3e2940a81badfb34c446662baf619ff0.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 71
 A comparative mapping resource for the grasses GRAMENE www. gramene. org Gramene Workshop @ Plant Biology July 25, 2004 Molly Fogleman Doreen Ware Pankaj Jaiswal www. gramene. org
A comparative mapping resource for the grasses GRAMENE www. gramene. org Gramene Workshop @ Plant Biology July 25, 2004 Molly Fogleman Doreen Ware Pankaj Jaiswal www. gramene. org
 Topics • General introduction to the grasses – Molly Fogleman • Gramene: a community resource – Doreen Ware • Answering biological questions with Gramene – Pankaj Jaiswal • Open Discussion We invite you to give feedback on this workshop by completing our survey. Gramene poster # 902 www. gramene. org
Topics • General introduction to the grasses – Molly Fogleman • Gramene: a community resource – Doreen Ware • Answering biological questions with Gramene – Pankaj Jaiswal • Open Discussion We invite you to give feedback on this workshop by completing our survey. Gramene poster # 902 www. gramene. org
 www. gramene. org
www. gramene. org
 Cereals as a Food Staple • 49% of the world’s calories (human consumption) are provided by rice (23%), wheat (17%) and maize (9%) • Wheat is the staple food for 35% of the world • Rice is the staple food for almost half the world’s population Source: Evolution and Adaptation of Cereal Crops, 2002 Science Publishers, Inc. www. gramene. org
Cereals as a Food Staple • 49% of the world’s calories (human consumption) are provided by rice (23%), wheat (17%) and maize (9%) • Wheat is the staple food for 35% of the world • Rice is the staple food for almost half the world’s population Source: Evolution and Adaptation of Cereal Crops, 2002 Science Publishers, Inc. www. gramene. org
 The USDA Food Guide Pyramid The USDA recommends 6 -11 servings of grains/day Diets high in grains can lead to reductions in: • Coronary Heart Disease • Cancer • Diabetes Source: www. usda. gov and Whole Grain Foods in Health and Disease, 2002 American Association of Cereal Chemists, Inc. www. gramene. org
The USDA Food Guide Pyramid The USDA recommends 6 -11 servings of grains/day Diets high in grains can lead to reductions in: • Coronary Heart Disease • Cancer • Diabetes Source: www. usda. gov and Whole Grain Foods in Health and Disease, 2002 American Association of Cereal Chemists, Inc. www. gramene. org
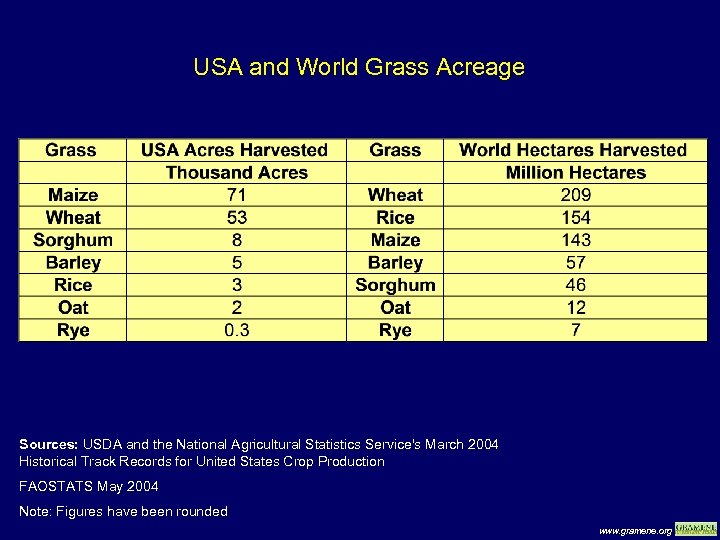 USA and World Grass Acreage Sources: USDA and the National Agricultural Statistics Service's March 2004 Historical Track Records for United States Crop Production FAOSTATS May 2004 Note: Figures have been rounded www. gramene. org
USA and World Grass Acreage Sources: USDA and the National Agricultural Statistics Service's March 2004 Historical Track Records for United States Crop Production FAOSTATS May 2004 Note: Figures have been rounded www. gramene. org
 Population vs. Acreage Amount of land farmed in the US and the World is decreasing due to: • Urbanization • Erosion • High soil salinity levels Source: EPA 2003 Agricultural Environmental Impacts in the US: • 48% of the impaired river miles • 41% of impaired lakes in the United States. • Nutrient, sediment and pesticide runoff Photo Source: USDA - National Resources Conservation Service www. gramene. org
