64790ddb825bbf57508af69ca77cb95c.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 32
 A Decision System Using ANP and Fuzzy Inputs Jaroslav Ramík Silesian University Opava School of Business Administration Karviná Czech Republic e-mail: ramik@opf. slu. cz FUR XII, Rome, June 2006
A Decision System Using ANP and Fuzzy Inputs Jaroslav Ramík Silesian University Opava School of Business Administration Karviná Czech Republic e-mail: ramik@opf. slu. cz FUR XII, Rome, June 2006
 Content • Problem -AHP • Dependent criteria – ANP • Solution • Case study • Conclusion
Content • Problem -AHP • Dependent criteria – ANP • Solution • Case study • Conclusion
 Problem- AHP • MADM problem – AHP • AHP- supermatrix • AHP- limiting matrix Content
Problem- AHP • MADM problem – AHP • AHP- supermatrix • AHP- limiting matrix Content
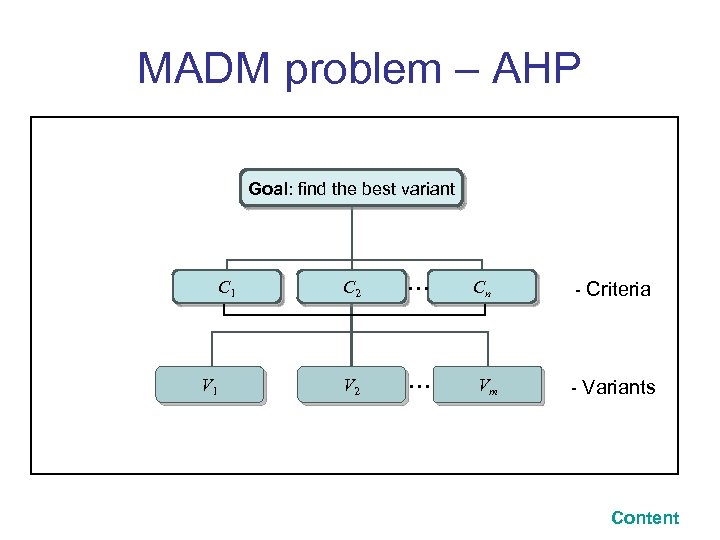 MADM problem – AHP Goal: find the best variant C 1 V 1 C 2 … Cn - Criteria V 2 … Vm - Variants Content
MADM problem – AHP Goal: find the best variant C 1 V 1 C 2 … Cn - Criteria V 2 … Vm - Variants Content
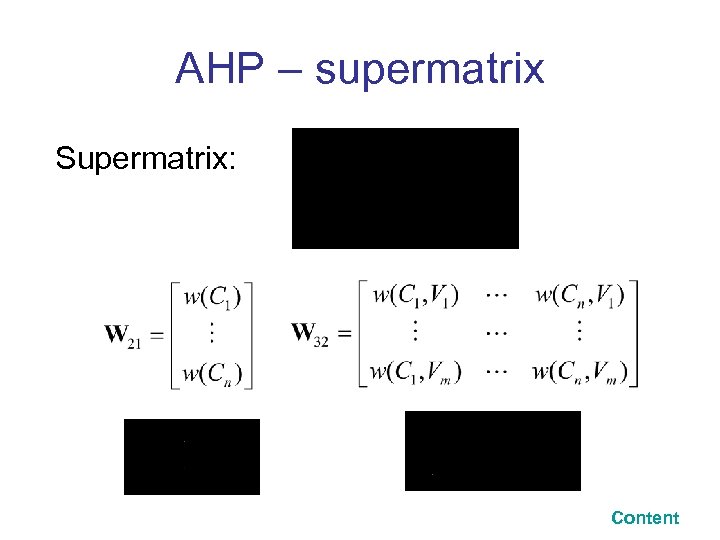 AHP – supermatrix Supermatrix: Content
AHP – supermatrix Supermatrix: Content
 AHP- limiting matrix Limiting matrix: - vector of evaluations of variants (weights) Content
