9940b0eeac58e1c80e1427708a031652.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 26
 A Cloud-Resolving Aqua Planet Experiment Frontier Research Center for Global Change Hirofumi TOMITA Masaki SATOH Tomoe NASUNO Shi-ichi IGA Hiroaki MIURA
A Cloud-Resolving Aqua Planet Experiment Frontier Research Center for Global Change Hirofumi TOMITA Masaki SATOH Tomoe NASUNO Shi-ichi IGA Hiroaki MIURA
 Contents n Brief introduction of our model n Global cloud resolving model • To avoid the ambiguity of cumulus parameterization n New framework for AGCM • • Icosahedral grid non-hydrostatic dynamics n Aqua Planet Experiment --- control run n Method of expermental setup for high-resolution GCRM • • Spin-up Model setup n Results • • Tropical variability Resolution dependency n Summary
Contents n Brief introduction of our model n Global cloud resolving model • To avoid the ambiguity of cumulus parameterization n New framework for AGCM • • Icosahedral grid non-hydrostatic dynamics n Aqua Planet Experiment --- control run n Method of expermental setup for high-resolution GCRM • • Spin-up Model setup n Results • • Tropical variability Resolution dependency n Summary
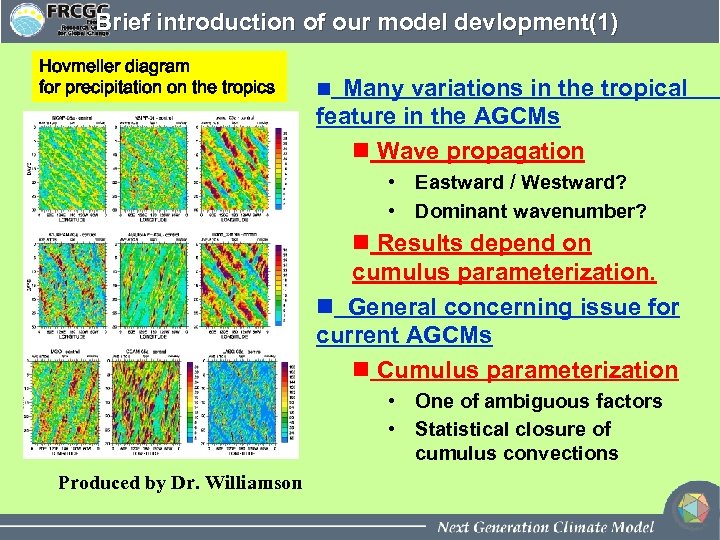 Brief introduction of our model devlopment(1) Hovmeller diagram for precipitation on the tropics n Many variations in the tropical feature in the AGCMs n Wave propagation • Eastward / Westward? • Dominant wavenumber? n Results depend on cumulus parameterization. n General concerning issue for current AGCMs n Cumulus parameterization • One of ambiguous factors • Statistical closure of cumulus convections Produced by Dr. Williamson
Brief introduction of our model devlopment(1) Hovmeller diagram for precipitation on the tropics n Many variations in the tropical feature in the AGCMs n Wave propagation • Eastward / Westward? • Dominant wavenumber? n Results depend on cumulus parameterization. n General concerning issue for current AGCMs n Cumulus parameterization • One of ambiguous factors • Statistical closure of cumulus convections Produced by Dr. Williamson
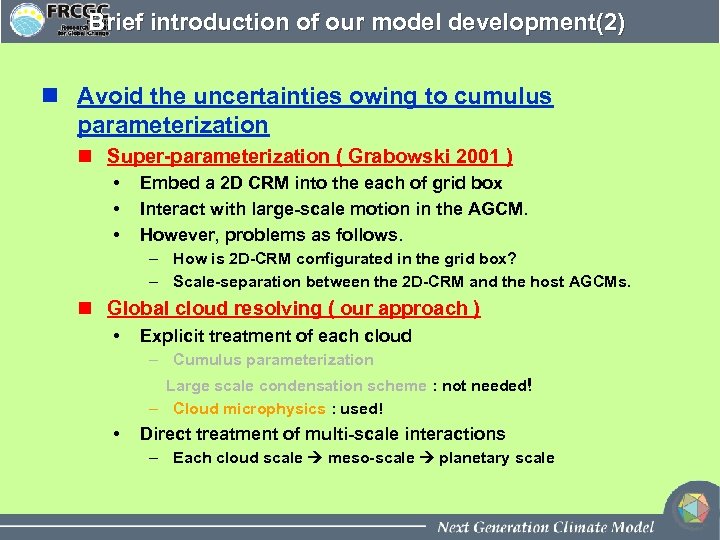 Brief introduction of our model development(2) n Avoid the uncertainties owing to cumulus parameterization n Super-parameterization ( Grabowski 2001 ) • • • Embed a 2 D CRM into the each of grid box Interact with large-scale motion in the AGCM. However, problems as follows. – How is 2 D-CRM configurated in the grid box? – Scale-separation between the 2 D-CRM and the host AGCMs. n Global cloud resolving ( our approach ) • Explicit treatment of each cloud – Cumulus parameterization Large scale condensation scheme : not needed! – Cloud microphysics : used! • Direct treatment of multi-scale interactions – Each cloud scale meso-scale planetary scale
Brief introduction of our model development(2) n Avoid the uncertainties owing to cumulus parameterization n Super-parameterization ( Grabowski 2001 ) • • • Embed a 2 D CRM into the each of grid box Interact with large-scale motion in the AGCM. However, problems as follows. – How is 2 D-CRM configurated in the grid box? – Scale-separation between the 2 D-CRM and the host AGCMs. n Global cloud resolving ( our approach ) • Explicit treatment of each cloud – Cumulus parameterization Large scale condensation scheme : not needed! – Cloud microphysics : used! • Direct treatment of multi-scale interactions – Each cloud scale meso-scale planetary scale
 Brief introduction of our model development (3) n Target resolutions n 5 km or less in the horizontal direction n Several 100 m in the vertical n Strategy of dycore development n Quasi-uniform grid • Spectral method : not efficient in high resolution simulations. – – • Latitude-longitude grid : the pole problem. – • Legendre transformation Massive data transfer between computer nodes Severe limitation of time interval by the CFL condition. The icosahedral grid: homogeneous grid over the sphere – To avoid the pole problem. n Non-hydrostatic equations system • Very high resolution in horizontal direction.
