230f4d4b16d908b46df1546dbfc3a957.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 46
 A Collapsed Giant Dr. Jacky Sia RHAED
A Collapsed Giant Dr. Jacky Sia RHAED
 TSKAED 1998 n n n No computer system No Toxicology database No CMS No internet No urinary test.
TSKAED 1998 n n n No computer system No Toxicology database No CMS No internet No urinary test.
 Case summary n n 39 -year Caucasian. 240 lbs giant. Well along Collapsed and convulsion in gym.
Case summary n n 39 -year Caucasian. 240 lbs giant. Well along Collapsed and convulsion in gym.
 DDx of collapse
DDx of collapse
 Reading!
Reading!
 Possible supplement n n n EFA: ephedrine, caffeine, aspirin. EFT: Ephedrine, Foskolin, Theophylline. Creatine. Steroids: oral, injectable. Herbal extract. Thyroid extract. Many more….
Possible supplement n n n EFA: ephedrine, caffeine, aspirin. EFT: Ephedrine, Foskolin, Theophylline. Creatine. Steroids: oral, injectable. Herbal extract. Thyroid extract. Many more….
 Drugs before gym
Drugs before gym
 History n another 260 -lbs giant.
History n another 260 -lbs giant.
 Case summary n n n BP 138/86, P 76/min. Temp: 36. 8 C GCS: 12/15 PERL: 3 mm Intermittent twitching of limbs Blood sugar: 6. 9 mmol. Systemic review were normal.
Case summary n n n BP 138/86, P 76/min. Temp: 36. 8 C GCS: 12/15 PERL: 3 mm Intermittent twitching of limbs Blood sugar: 6. 9 mmol. Systemic review were normal.
 Case summary n n n ECG was normal. No urinary for toxicology kit (1998) Valium 5 mg IVI. To RH medical ward. CBP, R/LFT, Toxicology screen, CT brain: normal.
Case summary n n n ECG was normal. No urinary for toxicology kit (1998) Valium 5 mg IVI. To RH medical ward. CBP, R/LFT, Toxicology screen, CT brain: normal.
 Case summary n n Rapid recovery 2 hours later. DAMA despite twitching of limbs and drooling of saliva. Dx: GHB (History) Reason for collapse: alcohol + GHB.
Case summary n n Rapid recovery 2 hours later. DAMA despite twitching of limbs and drooling of saliva. Dx: GHB (History) Reason for collapse: alcohol + GHB.
 GHB poisoning
GHB poisoning
 Media interview
Media interview

 Male - not exemption
Male - not exemption
 Layman Diagnostic kit
Layman Diagnostic kit
 Layman Diagnostic kit
Layman Diagnostic kit
 History n n n 1980 s: over-the-counter in health stores. Abused as recreational drugs. 1991: ? Political reason. Banned for its excellent GA property.
History n n n 1980 s: over-the-counter in health stores. Abused as recreational drugs. 1991: ? Political reason. Banned for its excellent GA property.
 GHB - naturally found n n n Hypothalamus Basal ganglia Kidney Heart Skeletal Brown fat tissue.
GHB - naturally found n n n Hypothalamus Basal ganglia Kidney Heart Skeletal Brown fat tissue.
 Physiology n n n 16 times increase in GH. Inhibit the protein breakdown. Facilitate fat loss. Induce hypotonia. Enhance sexual arousal.
Physiology n n n 16 times increase in GH. Inhibit the protein breakdown. Facilitate fat loss. Induce hypotonia. Enhance sexual arousal.
 Physiology n n n Colorless, odorless, tasteless. Excellent sedation, amnesia. “Date-rape” drug: rapid incapacitation. No toxic metabolites, only CO 2, H 2 O. Normalized after 2 - 5 hours.
Physiology n n n Colorless, odorless, tasteless. Excellent sedation, amnesia. “Date-rape” drug: rapid incapacitation. No toxic metabolites, only CO 2, H 2 O. Normalized after 2 - 5 hours.
