c6d41ea755a1277cc24a91fc4f966f1e.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 18

A 32 -bit ALU with Sleep Mode for Leakage Power Reduction Manish Kulkarni Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering Auburn University, Auburn, AL 36849 mmk 0002@auburn. edu 3/18/2018 Low Power Design of Electronic Circuits ELEC 6270, Spring 2009

Objectives: q Modify existing ALU circuit to incorporate Sleep mode in order to reduce leakage power q Study the effect of Sleep transistor network on the ALU circuit in Active and in Sleep mode q Design a Sleep transistor network for maximum Leakage Power savings for a given delay overhead q Find a set of vectors which causes minimum leakage power in ALU during the sleep mode 3/18/2018 2

Power Gating: VDD Sleep (a) Header(PMOS) Switches for power gating (b) Footer(NMOS) Switches for power gating (c) Both Header & Footer Switches for power gating David Chinnery, Kurt Keutzer, "Closing the Power Gap Between ASIC & Custom, Tools and Techniques for Low-Power Design", chapter 10, authored by Jerry Frenkil, co-author Srini Venkatraman, Springer 2007. 3/18/2018 3

Circuit Diagram: VDD Data 1 32 - bit ALU 32 Data 2 32 Data Out 32 (Low Vt) Add / Sub GND_V Sleep 3/18/2018 Sleep Transistor Network (High Vt) 4

Design of Sleep Transistor: q It is a tradeoff between Saving in Leakage power and Speed q This method tries to Minimize Leakage power during sleep mode for a given delay penalty Delay of a Gate without Sleep transistor is given by Delay of a Gate with Sleep transistor is given by Where, α is Velocity Saturation Index (1< α < 2) α = 1. 8 for 45 nm Anis, M. , Shawki, A. , Mahmoud , M. , Elmasry, M. , “ Dynamic And Leakage Power Reduction In MTCMOS Circuits Using An Automated Efficient Gate Clustering Technique”, Proc. of 3/18/2018 the 39 th conference on Design Automation, June 2002, pp. 480 -485 5

Design of Sleep Transistor (Cont. . ): Allowing 5% overhead on delay The current flowing through Sleep transistor is expressed as Where, μn = Electron mobility = 150 cm 2/V. s at 90 o. C Cox = 19. 7 X 10 -7 F/m for 45 nm Vt. L = 0. 466 V , Vt. H = 0. 6226 V and VDD = 1. 1 V for 45 nm This is obtained by simulating the ALU circuit and finding the Maximum current through GND The Sleep transistor size is then obtained as = 4774. 4 ≈ 4800 3/18/2018 6

Circuit Diagram: VDD Data 1 32 - bit ALU 32 Data 2 32 Data Out 32 (Low Vt) Add / Sub GND_V T 1 Sleep 3/18/2018 T 2 T 3 T 79 T 80 Sleep Transistor Network (High Vt) 7

Experiment Setup : q The 32 -bit ALU circuit is tested for 200 random vectors of 65 bit each q The vectors are applied with to the circuit in following modes ü 200 vectors with Sleep = 1 i. e. Active Mode ü 200 vectors with Sleep = 0 i. e. Sleep Mode ü 200 vectors with Sleep changing from 1 0 after 100 vectors to get Sleep time ü 200 vectors with Sleep changing from 0 1 after 100 vectors to get Wakeup time q During Sleep mode with 200 vectors a ‘Minimum Leakage’ power consuming vector is identified Some of Results from this experiment have been shown in following slides. 3/18/2018 8

Active Mode: Average Dynamic Power : -1. 804 d. Bm. W = 660. 0 u. W Average Leakage Power : - 14. 683 d. Bm. W = 34. 01 u. W 3/18/2018 9

Sleep Mode: Average Dynamic Power : -35. 197 d. Bm. W = 302. 204 n. W Average Leakage Power : - 36. 174 d. Bm. W = 241. 32 n. W 3/18/2018 10

Sleep Time: Time taken by the Sleep transistor network to bring circuit to sleep mode after the Sleep signal is asserted. Sleep time = 14 n. S 3/18/2018 11

Wakeup Time: Time taken by the Sleep transistor network to bring circuit to normal operation (active) mode after the Sleep signal is de-asserted. Wakeup time = 0. 4 n. S 3/18/2018 12

