e7925315c06a77da140a24cf3bb3101b.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 20
 A Genetic Algorithm Approach To Interactive Narrative Generation Teong. Joo Ong and John Leggett Texas A&M University
A Genetic Algorithm Approach To Interactive Narrative Generation Teong. Joo Ong and John Leggett Texas A&M University
 Introduction Stories are used to convey information, cultural values, and experiences n New technologies have constantly provided increasingly sophisticated means to tell stories n Recent trend is the convergence of technology, entertainment, and art in the computer n
Introduction Stories are used to convey information, cultural values, and experiences n New technologies have constantly provided increasingly sophisticated means to tell stories n Recent trend is the convergence of technology, entertainment, and art in the computer n
 Background n n Interactive storytelling is a major research area Many overlapping approaches have been used: n AI community (Narrative intelligence): n n n Immersive storytelling Emergent storytelling Plot-based systems Interactive authoring of stories Character-based systems
Background n n Interactive storytelling is a major research area Many overlapping approaches have been used: n AI community (Narrative intelligence): n n n Immersive storytelling Emergent storytelling Plot-based systems Interactive authoring of stories Character-based systems
 Background (cont. ) n Hypertext community: n Hypertext narratives n Adaptive hypermedia n Sculptural hypertext n Partial listing of related work from these areas: CHOROS (N. M. Sgouros) n Façade (M. Mataes, A. Stern) n Card Shark and Storyspace (M. Bernstein) n Metalinear Cinematic Narrative (K. M. Brooks) n Story. Beads (B. Barry) n
Background (cont. ) n Hypertext community: n Hypertext narratives n Adaptive hypermedia n Sculptural hypertext n Partial listing of related work from these areas: CHOROS (N. M. Sgouros) n Façade (M. Mataes, A. Stern) n Card Shark and Storyspace (M. Bernstein) n Metalinear Cinematic Narrative (K. M. Brooks) n Story. Beads (B. Barry) n
 Motivation n n The HEFTI storytelling engine attempts to merge results and ideas from both communities Recombination, mutation, selection of authored story elements with Genetic Algorithm (GA) Generate, remove and traverse links in the story elements as the story unfolds using the author’s predefined rules Story elements and rules are encoded in XML Provides a small drag-and-drop tool and tree-view tools for authors to create their stories
Motivation n n The HEFTI storytelling engine attempts to merge results and ideas from both communities Recombination, mutation, selection of authored story elements with Genetic Algorithm (GA) Generate, remove and traverse links in the story elements as the story unfolds using the author’s predefined rules Story elements and rules are encoded in XML Provides a small drag-and-drop tool and tree-view tools for authors to create their stories
 Definitions Story elements – Smallest units in HEFTI’s story search space n Story template – Describes combinations of various story elements at a particular stage in the story n Template sequences – Subdivision of story template to depict time-based relationships among story elements n Story component – Combination of story elements, agent scripts and variables generated by HEFTI based on the given set of story templates and elements n
Definitions Story elements – Smallest units in HEFTI’s story search space n Story template – Describes combinations of various story elements at a particular stage in the story n Template sequences – Subdivision of story template to depict time-based relationships among story elements n Story component – Combination of story elements, agent scripts and variables generated by HEFTI based on the given set of story templates and elements n
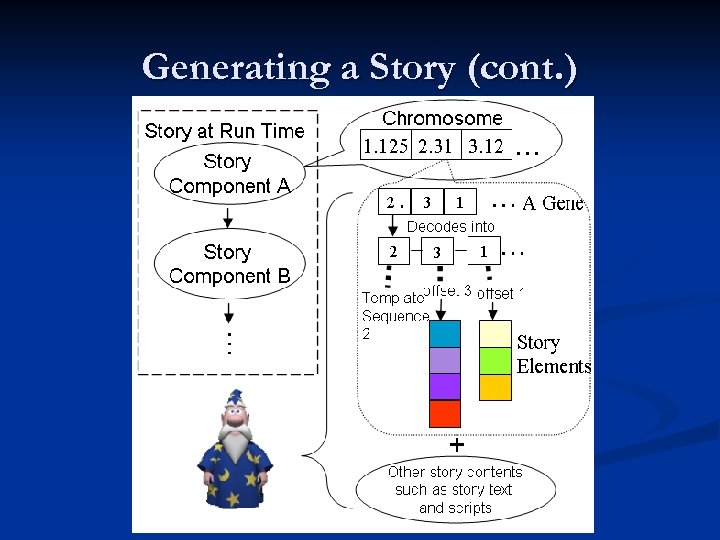
