of Confederation.
 Demand for Change Constitutional Convention 1. Respected delegates from all states except Rhode Island met in May 1787. 2. George Washington was chosen to lead the convention.
Demand for Change Constitutional Convention 1. Respected delegates from all states except Rhode Island met in May 1787. 2. George Washington was chosen to lead the convention.
 Need for a New Start The Purpose of the Convention 1. Delegates needed to develop a completely different system of government The Virginia Plan 1. Called for representation based on population The New Jersey Plan 1. Each State was to have an equal vote in the government for more control
Need for a New Start The Purpose of the Convention 1. Delegates needed to develop a completely different system of government The Virginia Plan 1. Called for representation based on population The New Jersey Plan 1. Each State was to have an equal vote in the government for more control
 A Need for a New Start Debates The key issue was how much power the central government and the states should have
A Need for a New Start Debates The key issue was how much power the central government and the states should have
 The Great Compromise The Compromise Committee 1. Proposed a legislative branch made up of two houses 2. Delegates accepted the plan on July 16, 1787
The Great Compromise The Compromise Committee 1. Proposed a legislative branch made up of two houses 2. Delegates accepted the plan on July 16, 1787
 The Great Compromise Other Compromises 1. The Three-Fifths Compromise permitted three out of every five slaves to be included in the population and taxation count 2. Congress could not affect the slave market until 1808 3. Congress would regulate trade between states and foreign countries 4. The central government would print money
The Great Compromise Other Compromises 1. The Three-Fifths Compromise permitted three out of every five slaves to be included in the population and taxation count 2. Congress could not affect the slave market until 1808 3. Congress would regulate trade between states and foreign countries 4. The central government would print money
 The Great Compromise Executive Branch 1. Would enforce laws Judicial Branch 1. Would interpret laws Legislative Branch 1. Would make laws A Federal Government 1. Is one that is divided between central and state governments
The Great Compromise Executive Branch 1. Would enforce laws Judicial Branch 1. Would interpret laws Legislative Branch 1. Would make laws A Federal Government 1. Is one that is divided between central and state governments
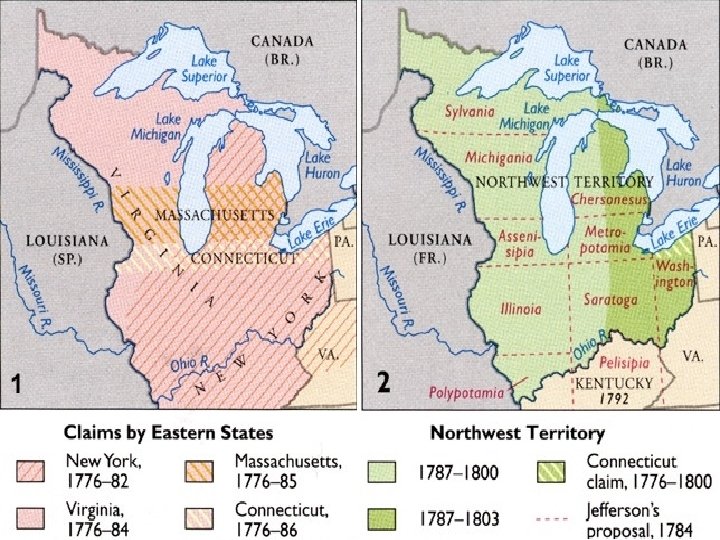
 The Great Compromise The Northwest Ordinance 1. Stated that land east of the Mississippi and north of Ohio would become three to five new states The Constitution 1. Was signed by the delegates on September 17, 1787
The Great Compromise The Northwest Ordinance 1. Stated that land east of the Mississippi and north of Ohio would become three to five new states The Constitution 1. Was signed by the delegates on September 17, 1787
 Executive Branch
Executive Branch
 Judicial Branch
Judicial Branch
 Legislative Branch
Legislative Branch
 State Conventions Are Organized The Constitution 1. Needed to be accepted by nine of the thirteen states 2. Anti-Federalist thought the Constitution did not provide protection of personal freedoms 3. Alexander Hamilton, James Madison, and John Jay explained what the Constitution really meant
