d3487c2ed5e7b1277bb120d3283956a1.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 44
 A Case for Economy Grid Architecture for Service Oriented Grid Computing Rajkumar Buyya, David Abramson, Jon Giddy School of Computer Science and Software Engineering, Monash University, Melbourne, Australia www. buyya. com/ecogrid http: //www. gridcomputing. com
A Case for Economy Grid Architecture for Service Oriented Grid Computing Rajkumar Buyya, David Abramson, Jon Giddy School of Computer Science and Software Engineering, Monash University, Melbourne, Australia www. buyya. com/ecogrid http: //www. gridcomputing. com
 Overview A brief introduction to Grid computing n Resource Management issues n A Glance at Approaches to Grid computing. n Grid Architecture for Computational Economy n Economy Grid = Globus + GRACE n Nimrod-G: A Grid Resource Broker Grid n Scheduling Experiments n Conclusions n Economy Grid Scheduling Economics
Overview A brief introduction to Grid computing n Resource Management issues n A Glance at Approaches to Grid computing. n Grid Architecture for Computational Economy n Economy Grid = Globus + GRACE n Nimrod-G: A Grid Resource Broker Grid n Scheduling Experiments n Conclusions n Economy Grid Scheduling Economics
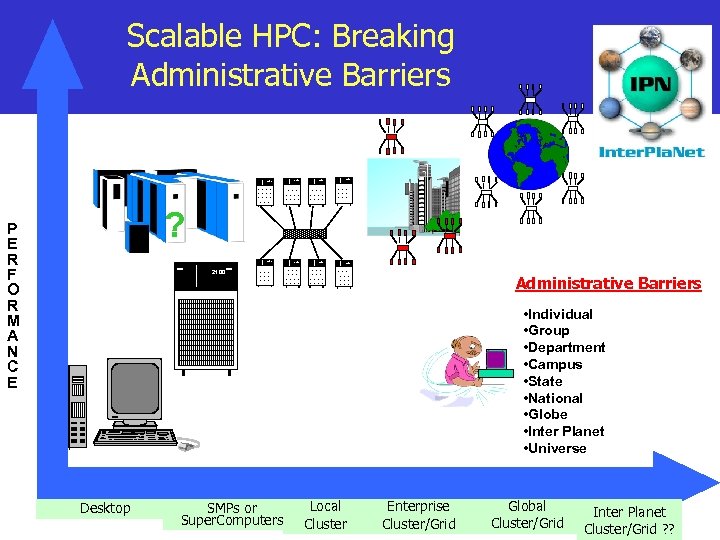 Scalable HPC: Breaking Administrative Barriers 2100 2100 ? P E R F O R M A N C E 2100 Administrative Barriers • Individual • Group • Department • Campus • State • National • Globe • Inter Planet • Universe Desktop SMPs or Super. Computers Local Cluster Enterprise Cluster/Grid Global Cluster/Grid Inter Planet Cluster/Grid ? ?
Scalable HPC: Breaking Administrative Barriers 2100 2100 ? P E R F O R M A N C E 2100 Administrative Barriers • Individual • Group • Department • Campus • State • National • Globe • Inter Planet • Universe Desktop SMPs or Super. Computers Local Cluster Enterprise Cluster/Grid Global Cluster/Grid Inter Planet Cluster/Grid ? ?
 Why Grids ? Large Scale Exploration needs them—Killer Applications. n Solving grand challenge applications using computer modeling, simulation and analysis Aerospace Life Sciences CAD/CAM Digital Biology Internet & Ecommerce Military Applications
Why Grids ? Large Scale Exploration needs them—Killer Applications. n Solving grand challenge applications using computer modeling, simulation and analysis Aerospace Life Sciences CAD/CAM Digital Biology Internet & Ecommerce Military Applications
 What is Grid ? n An infrastructure that couples: n n n q Computers – PCs, workstations, clusters, supercomputers, laptops, notebooks, mobile devices, PDA, etc; Software – e. g. , ASPs renting expensive special purpose applications on demand; Catalogued data and databases – e. g. transparent access to human genome database; Special devices – e. g. , radio telescope – SETI@Home searching for life in galaxy. People/collaborators. Potentially Offers a simple, consistent, dependable, and pervasive access across widearea networks and presents users with an integrated global resource.
What is Grid ? n An infrastructure that couples: n n n q Computers – PCs, workstations, clusters, supercomputers, laptops, notebooks, mobile devices, PDA, etc; Software – e. g. , ASPs renting expensive special purpose applications on demand; Catalogued data and databases – e. g. transparent access to human genome database; Special devices – e. g. , radio telescope – SETI@Home searching for life in galaxy. People/collaborators. Potentially Offers a simple, consistent, dependable, and pervasive access across widearea networks and presents users with an integrated global resource.
 Grid Applications-Drivers n Distributed HPC (Supercomputing): n n High-throughput computing: n n Data mining, particle physics (CERN), Drug Design. On-demand computing: n n Application service provides (ASPs). Data-intensive computing: n n Sharing digital contents among peers (e. g. , Napster) Remote software access/renting services: n n Large scale simulation/chip design & parameter studies. Content Sharing n n Computational science. Medical instrumentation & network-enabled solvers. Collaborative: n Collaborative design, data exploration, education.
Grid Applications-Drivers n Distributed HPC (Supercomputing): n n High-throughput computing: n n Data mining, particle physics (CERN), Drug Design. On-demand computing: n n Application service provides (ASPs). Data-intensive computing: n n Sharing digital contents among peers (e. g. , Napster) Remote software access/renting services: n n Large scale simulation/chip design & parameter studies. Content Sharing n n Computational science. Medical instrumentation & network-enabled solvers. Collaborative: n Collaborative design, data exploration, education.
 Building and Using Grids requires. . . n n n Services that make our systems Grid Ready! Security mechanisms that permit resources to be accessed only by authorized users. (New) programming tools that make our applications Grid Ready!. Tools that can translate the requirements of an application into requirements for computers, networks, and storage. Tools that perform resource discovery, trading, composition, scheduling and distribution of jobs and collects results.
Building and Using Grids requires. . . n n n Services that make our systems Grid Ready! Security mechanisms that permit resources to be accessed only by authorized users. (New) programming tools that make our applications Grid Ready!. Tools that can translate the requirements of an application into requirements for computers, networks, and storage. Tools that perform resource discovery, trading, composition, scheduling and distribution of jobs and collects results.