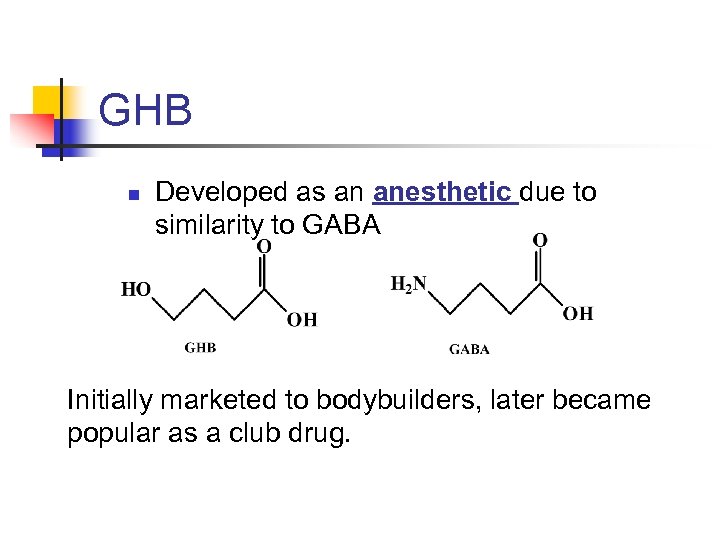 GHB n Developed as an anesthetic due to similarity to GABA Initially marketed to bodybuilders, later became popular as a club drug.
GHB n Developed as an anesthetic due to similarity to GABA Initially marketed to bodybuilders, later became popular as a club drug.
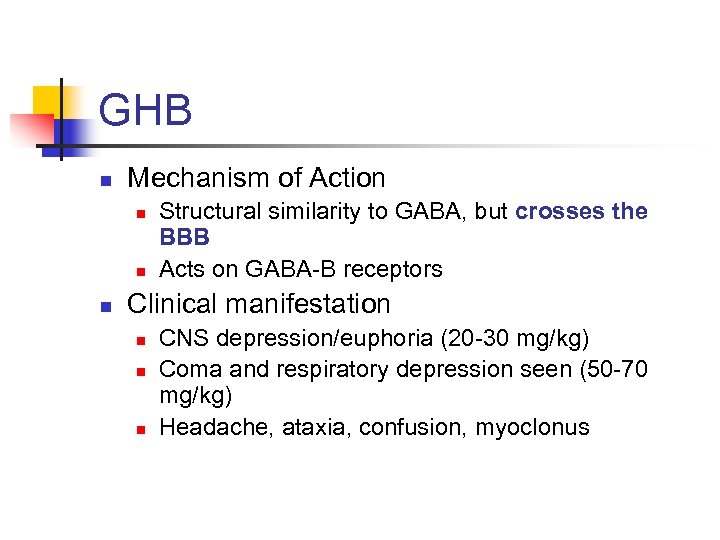 GHB n Mechanism of Action n Structural similarity to GABA, but crosses the BBB Acts on GABA-B receptors Clinical manifestation n CNS depression/euphoria (20 -30 mg/kg) Coma and respiratory depression seen (50 -70 mg/kg) Headache, ataxia, confusion, myoclonus
GHB n Mechanism of Action n Structural similarity to GABA, but crosses the BBB Acts on GABA-B receptors Clinical manifestation n CNS depression/euphoria (20 -30 mg/kg) Coma and respiratory depression seen (50 -70 mg/kg) Headache, ataxia, confusion, myoclonus
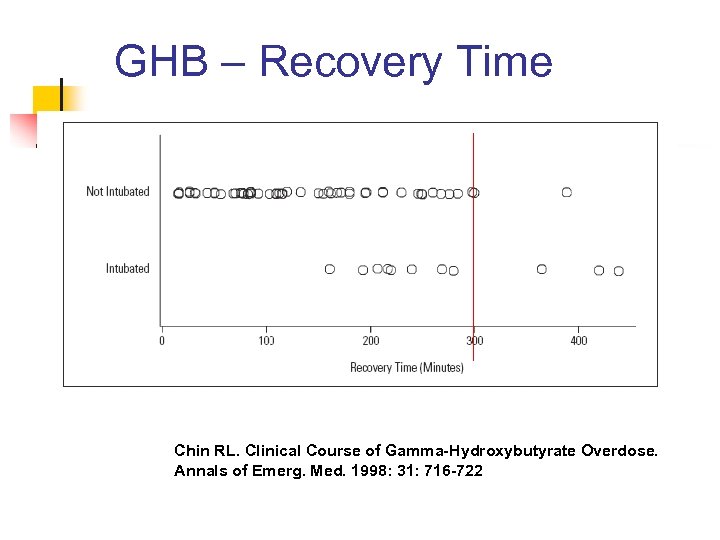 GHB – Recovery Time Chin RL. Clinical Course of Gamma-Hydroxybutyrate Overdose. Annals of Emerg. Med. 1998: 31: 716 -722
