704c7f592f52603e304e06412eb46104.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 25
 9 th International Fall Workshop VISION, MODELING, AND VISUALIZATION 2004 November 16 - 18, 2004 Stanford (California), USA Poster Session 1 Calibration, Registration, Tracking
9 th International Fall Workshop VISION, MODELING, AND VISUALIZATION 2004 November 16 - 18, 2004 Stanford (California), USA Poster Session 1 Calibration, Registration, Tracking
 9 th International Fall Workshop VISION, MODELING, AND VISUALIZATION 2004 November 16 - 18, 2004 Stanford (California), USA Markerless Real-Time Target Region Tracking Application to Frameless Stereotactic Radiosurgery T. Rohlfing 1, J. Denzler 2, D. B. Russakoff 3, C. Gräßl 4, C. R. Maurer, Jr. 5 1 Neuroscience Program, SRI International, Menlo Park, CA 2 Friedrich-Schiller-Universität Jena, Germany 3 Computer Science Department, Stanford University, Stanford, CA 4 Universität Erlangen, Germany 5 Department of Neurosurgery, Stanford University, Stanford, CA
9 th International Fall Workshop VISION, MODELING, AND VISUALIZATION 2004 November 16 - 18, 2004 Stanford (California), USA Markerless Real-Time Target Region Tracking Application to Frameless Stereotactic Radiosurgery T. Rohlfing 1, J. Denzler 2, D. B. Russakoff 3, C. Gräßl 4, C. R. Maurer, Jr. 5 1 Neuroscience Program, SRI International, Menlo Park, CA 2 Friedrich-Schiller-Universität Jena, Germany 3 Computer Science Department, Stanford University, Stanford, CA 4 Universität Erlangen, Germany 5 Department of Neurosurgery, Stanford University, Stanford, CA
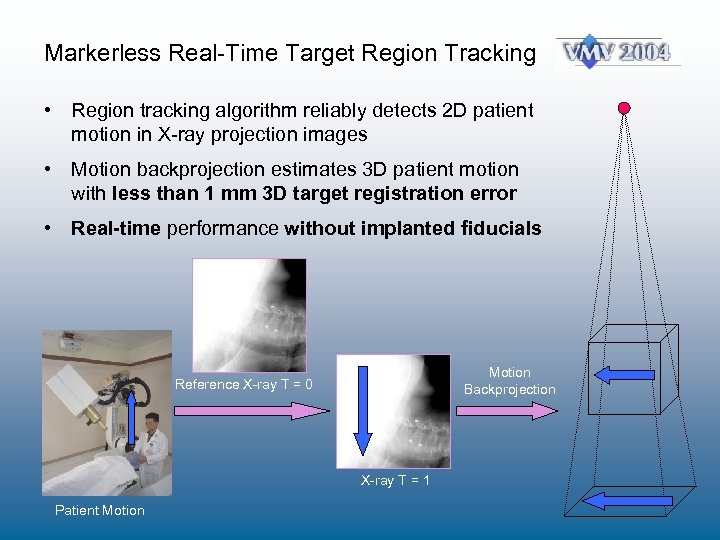 Markerless Real-Time Target Region Tracking • Region tracking algorithm reliably detects 2 D patient motion in X-ray projection images • Motion backprojection estimates 3 D patient motion with less than 1 mm 3 D target registration error • Real-time performance without implanted fiducials Motion Backprojection Reference X-ray T = 0 X-ray T = 1 Patient Motion
Markerless Real-Time Target Region Tracking • Region tracking algorithm reliably detects 2 D patient motion in X-ray projection images • Motion backprojection estimates 3 D patient motion with less than 1 mm 3 D target registration error • Real-time performance without implanted fiducials Motion Backprojection Reference X-ray T = 0 X-ray T = 1 Patient Motion
 9 th International Fall Workshop VISION, MODELING, AND VISUALIZATION 2004 November 16 - 18, 2004 Stanford (California), USA Stereo and Lidar-Based Pose Estimation With Uncertainty for 3 D Reconstruction Sanjit Jhala and Suresh Lodha Department of Computer Science, University of California Santa Cruz
