08304e68e23c2929c8a1d141177c6752.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 67





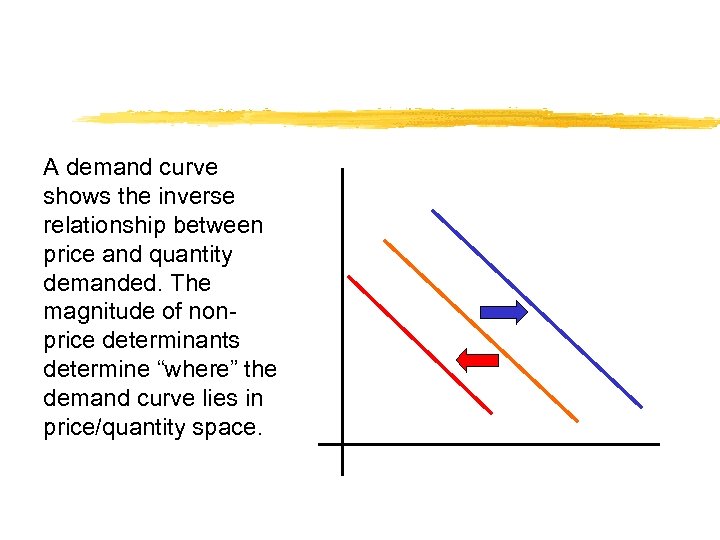
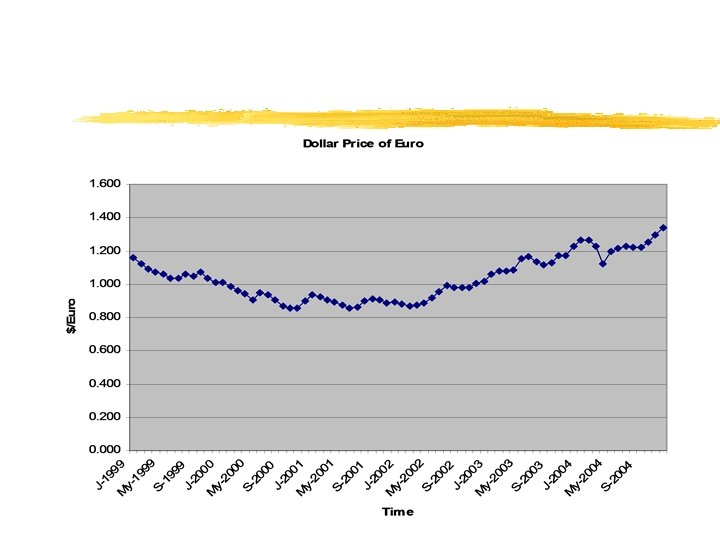
A demand curve shows the inverse relationship between price and quantity demanded. The magnitude of nonprice determinants determine “where” the demand curve lies in price/quantity space.


