eec50526e3da6b65fc49597a8fea171c.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 50
 a. D sl VD sl op ne ti tw ca l or k co ax Integrated Access Solutions - Digital Darkhorses - be gi r et ga h bi er t ne w t ir el es s s. D sl Jang-Rai Roh Product Planning Fi www. tellion. com 1
a. D sl VD sl op ne ti tw ca l or k co ax Integrated Access Solutions - Digital Darkhorses - be gi r et ga h bi er t ne w t ir el es s s. D sl Jang-Rai Roh Product Planning Fi www. tellion. com 1
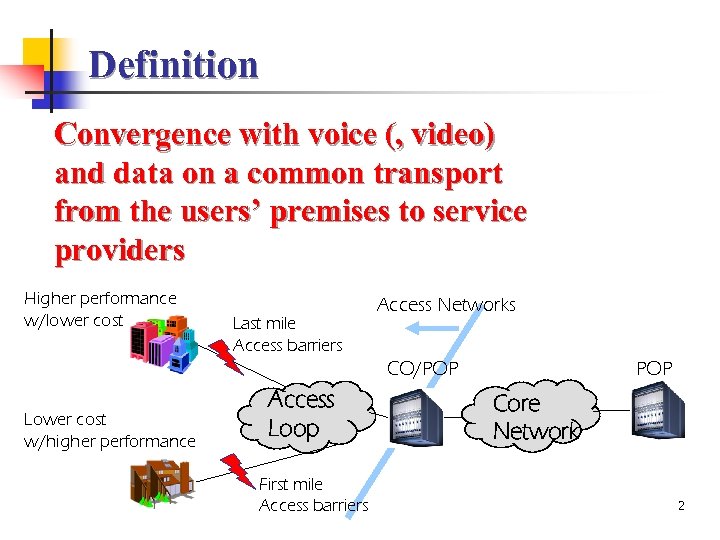 Definition Convergence with voice (, video) and data on a common transport from the users’ premises to service providers Higher performance w/lower cost Last mile Access barriers Access Networks POP CO/POP Lower cost w/higher performance Access Loop First mile Access barriers Core Network 2
Definition Convergence with voice (, video) and data on a common transport from the users’ premises to service providers Higher performance w/lower cost Last mile Access barriers Access Networks POP CO/POP Lower cost w/higher performance Access Loop First mile Access barriers Core Network 2
 I Will Talk About… n A variety of protocols and media… n n Trends/Opportunities in Access Networks n n n To reduce the technology risk of the transition from a circuitoriented to an emerging data centric Technical issues Technical and market trends Market Migration toward Integrated Access Networks n To support integration of IP, ATM and lambda in economic manner 3
I Will Talk About… n A variety of protocols and media… n n Trends/Opportunities in Access Networks n n n To reduce the technology risk of the transition from a circuitoriented to an emerging data centric Technical issues Technical and market trends Market Migration toward Integrated Access Networks n To support integration of IP, ATM and lambda in economic manner 3
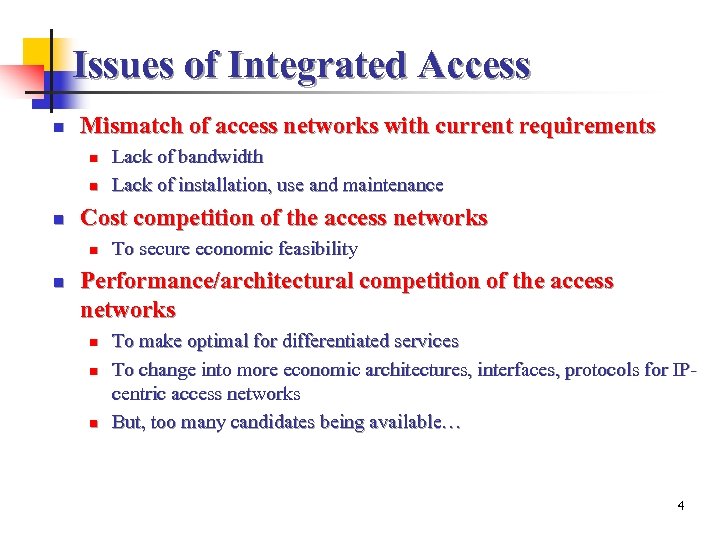 Issues of Integrated Access n Mismatch of access networks with current requirements n n n Cost competition of the access networks n n Lack of bandwidth Lack of installation, use and maintenance To secure economic feasibility Performance/architectural competition of the access networks n n n To make optimal for differentiated services To change into more economic architectures, interfaces, protocols for IPcentric access networks But, too many candidates being available… 4
Issues of Integrated Access n Mismatch of access networks with current requirements n n n Cost competition of the access networks n n Lack of bandwidth Lack of installation, use and maintenance To secure economic feasibility Performance/architectural competition of the access networks n n n To make optimal for differentiated services To change into more economic architectures, interfaces, protocols for IPcentric access networks But, too many candidates being available… 4
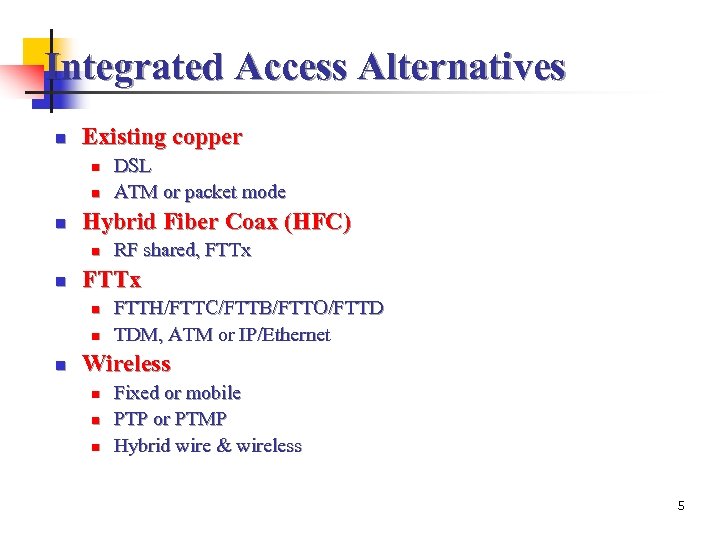 Integrated Access Alternatives n Existing copper n n n Hybrid Fiber Coax (HFC) n n RF shared, FTTx n n n DSL ATM or packet mode FTTH/FTTC/FTTB/FTTO/FTTD TDM, ATM or IP/Ethernet Wireless n n n Fixed or mobile PTP or PTMP Hybrid wire & wireless 5
Integrated Access Alternatives n Existing copper n n n Hybrid Fiber Coax (HFC) n n RF shared, FTTx n n n DSL ATM or packet mode FTTH/FTTC/FTTB/FTTO/FTTD TDM, ATM or IP/Ethernet Wireless n n n Fixed or mobile PTP or PTMP Hybrid wire & wireless 5
 x. DSL 6
x. DSL 6
 x. DSL Technologies n n ADSL VDSL SDSL/SHDSL Others 7
x. DSL Technologies n n ADSL VDSL SDSL/SHDSL Others 7
 Issues in x. DSL n n n CPE auto-configuration, retail availability Automatic loop qualification End-to-End flow through provisioing Interoperability Voice over DSL n n Short-term migration Long-term migration 8