Population vs. Acreage Amount of land farmed in the US and the World is decreasing due to: • Urbanization • Erosion • High soil salinity levels Source: EPA 2003 Agricultural Environmental Impacts in the US: • 48% of the impaired river miles • 41% of impaired lakes in the United States. • Nutrient, sediment and pesticide runoff Photo Source: USDA - National Resources Conservation Service www. gramene. org
 Question: How to Feed a Growing Population? • Genotypes (high yielding, pest resistance, drought tolerant, salt tolerant) from existing germplasms (gene pool)? • Bioengineered Food? Photo Source: The Washington Post Photo. Voyage: Rice a Global Grain www. gramene. org
Question: How to Feed a Growing Population? • Genotypes (high yielding, pest resistance, drought tolerant, salt tolerant) from existing germplasms (gene pool)? • Bioengineered Food? Photo Source: The Washington Post Photo. Voyage: Rice a Global Grain www. gramene. org
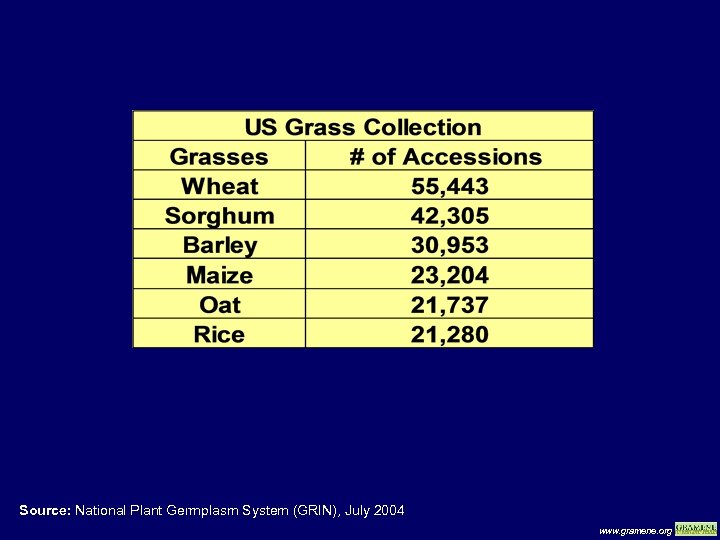 Source: National Plant Germplasm System (GRIN), July 2004 www. gramene. org
Source: National Plant Germplasm System (GRIN), July 2004 www. gramene. org
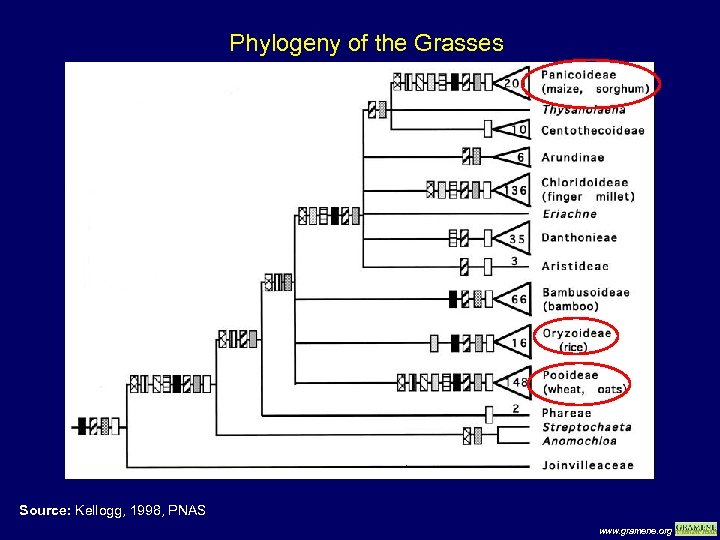 Phylogeny of the Grasses Source: Kellogg, 1998, PNAS www. gramene. org
Phylogeny of the Grasses Source: Kellogg, 1998, PNAS www. gramene. org
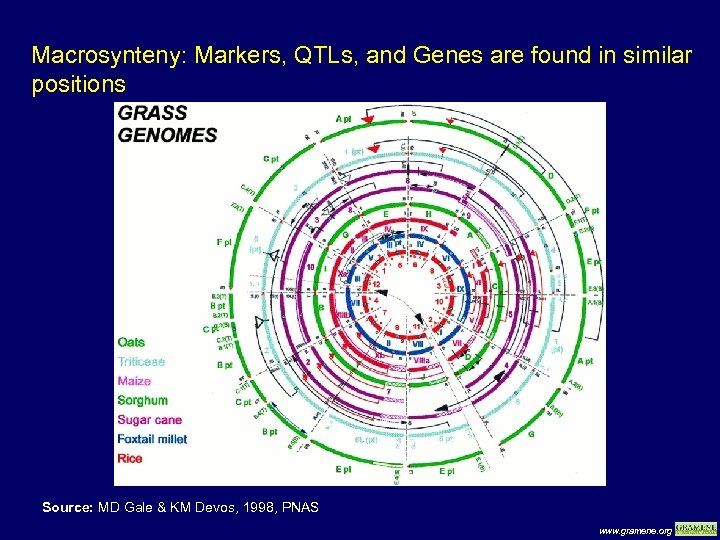 Macrosynteny: Markers, QTLs, and Genes are found in similar positions Source: MD Gale & KM Devos, 1998, PNAS www. gramene. org
Macrosynteny: Markers, QTLs, and Genes are found in similar positions Source: MD Gale & KM Devos, 1998, PNAS www. gramene. org
 Why use Rice as a leverage? – Smallest genome – Sequenced genome – Extensive genetic & physical map resources – Thousands of genes and quantitative trait loci mapped – Large mutant & germplasm collections www. gramene. org
Why use Rice as a leverage? – Smallest genome – Sequenced genome – Extensive genetic & physical map resources – Thousands of genes and quantitative trait loci mapped – Large mutant & germplasm collections www. gramene. org
 Gramene a community resource Doreen Ware USDA-ARS Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory www. gramene. org
Gramene a community resource Doreen Ware USDA-ARS Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory www. gramene. org
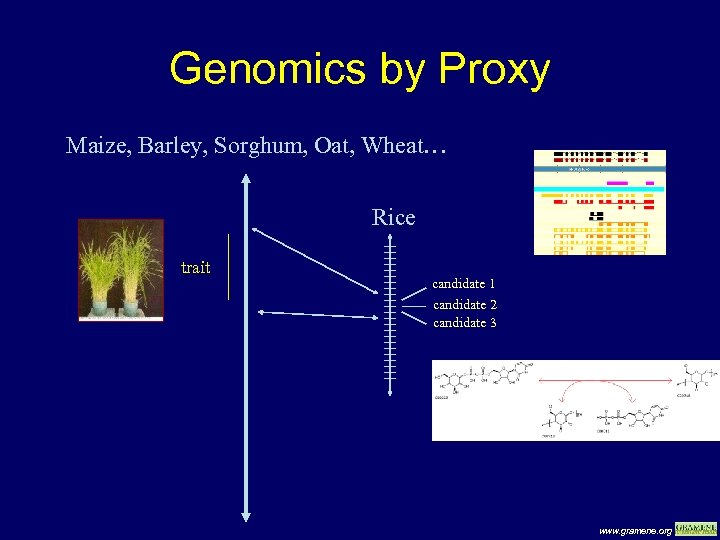 Genomics by Proxy Maize, Barley, Sorghum, Oat, Wheat… Rice trait candidate 1 candidate 2 candidate 3 www. gramene. org
Genomics by Proxy Maize, Barley, Sorghum, Oat, Wheat… Rice trait candidate 1 candidate 2 candidate 3 www. gramene. org
 Timeline and Funding • Gramene www. gramene. org – Funded October 2001 – Superceded USDA Rice. Genes – First release of the database January 2002 • Funding Sources – USDA CREES IFAS – USDA ARS Specific Cooperative Agreement – NSF Research Coordination Network – NSF Plant Genome Initiative www. gramene. org
Timeline and Funding • Gramene www. gramene. org – Funded October 2001 – Superceded USDA Rice. Genes – First release of the database January 2002 • Funding Sources – USDA CREES IFAS – USDA ARS Specific Cooperative Agreement – NSF Research Coordination Network – NSF Plant Genome Initiative www. gramene. org
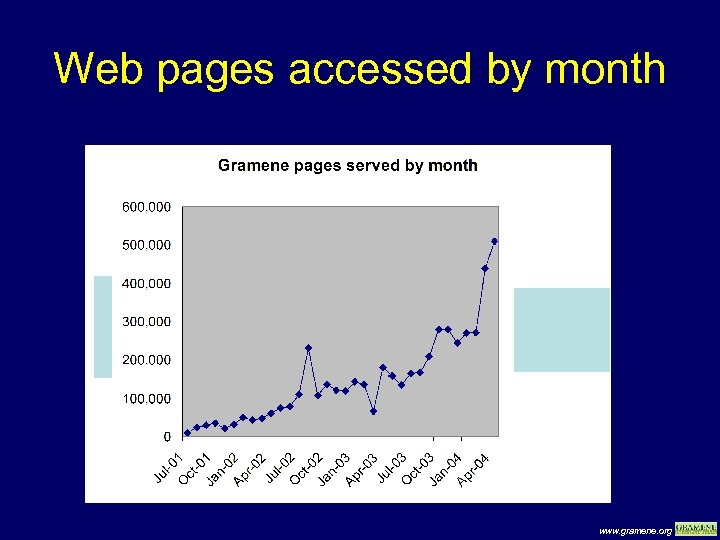 Web pages accessed by month www. gramene. org
Web pages accessed by month www. gramene. org
 Project Participants • Community Collaborators – Publicly funded projects – Individual researchers • Gramene Staff (Cornell and CSHL) – Curators • Information content – Software developers • Visualization tools and data management – Outreach • Scientific community and Secondary Educators www. gramene. org