 Generating a Story A story is divided into multiple time steps n Chromosomes represent a story component n Genes represent a collection of story elements pertaining to a template sequence within a story template n Genes are encoded as floating point numbers for convenience of manipulation (as shown later) n
Generating a Story A story is divided into multiple time steps n Chromosomes represent a story component n Genes represent a collection of story elements pertaining to a template sequence within a story template n Genes are encoded as floating point numbers for convenience of manipulation (as shown later) n
 Generating a Story (cont. ) A gene is generated by constructing valid story element sets based on the current state of the story and various conditions and rules imposed by the author (Encoding) n The encoding process is sequential due to dependencies and ordering of story elements n The encoding process is repeated several times to generate individuals in the GA population n
Generating a Story (cont. ) A gene is generated by constructing valid story element sets based on the current state of the story and various conditions and rules imposed by the author (Encoding) n The encoding process is sequential due to dependencies and ordering of story elements n The encoding process is repeated several times to generate individuals in the GA population n
 Generating a Story (cont. ) After the evolution process, the decoding process steps through each of the genes, decoding each gene based on its story context n The end result is a story component that describes the next story sequence n The process is repeated to generate subsequent story sequences n
Generating a Story (cont. ) After the evolution process, the decoding process steps through each of the genes, decoding each gene based on its story context n The end result is a story component that describes the next story sequence n The process is repeated to generate subsequent story sequences n
 Generating a Story (cont. )
Generating a Story (cont. )
 Operations on Story Components The original genetic operators are modified to handle authored ordering of story elements n Chromosome level operators: n Single point crossover n Multi point crossover n n Gene level operators: Crossover operators n Mutation n
Operations on Story Components The original genetic operators are modified to handle authored ordering of story elements n Chromosome level operators: n Single point crossover n Multi point crossover n n Gene level operators: Crossover operators n Mutation n
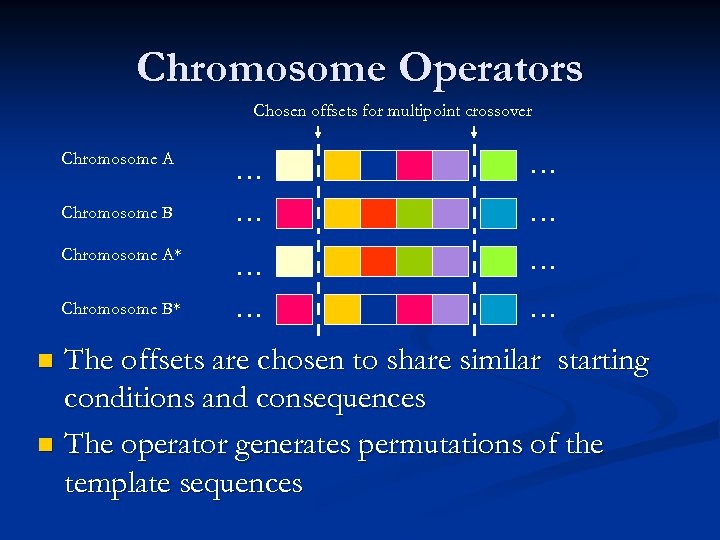 Chromosome Operators Chosen offsets for multipoint crossover Chromosome A Chromosome B Chromosome A* Chromosome B* … … … … The offsets are chosen to share similar starting conditions and consequences n The operator generates permutations of the template sequences n
Chromosome Operators Chosen offsets for multipoint crossover Chromosome A Chromosome B Chromosome A* Chromosome B* … … … … The offsets are chosen to share similar starting conditions and consequences n The operator generates permutations of the template sequences n
 Chromosome Operators (cont. ) n An example from The Three Little Pigs … n Given two chromosomes (A and B) with: Starting conditions: Wolf shows up in front of Angela Pig’s house Consequences: Wolf eats Angela Pig n If the state of the story is the same for both, the intermediary stages can be swapped between A and B
Chromosome Operators (cont. ) n An example from The Three Little Pigs … n Given two chromosomes (A and B) with: Starting conditions: Wolf shows up in front of Angela Pig’s house Consequences: Wolf eats Angela Pig n If the state of the story is the same for both, the intermediary stages can be swapped between A and B
 Gene Operators Gene A* (After mutation) 1 3 n n … … Gene A (Before mutation) 1 Chosen offset for mutation 1 6 6 4 4 … … n Alter selection of story elements Crossover operators are the same as at the chromosome level except they crossover story elements instead of genes Mutation operator changes the offset into a list of possible story elements