9 th International Fall Workshop VISION, MODELING, AND VISUALIZATION 2004 November 16 - 18, 2004 Stanford (California), USA Stereo and Lidar-Based Pose Estimation With Uncertainty for 3 D Reconstruction Sanjit Jhala and Suresh Lodha Department of Computer Science, University of California Santa Cruz
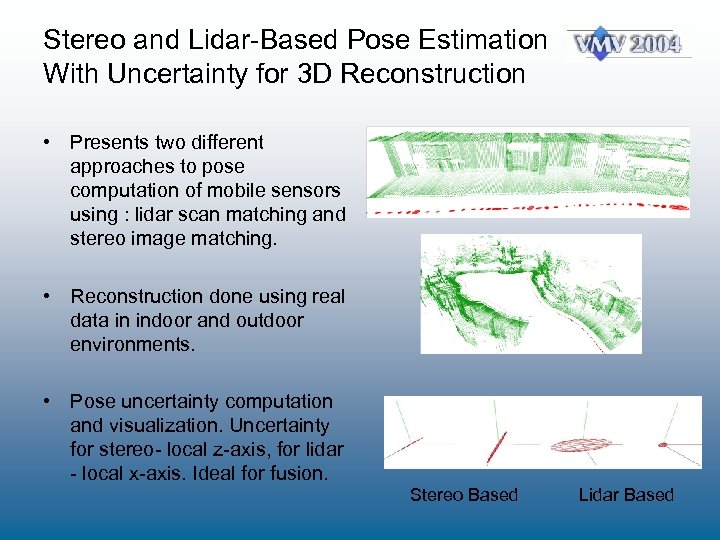 Stereo and Lidar-Based Pose Estimation With Uncertainty for 3 D Reconstruction • Presents two different approaches to pose computation of mobile sensors using : lidar scan matching and stereo image matching. • Reconstruction done using real data in indoor and outdoor environments. • Pose uncertainty computation and visualization. Uncertainty for stereo- local z-axis, for lidar - local x-axis. Ideal for fusion. Stereo Based Lidar Based
Stereo and Lidar-Based Pose Estimation With Uncertainty for 3 D Reconstruction • Presents two different approaches to pose computation of mobile sensors using : lidar scan matching and stereo image matching. • Reconstruction done using real data in indoor and outdoor environments. • Pose uncertainty computation and visualization. Uncertainty for stereo- local z-axis, for lidar - local x-axis. Ideal for fusion. Stereo Based Lidar Based
 9 th International Fall Workshop VISION, MODELING, AND VISUALIZATION 2004 November 16 - 18, 2004 Stanford (California), USA Vector Quantization Based Data Selection for Hand-Eye Calibration J. Schmidt, F. Vogt, and H. Niemann Chair for Pattern Recognition University of Erlangen-Nürnberg
9 th International Fall Workshop VISION, MODELING, AND VISUALIZATION 2004 November 16 - 18, 2004 Stanford (California), USA Vector Quantization Based Data Selection for Hand-Eye Calibration J. Schmidt, F. Vogt, and H. Niemann Chair for Pattern Recognition University of Erlangen-Nürnberg
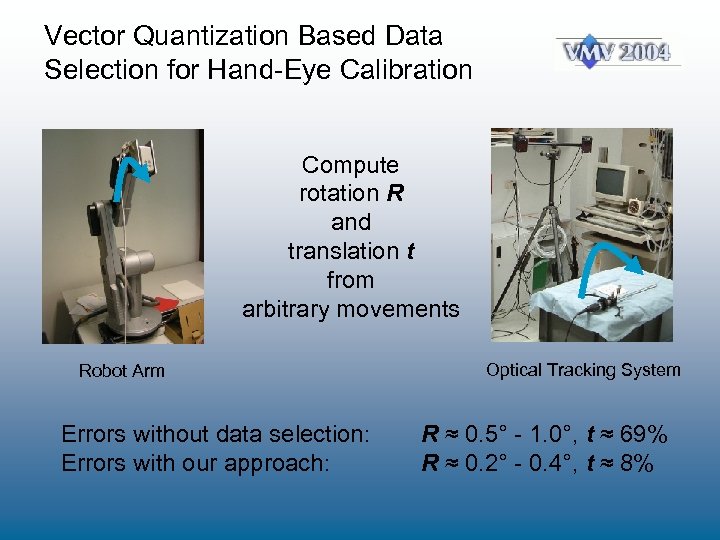 Vector Quantization Based Data Selection for Hand-Eye Calibration Compute rotation R and translation t from arbitrary movements Robot Arm Errors without data selection: Errors with our approach: Optical Tracking System R ≈ 0. 5° - 1. 0°, t ≈ 69% R ≈ 0. 2° - 0. 4°, t ≈ 8%
Vector Quantization Based Data Selection for Hand-Eye Calibration Compute rotation R and translation t from arbitrary movements Robot Arm Errors without data selection: Errors with our approach: Optical Tracking System R ≈ 0. 5° - 1. 0°, t ≈ 69% R ≈ 0. 2° - 0. 4°, t ≈ 8%
 9 th International Fall Workshop VISION, MODELING, AND VISUALIZATION 2004 November 16 - 18, 2004 Stanford (California), USA Active Stereo for Intersection Assistance Stefan K. Gehrig, J. Klappstein, U. Franke Daimler. Chrysler AG