Project Participants • Community Collaborators – Publicly funded projects – Individual researchers • Gramene Staff (Cornell and CSHL) – Curators • Information content – Software developers • Visualization tools and data management – Outreach • Scientific community and Secondary Educators www. gramene. org
 Collaborators and Contributors http: //www. gramene. org/collaborators www. gramene. org
Collaborators and Contributors http: //www. gramene. org/collaborators www. gramene. org
 Community Resource • Integrative set of web-based tools for discovery – Semi-automated – Curated • Software applications – CMap: Generic Model Organism Systems Database Project (GMOD) www. gmod. org • Controlled vocabularies – Open Biological Ontologies (OBO) • • Plant Ontology (POC workshop July 27 ) Gene Ontology Trait Ontology Environment Ontology www. gramene. org
Community Resource • Integrative set of web-based tools for discovery – Semi-automated – Curated • Software applications – CMap: Generic Model Organism Systems Database Project (GMOD) www. gmod. org • Controlled vocabularies – Open Biological Ontologies (OBO) • • Plant Ontology (POC workshop July 27 ) Gene Ontology Trait Ontology Environment Ontology www. gramene. org
 What’s in Gramene • High-throughput data – – Rice genome Rice proteins Functional annotation of gene products Grass EST collections • Curated data – – – Genetic maps Physical maps Protein annotation Mutant (phenotypic variant) Quantitative Trait Loci (QTL) • Documentation and Help Guide www. gramene. org
What’s in Gramene • High-throughput data – – Rice genome Rice proteins Functional annotation of gene products Grass EST collections • Curated data – – – Genetic maps Physical maps Protein annotation Mutant (phenotypic variant) Quantitative Trait Loci (QTL) • Documentation and Help Guide www. gramene. org
 Search Tools • • Genome browser BLAST CMap viewer Marker Protein Ontology Mutants QTL • Literature www. gramene. org
Search Tools • • Genome browser BLAST CMap viewer Marker Protein Ontology Mutants QTL • Literature www. gramene. org
 Web Interfaces • Standard • Customizable • Links – Within the database – Between database – Data sources www. gramene. org
Web Interfaces • Standard • Customizable • Links – Within the database – Between database – Data sources www. gramene. org
 Navigation bar standard www. gramene. org
Navigation bar standard www. gramene. org
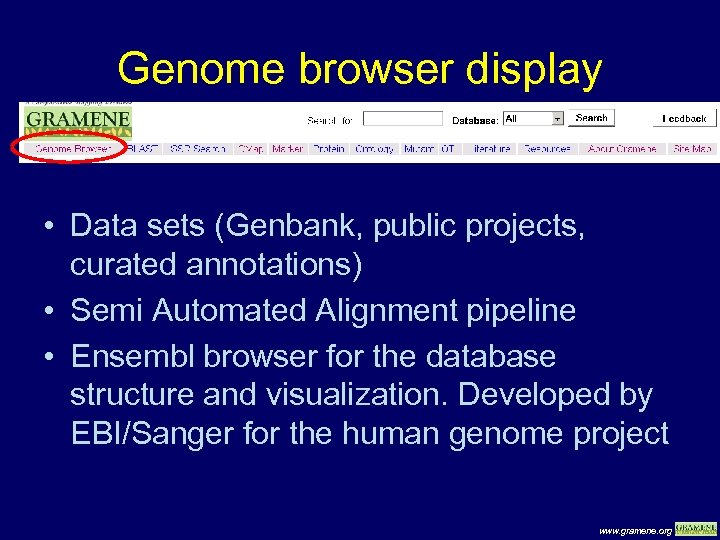 Genome browser display • Data sets (Genbank, public projects, curated annotations) • Semi Automated Alignment pipeline • Ensembl browser for the database structure and visualization. Developed by EBI/Sanger for the human genome project www. gramene. org
Genome browser display • Data sets (Genbank, public projects, curated annotations) • Semi Automated Alignment pipeline • Ensembl browser for the database structure and visualization. Developed by EBI/Sanger for the human genome project www. gramene. org
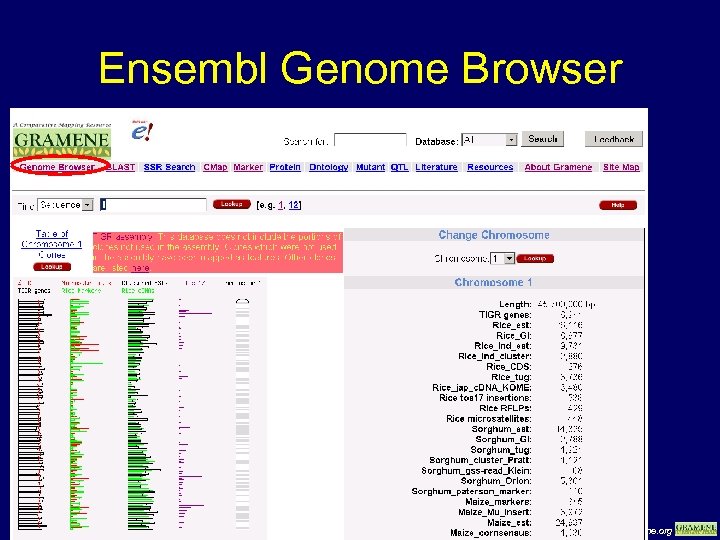 Ensembl Genome Browser www. gramene. org
Ensembl Genome Browser www. gramene. org
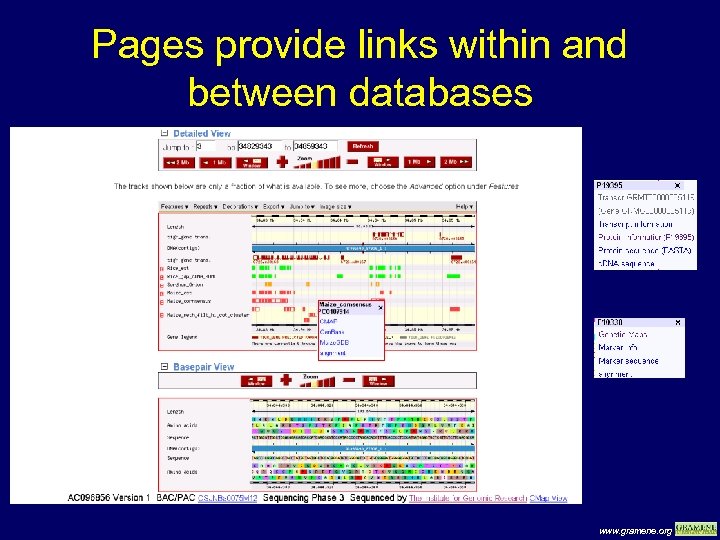 Pages provide links within and between databases www. gramene. org
Pages provide links within and between databases www. gramene. org
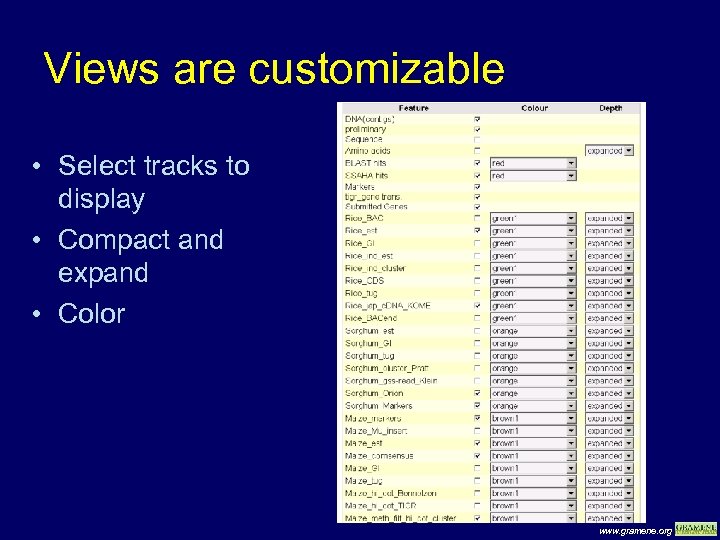 Views are customizable • Select tracks to display • Compact and expand • Color www. gramene. org
Views are customizable • Select tracks to display • Compact and expand • Color www. gramene. org