Brief introduction of our model development (3) n Target resolutions n 5 km or less in the horizontal direction n Several 100 m in the vertical n Strategy of dycore development n Quasi-uniform grid • Spectral method : not efficient in high resolution simulations. – – • Latitude-longitude grid : the pole problem. – • Legendre transformation Massive data transfer between computer nodes Severe limitation of time interval by the CFL condition. The icosahedral grid: homogeneous grid over the sphere – To avoid the pole problem. n Non-hydrostatic equations system • Very high resolution in horizontal direction.
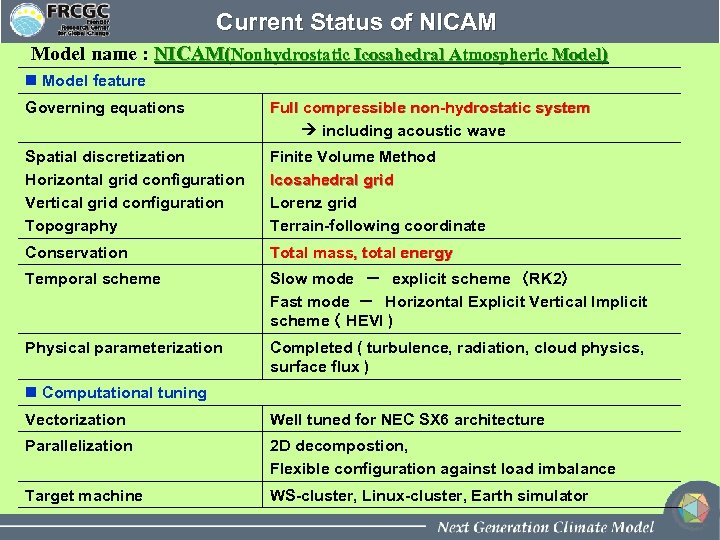 Current Status of NICAM Model name : NICAM(Nonhydrostatic Icosahedral Atmospheric Model) n Model feature Governing equations Full compressible non-hydrostatic system including acoustic wave Spatial discretization Horizontal grid configuration Vertical grid configuration Topography Finite Volume Method Icosahedral grid Lorenz grid Terrain-following coordinate Conservation Total mass, total energy Temporal scheme Slow mode - explicit scheme (RK 2) Fast mode - Horizontal Explicit Vertical Implicit scheme ( HEVI ) Physical parameterization Completed ( turbulence, radiation, cloud physics, surface flux ) n Computational tuning Vectorization Well tuned for NEC SX 6 architecture Parallelization 2 D decompostion, Flexible configuration against load imbalance Target machine WS-cluster, Linux-cluster, Earth simulator
Current Status of NICAM Model name : NICAM(Nonhydrostatic Icosahedral Atmospheric Model) n Model feature Governing equations Full compressible non-hydrostatic system including acoustic wave Spatial discretization Horizontal grid configuration Vertical grid configuration Topography Finite Volume Method Icosahedral grid Lorenz grid Terrain-following coordinate Conservation Total mass, total energy Temporal scheme Slow mode - explicit scheme (RK 2) Fast mode - Horizontal Explicit Vertical Implicit scheme ( HEVI ) Physical parameterization Completed ( turbulence, radiation, cloud physics, surface flux ) n Computational tuning Vectorization Well tuned for NEC SX 6 architecture Parallelization 2 D decompostion, Flexible configuration against load imbalance Target machine WS-cluster, Linux-cluster, Earth simulator
 Method (1) n Experimental setup n follow the CONTROL RUN of Neal & Hoskins(2000) • SST distribution / ozone distribution n Difficult to perform the 3. 5 years by GCRM. • • Owing to computational limitation Several months integration starting an appropriate climatology n Spin up n Initial condition • • • 3. 5 year integration by CCSR/NIES/FRCGC AGCM ver. 5. 7 with T 42 L 59. 3 years climatology as an initial condition. Interpolate to NICAM gridpoints.
Method (1) n Experimental setup n follow the CONTROL RUN of Neal & Hoskins(2000) • SST distribution / ozone distribution n Difficult to perform the 3. 5 years by GCRM. • • Owing to computational limitation Several months integration starting an appropriate climatology n Spin up n Initial condition • • • 3. 5 year integration by CCSR/NIES/FRCGC AGCM ver. 5. 7 with T 42 L 59. 3 years climatology as an initial condition. Interpolate to NICAM gridpoints.
