f27798674d59db59ce4d2f0f9897d11d.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 26
 9 TH EDITION Manning and Reece CHAPTER 7 UNDERSTANDING BUYER BEHAVIOR PART IV 1
9 TH EDITION Manning and Reece CHAPTER 7 UNDERSTANDING BUYER BEHAVIOR PART IV 1
 LEARNING OBJECTIVES-1 Discuss the meaning of a customer strategy Understand complex nature of consumer and business buyer behavior Discuss social and psychological influences shaping buying decisions Discuss power of perception in shaping buyer behavior 2
LEARNING OBJECTIVES-1 Discuss the meaning of a customer strategy Understand complex nature of consumer and business buyer behavior Discuss social and psychological influences shaping buying decisions Discuss power of perception in shaping buyer behavior 2
 LEARNING OBJECTIVES-2 Distinguish between emotional and rational buying motives Distinguish between patronage and product buying motives Explain two commonly accepted theories about how people arrive at buying decision Describe three ways to discover customer buying motives 3
LEARNING OBJECTIVES-2 Distinguish between emotional and rational buying motives Distinguish between patronage and product buying motives Explain two commonly accepted theories about how people arrive at buying decision Describe three ways to discover customer buying motives 3
 CUSTOMER STRATEGY DEFINED ”A customer strategy is a carefully conceived plan that results in maximum customer responsiveness. One major dimension of this strategy is to achieve a better understanding of the customer’s buying needs and motives. ” 4
CUSTOMER STRATEGY DEFINED ”A customer strategy is a carefully conceived plan that results in maximum customer responsiveness. One major dimension of this strategy is to achieve a better understanding of the customer’s buying needs and motives. ” 4
 STRATEGIC/CONSULTATIVE SELLING MODEL Figure 7. 1 5
STRATEGIC/CONSULTATIVE SELLING MODEL Figure 7. 1 5
 CONSUMER vs. BUSINESS BUYERS Consumer buyer behavior Individuals and households who buy for personal consumption Business buyer behavior Organizations that buy goods and services used in production of other products and services that are sold, rented, or supplied to others 6
CONSUMER vs. BUSINESS BUYERS Consumer buyer behavior Individuals and households who buy for personal consumption Business buyer behavior Organizations that buy goods and services used in production of other products and services that are sold, rented, or supplied to others 6