Issues in x. DSL n n n CPE auto-configuration, retail availability Automatic loop qualification End-to-End flow through provisioing Interoperability Voice over DSL n n Short-term migration Long-term migration 8
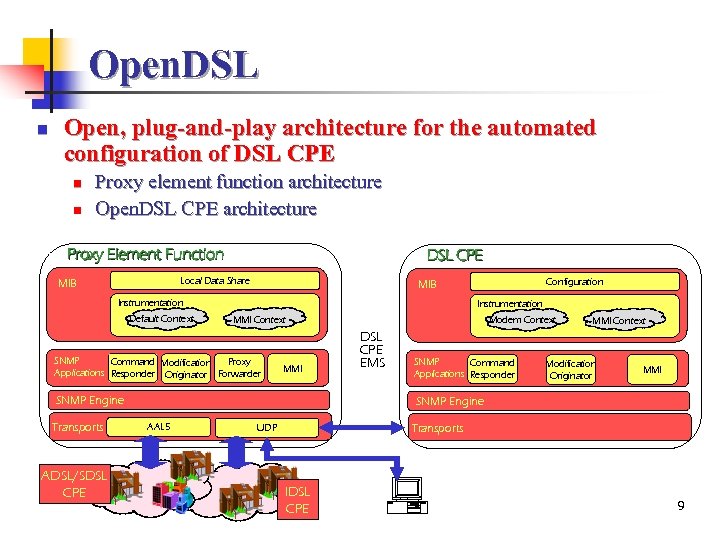 Open. DSL n Open, plug-and-play architecture for the automated configuration of DSL CPE n n Proxy element function architecture Open. DSL CPE architecture Proxy Element Function DSL CPE Local Data Share MIB Instrumentation Default Context Instrumentation MMI Context SNMP Proxy Command Modification Applications Responder Originator Forwarder MMI SNMP Engine Transports ADSL/SDSL CPE Configuration MIB Modem Context DSL CPE EMS SNMP Command Applications Responder MMI Context Modification Originator MMI SNMP Engine AAL 5 Transports UDP IDSL CPE 9
Open. DSL n Open, plug-and-play architecture for the automated configuration of DSL CPE n n Proxy element function architecture Open. DSL CPE architecture Proxy Element Function DSL CPE Local Data Share MIB Instrumentation Default Context Instrumentation MMI Context SNMP Proxy Command Modification Applications Responder Originator Forwarder MMI SNMP Engine Transports ADSL/SDSL CPE Configuration MIB Modem Context DSL CPE EMS SNMP Command Applications Responder MMI Context Modification Originator MMI SNMP Engine AAL 5 Transports UDP IDSL CPE 9
 Vo. DSL : Today & Tomorrow n Short-term architecture n n Broadband loop emulation service using AAL 2 Architecture n n AAL 2 enabled CPE DSLAM providing ATM cell multiplexing Vo. DSL gateway Long-term architecture n n Converging data and voice over IP Architecture n n Vo. DSL gateway would be integrated into the DSLAM New signaling and control switching used by Media Gateway Control Protocol and MEGACOP/H. 248 10
Vo. DSL : Today & Tomorrow n Short-term architecture n n Broadband loop emulation service using AAL 2 Architecture n n AAL 2 enabled CPE DSLAM providing ATM cell multiplexing Vo. DSL gateway Long-term architecture n n Converging data and voice over IP Architecture n n Vo. DSL gateway would be integrated into the DSLAM New signaling and control switching used by Media Gateway Control Protocol and MEGACOP/H. 248 10
 Issues in x. DSL n ADSL Issues n n n Self-configuration Installation and maintenance Performance issues n n n Warm/fast restart, Quiescent mode Dynamic rate adaptation, Out of service testing Revised/expanded bit swapping, Clip scaling RFI ingress/egress, Concatenated convolutional code VDSL issues n n n Line codes, Spectral compatibility Backward interoperability with ADSL Positioning 11
Issues in x. DSL n ADSL Issues n n n Self-configuration Installation and maintenance Performance issues n n n Warm/fast restart, Quiescent mode Dynamic rate adaptation, Out of service testing Revised/expanded bit swapping, Clip scaling RFI ingress/egress, Concatenated convolutional code VDSL issues n n n Line codes, Spectral compatibility Backward interoperability with ADSL Positioning 11
 x. DSL Standardization n n n n ADSL-Forum FSAN ITU-T ANSI ETSI VDSL Coalition VDSL Alliance Open. DSL 12
x. DSL Standardization n n n n ADSL-Forum FSAN ITU-T ANSI ETSI VDSL Coalition VDSL Alliance Open. DSL 12
 Convergence Issues n Vo. DSL n n Smart & intelligent DSLAM n n DSL Vo. B(Voice over Broadband) and Vo. IP BLES architecture AAL 2 for voice packetizing fine for today, not for tomorrow Embedded access server Optical networking n n Optical UNI MPLS based signaling & control n Converging connection-based forwarding techniques & IP routing protocols 13
Convergence Issues n Vo. DSL n n Smart & intelligent DSLAM n n DSL Vo. B(Voice over Broadband) and Vo. IP BLES architecture AAL 2 for voice packetizing fine for today, not for tomorrow Embedded access server Optical networking n n Optical UNI MPLS based signaling & control n Converging connection-based forwarding techniques & IP routing protocols 13
