860c94c8dd705c81cd021af12b3f11e6.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 26
 A Cs. I(Tl) Dark Matter Search Experiment - KIMS Korean Invisible Mass Search Yeongduk Kim Sejong University, Seoul, Korea IDM 2002 meeting, 2002. Sep 5
A Cs. I(Tl) Dark Matter Search Experiment - KIMS Korean Invisible Mass Search Yeongduk Kim Sejong University, Seoul, Korea IDM 2002 meeting, 2002. Sep 5
 Collaborators Seoul National Univ. : J. M. Choi, R. K. Jain, S. C. Kim, S. K. Kim*, T. Y. Kim, H. S. Lee, S. E. Lee, H. . Park, H. Y. Yang, M. S. Yang Sejong Univ. : W. K. Kang, J. I. Lee, D. S. Lim, Y. D. Kim, Yonsei Univ. : J. Hwang, H. J. Kim, Y. J. Kwon Iwha Womans Univ. : I. S. Han, E. K. Lee, I. H. Park Seong. Kyun. Kwan Univ. : I. Yu Chonbuk National Univ. : S. Y. Choi KAIST : P. Ko Univ. of Maryland : M. H. Lee, E. S. Seo National Taiwan Univ. , : H. B. Li, C. H. Tang, M. Z. Wang Academia Cinica : W. P. Lai, H. T. Wong Inst. Of High Energy Physics : J. Li, Y. Liu, Q. Yue Inst. Of Atomic Energy : B. Xin, Z. Y. Zhou Tsinghua University : J. Zhu * PI
Collaborators Seoul National Univ. : J. M. Choi, R. K. Jain, S. C. Kim, S. K. Kim*, T. Y. Kim, H. S. Lee, S. E. Lee, H. . Park, H. Y. Yang, M. S. Yang Sejong Univ. : W. K. Kang, J. I. Lee, D. S. Lim, Y. D. Kim, Yonsei Univ. : J. Hwang, H. J. Kim, Y. J. Kwon Iwha Womans Univ. : I. S. Han, E. K. Lee, I. H. Park Seong. Kyun. Kwan Univ. : I. Yu Chonbuk National Univ. : S. Y. Choi KAIST : P. Ko Univ. of Maryland : M. H. Lee, E. S. Seo National Taiwan Univ. , : H. B. Li, C. H. Tang, M. Z. Wang Academia Cinica : W. P. Lai, H. T. Wong Inst. Of High Energy Physics : J. Li, Y. Liu, Q. Yue Inst. Of Atomic Energy : B. Xin, Z. Y. Zhou Tsinghua University : J. Zhu * PI
 Outline • • • Cs. I(Tl) crystals Underground site Studies on background reduction Perspectives Summary
Outline • • • Cs. I(Tl) crystals Underground site Studies on background reduction Perspectives Summary
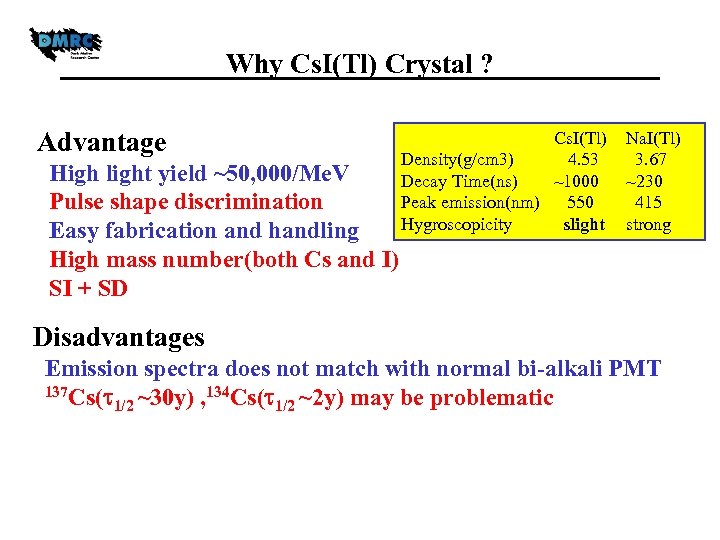 Why Cs. I(Tl) Crystal ? Advantage High light yield ~50, 000/Me. V Pulse shape discrimination Easy fabrication and handling High mass number(both Cs and I) SI + SD Cs. I(Tl) Density(g/cm 3) 4. 53 Decay Time(ns) ~1000 Peak emission(nm) 550 Hygroscopicity slight Na. I(Tl) 3. 67 ~230 415 strong Disadvantages Emission spectra does not match with normal bi-alkali PMT 137 Cs(t 134 Cs(t 1/2 ~30 y) , 1/2 ~2 y) may be problematic
Why Cs. I(Tl) Crystal ? Advantage High light yield ~50, 000/Me. V Pulse shape discrimination Easy fabrication and handling High mass number(both Cs and I) SI + SD Cs. I(Tl) Density(g/cm 3) 4. 53 Decay Time(ns) ~1000 Peak emission(nm) 550 Hygroscopicity slight Na. I(Tl) 3. 67 ~230 415 strong Disadvantages Emission spectra does not match with normal bi-alkali PMT 137 Cs(t 134 Cs(t 1/2 ~30 y) , 1/2 ~2 y) may be problematic