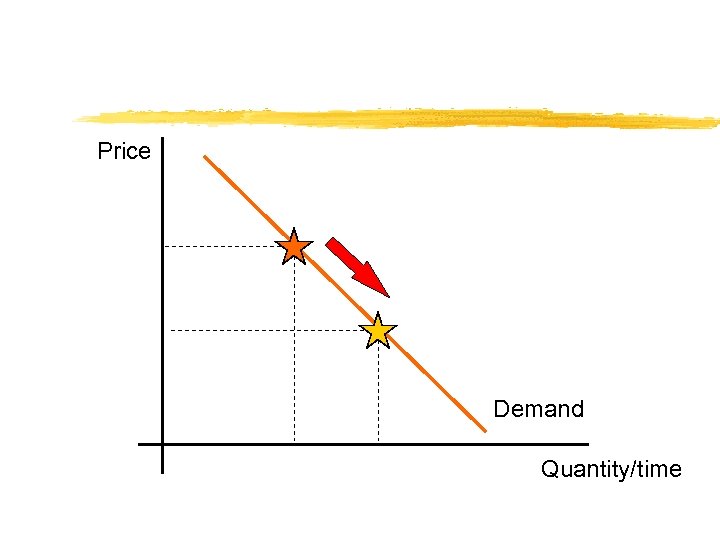
Price Demand Quantity/time
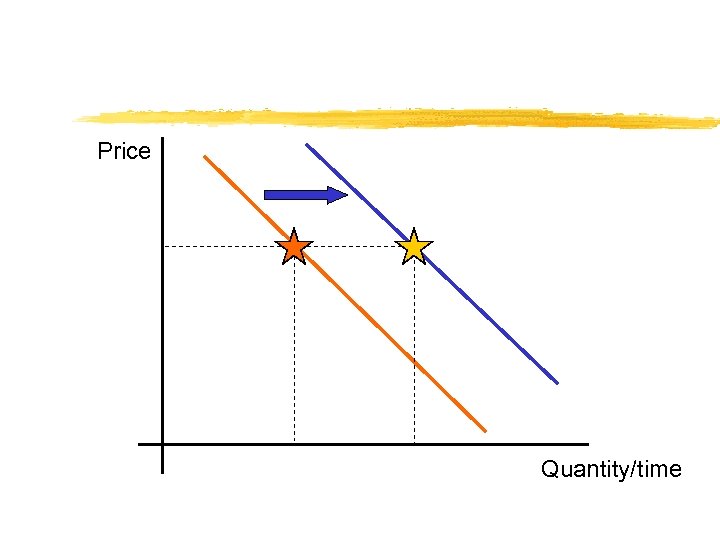
Price Quantity/time









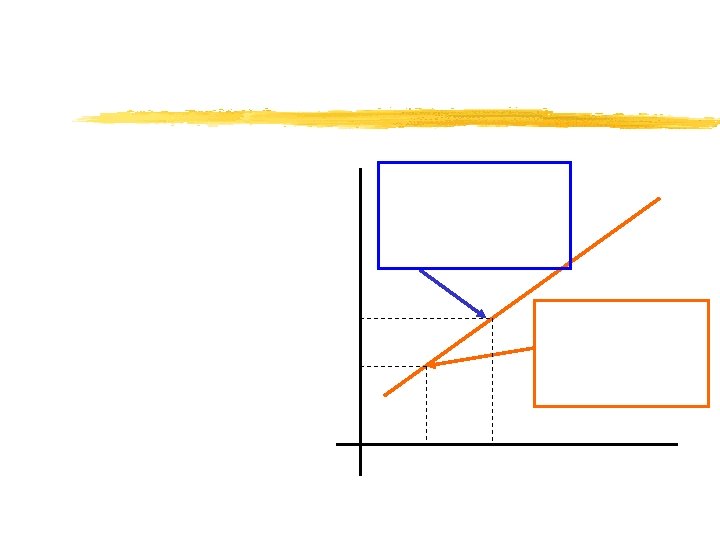
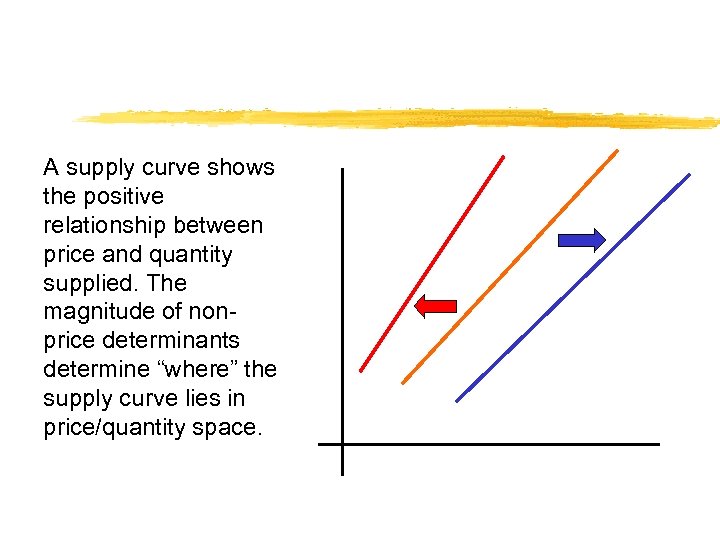
A supply curve shows the positive relationship between price and quantity supplied. The magnitude of nonprice determinants determine “where” the supply curve lies in price/quantity space.