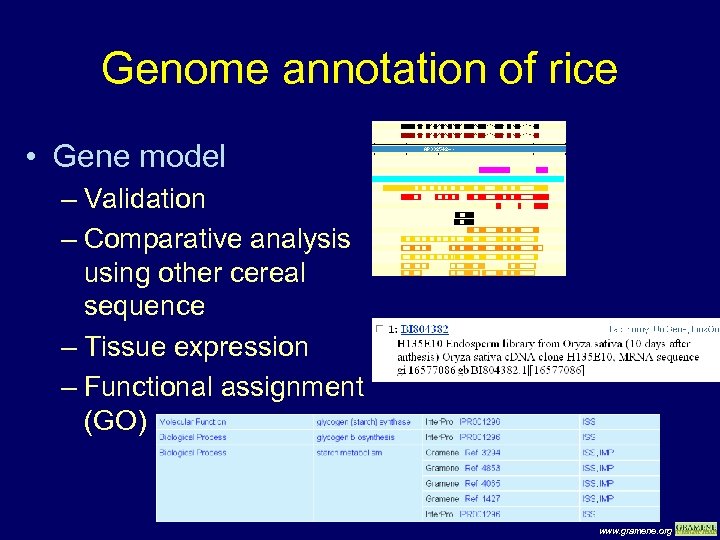 Genome annotation of rice • Gene model – Validation – Comparative analysis using other cereal sequence – Tissue expression – Functional assignment (GO) www. gramene. org
Genome annotation of rice • Gene model – Validation – Comparative analysis using other cereal sequence – Tissue expression – Functional assignment (GO) www. gramene. org
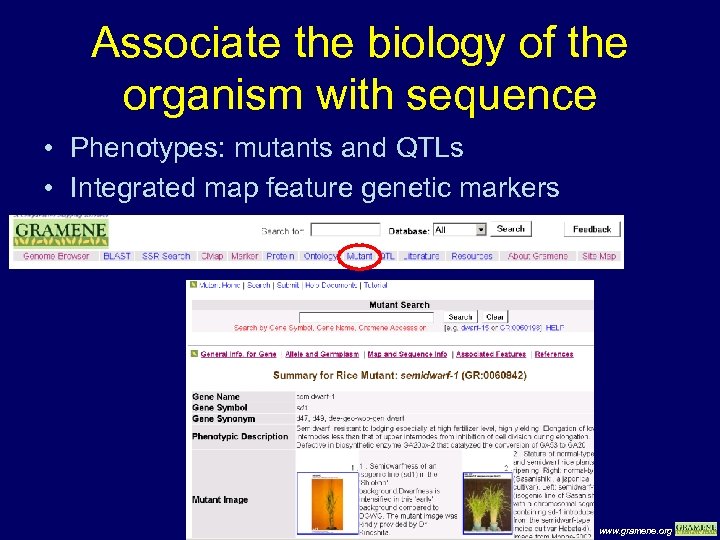 Associate the biology of the organism with sequence • Phenotypes: mutants and QTLs • Integrated map feature genetic markers www. gramene. org
Associate the biology of the organism with sequence • Phenotypes: mutants and QTLs • Integrated map feature genetic markers www. gramene. org
 Comparative Map display • Maps and Correspondences (public projects, curated) – Literature – Community curation – Alignment from sequence • Database structure and browser – CMap –GMOD project www. gramene. org
Comparative Map display • Maps and Correspondences (public projects, curated) – Literature – Community curation – Alignment from sequence • Database structure and browser – CMap –GMOD project www. gramene. org
 Correspondences in comparative map display • Rice Genome Assembly is the reference map in the comparative map browser • Sequence features and hybridized markers provide the correspondence within species and between species maps www. gramene. org
Correspondences in comparative map display • Rice Genome Assembly is the reference map in the comparative map browser • Sequence features and hybridized markers provide the correspondence within species and between species maps www. gramene. org
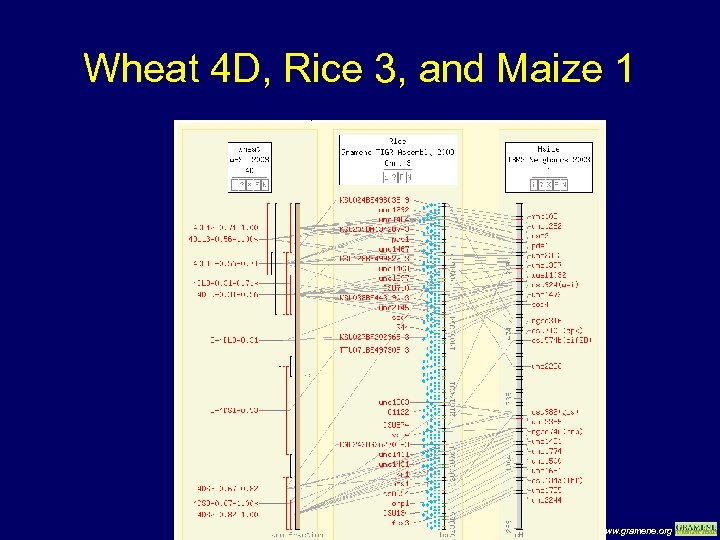 Wheat 4 D, Rice 3, and Maize 1 www. gramene. org
Wheat 4 D, Rice 3, and Maize 1 www. gramene. org
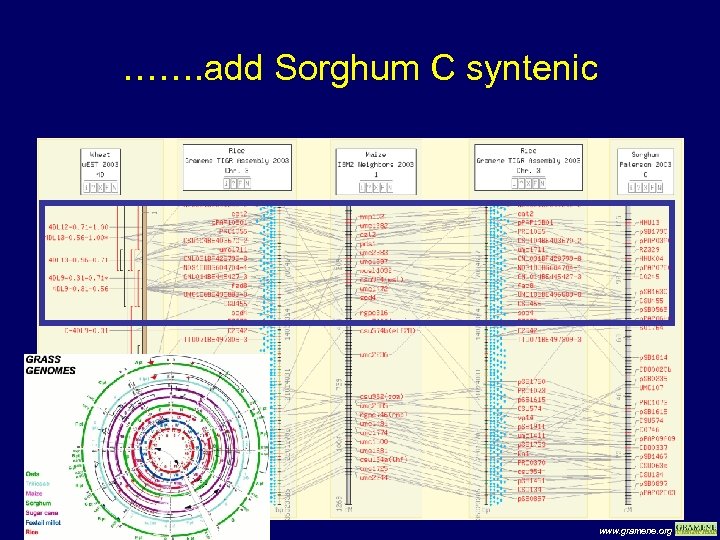 ……. add Sorghum C syntenic www. gramene. org
……. add Sorghum C syntenic www. gramene. org
 Protein Browser • Data sets – Swiss. Prot rice proteins, annotations and associated literature • Ontologies (controlled vocabulary) • Custom database structure and visualization software www. gramene. org
Protein Browser • Data sets – Swiss. Prot rice proteins, annotations and associated literature • Ontologies (controlled vocabulary) • Custom database structure and visualization software www. gramene. org
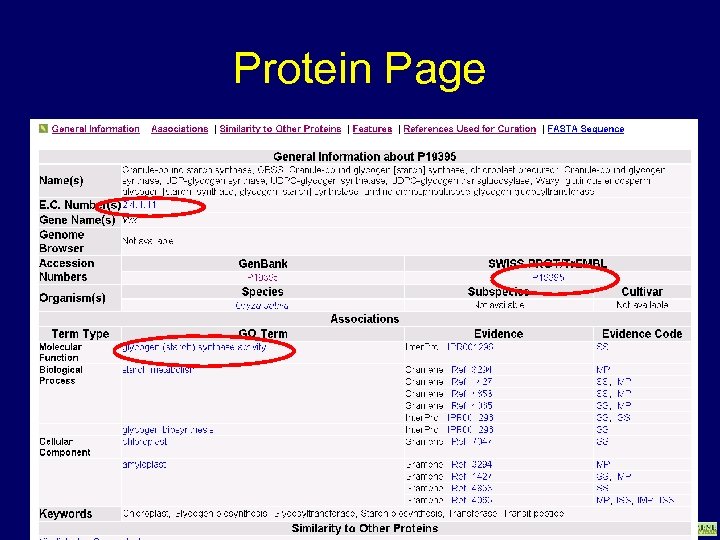 Protein Page www. gramene. org
Protein Page www. gramene. org
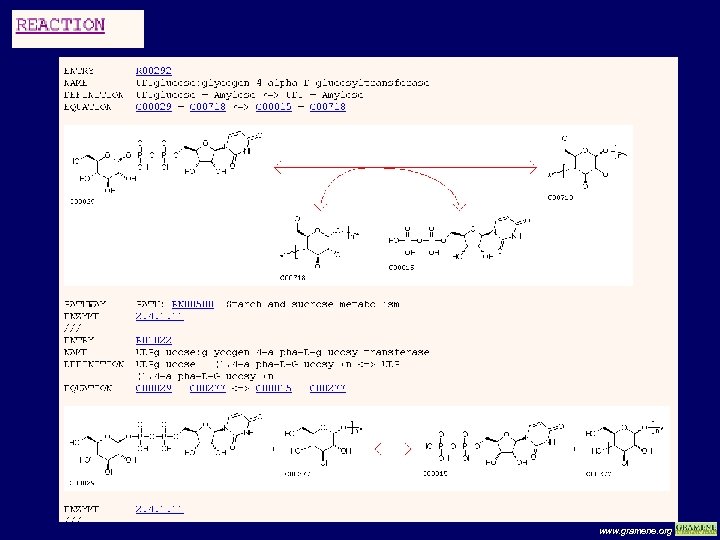
 KEGG www. gramene. org
KEGG www. gramene. org
 www. gramene. org
www. gramene. org
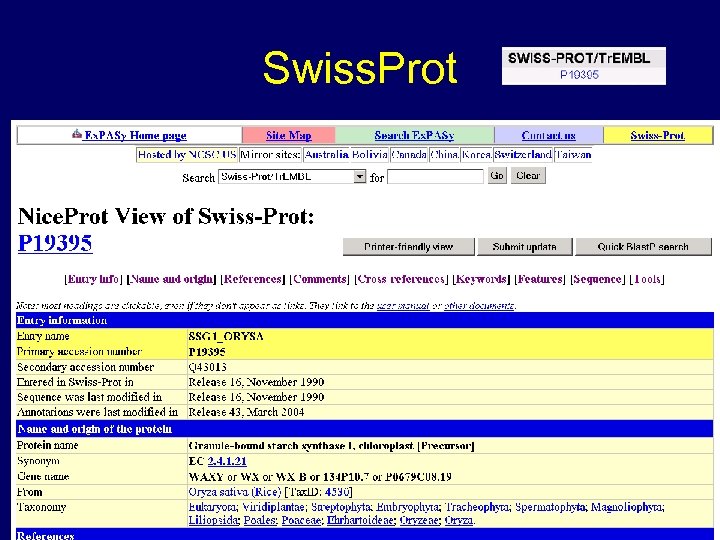 Swiss. Prot www. gramene. org
Swiss. Prot www. gramene. org
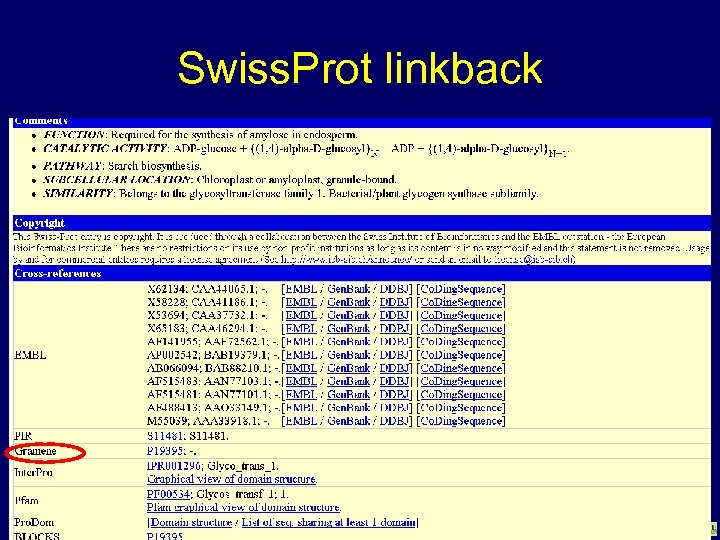 Swiss. Prot linkback www. gramene. org
Swiss. Prot linkback www. gramene. org
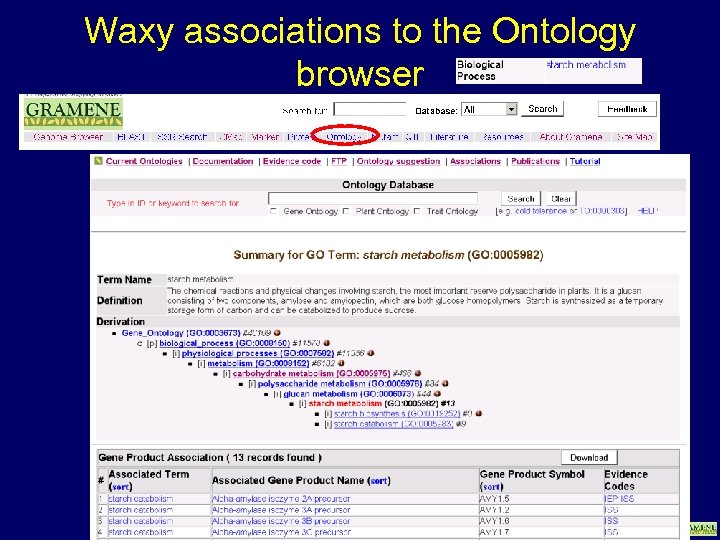 Waxy associations to the Ontology browser www. gramene. org
Waxy associations to the Ontology browser www. gramene. org
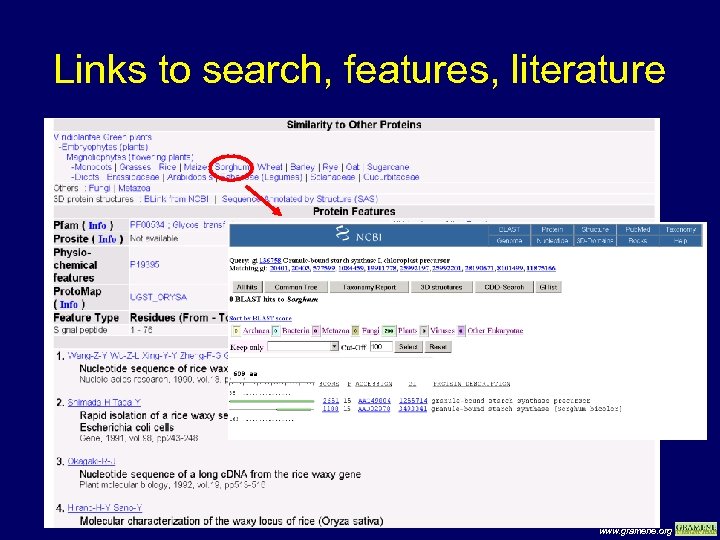 Links to search, features, literature www. gramene. org
Links to search, features, literature www. gramene. org
 Phenotypes assays • What do you want to capture? • How will you integrate this information into a database? www. gramene. org
Phenotypes assays • What do you want to capture? • How will you integrate this information into a database? www. gramene. org
