d1b2d72ff6b9b74e55e6abb2abd968fa.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 45
 A Complete Corporate Valuation for a Simple Company 1
A Complete Corporate Valuation for a Simple Company 1
 Three types of value • Book value: the company’s historical value as shown on its financial statements. • Market value: the current price at which an asset can be bought or sold. • Intrinsic value: estimate of the value an individual buyer places on an asset. 2
Three types of value • Book value: the company’s historical value as shown on its financial statements. • Market value: the current price at which an asset can be bought or sold. • Intrinsic value: estimate of the value an individual buyer places on an asset. 2
 Objective: • Objective is to provide a sound basis for estimating the intrinsic value of a stock. • This intrinsic value is also called its fundamental value. • The process is known as fundamental valuation—Warren Buffet is very successful at identifying a company’s fundamental value! 3
Objective: • Objective is to provide a sound basis for estimating the intrinsic value of a stock. • This intrinsic value is also called its fundamental value. • The process is known as fundamental valuation—Warren Buffet is very successful at identifying a company’s fundamental value! 3
 The three basic concepts of valuation • Investors can only spend cash so "Cash is good and more cash is better. " • Cash today is worth more than cash tomorrow. • Risky cash flows are worth less than safe cash flows. • These three imply the value of a company depends on the size, timing, and riskiness of its cash flows. 4
The three basic concepts of valuation • Investors can only spend cash so "Cash is good and more cash is better. " • Cash today is worth more than cash tomorrow. • Risky cash flows are worth less than safe cash flows. • These three imply the value of a company depends on the size, timing, and riskiness of its cash flows. 4
 Steps in the corporate valuation • Determine weighted average cost of capital • Estimate expected future free cash flows---cash flows available to all investors—called free cash flows (FCFs). • Discount free cash flows at the average rate of return required by all investors • Find value of company 5
Steps in the corporate valuation • Determine weighted average cost of capital • Estimate expected future free cash flows---cash flows available to all investors—called free cash flows (FCFs). • Discount free cash flows at the average rate of return required by all investors • Find value of company 5
