a33684673ae6fb60aac685147783190a.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 148
 A 2 year old would fall into which age group? 1. Infant 2. Early Childhood (Toddler) 3. Early Childhood (Preschooler) 4. Middle Childhood
A 2 year old would fall into which age group? 1. Infant 2. Early Childhood (Toddler) 3. Early Childhood (Preschooler) 4. Middle Childhood
 An adolescent is likely to respond to pain in what manner? 1. loud crying 2. stalling behavior 3. thrashing of limbs 4. more verbalizations
An adolescent is likely to respond to pain in what manner? 1. loud crying 2. stalling behavior 3. thrashing of limbs 4. more verbalizations
 By what age does the anterior fontanel usually close? 1. 6 -8 wks 2. 10 -12 wks 3. 4 -6 mos 4. 12 -18 mos
By what age does the anterior fontanel usually close? 1. 6 -8 wks 2. 10 -12 wks 3. 4 -6 mos 4. 12 -18 mos
 At what age should the nurse expect an infant to begin smiling in response to pleasurable stimuli? 1. 1 mo 2. 2 mos 3. 3 mos 4. 4 mos
At what age should the nurse expect an infant to begin smiling in response to pleasurable stimuli? 1. 1 mo 2. 2 mos 3. 3 mos 4. 4 mos
 When teaching a mother how to prevent accidents while caring for her 6 mo old, the nurse should emphasize that at this age the child can usually: 1. sit up 2. roll over 3. crawl lengthy distances 4. stand while holding furniture
When teaching a mother how to prevent accidents while caring for her 6 mo old, the nurse should emphasize that at this age the child can usually: 1. sit up 2. roll over 3. crawl lengthy distances 4. stand while holding furniture
 A 9 mo Megan reaches to touch an outlet. Her father firmly says “No” & removes her. The nurse should use this opportunity to teach that Megan: 1. is old enough to understand “No” 2. is too young to understand “No” 3. should already know the electrical outlet is dangerous 4. will learn safety issues better if she is spanked
A 9 mo Megan reaches to touch an outlet. Her father firmly says “No” & removes her. The nurse should use this opportunity to teach that Megan: 1. is old enough to understand “No” 2. is too young to understand “No” 3. should already know the electrical outlet is dangerous 4. will learn safety issues better if she is spanked
 9 mo infant has foods such as peas & corn in stools that are not digested. The nurse explains 1. child should not be given fibrous foods until digestive tract matures at 4 yrs 2. child should not be given solid foods until this digestive problem is solved 3. this is abnormal & requires further investigation 4. this is normal because of immaturity of digestive process at this age.
9 mo infant has foods such as peas & corn in stools that are not digested. The nurse explains 1. child should not be given fibrous foods until digestive tract matures at 4 yrs 2. child should not be given solid foods until this digestive problem is solved 3. this is abnormal & requires further investigation 4. this is normal because of immaturity of digestive process at this age.
 What is normally the earliest age at which an infant begins teething w/ eruption of lower central incisors? 1. 4 mo 2. 6 mos 3. 8 mos 4. 12 mos
What is normally the earliest age at which an infant begins teething w/ eruption of lower central incisors? 1. 4 mo 2. 6 mos 3. 8 mos 4. 12 mos
 Which immunizations would you anticipate for a 4 mo old well baby visit? 1. DTa. P, MMR, IPV 2. MMR, Hib, Dtap 3. Dtap, Hib, IPV 4. Varicella, Hep B
Which immunizations would you anticipate for a 4 mo old well baby visit? 1. DTa. P, MMR, IPV 2. MMR, Hib, Dtap 3. Dtap, Hib, IPV 4. Varicella, Hep B
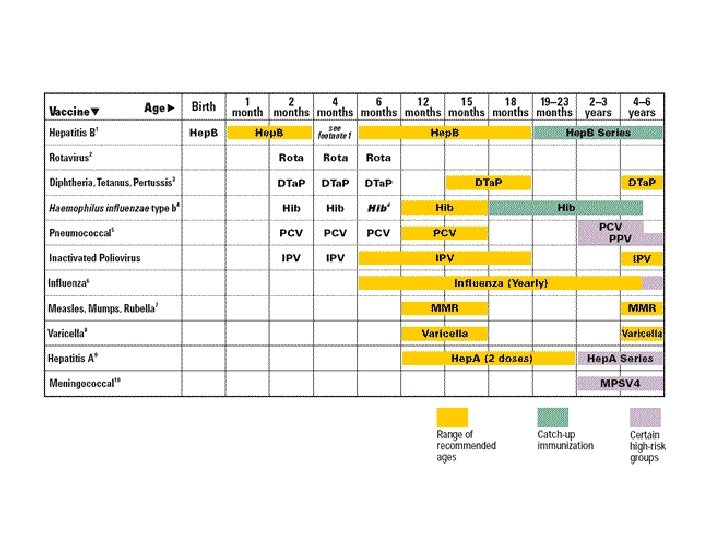
 A 6 mo old develops swelling & redness at site of Dta. P injection. Nurse tells mother to: 1. apply warm pack 2. bring infant back to clinic 3. apply ice pack 4. monitor fever
A 6 mo old develops swelling & redness at site of Dta. P injection. Nurse tells mother to: 1. apply warm pack 2. bring infant back to clinic 3. apply ice pack 4. monitor fever
 Contraindication to receiving an immunization is if a child has: 1. cold 2. otitis media 3. mild diarrhea 4. severe febrile illness
Contraindication to receiving an immunization is if a child has: 1. cold 2. otitis media 3. mild diarrhea 4. severe febrile illness
 Nurse asks which question before administering a 2 nd Dta. P to a child? 1. did the child spit up 2. did the child seem more fussy than usual 3. did you notice any seizure activity after the 1 st 4. was your child’s leg red & swollen
Nurse asks which question before administering a 2 nd Dta. P to a child? 1. did the child spit up 2. did the child seem more fussy than usual 3. did you notice any seizure activity after the 1 st 4. was your child’s leg red & swollen
 Nurse suggest to a mother of a 2 mo old baby w/ colic that she: 1. give her son a warm bath to calm him down 2. arrange for some time away from her son each day to rest 3. provide her son w/ warm sweetened tea when he begins to cry 4. sit comfortably in a quiet, darkened room to hold her son when he cries
Nurse suggest to a mother of a 2 mo old baby w/ colic that she: 1. give her son a warm bath to calm him down 2. arrange for some time away from her son each day to rest 3. provide her son w/ warm sweetened tea when he begins to cry 4. sit comfortably in a quiet, darkened room to hold her son when he cries
 The best strategy for feeding a child w/ failure to thrive is 1. avoid having the same nurse feed the child 2. distract child during meals w/ TV & toys 3. maintain calm, even temperament during feedings 4. vary feeding routines to make feeding time more interesting
The best strategy for feeding a child w/ failure to thrive is 1. avoid having the same nurse feed the child 2. distract child during meals w/ TV & toys 3. maintain calm, even temperament during feedings 4. vary feeding routines to make feeding time more interesting
 Suggestion to help minimize the risk of SIDS include all of the following except: 1. place baby bumpers in crib 2. put infant on back to sleep 3. avoid co-sleeping 4. avoid exposure to 2 nd hand smoke
Suggestion to help minimize the risk of SIDS include all of the following except: 1. place baby bumpers in crib 2. put infant on back to sleep 3. avoid co-sleeping 4. avoid exposure to 2 nd hand smoke
 By 2 ½ yrs a child’s birth wt: 1. doubles 2. triples 3. quadruples 4. is not important
By 2 ½ yrs a child’s birth wt: 1. doubles 2. triples 3. quadruples 4. is not important
 Which of the following is characteristic of development of a 2 ½ yr old? 1. birth wt doubles 2. primary dentition is complete 3. anterior fontanel is open 4 binocularity may be established
Which of the following is characteristic of development of a 2 ½ yr old? 1. birth wt doubles 2. primary dentition is complete 3. anterior fontanel is open 4 binocularity may be established
 A 2 yr old @ play: 1. builds a house w/ bricks 2. is extremely possessive w/ toys 3. attempts to stay in the lines when coloring 4. amuses himself w/ a picture book for 15 mins
A 2 yr old @ play: 1. builds a house w/ bricks 2. is extremely possessive w/ toys 3. attempts to stay in the lines when coloring 4. amuses himself w/ a picture book for 15 mins
 To assess normal physical task for a 15 mo in playpen, nurse observes the toddler is able to: 1. build tower of 6 blocks 2. walk across play pen w/ ease 3. throw toys out of play pen 4. stand holding onto sides
To assess normal physical task for a 15 mo in playpen, nurse observes the toddler is able to: 1. build tower of 6 blocks 2. walk across play pen w/ ease 3. throw toys out of play pen 4. stand holding onto sides
 At what age should a child understand prepositional phrases such as over, under, on? 1. 2 yrs 2. 3 yrs 3. 4 yrs 4. 5 yrs
At what age should a child understand prepositional phrases such as over, under, on? 1. 2 yrs 2. 3 yrs 3. 4 yrs 4. 5 yrs
 A 5 year old stutters a lot when he is excited. The nurse explains that 1. children at this age react negatively for no reason. Ignore it. 2. your child will need speech therapy, but it’s more successful w/ older children 3. do either of you stutter? It’s often inherited. 4. stuttering is common at this age. We can evaluate later if it continues
A 5 year old stutters a lot when he is excited. The nurse explains that 1. children at this age react negatively for no reason. Ignore it. 2. your child will need speech therapy, but it’s more successful w/ older children 3. do either of you stutter? It’s often inherited. 4. stuttering is common at this age. We can evaluate later if it continues
 A hospitalized 4 yr old tells the nurse he is sick because he was “bad”. The best interpretation is: 1. sign of stress 2. common at this age 3. suggestive of maladaptation 4. suggestive of excessive discipline at home
A hospitalized 4 yr old tells the nurse he is sick because he was “bad”. The best interpretation is: 1. sign of stress 2. common at this age 3. suggestive of maladaptation 4. suggestive of excessive discipline at home
 Which of following interventions is helpful for child scratching varicella lesions? 1. warm baths & antifungal powder 2. tepid sponge baths & lubricating creams 3. oatmeal baths & short fingernails 4. baths w/ baby soap & antibiotic ointments
Which of following interventions is helpful for child scratching varicella lesions? 1. warm baths & antifungal powder 2. tepid sponge baths & lubricating creams 3. oatmeal baths & short fingernails 4. baths w/ baby soap & antibiotic ointments
 Which statement accurately describes physical development during school age years? 1. wt almost triples 2. grows an average of 2 inches per year 3. few physical differences apparent among children at end of middle childhood 4. fat gradually increases, which contributes to child’s heavier appearance in the early school age period.