 HFC 14
HFC 14
 Cable Networks n Infrastructure n n Transport n n Analog, Digital Cable Modems n n QAM, FEC, MPEG-2, QPSK, Ingress Set Top Box n n CATV, HFC, FTTC, SDV Telephony, Return Channel Standards & Projects n n DOCSISTM, Open. Cable. TM, Packet. Cable. TM, ICNA Cable. Home Spec. released in 00 Q 1 15
Cable Networks n Infrastructure n n Transport n n Analog, Digital Cable Modems n n QAM, FEC, MPEG-2, QPSK, Ingress Set Top Box n n CATV, HFC, FTTC, SDV Telephony, Return Channel Standards & Projects n n DOCSISTM, Open. Cable. TM, Packet. Cable. TM, ICNA Cable. Home Spec. released in 00 Q 1 15
 Issues in the Cable Networks n Qo. S: One HFC Network, Multiple Revenue Streams n n Subscriber management and Billing Requirements for Advanced Cable Services n n Converging voice, data and video; Vo. B Contents delivery and intelligent provisioning Advanced Transport Architectures: Sustaining the Broadband Performance Edge and Access n Fiber-rich and WDM architecture 16
Issues in the Cable Networks n Qo. S: One HFC Network, Multiple Revenue Streams n n Subscriber management and Billing Requirements for Advanced Cable Services n n Converging voice, data and video; Vo. B Contents delivery and intelligent provisioning Advanced Transport Architectures: Sustaining the Broadband Performance Edge and Access n Fiber-rich and WDM architecture 16
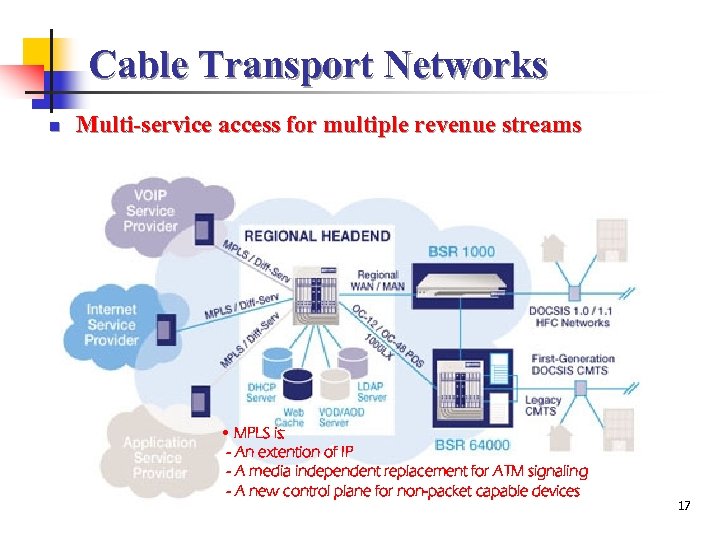 Cable Transport Networks n Multi-service access for multiple revenue streams • MPLS is: - An extention of IP - A media independent replacement for ATM signaling - A new control plane for non-packet capable devices 17
Cable Transport Networks n Multi-service access for multiple revenue streams • MPLS is: - An extention of IP - A media independent replacement for ATM signaling - A new control plane for non-packet capable devices 17
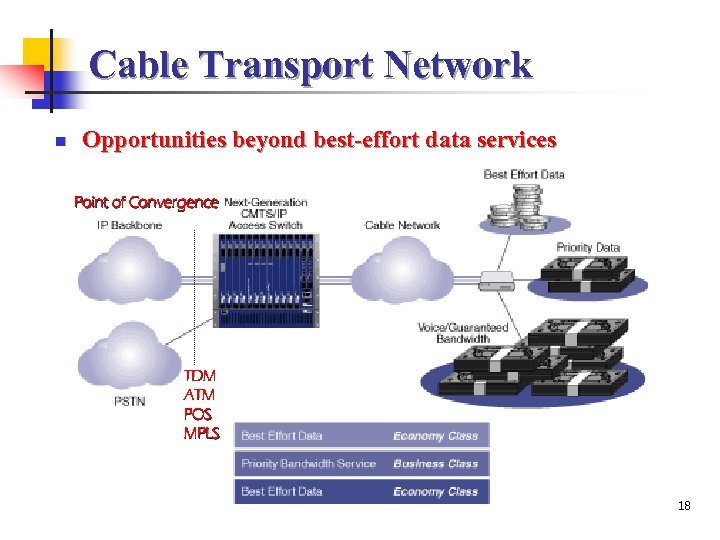 Cable Transport Network n Opportunities beyond best-effort data services Point of Convergence TDM ATM POS MPLS 18
Cable Transport Network n Opportunities beyond best-effort data services Point of Convergence TDM ATM POS MPLS 18
 Advanced Transport Architectures n Forward path designs n n n 1310 nm/1550 nm distributed feed 13010 nm/1550 nm ring 1550 nm with EDFA Amp 1310 nm/1550 nm with 1310 nm repeat Broadcast with CWDM Return path designs n n TDM return path transmitter to return path receiver repeat TDM utilizing DWDM 19
Advanced Transport Architectures n Forward path designs n n n 1310 nm/1550 nm distributed feed 13010 nm/1550 nm ring 1550 nm with EDFA Amp 1310 nm/1550 nm with 1310 nm repeat Broadcast with CWDM Return path designs n n TDM return path transmitter to return path receiver repeat TDM utilizing DWDM 19
 Cable Standardization n n Cable. Labs ANSI/SCTE 20
Cable Standardization n n Cable. Labs ANSI/SCTE 20
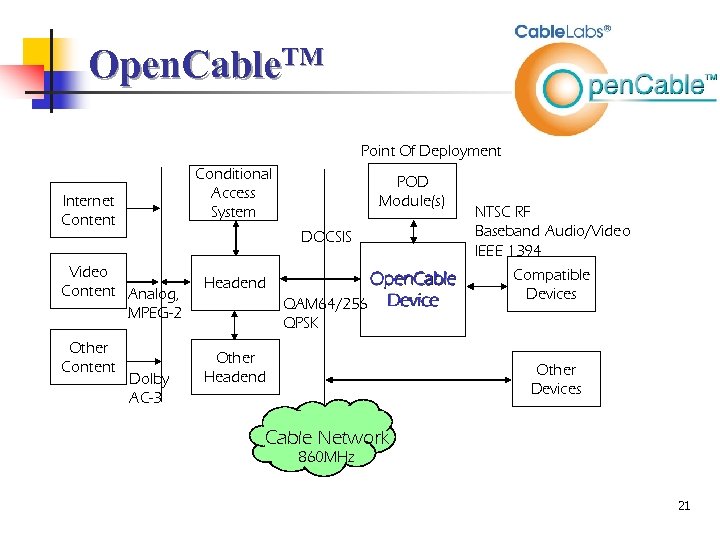 Open. Cable. TM Point Of Deployment Conditional Access System Internet Content DOCSIS Video Content Analog, MPEG-2 Other Content POD Module(s) Dolby AC-3 Headend Open. Cable QAM 64/256 Device NTSC RF Baseband Audio/Video IEEE 1394 Compatible Devices QPSK Other Headend Other Devices Cable Network 860 MHz 21
Open. Cable. TM Point Of Deployment Conditional Access System Internet Content DOCSIS Video Content Analog, MPEG-2 Other Content POD Module(s) Dolby AC-3 Headend Open. Cable QAM 64/256 Device NTSC RF Baseband Audio/Video IEEE 1394 Compatible Devices QPSK Other Headend Other Devices Cable Network 860 MHz 21
