34f949975c4042200d228967699695aa.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 11
 A Framework for Internetworking Heterogeneous High-Performance Networks via GMPLS and Web Services Xi Yang, Tom Lehman Information Sciences Institute (ISI) University of Southern California (USC) HONET, Charlotte NC September 7, 2006
A Framework for Internetworking Heterogeneous High-Performance Networks via GMPLS and Web Services Xi Yang, Tom Lehman Information Sciences Institute (ISI) University of Southern California (USC) HONET, Charlotte NC September 7, 2006
 Outline • High-performance internetworking • GMPLS based control plane (GMPLS-CP) and the DRAGON solution • Heterogeneous high-performance internetworking framework • Web services based control plane (WS-CP) • Conclusions Yang & Lehman A Framework for Internetworking Heterogeneous High-Performance Networks 2
Outline • High-performance internetworking • GMPLS based control plane (GMPLS-CP) and the DRAGON solution • Heterogeneous high-performance internetworking framework • Web services based control plane (WS-CP) • Conclusions Yang & Lehman A Framework for Internetworking Heterogeneous High-Performance Networks 2
 High Performance Networking • Today’s Internet relies on layer-3 (IP) networking – Simple, ubiquitous, scalable, failure-tolerant … – Best-effort, congested, not for high-performance apps. … • High-performance networking leverages dedicated virtual-circuit services through other layers – Layer 1, layer-1. 5, layer-2: WDM, SONET, ATM, Ethernet – Dedicated, high-capacity, low-latency, low-jitter, low-cost • Future Internet will provide hybrid best-effort IP and multi-layer dedicated virtual circuits – Enough options and tradeoffs in price, scalability and performance to satisfy varying application characteristics – Aligned with Internet’s evolutionism philosophy Yang & Lehman A Framework for Internetworking Heterogeneous High-Performance Networks 3
High Performance Networking • Today’s Internet relies on layer-3 (IP) networking – Simple, ubiquitous, scalable, failure-tolerant … – Best-effort, congested, not for high-performance apps. … • High-performance networking leverages dedicated virtual-circuit services through other layers – Layer 1, layer-1. 5, layer-2: WDM, SONET, ATM, Ethernet – Dedicated, high-capacity, low-latency, low-jitter, low-cost • Future Internet will provide hybrid best-effort IP and multi-layer dedicated virtual circuits – Enough options and tradeoffs in price, scalability and performance to satisfy varying application characteristics – Aligned with Internet’s evolutionism philosophy Yang & Lehman A Framework for Internetworking Heterogeneous High-Performance Networks 3
 High Performance Inter-networking • Real-world high-performance networks – NLR, Abilene, HOPI, ESnet, USN, DRAGON, Cheetah … – Limited footprint, bandwidth, users … • Future global high-performance internetworking environment Alliance of high-performance networks – Extending reach of individual networks – Lease and exchange of bandwidth – Traffic detour in emergency; and persistent mutual protection • Goal of high-performance internetworking – Common shared high-performance network infrastructures – Shared control intelligence under common service model Yang & Lehman A Framework for Internetworking Heterogeneous High-Performance Networks 4
High Performance Inter-networking • Real-world high-performance networks – NLR, Abilene, HOPI, ESnet, USN, DRAGON, Cheetah … – Limited footprint, bandwidth, users … • Future global high-performance internetworking environment Alliance of high-performance networks – Extending reach of individual networks – Lease and exchange of bandwidth – Traffic detour in emergency; and persistent mutual protection • Goal of high-performance internetworking – Common shared high-performance network infrastructures – Shared control intelligence under common service model Yang & Lehman A Framework for Internetworking Heterogeneous High-Performance Networks 4