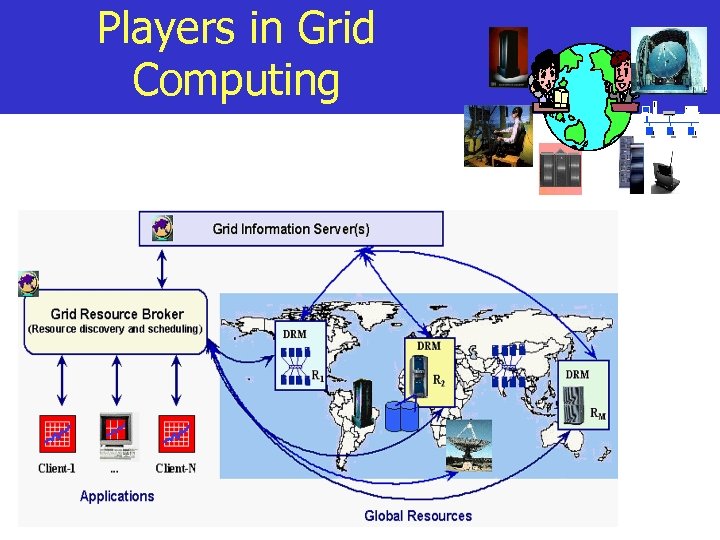 Players in Grid Computing
Players in Grid Computing
 What users want ? Users in Grid Economy & Strategy n Grid Consumers n n n Execute jobs for solving varying problem size and complexity Benefit by selecting and aggregating resources wisely Tradeoff timeframe and cost n n Strategy: minimise expenses Grid Providers n n n Contribute “idle” resource for executing consumer jobs Benefit by maximizing resource utilisation Tradeoff local requirements & market opportunity n Strategy: maximise returns on services
What users want ? Users in Grid Economy & Strategy n Grid Consumers n n n Execute jobs for solving varying problem size and complexity Benefit by selecting and aggregating resources wisely Tradeoff timeframe and cost n n Strategy: minimise expenses Grid Providers n n n Contribute “idle” resource for executing consumer jobs Benefit by maximizing resource utilisation Tradeoff local requirements & market opportunity n Strategy: maximise returns on services
 Sources of Complexity in Resource Management for World Wide Computing n n n n n Size (large number of nodes, providers, consumers) Heterogeneity of resources (PCs, Workstatations, clusters, and supercomputers) Heterogeneity of fabric management systems (single system image OS, queuing systems, etc. ) Heterogeneity of fabric management polices Heterogeneity of applications (scientific, engineering, and commerce) Heterogeneity of application requirements (CPU, I/O, memory, and/or network intensive) Heterogeneity in demand patters Geographic distribution and different time zones Differing goals (producers and consumers have different objectives and strategies) Unsecure and Unreliable environment
Sources of Complexity in Resource Management for World Wide Computing n n n n n Size (large number of nodes, providers, consumers) Heterogeneity of resources (PCs, Workstatations, clusters, and supercomputers) Heterogeneity of fabric management systems (single system image OS, queuing systems, etc. ) Heterogeneity of fabric management polices Heterogeneity of applications (scientific, engineering, and commerce) Heterogeneity of application requirements (CPU, I/O, memory, and/or network intensive) Heterogeneity in demand patters Geographic distribution and different time zones Differing goals (producers and consumers have different objectives and strategies) Unsecure and Unreliable environment
 Traditional approaches to resource management are NOT useful for Grid ? n They use centralised policy that need n n n Due to too many heterogenous parameters in the Grid it is impossible to define: n n n complete state-information and common fabric management policy or decentralised consensus-based policy. system-wide performance matrix and common fabric management policy that is acceptable to all. So, we propose the usage of “economics” paradigm for managing resources n n n proved successful in managing decentralization and heterogeneity that is present in human economies! We can easy leverage proven Economic principles and techniques Easy to regulate demand supply User-centric, scalable, adaptable, value-driven costing, etc. Offers incentive (money? ) for being part of the grid!
Traditional approaches to resource management are NOT useful for Grid ? n They use centralised policy that need n n n Due to too many heterogenous parameters in the Grid it is impossible to define: n n n complete state-information and common fabric management policy or decentralised consensus-based policy. system-wide performance matrix and common fabric management policy that is acceptable to all. So, we propose the usage of “economics” paradigm for managing resources n n n proved successful in managing decentralization and heterogeneity that is present in human economies! We can easy leverage proven Economic principles and techniques Easy to regulate demand supply User-centric, scalable, adaptable, value-driven costing, etc. Offers incentive (money? ) for being part of the grid!
 mix-and-match Object-oriented Internet-WWW Problem Solving Approach Market/Computational Economy
mix-and-match Object-oriented Internet-WWW Problem Solving Approach Market/Computational Economy
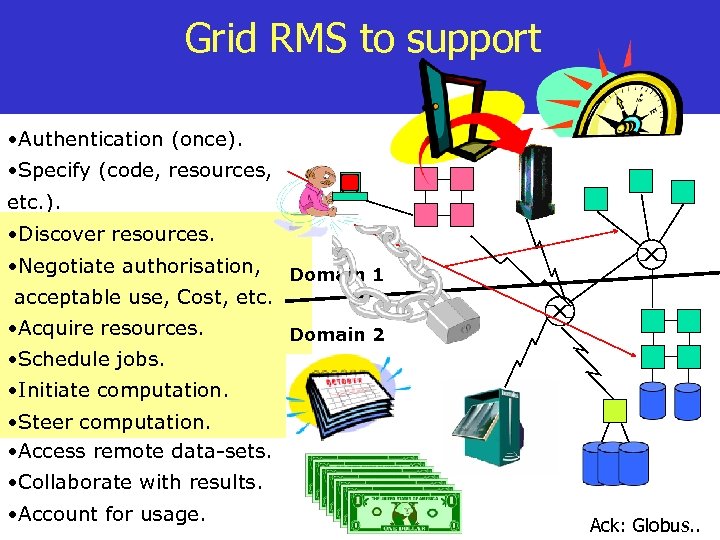 Grid RMS to support • Authentication (once). • Specify (code, resources, etc. ). • Discover resources. • Negotiate authorization, authorisation, Domain 1 acceptable use, Cost, etc. • Acquire resources. Domain 2 • Schedule Jobs. jobs. • Initiate computation. • Steer computation. • Access remote data-sets. • Collaborate with results. • Account for usage. Ack: Globus. .
Grid RMS to support • Authentication (once). • Specify (code, resources, etc. ). • Discover resources. • Negotiate authorization, authorisation, Domain 1 acceptable use, Cost, etc. • Acquire resources. Domain 2 • Schedule Jobs. jobs. • Initiate computation. • Steer computation. • Access remote data-sets. • Collaborate with results. • Account for usage. Ack: Globus. .