AHP- limiting matrix Limiting matrix: - vector of evaluations of variants (weights) Content
 Dependent criteria – ANP • • • Dependent evaluation criteria – ANP Dependent criteria – supermatrix Dependent criteria – limiting matrix Uncertain evaluations Uncertain pair-wise comparisons Content
Dependent criteria – ANP • • • Dependent evaluation criteria – ANP Dependent criteria – supermatrix Dependent criteria – limiting matrix Uncertain evaluations Uncertain pair-wise comparisons Content
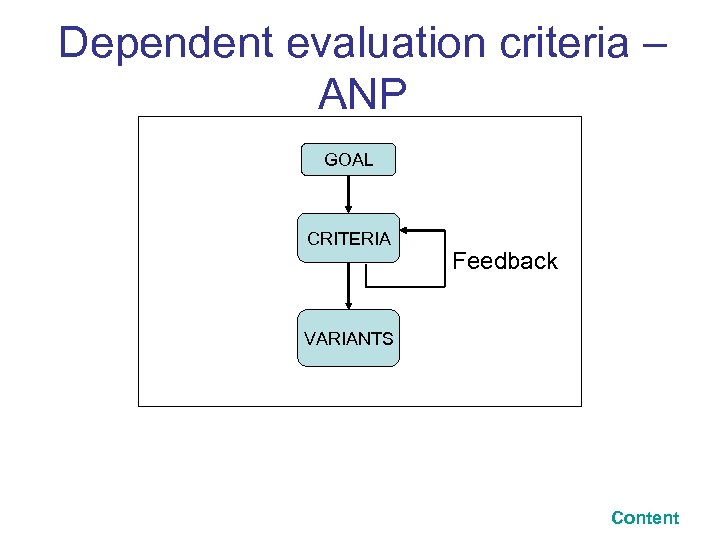 Dependent evaluation criteria – ANP GOAL CRITERIA Feedback VARIANTS Content
Dependent evaluation criteria – ANP GOAL CRITERIA Feedback VARIANTS Content
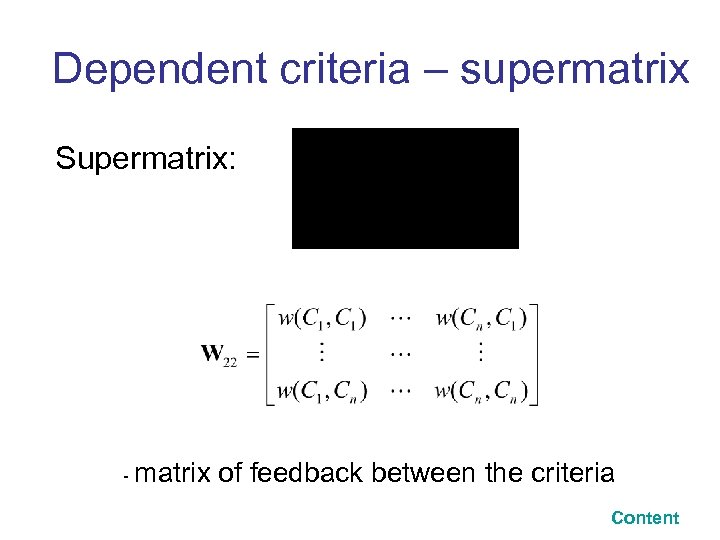 Dependent criteria – supermatrix Supermatrix: - matrix of feedback between the criteria Content
Dependent criteria – supermatrix Supermatrix: - matrix of feedback between the criteria Content
 Dependent criteria – limiting matrix Limiting matrix: - vector of evaluations of variants (weights) Content
Dependent criteria – limiting matrix Limiting matrix: - vector of evaluations of variants (weights) Content
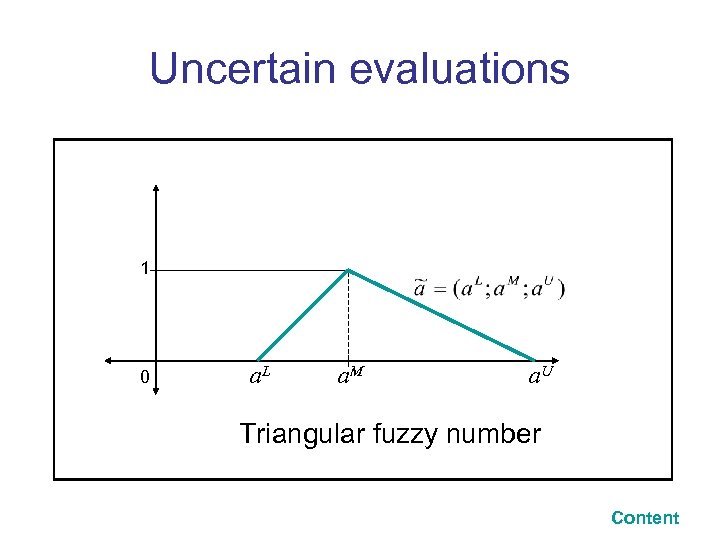 Uncertain evaluations 1 0 a. L a. M a. U Triangular fuzzy number Content