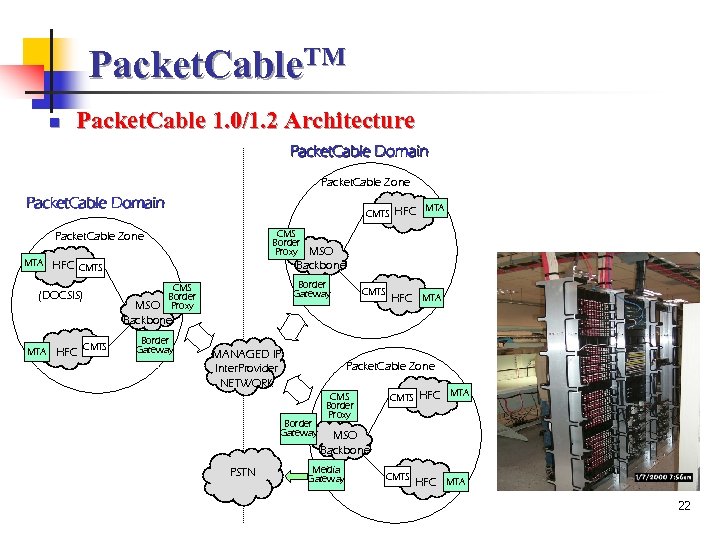 Packet. Cable. TM n Packet. Cable 1. 0/1. 2 Architecture Packet. Cable Domain Packet. Cable Zone Packet. Cable Domain CMTS CMS Border Proxy Packet. Cable Zone MTA MSO Backbone HFC CMTS HFC Border Gateway CMS Border Proxy (DOCSIS) MSO Backbone CMTS HFC MTA Border Gateway MANAGED IP Inter. Provider NETWORK HFC MTA Packet. Cable Zone Border Gateway PSTN CMTS CMS Border Proxy CMTS HFC MTA MSO Backbone Meidia Gateway CMTS HFC MTA 22
Packet. Cable. TM n Packet. Cable 1. 0/1. 2 Architecture Packet. Cable Domain Packet. Cable Zone Packet. Cable Domain CMTS CMS Border Proxy Packet. Cable Zone MTA MSO Backbone HFC CMTS HFC Border Gateway CMS Border Proxy (DOCSIS) MSO Backbone CMTS HFC MTA Border Gateway MANAGED IP Inter. Provider NETWORK HFC MTA Packet. Cable Zone Border Gateway PSTN CMTS CMS Border Proxy CMTS HFC MTA MSO Backbone Meidia Gateway CMTS HFC MTA 22
 HFC Alliance n Management and Control Interoperability Alliance n n To specify a robust protocol suite to support cost effective interoperability of management systems for evolving HFC networks SCTE Engineering subcommittees n n n n n DSS: Data Standards CAP: Cable Applications Platform DVS: Digital Video HMS: Hybrid Management IPS: Interface Practices and In-Home Cabling EAS: Emergency Alert System NES: National Electrical Safety CMS: Construction and Maintenance MMS: Material and Management 23
HFC Alliance n Management and Control Interoperability Alliance n n To specify a robust protocol suite to support cost effective interoperability of management systems for evolving HFC networks SCTE Engineering subcommittees n n n n n DSS: Data Standards CAP: Cable Applications Platform DVS: Digital Video HMS: Hybrid Management IPS: Interface Practices and In-Home Cabling EAS: Emergency Alert System NES: National Electrical Safety CMS: Construction and Maintenance MMS: Material and Management 23
 Ethernet 24
Ethernet 24
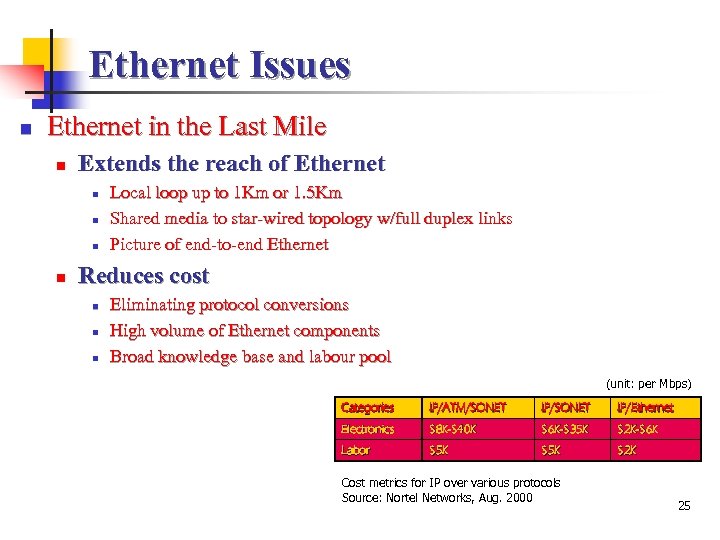 Ethernet Issues n Ethernet in the Last Mile n Extends the reach of Ethernet n n Local loop up to 1 Km or 1. 5 Km Shared media to star-wired topology w/full duplex links Picture of end-to-end Ethernet Reduces cost n n n Eliminating protocol conversions High volume of Ethernet components Broad knowledge base and labour pool (unit: per Mbps) Categories IP/ATM/SONET IP/Ethernet Electronics $8 K-$40 K $6 K-$35 K $2 K-$6 K Labor $5 K $5 K $2 K Cost metrics for IP over various protocols Source: Nortel Networks, Aug. 2000 25
Ethernet Issues n Ethernet in the Last Mile n Extends the reach of Ethernet n n Local loop up to 1 Km or 1. 5 Km Shared media to star-wired topology w/full duplex links Picture of end-to-end Ethernet Reduces cost n n n Eliminating protocol conversions High volume of Ethernet components Broad knowledge base and labour pool (unit: per Mbps) Categories IP/ATM/SONET IP/Ethernet Electronics $8 K-$40 K $6 K-$35 K $2 K-$6 K Labor $5 K $5 K $2 K Cost metrics for IP over various protocols Source: Nortel Networks, Aug. 2000 25
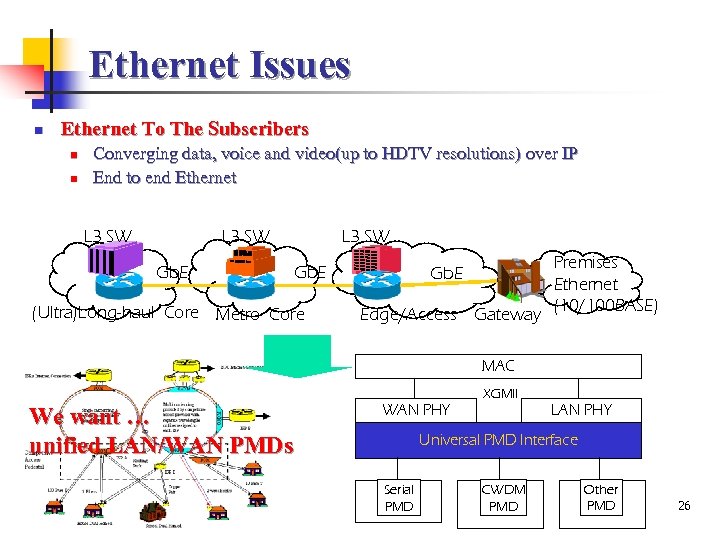 Ethernet Issues n Ethernet To The Subscribers n n Converging data, voice and video(up to HDTV resolutions) over IP End to end Ethernet L 3 SW Gb. E (Ultra)Long-haul Core Metro Core Gb. E Edge/Access Gateway Premises Ethernet (10/100 BASE) MAC XGMII We want … unified LAN/WAN PMDs WAN PHY LAN PHY Universal PMD Interface Serial PMD CWDM PMD Other PMD 26
Ethernet Issues n Ethernet To The Subscribers n n Converging data, voice and video(up to HDTV resolutions) over IP End to end Ethernet L 3 SW Gb. E (Ultra)Long-haul Core Metro Core Gb. E Edge/Access Gateway Premises Ethernet (10/100 BASE) MAC XGMII We want … unified LAN/WAN PMDs WAN PHY LAN PHY Universal PMD Interface Serial PMD CWDM PMD Other PMD 26