Which statement accurately describes physical development during school age years? 1. wt almost triples 2. grows an average of 2 inches per year 3. few physical differences apparent among children at end of middle childhood 4. fat gradually increases, which contributes to child’s heavier appearance in the early school age period.
 Which describes moral development in younger school age children? 1. standards of behavior now come from within themselves 2. do not yet experience a sense of guilt when they misbehave 3. know the rules & behaviors expected but do not understand the reasons behind them 4. they no longer interpret accidents & misfortunes as punishments for misdeeds
Which describes moral development in younger school age children? 1. standards of behavior now come from within themselves 2. do not yet experience a sense of guilt when they misbehave 3. know the rules & behaviors expected but do not understand the reasons behind them 4. they no longer interpret accidents & misfortunes as punishments for misdeeds
 When planning activities for a 6 yr old leukemia pt the nurse should include: 1. action toys such as a hula hoop 2. stuffed animals, large puzzles, large blocks 3. table games, simple card games & crayons 4. record player, portable radio, children’s magazines
When planning activities for a 6 yr old leukemia pt the nurse should include: 1. action toys such as a hula hoop 2. stuffed animals, large puzzles, large blocks 3. table games, simple card games & crayons 4. record player, portable radio, children’s magazines
 The school nurse has been asked to begin teaching sex ed in 5 th grade. The nurse should recognize that: 1. children in 5 th grade are too young for sex ed 2. children should be discouraged from asking too many questions 3. correct terminology should be reserved for children who are older 4. sex can be presented as a normal part of growth & development
The school nurse has been asked to begin teaching sex ed in 5 th grade. The nurse should recognize that: 1. children in 5 th grade are too young for sex ed 2. children should be discouraged from asking too many questions 3. correct terminology should be reserved for children who are older 4. sex can be presented as a normal part of growth & development
 Characteristics of Turner’s Syndrome include all of the following except: 1. XO chromosomes 2. XXY chromosomes 3. sexual infantilism 4. webbed neck
Characteristics of Turner’s Syndrome include all of the following except: 1. XO chromosomes 2. XXY chromosomes 3. sexual infantilism 4. webbed neck
 Klinefelter Syndromde is usually diagnosed in infancy? 1. True 2. False
Klinefelter Syndromde is usually diagnosed in infancy? 1. True 2. False
 School nurse tells adolescents in the clinic that confidentiality & privacy will be maintained unless a life-threatening situation arises. This practice is: 1. not appropriate in a school setting 2. never appropriate because adolescents are minors 3. important in establishing trusting relationship 4. suggestive that the nurse is meeting his or her own needs
School nurse tells adolescents in the clinic that confidentiality & privacy will be maintained unless a life-threatening situation arises. This practice is: 1. not appropriate in a school setting 2. never appropriate because adolescents are minors 3. important in establishing trusting relationship 4. suggestive that the nurse is meeting his or her own needs
 Adolescents feel an increased need for sleep because: 1. an inadequate diet 2. rapid physical growth 3. dec’d activity that contributes to a feeling of fatigue 4. lack of ambition typical of this age group
Adolescents feel an increased need for sleep because: 1. an inadequate diet 2. rapid physical growth 3. dec’d activity that contributes to a feeling of fatigue 4. lack of ambition typical of this age group
 SAD CHILDREN S- sex A- alcohol/drugs D- depression C- communication H- hostility I- impulsivity L- lethality D- demography R- recent events E- epidemiology (STD’s) N- no hope
SAD CHILDREN S- sex A- alcohol/drugs D- depression C- communication H- hostility I- impulsivity L- lethality D- demography R- recent events E- epidemiology (STD’s) N- no hope
 HEADSS H-home E-education A- activities D- drugs S- suicide/depression S- savagery
HEADSS H-home E-education A- activities D- drugs S- suicide/depression S- savagery
 Stroking sole of foot causes to fan & big toe to dorsiflex? 1. moro reflex 2. extrusion reflex 3. rooting reflex 4. babinski reflex
Stroking sole of foot causes to fan & big toe to dorsiflex? 1. moro reflex 2. extrusion reflex 3. rooting reflex 4. babinski reflex
 Which age group thinks their thoughts are all powerful? 1. school-age 2. toddler 3. pre-schooler 4. infant
Which age group thinks their thoughts are all powerful? 1. school-age 2. toddler 3. pre-schooler 4. infant
 The pre-K physical is an important indicator of a child’s readiness to attend school? 1. True 2. False
The pre-K physical is an important indicator of a child’s readiness to attend school? 1. True 2. False
 What are cues that a toddler is ready to begin potty training? 1. child expresses a desire to be clean & dry 2. child is able to sit, walk & squat 3. child stays dry for 2 hours 4. all of the above
What are cues that a toddler is ready to begin potty training? 1. child expresses a desire to be clean & dry 2. child is able to sit, walk & squat 3. child stays dry for 2 hours 4. all of the above
 Erikson’s task of school-age children: 1. industry v inferiority 2. trust v mistrust 3. autonomy v shame & doubt 4. initiative v guilt
Erikson’s task of school-age children: 1. industry v inferiority 2. trust v mistrust 3. autonomy v shame & doubt 4. initiative v guilt
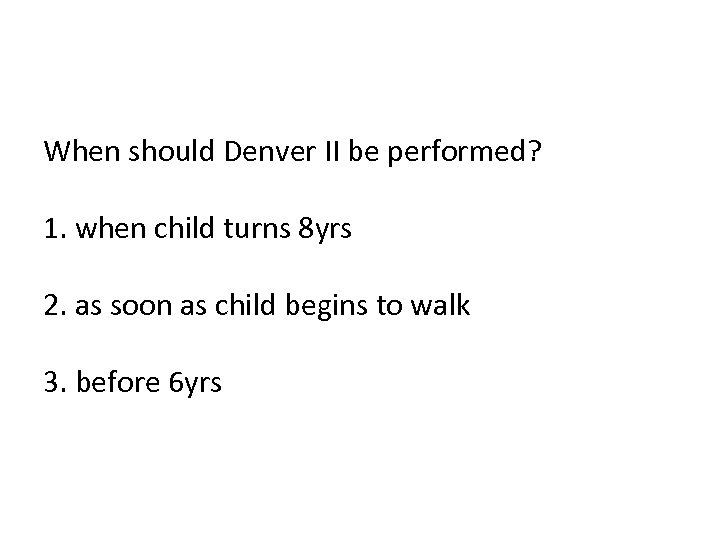 When should Denver II be performed? 1. when child turns 8 yrs 2. as soon as child begins to walk 3. before 6 yrs
When should Denver II be performed? 1. when child turns 8 yrs 2. as soon as child begins to walk 3. before 6 yrs
 MMR & varicella can be given before 12 mos. 1. true 2. false
MMR & varicella can be given before 12 mos. 1. true 2. false
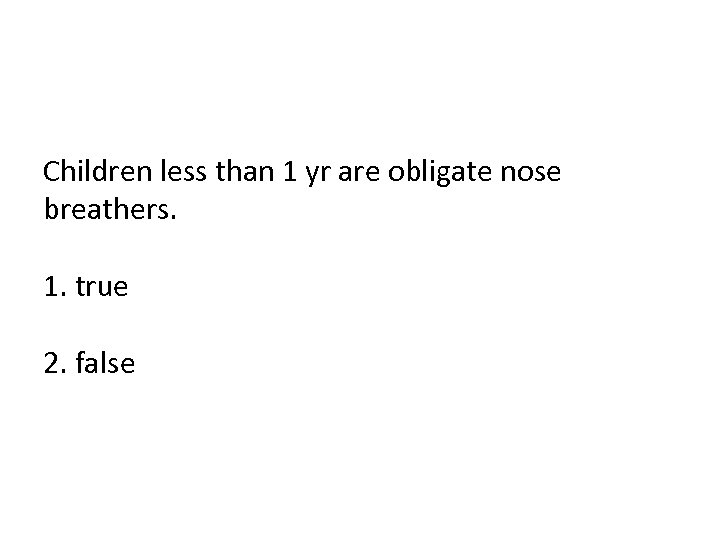 Children less than 1 yr are obligate nose breathers. 1. true 2. false
Children less than 1 yr are obligate nose breathers. 1. true 2. false
 After a tonsillectomy, child begins to vomit bright red blood. Most appropriate initial nursing action would be to: 1. administer prescribed antiemetic 2. turn child to the side 3. notify physician 4. maintain NPO status