Uncertain evaluations 1 0 a. L a. M a. U Triangular fuzzy number Content
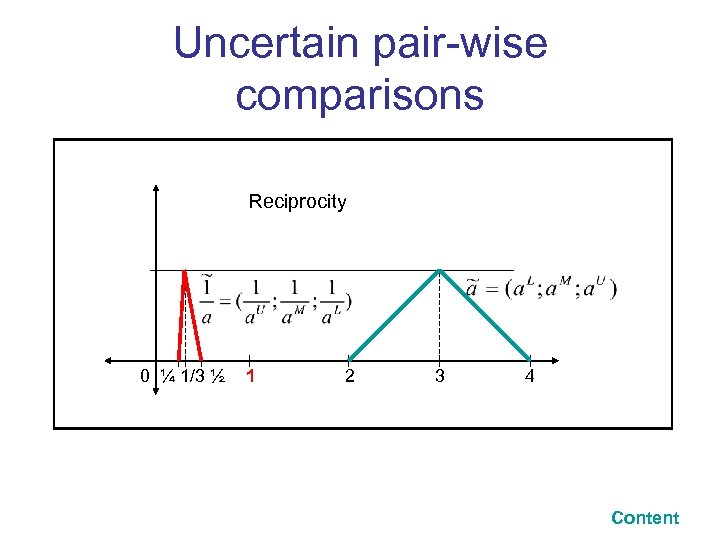 Uncertain pair-wise comparisons Reciprocity 0 ¼ 1/3 ½ 1 2 3 4 Content
Uncertain pair-wise comparisons Reciprocity 0 ¼ 1/3 ½ 1 2 3 4 Content
 Solution • • • Fuzzy evaluations Fuzzy arithmetic Fuzzy weights and values Defuzzyfication Algorithm Content
Solution • • • Fuzzy evaluations Fuzzy arithmetic Fuzzy weights and values Defuzzyfication Algorithm Content
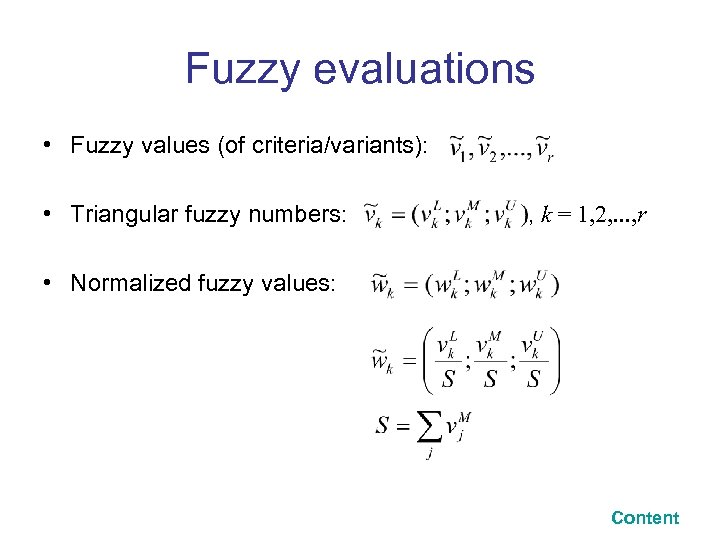 Fuzzy evaluations • Fuzzy values (of criteria/variants): • Triangular fuzzy numbers: , k = 1, 2, . . . , r • Normalized fuzzy values: Content
Fuzzy evaluations • Fuzzy values (of criteria/variants): • Triangular fuzzy numbers: , k = 1, 2, . . . , r • Normalized fuzzy values: Content
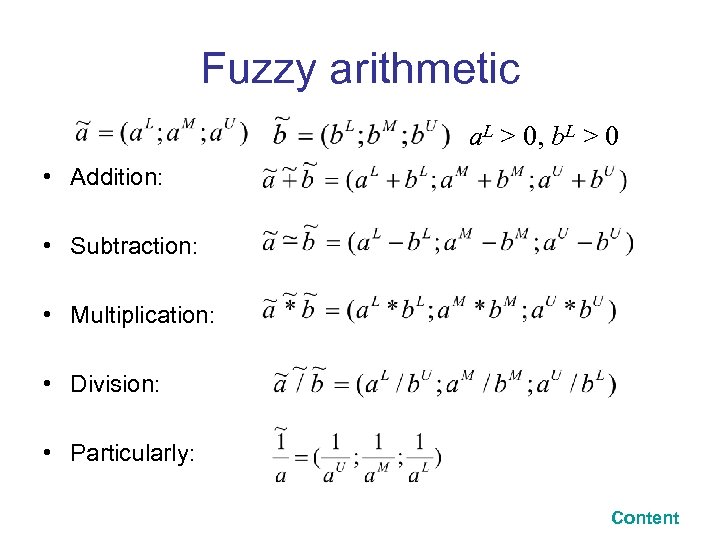 Fuzzy arithmetic a. L > 0, b. L > 0 • Addition: • Subtraction: • Multiplication: • Division: • Particularly: Content
Fuzzy arithmetic a. L > 0, b. L > 0 • Addition: • Subtraction: • Multiplication: • Division: • Particularly: Content
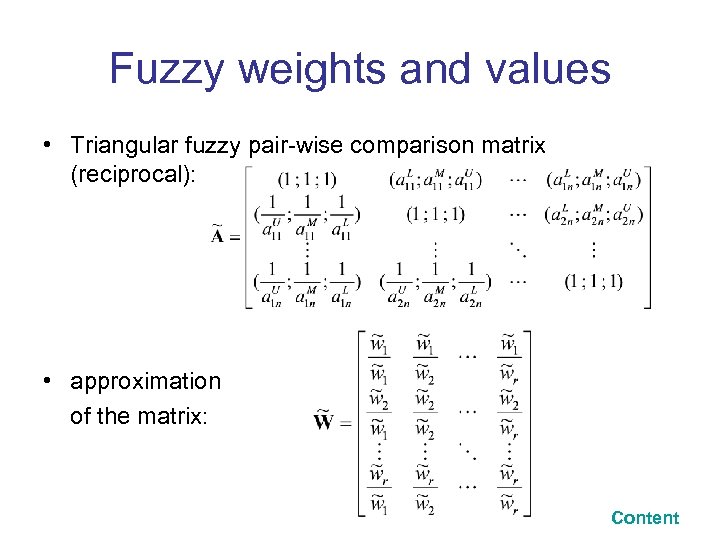 Fuzzy weights and values • Triangular fuzzy pair-wise comparison matrix (reciprocal): • approximation of the matrix: Content
Fuzzy weights and values • Triangular fuzzy pair-wise comparison matrix (reciprocal): • approximation of the matrix: Content