 Building an Economy Grid “brokerage” system…. . Foundation for the Grid Economy
Building an Economy Grid “brokerage” system…. . Foundation for the Grid Economy
 Economic Models for Resource Trading n n n Commodity Market Model Posted Prices Models Bargaining Model Tendering (Contract Net) Model Auction Model n n English, first-price sealed-bid, second-price sealded-bid (Vickrey), and Dutch. Proportional Resource Sharing Model Shareholder Model Partnership Model
Economic Models for Resource Trading n n n Commodity Market Model Posted Prices Models Bargaining Model Tendering (Contract Net) Model Auction Model n n English, first-price sealed-bid, second-price sealded-bid (Vickrey), and Dutch. Proportional Resource Sharing Model Shareholder Model Partnership Model
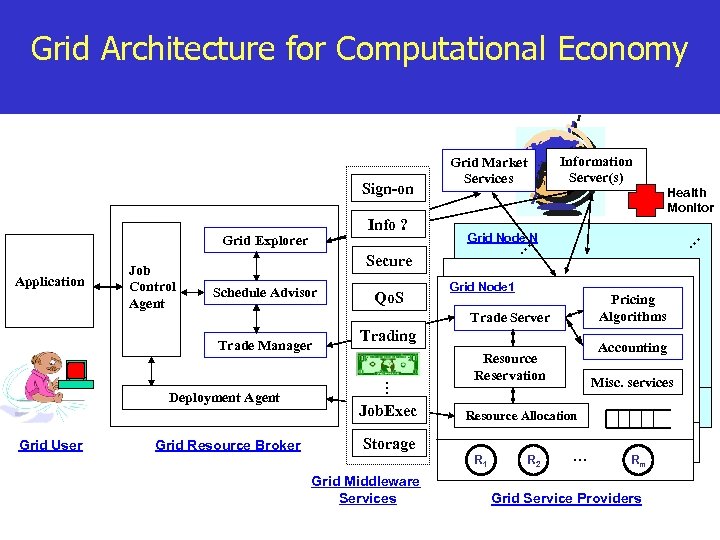 Grid Architecture for Computational Economy Grid Explorer Application Job Control Agent Qo. S Grid Node 1 Pricing Algorithms Trade Server Trade Manager Grid Resource Broker Trading … Deployment Agent Grid User Grid Node N Secure Schedule Advisor Job. Exec Accounting Resource Reservation Misc. services Resource Allocation Storage R 1 Grid Middleware Services Health Monitor … Info ? Information Server(s) … Sign-on Grid Market Services R 2 … Rm Grid Service Providers
Grid Architecture for Computational Economy Grid Explorer Application Job Control Agent Qo. S Grid Node 1 Pricing Algorithms Trade Server Trade Manager Grid Resource Broker Trading … Deployment Agent Grid User Grid Node N Secure Schedule Advisor Job. Exec Accounting Resource Reservation Misc. services Resource Allocation Storage R 1 Grid Middleware Services Health Monitor … Info ? Information Server(s) … Sign-on Grid Market Services R 2 … Rm Grid Service Providers
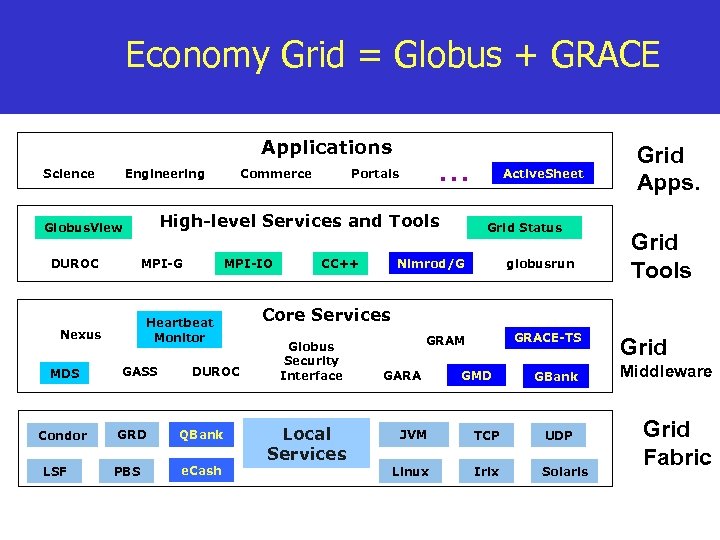 Economy Grid = Globus + GRACE Applications Science Engineering MPI-G MDS Condor LSF MPI-IO Heartbeat Monitor Nexus GASS GRD PBS … Portals High-level Services and Tools Globus. View DUROC Commerce DUROC QBank e. Cash Active. Sheet Grid Status Nimrod/G CC++ globusrun Grid Apps. Grid Tools Core Services Globus Security Interface Local Services GRACE-TS GRAM GARA GMD GBank JVM TCP UDP Linux Irix Solaris Grid Middleware Grid Fabric
Economy Grid = Globus + GRACE Applications Science Engineering MPI-G MDS Condor LSF MPI-IO Heartbeat Monitor Nexus GASS GRD PBS … Portals High-level Services and Tools Globus. View DUROC Commerce DUROC QBank e. Cash Active. Sheet Grid Status Nimrod/G CC++ globusrun Grid Apps. Grid Tools Core Services Globus Security Interface Local Services GRACE-TS GRAM GARA GMD GBank JVM TCP UDP Linux Irix Solaris Grid Middleware Grid Fabric
 GRACE components n n n n A resource broker (e. g. , Nimrod/G) Resource trading protocols A mediator for negotiating between users and grid service providers (Grid Market Directory) A deal template for specifying resource requirements and services offers A trade server A pricing policy specification Accounting (e. g. , QBank) and payment management (GBank)
GRACE components n n n n A resource broker (e. g. , Nimrod/G) Resource trading protocols A mediator for negotiating between users and grid service providers (Grid Market Directory) A deal template for specifying resource requirements and services offers A trade server A pricing policy specification Accounting (e. g. , QBank) and payment management (GBank)
