c43fb88962642d8a270c1f9801c4bcb3.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 20
 9 July, 2014 Darius Savolskis, Project Officer, DIA Future Naval Systems: Status and Way Ahead
9 July, 2014 Darius Savolskis, Project Officer, DIA Future Naval Systems: Status and Way Ahead
 Content of the Presentation 1. EDA Restructuring/New Structure 2. Future Naval Systems- initial in- house assessment 3. Follow to FNS initial assessment 2 www. eda. europa. eu
Content of the Presentation 1. EDA Restructuring/New Structure 2. Future Naval Systems- initial in- house assessment 3. Follow to FNS initial assessment 2 www. eda. europa. eu
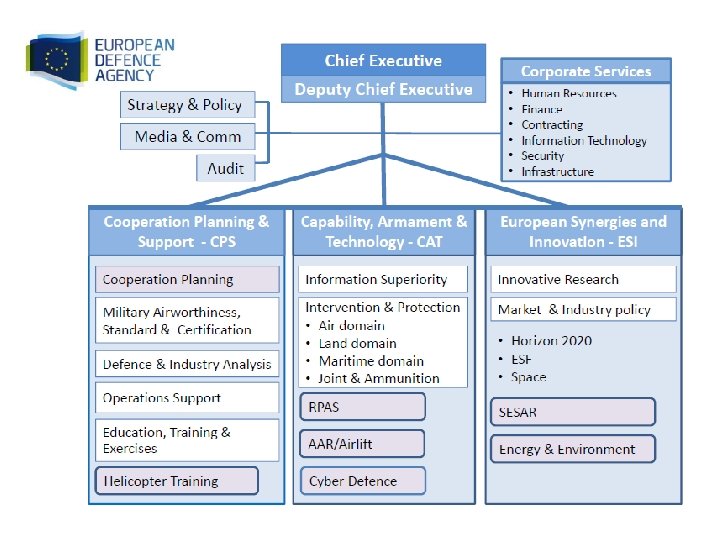 3 www. eda. europa. eu
3 www. eda. europa. eu
 Mission of DIA Unit To understand analyse the European and global defence industry landscape and assess the impact on Member States. To raise awareness and achieve a shared assessment of European defence and the defence industry. Providing timely and accurate information, crucial for strategic decision making. • Cascading industrial knowledge internally through the Agency; • Exploiting synergies within the CPS directorate – creating strong linkages to the CDP; • Being innovative, providing “out of the box” thinking; • Delivering on top management and MS defence industry priorities; • Pursue targeted actions aimed at strengthening the potential for industrial cooperation in Europe; • Connecting and engaging with industrial stakeholders; • Provide data on defence and defence industry. 4 www. eda. europa. eu
Mission of DIA Unit To understand analyse the European and global defence industry landscape and assess the impact on Member States. To raise awareness and achieve a shared assessment of European defence and the defence industry. Providing timely and accurate information, crucial for strategic decision making. • Cascading industrial knowledge internally through the Agency; • Exploiting synergies within the CPS directorate – creating strong linkages to the CDP; • Being innovative, providing “out of the box” thinking; • Delivering on top management and MS defence industry priorities; • Pursue targeted actions aimed at strengthening the potential for industrial cooperation in Europe; • Connecting and engaging with industrial stakeholders; • Provide data on defence and defence industry. 4 www. eda. europa. eu
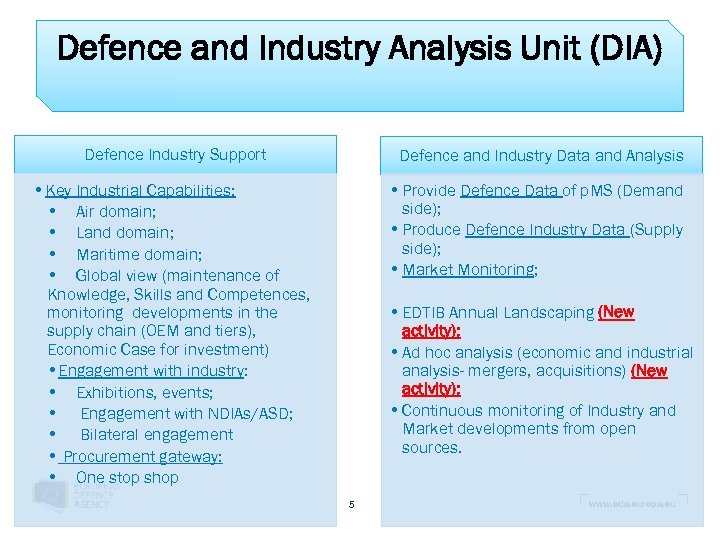 Defence and Industry Analysis Unit (DIA) Defence Industry Support Defence and Industry Data and Analysis • Key Industrial Capabilities: • Air domain; • Land domain; • Maritime domain; • Global view (maintenance of Knowledge, Skills and Competences, monitoring developments in the supply chain (OEM and tiers), Economic Case for investment) • Engagement with industry: • Exhibitions, events; • Engagement with NDIAs/ASD; • Bilateral engagement • Procurement gateway: • One stop shop • Provide Defence Data of p. MS (Demand side); • Produce Defence Industry Data (Supply side); • Market Monitoring; • EDTIB Annual Landscaping (New activity); • Ad hoc analysis (economic and industrial analysis- mergers, acquisitions) (New activity); • Continuous monitoring of Industry and Market developments from open sources. 5 www. eda. europa. eu
Defence and Industry Analysis Unit (DIA) Defence Industry Support Defence and Industry Data and Analysis • Key Industrial Capabilities: • Air domain; • Land domain; • Maritime domain; • Global view (maintenance of Knowledge, Skills and Competences, monitoring developments in the supply chain (OEM and tiers), Economic Case for investment) • Engagement with industry: • Exhibitions, events; • Engagement with NDIAs/ASD; • Bilateral engagement • Procurement gateway: • One stop shop • Provide Defence Data of p. MS (Demand side); • Produce Defence Industry Data (Supply side); • Market Monitoring; • EDTIB Annual Landscaping (New activity); • Ad hoc analysis (economic and industrial analysis- mergers, acquisitions) (New activity); • Continuous monitoring of Industry and Market developments from open sources. 5 www. eda. europa. eu
 Defence Council Conclusions Para. 16 “Europe needs a more integrated, sustainable, innovative and competitive defence technological and industrial base (EDTIB) to develop and sustain defence capabilities. ” “These efforts should be inclusive with opportunities for defence industry in the EU, balanced and in full compliance with EU law. The European Council stresses the need to further develop the necessary skills identified as essential to the future of the European defence industry. 6 www. eda. europa. eu