 Ethernet Issues n Gig. E/10 Gig. E or SONET/SDH ? n n n Infrastructure issues n A seamless extension of the LAN into the WAN Cost issues n Cost per port and labor cost saving due to the native protocol of data services for the internet Revenue issues n Competitive price vs performance Management issues n Shorter time to provision Topology issues n n Ring, Bus, Mesh PON 27
Ethernet Issues n Gig. E/10 Gig. E or SONET/SDH ? n n n Infrastructure issues n A seamless extension of the LAN into the WAN Cost issues n Cost per port and labor cost saving due to the native protocol of data services for the internet Revenue issues n Competitive price vs performance Management issues n Shorter time to provision Topology issues n n Ring, Bus, Mesh PON 27
 Ethernet Issues n Ethernet WAN standard n n n Inband management like SONET/SDH Remote loopback like DSU/CSU Built in BER management objects Restoration and protection Topology agnostic SP administered VLAN tags Granular bandwidth for subrate provisioning Traffic management and classification Discard eligible for over subscription Full duplex only SONET/SDH friendly 28
Ethernet Issues n Ethernet WAN standard n n n Inband management like SONET/SDH Remote loopback like DSU/CSU Built in BER management objects Restoration and protection Topology agnostic SP administered VLAN tags Granular bandwidth for subrate provisioning Traffic management and classification Discard eligible for over subscription Full duplex only SONET/SDH friendly 28
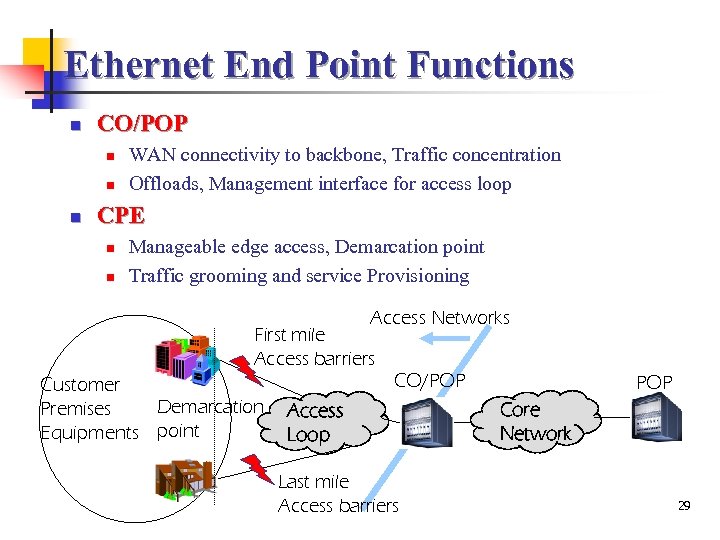 Ethernet End Point Functions n CO/POP n n n WAN connectivity to backbone, Traffic concentration Offloads, Management interface for access loop CPE n n Manageable edge access, Demarcation point Traffic grooming and service Provisioning Access Networks First mile Access barriers Customer Demarcation Premises Equipments point CO/POP Access Loop Last mile Access barriers POP Core Network 29
Ethernet End Point Functions n CO/POP n n n WAN connectivity to backbone, Traffic concentration Offloads, Management interface for access loop CPE n n Manageable edge access, Demarcation point Traffic grooming and service Provisioning Access Networks First mile Access barriers Customer Demarcation Premises Equipments point CO/POP Access Loop Last mile Access barriers POP Core Network 29
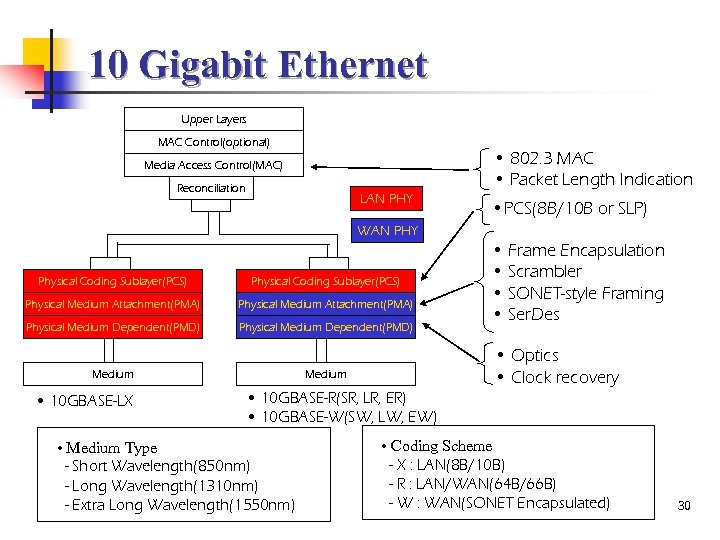 10 Gigabit Ethernet Upper Layers MAC Control(optional) • 802. 3 MAC • Packet Length Indication Media Access Control(MAC) Reconciliation LAN PHY • PCS(8 B/10 B or SLP) WAN PHY Physical Coding Sublayer(PCS) Physical Medium Attachment(PMA) Physical Medium Dependent(PMD) • 10 GBASE-LX • Optics • Clock recovery Medium • Frame Encapsulation • Scrambler • SONET-style Framing • Ser. Des • 10 GBASE-R(SR, LR, ER) • 10 GBASE-W(SW, LW, EW) • Medium Type - Short Wavelength(850 nm) - Long Wavelength(1310 nm) - Extra Long Wavelength(1550 nm) • Coding Scheme - X : LAN(8 B/10 B) - R : LAN/WAN(64 B/66 B) - W : WAN(SONET Encapsulated) 30
10 Gigabit Ethernet Upper Layers MAC Control(optional) • 802. 3 MAC • Packet Length Indication Media Access Control(MAC) Reconciliation LAN PHY • PCS(8 B/10 B or SLP) WAN PHY Physical Coding Sublayer(PCS) Physical Medium Attachment(PMA) Physical Medium Dependent(PMD) • 10 GBASE-LX • Optics • Clock recovery Medium • Frame Encapsulation • Scrambler • SONET-style Framing • Ser. Des • 10 GBASE-R(SR, LR, ER) • 10 GBASE-W(SW, LW, EW) • Medium Type - Short Wavelength(850 nm) - Long Wavelength(1310 nm) - Extra Long Wavelength(1550 nm) • Coding Scheme - X : LAN(8 B/10 B) - R : LAN/WAN(64 B/66 B) - W : WAN(SONET Encapsulated) 30
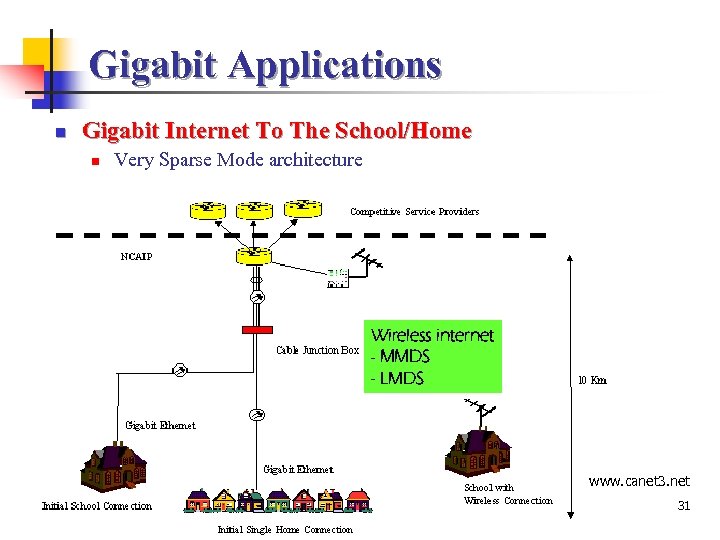 Gigabit Applications n Gigabit Internet To The School/Home n Very Sparse Mode architecture Wireless internet - MMDS - LMDS www. canet 31
Gigabit Applications n Gigabit Internet To The School/Home n Very Sparse Mode architecture Wireless internet - MMDS - LMDS www. canet 31