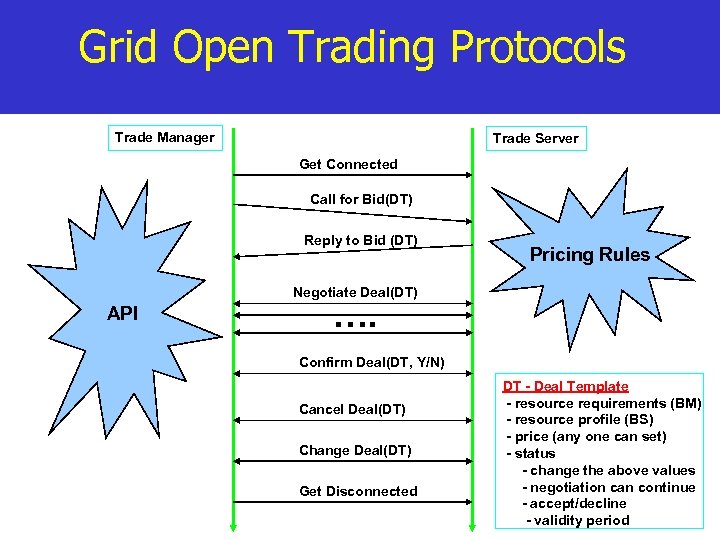 Grid Open Trading Protocols Trade Manager Trade Server Get Connected Call for Bid(DT) Reply to Bid (DT) Pricing Rules Negotiate Deal(DT) API …. Confirm Deal(DT, Y/N) Cancel Deal(DT) Change Deal(DT) Get Disconnected DT - Deal Template - resource requirements (BM) - resource profile (BS) - price (any one can set) - status - change the above values - negotiation can continue - accept/decline - validity period
Grid Open Trading Protocols Trade Manager Trade Server Get Connected Call for Bid(DT) Reply to Bid (DT) Pricing Rules Negotiate Deal(DT) API …. Confirm Deal(DT, Y/N) Cancel Deal(DT) Change Deal(DT) Get Disconnected DT - Deal Template - resource requirements (BM) - resource profile (BS) - price (any one can set) - status - change the above values - negotiation can continue - accept/decline - validity period
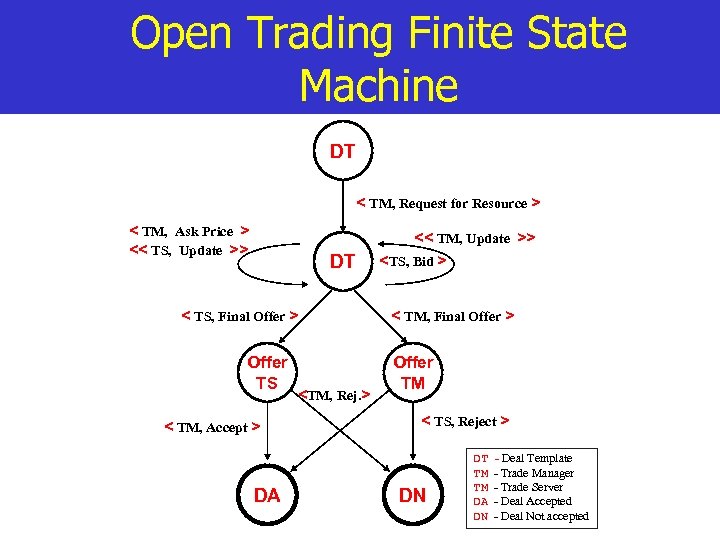 Open Trading Finite State Machine DT < TM, Request for Resource > < TM, Ask Price > << TS, Update >> DT < TS, Final Offer > Offer TS < TM, Accept > DA
Open Trading Finite State Machine DT < TM, Request for Resource > < TM, Ask Price > << TS, Update >> DT < TS, Final Offer > Offer TS < TM, Accept > DA
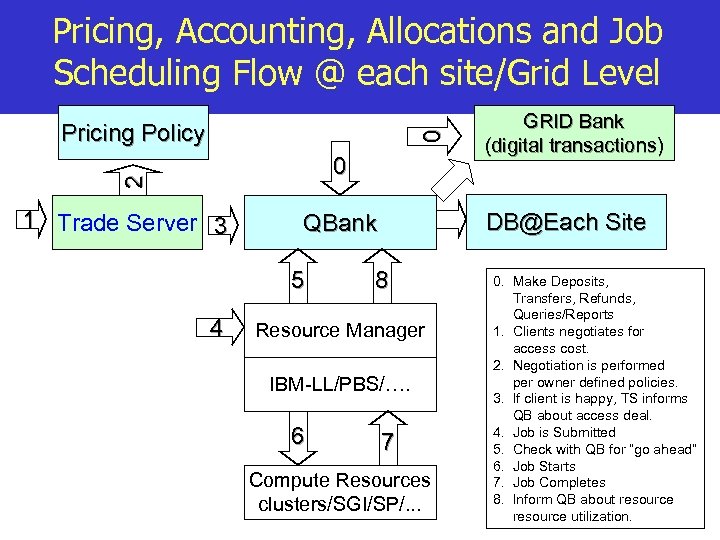 Pricing, Accounting, Allocations and Job Scheduling Flow @ each site/Grid Level 0 Pricing Policy 2 0 1 Trade Server 3 4 DB@Each Site QBank 5 8 Resource Manager IBM-LL/PBS/…. 6 GRID Bank (digital transactions) 7 Compute Resources clusters/SGI/SP/. . . 0. Make Deposits, Transfers, Refunds, Queries/Reports 1. Clients negotiates for access cost. 2. Negotiation is performed per owner defined policies. 3. If client is happy, TS informs QB about access deal. 4. Job is Submitted 5. Check with QB for “go ahead” 6. Job Starts 7. Job Completes 8. Inform QB about resource utilization.
Pricing, Accounting, Allocations and Job Scheduling Flow @ each site/Grid Level 0 Pricing Policy 2 0 1 Trade Server 3 4 DB@Each Site QBank 5 8 Resource Manager IBM-LL/PBS/…. 6 GRID Bank (digital transactions) 7 Compute Resources clusters/SGI/SP/. . . 0. Make Deposits, Transfers, Refunds, Queries/Reports 1. Clients negotiates for access cost. 2. Negotiation is performed per owner defined policies. 3. If client is happy, TS informs QB about access deal. 4. Job is Submitted 5. Check with QB for “go ahead” 6. Job Starts 7. Job Completes 8. Inform QB about resource utilization.
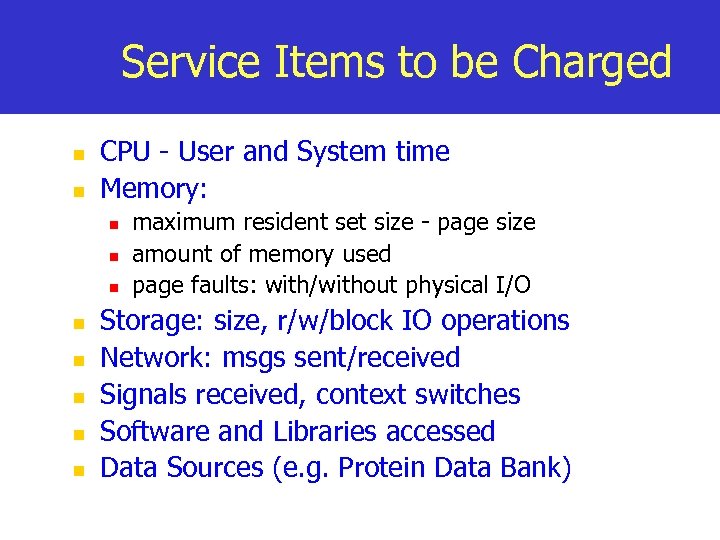 Service Items to be Charged n n CPU - User and System time Memory: n n n n maximum resident set size - page size amount of memory used page faults: with/without physical I/O Storage: size, r/w/block IO operations Network: msgs sent/received Signals received, context switches Software and Libraries accessed Data Sources (e. g. Protein Data Bank)
Service Items to be Charged n n CPU - User and System time Memory: n n n n maximum resident set size - page size amount of memory used page faults: with/without physical I/O Storage: size, r/w/block IO operations Network: msgs sent/received Signals received, context switches Software and Libraries accessed Data Sources (e. g. Protein Data Bank)