Defence Council Conclusions Para. 16 “Europe needs a more integrated, sustainable, innovative and competitive defence technological and industrial base (EDTIB) to develop and sustain defence capabilities. ” “These efforts should be inclusive with opportunities for defence industry in the EU, balanced and in full compliance with EU law. The European Council stresses the need to further develop the necessary skills identified as essential to the future of the European defence industry. 6 www. eda. europa. eu
 Defence Council Conclusions DIA Unit contribution: The EDTIB should be strengthened. Defence industry should be “balanced”. The necessary skills identified should be further developed. Actions/Progress: (i) Identify the main trends of the EDTIB in the years to come, EDA is assessing key future trends of the EDTIB, including the main specificities affecting the defence industry in Europe and the notion of balance in the EDTIB; (ii) Outline the specificities of defence industry, including geographical location with a focus on Eastern Europe better to understand the notion of “balance” and promote the concept of a “equal opportunities” for all Member States. EDA is outlining the specificities of the Eastern European defence industry encompassing balance and promoting equal opportunities concept; (iii) Identify critical defence industry skills (on the basis of the EDA study foreseen for 2014 – the scope of which will be determined) - EDA is analysing key skills and competences for defence across Europe. Results are expected in early 2015. 7 www. eda. europa. eu
Defence Council Conclusions DIA Unit contribution: The EDTIB should be strengthened. Defence industry should be “balanced”. The necessary skills identified should be further developed. Actions/Progress: (i) Identify the main trends of the EDTIB in the years to come, EDA is assessing key future trends of the EDTIB, including the main specificities affecting the defence industry in Europe and the notion of balance in the EDTIB; (ii) Outline the specificities of defence industry, including geographical location with a focus on Eastern Europe better to understand the notion of “balance” and promote the concept of a “equal opportunities” for all Member States. EDA is outlining the specificities of the Eastern European defence industry encompassing balance and promoting equal opportunities concept; (iii) Identify critical defence industry skills (on the basis of the EDA study foreseen for 2014 – the scope of which will be determined) - EDA is analysing key skills and competences for defence across Europe. Results are expected in early 2015. 7 www. eda. europa. eu
 Defence and Industry Analysis (DIA) Unit 6 Staff Tanya Armour John Mattiussi Vilem Kolin Darius Savolskis Fabio Liberti Silvija Guzelyte 8 www. eda. europa. eu
Defence and Industry Analysis (DIA) Unit 6 Staff Tanya Armour John Mattiussi Vilem Kolin Darius Savolskis Fabio Liberti Silvija Guzelyte 8 www. eda. europa. eu
 Future Naval Systems (FNS)
Future Naval Systems (FNS)
 Study Context Objective: Capture a snapshot of today’s Naval sector, its position in the global market and identify future trends • FNS part of the wider KIC work strand (FAS, FLS, Ammunition) • Choice of an in-house study (vs. industrial consortium) launched in October 2011 • Sensitivity of data and lack of comparable data sets • Inter-Directorate Team • Series of bilaterals and interviews with governments and industry • Consultation of key naval industry associations (NDIG, ASD, CESA, EMEC) • p. MS stakeholder workshop held in June 2012 • FNS report results discussed in bilaterals with p. MS in autumn 2013 10 www. eda. europa. eu
Study Context Objective: Capture a snapshot of today’s Naval sector, its position in the global market and identify future trends • FNS part of the wider KIC work strand (FAS, FLS, Ammunition) • Choice of an in-house study (vs. industrial consortium) launched in October 2011 • Sensitivity of data and lack of comparable data sets • Inter-Directorate Team • Series of bilaterals and interviews with governments and industry • Consultation of key naval industry associations (NDIG, ASD, CESA, EMEC) • p. MS stakeholder workshop held in June 2012 • FNS report results discussed in bilaterals with p. MS in autumn 2013 10 www. eda. europa. eu
 Main Study Outcomes • High fragmentation and duplication; • Shrinking public budgets; • Strong position in the global market; • Supply Chain Characteristics- vertical integration prevailing; • Shipyards are strategic and economic assets. 11 www. eda. europa. eu
Main Study Outcomes • High fragmentation and duplication; • Shrinking public budgets; • Strong position in the global market; • Supply Chain Characteristics- vertical integration prevailing; • Shipyards are strategic and economic assets. 11 www. eda. europa. eu