GHB – Recovery Time Chin RL. Clinical Course of Gamma-Hydroxybutyrate Overdose. Annals of Emerg. Med. 1998: 31: 716 -722
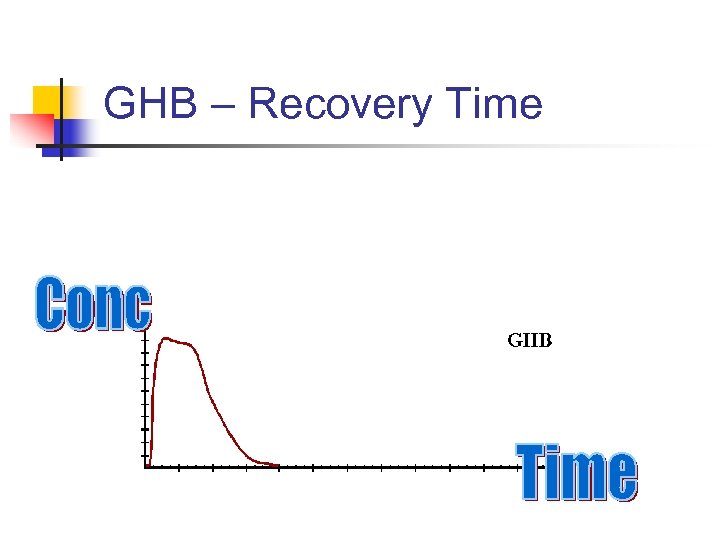 GHB – Recovery Time
GHB – Recovery Time
 Elimination of GHB n n n GHB exhibits zero-order kinetics - it has no half-life. Time required to eliminate half a given dose increases as the dose increases. Everyone excretes GHB - it is a normal urinary metabolite. Concentrations < 10 ug/m. L may be considered normal.
Elimination of GHB n n n GHB exhibits zero-order kinetics - it has no half-life. Time required to eliminate half a given dose increases as the dose increases. Everyone excretes GHB - it is a normal urinary metabolite. Concentrations < 10 ug/m. L may be considered normal.
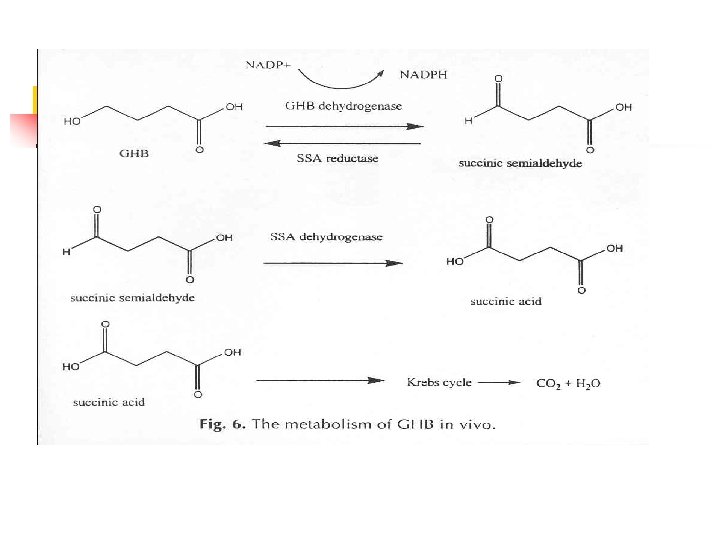
 Back to basic n n n House brewed in US. Different potencies, purities. Different side effects. Toxic effect unpredictable. 30 mg/kg to 60 mg/kg.
Back to basic n n n House brewed in US. Different potencies, purities. Different side effects. Toxic effect unpredictable. 30 mg/kg to 60 mg/kg.