 Estimating the Weighted Average Cost of Capital (WACC) • Company has two types of investors – Debtholders – Stockholders • Each type of investor expects to receive a return for their investment • The return an investor receives is a “cost of capital” from company’s viewpoint. 6
Estimating the Weighted Average Cost of Capital (WACC) • Company has two types of investors – Debtholders – Stockholders • Each type of investor expects to receive a return for their investment • The return an investor receives is a “cost of capital” from company’s viewpoint. 6
 Cost of Debt • MPR’s cost of debt: r. D = 9%. • But MPR can deduct interest, so cost to MPR is after-tax rate on debt. • If tax rate is 40%, then after-tax cost of debt is: – After-tax r. D = 9%(1 -0. 4) = 5. 4%. 7
Cost of Debt • MPR’s cost of debt: r. D = 9%. • But MPR can deduct interest, so cost to MPR is after-tax rate on debt. • If tax rate is 40%, then after-tax cost of debt is: – After-tax r. D = 9%(1 -0. 4) = 5. 4%. 7
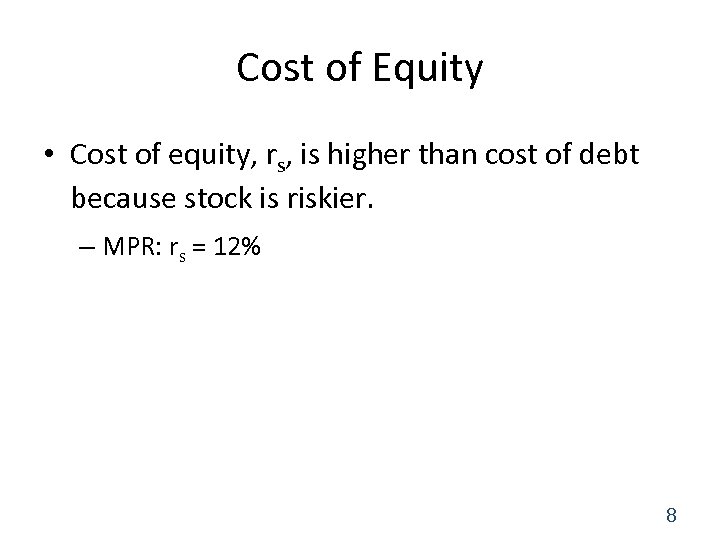 Cost of Equity • Cost of equity, rs, is higher than cost of debt because stock is riskier. – MPR: rs = 12% 8
Cost of Equity • Cost of equity, rs, is higher than cost of debt because stock is riskier. – MPR: rs = 12% 8
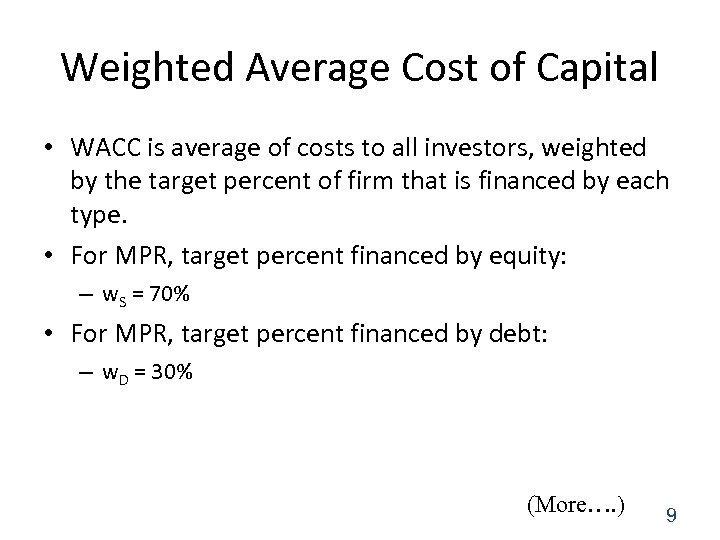 Weighted Average Cost of Capital • WACC is average of costs to all investors, weighted by the target percent of firm that is financed by each type. • For MPR, target percent financed by equity: – w. S = 70% • For MPR, target percent financed by debt: – w. D = 30% (More…. ) 9
Weighted Average Cost of Capital • WACC is average of costs to all investors, weighted by the target percent of firm that is financed by each type. • For MPR, target percent financed by equity: – w. S = 70% • For MPR, target percent financed by debt: – w. D = 30% (More…. ) 9
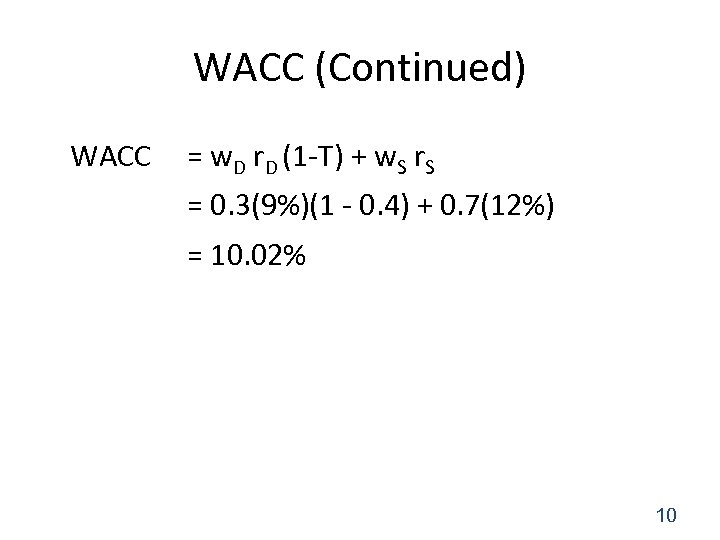 WACC (Continued) WACC = w. D r. D (1 -T) + w. S r. S = 0. 3(9%)(1 - 0. 4) + 0. 7(12%) = 10. 02% 10
WACC (Continued) WACC = w. D r. D (1 -T) + w. S r. S = 0. 3(9%)(1 - 0. 4) + 0. 7(12%) = 10. 02% 10
 Free Cash Flow (FCF) • FCF is the amount of cash available from operations for distribution to all investors (including stockholders and debtholders) after making the necessary investments to support operations. • A company’s value depends upon the amount of FCF it can generate. 11