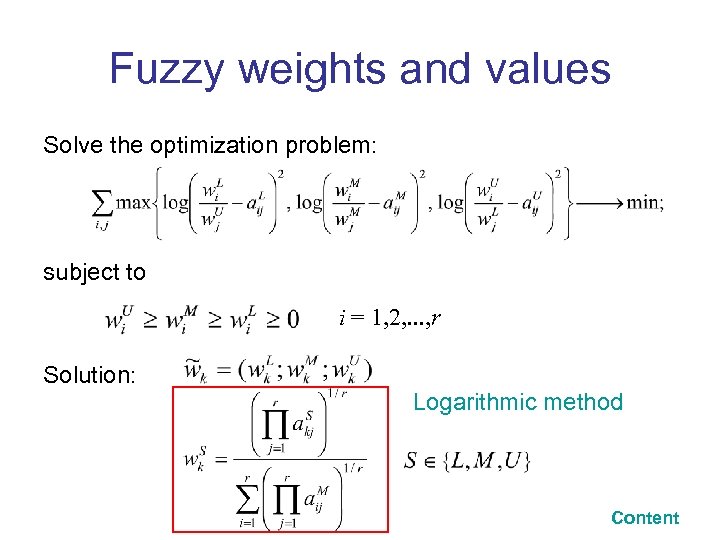 Fuzzy weights and values Solve the optimization problem: subject to i = 1, 2, . . . , r Solution: Logarithmic method Content
Fuzzy weights and values Solve the optimization problem: subject to i = 1, 2, . . . , r Solution: Logarithmic method Content
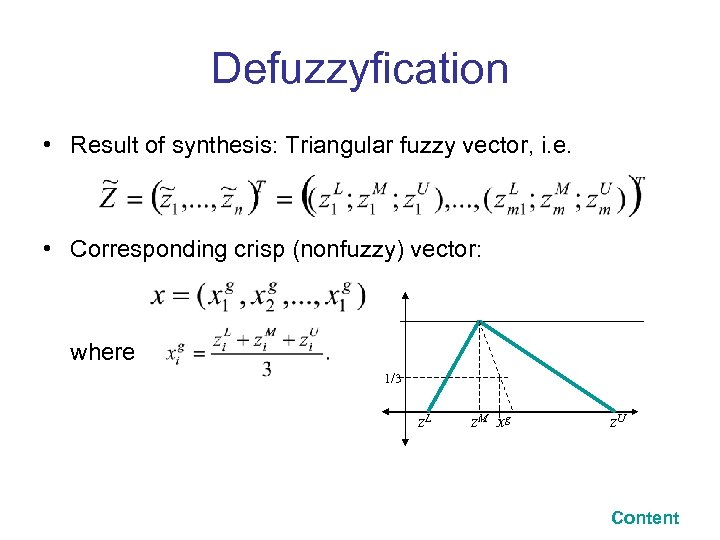 Defuzzyfication • Result of synthesis: Triangular fuzzy vector, i. e. • Corresponding crisp (nonfuzzy) vector: where 1/3 z. L z. M x g z. U Content
Defuzzyfication • Result of synthesis: Triangular fuzzy vector, i. e. • Corresponding crisp (nonfuzzy) vector: where 1/3 z. L z. M x g z. U Content
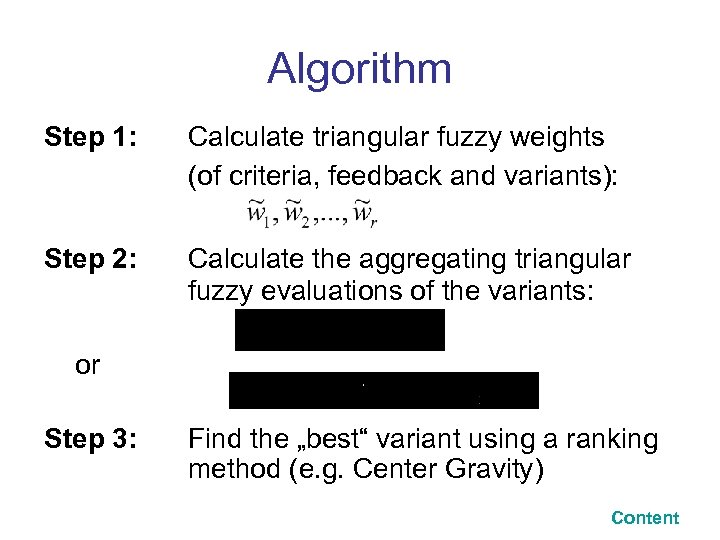 Algorithm Step 1: Calculate triangular fuzzy weights (of criteria, feedback and variants): Step 2: Calculate the aggregating triangular fuzzy evaluations of the variants: or Step 3: Find the „best“ variant using a ranking method (e. g. Center Gravity) Content
Algorithm Step 1: Calculate triangular fuzzy weights (of criteria, feedback and variants): Step 2: Calculate the aggregating triangular fuzzy evaluations of the variants: or Step 3: Find the „best“ variant using a ranking method (e. g. Center Gravity) Content