After a tonsillectomy, child begins to vomit bright red blood. Most appropriate initial nursing action would be to: 1. administer prescribed antiemetic 2. turn child to the side 3. notify physician 4. maintain NPO status
 Treatments for croup include all of the following except: 1. steroids (Dexamethasone) 2. racemic epi 3. high humidity 4. CPT
Treatments for croup include all of the following except: 1. steroids (Dexamethasone) 2. racemic epi 3. high humidity 4. CPT
 A child is hospitalized w/ epiglottitis. All of the following are appropriate interventions except: 1. keep trach tray @ bedside 2. throat swab to determine cause 3. initial IV Rocephin f/b po 4. corticosteroids
A child is hospitalized w/ epiglottitis. All of the following are appropriate interventions except: 1. keep trach tray @ bedside 2. throat swab to determine cause 3. initial IV Rocephin f/b po 4. corticosteroids
 Hospitalized infant w/ acute bronchitis is NPO & receiving IV fluids. What statement explains the rationale for eliminating feedings. 1. baby does not need as many calories now 2. there is an inc’d risk of fluid overload 3. feeding would be too much of an effort for baby right now 4. baby’s digestive system is slugglish because of the infection
Hospitalized infant w/ acute bronchitis is NPO & receiving IV fluids. What statement explains the rationale for eliminating feedings. 1. baby does not need as many calories now 2. there is an inc’d risk of fluid overload 3. feeding would be too much of an effort for baby right now 4. baby’s digestive system is slugglish because of the infection
 2 yr old hospitalized w/ bacterial pneumonia. Which manifestation would nurse ID as earliest indication of respiratory difficulty? 1. RR 40 -48 2. BP 80/60 3. cyanosis of mucous membranes 4. circumoral/periorbital pallor
2 yr old hospitalized w/ bacterial pneumonia. Which manifestation would nurse ID as earliest indication of respiratory difficulty? 1. RR 40 -48 2. BP 80/60 3. cyanosis of mucous membranes 4. circumoral/periorbital pallor
 4 yr old boy needs to use MDI to treat asthma. He cannot coordinate breathing in order to use it effectively. Nurse should suggest he use a: 1. spacer 2. nebulizer 3. peak flow meter 4. trial of CPT
4 yr old boy needs to use MDI to treat asthma. He cannot coordinate breathing in order to use it effectively. Nurse should suggest he use a: 1. spacer 2. nebulizer 3. peak flow meter 4. trial of CPT
 Child w/ asthma having PFT’s. What is the purpose of PEFR? 1. confirm diagnosis of asthma 2. determine cause of asthma 3. ID triggers of asthma 4. assess severity of asthma
Child w/ asthma having PFT’s. What is the purpose of PEFR? 1. confirm diagnosis of asthma 2. determine cause of asthma 3. ID triggers of asthma 4. assess severity of asthma
 A child w/ CF is predisposed to bronchitis mainly because of: 1. neuromuscular irritiability that causes spasm & constriction of bronchi 2. inc’d salt content in saliva that can irritate & necrose mucous membranes in nasopharynx 3. the associated heart defects of CF that cause CHF & resp distress 4. tenacious secretions that obstruct the bronchioles & resp tract & provide a favorable medium for growth of bacteria
A child w/ CF is predisposed to bronchitis mainly because of: 1. neuromuscular irritiability that causes spasm & constriction of bronchi 2. inc’d salt content in saliva that can irritate & necrose mucous membranes in nasopharynx 3. the associated heart defects of CF that cause CHF & resp distress 4. tenacious secretions that obstruct the bronchioles & resp tract & provide a favorable medium for growth of bacteria
 CF is sometimes first noted by the nurse in the newborn nursery because of the infant’s: 1. excessive crying 2. sternal retractions 3. inc’d HR 4. abdominal distention
CF is sometimes first noted by the nurse in the newborn nursery because of the infant’s: 1. excessive crying 2. sternal retractions 3. inc’d HR 4. abdominal distention
 What change indicates that digestive replacement enzymes in CF client are effective? 1. inc’d mucus excretion in stools 2. dec’d fat excretion in stools 3. inc’d expectoration of mucus 4. wt loss
What change indicates that digestive replacement enzymes in CF client are effective? 1. inc’d mucus excretion in stools 2. dec’d fat excretion in stools 3. inc’d expectoration of mucus 4. wt loss
 4 yr old w/ colostomy due to Hirschsprung’s is admitted b/c of poor wt gain. Which food should the nurse recommend be avoided? 1. ripe bananas 2. spaghetti 3. cheese 4. apples
4 yr old w/ colostomy due to Hirschsprung’s is admitted b/c of poor wt gain. Which food should the nurse recommend be avoided? 1. ripe bananas 2. spaghetti 3. cheese 4. apples
 Which symptom most likely led to mother seeking health care for child w/ Hirschsprung’s? 1. diarrhea 2. projectile vomiting 3. regurgitation of feedings 4. foul-smelling, ribbon-like stools
Which symptom most likely led to mother seeking health care for child w/ Hirschsprung’s? 1. diarrhea 2. projectile vomiting 3. regurgitation of feedings 4. foul-smelling, ribbon-like stools
 Which assessment would RN do first when child returns to unit after an emergency appendectomy? 1. bladder 2. IV fluid infusion site 3. NG tube function 4. dressing
Which assessment would RN do first when child returns to unit after an emergency appendectomy? 1. bladder 2. IV fluid infusion site 3. NG tube function 4. dressing
 Nurse should carefully observe infant w/ tentative dx of pyloric stenosis for: 1. quality of cry 2. quality of stool 3. signs of dehydration 4. coughing & gagging after feeding
Nurse should carefully observe infant w/ tentative dx of pyloric stenosis for: 1. quality of cry 2. quality of stool 3. signs of dehydration 4. coughing & gagging after feeding
 Infant returned to unit 4 hrs ago after surgery to correct pyloric stenosis. Most important nursing intervention: 1. feed small amounts frequently & assess emesis 2. keep infant NPO & encourage parent to perform oral care 3. monitor I/O & administer meds 4. monitor hydration status & encourage parents to rest.
Infant returned to unit 4 hrs ago after surgery to correct pyloric stenosis. Most important nursing intervention: 1. feed small amounts frequently & assess emesis 2. keep infant NPO & encourage parent to perform oral care 3. monitor I/O & administer meds 4. monitor hydration status & encourage parents to rest.