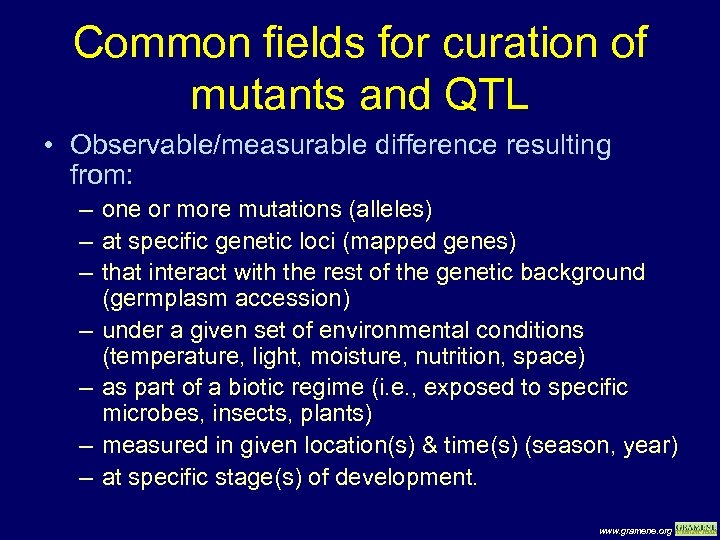 Common fields for curation of mutants and QTL • Observable/measurable difference resulting from: – one or more mutations (alleles) – at specific genetic loci (mapped genes) – that interact with the rest of the genetic background (germplasm accession) – under a given set of environmental conditions (temperature, light, moisture, nutrition, space) – as part of a biotic regime (i. e. , exposed to specific microbes, insects, plants) – measured in given location(s) & time(s) (season, year) – at specific stage(s) of development. www. gramene. org
Common fields for curation of mutants and QTL • Observable/measurable difference resulting from: – one or more mutations (alleles) – at specific genetic loci (mapped genes) – that interact with the rest of the genetic background (germplasm accession) – under a given set of environmental conditions (temperature, light, moisture, nutrition, space) – as part of a biotic regime (i. e. , exposed to specific microbes, insects, plants) – measured in given location(s) & time(s) (season, year) – at specific stage(s) of development. www. gramene. org
 Ontologies used in Gramene • Gene Ontology – Molecular Function – Biological process – Cellular location • Plant Ontology – Anatomy – Development • Trait Ontology www. gramene. org
Ontologies used in Gramene • Gene Ontology – Molecular Function – Biological process – Cellular location • Plant Ontology – Anatomy – Development • Trait Ontology www. gramene. org
 What Ontologies Let You Ask • Find all rice mutants in my favorite colinear region of rice associated with dwarfism. • What genes within a starch content QTL are predicted to be involved in carbohydrate metabolism? • Find protein orthologs between rice & maize whose stage-specific expression patterns have changed. www. gramene. org
What Ontologies Let You Ask • Find all rice mutants in my favorite colinear region of rice associated with dwarfism. • What genes within a starch content QTL are predicted to be involved in carbohydrate metabolism? • Find protein orthologs between rice & maize whose stage-specific expression patterns have changed. www. gramene. org
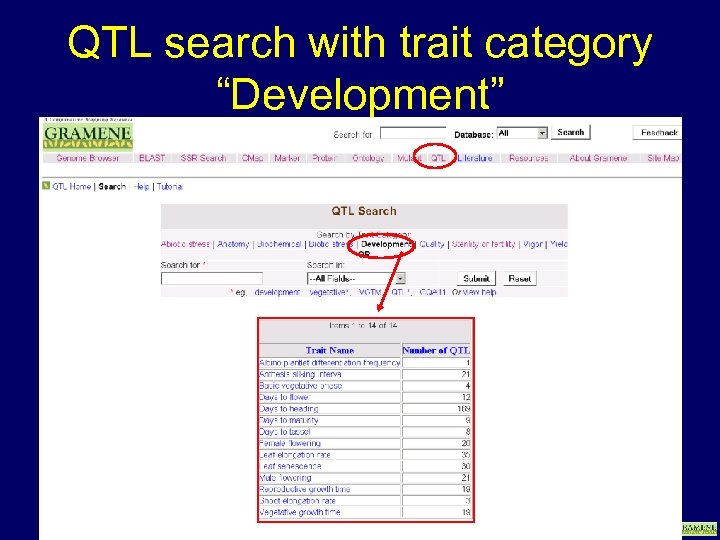 QTL search with trait category “Development” www. gramene. org
QTL search with trait category “Development” www. gramene. org
 Answering biological questions with Gramene workshop @ Plant Biology July 25, 2004 Pankaj Jaiswal www. gramene. org
Answering biological questions with Gramene workshop @ Plant Biology July 25, 2004 Pankaj Jaiswal www. gramene. org
 TASKS • Map a cloned rice resistance gene to its putative location in the rice genome • Compare its position to that of other mapped resistance genes What do we already know ? • The rice disease resistance gene Pi-ta • Genetically mapped to chromosome 12 Rybka et al. (1997). • It has also been sequenced Bryan et al. (1997). www. gramene. org
TASKS • Map a cloned rice resistance gene to its putative location in the rice genome • Compare its position to that of other mapped resistance genes What do we already know ? • The rice disease resistance gene Pi-ta • Genetically mapped to chromosome 12 Rybka et al. (1997). • It has also been sequenced Bryan et al. (1997). www. gramene. org
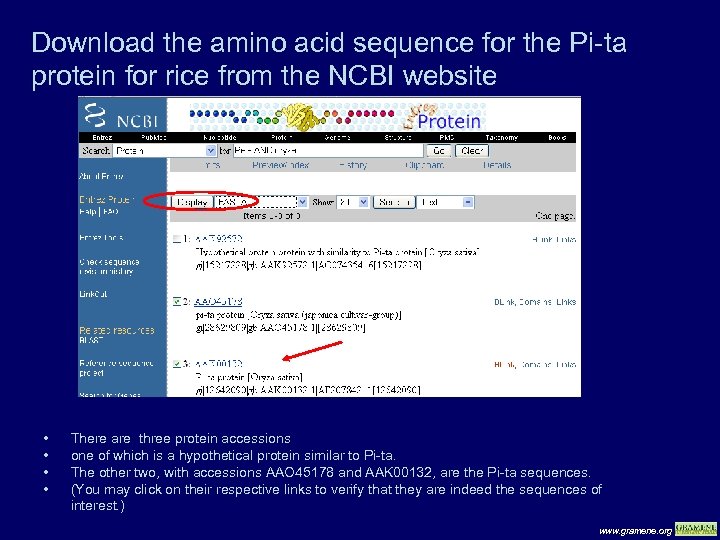 Download the amino acid sequence for the Pi-ta protein for rice from the NCBI website • • There are three protein accessions one of which is a hypothetical protein similar to Pi-ta. The other two, with accessions AAO 45178 and AAK 00132, are the Pi-ta sequences. (You may click on their respective links to verify that they are indeed the sequences of interest. ) www. gramene. org
