 9 Relevant Information and Decision Making: Production Decisions © 2007 Pearson Education Canada Slide 9 -1
9 Relevant Information and Decision Making: Production Decisions © 2007 Pearson Education Canada Slide 9 -1
 Opportunity Costs Opportunity Cost • The maximum available contribution to profit foregone by using limited resources for a particular purpose • Not a cost in the normal sense of the word • Consider the choice between staying with your current job or returning to school; if you quit your job to return to school the wages which you would have earned had you stayed in the job are an opportunity cost of returning to school © 2007 Pearson Education Canada Slide 9 -2
Opportunity Costs Opportunity Cost • The maximum available contribution to profit foregone by using limited resources for a particular purpose • Not a cost in the normal sense of the word • Consider the choice between staying with your current job or returning to school; if you quit your job to return to school the wages which you would have earned had you stayed in the job are an opportunity cost of returning to school © 2007 Pearson Education Canada Slide 9 -2
 Differential Costs Differential Analysis • Differences in revenues and costs between two alternatives • Also called incremental analysis Remain As An Employee Revenues Outlay costs Income effect per year © 2007 Pearson Education Canada Open An Independent Practice Difference $60, 000 0 $60, 000 $200, 000 120, 000 $80, 000 $140, 000 120, 000 $ 20, 000 Slide 9 -3
Differential Costs Differential Analysis • Differences in revenues and costs between two alternatives • Also called incremental analysis Remain As An Employee Revenues Outlay costs Income effect per year © 2007 Pearson Education Canada Open An Independent Practice Difference $60, 000 0 $60, 000 $200, 000 120, 000 $80, 000 $140, 000 120, 000 $ 20, 000 Slide 9 -3
 Make or Buy Decision • decision to manufacture the product or subcontract to an independent supplier (outsource) Make Buy Relevant costs: Direct material Direct labour Variable overhead Fixed overhead Cost to buy Total cost © 2007 Pearson Education Canada $20, 000 80, 000 40, 000 20, 000 $200, 000 $160, 000 $200, 000 Slide 9 -4
Make or Buy Decision • decision to manufacture the product or subcontract to an independent supplier (outsource) Make Buy Relevant costs: Direct material Direct labour Variable overhead Fixed overhead Cost to buy Total cost © 2007 Pearson Education Canada $20, 000 80, 000 40, 000 20, 000 $200, 000 $160, 000 $200, 000 Slide 9 -4
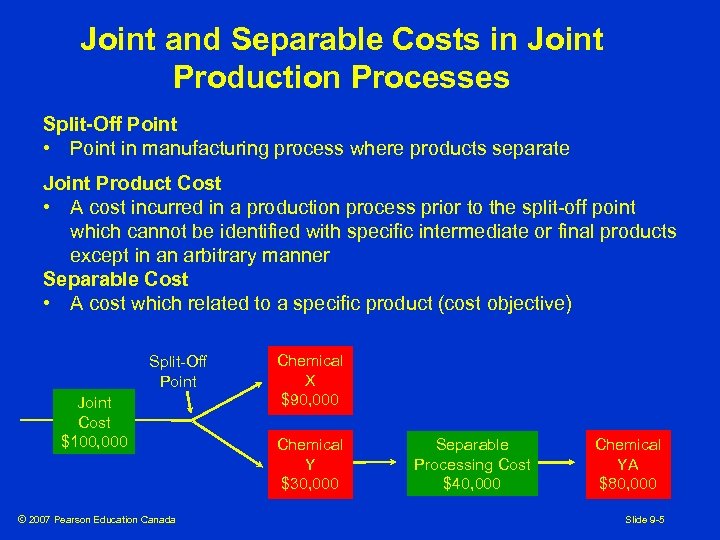 Joint and Separable Costs in Joint Production Processes Split-Off Point • Point in manufacturing process where products separate Joint Product Cost • A cost incurred in a production process prior to the split-off point which cannot be identified with specific intermediate or final products except in an arbitrary manner Separable Cost • A cost which related to a specific product (cost objective) Split-Off Point Joint Cost $100, 000 © 2007 Pearson Education Canada Chemical X $90, 000 Chemical Y $30, 000 Separable Processing Cost $40, 000 Chemical YA $80, 000 Slide 9 -5