Gene Operators Gene A* (After mutation) 1 3 n n … … Gene A (Before mutation) 1 Chosen offset for mutation 1 6 6 4 4 … … n Alter selection of story elements Crossover operators are the same as at the chromosome level except they crossover story elements instead of genes Mutation operator changes the offset into a list of possible story elements
 Story Threads n n Authors create potential story threads Story thread is an indicator for: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Length of story Choice of story elements from a story template Sets of story templates to be used at certain story time steps Rules that change the flow of the story Evaluation criteria for chromosome fitness
Story Threads n n Authors create potential story threads Story thread is an indicator for: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Length of story Choice of story elements from a story template Sets of story templates to be used at certain story time steps Rules that change the flow of the story Evaluation criteria for chromosome fitness
 Fitness Evaluation n n HEFTI is free to generate stories that adhere only so closely (within a threshold) to a story thread Fitness evaluation takes place on the chromosomes of a story thread Authors can indicate preference, indifference, or dislike towards certain story elements by assigning positive or negative values to the story elements The existence of certain story elements in story components are influenced accordingly through the selection mechanisms of GA
Fitness Evaluation n n HEFTI is free to generate stories that adhere only so closely (within a threshold) to a story thread Fitness evaluation takes place on the chromosomes of a story thread Authors can indicate preference, indifference, or dislike towards certain story elements by assigning positive or negative values to the story elements The existence of certain story elements in story components are influenced accordingly through the selection mechanisms of GA
 Story Thread with Fitness Evaluation
Story Thread with Fitness Evaluation
 Scenarios of Use Interactive fiction: A murder mystery with multiple dynamically generated story threads n Sub-module of a computer game engine that dynamically combines various story and agent scripts from existing story elements n An educational environment that can present new concepts in various forms while preserving the goals of the story n
Scenarios of Use Interactive fiction: A murder mystery with multiple dynamically generated story threads n Sub-module of a computer game engine that dynamically combines various story and agent scripts from existing story elements n An educational environment that can present new concepts in various forms while preserving the goals of the story n
 Conclusions HEFTI needs a large enough set of story elements and templates for it to create the story components n Authoring a story from scratch can be tedious n Story templates allow authors to create story elements at different granularities n Story elements can be reused in similar story settings n
Conclusions HEFTI needs a large enough set of story elements and templates for it to create the story components n Authoring a story from scratch can be tedious n Story templates allow authors to create story elements at different granularities n Story elements can be reused in similar story settings n
 Future Work Genetic programming might be used to generate agent scripts given the starting and ending agent actions n Evaluation of fitness data on all of the story variants that HEFTI is capable of generating n Better support for user interaction and control of the story n
Future Work Genetic programming might be used to generate agent scripts given the starting and ending agent actions n Evaluation of fitness data on all of the story variants that HEFTI is capable of generating n Better support for user interaction and control of the story n