 Case study • • • Case study - outline Case study - criteria Case study - variants Case study - feedback Case study - W 32* and W 22* Case study - synthesis Case study - crisp case with fedback Case study - crisp case NO fedback Case study - comparison Content
Case study • • • Case study - outline Case study - criteria Case study - variants Case study - feedback Case study - W 32* and W 22* Case study - synthesis Case study - crisp case with fedback Case study - crisp case NO fedback Case study - comparison Content
 Case study - outline • Problem: Buy the best product (a car) 3 criteria 4 variants • Data: triangular fuzzy pair-wise comparisons fuzzy weights • Calculations: 1. with feedback 2. without feedback • Crisp case: „middle values of triangles“ Case study
Case study - outline • Problem: Buy the best product (a car) 3 criteria 4 variants • Data: triangular fuzzy pair-wise comparisons fuzzy weights • Calculations: 1. with feedback 2. without feedback • Crisp case: „middle values of triangles“ Case study
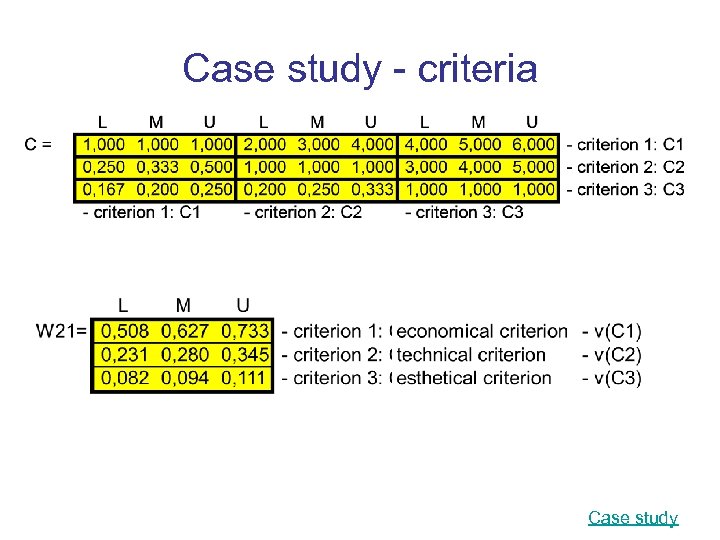 Case study - criteria Case study
Case study - criteria Case study
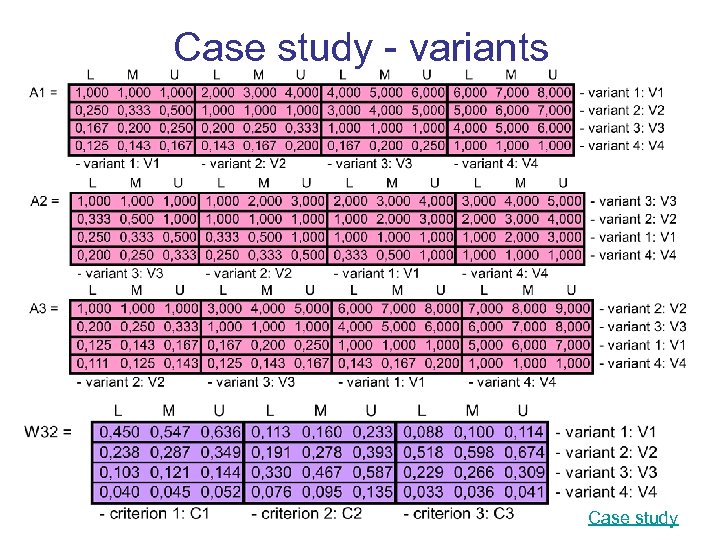 Case study - variants Case study
Case study - variants Case study
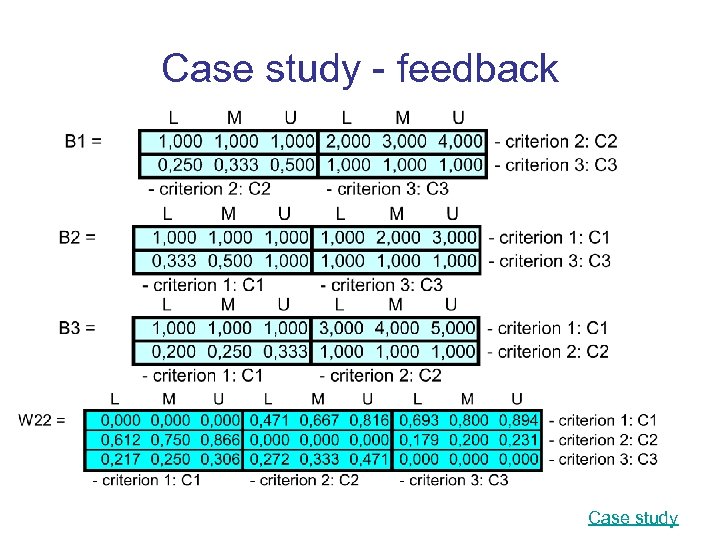 Case study - feedback Case study
Case study - feedback Case study