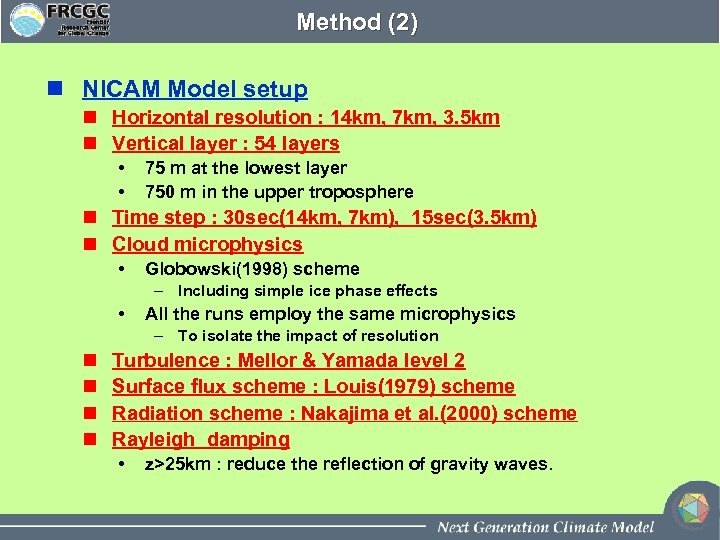 Method (2) n NICAM Model setup n Horizontal resolution : 14 km, 7 km, 3. 5 km n Vertical layer : 54 layers • • 75 m at the lowest layer 750 m in the upper troposphere n Time step : 30 sec(14 km, 7 km), 15 sec(3. 5 km) n Cloud microphysics • Globowski(1998) scheme – Including simple ice phase effects • All the runs employ the same microphysics – To isolate the impact of resolution n n Turbulence : Mellor & Yamada level 2 Surface flux scheme : Louis(1979) scheme Radiation scheme : Nakajima et al. (2000) scheme Rayleigh damping • z>25 km : reduce the reflection of gravity waves.
Method (2) n NICAM Model setup n Horizontal resolution : 14 km, 7 km, 3. 5 km n Vertical layer : 54 layers • • 75 m at the lowest layer 750 m in the upper troposphere n Time step : 30 sec(14 km, 7 km), 15 sec(3. 5 km) n Cloud microphysics • Globowski(1998) scheme – Including simple ice phase effects • All the runs employ the same microphysics – To isolate the impact of resolution n n Turbulence : Mellor & Yamada level 2 Surface flux scheme : Louis(1979) scheme Radiation scheme : Nakajima et al. (2000) scheme Rayleigh damping • z>25 km : reduce the reflection of gravity waves.
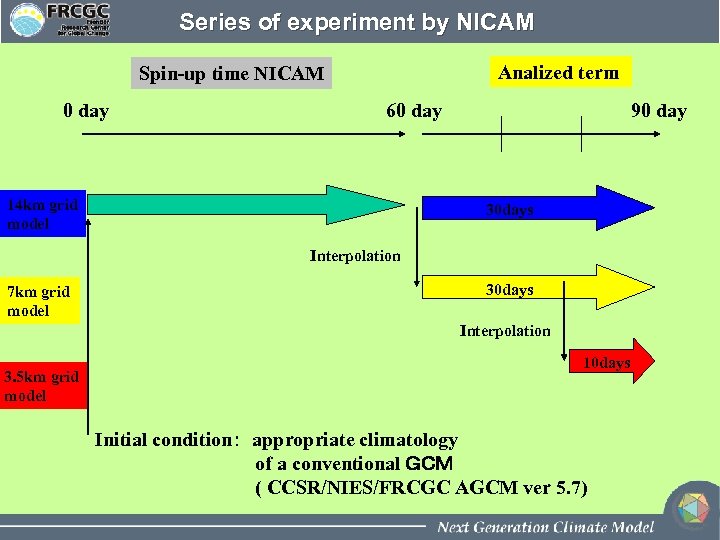 Series of experiment by NICAM Analized term Spin-up time NICAM 0 day 60 day 14 km grid model 90 day 30 days Interpolation 7 km grid model 30 days Interpolation 3. 5 km grid model 10 days Initial condition: appropriate climatology of a conventional GCM ( CCSR/NIES/FRCGC AGCM ver 5. 7)
Series of experiment by NICAM Analized term Spin-up time NICAM 0 day 60 day 14 km grid model 90 day 30 days Interpolation 7 km grid model 30 days Interpolation 3. 5 km grid model 10 days Initial condition: appropriate climatology of a conventional GCM ( CCSR/NIES/FRCGC AGCM ver 5. 7)
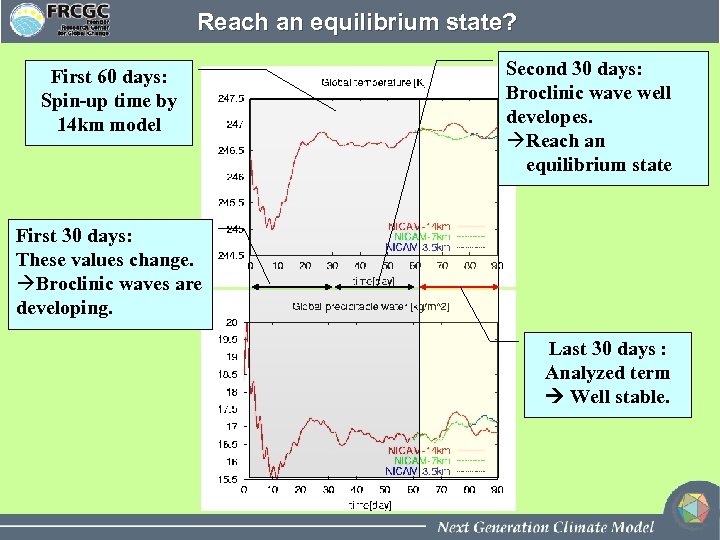 Reach an equilibrium state? First 60 days: Spin-up time by 14 km model Second 30 days: Broclinic wave well developes. àReach an equilibrium state First 30 days: These values change. àBroclinic waves are developing. Last 30 days : Analyzed term Well stable.