 BUYER BEHAVIOR COMPLEXITY ADOPT ONE-TO-ONE MARKETING STRATEGY CULTIVATE LONG-TERM RELATIONSHIP WITH EACH CUSTOMER WORKS FOR BOTH RETAIL AND BUSINESS-TOBUSINESS 7
BUYER BEHAVIOR COMPLEXITY ADOPT ONE-TO-ONE MARKETING STRATEGY CULTIVATE LONG-TERM RELATIONSHIP WITH EACH CUSTOMER WORKS FOR BOTH RETAIL AND BUSINESS-TOBUSINESS 7
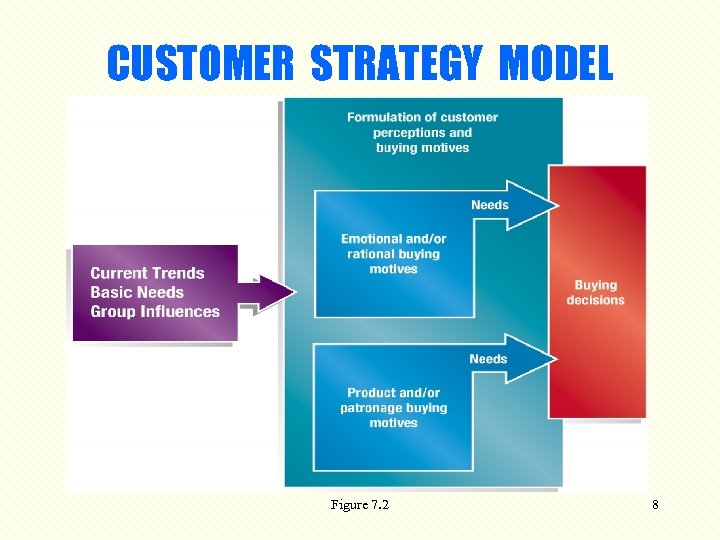 CUSTOMER STRATEGY MODEL Figure 7. 2 8
CUSTOMER STRATEGY MODEL Figure 7. 2 8
 CURRENT TRENDS Consumers moving upscale to premium, luxury goods Customer respect central to success in every market Customers from diverse racial, ethnic, and cultural backgrounds See Figure 7. 3. 9
CURRENT TRENDS Consumers moving upscale to premium, luxury goods Customer respect central to success in every market Customers from diverse racial, ethnic, and cultural backgrounds See Figure 7. 3. 9
 BASIC NEEDS—MASLOW Physiological –food, shelter Security –free from danger Social –identification with social groups, friendship Esteem –desire to feel worthy in eyes of others Self-Actualization –need for mastery, self-fulfillment 10
BASIC NEEDS—MASLOW Physiological –food, shelter Security –free from danger Social –identification with social groups, friendship Esteem –desire to feel worthy in eyes of others Self-Actualization –need for mastery, self-fulfillment 10
 GROUP INFLUENCES Role –expectations associated with position Reference Groups –categories of people you see self belonging to Social Class –group with similar jobs, values, interests, lifestyles Culture –influences of group with common language, environment, also sub-cultures See Figure 7. 4, next slide. 11
GROUP INFLUENCES Role –expectations associated with position Reference Groups –categories of people you see self belonging to Social Class –group with similar jobs, values, interests, lifestyles Culture –influences of group with common language, environment, also sub-cultures See Figure 7. 4, next slide. 11
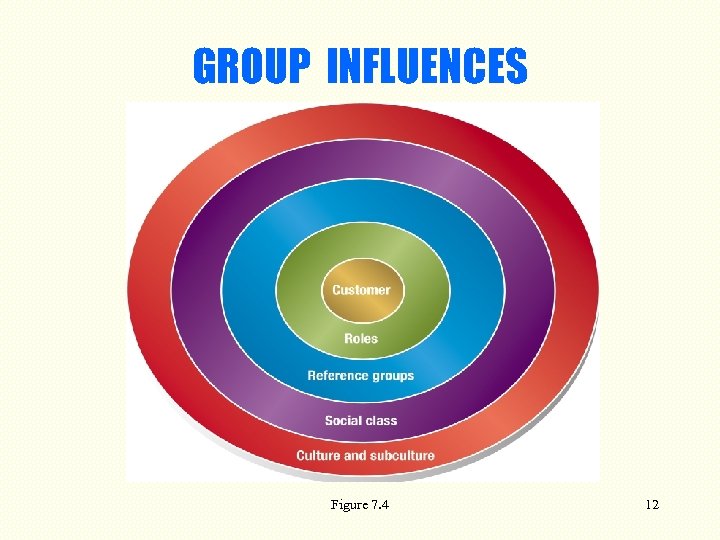 GROUP INFLUENCES Figure 7. 4 12
GROUP INFLUENCES Figure 7. 4 12
 DAIMLER/CHRYSLER 13
DAIMLER/CHRYSLER 13
 APPLICATION: OVER-GENERALIZING Remember, prospects act as individuals, not stereotypes “Facts are negotiable. Perception is rock-solid. ” Some predict the demise of “demographics” in marketing …How would this impact customer analysis? 14
APPLICATION: OVER-GENERALIZING Remember, prospects act as individuals, not stereotypes “Facts are negotiable. Perception is rock-solid. ” Some predict the demise of “demographics” in marketing …How would this impact customer analysis? 14