Free Cash Flow (FCF) • FCF is the amount of cash available from operations for distribution to all investors (including stockholders and debtholders) after making the necessary investments to support operations. • A company’s value depends upon the amount of FCF it can generate. 11
 Calculating FCF • FCF = net operating profit after taxes minus investment in operating capital 12
Calculating FCF • FCF = net operating profit after taxes minus investment in operating capital 12
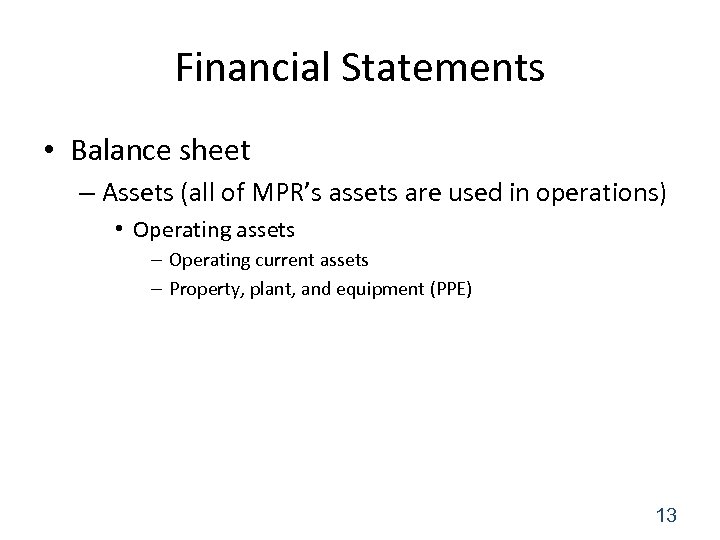 Financial Statements • Balance sheet – Assets (all of MPR’s assets are used in operations) • Operating assets – Operating current assets – Property, plant, and equipment (PPE) 13
Financial Statements • Balance sheet – Assets (all of MPR’s assets are used in operations) • Operating assets – Operating current assets – Property, plant, and equipment (PPE) 13
 Operating Current Assets • Operating current assets are the CA needed to support operations. – Op CA include: cash, inventory, receivables. – Op CA exclude: short-term investments, because these are not a part of operations. 14
Operating Current Assets • Operating current assets are the CA needed to support operations. – Op CA include: cash, inventory, receivables. – Op CA exclude: short-term investments, because these are not a part of operations. 14
 Operating Current Liabilities • Operating current liabilities are the CL resulting as a normal part of operations. – Op CL include: accounts payable and accruals. – Op CA exclude: notes payable, because this is a source of financing, not a part of operations. 15
Operating Current Liabilities • Operating current liabilities are the CL resulting as a normal part of operations. – Op CL include: accounts payable and accruals. – Op CA exclude: notes payable, because this is a source of financing, not a part of operations. 15
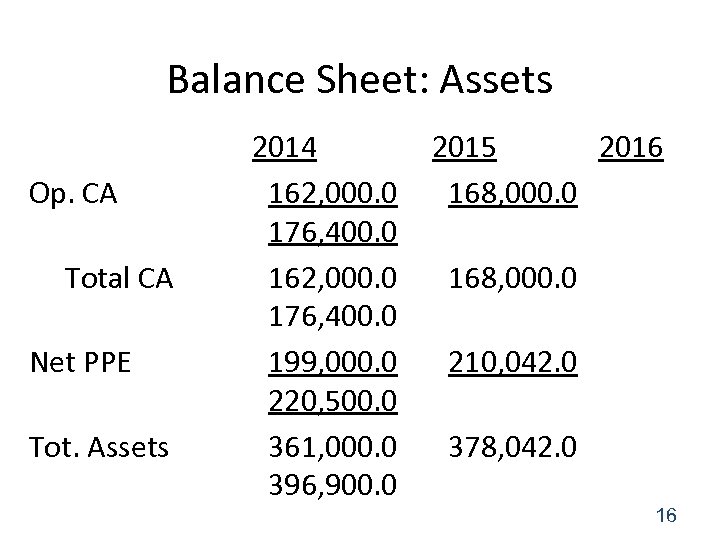 Balance Sheet: Assets Op. CA Total CA Net PPE Tot. Assets 2014 162, 000. 0 176, 400. 0 199, 000. 0 220, 500. 0 361, 000. 0 396, 900. 0 2015 2016 168, 000. 0 210, 042. 0 378, 042. 0 16
Balance Sheet: Assets Op. CA Total CA Net PPE Tot. Assets 2014 162, 000. 0 176, 400. 0 199, 000. 0 220, 500. 0 361, 000. 0 396, 900. 0 2015 2016 168, 000. 0 210, 042. 0 378, 042. 0 16
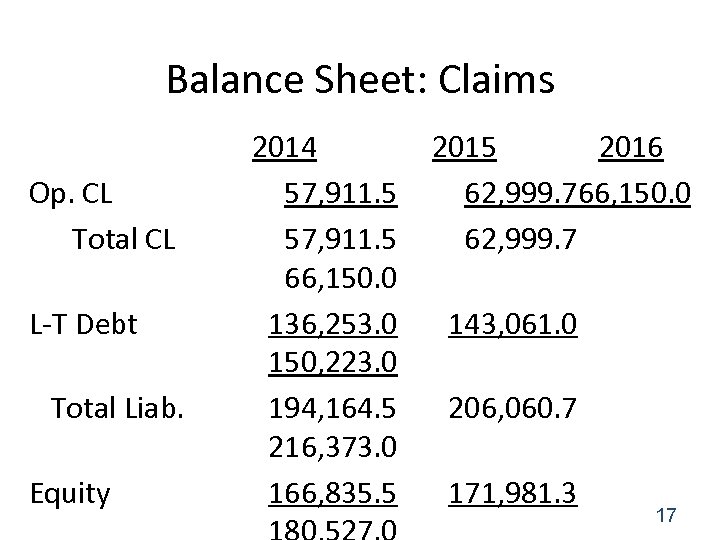 Balance Sheet: Claims Op. CL Total CL L-T Debt Total Liab. Equity 2014 57, 911. 5 66, 150. 0 136, 253. 0 150, 223. 0 194, 164. 5 216, 373. 0 166, 835. 5 2016 62, 999. 766, 150. 0 62, 999. 7 143, 061. 0 206, 060. 7 171, 981. 3 17