Reach an equilibrium state? First 60 days: Spin-up time by 14 km model Second 30 days: Broclinic wave well developes. àReach an equilibrium state First 30 days: These values change. àBroclinic waves are developing. Last 30 days : Analyzed term Well stable.
![OLR(1 S-1 S平均) Precipitation rate [mm/day] at day 85 : log-scale by NICAM-3. 5 OLR(1 S-1 S平均) Precipitation rate [mm/day] at day 85 : log-scale by NICAM-3. 5](https://present5.com/presentation/9940b0eeac58e1c80e1427708a031652/image-11.jpg) OLR(1 S-1 S平均) Precipitation rate [mm/day] at day 85 : log-scale by NICAM-3. 5 km model Super cloud cluster Mid-latitude cyclone
OLR(1 S-1 S平均) Precipitation rate [mm/day] at day 85 : log-scale by NICAM-3. 5 km model Super cloud cluster Mid-latitude cyclone
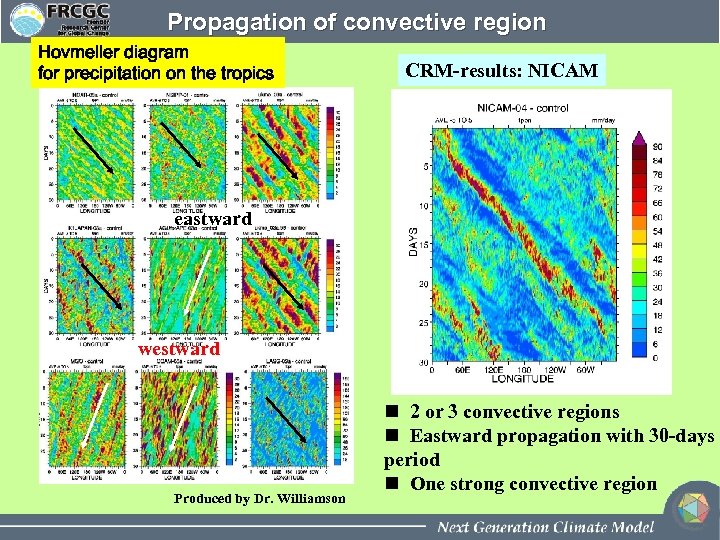 Propagation of convective region Hovmeller diagram for precipitation on the tropics CRM-results: NICAM eastward westward Produced by Dr. Williamson n 2 or 3 convective regions n Eastward propagation with 30 -days period n One strong convective region
Propagation of convective region Hovmeller diagram for precipitation on the tropics CRM-results: NICAM eastward westward Produced by Dr. Williamson n 2 or 3 convective regions n Eastward propagation with 30 -days period n One strong convective region
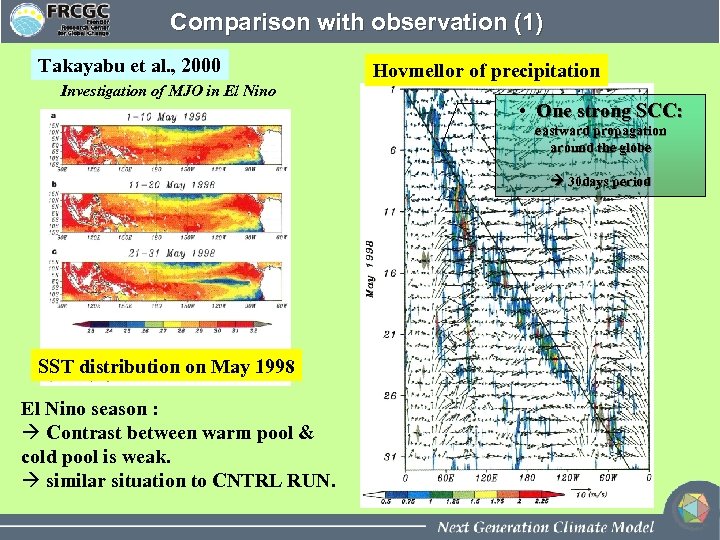 Comparison with observation (1) Takayabu et al. , 2000 Investigation of MJO in El Nino Hovmellor of precipitation • One strong SCC: eastward propagation around the globe 30 days period SST distribution on May 1998 El Nino season : à Contrast between warm pool & cold pool is weak. à similar situation to CNTRL RUN.
Comparison with observation (1) Takayabu et al. , 2000 Investigation of MJO in El Nino Hovmellor of precipitation • One strong SCC: eastward propagation around the globe 30 days period SST distribution on May 1998 El Nino season : à Contrast between warm pool & cold pool is weak. à similar situation to CNTRL RUN.