 Therapeutic Value n n Sleeping disorder Narcolepsy Alcohol withdrawal Depression
Therapeutic Value n n Sleeping disorder Narcolepsy Alcohol withdrawal Depression
 Case series By Okun, Michael S; Doering, Paul L; Bartfield, Richard B (Emedicine abstract) 2000 Emergency Medicine. via Bell&Howell Information and Learning Company
Case series By Okun, Michael S; Doering, Paul L; Bartfield, Richard B (Emedicine abstract) 2000 Emergency Medicine. via Bell&Howell Information and Learning Company
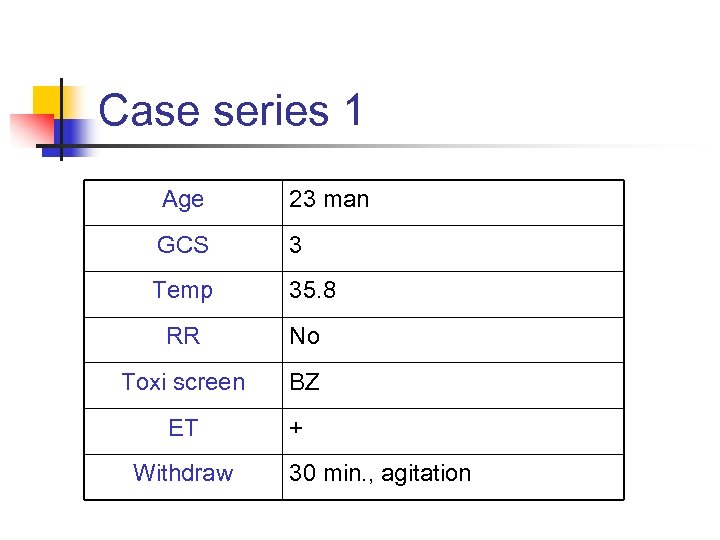 Case series 1 Age 23 man GCS 3 Temp 35. 8 RR No Toxi screen BZ ET Withdraw + 30 min. , agitation
Case series 1 Age 23 man GCS 3 Temp 35. 8 RR No Toxi screen BZ ET Withdraw + 30 min. , agitation
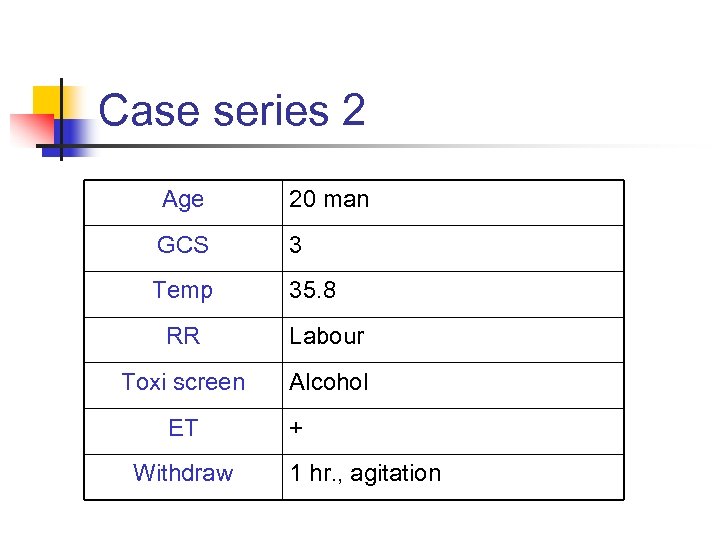 Case series 2 Age 20 man GCS 3 Temp 35. 8 RR Labour Toxi screen Alcohol ET Withdraw + 1 hr. , agitation
Case series 2 Age 20 man GCS 3 Temp 35. 8 RR Labour Toxi screen Alcohol ET Withdraw + 1 hr. , agitation
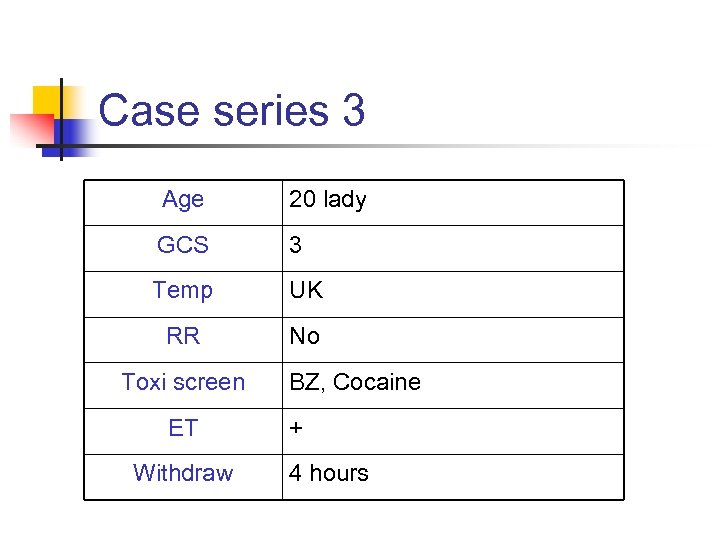 Case series 3 Age 20 lady GCS 3 Temp UK RR No Toxi screen ET Withdraw BZ, Cocaine + 4 hours
Case series 3 Age 20 lady GCS 3 Temp UK RR No Toxi screen ET Withdraw BZ, Cocaine + 4 hours
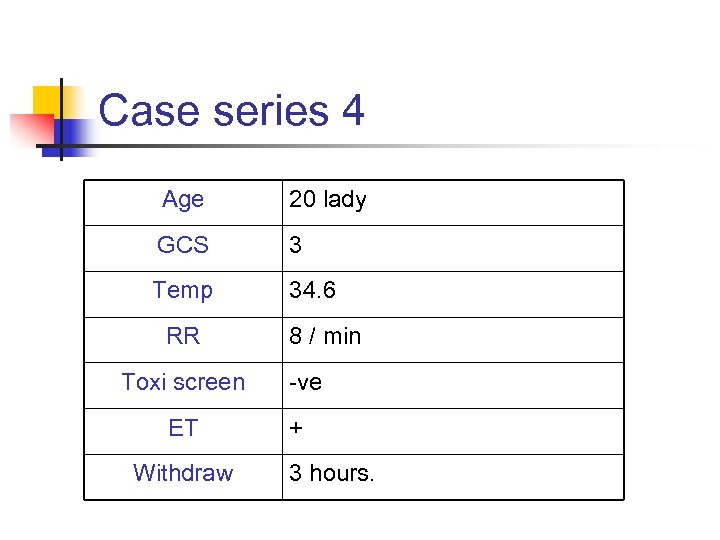 Case series 4 Age 20 lady GCS 3 Temp 34. 6 RR Toxi screen ET Withdraw 8 / min -ve + 3 hours.
Case series 4 Age 20 lady GCS 3 Temp 34. 6 RR Toxi screen ET Withdraw 8 / min -ve + 3 hours.