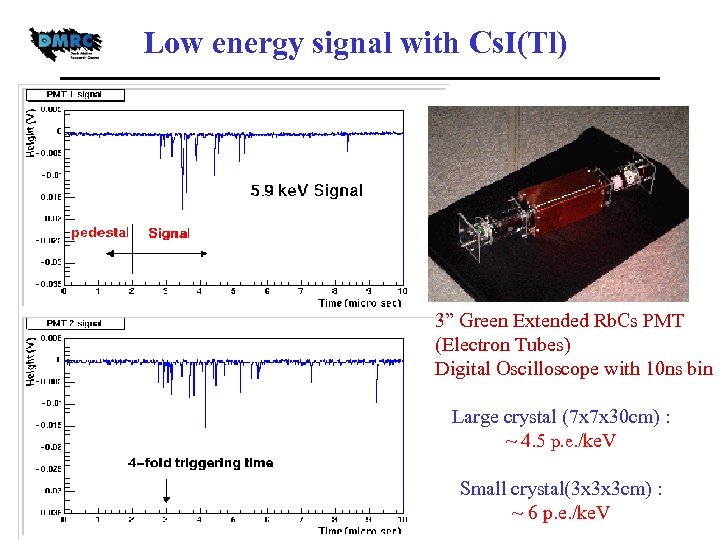 Low energy signal with Cs. I(Tl) 3” Green Extended Rb. Cs PMT (Electron Tubes) Digital Oscilloscope with 10 ns bin Large crystal (7 x 7 x 30 cm) : ~ 4. 5 p. e. /ke. V Small crystal(3 x 3 x 3 cm) : ~ 6 p. e. /ke. V
Low energy signal with Cs. I(Tl) 3” Green Extended Rb. Cs PMT (Electron Tubes) Digital Oscilloscope with 10 ns bin Large crystal (7 x 7 x 30 cm) : ~ 4. 5 p. e. /ke. V Small crystal(3 x 3 x 3 cm) : ~ 6 p. e. /ke. V
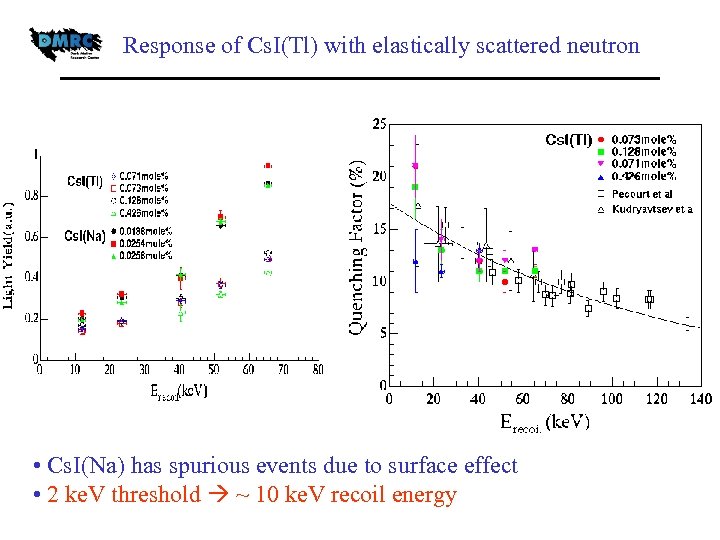 Response of Cs. I(Tl) with elastically scattered neutron • Cs. I(Na) has spurious events due to surface effect • 2 ke. V threshold ~ 10 ke. V recoil energy
Response of Cs. I(Tl) with elastically scattered neutron • Cs. I(Na) has spurious events due to surface effect • 2 ke. V threshold ~ 10 ke. V recoil energy
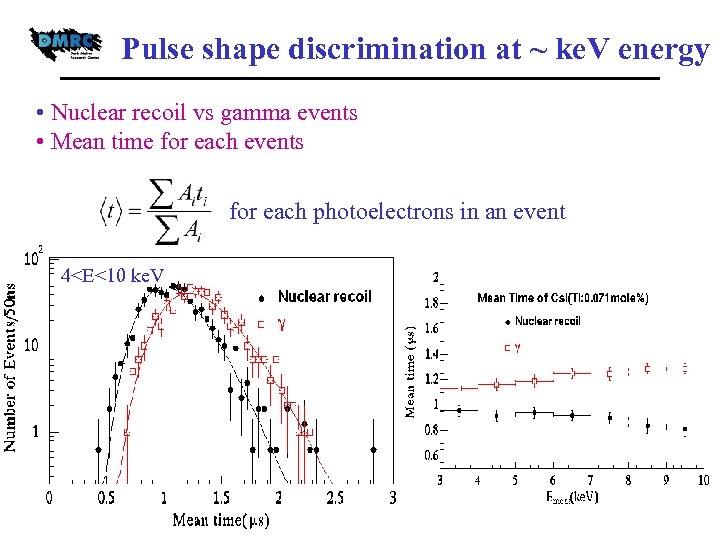 Pulse shape discrimination at ~ ke. V energy • Nuclear recoil vs gamma events • Mean time for each events for each photoelectrons in an event 4
Pulse shape discrimination at ~ ke. V energy • Nuclear recoil vs gamma events • Mean time for each events for each photoelectrons in an event 4
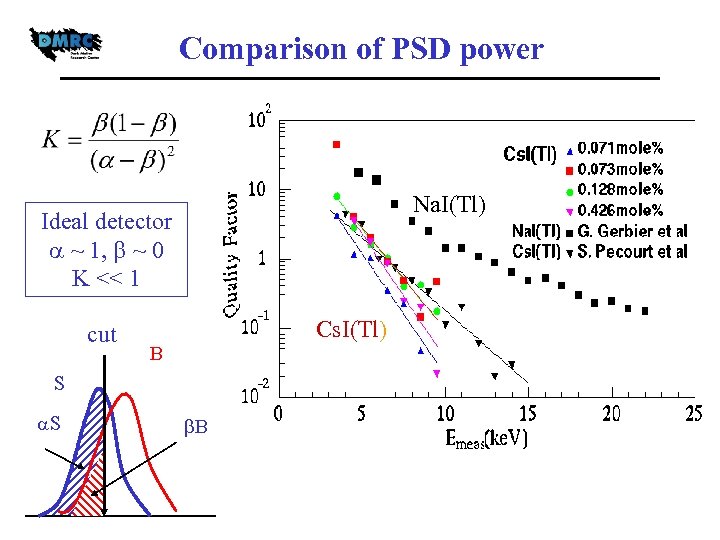 Comparison of PSD power Na. I(Tl) Ideal detector ~ 1, ~ 0 K << 1 cut Cs. I(Tl) B S S B
Comparison of PSD power Na. I(Tl) Ideal detector ~ 1, ~ 0 K << 1 cut Cs. I(Tl) B S S B
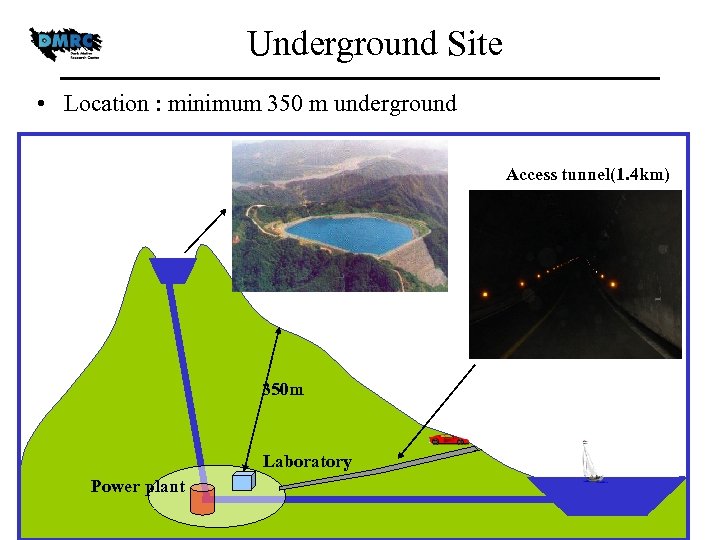 Underground Site • Location : minimum 350 m underground Access tunnel(1. 4 km) 350 m Laboratory Power plant