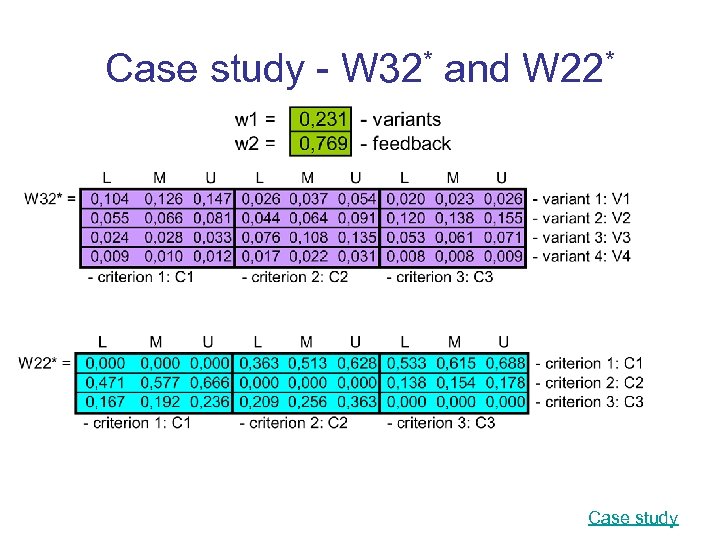 Case study - W 32* and W 22* Case study
Case study - W 32* and W 22* Case study
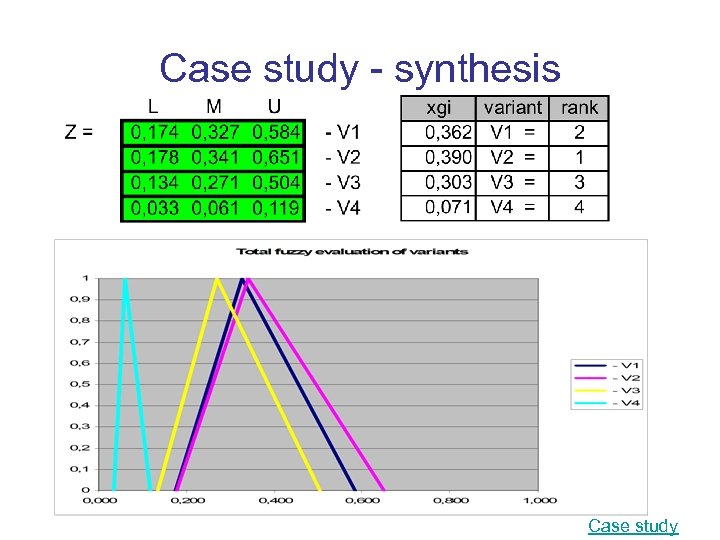 Case study - synthesis Case study
Case study - synthesis Case study
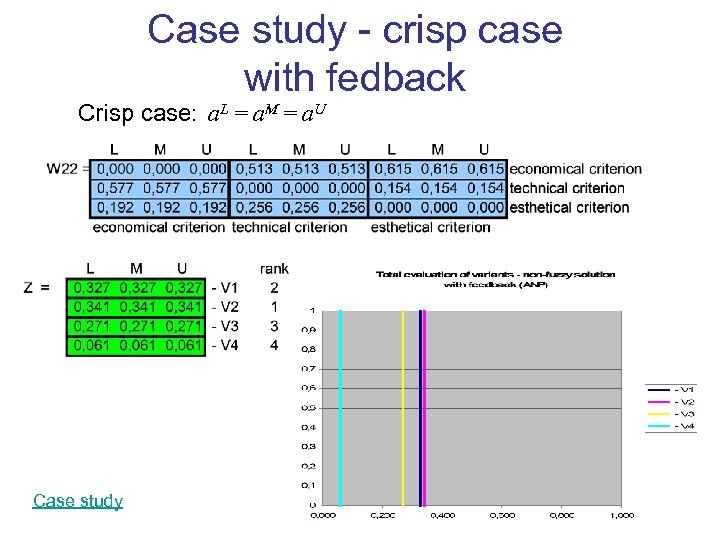 Case study - crisp case with fedback Crisp case: a. L = a. M = a. U Case study
Case study - crisp case with fedback Crisp case: a. L = a. M = a. U Case study
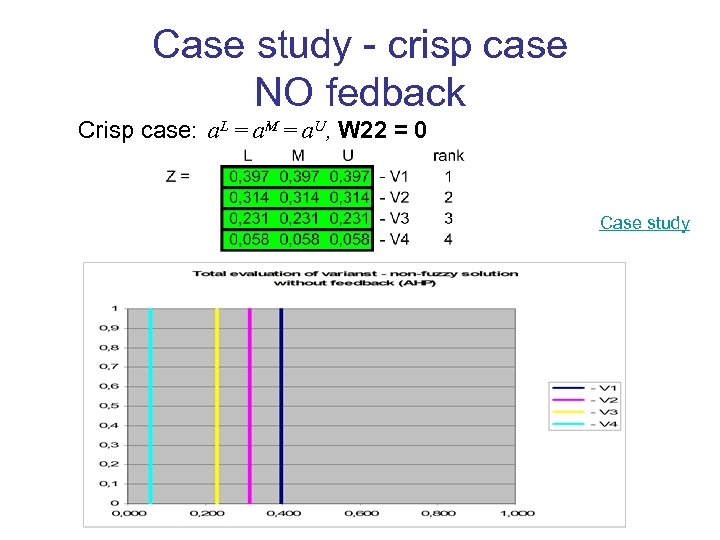 Case study - crisp case NO fedback Crisp case: a. L = a. M = a. U, W 22 = 0 Case study
Case study - crisp case NO fedback Crisp case: a. L = a. M = a. U, W 22 = 0 Case study
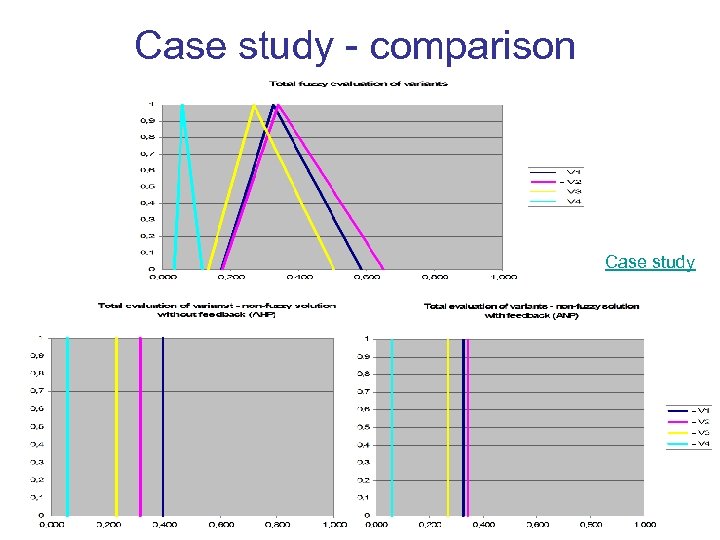 Case study - comparison Case study
Case study - comparison Case study
 Conclusion • Fuzzy evaluation of pair-wise comparisons may be more comfortable and appropriate for DM • Occurance of dependences among criteria is realistic and frequent • Dependences among criteria may influence the final rank of variants • Presence of fuzziness in evaluations may change the final rank of variants Case study
Conclusion • Fuzzy evaluation of pair-wise comparisons may be more comfortable and appropriate for DM • Occurance of dependences among criteria is realistic and frequent • Dependences among criteria may influence the final rank of variants • Presence of fuzziness in evaluations may change the final rank of variants Case study