Download the amino acid sequence for the Pi-ta protein for rice from the NCBI website • • There are three protein accessions one of which is a hypothetical protein similar to Pi-ta. The other two, with accessions AAO 45178 and AAK 00132, are the Pi-ta sequences. (You may click on their respective links to verify that they are indeed the sequences of interest. ) www. gramene. org
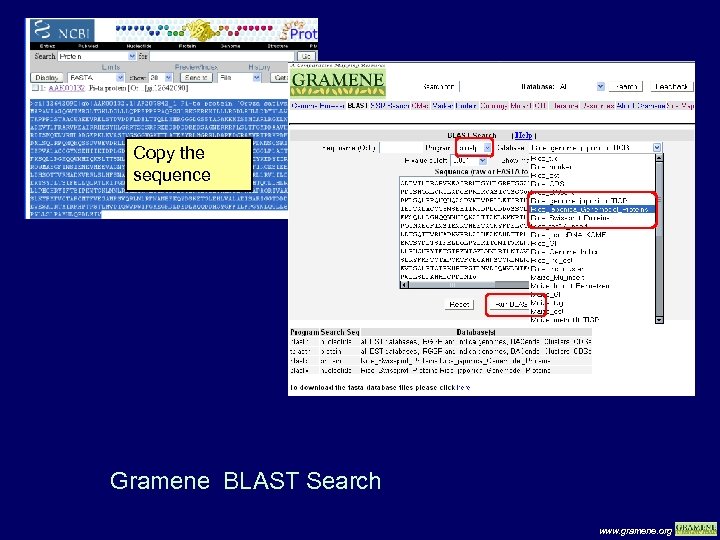 Copy the sequence Gramene BLAST Search www. gramene. org
Copy the sequence Gramene BLAST Search www. gramene. org
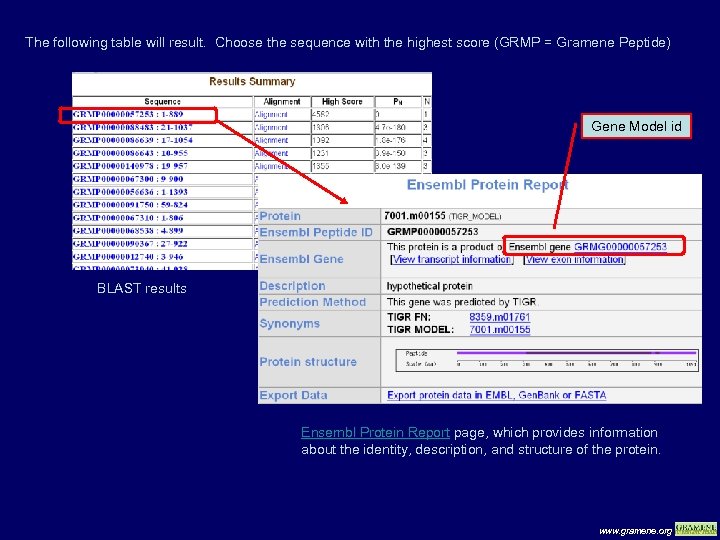 The following table will result. Choose the sequence with the highest score (GRMP = Gramene Peptide) Gene Model id BLAST results Ensembl Protein Report page, which provides information about the identity, description, and structure of the protein. www. gramene. org
The following table will result. Choose the sequence with the highest score (GRMP = Gramene Peptide) Gene Model id BLAST results Ensembl Protein Report page, which provides information about the identity, description, and structure of the protein. www. gramene. org
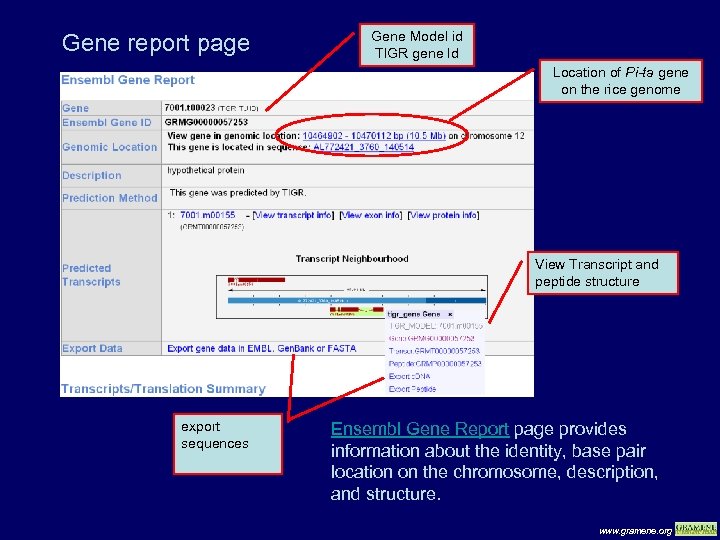 Gene report page Gene Model id TIGR gene Id Location of Pi-ta gene on the rice genome View Transcript and peptide structure export sequences Ensembl Gene Report page provides information about the identity, base pair location on the chromosome, description, and structure. www. gramene. org
Gene report page Gene Model id TIGR gene Id Location of Pi-ta gene on the rice genome View Transcript and peptide structure export sequences Ensembl Gene Report page provides information about the identity, base pair location on the chromosome, description, and structure. www. gramene. org
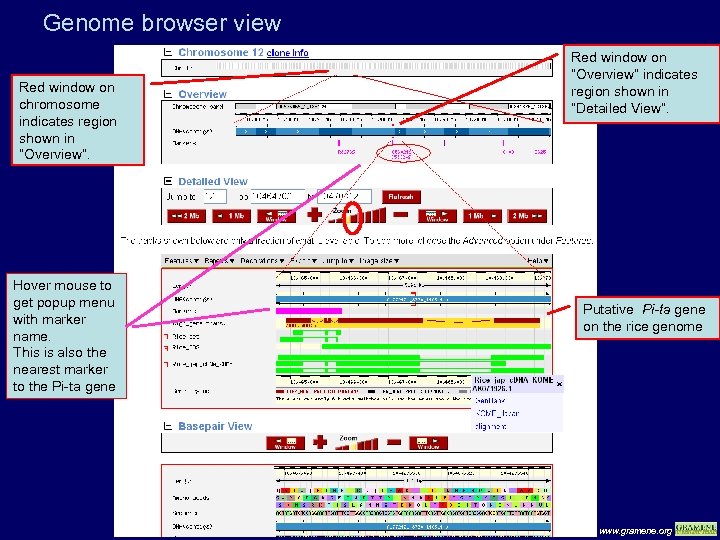 Genome browser view Red window on chromosome indicates region shown in “Overview”. Hover mouse to get popup menu with marker name. This is also the nearest marker to the Pi-ta gene Red window on “Overview” indicates region shown in “Detailed View”. Putative Pi-ta gene on the rice genome www. gramene. org
Genome browser view Red window on chromosome indicates region shown in “Overview”. Hover mouse to get popup menu with marker name. This is also the nearest marker to the Pi-ta gene Red window on “Overview” indicates region shown in “Detailed View”. Putative Pi-ta gene on the rice genome www. gramene. org
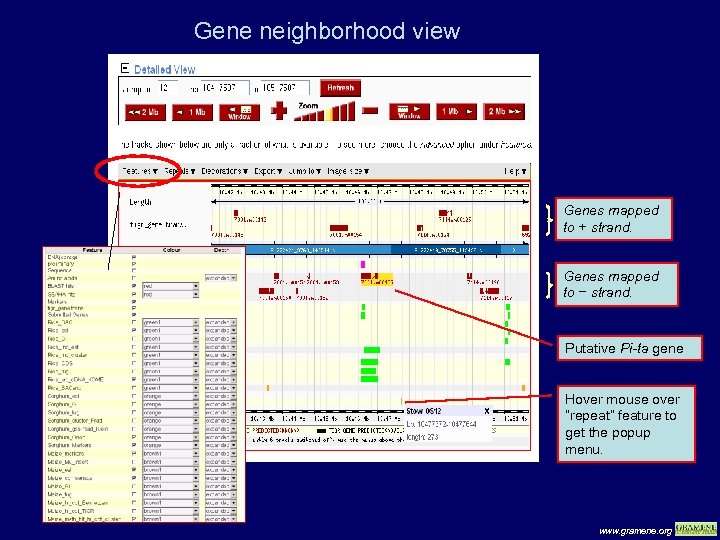 Gene neighborhood view Genes mapped to + strand. Genes mapped to − strand. Putative Pi-ta gene Hover mouse over “repeat” feature to get the popup menu. www. gramene. org
Gene neighborhood view Genes mapped to + strand. Genes mapped to − strand. Putative Pi-ta gene Hover mouse over “repeat” feature to get the popup menu. www. gramene. org
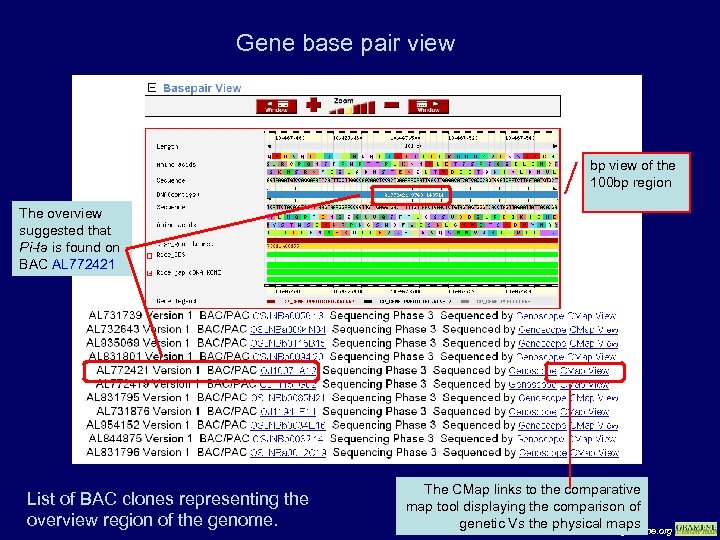 Gene base pair view bp view of the 100 bp region The overview suggested that Pi-ta is found on BAC AL 772421 List of BAC clones representing the overview region of the genome. The CMap links to the comparative map tool displaying the comparison of genetic Vs the physical maps www. gramene. org
Gene base pair view bp view of the 100 bp region The overview suggested that Pi-ta is found on BAC AL 772421 List of BAC clones representing the overview region of the genome. The CMap links to the comparative map tool displaying the comparison of genetic Vs the physical maps www. gramene. org
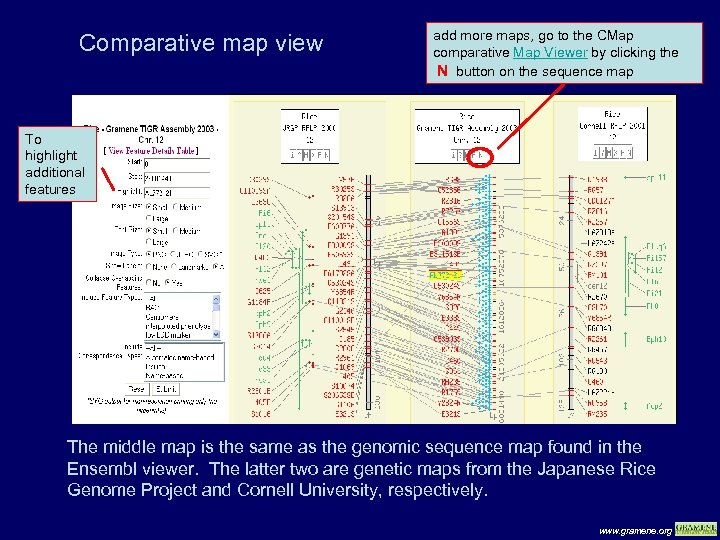 Comparative map view add more maps, go to the CMap comparative Map Viewer by clicking the N button on the sequence map To highlight additional features The middle map is the same as the genomic sequence map found in the Ensembl viewer. The latter two are genetic maps from the Japanese Rice Genome Project and Cornell University, respectively. www. gramene. org