 A barium enema can dx & may also treat intussusception. 1. true 2. false
A barium enema can dx & may also treat intussusception. 1. true 2. false
 Which measure is inappropriate for pediatric client returning to unit after repair of cleft palate? 1. close observation for early manifestations of resp obstruction 2. position on abd or side to provide adequate drainage 3. frequent sxn of oropharynx to clear secretions 4. arm restraints to prevent hands or other objects from getting in mouth
Which measure is inappropriate for pediatric client returning to unit after repair of cleft palate? 1. close observation for early manifestations of resp obstruction 2. position on abd or side to provide adequate drainage 3. frequent sxn of oropharynx to clear secretions 4. arm restraints to prevent hands or other objects from getting in mouth
 1 hr after admission to nursery, nurse observes infant RR 70 w/ excessive drooling. 1 st action should be: 1. continue to observe closely for other s/s 2. reposition to side-lying position & call physician 3. sxn mouth & place supine w/ HOB elevated 4. provide supplemental O 2 when RR>70
1 hr after admission to nursery, nurse observes infant RR 70 w/ excessive drooling. 1 st action should be: 1. continue to observe closely for other s/s 2. reposition to side-lying position & call physician 3. sxn mouth & place supine w/ HOB elevated 4. provide supplemental O 2 when RR>70
 What is the reason for positioning an infant w/ TEF supine w/ HOB elevated prior to surgery? 1. reduce resp & cardiac workload 2. alleviate press of distended abd contents on diaphragm 3. inc pooling of secretions in bottom of upper esophageal pouch 4. reduce gastric distention by allowing air bubbles from fistual to escape
What is the reason for positioning an infant w/ TEF supine w/ HOB elevated prior to surgery? 1. reduce resp & cardiac workload 2. alleviate press of distended abd contents on diaphragm 3. inc pooling of secretions in bottom of upper esophageal pouch 4. reduce gastric distention by allowing air bubbles from fistual to escape
 Characteristics of celiac disease include all except: 1. constipation 2. general malnutrition 3. abdominal distention 4. vitamin deficiencies
Characteristics of celiac disease include all except: 1. constipation 2. general malnutrition 3. abdominal distention 4. vitamin deficiencies
 The normal life span for a sickled cell is: 1. 120 days 2. 40 -60 days 3. 20 -25 days 4. 7 -10 days
The normal life span for a sickled cell is: 1. 120 days 2. 40 -60 days 3. 20 -25 days 4. 7 -10 days
 10 yr old client w/ sickle cell crisis. Which action is contraindicated? 1. administer O 2 via NC as prescribed 2. encourage increase oral fluid intake 3. administer narcotics for pain 4. encourage as much exercise as possible
10 yr old client w/ sickle cell crisis. Which action is contraindicated? 1. administer O 2 via NC as prescribed 2. encourage increase oral fluid intake 3. administer narcotics for pain 4. encourage as much exercise as possible
 To prevent thrombus formation in capillaries, as well as other problems from stasis & clotting of blood in the sickling process, the nurse should: 1. administer O 2 2. see client maintains bed rest 3. increase fluids by mouth 4. administer ordered heparin or other anticoagulant
To prevent thrombus formation in capillaries, as well as other problems from stasis & clotting of blood in the sickling process, the nurse should: 1. administer O 2 2. see client maintains bed rest 3. increase fluids by mouth 4. administer ordered heparin or other anticoagulant
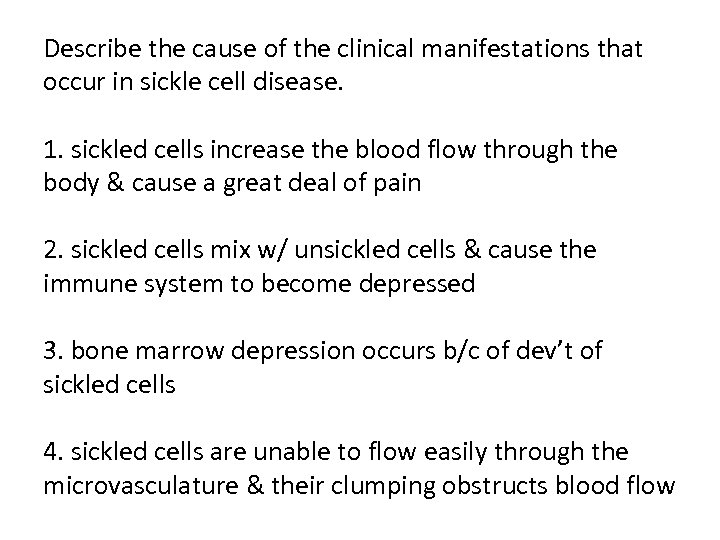 Describe the cause of the clinical manifestations that occur in sickle cell disease. 1. sickled cells increase the blood flow through the body & cause a great deal of pain 2. sickled cells mix w/ unsickled cells & cause the immune system to become depressed 3. bone marrow depression occurs b/c of dev’t of sickled cells 4. sickled cells are unable to flow easily through the microvasculature & their clumping obstructs blood flow
Describe the cause of the clinical manifestations that occur in sickle cell disease. 1. sickled cells increase the blood flow through the body & cause a great deal of pain 2. sickled cells mix w/ unsickled cells & cause the immune system to become depressed 3. bone marrow depression occurs b/c of dev’t of sickled cells 4. sickled cells are unable to flow easily through the microvasculature & their clumping obstructs blood flow
 A home care nurse instructing parents of child w/ iron deficiency anemia regarding the admin of liquid oral iron agent supplement tells them to: 1. admin through a straw 2. admin at mealtimes 3. add to formula for easy admin 4. mix w/ cereal to admin
A home care nurse instructing parents of child w/ iron deficiency anemia regarding the admin of liquid oral iron agent supplement tells them to: 1. admin through a straw 2. admin at mealtimes 3. add to formula for easy admin 4. mix w/ cereal to admin
 Child w/ B-thalassemia (Cooleys Anemia) receiving long term blood transfusion therapy. Chelation therapy is prescribed to prevent organ damage from presence of too much Fe as result of transfusions. Which med would nurse anticipate to be prescribed in chelation therapy? 1. dalterparin sodium (Fragmin) 2. meropenem (Merrem) 3. molindone (Moban) 4. deferoxamine (Desferal)
Child w/ B-thalassemia (Cooleys Anemia) receiving long term blood transfusion therapy. Chelation therapy is prescribed to prevent organ damage from presence of too much Fe as result of transfusions. Which med would nurse anticipate to be prescribed in chelation therapy? 1. dalterparin sodium (Fragmin) 2. meropenem (Merrem) 3. molindone (Moban) 4. deferoxamine (Desferal)
 Medical management/interventions for hemophilia may include all of the following except: 1. DDAVP 2. transfusions 3. aspirin 4. shaving only w/ electric razor
Medical management/interventions for hemophilia may include all of the following except: 1. DDAVP 2. transfusions 3. aspirin 4. shaving only w/ electric razor
 8 yr old has neutrophil count of 200 after prolong course of Cytarabine & methotrexate. Primary nursing action: 1. initiate strict isolation 2. notify physcian 3. increase fluid intake 4. restrict staff & visitors
8 yr old has neutrophil count of 200 after prolong course of Cytarabine & methotrexate. Primary nursing action: 1. initiate strict isolation 2. notify physcian 3. increase fluid intake 4. restrict staff & visitors
 Child w/ leukemia has mucosal ulceration in mouth & throat d/t neutropenia. An intervention to ease discomfort is: 1. suck on lemon glycerin swabs 2. apply milk of mag w/ soft applicator 3. rinse w/ NS frequently 4. gargle w/ hydrogen peroxide q 2
Child w/ leukemia has mucosal ulceration in mouth & throat d/t neutropenia. An intervention to ease discomfort is: 1. suck on lemon glycerin swabs 2. apply milk of mag w/ soft applicator 3. rinse w/ NS frequently 4. gargle w/ hydrogen peroxide q 2
 What is the major assessment parameter that would lead the nurse to conclude that an infant has coarctation of the aorta? 1. lower extremity BP is >10 mm less than upper extremity 2. tachycardia & cyanosis 3. washing machine murmur 4. tet spells
What is the major assessment parameter that would lead the nurse to conclude that an infant has coarctation of the aorta? 1. lower extremity BP is >10 mm less than upper extremity 2. tachycardia & cyanosis 3. washing machine murmur 4. tet spells
 Nurse caring for infant w/ congenital heart disease monitoring closely for signs of CHF. Nurse assesses for which early sign? 1. cough 2. tachycardia 3. slow & shallow breathing 4. pallor
Nurse caring for infant w/ congenital heart disease monitoring closely for signs of CHF. Nurse assesses for which early sign? 1. cough 2. tachycardia 3. slow & shallow breathing 4. pallor