 How to decide Price ? n n n n Fixed price model (like today’s Internet) Dynamic/Demand Supply (like tomorrow’s Internet) Usage Period Loyalty of Customers (like Airlines favoring frequent flyers!) Historical data Advance Agreement (high discount for corporations) Usage Timing (peak, off-peak, lunch time) Calendar based (holiday/vacation period) Bulk Purchase (register 100. com domains at once!) Voting -- trade unions decide pricing structure Resource capability as benchmarked in the market! Academic R&D/public-good application users can be offered at cheaper rate compared to commercial use. Customer Type – Quality or price sensitive buyers. Can be Prescribed by Regulating (Govt. ) authorities
How to decide Price ? n n n n Fixed price model (like today’s Internet) Dynamic/Demand Supply (like tomorrow’s Internet) Usage Period Loyalty of Customers (like Airlines favoring frequent flyers!) Historical data Advance Agreement (high discount for corporations) Usage Timing (peak, off-peak, lunch time) Calendar based (holiday/vacation period) Bulk Purchase (register 100. com domains at once!) Voting -- trade unions decide pricing structure Resource capability as benchmarked in the market! Academic R&D/public-good application users can be offered at cheaper rate compared to commercial use. Customer Type – Quality or price sensitive buyers. Can be Prescribed by Regulating (Govt. ) authorities
 Payments- Options & Automation n n Buy credits in advance / GSPs bill the user later--”pay as you go” Pay by Electronic Currency via Grid Bank n n Net. Cash (anonymity), Net. Cheque, and Paypal Net. Cheque: - http: //www. isi. edu/gost/info/netcash/ n n Net. Cash - http: //www. isi. edu/gost/info/netcheque/ n n Users register with NC accounting servers, can write electronic cheques and send (e. g email). When deposited, balance is transferred from sender to receiver account. It supports anonymity and it uses the Net. Cheque system to clear payments between currency servers. Paypal. com– account+email is linked to credit card. n n Enter the recipient’s email address and the amount you wish to request. The recipient gets an email notification and pays you at www. Pay. Pal. com
Payments- Options & Automation n n Buy credits in advance / GSPs bill the user later--”pay as you go” Pay by Electronic Currency via Grid Bank n n Net. Cash (anonymity), Net. Cheque, and Paypal Net. Cheque: - http: //www. isi. edu/gost/info/netcash/ n n Net. Cash - http: //www. isi. edu/gost/info/netcheque/ n n Users register with NC accounting servers, can write electronic cheques and send (e. g email). When deposited, balance is transferred from sender to receiver account. It supports anonymity and it uses the Net. Cheque system to clear payments between currency servers. Paypal. com– account+email is linked to credit card. n n Enter the recipient’s email address and the amount you wish to request. The recipient gets an email notification and pays you at www. Pay. Pal. com
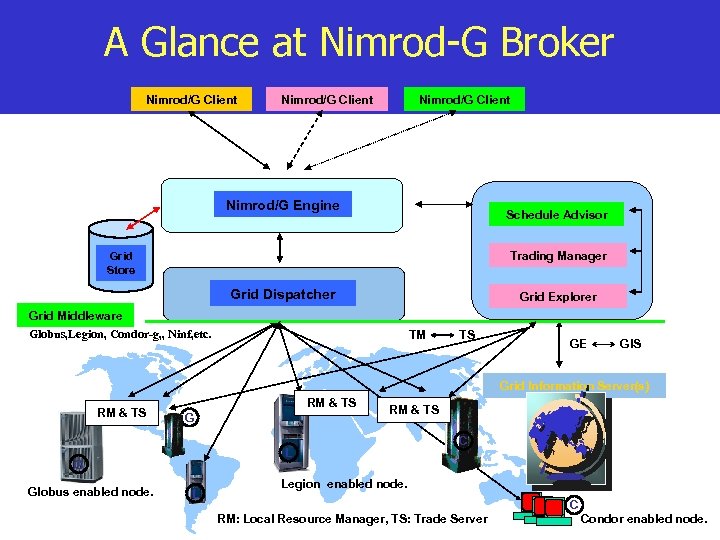 A Glance at Nimrod-G Broker Nimrod/G Client Nimrod/G Engine Schedule Advisor Trading Manager Grid Store Grid Dispatcher Grid Explorer Grid Middleware Globus, Legion, Condor-g, , Ninf, etc. TM TS GE GIS Grid Information Server(s) RM & TS G L G Globus enabled node. RM & TS L C Legion enabled node. C RM: Local Resource Manager, TS: Trade Server Condor enabled node.