Comparative map view add more maps, go to the CMap comparative Map Viewer by clicking the N button on the sequence map To highlight additional features The middle map is the same as the genomic sequence map found in the Ensembl viewer. The latter two are genetic maps from the Japanese Rice Genome Project and Cornell University, respectively. www. gramene. org
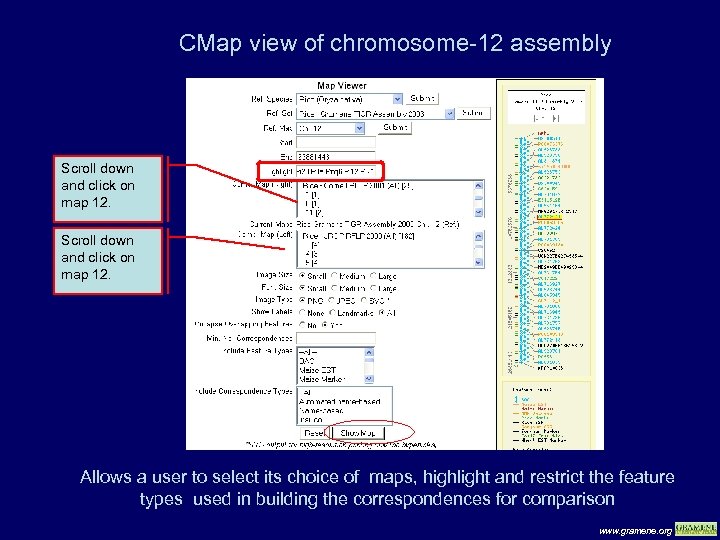 CMap view of chromosome-12 assembly Scroll down and click on map 12. Allows a user to select its choice of maps, highlight and restrict the feature types used in building the correspondences for comparison www. gramene. org
CMap view of chromosome-12 assembly Scroll down and click on map 12. Allows a user to select its choice of maps, highlight and restrict the feature types used in building the correspondences for comparison www. gramene. org
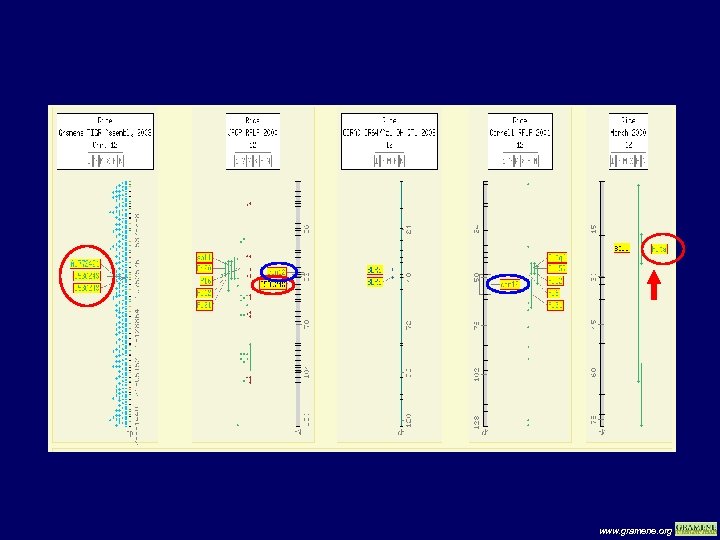
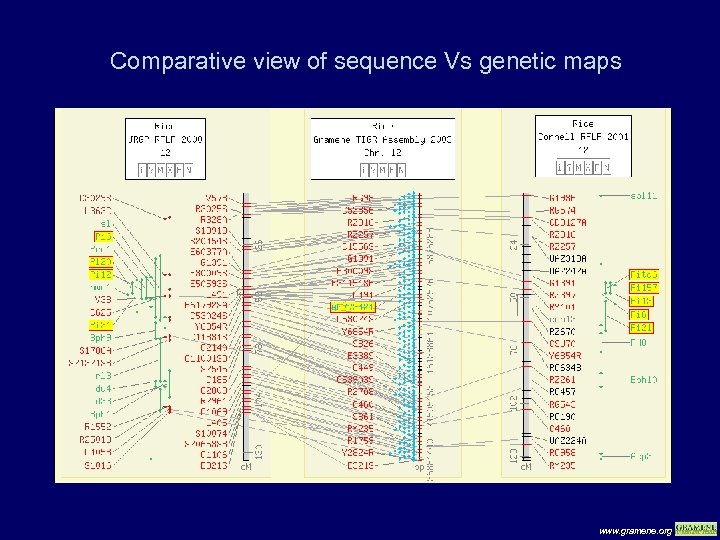 Comparative view of sequence Vs genetic maps www. gramene. org
Comparative view of sequence Vs genetic maps www. gramene. org
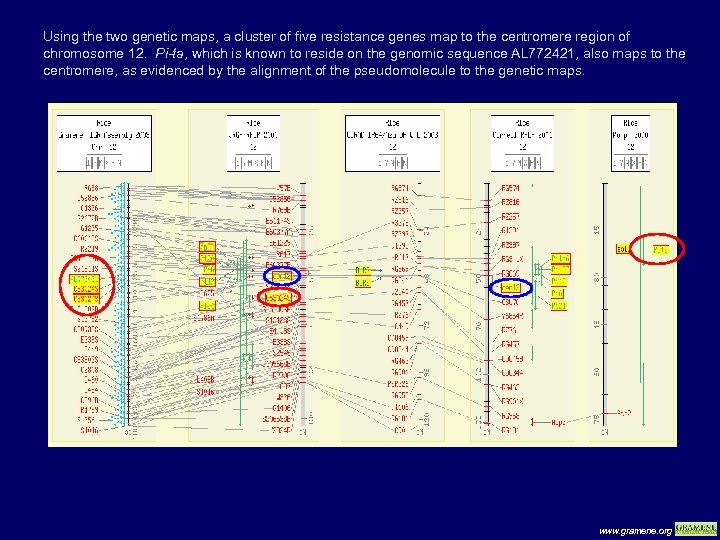 Using the two genetic maps, a cluster of five resistance genes map to the centromere region of chromosome 12. Pi-ta, which is known to reside on the genomic sequence AL 772421, also maps to the centromere, as evidenced by the alignment of the pseudomolecule to the genetic maps. www. gramene. org
Using the two genetic maps, a cluster of five resistance genes map to the centromere region of chromosome 12. Pi-ta, which is known to reside on the genomic sequence AL 772421, also maps to the centromere, as evidenced by the alignment of the pseudomolecule to the genetic maps. www. gramene. org
 www. gramene. org
www. gramene. org
 www. gramene. org
www. gramene. org
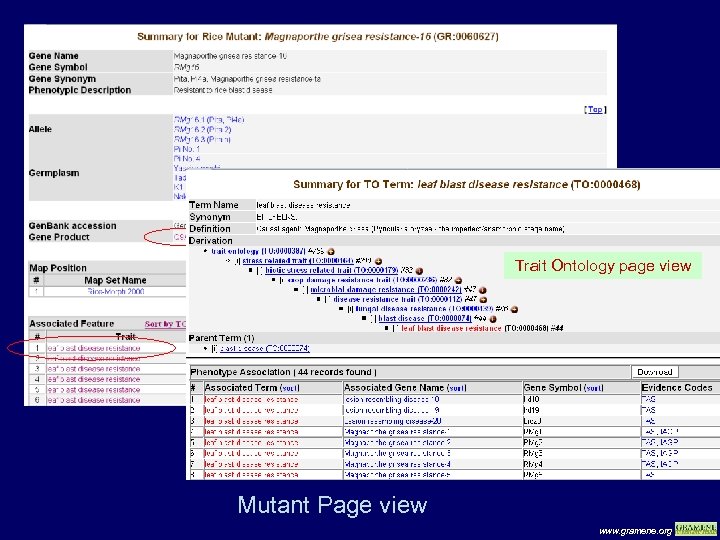 Trait Ontology page view Mutant Page view www. gramene. org
Trait Ontology page view Mutant Page view www. gramene. org
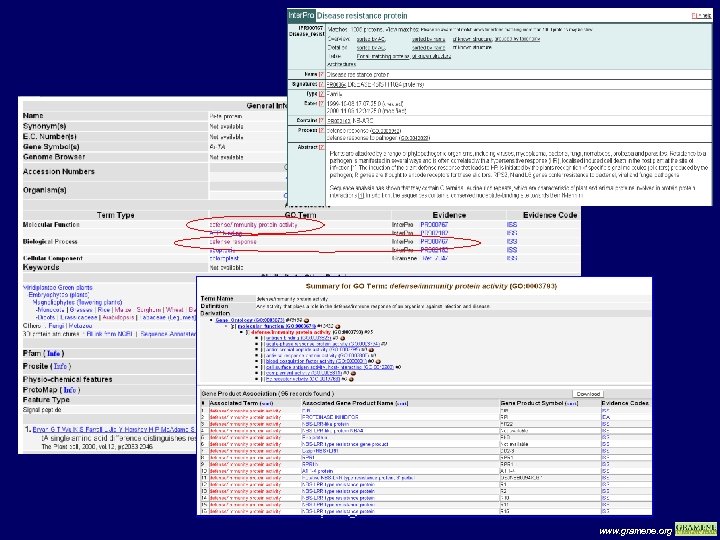 Protein page view www. gramene. org
Protein page view www. gramene. org
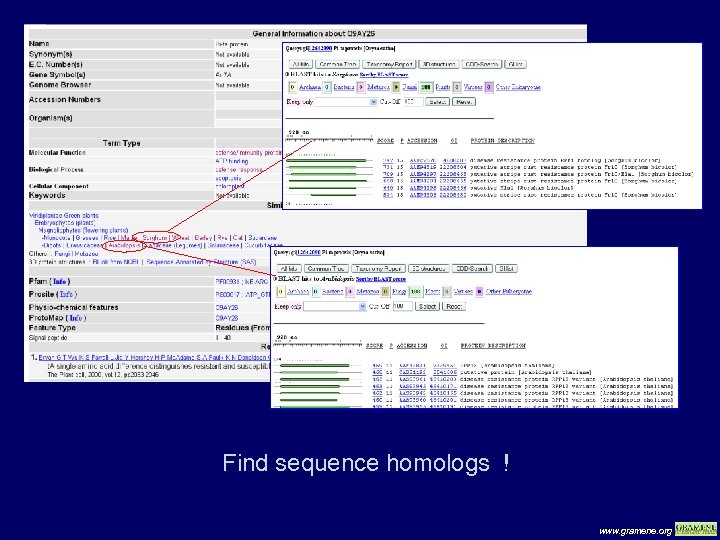 Find sequence homologs ! www. gramene. org
Find sequence homologs ! www. gramene. org
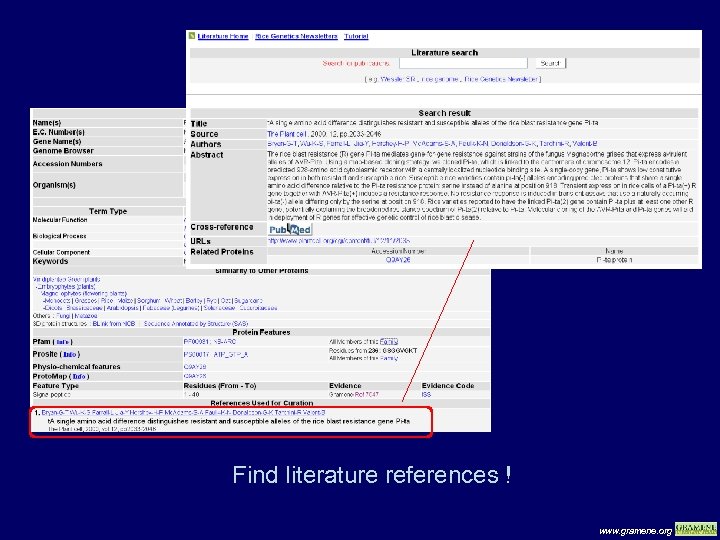 Find literature references ! www. gramene. org
Find literature references ! www. gramene. org
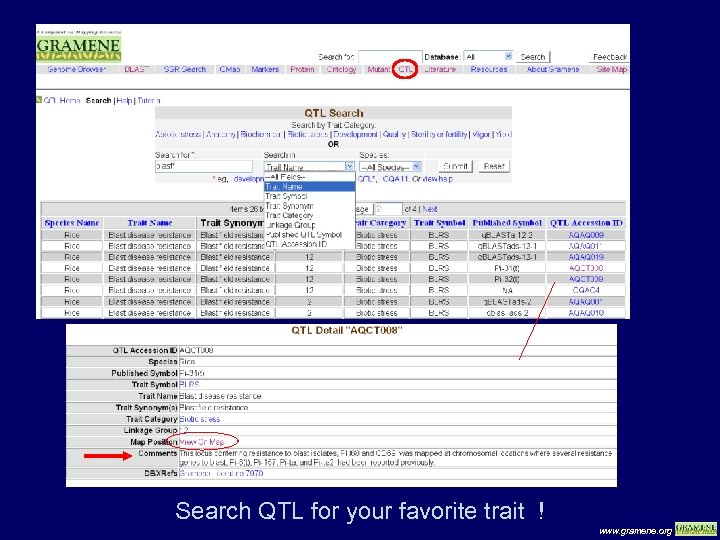 Search QTL for your favorite trait ! www. gramene. org
Search QTL for your favorite trait ! www. gramene. org
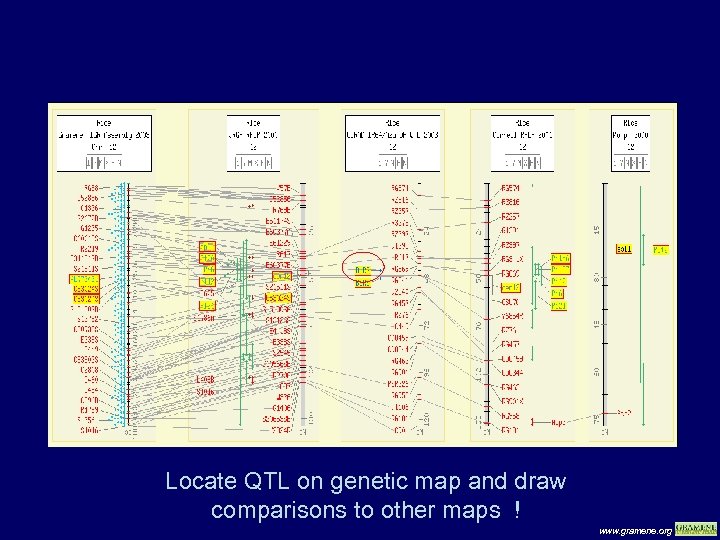 Locate QTL on genetic map and draw comparisons to other maps ! www. gramene. org
Locate QTL on genetic map and draw comparisons to other maps ! www. gramene. org
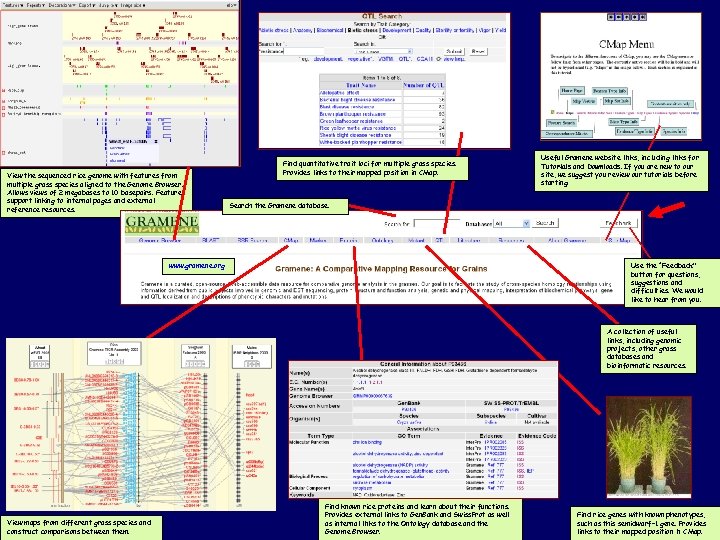 View the sequenced rice genome with features from multiple grass species aligned to the Genome Browser. Allows views of 2 megabases to 10 basepairs. Features support linking to internal pages and external reference resources. Find quantitative trait loci for multiple grass species. Provides links to their mapped position in CMap. Useful Gramene website links, including links for Tutorials and Downloads. If you are new to our site, we suggest you review our tutorials before starting. Search the Gramene database. Use the “Feedback” button for questions, suggestions and difficulties. We would like to