 Prostaglandin prescribed for child w/ transposition of great arteries. Mother asks why child needs this medicine. Most appropriate response: 1. maintains adequate hormone control 2. maintains position of great arteries 3. provides adequate O 2 saturation & maintains cardiac output 4. prevents Tet spells
Prostaglandin prescribed for child w/ transposition of great arteries. Mother asks why child needs this medicine. Most appropriate response: 1. maintains adequate hormone control 2. maintains position of great arteries 3. provides adequate O 2 saturation & maintains cardiac output 4. prevents Tet spells
 RN caring for child w/ Kawasaki’s. Mother asks about disorder. RN responds that: 1. it is an acquired cell-mediated immunodeficiency disorder 2. it is an inflammatory autoimmune disease that affects connective tissue of heart, joints & subq tissue 3. chronic multi-system autoimmune disease characterized by inflammation of connnective tissue 4. aka mucocutaneous lymph node syndrome & is a febrile, generalized vasculitis of unknown origin
RN caring for child w/ Kawasaki’s. Mother asks about disorder. RN responds that: 1. it is an acquired cell-mediated immunodeficiency disorder 2. it is an inflammatory autoimmune disease that affects connective tissue of heart, joints & subq tissue 3. chronic multi-system autoimmune disease characterized by inflammation of connnective tissue 4. aka mucocutaneous lymph node syndrome & is a febrile, generalized vasculitis of unknown origin
 5 yr old w/ autism lives w/ mother, 2 brothers, grandmother. Child was recently w/ resp infection & has special needs b/c of autism. Which of following describes family’s composition. 1. nuclear family 2. blended family 3. extended family 4 same sex family
5 yr old w/ autism lives w/ mother, 2 brothers, grandmother. Child was recently w/ resp infection & has special needs b/c of autism. Which of following describes family’s composition. 1. nuclear family 2. blended family 3. extended family 4 same sex family
 Above scenario: what would be best approach for nurse to take when first assessing this child? 1. ask child’s family to step out of room 2. ask child’s mother what approach would work best 3. ask child if she is allergic to anything 4. ask child’s grandmother to interpret child’s behavior
Above scenario: what would be best approach for nurse to take when first assessing this child? 1. ask child’s family to step out of room 2. ask child’s mother what approach would work best 3. ask child if she is allergic to anything 4. ask child’s grandmother to interpret child’s behavior

 Match the parenting styles • Democratic • Dictatorial • Permissive • A. your curfew is 10 pm. You know that • As long as you have your homework done, I don’t care when you come home • Tonight is a school night, so you need to come by 10 pm
Match the parenting styles • Democratic • Dictatorial • Permissive • A. your curfew is 10 pm. You know that • As long as you have your homework done, I don’t care when you come home • Tonight is a school night, so you need to come by 10 pm
 When providing care to a child, the nurse should not be concerned about what the child thinks about care. 1. True 2. false
When providing care to a child, the nurse should not be concerned about what the child thinks about care. 1. True 2. false
 When a child is admitted to the pediatric unit, the RN should keep in mind the family of child also needs nursing care. 1. true 2. false
When a child is admitted to the pediatric unit, the RN should keep in mind the family of child also needs nursing care. 1. true 2. false
 Info: guidelines for promoting healthy behaviors in children: -set realistic limits & expectations based on developmental tasks -validate child’s feelings -provide reinforcement for appropriate behavior -focus on child’s behavior when disciplining the child -explain expectations to a child in a manner the child can understand
Info: guidelines for promoting healthy behaviors in children: -set realistic limits & expectations based on developmental tasks -validate child’s feelings -provide reinforcement for appropriate behavior -focus on child’s behavior when disciplining the child -explain expectations to a child in a manner the child can understand
 List 5 basic assessments that should be included in the physical assessment of a child over 3 years of age:
List 5 basic assessments that should be included in the physical assessment of a child over 3 years of age:
 List 5 basic assessments that should be included in the physical assessment of a child over 3 years of age: -height -weight -temperature -RR -HR -BP
List 5 basic assessments that should be included in the physical assessment of a child over 3 years of age: -height -weight -temperature -RR -HR -BP
 Rank the following in the order they should be performed on a 9 mo old. __axillary temp __RR __wt __HR
Rank the following in the order they should be performed on a 9 mo old. __axillary temp __RR __wt __HR
 Match the reflex • Rooting • Palmar • Plantar A. Extension of arm & leg on side when head is turned to that side w/ flexion of arm & leg on opposite side B. Legs flex, arms & hands extend when startled by loud noise C. Turns head to side when cheek or mouth is touched • Moro D. Will grasp object when palm is touched • Asymmetric tonic neck E. Toes will curl downward when sole of foot it touched
Match the reflex • Rooting • Palmar • Plantar A. Extension of arm & leg on side when head is turned to that side w/ flexion of arm & leg on opposite side B. Legs flex, arms & hands extend when startled by loud noise C. Turns head to side when cheek or mouth is touched • Moro D. Will grasp object when palm is touched • Asymmetric tonic neck E. Toes will curl downward when sole of foot it touched
 Parent of a 17 mo old toddler is frustrated w/ toddler’s behavior. Parent tells RN the child is “bad” but doesn’t know how to make toddler behave better. Which response should RN make? 1. allow your child to learn by trial & error 2. consistently enforce well-defined limits, such as no climbing on the counters 3. reward your child’s good behavior, but ignore the bad behaviors 4. punish your child when he behaves badly
Parent of a 17 mo old toddler is frustrated w/ toddler’s behavior. Parent tells RN the child is “bad” but doesn’t know how to make toddler behave better. Which response should RN make? 1. allow your child to learn by trial & error 2. consistently enforce well-defined limits, such as no climbing on the counters 3. reward your child’s good behavior, but ignore the bad behaviors 4. punish your child when he behaves badly
 2 yr old throws tantrums & says “No” every time parent tries to help her. Parent knows toddlers do this but does not understand why. Nurse explains it is normal expression of desire to: 1. increase independence 2. develop sense of trust 3. gratify oral fixation 4. finish project they set out to do
2 yr old throws tantrums & says “No” every time parent tries to help her. Parent knows toddlers do this but does not understand why. Nurse explains it is normal expression of desire to: 1. increase independence 2. develop sense of trust 3. gratify oral fixation 4. finish project they set out to do
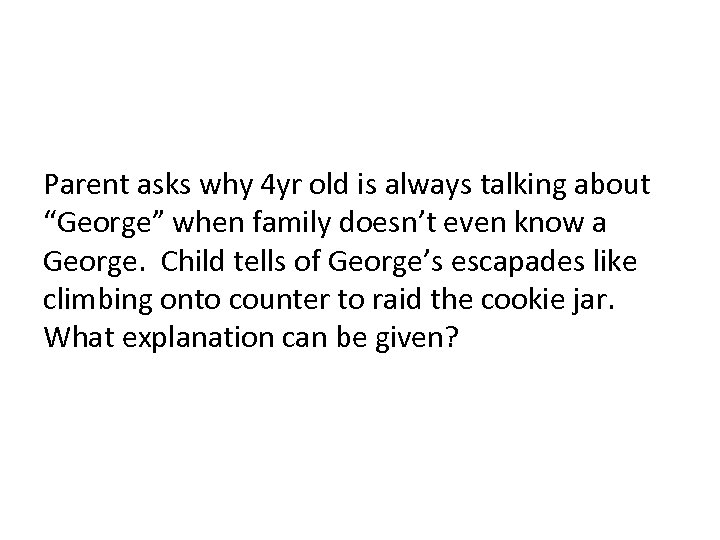 Parent asks why 4 yr old is always talking about “George” when family doesn’t even know a George. Child tells of George’s escapades like climbing onto counter to raid the cookie jar. What explanation can be given?
Parent asks why 4 yr old is always talking about “George” when family doesn’t even know a George. Child tells of George’s escapades like climbing onto counter to raid the cookie jar. What explanation can be given?