A Glance at Nimrod-G Broker Nimrod/G Client Nimrod/G Engine Schedule Advisor Trading Manager Grid Store Grid Dispatcher Grid Explorer Grid Middleware Globus, Legion, Condor-g, , Ninf, etc. TM TS GE GIS Grid Information Server(s) RM & TS G L G Globus enabled node. RM & TS L C Legion enabled node. C RM: Local Resource Manager, TS: Trade Server Condor enabled node.
 Nimrod/G : A Grid Resource Broker n n A resource broker for managing and steering task farming (parametric sweep) applications on computational Grids based on deadline and computational economy. Key Features n n n A single window to manage & control experiment Resource Discovery Trade for Resources Resource Composition & Scheduling Steering & data management It allows to study the behaviour of some of the output variables against a range of different input scenarios.
Nimrod/G : A Grid Resource Broker n n A resource broker for managing and steering task farming (parametric sweep) applications on computational Grids based on deadline and computational economy. Key Features n n n A single window to manage & control experiment Resource Discovery Trade for Resources Resource Composition & Scheduling Steering & data management It allows to study the behaviour of some of the output variables against a range of different input scenarios.
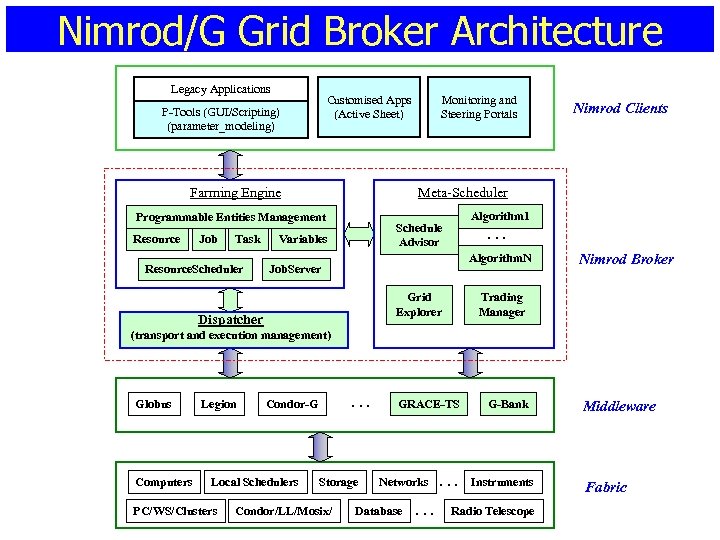 Nimrod/G Grid Broker Architecture Legacy Applications Customised Apps (Active Sheet) P-Tools (GUI/Scripting) (parameter_modeling) Farming Engine Job Task Resource. Scheduler Nimrod Clients Meta-Scheduler Programmable Entities Management Resource Monitoring and Steering Portals Algorithm 1 Schedule Advisor Variables . . . Algorithm. N Job. Server Grid Explorer Dispatcher Nimrod Broker Trading Manager (transport and execution management) Globus Computers Legion Local Schedulers PC/WS/Clusters . . . Condor-G Storage Condor/LL/Mosix/ GRACE-TS Networks Database . . . G-Bank Instruments Radio Telescope Middleware Fabric
Nimrod/G Grid Broker Architecture Legacy Applications Customised Apps (Active Sheet) P-Tools (GUI/Scripting) (parameter_modeling) Farming Engine Job Task Resource. Scheduler Nimrod Clients Meta-Scheduler Programmable Entities Management Resource Monitoring and Steering Portals Algorithm 1 Schedule Advisor Variables . . . Algorithm. N Job. Server Grid Explorer Dispatcher Nimrod Broker Trading Manager (transport and execution management) Globus Computers Legion Local Schedulers PC/WS/Clusters . . . Condor-G Storage Condor/LL/Mosix/ GRACE-TS Networks Database . . . G-Bank Instruments Radio Telescope Middleware Fabric
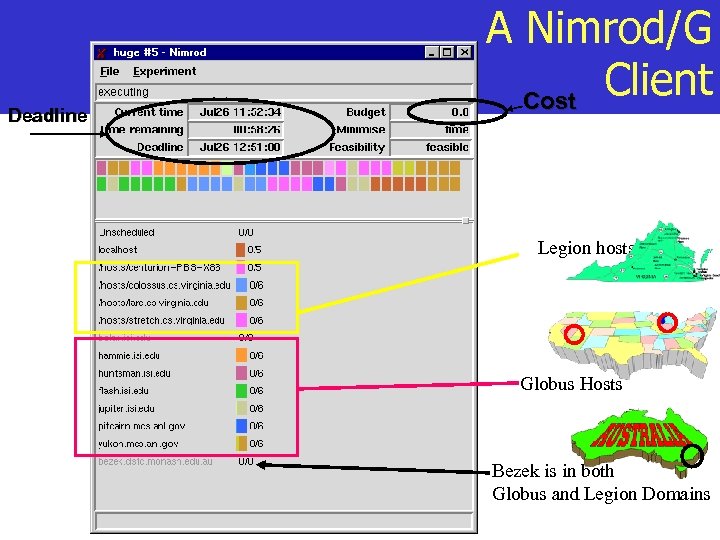 Deadline A Nimrod/G Client Cost Legion hosts Globus Hosts Bezek is in both Globus and Legion Domains
Deadline A Nimrod/G Client Cost Legion hosts Globus Hosts Bezek is in both Globus and Legion Domains
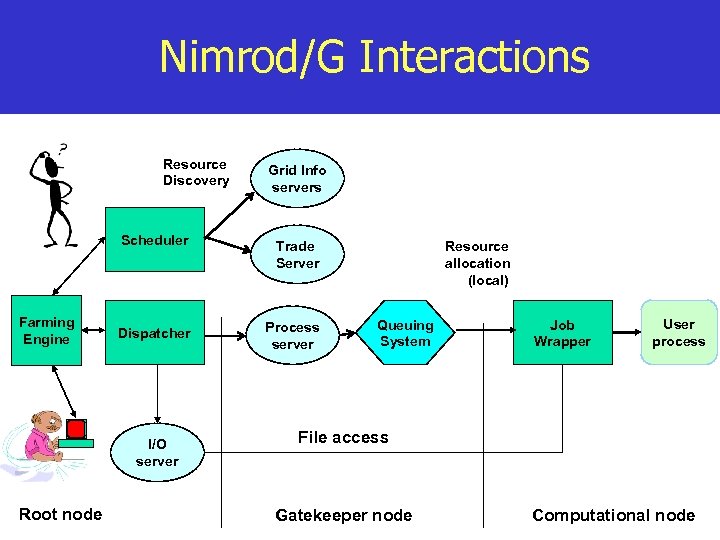 Nimrod/G Interactions Resource Discovery Grid Info servers Scheduler Farming Engine Trade Server Dispatcher Process server I/O server Root node Resource allocation (local) Queuing System Job Wrapper User process File access Gatekeeper node Computational node
Nimrod/G Interactions Resource Discovery Grid Info servers Scheduler Farming Engine Trade Server Dispatcher Process server I/O server Root node Resource allocation (local) Queuing System Job Wrapper User process File access Gatekeeper node Computational node