 USING JUST DEMOGRAPHICS 21 -34 -year-old female $40, 000+ income college educated owns home Could yield 15
USING JUST DEMOGRAPHICS 21 -34 -year-old female $40, 000+ income college educated owns home Could yield 15
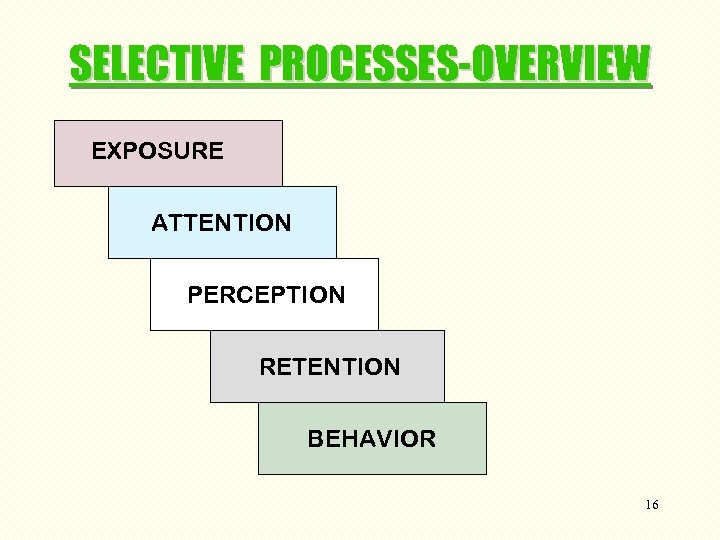 SELECTIVE PROCESSES-OVERVIEW EXPOSURE ATTENTION PERCEPTION RETENTION BEHAVIOR 16
SELECTIVE PROCESSES-OVERVIEW EXPOSURE ATTENTION PERCEPTION RETENTION BEHAVIOR 16
 PERCEPTION: CUSTOMER NEED FORMATION Selective Attention—We tend to screen out certain messages …information overload Buyers conditioned by sociocultural background and need to use various selective processes Salespersons should encourage client to discuss “perceptions” of products 17
PERCEPTION: CUSTOMER NEED FORMATION Selective Attention—We tend to screen out certain messages …information overload Buyers conditioned by sociocultural background and need to use various selective processes Salespersons should encourage client to discuss “perceptions” of products 17
 BUYING MOTIVES A buying motive is an aroused need, drive, or desire that stimulates behavior to satisfy the aroused need It’s helpful to discover the “dominant buying motive” or DBM Four basic motive types—emotional, rational, patronage, and product 18
BUYING MOTIVES A buying motive is an aroused need, drive, or desire that stimulates behavior to satisfy the aroused need It’s helpful to discover the “dominant buying motive” or DBM Four basic motive types—emotional, rational, patronage, and product 18
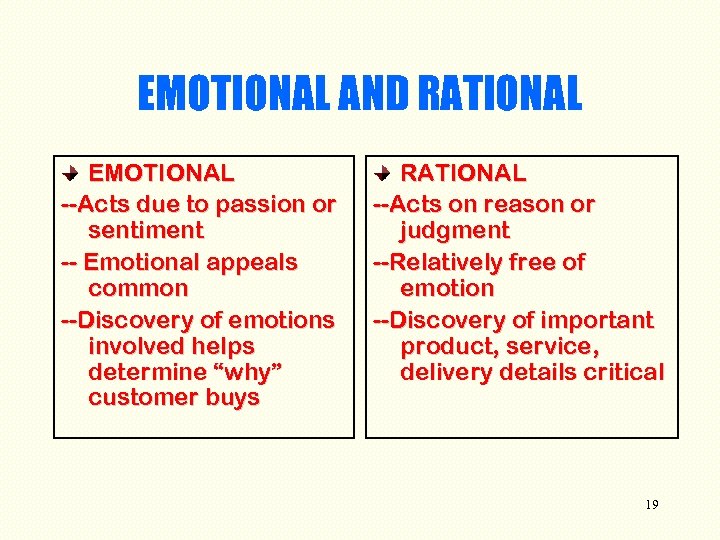 EMOTIONAL AND RATIONAL EMOTIONAL --Acts due to passion or sentiment -- Emotional appeals common --Discovery of emotions involved helps determine “why” customer buys RATIONAL --Acts on reason or judgment --Relatively free of emotion --Discovery of important product, service, delivery details critical 19
EMOTIONAL AND RATIONAL EMOTIONAL --Acts due to passion or sentiment -- Emotional appeals common --Discovery of emotions involved helps determine “why” customer buys RATIONAL --Acts on reason or judgment --Relatively free of emotion --Discovery of important product, service, delivery details critical 19
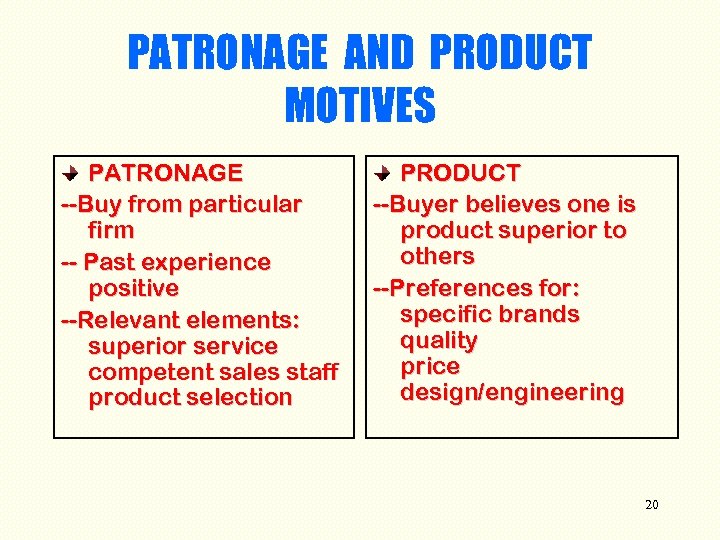 PATRONAGE AND PRODUCT MOTIVES PATRONAGE --Buy from particular firm -- Past experience positive --Relevant elements: superior service competent sales staff product selection PRODUCT --Buyer believes one is product superior to others --Preferences for: specific brands quality price design/engineering 20