State Conventions Are Organized The Constitution 1. Needed to be accepted by nine of the thirteen states 2. Anti-Federalist thought the Constitution did not provide protection of personal freedoms 3. Alexander Hamilton, James Madison, and John Jay explained what the Constitution really meant
 State Conventions Are Organized Ratification of the Constitution 1. Delaware was the first state to ratify in 1787 2. Rhode Island was the last state to ratify on May 29, 1790 A New Government 1. George Washington was elected President in April of 1789
State Conventions Are Organized Ratification of the Constitution 1. Delaware was the first state to ratify in 1787 2. Rhode Island was the last state to ratify on May 29, 1790 A New Government 1. George Washington was elected President in April of 1789
 State Conventions Are Organized A New Government 2. John Adams was elected Vice President Bill of Rights 1. Was added to the Constitution to provide for personal freedoms
State Conventions Are Organized A New Government 2. John Adams was elected Vice President Bill of Rights 1. Was added to the Constitution to provide for personal freedoms
 The Bill of Rights • Even though the Constitution was ratified, many people feared the central government would have too much power. The Bill of Rights was added to the Constitution after opponents of the Constitution convinced the nation that a strong central government without safeguards for the people was a danger to liberty.
The Bill of Rights • Even though the Constitution was ratified, many people feared the central government would have too much power. The Bill of Rights was added to the Constitution after opponents of the Constitution convinced the nation that a strong central government without safeguards for the people was a danger to liberty.
 The Bill of Rights • The Bill of Rights consists of ten amendments, or additions, to the Constitution. It guarantees basic liberties, such as freedom of speech, of the press, and of religion. It was ratified in 1791, three years after the Constitution went into effect.
The Bill of Rights • The Bill of Rights consists of ten amendments, or additions, to the Constitution. It guarantees basic liberties, such as freedom of speech, of the press, and of religion. It was ratified in 1791, three years after the Constitution went into effect.
 Connections 1. How many amendments have been added to the Constitution? 2. What are the first ten amendments called? 3. What five freedoms does the First Amendment guarantee? 4. What does the Second Amendment guarantee? 5. What does the Third Amendment prohibit? 6. If First Amendment guarantees us freedom of speech do you think it’s okay to scream “Fire!” in a crowded theater when there is no fire? Why or why not? 7. What is a search warrant?
Connections 1. How many amendments have been added to the Constitution? 2. What are the first ten amendments called? 3. What five freedoms does the First Amendment guarantee? 4. What does the Second Amendment guarantee? 5. What does the Third Amendment prohibit? 6. If First Amendment guarantees us freedom of speech do you think it’s okay to scream “Fire!” in a crowded theater when there is no fire? Why or why not? 7. What is a search warrant?
 Constitutional Amendments (Bonus Features)
Constitutional Amendments (Bonus Features)
 From memory (no using notes) try to list as many of the Bill of Rights by number as you can.
From memory (no using notes) try to list as many of the Bill of Rights by number as you can.