Sleep Mode Power for Complete Vector Set: Leakage Power = -38. 948 d. Bm. W = 0. 1274 u. W Min. Observed when Input vectors 0 X 3 FB 1 F 6 F 7 & 0 X 84 AA 877 B are applied. Minimum Leakage Power Vector @ 6. 9 u. S 3/18/2018 13

Circuit Diagram (Modified): VDD Sleep Data 1 32 0 X 3 FB 1 F 6 F 7 Data 2 32 - bit ALU 32 0 X 84 AA 877 B Data Out 32 (Low Vt) Add / Sub GND_V T 1 Sleep 3/18/2018 T 2 T 3 T 79 T 80 Sleep Transistor Network (High Vt) 14

Active Sleep with changing input vectors 3/18/2018 15

Active Sleep with Min. Power Vector at input Power Consumption during sleep mode when vectors are varying at the input Power Consumption during sleep mode when constant vector is applied at the input 3/18/2018 16
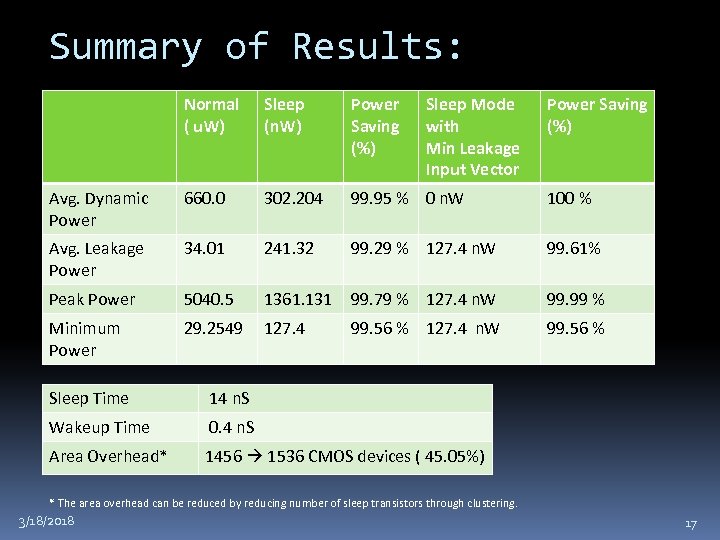
Summary of Results: Normal ( u. W) Sleep (n. W) Power Saving (%) Sleep Mode with Min Leakage Input Vector Avg. Dynamic Power 660. 0 302. 204 99. 95 % 0 n. W 100 % Avg. Leakage Power 34. 01 241. 32 99. 29 % 127. 4 n. W 99. 61% Peak Power 5040. 5 1361. 131 99. 79 % 127. 4 n. W 99. 99 % Minimum Power 29. 2549 127. 4 99. 56 % 127. 4 n. W 99. 56 % Sleep Time 14 n. S Wakeup Time 0. 4 n. S Area Overhead* Power Saving (%) 1456 1536 CMOS devices ( 45. 05%) * The area overhead can be reduced by reducing number of sleep transistors through clustering. 3/18/2018 17

References: q Michael Keating, David Flynn, Robert Aitken, Alan Gibbons, Kaijian Shi, “ Low Power Methodology Manual for System On Chip design” Springer 2008 q Zhigang Hu, Alper Buyuktosunoglu, Viji Srinivasan, Victor Zyuban, Hans Jacobson, Pradip Bose, “Microarchitectural Techniques for Power Gating of Execution Units”, proc. Of ISLPED 2004, pp. 32 -37 q Bushnell, M. , Yu, B. , “A novel dynamic power cutoff technique(DPCT) for active leakage reduction in Deep Submicron CMOS circuits”, Proc. Of ISLPED october, 2006, pp. 214 -219 q Neil H. E. Weste, David Harris, “CMOS VLSI Design” Third Edition, Boston: Pearson, 2005 q David Chinnery, Kurt Keutzer, "Closing the Power Gap Between ASIC & Custom, Tools and Techniques for Low-Power Design", chapter 10, authored by Jerry Frenkil, co-author Srini Venkatraman, Springer 2007. q Anis, M. , Shawki, A. , Mahmoud , M. , Elmasry, M. , “ Dynamic And Leakage Power Reduction In MTCMOS Circuits Using An Automated Efficient Gate Clustering Technique”, Proc. of the 39 th conference on Design Automation, June 2002, pp. 480 -485 3/18/2018 18
c6d41ea755a1277cc24a91fc4f966f1e.ppt