9 th International Fall Workshop VISION, MODELING, AND VISUALIZATION 2004 November 16 - 18, 2004 Stanford (California), USA Active Stereo for Intersection Assistance Stefan K. Gehrig, J. Klappstein, U. Franke Daimler. Chrysler AG
 Active Stereo for Intersection Assistance • Intersection Assistance can reduce collisions at crossings significantly • Hardware setup: Two cameras on separate Pan -Tilt-Units • Elaborate Calibration allows 3 D Measurement in any direction in realtime • Cross Traffic Warning Scheme demonstrated
Active Stereo for Intersection Assistance • Intersection Assistance can reduce collisions at crossings significantly • Hardware setup: Two cameras on separate Pan -Tilt-Units • Elaborate Calibration allows 3 D Measurement in any direction in realtime • Cross Traffic Warning Scheme demonstrated
 9 th International Fall Workshop VISION, MODELING, AND VISUALIZATION 2004 November 16 - 18, 2004 Stanford (California), USA Non-invasive attitude detection for full-body interaction in MEDIATE, a multisensory interactive environment for children with autism Narcís Parés, Anna Carreras, Miquel Soler Experimentation on Interactive Communication group Universitat Pompeu Fabra (Barcelona, Spain)
9 th International Fall Workshop VISION, MODELING, AND VISUALIZATION 2004 November 16 - 18, 2004 Stanford (California), USA Non-invasive attitude detection for full-body interaction in MEDIATE, a multisensory interactive environment for children with autism Narcís Parés, Anna Carreras, Miquel Soler Experimentation on Interactive Communication group Universitat Pompeu Fabra (Barcelona, Spain)
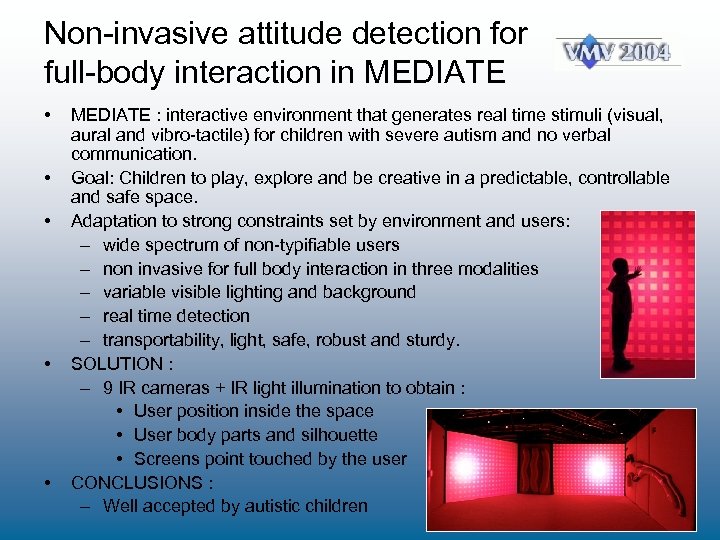 Non-invasive attitude detection for full-body interaction in MEDIATE • • • MEDIATE : interactive environment that generates real time stimuli (visual, aural and vibro-tactile) for children with severe autism and no verbal communication. Goal: Children to play, explore and be creative in a predictable, controllable and safe space. Adaptation to strong constraints set by environment and users: – wide spectrum of non-typifiable users – non invasive for full body interaction in three modalities – variable visible lighting and background – real time detection – transportability, light, safe, robust and sturdy. SOLUTION : – 9 IR cameras + IR light illumination to obtain : • User position inside the space • User body parts and silhouette • Screens point touched by the user CONCLUSIONS : – Well accepted by autistic children