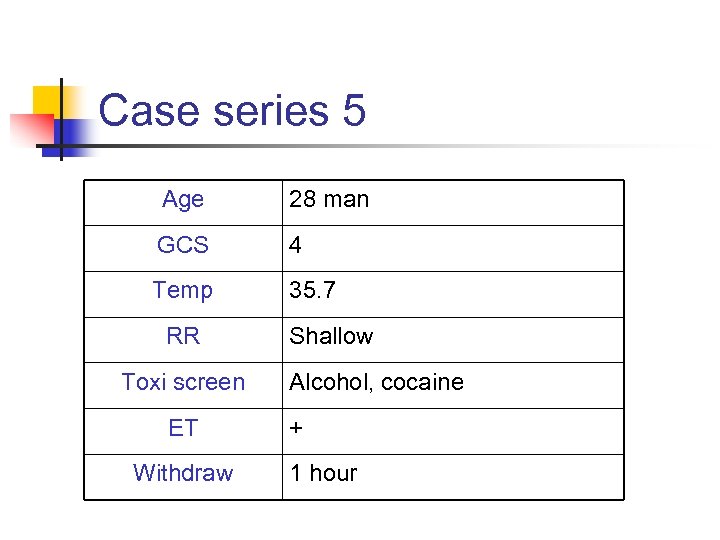 Case series 5 Age 28 man GCS 4 Temp 35. 7 RR Toxi screen ET Withdraw Shallow Alcohol, cocaine + 1 hour
Case series 5 Age 28 man GCS 4 Temp 35. 7 RR Toxi screen ET Withdraw Shallow Alcohol, cocaine + 1 hour
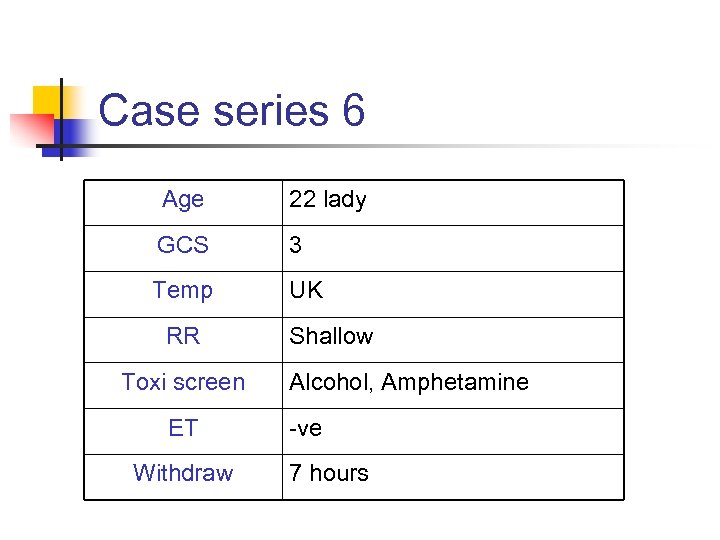 Case series 6 Age 22 lady GCS 3 Temp UK RR Toxi screen ET Withdraw Shallow Alcohol, Amphetamine -ve 7 hours
Case series 6 Age 22 lady GCS 3 Temp UK RR Toxi screen ET Withdraw Shallow Alcohol, Amphetamine -ve 7 hours
 Retrospective - Chin RL n n n Ref 14 1993 to 1996 69% male with mean age 28 years. Co-ingestion (alcohol, club drugs) Deep coma. Hypothermia. Bradycardia to AF; Hypotension. Respiratory acidosis.
Retrospective - Chin RL n n n Ref 14 1993 to 1996 69% male with mean age 28 years. Co-ingestion (alcohol, club drugs) Deep coma. Hypothermia. Bradycardia to AF; Hypotension. Respiratory acidosis.
 Retrospective - Chin RL n n Ref 14 Must rule out AEIOU TIPS. Conservative approach if history is reliable. One study: 17/25 patients (GCS 3) NOT intubated. Emergence feature: myoclonic jerking, confusion and combativeness.
Retrospective - Chin RL n n Ref 14 Must rule out AEIOU TIPS. Conservative approach if history is reliable. One study: 17/25 patients (GCS 3) NOT intubated. Emergence feature: myoclonic jerking, confusion and combativeness.
 ? Toxidrome
? Toxidrome
 National laboratories n n n Lab tests not readily available. LOC: serum level 50 mg/d. L. Coma: serum level 260 mg/d. L.