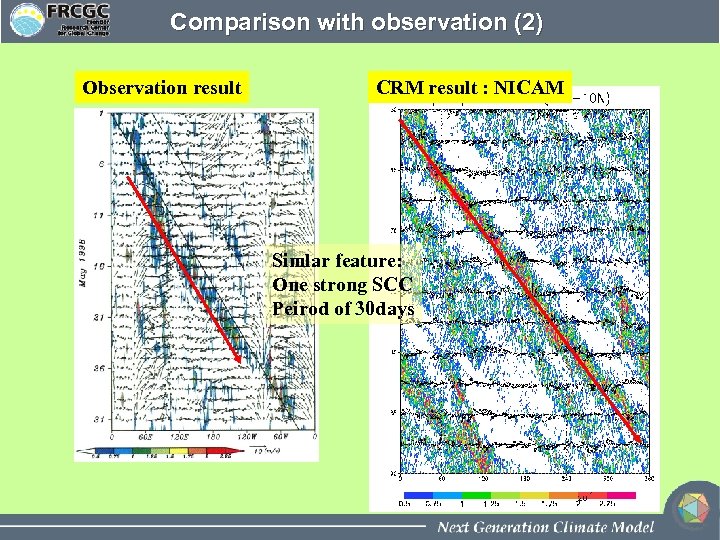 Comparison with observation (2) Observation result CRM result : NICAM Simlar feature: One strong SCC Peirod of 30 days
Comparison with observation (2) Observation result CRM result : NICAM Simlar feature: One strong SCC Peirod of 30 days
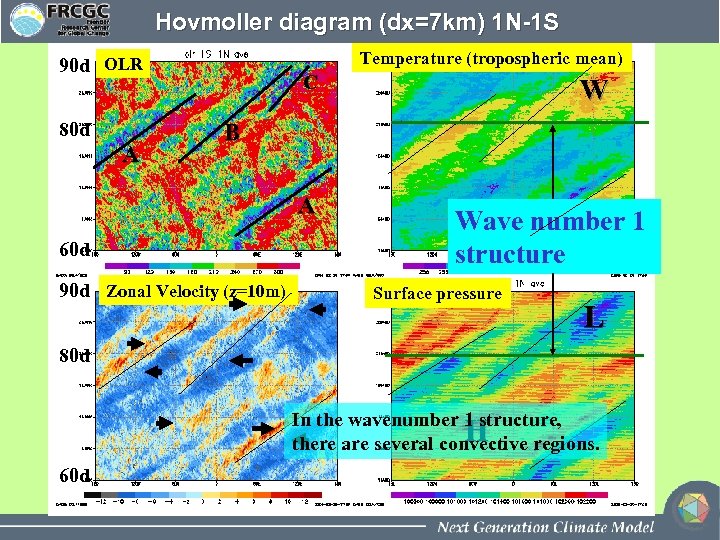 Hovmoller diagram (dx=7 km) 1 N-1 S Temperature (tropospheric mean) 90 d OLR 80 d A C W B A 60 d 90 d Zonal Velocity (z=10 m) C Wave number 1 structure Surface pressure L 80 d In the wavenumber 1 structure, there are several convective regions. H 60 d
Hovmoller diagram (dx=7 km) 1 N-1 S Temperature (tropospheric mean) 90 d OLR 80 d A C W B A 60 d 90 d Zonal Velocity (z=10 m) C Wave number 1 structure Surface pressure L 80 d In the wavenumber 1 structure, there are several convective regions. H 60 d
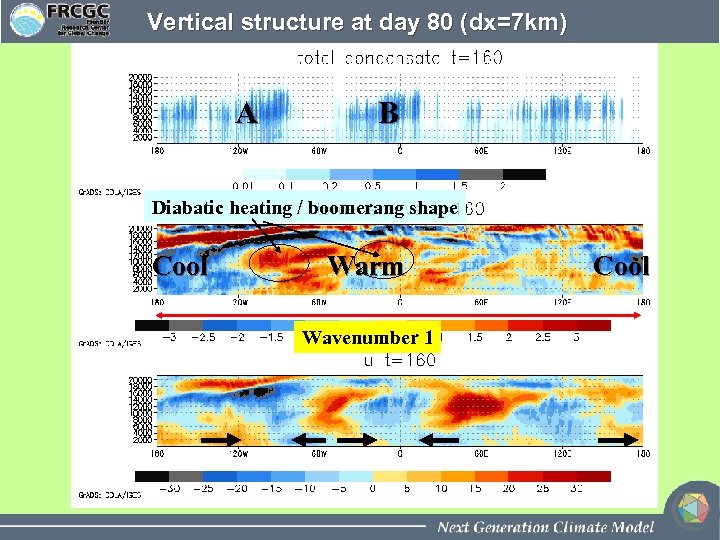 Vertical structure at day 80 (dx=7 km) A B Diabatic heating / boomerang shape Cool Warm Wavenumber 1 Cool
Vertical structure at day 80 (dx=7 km) A B Diabatic heating / boomerang shape Cool Warm Wavenumber 1 Cool
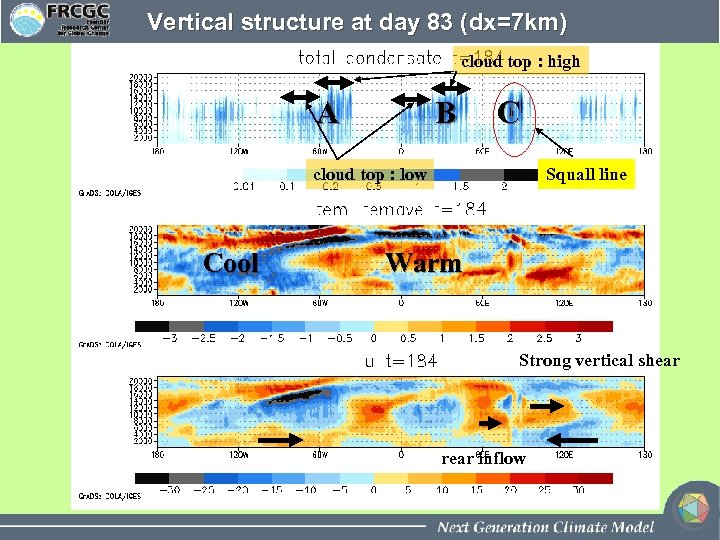 Vertical structure at day 83 (dx=7 km) cloud top : high A B C cloud top : low Cool Squall line Warm Strong vertical shear rear inflow