 Wider issues addressed by the study • The need for industry to adapt its business and marketing ; • The receptiveness by p. MS to cooperate to an extent at the R&T level; • The need to develop or improve new capabilities. 12 www. eda. europa. eu
Wider issues addressed by the study • The need for industry to adapt its business and marketing ; • The receptiveness by p. MS to cooperate to an extent at the R&T level; • The need to develop or improve new capabilities. 12 www. eda. europa. eu
 From p. MS Strategies to concrete action • ESM 1 Strategic Research Agenda (R&T) and Maritime Landscaping Exercise (CAP) Study as a starting point • Support to agreed p. MS priorities • Reinforcing existing EDA activities and work strands by analysing supply chain issues regarding concrete future capability trends ESM 1 Strategic Research Agenda: Wise Pen - Future EU Maritime Operations Requirements : “The industrial aspects will also need to be designed so that modularized and open-system architecture allows the creation of center of excellence with regard to different standardised modules. New civil-military concepts in the area of modular construction, sharing of costs for dual platforms… “ “The interaction between the platform and the sensor is paramount, both for navies and coast guards… The trend toward multipurpose and modular platforms. ” 13 www. eda. europa. eu
From p. MS Strategies to concrete action • ESM 1 Strategic Research Agenda (R&T) and Maritime Landscaping Exercise (CAP) Study as a starting point • Support to agreed p. MS priorities • Reinforcing existing EDA activities and work strands by analysing supply chain issues regarding concrete future capability trends ESM 1 Strategic Research Agenda: Wise Pen - Future EU Maritime Operations Requirements : “The industrial aspects will also need to be designed so that modularized and open-system architecture allows the creation of center of excellence with regard to different standardised modules. New civil-military concepts in the area of modular construction, sharing of costs for dual platforms… “ “The interaction between the platform and the sensor is paramount, both for navies and coast guards… The trend toward multipurpose and modular platforms. ” 13 www. eda. europa. eu
 Modularity – way forward? • The follow-on study on modularity could aim at analyzing the implications of overarching future trends for Maritime Capabilities, such as e. g. “modularity” concepts (ability to rely on modular systems and subsystems), on the naval supply chain in terms of e. g. - Potential market size and characteristics for modules - Scope for role specialisation across p. MS and industry - Broadening the pool of potential subcontractors and facilitating the entry of SMEs in the supply chain - Scope for civil-military synergies (incl. non-defence specific Co. E, standardisation aspects, economies of scale…) 14 www. eda. europa. eu
Modularity – way forward? • The follow-on study on modularity could aim at analyzing the implications of overarching future trends for Maritime Capabilities, such as e. g. “modularity” concepts (ability to rely on modular systems and subsystems), on the naval supply chain in terms of e. g. - Potential market size and characteristics for modules - Scope for role specialisation across p. MS and industry - Broadening the pool of potential subcontractors and facilitating the entry of SMEs in the supply chain - Scope for civil-military synergies (incl. non-defence specific Co. E, standardisation aspects, economies of scale…) 14 www. eda. europa. eu
 9 July, 2014 Darius Savolskis, Project Officer, DIA Study on Industrial and Technological Competences in the Naval Sector
9 July, 2014 Darius Savolskis, Project Officer, DIA Study on Industrial and Technological Competences in the Naval Sector
 Background • Follow- up study to FNS initial in-house assessment; • Important- factors: 2013 EU Council; EU Maritime Security Strategy adopted in 2014; • Defence budgets cuts- fewer programmes, threat to the industrial and technological competences of the EDTIB; • Study aim: to map European industrial and technological competences which are critical to the future of strong, competent of competitive European Naval Defence Industrial Base, as well as provide recommendations for the further actions aimed at strengthening Naval DTIB. 16 www. eda. europa. eu
Background • Follow- up study to FNS initial in-house assessment; • Important- factors: 2013 EU Council; EU Maritime Security Strategy adopted in 2014; • Defence budgets cuts- fewer programmes, threat to the industrial and technological competences of the EDTIB; • Study aim: to map European industrial and technological competences which are critical to the future of strong, competent of competitive European Naval Defence Industrial Base, as well as provide recommendations for the further actions aimed at strengthening Naval DTIB. 16 www. eda. europa. eu