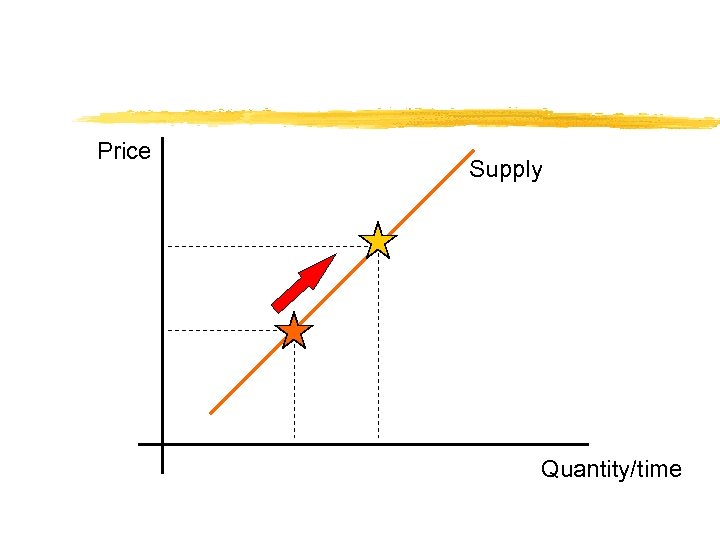
Price Supply Quantity/time
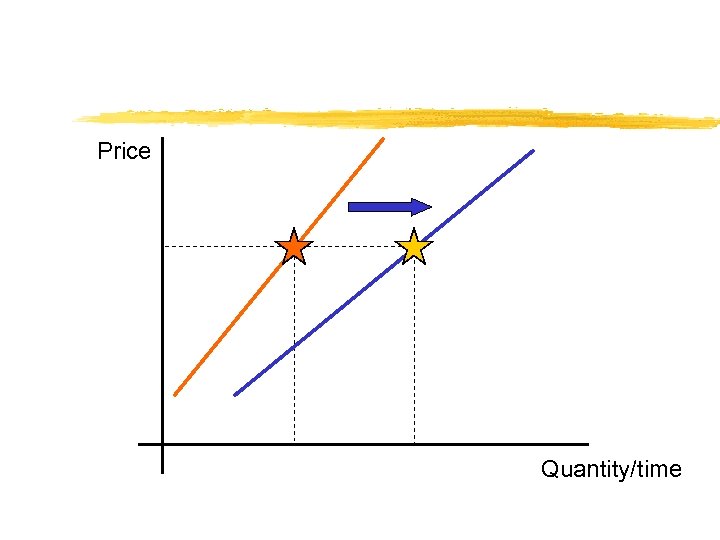
Price Quantity/time






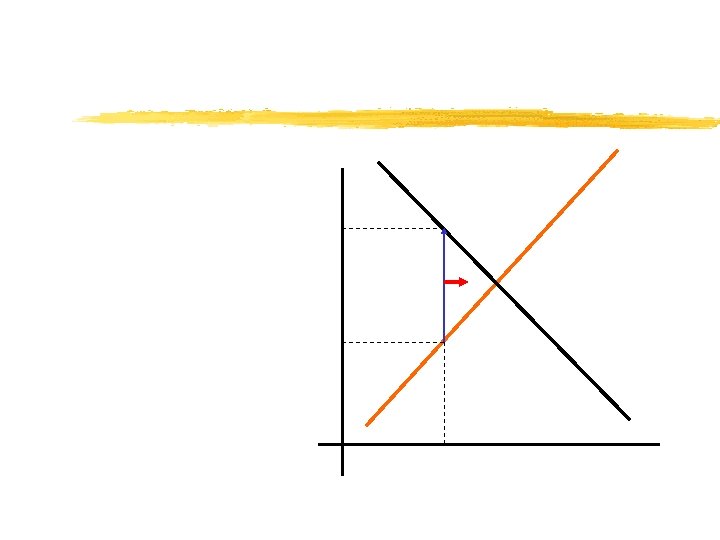




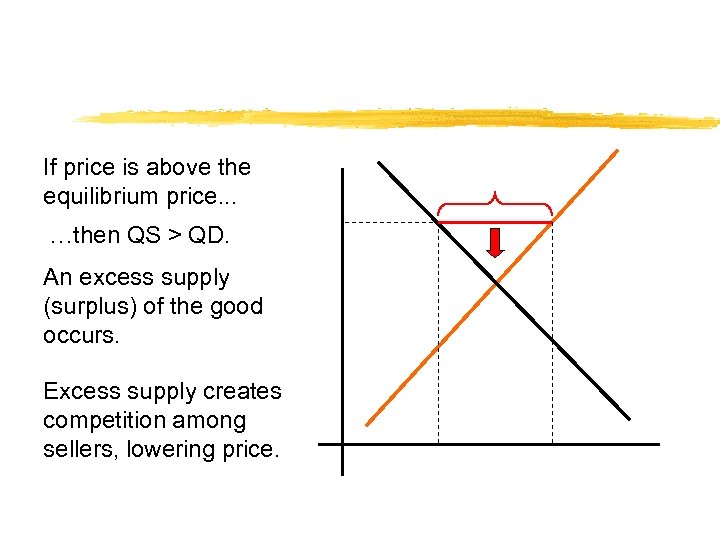