Underground Site • Location : minimum 350 m underground Access tunnel(1. 4 km) 350 m Laboratory Power plant
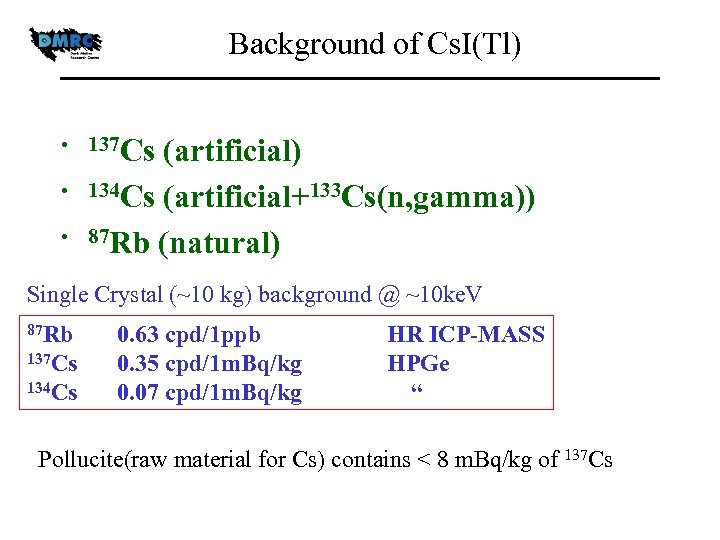 Background of Cs. I(Tl) • 137 Cs • • (artificial) 134 Cs (artificial+133 Cs(n, gamma)) 87 Rb (natural) Single Crystal (~10 kg) background @ ~10 ke. V 87 Rb 137 Cs 134 Cs 0. 63 cpd/1 ppb 0. 35 cpd/1 m. Bq/kg 0. 07 cpd/1 m. Bq/kg HR ICP-MASS HPGe “ Pollucite(raw material for Cs) contains < 8 m. Bq/kg of 137 Cs
Background of Cs. I(Tl) • 137 Cs • • (artificial) 134 Cs (artificial+133 Cs(n, gamma)) 87 Rb (natural) Single Crystal (~10 kg) background @ ~10 ke. V 87 Rb 137 Cs 134 Cs 0. 63 cpd/1 ppb 0. 35 cpd/1 m. Bq/kg 0. 07 cpd/1 m. Bq/kg HR ICP-MASS HPGe “ Pollucite(raw material for Cs) contains < 8 m. Bq/kg of 137 Cs
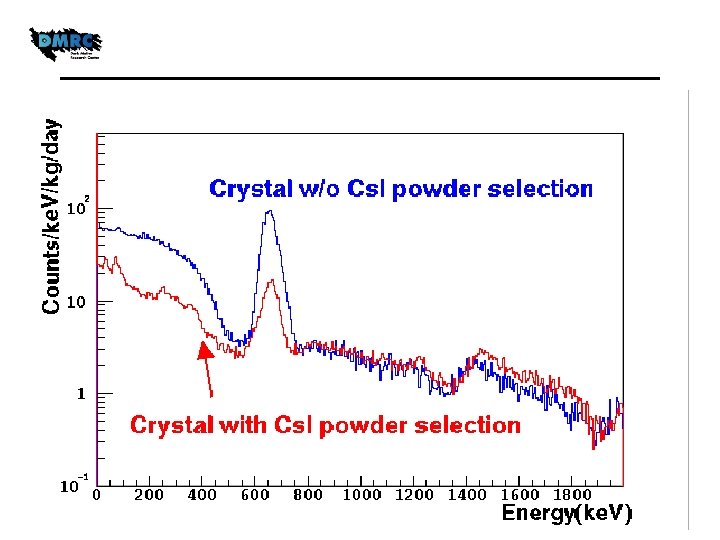
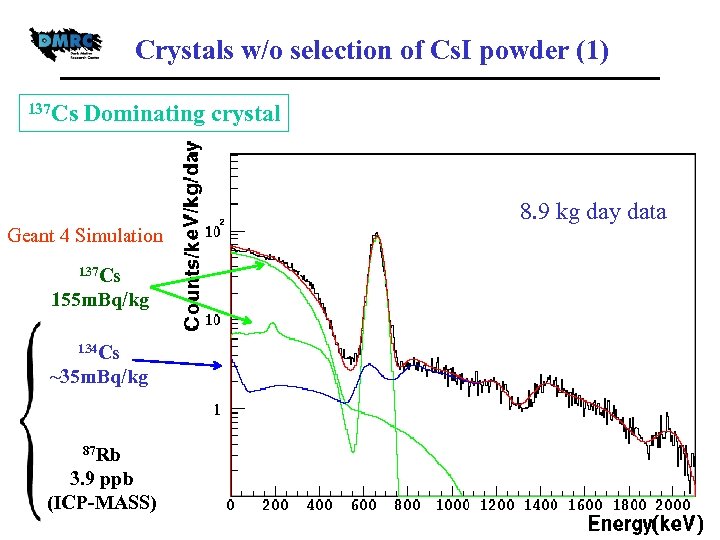 Crystals w/o selection of Cs. I powder (1) 137 Cs Dominating crystal 8. 9 kg day data Geant 4 Simulation 137 Cs 155 m. Bq/kg 134 Cs ~35 m. Bq/kg 87 Rb 3. 9 ppb (ICP-MASS)
Crystals w/o selection of Cs. I powder (1) 137 Cs Dominating crystal 8. 9 kg day data Geant 4 Simulation 137 Cs 155 m. Bq/kg 134 Cs ~35 m. Bq/kg 87 Rb 3. 9 ppb (ICP-MASS)
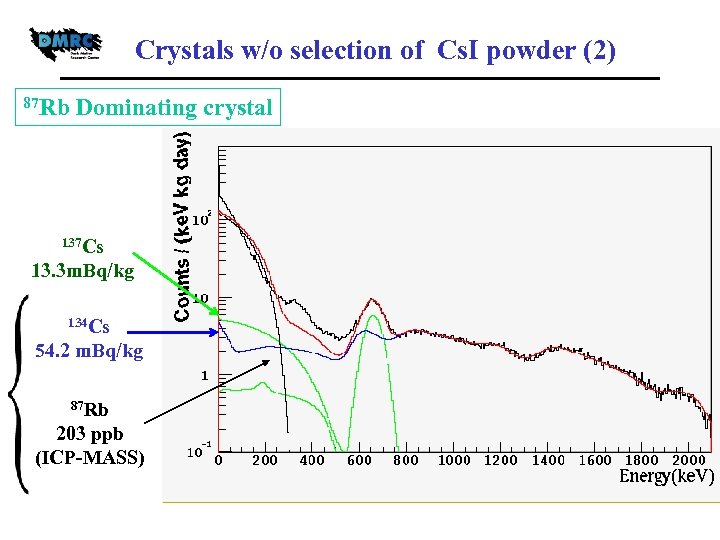 Crystals w/o selection of Cs. I powder (2) 87 Rb Dominating crystal Cs. I(Tl) from IHEP(China) 137 Cs 13. 3 m. Bq/kg 134 Cs 54. 2 m. Bq/kg 87 Rb 203 ppb (ICP-MASS)
