c5ae0e85439f455907b8d32f997d3acc.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 20

A Crawler-based Study of Spyware on the Web Authors: Alexander Moshchuk, Tanya Bragin, Steven D. Gribble, and Henry M. Levy University of Washington 13 th Annual Network and Distributed System Security Symposium (NDSS 2006) Presented by Hao Cheng, 2006. 03

What is Spyware? • Spyware (wiki): “a broad category of malicious software designed to intercept or take partial control of a computer’s operation without the informed consent of that machine’s owner or legitimate user”. • no self-replica • keylogging, dialer, Trojan downloader, browser hijacker, adware.

• Two types of spyware: – spyware-infected executables: piggy-backed spyware code attached. – drive-by download: exploit vulnerability in user’s browser. from wiki

Contribution • A quantitative analysis of the extent of spyware content in the Web. • Internet point of view, study websites. • have answers to below questions:

. • Crawl webpages – May 2005, 18. 2 millions URL – Oct 2005, 21. 8 millions URL • Virtual Machine (VM) to sandbox and analyze malicious content • spyware-infected executables: commercial anti-spyware tools • Drive-by download: heuristic triggers

Spyware-Infected • automated solution – determine whether a web object has executable software – download, install, and execute in VM – analyze, identify. • .

steps • Finding executables in web – HTTP header content-type = application/octet-stream – URL has extension (. exe, . cab, . msi) – After downloading, the beginning bits in a file to identify file type. • Automatic Install – use heuristic to simulate common user interaction during the process of installation.

steps • The last step- Analyze – Lavasoft Ad. Aware anti-spyware tool. (use signature within its detection database). – script to launch the installed software and collect the logs generated by the anti-spyware tool. – identify functions of those spywares. • .

Drive-by Download • automated solution – visit potential malicious webpage in unmodified browser in a clean VM – any attempt to break out of security sandbox of browser- suspicious – perform Ad. Aware scan to detect installed spyaware. • .

Complex web content • Complex web content (Java. Script) • Time bomb code (occur in some future): accelerate OS wall-clock 15 times • Page-close code, simulate page-close by fetching a clear webpage to cause code insurgence. • Pop-up code, wait for all pop-up window to finish loading and then closed them in order to trigger any potential codes.

Browser Configuration • IE 6. 0 on unpatched XP. • cfg_y, when IE ask for permission, all approved. • cfg_n, refuse all requests for permission. • most malicious, simple visit a webpage will cause infection. • also study Firefox, basically more secure.
System • 10 -node cluster • dual-processor, 4 GB RAM, 80 GB disk • one VM per processor
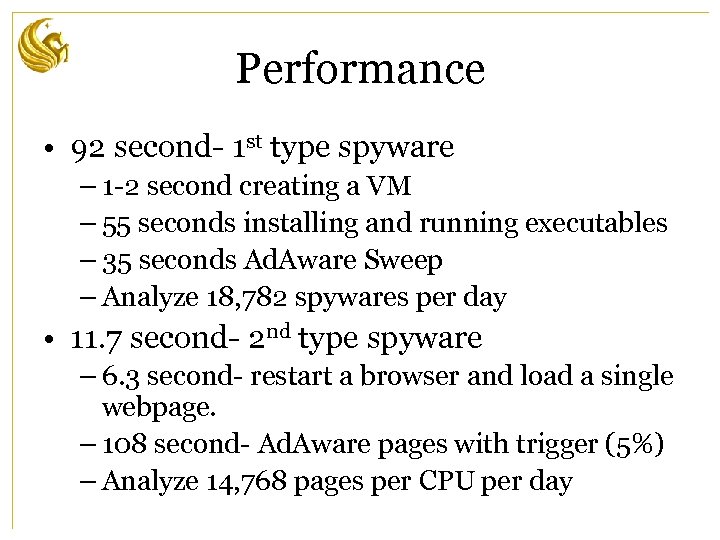
Performance • 92 second- 1 st type spyware – 1 -2 second creating a VM – 55 seconds installing and running executables – 35 seconds Ad. Aware Sweep – Analyze 18, 782 spywares per day • 11. 7 second- 2 nd type spyware – 6. 3 second- restart a browser and load a single webpage. – 108 second- Ad. Aware pages with trigger (5%) – Analyze 14, 768 pages per CPU per day