 Which strategies can be used to help a preschool child go to sleep? (all that apply) 1. let child fall asleep in another room 2. place a night light in child’s room 3. keep a regular bedtime schedule 4. insist child take a nap to make up for lost nighttime sleep 5. read a bedtime story to child 6. allow child to play quietly in room
Which strategies can be used to help a preschool child go to sleep? (all that apply) 1. let child fall asleep in another room 2. place a night light in child’s room 3. keep a regular bedtime schedule 4. insist child take a nap to make up for lost nighttime sleep 5. read a bedtime story to child 6. allow child to play quietly in room
 Magical thinking can be the cause of preschooler’s feelings of guilt. 1. true 2. false
Magical thinking can be the cause of preschooler’s feelings of guilt. 1. true 2. false
 Which statement indicates that the parent of a preschooler understands the need for injury prevention? 1. my hcild is able to watch his younger brother when they play outside 2. now that my child does not put everything in his mouth, I can remove the locks on my cabinets 3. I programmed the number to poison control into my cell phone 4. my child rides his bike in the street w/ the bigger kids
Which statement indicates that the parent of a preschooler understands the need for injury prevention? 1. my hcild is able to watch his younger brother when they play outside 2. now that my child does not put everything in his mouth, I can remove the locks on my cabinets 3. I programmed the number to poison control into my cell phone 4. my child rides his bike in the street w/ the bigger kids
 Which activity demonstrates a school-age child is working toward a healthy achievement of Erikson’s task of industry? 1. child brings home completed school work to show parents 2. child prefers to watch cartoons on TV rather than practice piano 3. child depends on older siblings to tell him what to wear to school 4. child refuses to play by rules of a board game
Which activity demonstrates a school-age child is working toward a healthy achievement of Erikson’s task of industry? 1. child brings home completed school work to show parents 2. child prefers to watch cartoons on TV rather than practice piano 3. child depends on older siblings to tell him what to wear to school 4. child refuses to play by rules of a board game
 What should be included in a course on safety during school-age years? (all that apply) 1. keeping stair gates closed 2. wearing helmets when riding bikes or skateboards 3. playing safely on trampolines 4. firearm safety 5. wearing seat belts
What should be included in a course on safety during school-age years? (all that apply) 1. keeping stair gates closed 2. wearing helmets when riding bikes or skateboards 3. playing safely on trampolines 4. firearm safety 5. wearing seat belts
 Info: strategies to decrease risk of obesity in school-age children: -avoid or reduce fast-food meals -encourage physical activities -do not use food as a reward -provide nutritious meals
Info: strategies to decrease risk of obesity in school-age children: -avoid or reduce fast-food meals -encourage physical activities -do not use food as a reward -provide nutritious meals
 ID order of sexual maturation in males: __voice changes __pubic hair appears __size of testes increase __downy hair appears on upper lip __axillary hair grows __rapid growth of genitalia occurs
ID order of sexual maturation in males: __voice changes __pubic hair appears __size of testes increase __downy hair appears on upper lip __axillary hair grows __rapid growth of genitalia occurs
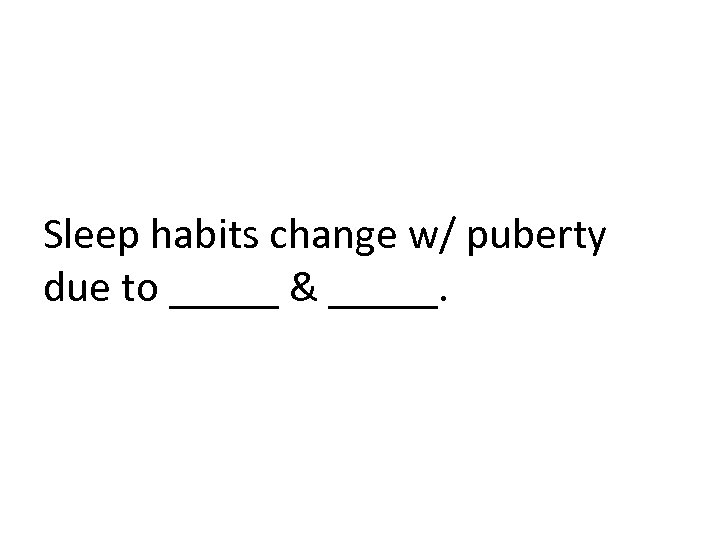 Sleep habits change w/ puberty due to _____ & _____.
Sleep habits change w/ puberty due to _____ & _____.
 Adolescents are likely to take risks because 1. they are incapable of thinking at an adult level 2. they see themselves as invincible to bad outcomes 3. they have a short attention span 4. they have no respect for the rules
Adolescents are likely to take risks because 1. they are incapable of thinking at an adult level 2. they see themselves as invincible to bad outcomes 3. they have a short attention span 4. they have no respect for the rules
 Adolescent see school nurse for shoulder pain. Nurse discovers he’s lifting weights daily to prepare for baseball. Nurse should: 1. encourage use of braces when lifting 2. discourage continuation of weight lifting 3. instruct him to consult w/ coach to make sure proper technique is being used 4. discuss possibility of arthritis d/t shoulder injury
Adolescent see school nurse for shoulder pain. Nurse discovers he’s lifting weights daily to prepare for baseball. Nurse should: 1. encourage use of braces when lifting 2. discourage continuation of weight lifting 3. instruct him to consult w/ coach to make sure proper technique is being used 4. discuss possibility of arthritis d/t shoulder injury
 Info: behavioral changes that may indicate an adolescent is socially isolated or depressed: -poor school performance -lack of interest in things that had been of interest in the past -disturbances in sleep or appetite -expression of suicidal thoughts
Info: behavioral changes that may indicate an adolescent is socially isolated or depressed: -poor school performance -lack of interest in things that had been of interest in the past -disturbances in sleep or appetite -expression of suicidal thoughts
 When working w/ a child who is developmentally delayed, the nurse should use diversional activities appropriate for the child’s age. 1. true 2. false
When working w/ a child who is developmentally delayed, the nurse should use diversional activities appropriate for the child’s age. 1. true 2. false
 Match the play activities w/ the appropriate age 1. Wacthing black & white mobiles 2. Playing peek-a-boo 3. Holding a soft rattle 4. Playing w/ cloth books 5. Banging large blocks A. B. C. D. E. 1 -3 yrs 3 -6 mos Birth-3 mos 9 -12 mos 6 -9 mos
Match the play activities w/ the appropriate age 1. Wacthing black & white mobiles 2. Playing peek-a-boo 3. Holding a soft rattle 4. Playing w/ cloth books 5. Banging large blocks A. B. C. D. E. 1 -3 yrs 3 -6 mos Birth-3 mos 9 -12 mos 6 -9 mos
 Which activity is expected for a preschooler? 1. playing on a soccer team 2. reading a book quietly 3. playing the violin 4. finger painting
Which activity is expected for a preschooler? 1. playing on a soccer team 2. reading a book quietly 3. playing the violin 4. finger painting
 What age group is most likely to engage in collecting trading cards? 1. toddler 2. preschooler 3. school-age 4. adolescent
What age group is most likely to engage in collecting trading cards? 1. toddler 2. preschooler 3. school-age 4. adolescent
 Which of following interventions is most appropriate for needs of a 7 yr old being hospitalized for an extended time? 1. bring security items such as a toy & blanket 2. provide play activities that foster sense of normal routine 3. limit choices whenever possible 4. restrict family visiting hours
Which of following interventions is most appropriate for needs of a 7 yr old being hospitalized for an extended time? 1. bring security items such as a toy & blanket 2. provide play activities that foster sense of normal routine 3. limit choices whenever possible 4. restrict family visiting hours
 Which tests will be most accurate for diagnosing asthma? 1. ABG’s 2. CXR 3. PFT’s 4. allergy tests
Which tests will be most accurate for diagnosing asthma? 1. ABG’s 2. CXR 3. PFT’s 4. allergy tests
 Which med should nurse prepare for an acute asthma attack? 1. terbutaline (Brethine) 2. beclomethasone dipropionate (QVAR) 3. prenisone (Deltasone) 4. albuterol (Proventil)
Which med should nurse prepare for an acute asthma attack? 1. terbutaline (Brethine) 2. beclomethasone dipropionate (QVAR) 3. prenisone (Deltasone) 4. albuterol (Proventil)
 Which of the following is an adverse reaction to fluticasone propionate (Flovent) that should be reported to the PCP? 1. change in mood 2. difficulty speaking, hoarseness, &/or white patches in mouth 3. tachycardia & tremors 4. fatigue & malaise
Which of the following is an adverse reaction to fluticasone propionate (Flovent) that should be reported to the PCP? 1. change in mood 2. difficulty speaking, hoarseness, &/or white patches in mouth 3. tachycardia & tremors 4. fatigue & malaise
 Which of the following should be included in client teaching to eliminate allergens? 1. avoid keeping pets in the home 2. prepare meals w/ foods that contain no allergens 3. enforce a no-smoking policy in the house & car 4. maintain humidity in home between 30 -50% 5. avoid excessive temperature extremes 6. keep air & heating ducts clean & change filters monthly 7. keep furniture, floors & walls clean & dry 8. dust near sleeping & personal spaces 9. monitor periods of exercise for exacerbations 10. cover mouth in cold weather 11. try to remain calm during periods of extreme emotions
Which of the following should be included in client teaching to eliminate allergens? 1. avoid keeping pets in the home 2. prepare meals w/ foods that contain no allergens 3. enforce a no-smoking policy in the house & car 4. maintain humidity in home between 30 -50% 5. avoid excessive temperature extremes 6. keep air & heating ducts clean & change filters monthly 7. keep furniture, floors & walls clean & dry 8. dust near sleeping & personal spaces 9. monitor periods of exercise for exacerbations 10. cover mouth in cold weather 11. try to remain calm during periods of extreme emotions
 6 yr old pre-op for tonsillectomy. Temp 38 (100. 6), HR 104, RR 32, BP 96/62, Sp. O 2 97%. Child c/o sore throat. What is the next appropriate action the nurse should take? 1. record VS & prepare for transport to OR 2. ask parents how long child has had sore throat & document 3. notify OR & PCP & await response 4. offer analgesic & warm fluids until PCP evaluates child for surgery
6 yr old pre-op for tonsillectomy. Temp 38 (100. 6), HR 104, RR 32, BP 96/62, Sp. O 2 97%. Child c/o sore throat. What is the next appropriate action the nurse should take? 1. record VS & prepare for transport to OR 2. ask parents how long child has had sore throat & document 3. notify OR & PCP & await response 4. offer analgesic & warm fluids until PCP evaluates child for surgery
 Post-op tonsillectomy. Which of following is s/s of post-op bleeding? 1. Hgb 11. 6 & Hct 37% 2. inflamed & reddened throat 3. frequent swallowing & clearing of throat 4. blood tinged mucus
Post-op tonsillectomy. Which of following is s/s of post-op bleeding? 1. Hgb 11. 6 & Hct 37% 2. inflamed & reddened throat 3. frequent swallowing & clearing of throat 4. blood tinged mucus
 A pediatric resp disorder that is considered a medical emergency is: 1. pharyngitis 2. bronchitis 3. bacterial epiglottitis 4. acute spasmodic laryngitis
A pediatric resp disorder that is considered a medical emergency is: 1. pharyngitis 2. bronchitis 3. bacterial epiglottitis 4. acute spasmodic laryngitis
 Manifestations of bacterial epiglottitis include: 1. hoarseness & difficulty speaking 2. difficulty swallowing 3. low-grade fever 4. drooling 5. dry, barking cough 6. stridor
Manifestations of bacterial epiglottitis include: 1. hoarseness & difficulty speaking 2. difficulty swallowing 3. low-grade fever 4. drooling 5. dry, barking cough 6. stridor
 How do you prevent most cases of bacterial epiglottitis?