Vertical structure at day 83 (dx=7 km) cloud top : high A B C cloud top : low Cool Squall line Warm Strong vertical shear rear inflow
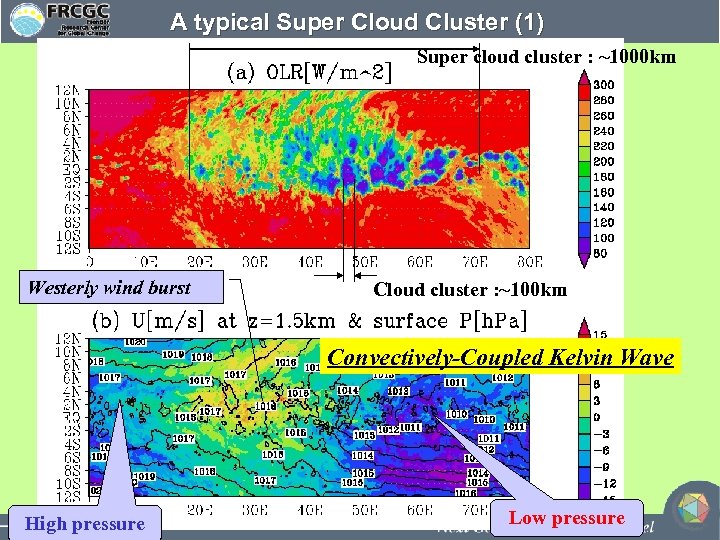 A typical Super Cloud Cluster (1) Super cloud cluster : ~1000 km Westerly wind burst Cloud cluster : ~100 km Convectively-Coupled Kelvin Wave High pressure Low pressure
A typical Super Cloud Cluster (1) Super cloud cluster : ~1000 km Westerly wind burst Cloud cluster : ~100 km Convectively-Coupled Kelvin Wave High pressure Low pressure
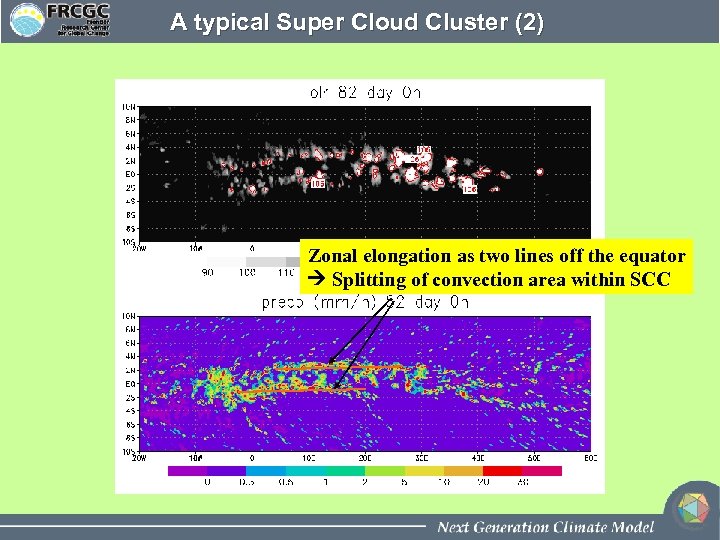 A typical Super Cloud Cluster (2) Zonal elongation as two lines off the equator Splitting of convection area within SCC
A typical Super Cloud Cluster (2) Zonal elongation as two lines off the equator Splitting of convection area within SCC
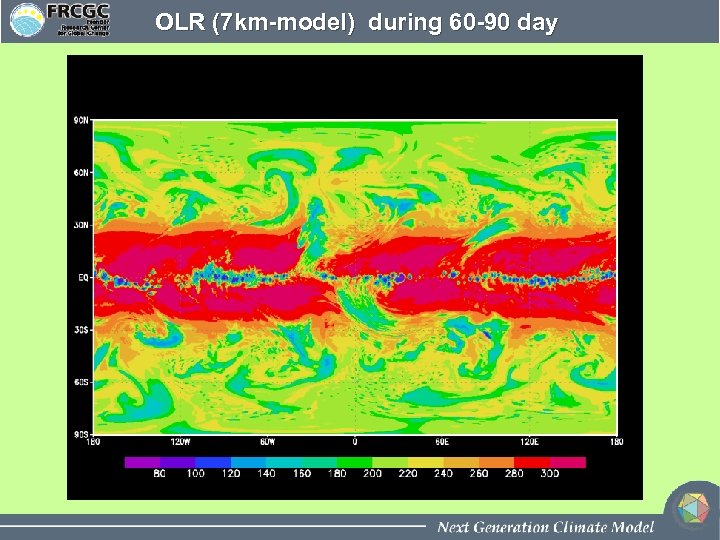 OLR (7 km-model) during 60 -90 day
OLR (7 km-model) during 60 -90 day
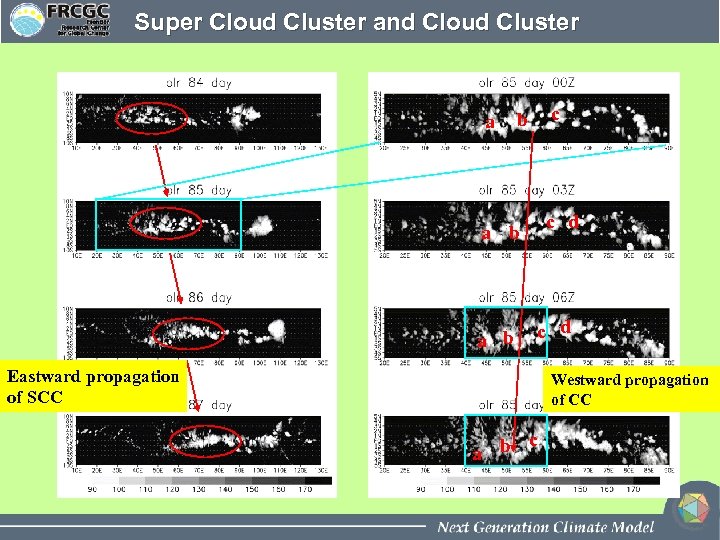 Super Cloud Cluster and Cloud Cluster a c b c d a b c d Eastward propagation of SCC Westward propagation of CC b c a
Super Cloud Cluster and Cloud Cluster a c b c d a b c d Eastward propagation of SCC Westward propagation of CC b c a