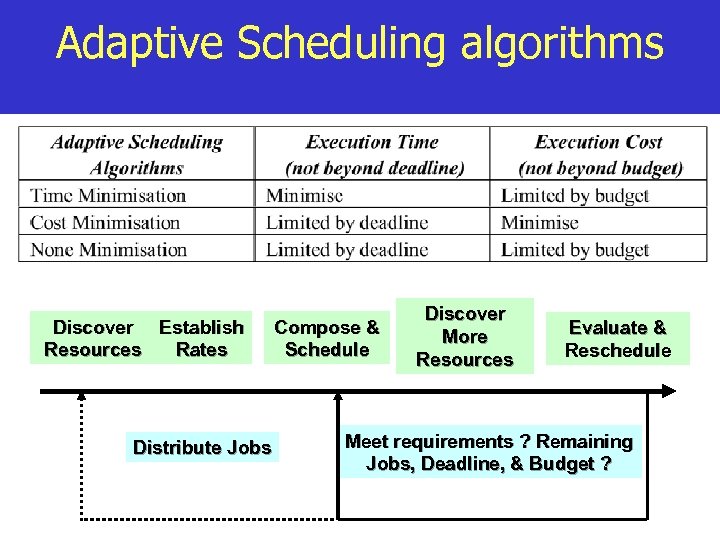 Adaptive Scheduling algorithms Discover Establish Resources Rates Distribute Jobs Compose & Schedule Discover More Resources Evaluate & Reschedule Meet requirements ? Remaining Jobs, Deadline, & Budget ?
Adaptive Scheduling algorithms Discover Establish Resources Rates Distribute Jobs Compose & Schedule Discover More Resources Evaluate & Reschedule Meet requirements ? Remaining Jobs, Deadline, & Budget ?
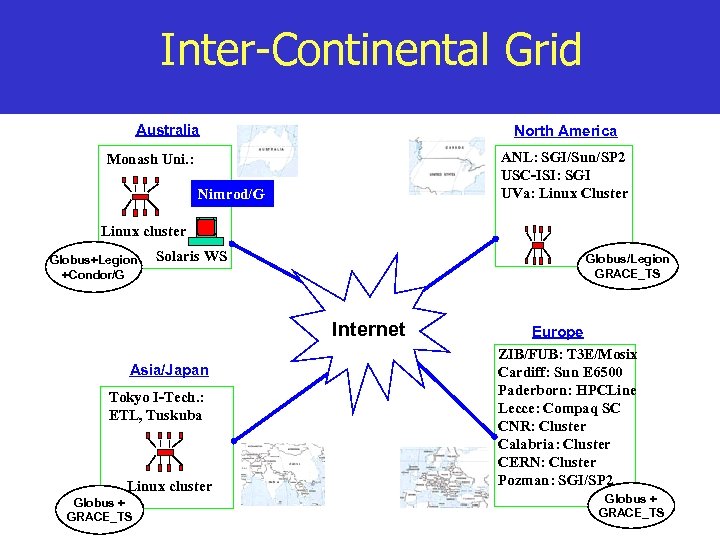 Inter-Continental Grid Australia North America ANL: SGI/Sun/SP 2 USC-ISI: SGI UVa: Linux Cluster Monash Uni. : Nimrod/G Linux cluster Globus+Legion +Condor/G Solaris WS Globus/Legion GRACE_TS Internet Asia/Japan Tokyo I-Tech. : ETL, Tuskuba Linux cluster Globus + GRACE_TS Europe ZIB/FUB: T 3 E/Mosix Cardiff: Sun E 6500 Paderborn: HPCLine Lecce: Compaq SC CNR: Cluster Calabria: Cluster CERN: Cluster Pozman: SGI/SP 2 Globus + GRACE_TS
Inter-Continental Grid Australia North America ANL: SGI/Sun/SP 2 USC-ISI: SGI UVa: Linux Cluster Monash Uni. : Nimrod/G Linux cluster Globus+Legion +Condor/G Solaris WS Globus/Legion GRACE_TS Internet Asia/Japan Tokyo I-Tech. : ETL, Tuskuba Linux cluster Globus + GRACE_TS Europe ZIB/FUB: T 3 E/Mosix Cardiff: Sun E 6500 Paderborn: HPCLine Lecce: Compaq SC CNR: Cluster Calabria: Cluster CERN: Cluster Pozman: SGI/SP 2 Globus + GRACE_TS
 Experiment-1 Setup n Workload: n n 165 jobs, each need 5 minute of cpu time Deadline: 1 hrs. and budget: 800, 000 units Strategy: minimise cost and meet deadline Execution Cost with cost optimisation n n AU Peaktime: 471205 (G$) AU Offpeak time: 427155 (G$)
Experiment-1 Setup n Workload: n n 165 jobs, each need 5 minute of cpu time Deadline: 1 hrs. and budget: 800, 000 units Strategy: minimise cost and meet deadline Execution Cost with cost optimisation n n AU Peaktime: 471205 (G$) AU Offpeak time: 427155 (G$)
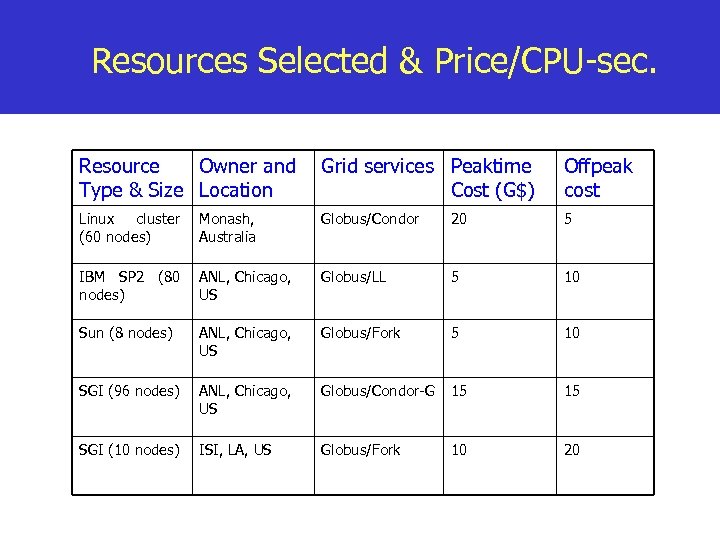 Resources Selected & Price/CPU-sec. Resource Owner and Type & Size Location Grid services Peaktime Cost (G$) Offpeak cost Linux cluster (60 nodes) Monash, Australia Globus/Condor 20 5 IBM SP 2 (80 nodes) ANL, Chicago, US Globus/LL 5 10 Sun (8 nodes) ANL, Chicago, US Globus/Fork 5 10 SGI (96 nodes) ANL, Chicago, US Globus/Condor-G 15 15 SGI (10 nodes) ISI, LA, US Globus/Fork 10 20
Resources Selected & Price/CPU-sec. Resource Owner and Type & Size Location Grid services Peaktime Cost (G$) Offpeak cost Linux cluster (60 nodes) Monash, Australia Globus/Condor 20 5 IBM SP 2 (80 nodes) ANL, Chicago, US Globus/LL 5 10 Sun (8 nodes) ANL, Chicago, US Globus/Fork 5 10 SGI (96 nodes) ANL, Chicago, US Globus/Condor-G 15 15 SGI (10 nodes) ISI, LA, US Globus/Fork 10 20
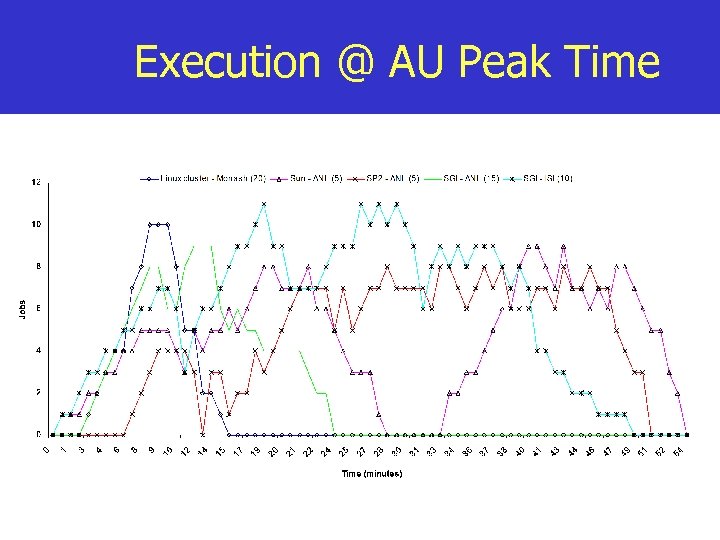 Execution @ AU Peak Time
Execution @ AU Peak Time
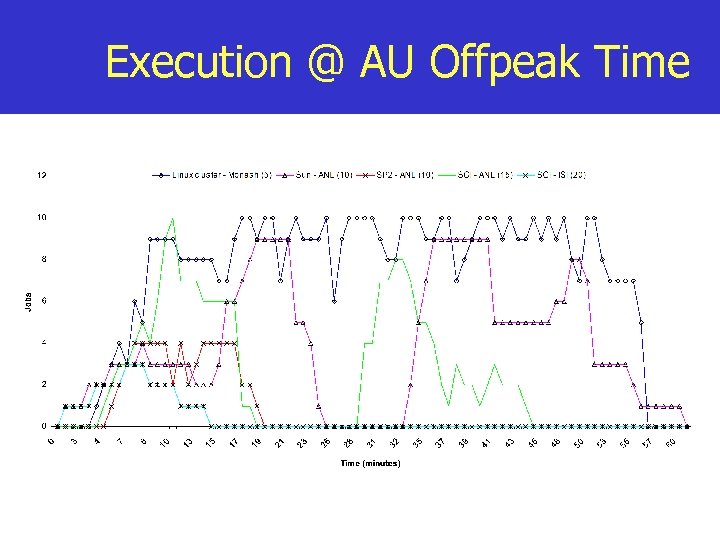 Execution @ AU Offpeak Time
Execution @ AU Offpeak Time
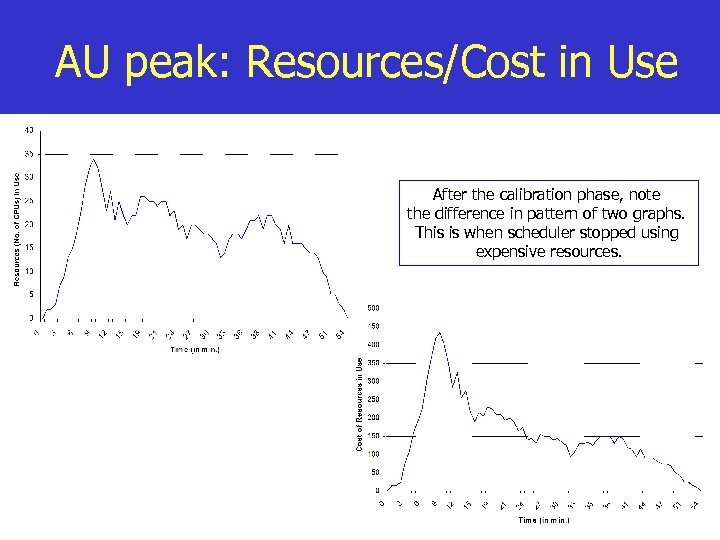 AU peak: Resources/Cost in Use After the calibration phase, note the difference in pattern of two graphs. This is when scheduler stopped using expensive resources.
AU peak: Resources/Cost in Use After the calibration phase, note the difference in pattern of two graphs. This is when scheduler stopped using expensive resources.