Balance Sheet: Claims Op. CL Total CL L-T Debt Total Liab. Equity 2014 57, 911. 5 66, 150. 0 136, 253. 0 150, 223. 0 194, 164. 5 216, 373. 0 166, 835. 5 2016 62, 999. 766, 150. 0 62, 999. 7 143, 061. 0 206, 060. 7 171, 981. 3 17
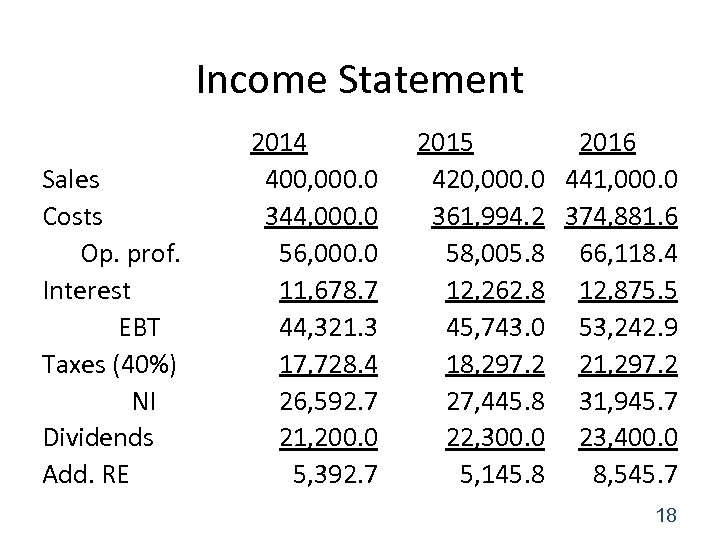 Income Statement Sales Costs Op. prof. Interest EBT Taxes (40%) NI Dividends Add. RE 2014 400, 000. 0 344, 000. 0 56, 000. 0 11, 678. 7 44, 321. 3 17, 728. 4 26, 592. 7 21, 200. 0 5, 392. 7 2015 2016 420, 000. 0 441, 000. 0 361, 994. 2 374, 881. 6 58, 005. 8 66, 118. 4 12, 262. 8 12, 875. 5 45, 743. 0 53, 242. 9 18, 297. 2 21, 297. 2 27, 445. 8 31, 945. 7 22, 300. 0 23, 400. 0 5, 145. 8 8, 545. 7 18
Income Statement Sales Costs Op. prof. Interest EBT Taxes (40%) NI Dividends Add. RE 2014 400, 000. 0 344, 000. 0 56, 000. 0 11, 678. 7 44, 321. 3 17, 728. 4 26, 592. 7 21, 200. 0 5, 392. 7 2015 2016 420, 000. 0 441, 000. 0 361, 994. 2 374, 881. 6 58, 005. 8 66, 118. 4 12, 262. 8 12, 875. 5 45, 743. 0 53, 242. 9 18, 297. 2 21, 297. 2 27, 445. 8 31, 945. 7 22, 300. 0 23, 400. 0 5, 145. 8 8, 545. 7 18
 NOPAT (Net Operating Profit After Taxes) • NOPAT is the amount of after-tax profit generated by operations. • NOPAT is the amount of net income, or earnings, that a company with no debt or interest-income would have. NOPAT = (Operating profit) (1 -T) = EBIT (1 -T) 19
NOPAT (Net Operating Profit After Taxes) • NOPAT is the amount of after-tax profit generated by operations. • NOPAT is the amount of net income, or earnings, that a company with no debt or interest-income would have. NOPAT = (Operating profit) (1 -T) = EBIT (1 -T) 19
 Calculating NOPAT = (Operating profit) (1 -T) = EBIT (1 -T) NOPAT 16 = 66. 1184 (1 -0. 4) = 39. 67104 million. 20
Calculating NOPAT = (Operating profit) (1 -T) = EBIT (1 -T) NOPAT 16 = 66. 1184 (1 -0. 4) = 39. 67104 million. 20
 Calculating Operating Capital • Operating capital (also called total operating capital, or just capital) is the amount of assets required to support the company’s operations, less the liabilities that arise from those operations. – The short-term component is net operating working capital (NOWC). – The long-term component is factories, land, equipment. 21