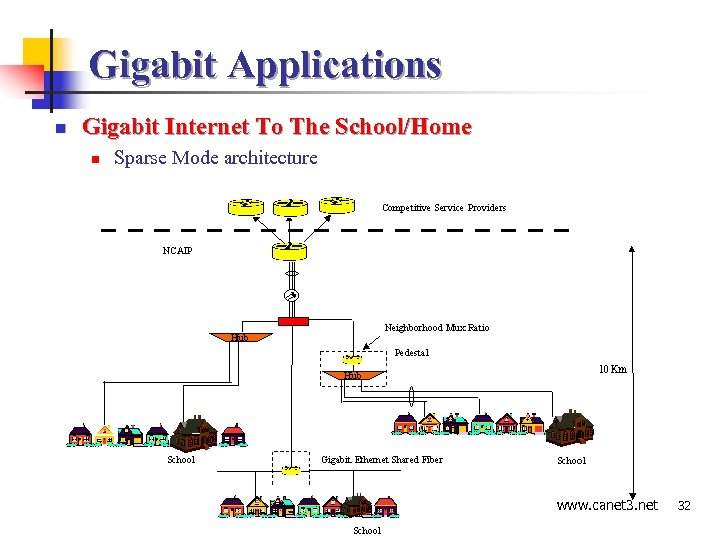 Gigabit Applications n Gigabit Internet To The School/Home n Sparse Mode architecture www. canet 32
Gigabit Applications n Gigabit Internet To The School/Home n Sparse Mode architecture www. canet 32
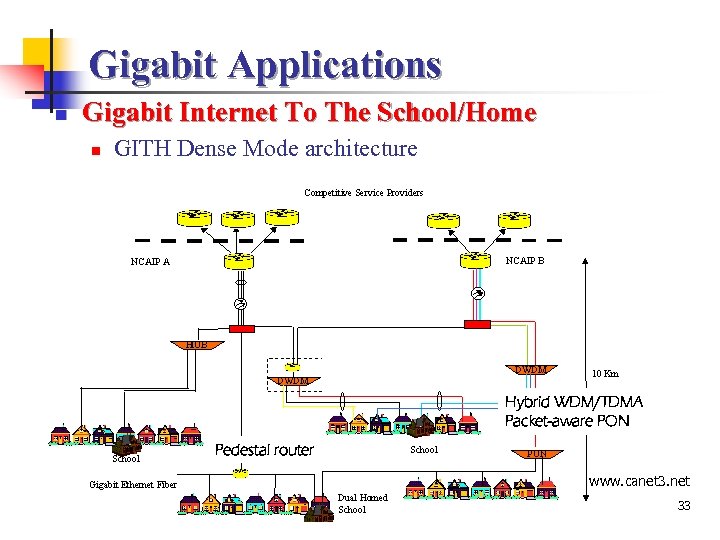 Gigabit Applications n Gigabit Internet To The School/Home n GITH Dense Mode architecture Hybrid WDM/TDMA Packet-aware PON Pedestal router www. canet 33
Gigabit Applications n Gigabit Internet To The School/Home n GITH Dense Mode architecture Hybrid WDM/TDMA Packet-aware PON Pedestal router www. canet 33
 Gb. E/10 Gb. E Standardization n IEEE 802 n n n IETF n n IPo. PTR; IP over packet transport rings T 1 X 1. 5 Optical Hierarchical Interfaces n n n IEEE P 802. 3 ae RPR SG; Resilient packet ring T 1 X 1. 5/99 -038 IEEE 802. 3 MAC frames to SONET payload Generic format…carrying Ethernet MAC frames over SONET OIF n OIF 99. 138 Generic format…carrying Ethernet MAC frames over SONET(T 1 X 1. 5/99 -268 ) 34
Gb. E/10 Gb. E Standardization n IEEE 802 n n n IETF n n IPo. PTR; IP over packet transport rings T 1 X 1. 5 Optical Hierarchical Interfaces n n n IEEE P 802. 3 ae RPR SG; Resilient packet ring T 1 X 1. 5/99 -038 IEEE 802. 3 MAC frames to SONET payload Generic format…carrying Ethernet MAC frames over SONET OIF n OIF 99. 138 Generic format…carrying Ethernet MAC frames over SONET(T 1 X 1. 5/99 -268 ) 34
 Optical Access: FTTx 35
Optical Access: FTTx 35
 Optical Access Technologies n Small Business and Residential n n n Mid-size Business n n n Ethernet/HPNA/x. DSL-based access Last mile issues Ethernet/x. DSL-based access Last mile & first mile issues Enterprises and Large Business n n 10/100/Gigabit/10 G Ethernet-based access First mile issues: metro access based on Ethernet native LAN interfaces 36
Optical Access Technologies n Small Business and Residential n n n Mid-size Business n n n Ethernet/HPNA/x. DSL-based access Last mile issues Ethernet/x. DSL-based access Last mile & first mile issues Enterprises and Large Business n n 10/100/Gigabit/10 G Ethernet-based access First mile issues: metro access based on Ethernet native LAN interfaces 36
 Issues in Optical Access n Subscriber Loop n n PON(TDM, WDM, Packet) Multi-service access Access Concentrator + Router (L 2/L 3) Metro Access n n Optical networking(SDH, WDM) Optical edge IP/SDH, IP/WDM, IP/Gb. E MPLS enabler 37
Issues in Optical Access n Subscriber Loop n n PON(TDM, WDM, Packet) Multi-service access Access Concentrator + Router (L 2/L 3) Metro Access n n Optical networking(SDH, WDM) Optical edge IP/SDH, IP/WDM, IP/Gb. E MPLS enabler 37
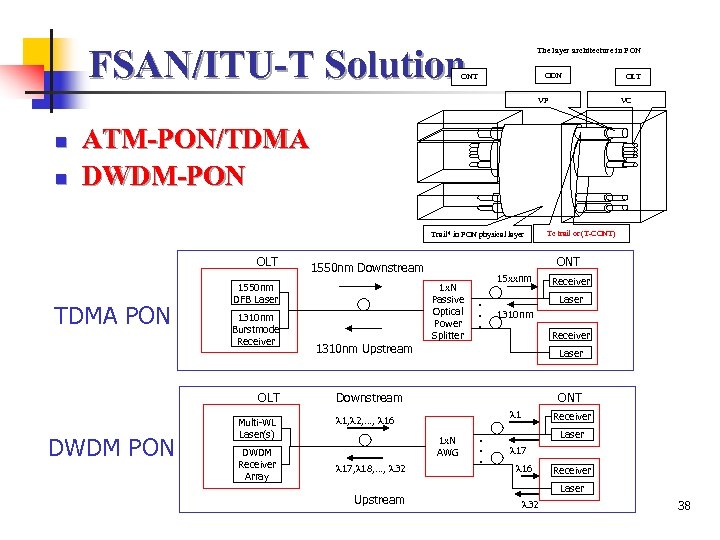 FSAN/ITU-T Solution The layer architecture in PON ODN ONT VP n n OLT VC ATM-PON/TDMA DWDM-PON Trail* in PON physical layer OLT TDMA PON 1310 nm Burstmode Receiver OLT DWDM PON Multi-WL Laser(s) DWDM Receiver Array ONT 1550 nm Downstream 1550 nm DFB Laser 1 x. N Passive Optical Power Splitter 15 xxnm. . . 1310 nm Receiver Laser Downstream ONT 1 1, 2, …, 16 1 x. N AWG Upstream Receiver Laser 1310 nm Upstream 17, 18, …, 32 Tc trail or (T-CONT) . . . Receiver Laser 17 16 Receiver Laser 32 38
FSAN/ITU-T Solution The layer architecture in PON ODN ONT VP n n OLT VC ATM-PON/TDMA DWDM-PON Trail* in PON physical layer OLT TDMA PON 1310 nm Burstmode Receiver OLT DWDM PON Multi-WL Laser(s) DWDM Receiver Array ONT 1550 nm Downstream 1550 nm DFB Laser 1 x. N Passive Optical Power Splitter 15 xxnm. . . 1310 nm Receiver Laser Downstream ONT 1 1, 2, …, 16 1 x. N AWG Upstream Receiver Laser 1310 nm Upstream 17, 18, …, 32 Tc trail or (T-CONT) . . . Receiver Laser 17 16 Receiver Laser 32 38