 HPN Internetworking Challenges • High-performance networking requires control plane – Dynamic, end-to-end services; Fast, automated provisioning – Data plane and management plane are not enough • Heterogeneous internetworking environment – Diverse data plane technologies; Services at different layers • IP/MPLS; Ethernet VLAN; SONET … – Administrative barriers • Policy restriction on exchange of routing and signaling information… • Internetworking option I – Unified control plane – Tight coupling – Routing and signaling interoperability – Generalized Multi-Protocol Label Switching (GMPLS) • A true multi-layer heterogeneous networking solution Yang & Lehman A Framework for Internetworking Heterogeneous High-Performance Networks 5
HPN Internetworking Challenges • High-performance networking requires control plane – Dynamic, end-to-end services; Fast, automated provisioning – Data plane and management plane are not enough • Heterogeneous internetworking environment – Diverse data plane technologies; Services at different layers • IP/MPLS; Ethernet VLAN; SONET … – Administrative barriers • Policy restriction on exchange of routing and signaling information… • Internetworking option I – Unified control plane – Tight coupling – Routing and signaling interoperability – Generalized Multi-Protocol Label Switching (GMPLS) • A true multi-layer heterogeneous networking solution Yang & Lehman A Framework for Internetworking Heterogeneous High-Performance Networks 5
 DRAGON – A GMPLS Based High. Performance Networking Project • NSF funded program – Dynamic Resource Allocation via GMPLS Optical Networks (DRAGON) – Testbed deployed in the Washington DC region • Research focused on multi-layer, multi-domain highperformance networking • GMPLS based control plane – Dynamic provisioning across heterogeneous network technologies • Fiber (FSC), Lambda (LSC), SONET (TDM), Ethernet (L 2 SC), Packet (PSC) • Multi-layer Traffic Engineering (TE) – Open Source Software – Interdomain Provisioning (routing, path computation, signaling) – Authentication, Authorization, Accounting (AAA) and Scheduling • http: //dragon. east. isi. edu Yang & Lehman A Framework for Internetworking Heterogeneous High-Performance Networks 6
DRAGON – A GMPLS Based High. Performance Networking Project • NSF funded program – Dynamic Resource Allocation via GMPLS Optical Networks (DRAGON) – Testbed deployed in the Washington DC region • Research focused on multi-layer, multi-domain highperformance networking • GMPLS based control plane – Dynamic provisioning across heterogeneous network technologies • Fiber (FSC), Lambda (LSC), SONET (TDM), Ethernet (L 2 SC), Packet (PSC) • Multi-layer Traffic Engineering (TE) – Open Source Software – Interdomain Provisioning (routing, path computation, signaling) – Authentication, Authorization, Accounting (AAA) and Scheduling • http: //dragon. east. isi. edu Yang & Lehman A Framework for Internetworking Heterogeneous High-Performance Networks 6
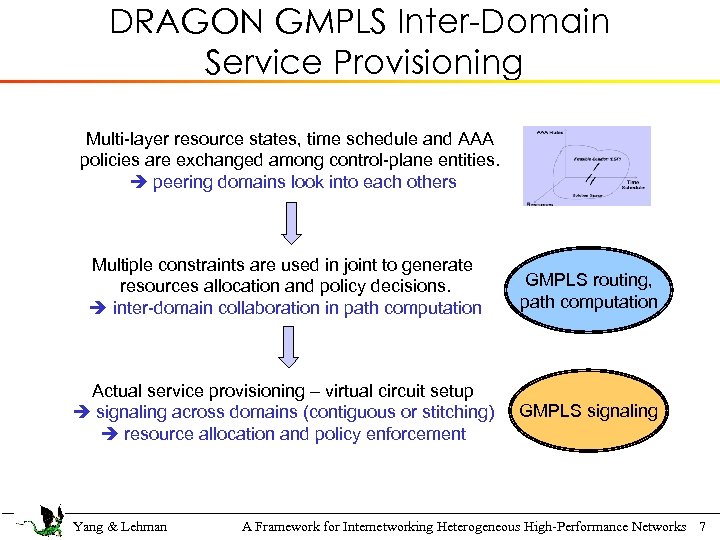 DRAGON GMPLS Inter-Domain Service Provisioning Multi-layer resource states, time schedule and AAA policies are exchanged among control-plane entities. peering domains look into each others Multiple constraints are used in joint to generate resources allocation and policy decisions. inter-domain collaboration in path computation GMPLS routing, path computation Actual service provisioning – virtual circuit setup signaling across domains (contiguous or stitching) resource allocation and policy enforcement GMPLS signaling Yang & Lehman A Framework for Internetworking Heterogeneous High-Performance Networks 7