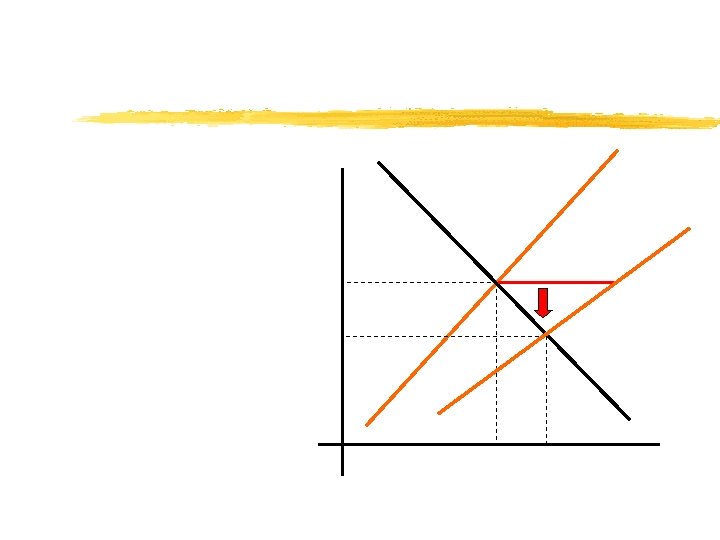
If price is above the equilibrium price. . . …then QS > QD. An excess supply (surplus) of the good occurs. Excess supply creates competition among sellers, lowering price.