How do you prevent most cases of bacterial epiglottitis?
 RSV is dx’d w/: 1. collection of sputum specimen 2. throat culture 3. nasal aspiration 4. obtaining blood for CBC
RSV is dx’d w/: 1. collection of sputum specimen 2. throat culture 3. nasal aspiration 4. obtaining blood for CBC
 Info: cystic fibrosis is hereditary & transmitted as an autosomal recessive trait’ thus, both parents must be carriers of the gene.
Info: cystic fibrosis is hereditary & transmitted as an autosomal recessive trait’ thus, both parents must be carriers of the gene.
 Which best describes the stools of a child w/ CF? 1. hard & dry w/ difficult evacuation 2. dark-colored tarry stools 3. blood-streaked w/ mucus strands 4. fatty & foul-smelling
Which best describes the stools of a child w/ CF? 1. hard & dry w/ difficult evacuation 2. dark-colored tarry stools 3. blood-streaked w/ mucus strands 4. fatty & foul-smelling
 Which of the following are seen in CF? (all that apply) 1. wheezy respirations 2. clubbing of fingers & toes 3. barrel shaped chest 4. thin watery mucus drainage 5. rapid growth spurts
Which of the following are seen in CF? (all that apply) 1. wheezy respirations 2. clubbing of fingers & toes 3. barrel shaped chest 4. thin watery mucus drainage 5. rapid growth spurts
 Appropriate intervention for CF? 1. admin fat-soluble forms of vit A, D, E & K 2. admin pancreatic enzymes w/ food & snacks 3. place child on low-cal, low-protein diet 4. limit fluids
Appropriate intervention for CF? 1. admin fat-soluble forms of vit A, D, E & K 2. admin pancreatic enzymes w/ food & snacks 3. place child on low-cal, low-protein diet 4. limit fluids
 Info: Manifestations of Digoxin toxicity: decreased appetite N&V increased sweating decreased urine output
Info: Manifestations of Digoxin toxicity: decreased appetite N&V increased sweating decreased urine output
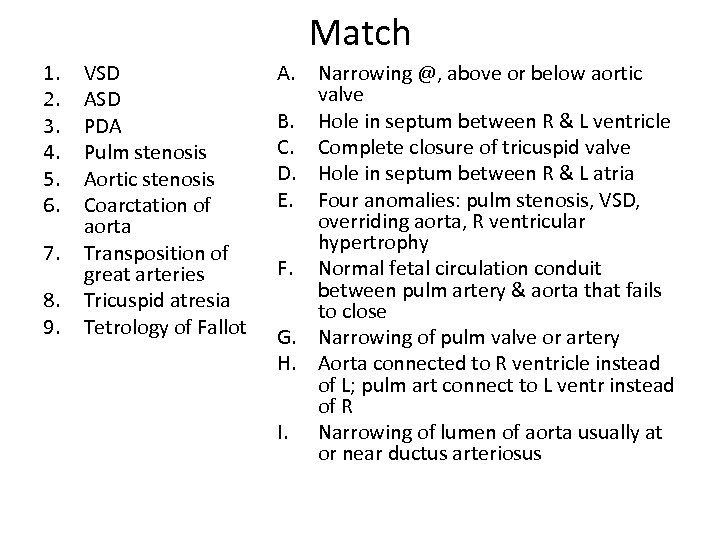 Match 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. VSD ASD PDA Pulm stenosis Aortic stenosis Coarctation of aorta Transposition of great arteries Tricuspid atresia Tetrology of Fallot A. Narrowing @, above or below aortic valve B. Hole in septum between R & L ventricle C. Complete closure of tricuspid valve D. Hole in septum between R & L atria E. Four anomalies: pulm stenosis, VSD, overriding aorta, R ventricular hypertrophy F. Normal fetal circulation conduit between pulm artery & aorta that fails to close G. Narrowing of pulm valve or artery H. Aorta connected to R ventricle instead of L; pulm art connect to L ventr instead of R I. Narrowing of lumen of aorta usually at or near ductus arteriosus
Match 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. VSD ASD PDA Pulm stenosis Aortic stenosis Coarctation of aorta Transposition of great arteries Tricuspid atresia Tetrology of Fallot A. Narrowing @, above or below aortic valve B. Hole in septum between R & L ventricle C. Complete closure of tricuspid valve D. Hole in septum between R & L atria E. Four anomalies: pulm stenosis, VSD, overriding aorta, R ventricular hypertrophy F. Normal fetal circulation conduit between pulm artery & aorta that fails to close G. Narrowing of pulm valve or artery H. Aorta connected to R ventricle instead of L; pulm art connect to L ventr instead of R I. Narrowing of lumen of aorta usually at or near ductus arteriosus
 match 1. Digoxin (Lanoxin) 2. Furosemide (Lasix) 3. Captopril (Capoten) 4. oxygen A. Rids body of excess fluid & sodium B. Increases tissue oxygenation C. Improves myocardial contractility D. Reduces afterload
match 1. Digoxin (Lanoxin) 2. Furosemide (Lasix) 3. Captopril (Capoten) 4. oxygen A. Rids body of excess fluid & sodium B. Increases tissue oxygenation C. Improves myocardial contractility D. Reduces afterload
 Match condition w/ possible manifestation/complication 1. Anemia A. Bruising, nosebleed 2. Neutropenia B. Fever, pneumonia 3. Thrombocytopenia C. Fatigue, SOB
Match condition w/ possible manifestation/complication 1. Anemia A. Bruising, nosebleed 2. Neutropenia B. Fever, pneumonia 3. Thrombocytopenia C. Fatigue, SOB
 Child w/ leukemia is experiencing severe thrombocytopenia. Which nursing interventions will avoid the risk for injury based on this dx? 1. avoid injections & skin punctures 2. wash hands frequently 3. limit visitors 4. monitor platelet count 5. avoid rectal temperatures 6. monitor fever
Child w/ leukemia is experiencing severe thrombocytopenia. Which nursing interventions will avoid the risk for injury based on this dx? 1. avoid injections & skin punctures 2. wash hands frequently 3. limit visitors 4. monitor platelet count 5. avoid rectal temperatures 6. monitor fever
 Child w/ leukemia is hospitalized w/ lethargy, HA, vomiting, blurred vision. Which complication do these suggest? 1. anemia 2. hypermetabolism 3. increased intracranial pressure 4. infiltration of leukemic cells into bone marrow
Child w/ leukemia is hospitalized w/ lethargy, HA, vomiting, blurred vision. Which complication do these suggest? 1. anemia 2. hypermetabolism 3. increased intracranial pressure 4. infiltration of leukemic cells into bone marrow
 List nursing interventions to promote adequate nutritional intake in a child w/ leukemia undergoing chemotherapy.