Calculating Operating Capital • Operating capital (also called total operating capital, or just capital) is the amount of assets required to support the company’s operations, less the liabilities that arise from those operations. – The short-term component is net operating working capital (NOWC). – The long-term component is factories, land, equipment. 21
 Net Operating Working Capital NOWC = Operating current assets – Operating current liabilities This is the net amount tied up in the “things” needed to run the company on a day-to-day basis. 22
Net Operating Working Capital NOWC = Operating current assets – Operating current liabilities This is the net amount tied up in the “things” needed to run the company on a day-to-day basis. 22
 Net Operating Working Capital NOWC 16 = Operating CA – Operating CL = $176. 4 – $66. 15 = $110. 25 million 23
Net Operating Working Capital NOWC 16 = Operating CA – Operating CL = $176. 4 – $66. 15 = $110. 25 million 23
 Operating Capital • Operating capital = – Net operating working capital (NOWC) plus – Long-term capital, such as factories, land, equipment. 24
Operating Capital • Operating capital = – Net operating working capital (NOWC) plus – Long-term capital, such as factories, land, equipment. 24
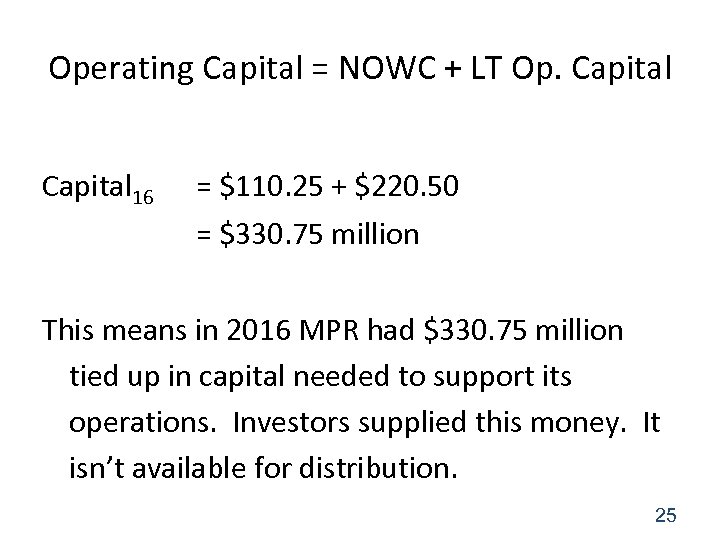 Operating Capital = NOWC + LT Op. Capital 16 = $110. 25 + $220. 50 = $330. 75 million This means in 2016 MPR had $330. 75 million tied up in capital needed to support its operations. Investors supplied this money. It isn’t available for distribution. 25
Operating Capital = NOWC + LT Op. Capital 16 = $110. 25 + $220. 50 = $330. 75 million This means in 2016 MPR had $330. 75 million tied up in capital needed to support its operations. Investors supplied this money. It isn’t available for distribution. 25
 Investment in operating capital • Operating capital in 2015 was $315. 0423 million • Operating capital in 2016 was $330. 75 million • MPR had to make a net investment of $330. 75 – $315. 0423 = $15. 7077 million in operating capital in 2016. 26
Investment in operating capital • Operating capital in 2015 was $315. 0423 million • Operating capital in 2016 was $330. 75 million • MPR had to make a net investment of $330. 75 – $315. 0423 = $15. 7077 million in operating capital in 2016. 26
 Calculating FCF = NOPAT – Investment in operating capital FCF 16 = $39. 67104 – (330. 75 – 315. 0423) = $39. 67104 – $15. 7077 = $23. 96334 million 27
Calculating FCF = NOPAT – Investment in operating capital FCF 16 = $39. 67104 – (330. 75 – 315. 0423) = $39. 67104 – $15. 7077 = $23. 96334 million 27