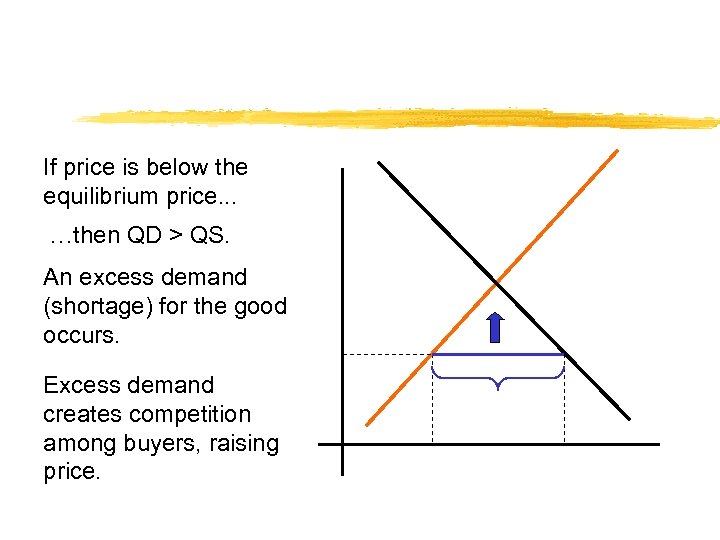
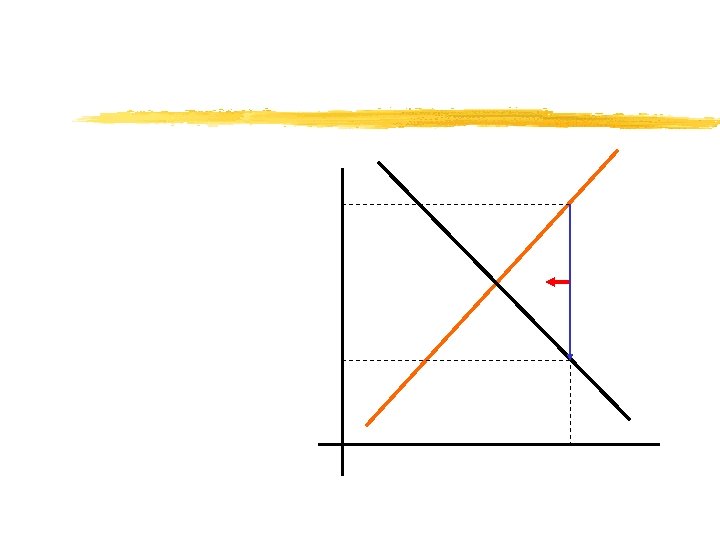
If price is below the equilibrium price. . . …then QD > QS. An excess demand (shortage) for the good occurs. Excess demand creates competition among buyers, raising price.

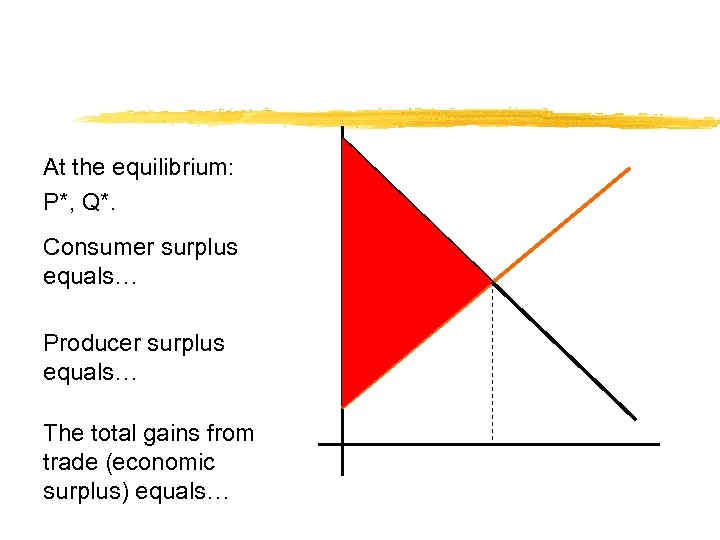
At the equilibrium: P*, Q*. Consumer surplus equals… Producer surplus equals… The total gains from trade (economic surplus) equals…
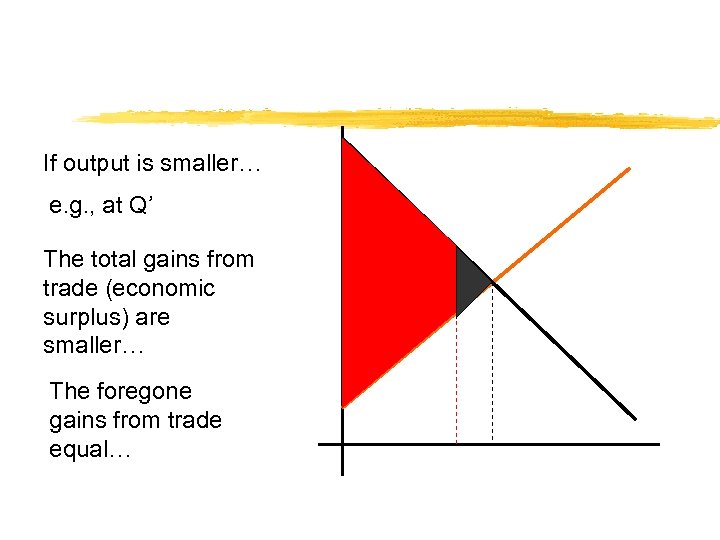