hear from you. www. gramene. org A collection of useful links, including genomic projects, other grass databases and bioinformatic resources. View maps from different grass species and construct comparisons between them. Find known rice proteins and learn about their functions. Provides external links to Gen. Bank and Swiss. Prot as well as internal links to the Ontology database and the Genome Browser. Find rice genes with known phenotypes, such as this semidwarf-1 gene. Provides www. gramene. org links to their mapped position in CMap.
View the sequenced rice genome with features from multiple grass species aligned to the Genome Browser. Allows views of 2 megabases to 10 basepairs. Features support linking to internal pages and external reference resources. Find quantitative trait loci for multiple grass species. Provides links to their mapped position in CMap. Useful Gramene website links, including links for Tutorials and Downloads. If you are new to our site, we suggest you review our tutorials before starting. Search the Gramene database. Use the “Feedback” button for questions, suggestions and difficulties. We would like to hear from you. www. gramene. org A collection of useful links, including genomic projects, other grass databases and bioinformatic resources. View maps from different grass species and construct comparisons between them. Find known rice proteins and learn about their functions. Provides external links to Gen. Bank and Swiss. Prot as well as internal links to the Ontology database and the Genome Browser. Find rice genes with known phenotypes, such as this semidwarf-1 gene. Provides www. gramene. org links to their mapped position in CMap.
 Site Map, Help Guides and tutorials www. gramene. org
Site Map, Help Guides and tutorials www. gramene. org
 Future plans • Training and community outreach • Provide information from other grasses on – – – Maps and markers Phenotypes (mutant + QTL) Genes and proteins Maize genome sequences Germplasm / genetic stocks • Tools to study diversity in the grasses • Raw datasets from genotype and phenotypes studies www. gramene. org
Future plans • Training and community outreach • Provide information from other grasses on – – – Maps and markers Phenotypes (mutant + QTL) Genes and proteins Maize genome sequences Germplasm / genetic stocks • Tools to study diversity in the grasses • Raw datasets from genotype and phenotypes studies www. gramene. org
 Gramene and you: a partnership • Involve high school and college teachers to help generate interest in Biology (Dolan center-CSHL) • Invite YOU (the authors) to curate your own dataset • Your suggestions and feedback – – Do you think we should organize an advanced level workshop ? Suggestions on Gramene workshops in your institution ? What new features would you like us to provide ? Let us know how would you like to use the genomic and genetic information for your project. – Any other way we can help you ? www. gramene. org
Gramene and you: a partnership • Involve high school and college teachers to help generate interest in Biology (Dolan center-CSHL) • Invite YOU (the authors) to curate your own dataset • Your suggestions and feedback – – Do you think we should organize an advanced level workshop ? Suggestions on Gramene workshops in your institution ? What new features would you like us to provide ? Let us know how would you like to use the genomic and genetic information for your project. – Any other way we can help you ? www. gramene. org