List nursing interventions to promote adequate nutritional intake in a child w/ leukemia undergoing chemotherapy.
 -Involve child in food selection -do not give favorite foods when nauseated -medicate for nausea before meals -encourage small, frequent meals -encourage high protein, high calorie foods -give high protein, high calorie shakes -weigh daily to monitor wt loss or gain -make food attractive & unusual (cut sandwich into star shape) -allow parents to bring child’s favorite food from home -involve parents in order to learn about child’s preferences
-Involve child in food selection -do not give favorite foods when nauseated -medicate for nausea before meals -encourage small, frequent meals -encourage high protein, high calorie foods -give high protein, high calorie shakes -weigh daily to monitor wt loss or gain -make food attractive & unusual (cut sandwich into star shape) -allow parents to bring child’s favorite food from home -involve parents in order to learn about child’s preferences
 Info: foods high in iron -red meats -legumes (dried beans & peas) -green leafy vegs (spinach, chard, beet greens) -iron-fortified breads & cereals & whole grains -nuts & seeds -dried fruits
Info: foods high in iron -red meats -legumes (dried beans & peas) -green leafy vegs (spinach, chard, beet greens) -iron-fortified breads & cereals & whole grains -nuts & seeds -dried fruits
 List s/s of Iron Deficiency Anemia:
List s/s of Iron Deficiency Anemia:
 -fatigue, lethargy, irritability, muscle weakness -SOB -tachycardia, tachypnea, possible low-grade fever -dizziness or fainting w/ exertion -pallor -nail bed deformities -impaired healing, loss of skin elasticity, thinning of hair -systolic heart murmur, heart failure
-fatigue, lethargy, irritability, muscle weakness -SOB -tachycardia, tachypnea, possible low-grade fever -dizziness or fainting w/ exertion -pallor -nail bed deformities -impaired healing, loss of skin elasticity, thinning of hair -systolic heart murmur, heart failure
 Normal H & H for a 7 yr old: 1. Hgb 6 g/d. L, Hct 18% 2. Hgb 10 g/d. L, Hct 30% 3. Hgb 14 g/d. L, Hct 42% 4. Hgb 20 g/d. L, Hct 60%
Normal H & H for a 7 yr old: 1. Hgb 6 g/d. L, Hct 18% 2. Hgb 10 g/d. L, Hct 30% 3. Hgb 14 g/d. L, Hct 42% 4. Hgb 20 g/d. L, Hct 60%
 Parents understand the effects of oral iron therapy if they state: 1. my child may develop diarrhea while on iron 2. I should call dr. if my child has tarry stools 3. I will give iron w/ milk to help prevent upset stomach 4. my child should rinse mouth after taking
Parents understand the effects of oral iron therapy if they state: 1. my child may develop diarrhea while on iron 2. I should call dr. if my child has tarry stools 3. I will give iron w/ milk to help prevent upset stomach 4. my child should rinse mouth after taking
 What is the priority nursing diagnosis for child w/ sickle cell crisis?
What is the priority nursing diagnosis for child w/ sickle cell crisis?
 Info: Sickle cell interventions include: -bedrest -around the clock pain management or PCA -frequent assessment of pain rating -fluids @ 125 -150% of 24 hr maintenance requirements -application of warm packs to painful joints
Info: Sickle cell interventions include: -bedrest -around the clock pain management or PCA -frequent assessment of pain rating -fluids @ 125 -150% of 24 hr maintenance requirements -application of warm packs to painful joints
 Possible causes of jaundice in 9 yr old w/ frequent sickle cells crisis include: (all that apply) 1. liver failure caused by chronic vaso-occlusive crisis 2. cardiomegaly 3. obstruction of bile ducts 4. rapid destruction of sickled RBC’s 5. an aplastic crisis
Possible causes of jaundice in 9 yr old w/ frequent sickle cells crisis include: (all that apply) 1. liver failure caused by chronic vaso-occlusive crisis 2. cardiomegaly 3. obstruction of bile ducts 4. rapid destruction of sickled RBC’s 5. an aplastic crisis
 Interventions to prevent infection in child hospitalized w/ sickle cell crisis include: 1. IV fluids w/ electrolyte replacment 2. IV narcotics for pain relief 3. pneumococcal vaccine 4. exchange transfusions
Interventions to prevent infection in child hospitalized w/ sickle cell crisis include: 1. IV fluids w/ electrolyte replacment 2. IV narcotics for pain relief 3. pneumococcal vaccine 4. exchange transfusions
 Encouraging appropriate physical activity in children w/ hemophilia strengthens muscles & joints & may actually prevent frequent bleeding episodes. 1. true 2. false
Encouraging appropriate physical activity in children w/ hemophilia strengthens muscles & joints & may actually prevent frequent bleeding episodes. 1. true 2. false
 Sudden onset of slurred speech & HA in child w/ hemophilia may indicate the onset of an episode of hemarthrosis. 1. true 2. false
Sudden onset of slurred speech & HA in child w/ hemophilia may indicate the onset of an episode of hemarthrosis. 1. true 2. false
 Aspirin & ibuprofen are best choices for pain relief in child w/ hemophilia. 1. true 2. false
Aspirin & ibuprofen are best choices for pain relief in child w/ hemophilia. 1. true 2. false
 Which are manifestations of rheumatic fever? (all that apply) 1. erythema marginatum (rash) 2. continuous joint pain of digits 3. tender, subq nodules 4. dec’d ESR 5. elevated C-reactive protein 6. uncoordinated movements of extremities
Which are manifestations of rheumatic fever? (all that apply) 1. erythema marginatum (rash) 2. continuous joint pain of digits 3. tender, subq nodules 4. dec’d ESR 5. elevated C-reactive protein 6. uncoordinated movements of extremities
 which is most definitive for diagnosing rheumatic fever? 1. throat swab & culture 2. ECG & echo 3. CRP or ESR 4. elevated or rising serum antistreptolysin-O (ASO) titre
which is most definitive for diagnosing rheumatic fever? 1. throat swab & culture 2. ECG & echo 3. CRP or ESR 4. elevated or rising serum antistreptolysin-O (ASO) titre
 Which med should nurse admin for comfort in a 6 yr old w/ rheumatic fever. 1. aspirin 2. ibuprofen 3. penicillin 4. erythromycin
Which med should nurse admin for comfort in a 6 yr old w/ rheumatic fever. 1. aspirin 2. ibuprofen 3. penicillin 4. erythromycin
 Chorea leads to permanent nerve damage & seizures. 1. true 2. false
Chorea leads to permanent nerve damage & seizures. 1. true 2. false
 w/ rheumatic fever, antibiotics may need to be continued for an extended period of time for prophylaxis. 1. true 2. false
w/ rheumatic fever, antibiotics may need to be continued for an extended period of time for prophylaxis. 1. true 2. false
 Which of the following fluids is appropriate choice to rehydrate a child who has experienced diarrhea due to E. coli for the past 3 days? 1. oral rehydration therapy 2. IV isotonic saline w/ glucose 3. gelatin 4. chicken broth
Which of the following fluids is appropriate choice to rehydrate a child who has experienced diarrhea due to E. coli for the past 3 days? 1. oral rehydration therapy 2. IV isotonic saline w/ glucose 3. gelatin 4. chicken broth
 match 1. Hirschsprung’s disease 2. Intussusception 3. Hypertrophic pyloric stenosis 4. GERD 5. Meckel’s diverticulum A. Olive-shaped mass RUQ B. Painless, bloody stools C. Severe constipation w/ bouts of diarrhea; failure to pass meconium in newborns D. Stool of currant jelly consistency E. Excess spitting up or forceful vomiting
match 1. Hirschsprung’s disease 2. Intussusception 3. Hypertrophic pyloric stenosis 4. GERD 5. Meckel’s diverticulum A. Olive-shaped mass RUQ B. Painless, bloody stools C. Severe constipation w/ bouts of diarrhea; failure to pass meconium in newborns D. Stool of currant jelly consistency E. Excess spitting up or forceful vomiting
 Infant w/ severe GERD may have orders to be placed on his stomach to sleep, rather than the usual back to sleep position. 1. true 2. false
Infant w/ severe GERD may have orders to be placed on his stomach to sleep, rather than the usual back to sleep position. 1. true 2. false