National laboratories n n n Lab tests not readily available. LOC: serum level 50 mg/d. L. Coma: serum level 260 mg/d. L.
 Drugs Combinations!
Drugs Combinations!
 Lessons
Lessons
 Lessons n n n Wanchai: > 3 cases (1 M, 2 F) GHB: unreported? History, clinical signs & suspicion. Intubate or not ? Supportive treatment. Further research: test kit.
Lessons n n n Wanchai: > 3 cases (1 M, 2 F) GHB: unreported? History, clinical signs & suspicion. Intubate or not ? Supportive treatment. Further research: test kit.

 References n n n n n Gal l imber ti L, Canton G, Gent i le N, e t al. Gamma hydroxybutyric acid for treatment of alcohol withdrawal syndrome. Lancet 1989; 2 (8666): 787 -9. 2. Chin MY, Krentzer RA, Dyer JE. Acute poisoning from gamma hydroxybutyrate in California. West J Med 992; 156(4): 380 -4. 3. Hodges B, Everett J. Acute toxicity from homebrewed gamma hydroxybutyrate. J Am Board Fam Pract 1998; 11(2): 154 -7. 4. John Mor g entha l e r and Dan Joy. Gamma - hydroxybutyrate. Smart drug news. September 10 th, 1994 [v 3 n 6]. 5. Ta kaha r a J, Yunok i S, Ya kushi j i W, e t a l. Stimulatory effects of gamma-hydroxybutyric acid on growth hormone and prolactin release in humans. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 1977; 44(5): 1014 -7. 6. Laborit H. Sodium 4 -hydroxybutyrate. Int J Neuropharmacol 1964; 3: 433 -52. 7. Laborit H. Cor relations between protein and serotonin synthesis during various activities of the central nervous system. Res Commun Chem Pathol Pharmacol 1972; 3(1): 51 -81.