Executable • over 2, 500 web sites • 8 different categories • for each web site, crawl to a depth = 3 from the top page. • Average 6, 577 pages per site. • Also crawl “random selected” web sites.
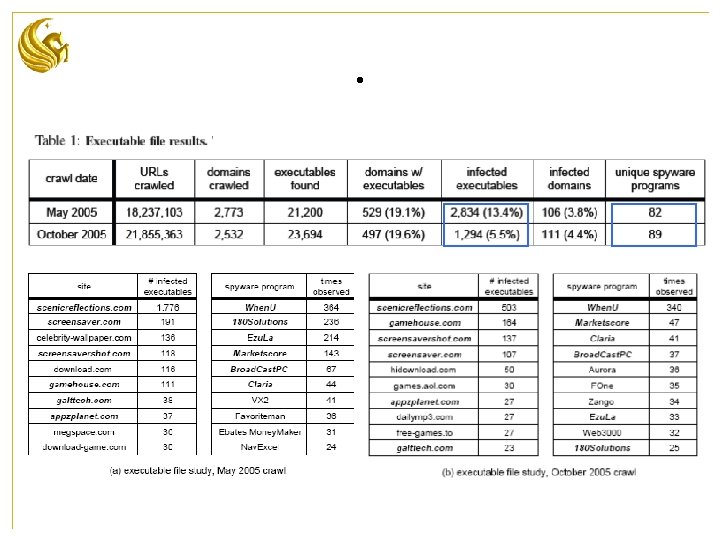
.
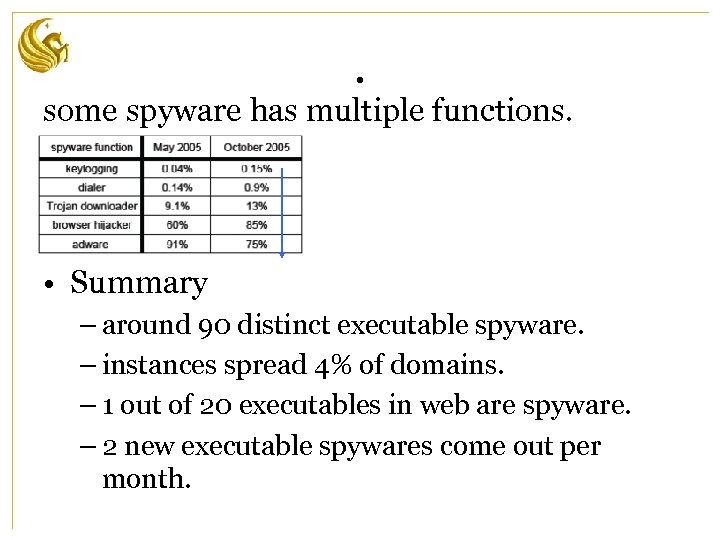
. some spyware has multiple functions. • Summary – around 90 distinct executable spyware. – instances spread 4% of domains. – 1 out of 20 executables in web are spyware. – 2 new executable spywares come out per month.
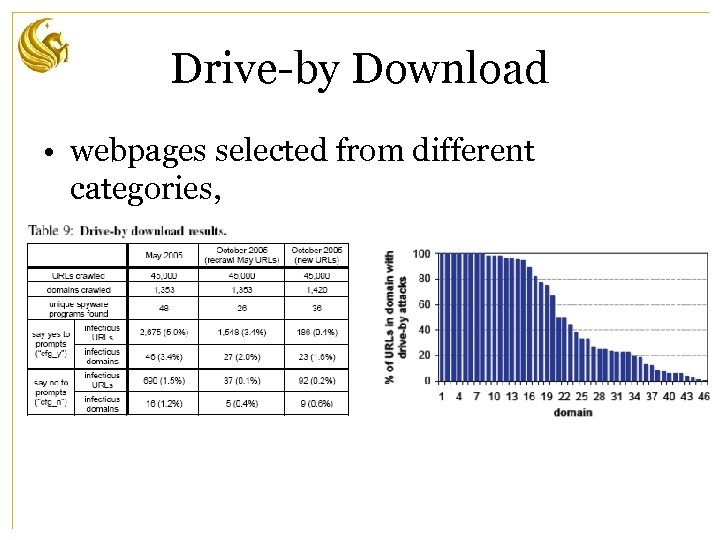
Drive-by Download • webpages selected from different categories,
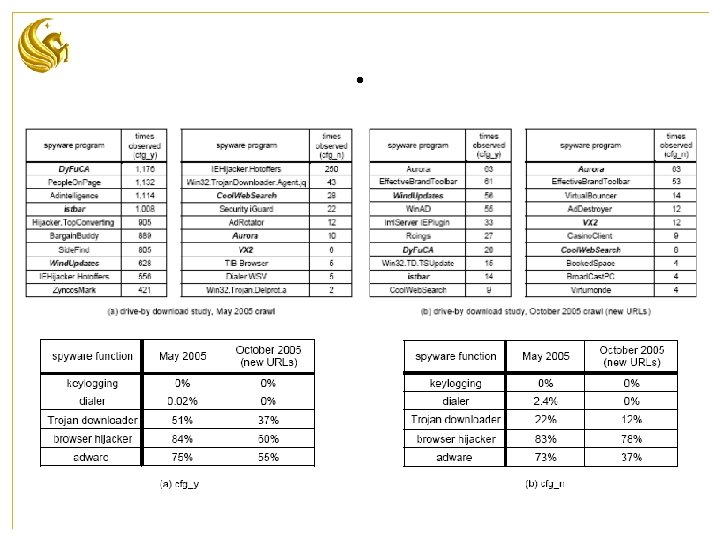
.

limitation • heavily rely on commercial anti-spyware software. • Many computers are patched, and now less vulnerabilities.

Questions?
c5ae0e85439f455907b8d32f997d3acc.ppt