PATRONAGE AND PRODUCT MOTIVES PATRONAGE --Buy from particular firm -- Past experience positive --Relevant elements: superior service competent sales staff product selection PRODUCT --Buyer believes one is product superior to others --Preferences for: specific brands quality price design/engineering 20
 BUYER RESOLUTION THEORY Sometimes called the 5 -Ws – Why should I buy? (need) – What should I buy? (product) – Where should I buy? (source) – What is a fair price? (price) – When should I buy? (time) 21
BUYER RESOLUTION THEORY Sometimes called the 5 -Ws – Why should I buy? (need) – What should I buy? (product) – Where should I buy? (source) – What is a fair price? (price) – When should I buy? (time) 21
 NEED-SATISFACTION THEORY Beliefs about salesperson’s role – Foundation of consultative selling – Effective two-way communication – Systematic inquiry with prospect – Two-way advocacy position – Provides “best” solution – Aims to develop long-term customer relationship 22
NEED-SATISFACTION THEORY Beliefs about salesperson’s role – Foundation of consultative selling – Effective two-way communication – Systematic inquiry with prospect – Two-way advocacy position – Provides “best” solution – Aims to develop long-term customer relationship 22
 THEORIES COMPARED-NEEDS WINS Needs approach based on systematic analysis of buyer situation Needs approach works well in all selling situations Customers experience less stress with needs approach 23
THEORIES COMPARED-NEEDS WINS Needs approach based on systematic analysis of buyer situation Needs approach works well in all selling situations Customers experience less stress with needs approach 23
 BUSINESS-TO-BUSINESS Differs from consumer level Often a group or committee decision Buyer often does – Purchase requisition or request – Systematic information search – Evaluates alternatives – Issues purchase order – Performs post-buy evaluation See Figure 7. 5, next slide. 24
BUSINESS-TO-BUSINESS Differs from consumer level Often a group or committee decision Buyer often does – Purchase requisition or request – Systematic information search – Evaluates alternatives – Issues purchase order – Performs post-buy evaluation See Figure 7. 5, next slide. 24
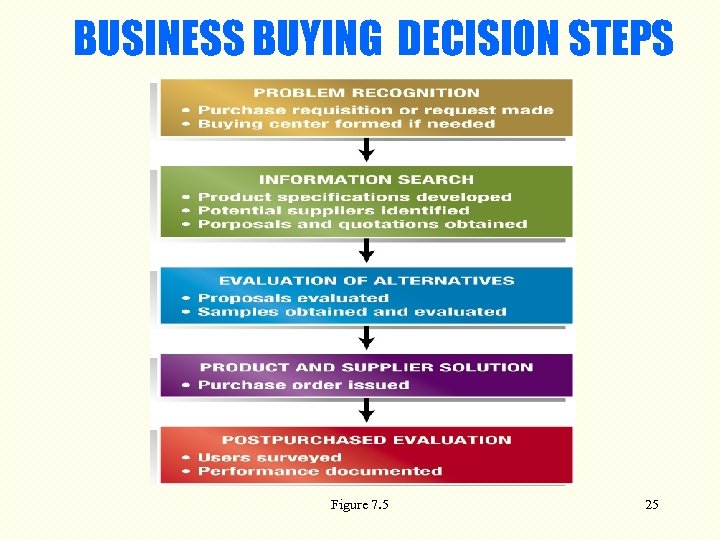 BUSINESS BUYING DECISION STEPS Figure 7. 5 25
BUSINESS BUYING DECISION STEPS Figure 7. 5 25
 DISCOVERING CUSTOMER’S BUYING MOTIVES ASK QU EST BE ION S A GO OD LIST BE ENE A RGO OD OBS ERV ER Last slide Chapter 7. 26
DISCOVERING CUSTOMER’S BUYING MOTIVES ASK QU EST BE ION S A GO OD LIST BE ENE A RGO OD OBS ERV ER Last slide Chapter 7. 26