 Tasks for the Study Contractor I Examination of Supply and Demand • Identify of major European entities and the geographical footprint of the European naval industries (public or private, such as research institutes, centres of excellence and shipyards etc. ) which are the main sources of industrial and technological competences in naval sector (identifying the competences in process). This task will also include geographical mapping of dry docks and identification of the overcapacity of the Naval DTIB in Europe; • Conduct an analysis of the trends regarding technological and industrial competences of Naval sector in Europe; This task will also include identification of the currently existing and potentially appearing gaps with regard to these competences and providing recommendations to address them. The current and potential gaps in competences shall be prioritised; • Identify new technologies with potential impact on the naval sector and assess the impact of these new emerging technologies for Naval EDTIB. 17 www. eda. europa. eu
Tasks for the Study Contractor I Examination of Supply and Demand • Identify of major European entities and the geographical footprint of the European naval industries (public or private, such as research institutes, centres of excellence and shipyards etc. ) which are the main sources of industrial and technological competences in naval sector (identifying the competences in process). This task will also include geographical mapping of dry docks and identification of the overcapacity of the Naval DTIB in Europe; • Conduct an analysis of the trends regarding technological and industrial competences of Naval sector in Europe; This task will also include identification of the currently existing and potentially appearing gaps with regard to these competences and providing recommendations to address them. The current and potential gaps in competences shall be prioritised; • Identify new technologies with potential impact on the naval sector and assess the impact of these new emerging technologies for Naval EDTIB. 17 www. eda. europa. eu
 Tasks for the Study Contractor II Providing recommendations • Provide recommendations for specific EDA actions in Naval domain in order to ensure that naval technological in industrial competences in Europe are retained and improved. • Each recommendation/proposed measure shall be in the form of a business case, accompanied by a detailed analysis, outlining the issues this recommendation/measure seeks to address, its cost, benefits, risks and timeframe for implementation. 18 www. eda. europa. eu
Tasks for the Study Contractor II Providing recommendations • Provide recommendations for specific EDA actions in Naval domain in order to ensure that naval technological in industrial competences in Europe are retained and improved. • Each recommendation/proposed measure shall be in the form of a business case, accompanied by a detailed analysis, outlining the issues this recommendation/measure seeks to address, its cost, benefits, risks and timeframe for implementation. 18 www. eda. europa. eu
 Use of the Study Output • One of the critical elements in a longer-term assessment (in-house/outhouse) of this sector. • The resulting recommendations will be considered for implementation, taking into account EDA activities in R&T domain, as well as the European Commission’s activities in the maritime domain, possibly utilizing some EC instruments. Moreover, the results will support on-going activities in the Maritime Domain (CAT). • The study output/results, elaborating further on the Sectorial Considerations, Critical Defence Technologies and Key Industrial Capabilities for the Naval Sector, will be used as input to the EDA work on sectorial Security of Supply. 19 www. eda. europa. eu
Use of the Study Output • One of the critical elements in a longer-term assessment (in-house/outhouse) of this sector. • The resulting recommendations will be considered for implementation, taking into account EDA activities in R&T domain, as well as the European Commission’s activities in the maritime domain, possibly utilizing some EC instruments. Moreover, the results will support on-going activities in the Maritime Domain (CAT). • The study output/results, elaborating further on the Sectorial Considerations, Critical Defence Technologies and Key Industrial Capabilities for the Naval Sector, will be used as input to the EDA work on sectorial Security of Supply. 19 www. eda. europa. eu
 Thank you for your attention!
Thank you for your attention!