 There are five ways for a company to use FCF 1. Pay interest on debt. 2. Pay back principal on debt. 3. Pay dividends. 4. Buy back stock. 5. Buy nonoperating assets (e. g. , marketable securities, investments in other companies, etc. ) 28
There are five ways for a company to use FCF 1. Pay interest on debt. 2. Pay back principal on debt. 3. Pay dividends. 4. Buy back stock. 5. Buy nonoperating assets (e. g. , marketable securities, investments in other companies, etc. ) 28
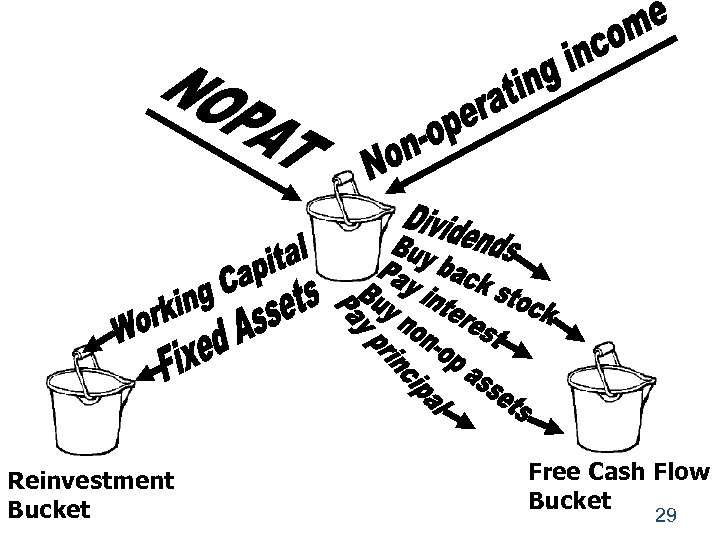 Reinvestment Bucket Free Cash Flow Bucket 29
Reinvestment Bucket Free Cash Flow Bucket 29
 How Did MPR use its FCF? • Paid dividends: $23. 4 million • Paid after-tax interest of: $12, 875. 5 (1 -0. 4) = $7. 7253 million • For a total of $31. 1253 million! This is $7. 162 million more than the $23. 9 million FCF available! Where did it come from? • MPR increased its borrowing by $150. 223 – $143. 061) = $7. 162 million to make up the difference. 30
How Did MPR use its FCF? • Paid dividends: $23. 4 million • Paid after-tax interest of: $12, 875. 5 (1 -0. 4) = $7. 7253 million • For a total of $31. 1253 million! This is $7. 162 million more than the $23. 9 million FCF available! Where did it come from? • MPR increased its borrowing by $150. 223 – $143. 061) = $7. 162 million to make up the difference. 30
 Corporate Valuation • Forecast financial statements and use them to project FCF. • Discount the FCFs at the WACC This gives the value of operations 31
Corporate Valuation • Forecast financial statements and use them to project FCF. • Discount the FCFs at the WACC This gives the value of operations 31
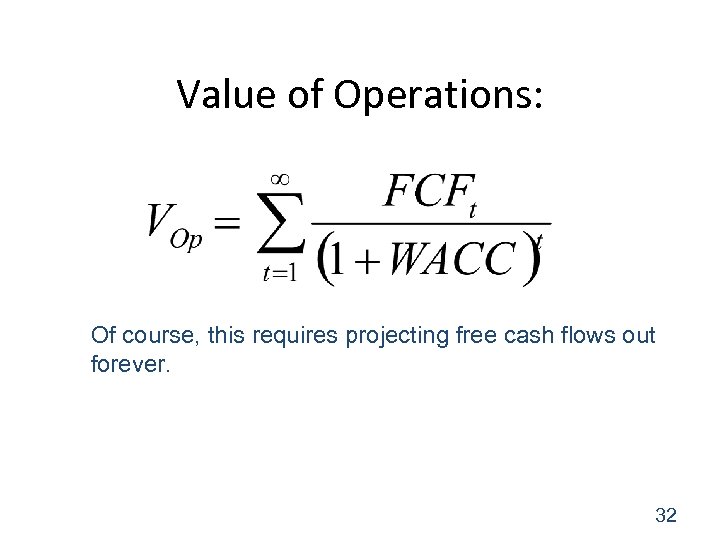 Value of Operations: Of course, this requires projecting free cash flows out forever. 32
Value of Operations: Of course, this requires projecting free cash flows out forever. 32
 Constant growth • If free cash flows are expected to grow at a constant rate of 5%, then this is easy: FCF 2016 23. 963 2017 25. 161 2018 26. 419 2019 27. 740 2020 29. 127 2021 30. 584 There is an easy formula for the present value of free cash flows that grow forever at a constant rate… 33
Constant growth • If free cash flows are expected to grow at a constant rate of 5%, then this is easy: FCF 2016 23. 963 2017 25. 161 2018 26. 419 2019 27. 740 2020 29. 127 2021 30. 584 There is an easy formula for the present value of free cash flows that grow forever at a constant rate… 33