References n n n n n Gal l imber ti L, Canton G, Gent i le N, e t al. Gamma hydroxybutyric acid for treatment of alcohol withdrawal syndrome. Lancet 1989; 2 (8666): 787 -9. 2. Chin MY, Krentzer RA, Dyer JE. Acute poisoning from gamma hydroxybutyrate in California. West J Med 992; 156(4): 380 -4. 3. Hodges B, Everett J. Acute toxicity from homebrewed gamma hydroxybutyrate. J Am Board Fam Pract 1998; 11(2): 154 -7. 4. John Mor g entha l e r and Dan Joy. Gamma - hydroxybutyrate. Smart drug news. September 10 th, 1994 [v 3 n 6]. 5. Ta kaha r a J, Yunok i S, Ya kushi j i W, e t a l. Stimulatory effects of gamma-hydroxybutyric acid on growth hormone and prolactin release in humans. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 1977; 44(5): 1014 -7. 6. Laborit H. Sodium 4 -hydroxybutyrate. Int J Neuropharmacol 1964; 3: 433 -52. 7. Laborit H. Cor relations between protein and serotonin synthesis during various activities of the central nervous system. Res Commun Chem Pathol Pharmacol 1972; 3(1): 51 -81.
 References n n n n 8. Vickers MD. Gamma-hydroxybutyric acid. Int Anesthesiol Clin 1969; 7(1): 75 -89. 9. Chin RL, Sporer KA, Cullison B, et al. Clinical course of gamma-hydroxybutyrate overdose. Ann Emerg Med 1998; 31(6): 716 -22. 10. Fadda F, Colombo G, Mosca E, et al. Suppression by g amma -hydroxybuty r i c a c id of e thanol withdrawal syndrome in rats. Alcohol 1989; 24(5): 447 -51. 11. Leikin JB, Paloucek FP. Poisoning & Toxicology Handbook, 2 nd ed. Hudson, Ohio, Lexi-Comp Inc. , 1995. 12. Baselt RC, Cravey RH. Disposition of Toxic drugs and Chemicals in Man, 4 th ed. Foster City, CA, CTI, 1995. 13. Ejjenhorn MJ, Schonwald S, Ordog G, et al. Drug of Abuse. In Ejjenhorn MJ(ed): Ejjenhorn's Medical Toxicology: Diagnosis and Treatment of Human Poisoning, 2 nd ed. Baltimore, Williams and Wilkins, 1997. 14. Chin RL, Sporer KA, Cullison B, Dyer JE, Wu TD: Clinical course of GHB overdose. Ann Emerg Med June 1998; 31: 716 -722. 15. David GEC, Fiona YC, Brian JB, Peter DF, Roger WB. Fatalities associated with theuse of GHB and its analogue in Australasia. MJA 2004; 181(6): 310 -313.
References n n n n 8. Vickers MD. Gamma-hydroxybutyric acid. Int Anesthesiol Clin 1969; 7(1): 75 -89. 9. Chin RL, Sporer KA, Cullison B, et al. Clinical course of gamma-hydroxybutyrate overdose. Ann Emerg Med 1998; 31(6): 716 -22. 10. Fadda F, Colombo G, Mosca E, et al. Suppression by g amma -hydroxybuty r i c a c id of e thanol withdrawal syndrome in rats. Alcohol 1989; 24(5): 447 -51. 11. Leikin JB, Paloucek FP. Poisoning & Toxicology Handbook, 2 nd ed. Hudson, Ohio, Lexi-Comp Inc. , 1995. 12. Baselt RC, Cravey RH. Disposition of Toxic drugs and Chemicals in Man, 4 th ed. Foster City, CA, CTI, 1995. 13. Ejjenhorn MJ, Schonwald S, Ordog G, et al. Drug of Abuse. In Ejjenhorn MJ(ed): Ejjenhorn's Medical Toxicology: Diagnosis and Treatment of Human Poisoning, 2 nd ed. Baltimore, Williams and Wilkins, 1997. 14. Chin RL, Sporer KA, Cullison B, Dyer JE, Wu TD: Clinical course of GHB overdose. Ann Emerg Med June 1998; 31: 716 -722. 15. David GEC, Fiona YC, Brian JB, Peter DF, Roger WB. Fatalities associated with theuse of GHB and its analogue in Australasia. MJA 2004; 181(6): 310 -313.