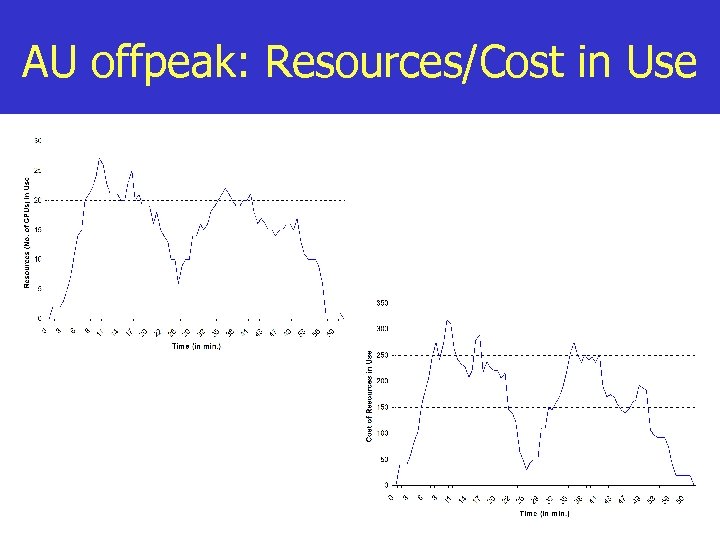 AU offpeak: Resources/Cost in Use
AU offpeak: Resources/Cost in Use
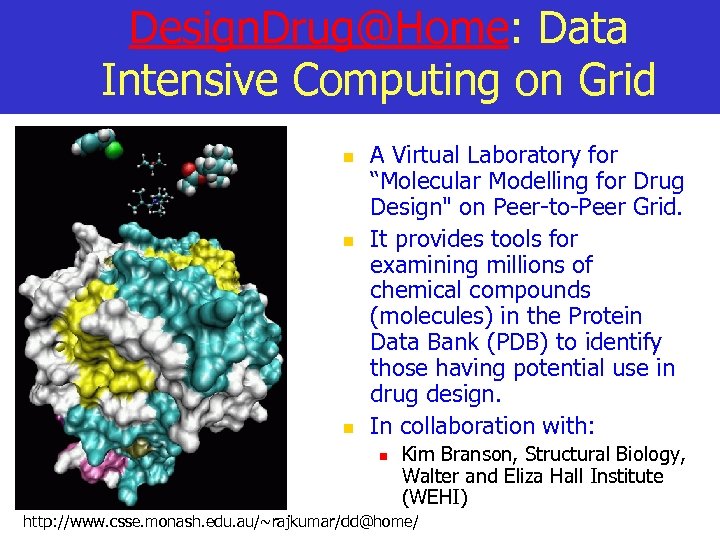 Design. Drug@Home: Data Intensive Computing on Grid n n n A Virtual Laboratory for “Molecular Modelling for Drug Design" on Peer-to-Peer Grid. It provides tools for examining millions of chemical compounds (molecules) in the Protein Data Bank (PDB) to identify those having potential use in drug design. In collaboration with: n Kim Branson, Structural Biology, Walter and Eliza Hall Institute (WEHI) http: //www. csse. monash. edu. au/~rajkumar/dd@home/
Design. Drug@Home: Data Intensive Computing on Grid n n n A Virtual Laboratory for “Molecular Modelling for Drug Design" on Peer-to-Peer Grid. It provides tools for examining millions of chemical compounds (molecules) in the Protein Data Bank (PDB) to identify those having potential use in drug design. In collaboration with: n Kim Branson, Structural Biology, Walter and Eliza Hall Institute (WEHI) http: //www. csse. monash. edu. au/~rajkumar/dd@home/
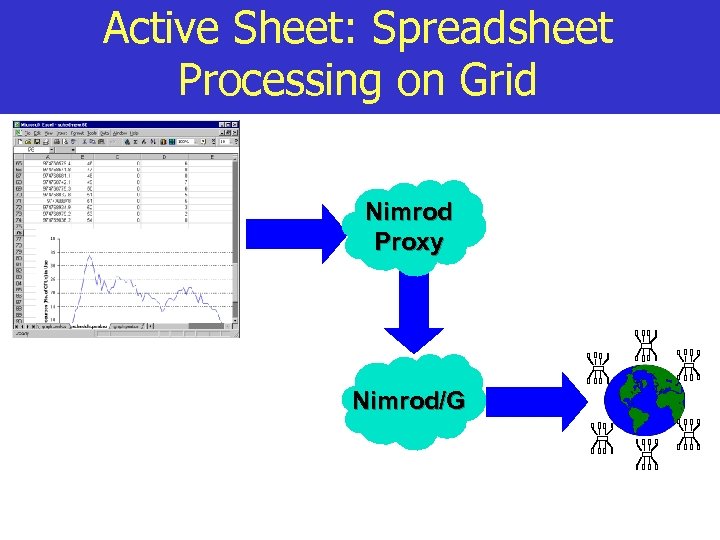 Active Sheet: Spreadsheet Processing on Grid Nimrod Proxy Nimrod/G
Active Sheet: Spreadsheet Processing on Grid Nimrod Proxy Nimrod/G
 Related Works (contd) n Mariposa-Distributed Database system (UCB) n n UCB Millennium clusters n n query with budget, creates sub-query & divides budget, trades with (remote) servers remote execution environment on clusters and supports computational economy rexec for clusters proportional resource sharing UNSW Mungi n Storage management: allocation of backing store and garbage collection of unwanted memory segments depending available credit. Amount of credit required to store increases as available storage space becomes minimum.
Related Works (contd) n Mariposa-Distributed Database system (UCB) n n UCB Millennium clusters n n query with budget, creates sub-query & divides budget, trades with (remote) servers remote execution environment on clusters and supports computational economy rexec for clusters proportional resource sharing UNSW Mungi n Storage management: allocation of backing store and garbage collection of unwanted memory segments depending available credit. Amount of credit required to store increases as available storage space becomes minimum.
 Related Works n Ja. WS - Java based Webcomputing system n n n offers market oriented programming and computing mechanisms on the Web. Xenoservers - Accounted execution of untrusted code D’Agents - Agents and computational economy MOSIX - cost based cluster load balancing A number of theoretical works on pricing. FIPA standard Agents Interaction Protocols (for trading) - we plan to explore this!
Related Works n Ja. WS - Java based Webcomputing system n n n offers market oriented programming and computing mechanisms on the Web. Xenoservers - Accounted execution of untrusted code D’Agents - Agents and computational economy MOSIX - cost based cluster load balancing A number of theoretical works on pricing. FIPA standard Agents Interaction Protocols (for trading) - we plan to explore this!
 Can we Predict its Future ? “I think there is a world market for about five computers. ” Thomas J. Watson Sr. , IBM Founder, 1943
Can we Predict its Future ? “I think there is a world market for about five computers. ” Thomas J. Watson Sr. , IBM Founder, 1943
 Conclusions n n n The HPC will be dominated by Peer-to-Peer Grid of clusters. Adaptive, scalable, and easy to use Systems and End-User applications will be prominent. Access electricity, internet, entertainment (music, movie, …), etc. from the wall socket! An Economics –based Service Oriented Grid Computing computing needed for eventual success of Grids! The impact of World-Wide Grid on 21 st century economy will be the same as electricity on 20 th century economy.
Conclusions n n n The HPC will be dominated by Peer-to-Peer Grid of clusters. Adaptive, scalable, and easy to use Systems and End-User applications will be prominent. Access electricity, internet, entertainment (music, movie, …), etc. from the wall socket! An Economics –based Service Oriented Grid Computing computing needed for eventual success of Grids! The impact of World-Wide Grid on 21 st century economy will be the same as electricity on 20 th century economy.
 Thank You… Any ? ?
Thank You… Any ? ?