 References • • Buckley, J. J. , Fuzzy hierarchical analysis. Fuzzy Sets and Systems 17, 1985, 1, p. 233 -247, ISSN 0165 -0114. Chen, S. J. , Hwang, C. L. and Hwang, F. P. , Fuzzy multiple attribute decision making. Lecture Notes in Economics and Math. Syst. , Vol. 375, Springer-Verlag, Berlin – Heidelberg 1992, ISBN 3 -540 -54998 -6. Horn, R. A. , Johnson, C. R. , Matrix Analysis, Cambridge University Press, 1990, ISBN 0521305861. Ramik, J. , Duality in fuzzy linear programming with possibility and necessity relations. Fuzzy Sets and Systems 157, 2006, 1, p. 1283 -1302, ISSN 0165 -0114. Saaty, T. L. , Exploring the interface between hierarchies, multiple objectives and fuzzy sets. Fuzzy Sets and Systems 1, 1978, p. 57 -68, ISSN 0165 -0114. Saaty, T. L. , Multicriteria decision making - the Analytical Hierarchy Process. Vol. I. , RWS Publications, Pittsburgh, 1991, ISBN. Saaty, T. L. , Decision Making with Dependence and Feedback – The Analytic Network Process. RWS Publications, Pittsburgh, 2001, ISBN 09620317 -9 -8. Van Laarhoven, P. J. M. and Pedrycz, W. , A fuzzy extension of Saaty's priority theory. Fuzzy Sets and Systems 11, 1983, 4, p. 229 -241, ISSN 0165 -0114.