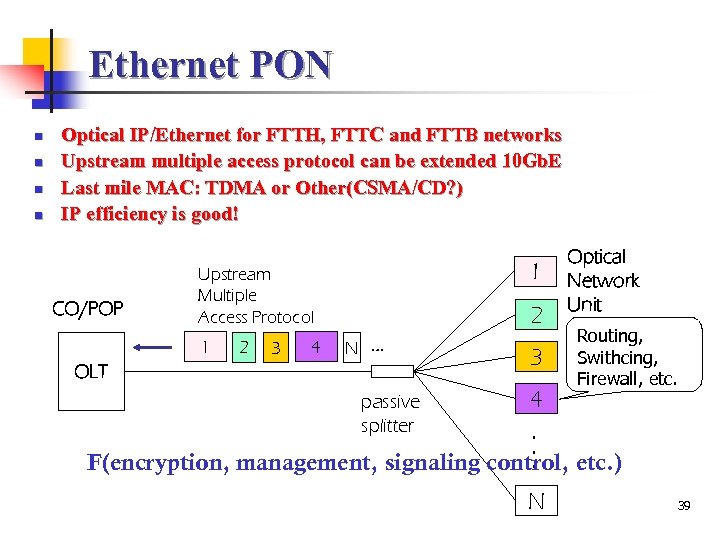 Ethernet PON n n Optical IP/Ethernet for FTTH, FTTC and FTTB networks Upstream multiple access protocol can be extended 10 Gb. E Last mile MAC: TDMA or Other(CSMA/CD? ) IP efficiency is good! CO/POP 1 Upstream Multiple Access Protocol 1 2 3 4 2 N … OLT 3 Optical Network Unit Routing, Swithcing, Firewall, etc. 4. . . F(encryption, management, signaling control, etc. ) passive splitter N 39
Ethernet PON n n Optical IP/Ethernet for FTTH, FTTC and FTTB networks Upstream multiple access protocol can be extended 10 Gb. E Last mile MAC: TDMA or Other(CSMA/CD? ) IP efficiency is good! CO/POP 1 Upstream Multiple Access Protocol 1 2 3 4 2 N … OLT 3 Optical Network Unit Routing, Swithcing, Firewall, etc. 4. . . F(encryption, management, signaling control, etc. ) passive splitter N 39
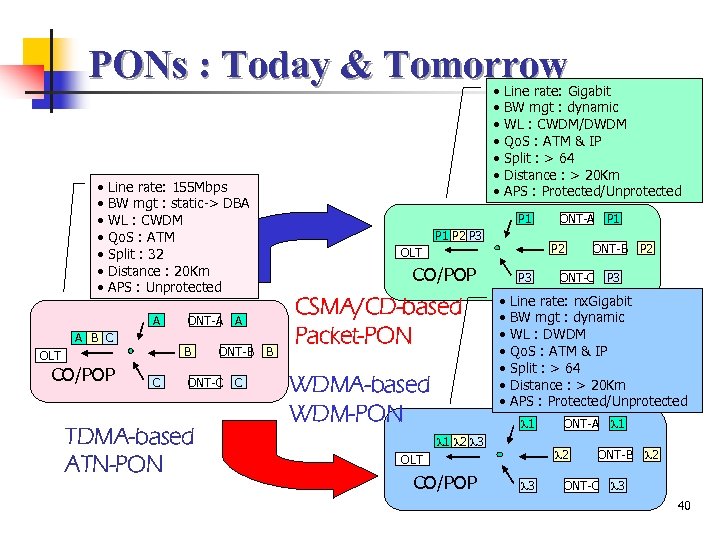 PONs : Today & Tomorrow • • • • Line rate: 155 Mbps BW mgt : static-> DBA WL : CWDM Qo. S : ATM Split : 32 Distance : 20 Km APS : Unprotected A A B C B OLT CO/POP ONT-A C ONT-C TDMA-based ATN-PON P 1 P 2 P 3 CO/POP C B CSMA/CD-based Packet-PON WDMA-based WDM-PON P 3 • • ONT-B P 2 ONT-C P 3 Line rate: nx. Gigabit BW mgt : dynamic WL : DWDM Qo. S : ATM & IP Split : > 64 Distance : > 20 Km APS : Protected/Unprotected 1 1 2 3 ONT-A 2 OLT CO/POP ONT-A P 1 P 2 OLT A ONT-B Line rate: Gigabit BW mgt : dynamic WL : CWDM/DWDM Qo. S : ATM & IP Split : > 64 Distance : > 20 Km APS : Protected/Unprotected 3 1 ONT-B ONT-C 2 3 40
PONs : Today & Tomorrow • • • • Line rate: 155 Mbps BW mgt : static-> DBA WL : CWDM Qo. S : ATM Split : 32 Distance : 20 Km APS : Unprotected A A B C B OLT CO/POP ONT-A C ONT-C TDMA-based ATN-PON P 1 P 2 P 3 CO/POP C B CSMA/CD-based Packet-PON WDMA-based WDM-PON P 3 • • ONT-B P 2 ONT-C P 3 Line rate: nx. Gigabit BW mgt : dynamic WL : DWDM Qo. S : ATM & IP Split : > 64 Distance : > 20 Km APS : Protected/Unprotected 1 1 2 3 ONT-A 2 OLT CO/POP ONT-A P 1 P 2 OLT A ONT-B Line rate: Gigabit BW mgt : dynamic WL : CWDM/DWDM Qo. S : ATM & IP Split : > 64 Distance : > 20 Km APS : Protected/Unprotected 3 1 ONT-B ONT-C 2 3 40
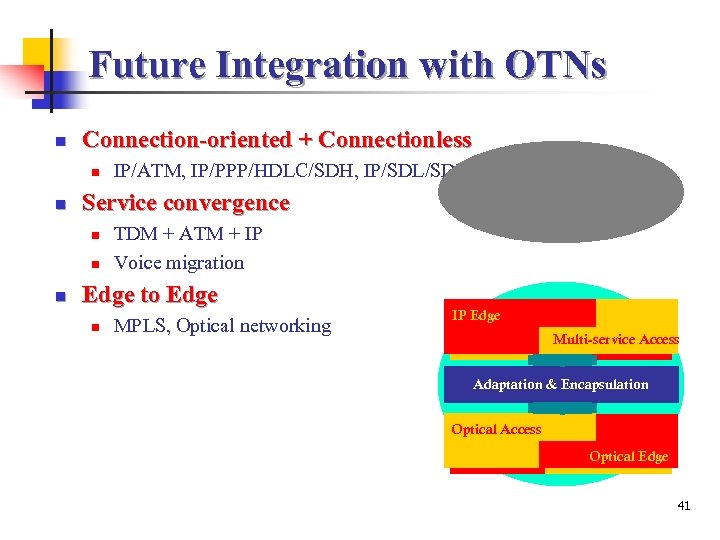 Future Integration with OTNs n Connection-oriented + Connectionless n n Service convergence n n n IP/ATM, IP/PPP/HDLC/SDH, IP/SDL/SDH, IP/WDM TDM + ATM + IP Voice migration Edge to Edge n MPLS, Optical networking IP Edge Multi-service Access Adaptation & Encapsulation Optical Access Optical Edge 41
Future Integration with OTNs n Connection-oriented + Connectionless n n Service convergence n n n IP/ATM, IP/PPP/HDLC/SDH, IP/SDL/SDH, IP/WDM TDM + ATM + IP Voice migration Edge to Edge n MPLS, Optical networking IP Edge Multi-service Access Adaptation & Encapsulation Optical Access Optical Edge 41
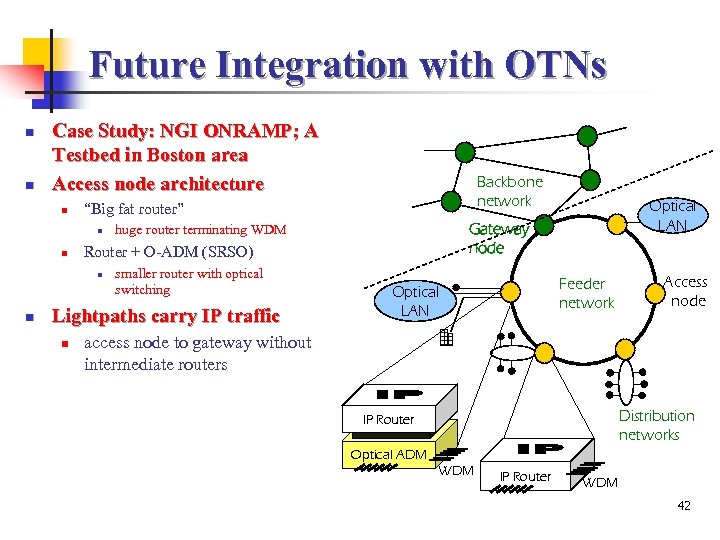 Future Integration with OTNs n n Case Study: NGI ONRAMP; A Testbed in Boston area Access node architecture n “Big fat router” n n smaller router with optical switching Lightpaths carry IP traffic n Optical LAN Gateway node huge router terminating WDM Router + O-ADM (SRSO) n n Backbone network Feeder network Optical LAN Access node access node to gateway without intermediate routers Distribution networks IP Router Optical ADM WDM IP Router WDM 42
Future Integration with OTNs n n Case Study: NGI ONRAMP; A Testbed in Boston area Access node architecture n “Big fat router” n n smaller router with optical switching Lightpaths carry IP traffic n Optical LAN Gateway node huge router terminating WDM Router + O-ADM (SRSO) n n Backbone network Feeder network Optical LAN Access node access node to gateway without intermediate routers Distribution networks IP Router Optical ADM WDM IP Router WDM 42
 Future Integration with OTNs n n n n Opto-Electronics Short-Haul Multichannel Optical Channel Management Digital Wrapper DPRINGs vs. SPRINGs ASON MPL(Label and Lambda)S 43