 Constant Growth Formula • The summation can be replaced by a single formula: 34
Constant Growth Formula • The summation can be replaced by a single formula: 34
 The value of operations 35
The value of operations 35
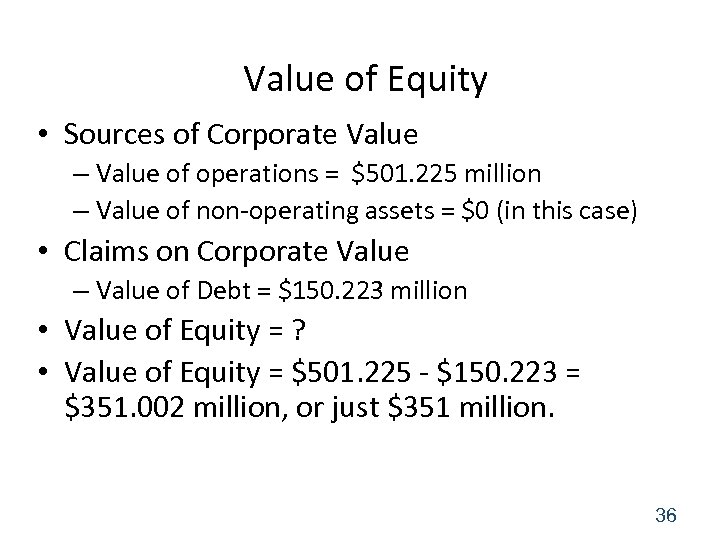 Value of Equity • Sources of Corporate Value – Value of operations = $501. 225 million – Value of non-operating assets = $0 (in this case) • Claims on Corporate Value – Value of Debt = $150. 223 million • Value of Equity = ? • Value of Equity = $501. 225 - $150. 223 = $351. 002 million, or just $351 million. 36
Value of Equity • Sources of Corporate Value – Value of operations = $501. 225 million – Value of non-operating assets = $0 (in this case) • Claims on Corporate Value – Value of Debt = $150. 223 million • Value of Equity = ? • Value of Equity = $501. 225 - $150. 223 = $351. 002 million, or just $351 million. 36
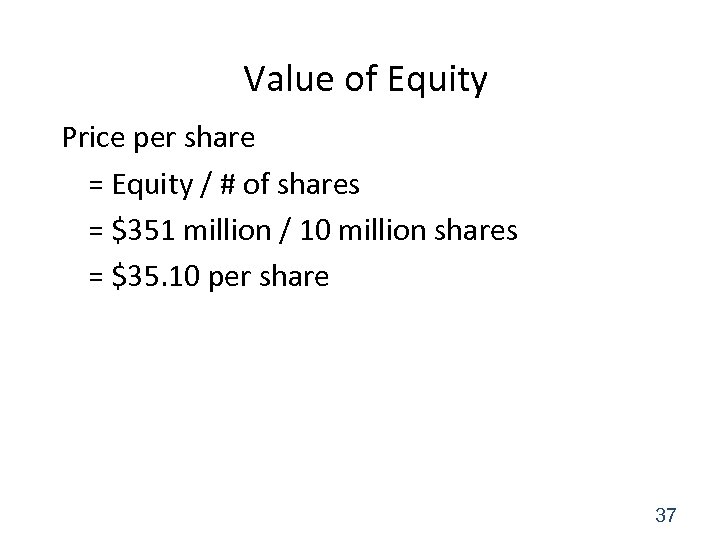 Value of Equity Price per share = Equity / # of shares = $351 million / 10 million shares = $35. 10 per share 37
Value of Equity Price per share = Equity / # of shares = $351 million / 10 million shares = $35. 10 per share 37
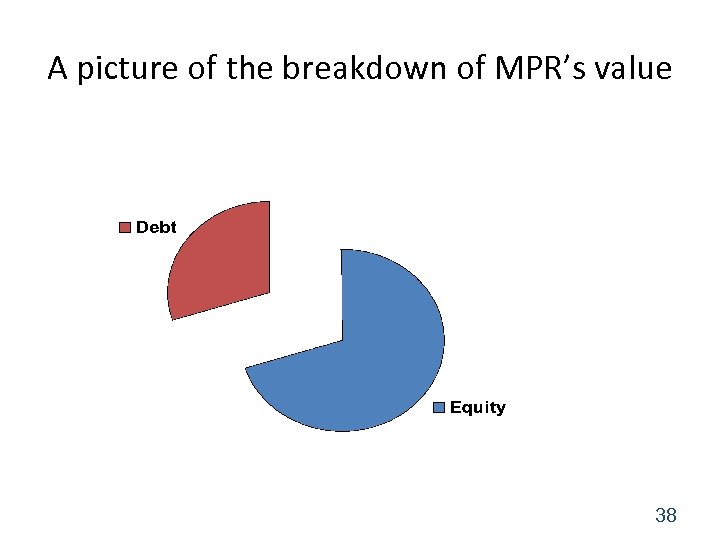 A picture of the breakdown of MPR’s value 38
A picture of the breakdown of MPR’s value 38
 Return on Invested Capital (ROIC) ROIC can be used to evaluate MPR’s performance: ROIC = NOPAT / Total operating capital in place at the beginning of the year 39
Return on Invested Capital (ROIC) ROIC can be used to evaluate MPR’s performance: ROIC = NOPAT / Total operating capital in place at the beginning of the year 39
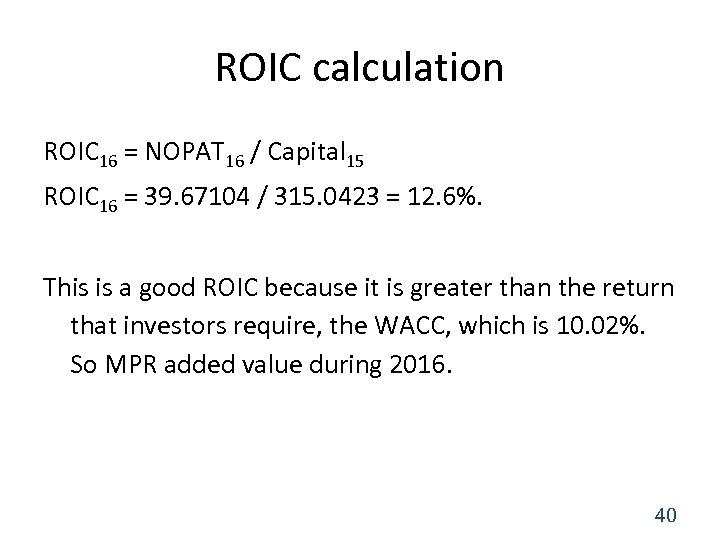 ROIC calculation ROIC 16 = NOPAT 16 / Capital 15 ROIC 16 = 39. 67104 / 315. 0423 = 12. 6%. This is a good ROIC because it is greater than the return that investors require, the WACC, which is 10. 02%. So MPR added value during 2016. 40
ROIC calculation ROIC 16 = NOPAT 16 / Capital 15 ROIC 16 = 39. 67104 / 315. 0423 = 12. 6%. This is a good ROIC because it is greater than the return that investors require, the WACC, which is 10. 02%. So MPR added value during 2016. 40
 Economic Value Added (EVATM) (also called Economic Profit) • EVA is another key measure of operating performance. • EVA is trademarked by Stern Stewart, Inc. • It measures the amount of profit the company earned, over and above the amount of profit that investors required. • EP = NOPATt – WACC(Capitalt-1) 41