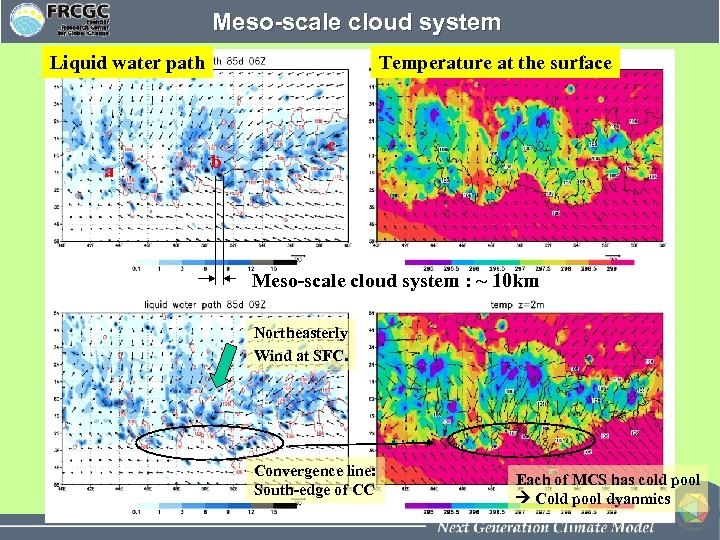 Meso-scale cloud system Liquid water path a Temperature at the surface b c Meso-scale cloud system : ~ 10 km Northeasterly Wind at SFC. Convergence line: South-edge of CC Each of MCS has cold pool Cold pool dyanmics
Meso-scale cloud system Liquid water path a Temperature at the surface b c Meso-scale cloud system : ~ 10 km Northeasterly Wind at SFC. Convergence line: South-edge of CC Each of MCS has cold pool Cold pool dyanmics
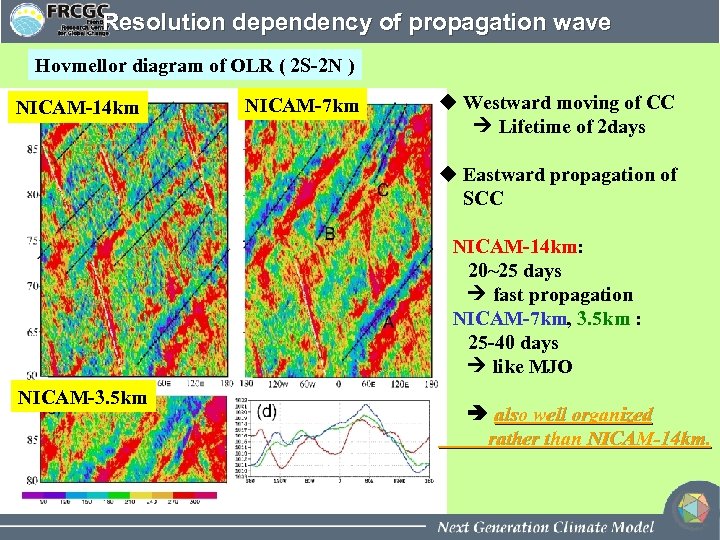 Resolution dependency of propagation wave Hovmellor diagram of OLR ( 2 S-2 N ) NICAM-14 km NICAM-7 km u Westward moving of CC Lifetime of 2 days u Eastward propagation of SCC NICAM-14 km: 20~25 days fast propagation NICAM-7 km, 3. 5 km : 25 -40 days like MJO NICAM-3. 5 km also well organized rather than NICAM-14 km.
Resolution dependency of propagation wave Hovmellor diagram of OLR ( 2 S-2 N ) NICAM-14 km NICAM-7 km u Westward moving of CC Lifetime of 2 days u Eastward propagation of SCC NICAM-14 km: 20~25 days fast propagation NICAM-7 km, 3. 5 km : 25 -40 days like MJO NICAM-3. 5 km also well organized rather than NICAM-14 km.