Future Integration with OTNs n n n n Opto-Electronics Short-Haul Multichannel Optical Channel Management Digital Wrapper DPRINGs vs. SPRINGs ASON MPL(Label and Lambda)S 43
 Standardization n n n ITU-T IETF ODSI OIF FSAN IEEE 44
Standardization n n n ITU-T IETF ODSI OIF FSAN IEEE 44
 Wireless 45
Wireless 45
 Wireless Technologies n Fixed wireless access n MMDS n n n LMDS n n Operation in 2. 1 to 2. 7 GHz RF Data rates up to 10 Mbps Up to 35 -mile range Non LOS requirements Operation in 24 GHz, 28 GHz, 31 GHz, 38 GHz and 40 GHz RF Data rates up to 155 Mbps with 2 -mile ranges LOS operation Multiple access technologies & duplex methods n n n TDMA/FDD, FDMA/TDD, TDMA/TDD OFDM, VOFDM CDMA/FDD 46
Wireless Technologies n Fixed wireless access n MMDS n n n LMDS n n Operation in 2. 1 to 2. 7 GHz RF Data rates up to 10 Mbps Up to 35 -mile range Non LOS requirements Operation in 24 GHz, 28 GHz, 31 GHz, 38 GHz and 40 GHz RF Data rates up to 155 Mbps with 2 -mile ranges LOS operation Multiple access technologies & duplex methods n n n TDMA/FDD, FDMA/TDD, TDMA/TDD OFDM, VOFDM CDMA/FDD 46
 Issues in Wireless Access n n n Converging data, voice and video Data over open air interface Qo. S control & LOS n n Upstream operation n Robust burst-mode demodulation in severe time-varying and/or delay spread environments n Higher spectral efficiency Downstream operation n High delay spread and time varying environments n Dual antenna capability at lower complexity for interference cancellation 47
Issues in Wireless Access n n n Converging data, voice and video Data over open air interface Qo. S control & LOS n n Upstream operation n Robust burst-mode demodulation in severe time-varying and/or delay spread environments n Higher spectral efficiency Downstream operation n High delay spread and time varying environments n Dual antenna capability at lower complexity for interference cancellation 47
 Standardization n OFDM Forum n n Wireless DSL Consortium n n n 11 GHz Fixed Wireless Access, Road Wireless Access, Wireless LAN Resolving shortage of CDMA n Short-link distance, Co. S, Antenna limitations 2~4 GHz BWA (PTMPT) DOCSIS-based MAC, TDMA/FDD BWIF (Broadband Wireless Internet Forum) n n Vector OFDM n Pros : Burst-mode demodulation, Higher spectral efficiency n Cons : Power amplifier back-off, Phase noise DOCSIS-based MAC 48
Standardization n OFDM Forum n n Wireless DSL Consortium n n n 11 GHz Fixed Wireless Access, Road Wireless Access, Wireless LAN Resolving shortage of CDMA n Short-link distance, Co. S, Antenna limitations 2~4 GHz BWA (PTMPT) DOCSIS-based MAC, TDMA/FDD BWIF (Broadband Wireless Internet Forum) n n Vector OFDM n Pros : Burst-mode demodulation, Higher spectral efficiency n Cons : Power amplifier back-off, Phase noise DOCSIS-based MAC 48
 Wrap-up 49
Wrap-up 49
 Conclusion n n It’s time to bring broadband home and wire-speed first mile… Bandwidth is no longer a scarce resource, just in a view of access technolgy n n Problem solving approach for enforcing Qo. S to customers can be changed ‘IP-centric provisioning on the optical access networks’ is an emerging success factor… n n ATM’s lack of acceptance among the new generation service providers Standard Qo. S mechanism for IP will soon emerge…? 50
Conclusion n n It’s time to bring broadband home and wire-speed first mile… Bandwidth is no longer a scarce resource, just in a view of access technolgy n n Problem solving approach for enforcing Qo. S to customers can be changed ‘IP-centric provisioning on the optical access networks’ is an emerging success factor… n n ATM’s lack of acceptance among the new generation service providers Standard Qo. S mechanism for IP will soon emerge…? 50