Non-invasive attitude detection for full-body interaction in MEDIATE • • • MEDIATE : interactive environment that generates real time stimuli (visual, aural and vibro-tactile) for children with severe autism and no verbal communication. Goal: Children to play, explore and be creative in a predictable, controllable and safe space. Adaptation to strong constraints set by environment and users: – wide spectrum of non-typifiable users – non invasive for full body interaction in three modalities – variable visible lighting and background – real time detection – transportability, light, safe, robust and sturdy. SOLUTION : – 9 IR cameras + IR light illumination to obtain : • User position inside the space • User body parts and silhouette • Screens point touched by the user CONCLUSIONS : – Well accepted by autistic children
 9 th International Fall Workshop VISION, MODELING, AND VISUALIZATION 2004 November 16 - 18, 2004 Stanford (California), USA A Fast Cost Relaxation Stereo Algorithm with Occlusion Detection for Mobile Robot Applications Roland Brockers, Marcus Hund, Bärbel Mertsching GET Lab, University of Paderborn, Germany
9 th International Fall Workshop VISION, MODELING, AND VISUALIZATION 2004 November 16 - 18, 2004 Stanford (California), USA A Fast Cost Relaxation Stereo Algorithm with Occlusion Detection for Mobile Robot Applications Roland Brockers, Marcus Hund, Bärbel Mertsching GET Lab, University of Paderborn, Germany
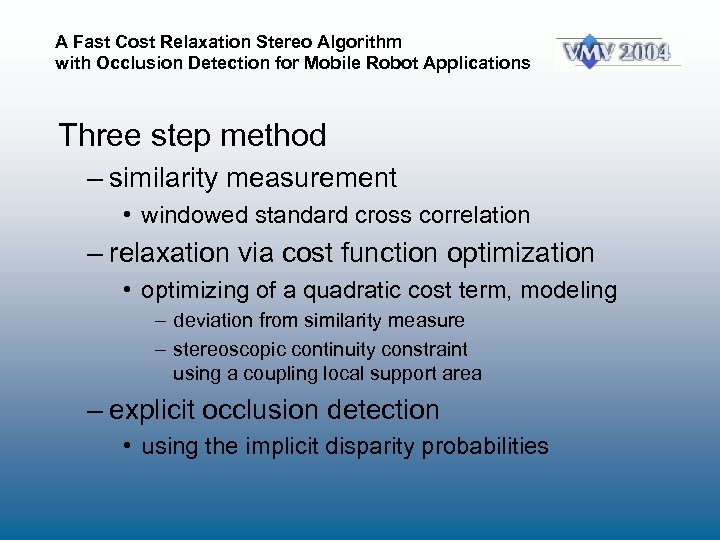 A Fast Cost Relaxation Stereo Algorithm with Occlusion Detection for Mobile Robot Applications Three step method – similarity measurement • windowed standard cross correlation – relaxation via cost function optimization • optimizing of a quadratic cost term, modeling – deviation from similarity measure – stereoscopic continuity constraint using a coupling local support area – explicit occlusion detection • using the implicit disparity probabilities
A Fast Cost Relaxation Stereo Algorithm with Occlusion Detection for Mobile Robot Applications Three step method – similarity measurement • windowed standard cross correlation – relaxation via cost function optimization • optimizing of a quadratic cost term, modeling – deviation from similarity measure – stereoscopic continuity constraint using a coupling local support area – explicit occlusion detection • using the implicit disparity probabilities
 A Fast Cost Relaxation Stereo Algorithm with Occlusion Detection for Mobile Robot Applications Relaxation – optimization of a quadratic cost function leads to resolution of a linear equation system – global optimum via fast numerical algorithm Results – given for Middlebury Stereo Vision Images – 100 x 100 image with 20 disparity levels with 2. 5 FPS
A Fast Cost Relaxation Stereo Algorithm with Occlusion Detection for Mobile Robot Applications Relaxation – optimization of a quadratic cost function leads to resolution of a linear equation system – global optimum via fast numerical algorithm Results – given for Middlebury Stereo Vision Images – 100 x 100 image with 20 disparity levels with 2. 5 FPS