Crystals w/o selection of Cs. I powder (2) 87 Rb Dominating crystal Cs. I(Tl) from IHEP(China) 137 Cs 13. 3 m. Bq/kg 134 Cs 54. 2 m. Bq/kg 87 Rb 203 ppb (ICP-MASS)
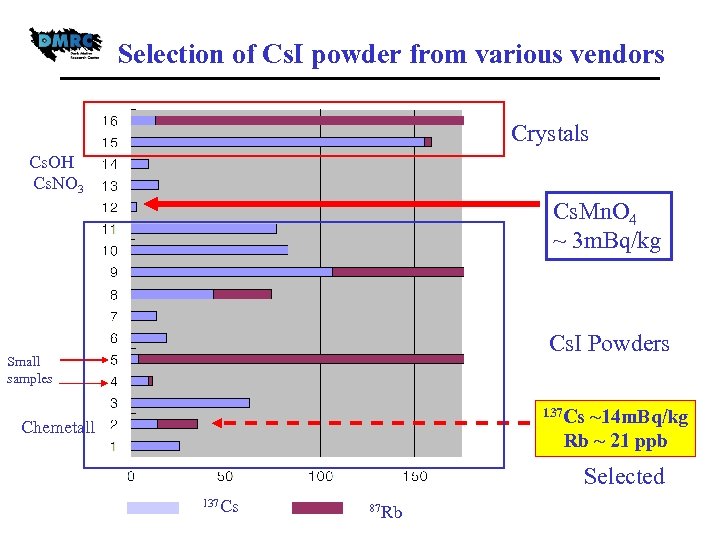 Selection of Cs. I powder from various vendors Crystals Cs. OH Cs. NO 3 Cs. Mn. O 4 ~ 3 m. Bq/kg Cs. I Powders Small samples 137 Cs ~14 m. Bq/kg Rb ~ 21 ppb Chemetall Selected 137 Cs 87 Rb
Selection of Cs. I powder from various vendors Crystals Cs. OH Cs. NO 3 Cs. Mn. O 4 ~ 3 m. Bq/kg Cs. I Powders Small samples 137 Cs ~14 m. Bq/kg Rb ~ 21 ppb Chemetall Selected 137 Cs 87 Rb
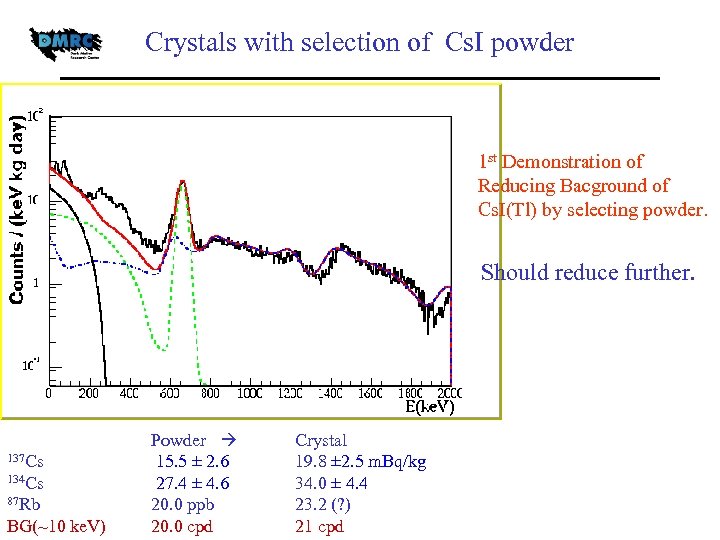 Crystals with selection of Cs. I powder 1 st Demonstration of Reducing Bacground of Cs. I(Tl) by selecting powder. Should reduce further. 137 Cs 134 Cs 87 Rb BG(~10 ke. V) Powder 15. 5 ± 2. 6 27. 4 ± 4. 6 20. 0 ppb 20. 0 cpd Crystal 19. 8 ± 2. 5 m. Bq/kg 34. 0 ± 4. 4 23. 2 (? ) 21 cpd
Crystals with selection of Cs. I powder 1 st Demonstration of Reducing Bacground of Cs. I(Tl) by selecting powder. Should reduce further. 137 Cs 134 Cs 87 Rb BG(~10 ke. V) Powder 15. 5 ± 2. 6 27. 4 ± 4. 6 20. 0 ppb 20. 0 cpd Crystal 19. 8 ± 2. 5 m. Bq/kg 34. 0 ± 4. 4 23. 2 (? ) 21 cpd
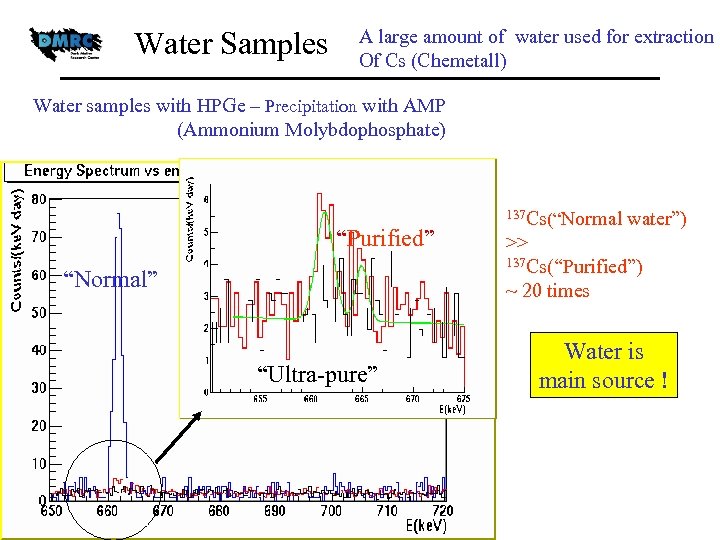 Water Samples A large amount of water used for extraction Of Cs (Chemetall) Water samples with HPGe – Precipitation with AMP (Ammonium Molybdophosphate) “Purified” “Normal” “Ultra-pure” 137 Cs(“Normal water”) >> 137 Cs(“Purified”) ~ 20 times Water is main source !