DRAGON GMPLS Inter-Domain Service Provisioning Multi-layer resource states, time schedule and AAA policies are exchanged among control-plane entities. peering domains look into each others Multiple constraints are used in joint to generate resources allocation and policy decisions. inter-domain collaboration in path computation GMPLS routing, path computation Actual service provisioning – virtual circuit setup signaling across domains (contiguous or stitching) resource allocation and policy enforcement GMPLS signaling Yang & Lehman A Framework for Internetworking Heterogeneous High-Performance Networks 7
 Beyond GMPLS – A Heterogeneous Internetworking Framework • GMPLS is an option, not a limitation – Many networks do not support GMPLS, e. g. , Abilene, Do. E ESNet – Some networks only have a management plane (no control plane) – GMPLS Control Plane (GMPLS-CP) needs tight coupling which is not allowed by many networks • Option II – Shared intelligence btw control planes – Web Services based Control Plane (WS-CP) – loose coupling – A Web services wrapper layer for existing network control and management planes. – Core intra-network functions unchanged; inter-network enhancements – Web services are simple, standard with lots of handy tools. – Service oriented architecture (SOA) and security infrastructure (WSS) Yang & Lehman A Framework for Internetworking Heterogeneous High-Performance Networks 8
Beyond GMPLS – A Heterogeneous Internetworking Framework • GMPLS is an option, not a limitation – Many networks do not support GMPLS, e. g. , Abilene, Do. E ESNet – Some networks only have a management plane (no control plane) – GMPLS Control Plane (GMPLS-CP) needs tight coupling which is not allowed by many networks • Option II – Shared intelligence btw control planes – Web Services based Control Plane (WS-CP) – loose coupling – A Web services wrapper layer for existing network control and management planes. – Core intra-network functions unchanged; inter-network enhancements – Web services are simple, standard with lots of handy tools. – Service oriented architecture (SOA) and security infrastructure (WSS) Yang & Lehman A Framework for Internetworking Heterogeneous High-Performance Networks 8
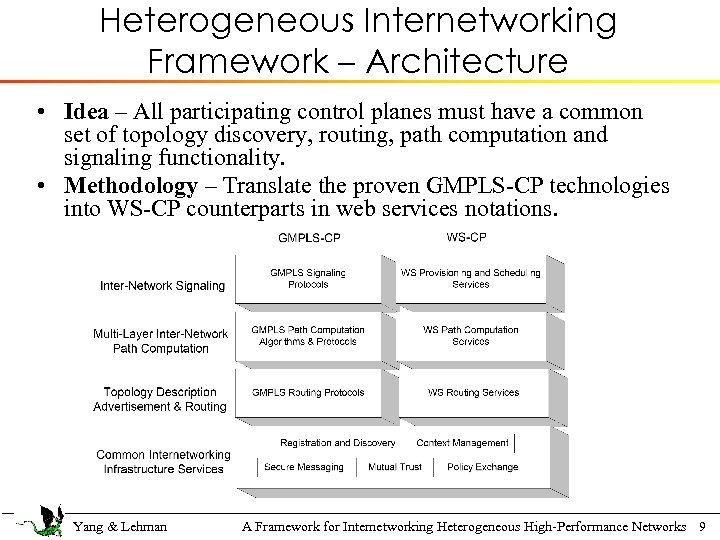 Heterogeneous Internetworking Framework – Architecture • Idea – All participating control planes must have a common set of topology discovery, routing, path computation and signaling functionality. • Methodology – Translate the proven GMPLS-CP technologies into WS-CP counterparts in web services notations. Yang & Lehman A Framework for Internetworking Heterogeneous High-Performance Networks 9
Heterogeneous Internetworking Framework – Architecture • Idea – All participating control planes must have a common set of topology discovery, routing, path computation and signaling functionality. • Methodology – Translate the proven GMPLS-CP technologies into WS-CP counterparts in web services notations. Yang & Lehman A Framework for Internetworking Heterogeneous High-Performance Networks 9
 Conclusions • HPN’s of the World, Unite! • HPN provisioning will best be via control plane. • Any control plane for multi-layer multi-domain heterogeneous networking should support topology discovery, routing, path computation and signaling as GMPLS-CP does. • WS-CP enables loose inter-network coupling and implements the GMPLS-like functionalities around Web services. • The proposed heterogeneous internetworking framework supports both GMLS-CP and WS-CP. The latter will be more widely accepted. Yang & Lehman A Framework for Internetworking Heterogeneous High-Performance Networks 11
Conclusions • HPN’s of the World, Unite! • HPN provisioning will best be via control plane. • Any control plane for multi-layer multi-domain heterogeneous networking should support topology discovery, routing, path computation and signaling as GMPLS-CP does. • WS-CP enables loose inter-network coupling and implements the GMPLS-like functionalities around Web services. • The proposed heterogeneous internetworking framework supports both GMLS-CP and WS-CP. The latter will be more widely accepted. Yang & Lehman A Framework for Internetworking Heterogeneous High-Performance Networks 11