Economic Value Added (EVATM) (also called Economic Profit) • EVA is another key measure of operating performance. • EVA is trademarked by Stern Stewart, Inc. • It measures the amount of profit the company earned, over and above the amount of profit that investors required. • EP = NOPATt – WACC(Capitalt-1) 41
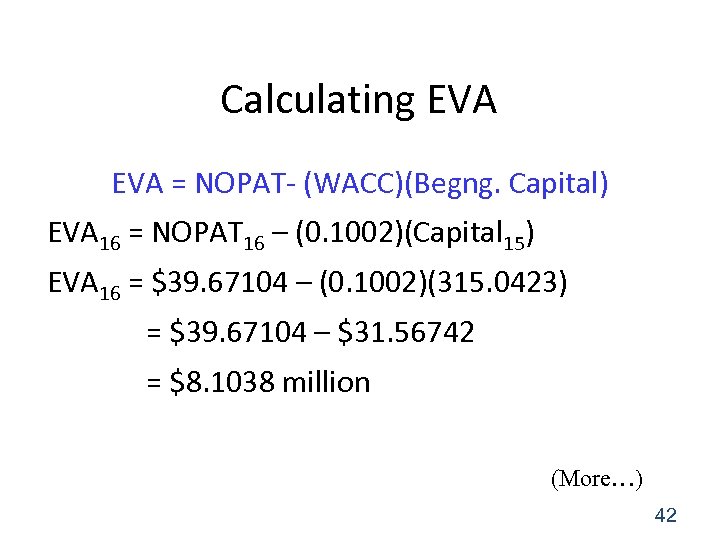 Calculating EVA = NOPAT- (WACC)(Begng. Capital) EVA 16 = NOPAT 16 – (0. 1002)(Capital 15) EVA 16 = $39. 67104 – (0. 1002)(315. 0423) = $39. 67104 – $31. 56742 = $8. 1038 million (More…) 42
Calculating EVA = NOPAT- (WACC)(Begng. Capital) EVA 16 = NOPAT 16 – (0. 1002)(Capital 15) EVA 16 = $39. 67104 – (0. 1002)(315. 0423) = $39. 67104 – $31. 56742 = $8. 1038 million (More…) 42
 Economic profit… This shows that in 2016 MPR earned about $8 million more than its investors required. Another way to calculate EP is EPt = (ROIC – WACC)Capitalt-1 = (0. 125923 – 0. 1002)$315. 0423 = $8. 1038 million 43
Economic profit… This shows that in 2016 MPR earned about $8 million more than its investors required. Another way to calculate EP is EPt = (ROIC – WACC)Capitalt-1 = (0. 125923 – 0. 1002)$315. 0423 = $8. 1038 million 43
 Intuition behind EP If the ROIC – WACC spread is positive, then the firm is generating more than enough “profit, ” and is increasing value. But, if the ROIC – WACC spread is negative, then the firm is destroying value, in the sense that investors would be better off taking their money and investing it elsewhere. 44
Intuition behind EP If the ROIC – WACC spread is positive, then the firm is generating more than enough “profit, ” and is increasing value. But, if the ROIC – WACC spread is negative, then the firm is destroying value, in the sense that investors would be better off taking their money and investing it elsewhere. 44
 Applications of the corporate valuation model • Mergers and acquisitions – Evaluate how much a target is worth under various operating scenarios • Value-based management – Make decisions with the goal of increasing the company’s value • Fundamental investing – Identify firms that are worth more than the current stock price 45
Applications of the corporate valuation model • Mergers and acquisitions – Evaluate how much a target is worth under various operating scenarios • Value-based management – Make decisions with the goal of increasing the company’s value • Fundamental investing – Identify firms that are worth more than the current stock price 45