References • • Buckley, J. J. , Fuzzy hierarchical analysis. Fuzzy Sets and Systems 17, 1985, 1, p. 233 -247, ISSN 0165 -0114. Chen, S. J. , Hwang, C. L. and Hwang, F. P. , Fuzzy multiple attribute decision making. Lecture Notes in Economics and Math. Syst. , Vol. 375, Springer-Verlag, Berlin – Heidelberg 1992, ISBN 3 -540 -54998 -6. Horn, R. A. , Johnson, C. R. , Matrix Analysis, Cambridge University Press, 1990, ISBN 0521305861. Ramik, J. , Duality in fuzzy linear programming with possibility and necessity relations. Fuzzy Sets and Systems 157, 2006, 1, p. 1283 -1302, ISSN 0165 -0114. Saaty, T. L. , Exploring the interface between hierarchies, multiple objectives and fuzzy sets. Fuzzy Sets and Systems 1, 1978, p. 57 -68, ISSN 0165 -0114. Saaty, T. L. , Multicriteria decision making - the Analytical Hierarchy Process. Vol. I. , RWS Publications, Pittsburgh, 1991, ISBN. Saaty, T. L. , Decision Making with Dependence and Feedback – The Analytic Network Process. RWS Publications, Pittsburgh, 2001, ISBN 09620317 -9 -8. Van Laarhoven, P. J. M. and Pedrycz, W. , A fuzzy extension of Saaty's priority theory. Fuzzy Sets and Systems 11, 1983, 4, p. 229 -241, ISSN 0165 -0114.
 DĚKUJI VÁM (Thank You)
DĚKUJI VÁM (Thank You)