Water Samples A large amount of water used for extraction Of Cs (Chemetall) Water samples with HPGe – Precipitation with AMP (Ammonium Molybdophosphate) “Purified” “Normal” “Ultra-pure” 137 Cs(“Normal water”) >> 137 Cs(“Purified”) ~ 20 times Water is main source !
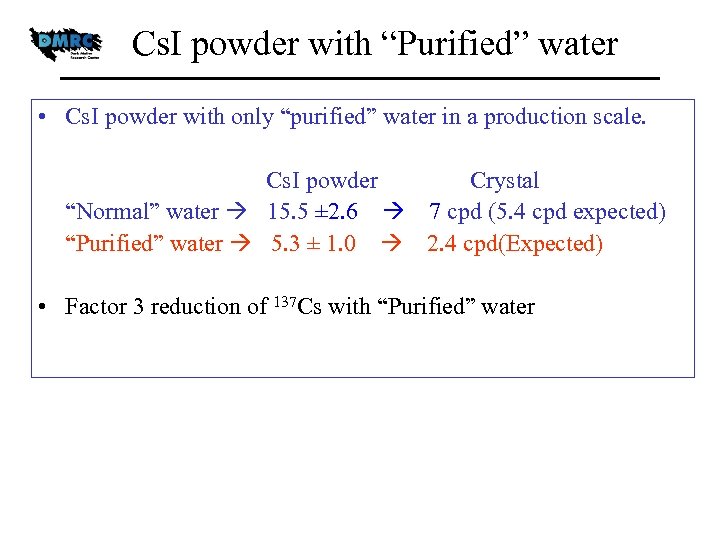 Cs. I powder with “Purified” water • Cs. I powder with only “purified” water in a production scale. Cs. I powder Crystal “Normal” water 15. 5 ± 2. 6 7 cpd (5. 4 cpd expected) “Purified” water 5. 3 ± 1. 0 2. 4 cpd(Expected) • Factor 3 reduction of 137 Cs with “Purified” water
Cs. I powder with “Purified” water • Cs. I powder with only “purified” water in a production scale. Cs. I powder Crystal “Normal” water 15. 5 ± 2. 6 7 cpd (5. 4 cpd expected) “Purified” water 5. 3 ± 1. 0 2. 4 cpd(Expected) • Factor 3 reduction of 137 Cs with “Purified” water
 Rb reduction by Recrystallization • Cs. I solubility in water is very high. • Recrystallization is done at slightly lower temperature from saturation point. • 20 ppb powder ~ 1 ppb (< 1 cpd) Crystal growing by Bridgmann reduced Rb by about 25%
Rb reduction by Recrystallization • Cs. I solubility in water is very high. • Recrystallization is done at slightly lower temperature from saturation point. • 20 ppb powder ~ 1 ppb (< 1 cpd) Crystal growing by Bridgmann reduced Rb by about 25%
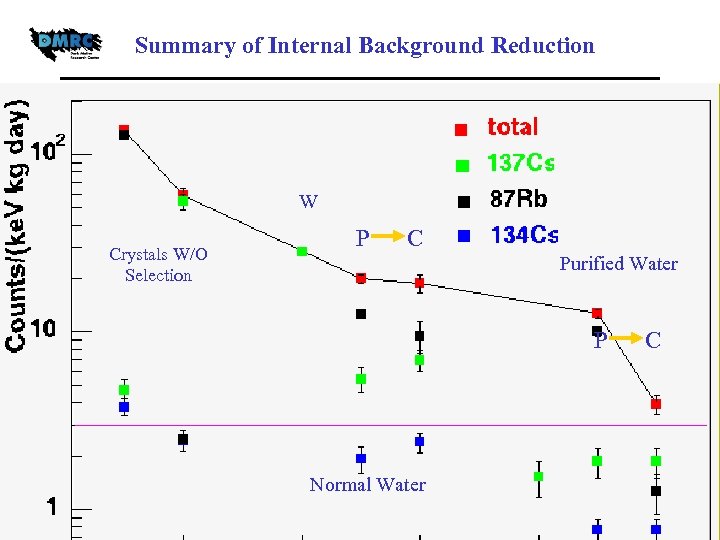 Summary of Internal Background Reduction W Crystals W/O Selection P C Purified Water P Normal Water C