Joint and Separable Costs in Joint Production Processes Split-Off Point • Point in manufacturing process where products separate Joint Product Cost • A cost incurred in a production process prior to the split-off point which cannot be identified with specific intermediate or final products except in an arbitrary manner Separable Cost • A cost which related to a specific product (cost objective) Split-Off Point Joint Cost $100, 000 © 2007 Pearson Education Canada Chemical X $90, 000 Chemical Y $30, 000 Separable Processing Cost $40, 000 Chemical YA $80, 000 Slide 9 -5
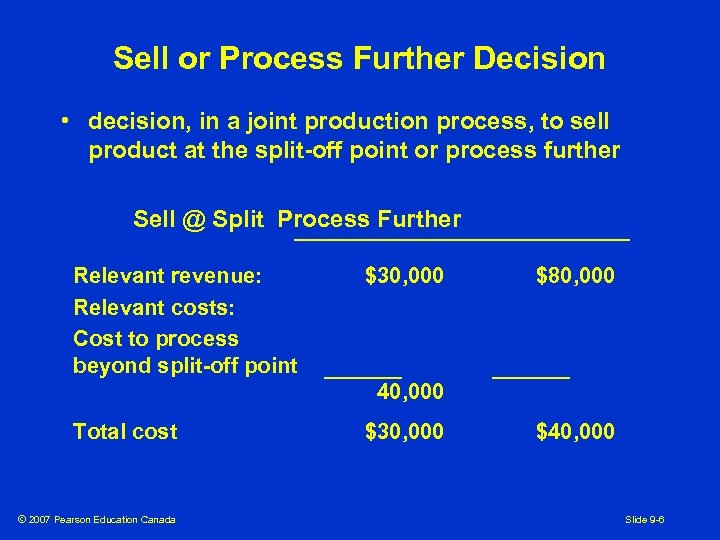 Sell or Process Further Decision • decision, in a joint production process, to sell product at the split-off point or process further Sell @ Split Process Further Relevant revenue: Relevant costs: Cost to process beyond split-off point $30, 000 $80, 000 40, 000 Total cost © 2007 Pearson Education Canada $30, 000 $40, 000 Slide 9 -6
Sell or Process Further Decision • decision, in a joint production process, to sell product at the split-off point or process further Sell @ Split Process Further Relevant revenue: Relevant costs: Cost to process beyond split-off point $30, 000 $80, 000 40, 000 Total cost © 2007 Pearson Education Canada $30, 000 $40, 000 Slide 9 -6
 Irrelevance of Past Costs • Need to irrelevant costs • Past cost are typically irrelevant e. g. obsolete inventory, book value of old equipment • Also known as “sunk” costs © 2007 Pearson Education Canada Slide 9 -7
Irrelevance of Past Costs • Need to irrelevant costs • Past cost are typically irrelevant e. g. obsolete inventory, book value of old equipment • Also known as “sunk” costs © 2007 Pearson Education Canada Slide 9 -7
 Conflicts Between Decision Making and Performance Evaluation • To motivate employees to make optimal decisions, methods of performance evaluation should be consistent with decision making • Sometimes there is a conflict between decision making analysis and the method used to evaluate performance • Organizations need to protect against this to avoid dysfunctional decision making © 2007 Pearson Education Canada Slide 9 -8
Conflicts Between Decision Making and Performance Evaluation • To motivate employees to make optimal decisions, methods of performance evaluation should be consistent with decision making • Sometimes there is a conflict between decision making analysis and the method used to evaluate performance • Organizations need to protect against this to avoid dysfunctional decision making © 2007 Pearson Education Canada Slide 9 -8
 Irrelevance of Future Costs? • Some future costs may be irrelevant because they are the same under all feasible alternatives • They may be safely ignored for the purposes of making a particular decision • Example: salaries of top management © 2007 Pearson Education Canada Slide 9 -9
Irrelevance of Future Costs? • Some future costs may be irrelevant because they are the same under all feasible alternatives • They may be safely ignored for the purposes of making a particular decision • Example: salaries of top management © 2007 Pearson Education Canada Slide 9 -9