If output is smaller… e. g. , at Q’ The total gains from trade (economic surplus) are smaller… The foregone gains from trade equal…
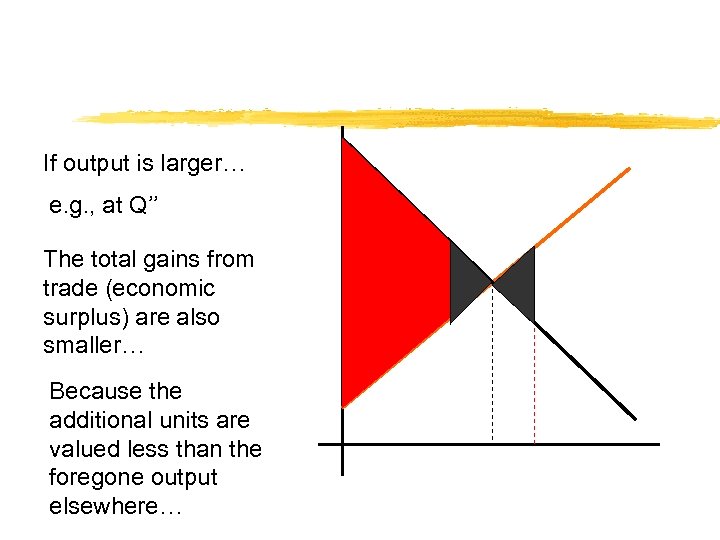
If output is larger… e. g. , at Q’’ The total gains from trade (economic surplus) are also smaller… Because the additional units are valued less than the foregone output elsewhere…
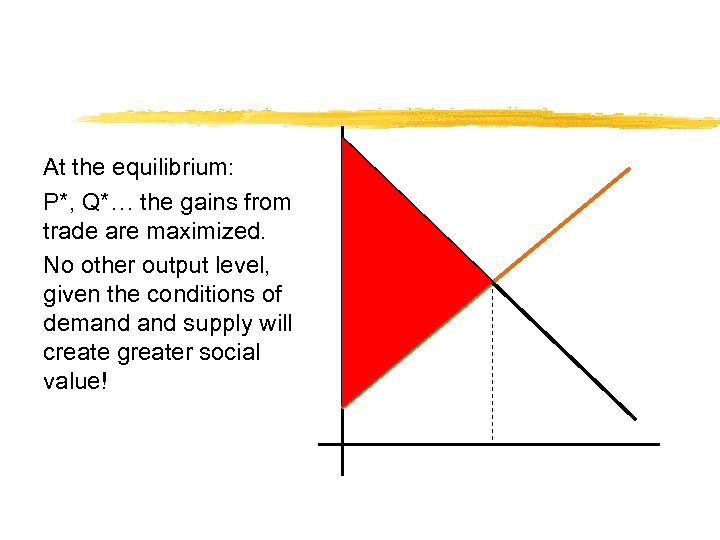
At the equilibrium: P*, Q*… the gains from trade are maximized. No other output level, given the conditions of demand supply will create greater social value!










08304e68e23c2929c8a1d141177c6752.ppt