Summary of Internal Background Reduction W Crystals W/O Selection P C Purified Water P Normal Water C
 External background Cosmic rays : ~ 10 -4 relative to the sea level The rock composition (ICP-MASS) 238 U ~ 4. 8 ppm, 232 Th ~ 6 ppm, 40 K ~ 4 ppm With a shielding of 15 cm Pb(Boliden) + 10 cm Cu(OFHC) Can be controlled < 0. 005 cpd based a MC simulation study (GEANT 4)
External background Cosmic rays : ~ 10 -4 relative to the sea level The rock composition (ICP-MASS) 238 U ~ 4. 8 ppm, 232 Th ~ 6 ppm, 40 K ~ 4 ppm With a shielding of 15 cm Pb(Boliden) + 10 cm Cu(OFHC) Can be controlled < 0. 005 cpd based a MC simulation study (GEANT 4)
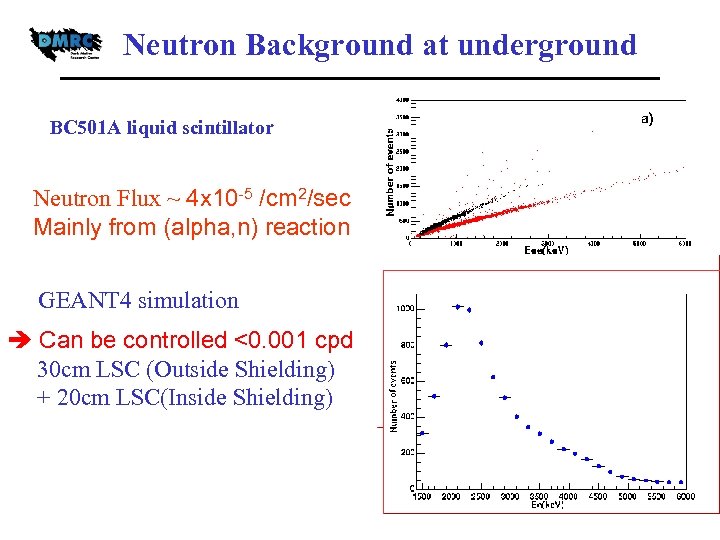 Neutron Background at underground BC 501 A liquid scintillator Neutron Flux ~ 4 x 10 -5 /cm 2/sec Mainly from (alpha, n) reaction GEANT 4 simulation Can be controlled <0. 001 cpd 30 cm LSC (Outside Shielding) + 20 cm LSC(Inside Shielding)
Neutron Background at underground BC 501 A liquid scintillator Neutron Flux ~ 4 x 10 -5 /cm 2/sec Mainly from (alpha, n) reaction GEANT 4 simulation Can be controlled <0. 001 cpd 30 cm LSC (Outside Shielding) + 20 cm LSC(Inside Shielding)
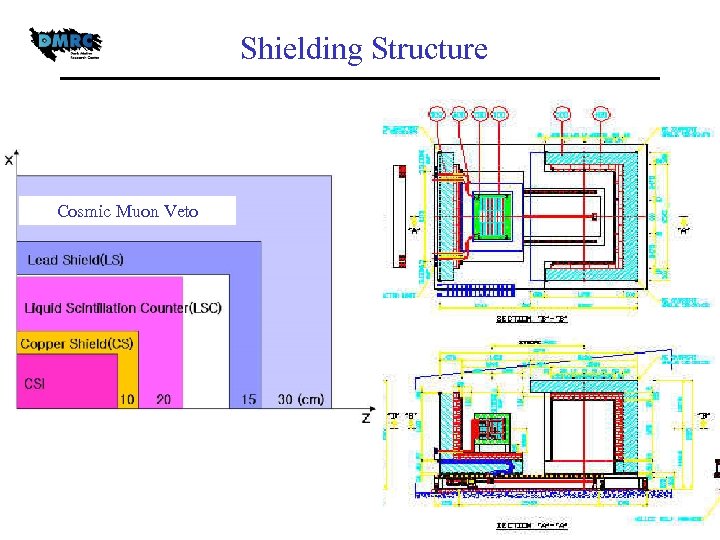 Shielding Structure Cosmic Muon Veto
Shielding Structure Cosmic Muon Veto
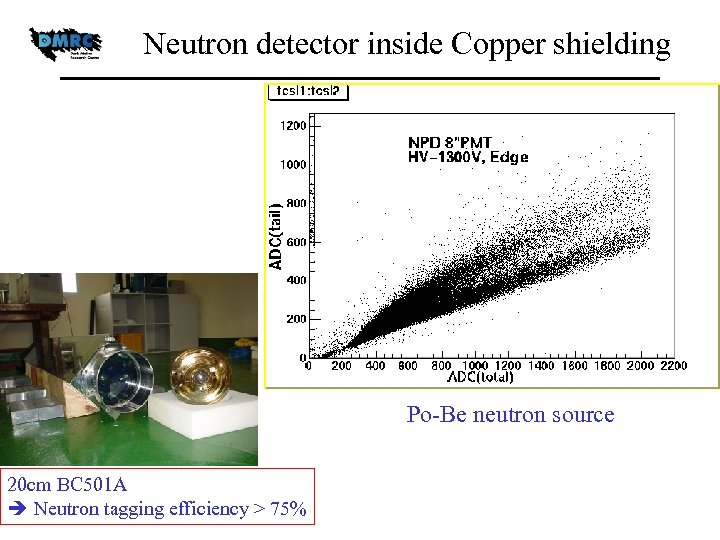 Neutron detector inside Copper shielding Po-Be neutron source 20 cm BC 501 A Neutron tagging efficiency > 75%