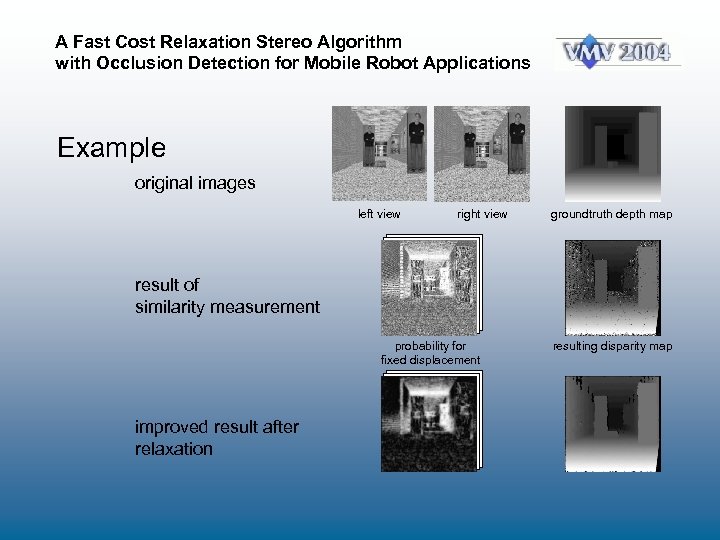 A Fast Cost Relaxation Stereo Algorithm with Occlusion Detection for Mobile Robot Applications Example original images left view right view groundtruth depth map result of similarity measurement probability for fixed displacement improved result after relaxation resulting disparity map
A Fast Cost Relaxation Stereo Algorithm with Occlusion Detection for Mobile Robot Applications Example original images left view right view groundtruth depth map result of similarity measurement probability for fixed displacement improved result after relaxation resulting disparity map
 9 th International Fall Workshop VISION, MODELING, AND VISUALIZATION 2004 November 16 - 18, 2004 Stanford (California), USA 1 D camera calibration and 3 D reconstruction accuracy Yannick Caulier Fraunhofer Institute for Integrated Circuits IIS Erlangen (Germany)
9 th International Fall Workshop VISION, MODELING, AND VISUALIZATION 2004 November 16 - 18, 2004 Stanford (California), USA 1 D camera calibration and 3 D reconstruction accuracy Yannick Caulier Fraunhofer Institute for Integrated Circuits IIS Erlangen (Germany)
 3 D with 1 D sensors • Elaboration of a new 1 D model based on 1 D image construction • Design of an appropriate 3 D calibration object • Determination of camera focal distance and extrinsic parameters • Calibration is validated by considering the variance of results • Reconstruction is validated with regard to the back-projection error
3 D with 1 D sensors • Elaboration of a new 1 D model based on 1 D image construction • Design of an appropriate 3 D calibration object • Determination of camera focal distance and extrinsic parameters • Calibration is validated by considering the variance of results • Reconstruction is validated with regard to the back-projection error
 9 th International Fall Workshop VISION, MODELING, AND VISUALIZATION 2004 November 16 - 18, 2004 Stanford (California), USA Extracting Animated Meshes with Adaptive Motion Estimation Nizam Anuar and Igor Guskov University of Michigan, Ann Arbor http: //graphics. eecs. umich. edu
9 th International Fall Workshop VISION, MODELING, AND VISUALIZATION 2004 November 16 - 18, 2004 Stanford (California), USA Extracting Animated Meshes with Adaptive Motion Estimation Nizam Anuar and Igor Guskov University of Michigan, Ann Arbor http: //graphics. eecs. umich. edu