 Bill of Rights I Freedom of speech, religion, press, petition & assembly II Right to bear arms III No Quartering of troops IV Search and seizures V Rights of accused persons (no double jeopardy)
Bill of Rights I Freedom of speech, religion, press, petition & assembly II Right to bear arms III No Quartering of troops IV Search and seizures V Rights of accused persons (no double jeopardy)
 Bill of VI Rights Right to a speedy trial VII Trial by jury in civil suits VIII No excessive bail and punishment IX Powers reserved to the people (the people’s rights are not limited to those mentioned in the written document) X Powers reserved to the state (check on the necessary and proper clause in Article I)
Bill of VI Rights Right to a speedy trial VII Trial by jury in civil suits VIII No excessive bail and punishment IX Powers reserved to the people (the people’s rights are not limited to those mentioned in the written document) X Powers reserved to the state (check on the necessary and proper clause in Article I)
 AMENDMENTS 11 -27
AMENDMENTS 11 -27
 -11(1792) Citizens, states, or States cannot file lawsuits against states without the consent of the state A. K. A. Sovereign Immunity (All state waived 11 th except VA)
-11(1792) Citizens, states, or States cannot file lawsuits against states without the consent of the state A. K. A. Sovereign Immunity (All state waived 11 th except VA)
 -12 Presidential/VP elections
-12 Presidential/VP elections
 -13 Abolition of slavery Aboli(sh)tion: doing away with
-13 Abolition of slavery Aboli(sh)tion: doing away with
 -14 Citizenship Life, Liberty, Property
-14 Citizenship Life, Liberty, Property
 -15 Black Male Suffrage: the right to vote in elections
-15 Black Male Suffrage: the right to vote in elections
 -16 Congress has the power to collect Income Tax
-16 Congress has the power to collect Income Tax
 -17 Direct election of senators (2) for six (6) year terms
-17 Direct election of senators (2) for six (6) year terms
 -18 Prohibition of alcoholic beverages 1917 Prohibition: To not allow the sale of alcohol
-18 Prohibition of alcoholic beverages 1917 Prohibition: To not allow the sale of alcohol

 -19 Women’s Suffrage
-19 Women’s Suffrage
 Lame Duck -20 March 4 th pushed up to January 20 th
Lame Duck -20 March 4 th pushed up to January 20 th
 -21 Repeal of Prohibition 1933
-21 Repeal of Prohibition 1933
 -22 Limit of two terms as President
-22 Limit of two terms as President
 -23 Suffrage for DC (District of Columbia)
-23 Suffrage for DC (District of Columbia)
 -24 Abolition of poll taxes
-24 Abolition of poll taxes
 -25 Presidential Succession 1. Vice President, Joe Biden 2. Speaker of the House, Nancy Pelosi 3. President Pro Tempore of the Senate, Robert Byrd 4. Secretary of State, Hillary Clinton 5. Secretary of the Treasury, Timothy Geithner 6. Secretary of Defense, Robert Gates 7. Attorney General, Eric Holder 8. Secretary of Homeland Security, Janet Napolitano 8. Secretary of the Interior, Ken Salazar 9. Secretary of Agriculture, Tom Vilsack 10. Secretary of Commerce, Gary Locke 11. Secretary of Labor, Hilda Solis 12. Secretary of Health and Human Services, Kathleen Sebelius 13. Secretary of Housing and Urban Development, Shaun Donovan 14. Secretary of Transportation, Ray La. Hood 15. Secretary of Energy, Steven Chu 16. Secretary of Education, Arne Duncan 17. Secretary of Veterans Affairs, Eric Shinseki
-25 Presidential Succession 1. Vice President, Joe Biden 2. Speaker of the House, Nancy Pelosi 3. President Pro Tempore of the Senate, Robert Byrd 4. Secretary of State, Hillary Clinton 5. Secretary of the Treasury, Timothy Geithner 6. Secretary of Defense, Robert Gates 7. Attorney General, Eric Holder 8. Secretary of Homeland Security, Janet Napolitano 8. Secretary of the Interior, Ken Salazar 9. Secretary of Agriculture, Tom Vilsack 10. Secretary of Commerce, Gary Locke 11. Secretary of Labor, Hilda Solis 12. Secretary of Health and Human Services, Kathleen Sebelius 13. Secretary of Housing and Urban Development, Shaun Donovan 14. Secretary of Transportation, Ray La. Hood 15. Secretary of Energy, Steven Chu 16. Secretary of Education, Arne Duncan 17. Secretary of Veterans Affairs, Eric Shinseki
 -26 Must be 18 years old to vote Previously 21 was the age
-26 Must be 18 years old to vote Previously 21 was the age
 -27 Limits on Congressional pay raises 1992
-27 Limits on Congressional pay raises 1992
 Amendments • More than 11, 000 have been introduced Congress • 33 have gone to the states to be ratified • 27 have been passed to become amendments to the Constitution
Amendments • More than 11, 000 have been introduced Congress • 33 have gone to the states to be ratified • 27 have been passed to become amendments to the Constitution
 Brainstorm one amendment that you would seriously like to add to our constitution. It must be something that is legal and could be practical
Brainstorm one amendment that you would seriously like to add to our constitution. It must be something that is legal and could be practical