Neutron detector inside Copper shielding Po-Be neutron source 20 cm BC 501 A Neutron tagging efficiency > 75%
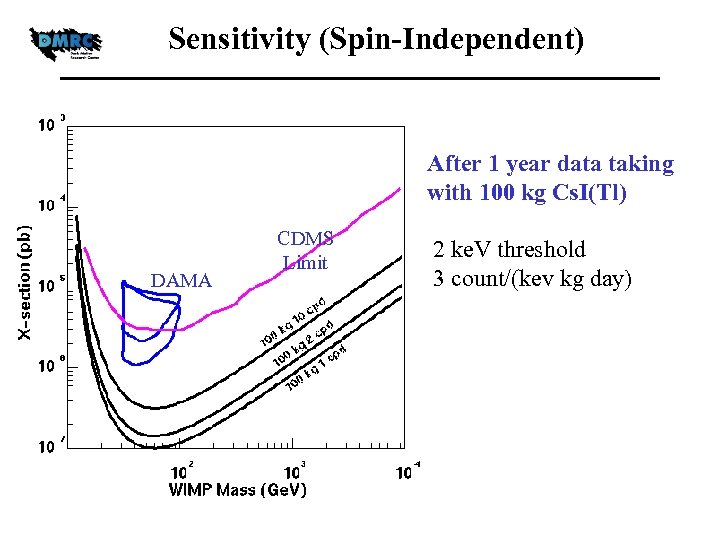 Sensitivity (Spin-Independent) After 1 year data taking with 100 kg Cs. I(Tl) DAMA CDMS Limit 2 ke. V threshold 3 count/(kev kg day)
Sensitivity (Spin-Independent) After 1 year data taking with 100 kg Cs. I(Tl) DAMA CDMS Limit 2 ke. V threshold 3 count/(kev kg day)
 Summary l Extensive R&D on Cs. I(Tl) crystal has been carried out • Pulse shape discrimination from -rays • Main source of 137 Cs contamination due to impure water. • Rb reduction down to ~1 ppb achieved. < 5 cpd from internal background. l Shielding capable of 250 kg of Cs. I(Tl) under construction. • Environmental background : small enough • Large (n, gamma) separable LSC inside shielding is tested. l Perspectives ~100 kg Cs. I(Tl) crystal within 1 year data taking will cover DAMA region
Summary l Extensive R&D on Cs. I(Tl) crystal has been carried out • Pulse shape discrimination from -rays • Main source of 137 Cs contamination due to impure water. • Rb reduction down to ~1 ppb achieved. < 5 cpd from internal background. l Shielding capable of 250 kg of Cs. I(Tl) under construction. • Environmental background : small enough • Large (n, gamma) separable LSC inside shielding is tested. l Perspectives ~100 kg Cs. I(Tl) crystal within 1 year data taking will cover DAMA region