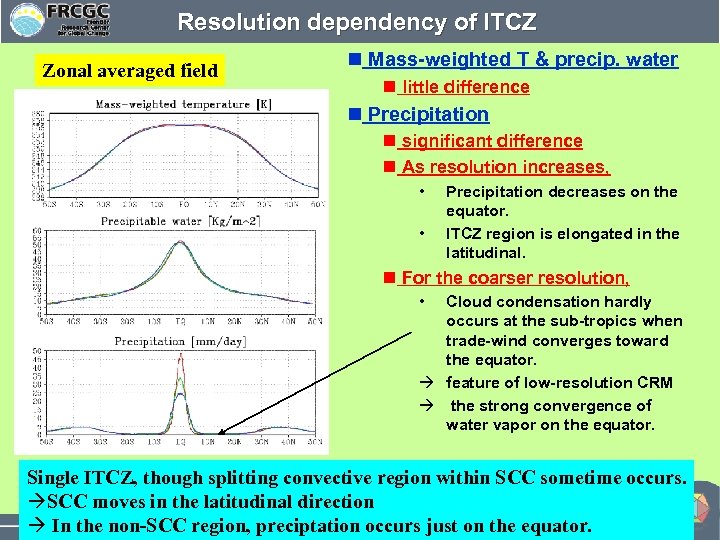 Resolution dependency of ITCZ Zonal averaged field n Mass-weighted T & precip. water n little difference n Precipitation n significant difference n As resolution increases, • • Precipitation decreases on the equator. ITCZ region is elongated in the latitudinal. n For the coarser resolution, • Cloud condensation hardly occurs at the sub-tropics when trade-wind converges toward the equator. à feature of low-resolution CRM à the strong convergence of water vapor on the equator. Single ITCZ, though splitting convective region within SCC sometime occurs. àSCC moves in the latitudinal direction à In the non-SCC region, preciptation occurs just on the equator.
Resolution dependency of ITCZ Zonal averaged field n Mass-weighted T & precip. water n little difference n Precipitation n significant difference n As resolution increases, • • Precipitation decreases on the equator. ITCZ region is elongated in the latitudinal. n For the coarser resolution, • Cloud condensation hardly occurs at the sub-tropics when trade-wind converges toward the equator. à feature of low-resolution CRM à the strong convergence of water vapor on the equator. Single ITCZ, though splitting convective region within SCC sometime occurs. àSCC moves in the latitudinal direction à In the non-SCC region, preciptation occurs just on the equator.
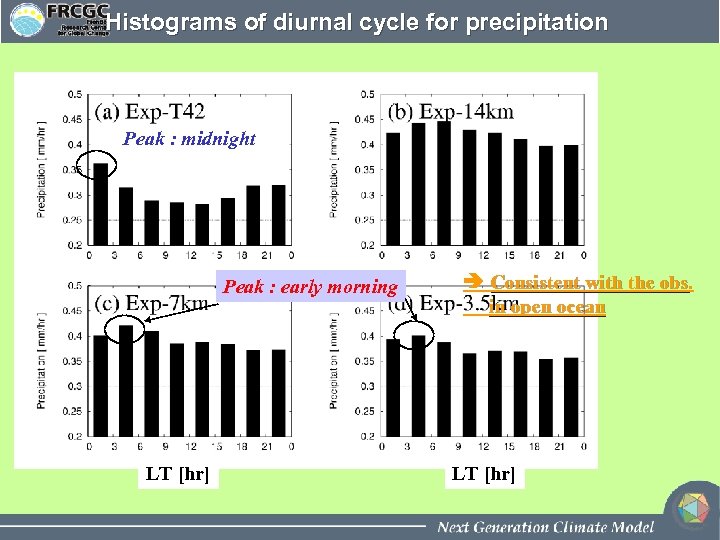 Histograms of diurnal cycle for precipitation Peak : midnight Peak : early morning LT [hr] Consistent with the obs in open ocean LT [hr]
Histograms of diurnal cycle for precipitation Peak : midnight Peak : early morning LT [hr] Consistent with the obs in open ocean LT [hr]
 Summary n We have performed the control run of APE by a global cloudresolving model. n Resolution : 14 km, 7 km, 3. 5 km n Hierarchical structure of cloud field can be well captured. n MJO-like wavenumber 1 structure n Eastward propagation of several super cloud clusters of ~1000 km with 30 -days period. n Westward propagation of cloud clusters of ~100 km with the lifetime of 2 days n Meso-scale cloud system of ~10 km with the lifetime of several hours. n Resolution dependency is found at ITCZ in CRM. n As resolution increases, its intensity is smaller and its width is larger. n Cloud resolving model has the reasonable diurnal cycle of precipitation rate at the tropics. n Its primary peak is at the early morning, consistent with observations.
Summary n We have performed the control run of APE by a global cloudresolving model. n Resolution : 14 km, 7 km, 3. 5 km n Hierarchical structure of cloud field can be well captured. n MJO-like wavenumber 1 structure n Eastward propagation of several super cloud clusters of ~1000 km with 30 -days period. n Westward propagation of cloud clusters of ~100 km with the lifetime of 2 days n Meso-scale cloud system of ~10 km with the lifetime of several hours. n Resolution dependency is found at ITCZ in CRM. n As resolution increases, its intensity is smaller and its width is larger. n Cloud resolving model has the reasonable diurnal cycle of precipitation rate at the tropics. n Its primary peak is at the early morning, consistent with observations.