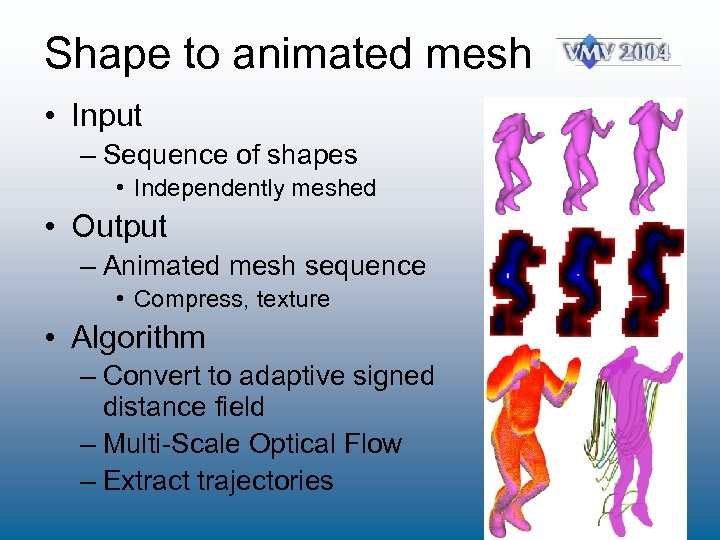 Shape to animated mesh • Input – Sequence of shapes • Independently meshed • Output – Animated mesh sequence • Compress, texture • Algorithm – Convert to adaptive signed distance field – Multi-Scale Optical Flow – Extract trajectories
Shape to animated mesh • Input – Sequence of shapes • Independently meshed • Output – Animated mesh sequence • Compress, texture • Algorithm – Convert to adaptive signed distance field – Multi-Scale Optical Flow – Extract trajectories
 9 th International Fall Workshop VISION, MODELING, AND VISUALIZATION 2004 November 16 - 18, 2004 Stanford (California), USA Automatic Generation of Shape Models Using Nonrigid Registration with a Single Segmented Template Mesh Geremy Heitz, Torsten Rohlfing, Calvin R. Maurer, Jr. Department of Electrical Engineering Stanford University
9 th International Fall Workshop VISION, MODELING, AND VISUALIZATION 2004 November 16 - 18, 2004 Stanford (California), USA Automatic Generation of Shape Models Using Nonrigid Registration with a Single Segmented Template Mesh Geremy Heitz, Torsten Rohlfing, Calvin R. Maurer, Jr. Department of Electrical Engineering Stanford University
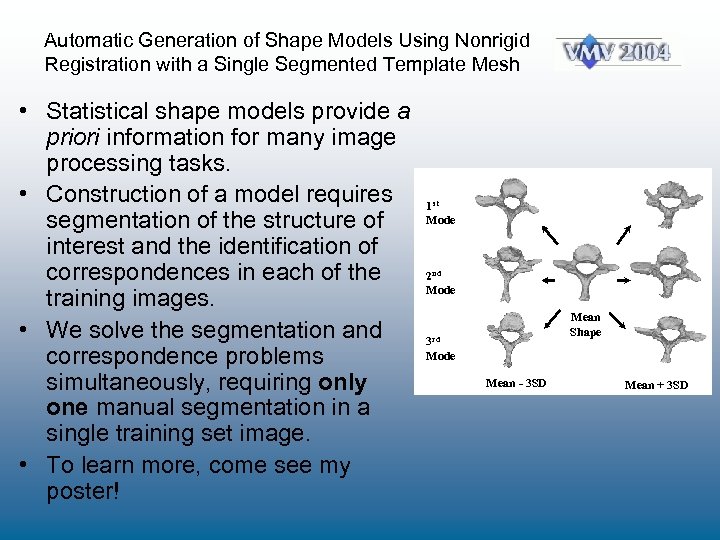 Automatic Generation of Shape Models Using Nonrigid Registration with a Single Segmented Template Mesh • Statistical shape models provide a priori information for many image processing tasks. • Construction of a model requires segmentation of the structure of interest and the identification of correspondences in each of the training images. • We solve the segmentation and correspondence problems simultaneously, requiring only one manual segmentation in a single training set image. • To learn more, come see my poster! 1 st Mode 2 nd Mode Mean Shape 3 rd Mode Mean - 3 SD Mean + 3 SD
Automatic Generation of Shape Models Using Nonrigid Registration with a Single Segmented Template Mesh • Statistical shape models provide a priori information for many image processing tasks. • Construction of a model requires segmentation of the structure of interest and the identification of correspondences in each of the training images. • We solve the segmentation and correspondence problems simultaneously, requiring only one manual segmentation in a single training set image. • To learn more, come see my poster! 1 st Mode 2 nd Mode Mean Shape 3 rd Mode Mean - 3 SD Mean + 3 SD
 9 th International Fall Workshop VISION, MODELING, AND VISUALIZATION 2004 November 16 - 18, 2004 Stanford (California), USA A Probabilistic Model-Based Template Matching Approach for Robust Object Tracking in Real-Time Ch. Gräßl, T. Zinßer, and H. Nieman Chair for Pattern Recognition University of Erlangen-Nürnberg
9 th International Fall Workshop VISION, MODELING, AND VISUALIZATION 2004 November 16 - 18, 2004 Stanford (California), USA A Probabilistic Model-Based Template Matching Approach for Robust Object Tracking in Real-Time Ch. Gräßl, T. Zinßer, and H. Nieman Chair for Pattern Recognition University of Erlangen-Nürnberg
 A Probabilistic Model-Based Template Matching Approach for Robust Object Tracking in Real-Time • Combination of the hyperplane approach for template matching and the CONDENSATION algorithm for viewpoint estimation • Robust against illumination changes and cluttered background • Tolerates camera motion • Real-time capability
A Probabilistic Model-Based Template Matching Approach for Robust Object Tracking in Real-Time • Combination of the hyperplane approach for template matching and the CONDENSATION algorithm for viewpoint estimation • Robust against illumination changes and cluttered background • Tolerates camera motion • Real-time capability
 9 th International Fall Workshop VISION, MODELING, AND VISUALIZATION 2004 November 16 - 18, 2004 Stanford (California), USA Gradient-based Approach for Fine Registration of Panorama Images Hui Chen Associate professor, Shandong Univ.
9 th International Fall Workshop VISION, MODELING, AND VISUALIZATION 2004 November 16 - 18, 2004 Stanford (California), USA Gradient-based Approach for Fine Registration of Panorama Images Hui Chen Associate professor, Shandong Univ.
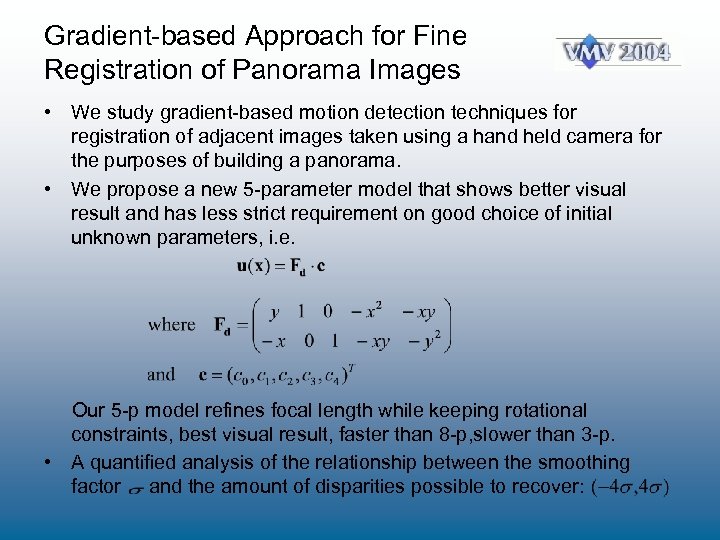 Gradient-based Approach for Fine Registration of Panorama Images • We study gradient-based motion detection techniques for registration of adjacent images taken using a hand held camera for the purposes of building a panorama. • We propose a new 5 -parameter model that shows better visual result and has less strict requirement on good choice of initial unknown parameters, i. e. Our 5 -p model refines focal length while keeping rotational constraints, best visual result, faster than 8 -p, slower than 3 -p. • A quantified analysis of the relationship between the smoothing factor and the amount of disparities possible to recover:
Gradient-based Approach for Fine Registration of Panorama Images • We study gradient-based motion detection techniques for registration of adjacent images taken using a hand held camera for the purposes of building a panorama. • We propose a new 5 -parameter model that shows better visual result and has less strict requirement on good choice of initial unknown parameters, i. e. Our 5 -p model refines focal length while keeping rotational constraints, best visual result, faster than 8 -p, slower than 3 -p. • A quantified analysis of the relationship between the smoothing factor and the amount of disparities possible to recover:


