96ecd7467d34ba8653701f37824e1bde.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 42

9 chapter Human Resource Management Better Business 1 st Edition Poatsy · Martin Slide presentation prepared by Pam Janson Stark State College of Technology © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. 1

All rights reserved. No part of this publication may be reproduced, stored in a retrieval system, or transmitted, in any form or by any means, electronic, mechanical, photocopying, recording, or otherwise, without the prior written permission of the publisher. Printed in the United States of America. © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. 2

Learning Objectives 1. What processes are involved in human resource management? 2. Why is the performance management process proven to be more effective than performance appraisals? 3. What are the main components of compensating and scheduling employees? 4. How does employee status change through promotions, transfers, retirement, and termination? 5. How does incorporating diversity affect the workforce? 6. What are the objectives, structures, and future of labor unions in the global business environment? © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. 3
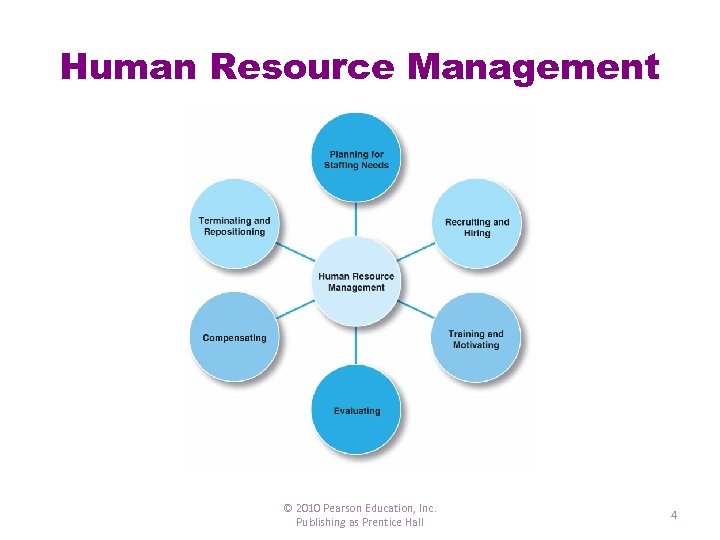
Human Resource Management © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall 4
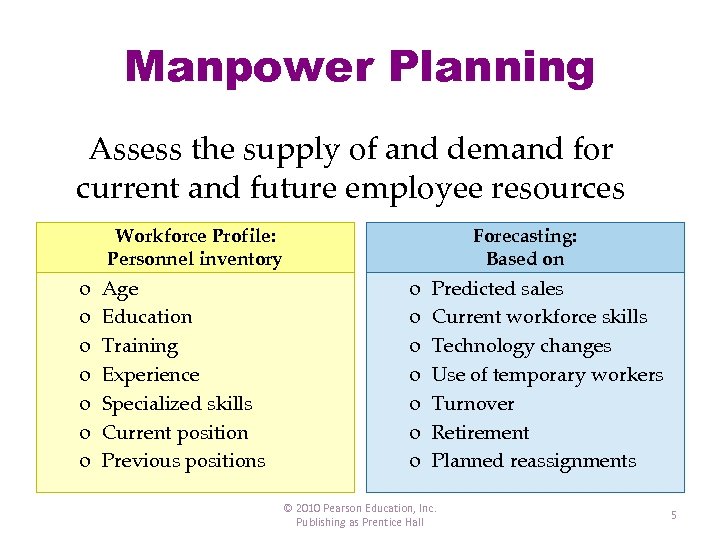
Manpower Planning Assess the supply of and demand for current and future employee resources Workforce Profile: Personnel inventory o o o o Age Education Training Experience Specialized skills Current position Previous positions Forecasting: Based on o o o o Predicted sales Current workforce skills Technology changes Use of temporary workers Turnover Retirement Planned reassignments © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall 5

Job Descriptions and Job Specifications © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall 6

Internal Recruiting • Methods o Company intranet o Staff notice boards o In-house newsletters o Staff meetings © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall 7
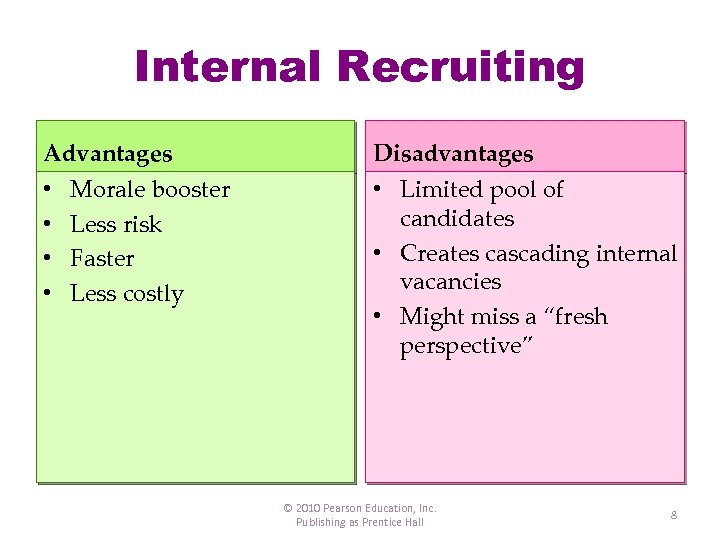
Internal Recruiting Advantages • • Morale booster Less risk Faster Less costly Disadvantages • Limited pool of candidates • Creates cascading internal vacancies • Might miss a “fresh perspective” © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall 8

External Recruiting © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. 9

Recruiting Challenges • One of the newer challenges is the use of technology o Online job and resume posting sites o Web and video blogs o Virtual job fairs o Social networking technologies o Web 2. 0 techniques o Creating enhanced online job postings that stand out • Sifting through these responses to find the right person for the job can be time-consuming and burdensome • Finding qualified candidates for critical positions is still a major challenge © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. 10
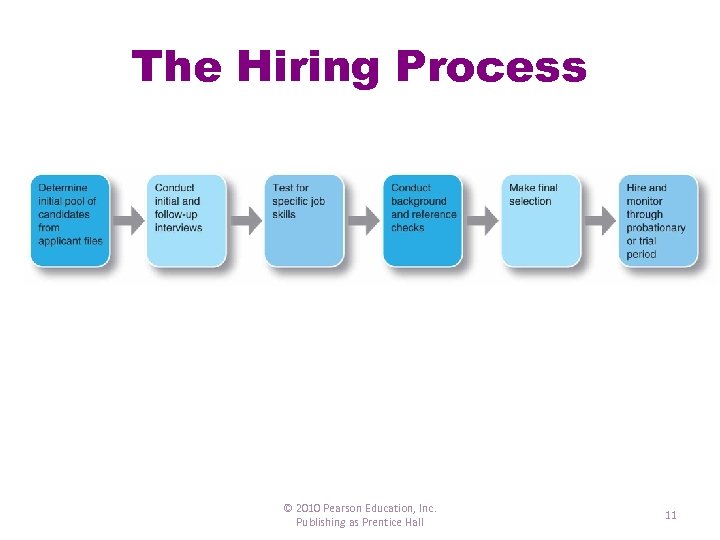
The Hiring Process © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall 11

Federal Laws that Impact Human Resource Management • • Federal Equal Employment Opportunity The Civil Rights Act of 1964 Americans with Disabilities Act Age Discrimination in Employment Act © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall 12

Employee Training Benefits • Increased job satisfaction, motivation, and morale among employees • Greater efficiency in work, resulting in financial gain • More effective use of new technologies and methods • Development of new strategies and products • Lower employee turnover • Fewer interpersonal conflicts and better communication © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. 13

Training Methods • Orientation program • On-the-job training • Apprentice training program • Programmed learning approach • Simulation/vestibule training • Online training © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall 14
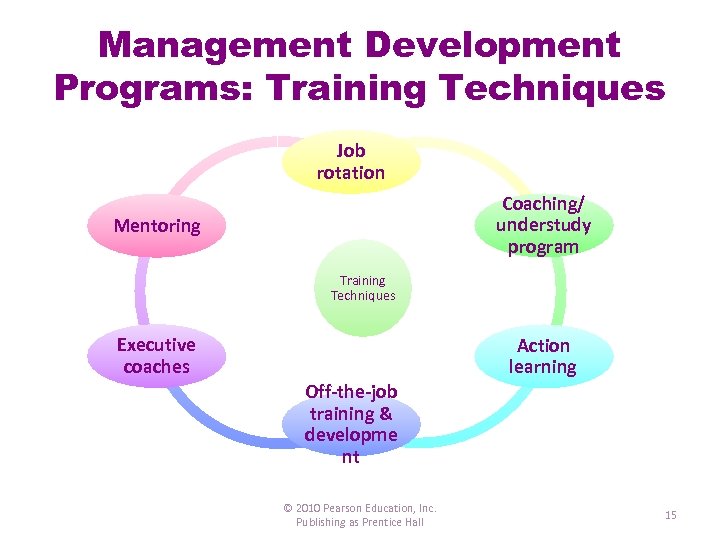
Management Development Programs: Training Techniques Job rotation Coaching/ understudy program Mentoring Training Techniques Executive coaches Action learning Off-the-job training & developme nt © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall 15

Performance Appraisal Process 1. Determine standards that employees should aim for in their work. 2. Evaluate the employee’s performance in comparison with these standards. 3. Provide feedback to reduce and eliminate poor performance and improve or enhance positive performance. © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall 16
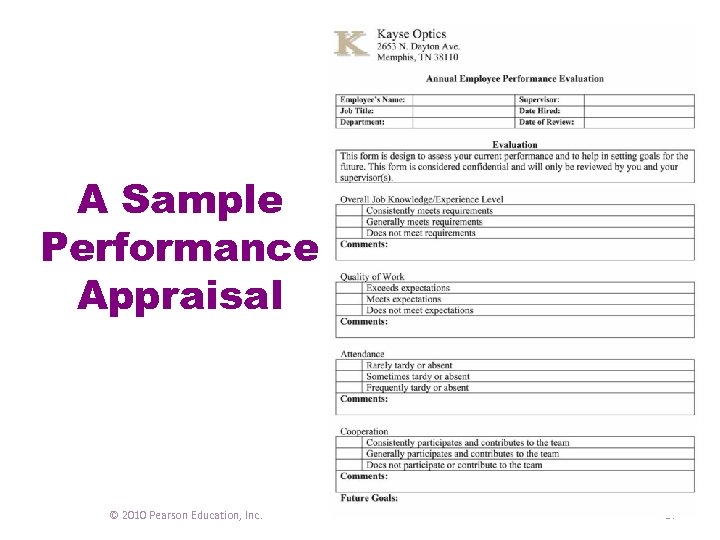
A Sample Performance Appraisal © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. 17

Problems with Performance Appraisals • Managers may shy away from them if they are not comfortable criticizing • Managers may have difficulty quantifying performance • The process does not always offer the opportunity to follow up • With large time spans between appraisals, follow-up items may not occur © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. 18

Performance Management • An alternative to performance appraisals • Combines goal setting, performance appraisal, and training and development into a unified and ongoing process • Employees constantly receive feedback and opportunities for training and development © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall 19

Compensation Strategies • Salary • Wages • Incentive-based payment o Commissions • Bonuses © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall 20

Retirement Plans and Other Financial Incentives • 401(k) plans • Pension plans o Defined benefit plans o Defined contribution plans • • Profit sharing plans Stock option plans Employee stock purchase plans Employee stock ownership plans (ESOPs) © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall 21

Employee Benefits • Benefits are non-cash compensation payment structures • They can come in many forms: o Health and disability insurance o Vacation and sick pay o Retirement plans • Flexible benefit plans o “Cafeteria plans” • Work/life benefits © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall 22

Alternative Scheduling Arrangements • • • Alternative scheduling plans (flextime) Permanent part-time Job sharing Compressed work week Telecommuting © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall 23
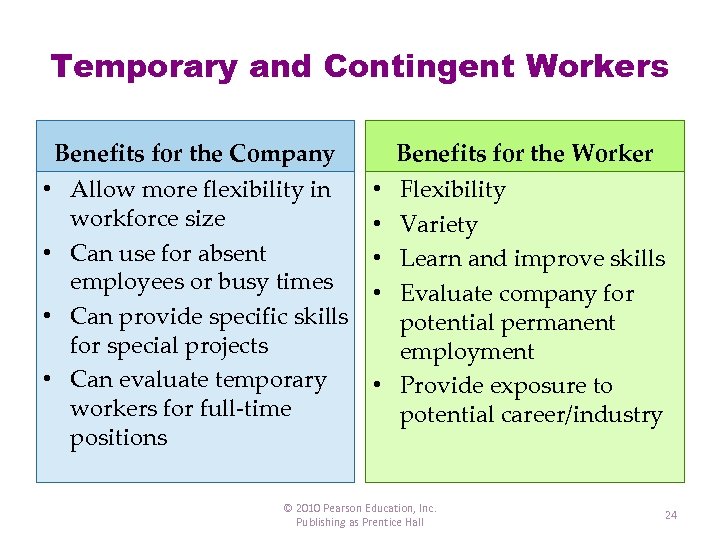
Temporary and Contingent Workers Benefits for the Company • Allow more flexibility in workforce size • Can use for absent employees or busy times • Can provide specific skills for special projects • Can evaluate temporary workers for full-time positions Benefits for the Worker Flexibility Variety Learn and improve skills Evaluate company for potential permanent employment • Provide exposure to potential career/industry • • © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall 24

Promotions and Transfers From the Employer Perspective From the Employee Perspective • Employees look to increase their stature, responsibility, and pay through promotion • Promotion may not always result in a positive situation if it is done with secrecy, unfairness, or arbitrariness • Two career paths o Management o “Individual contributors” • Employers like to promote from within when possible • Management must ensure promotions are based on a distinct set of criteria such as seniority or competency • Two promotion paths o Management o “Individual contributors” © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. 25

Retirement • Mandatory retirement o Historically, age 65 o Nearly ¾ of workers would like to retire before age 60 o 7 out of 10 of workers plan to keep working past retirement age • The major contributing factor is financial need • Worker buyouts o Also called golden parachutes o Offer financial incentives for older workers to retire © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall 26

Terminating Employees • Due to corporate downsizing, etc. o Outplacement services often offered • Due to poor performance or policy violation o Employment at will • Exceptions: discrimination, whistle-blowing, worker’s compensation o Must have written record of issues leading to dismissal © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall 27

Managing Workforce Diversity • Cultural diversity o International expansion o Domestic hiring of international workers • Religion o Provide for religious observations at work o Strive to avoid potential friction between groups • Gender o Gender-related issues have improved, but not gone away • Age o The benefits and challenges of an aging workforce © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall 28

Impact of Diversity • View diversity as: o More than just a response to affirmative action requirements o A competitive advantage o Mission-critical to the organization, requiring: • • • Training Executive accountability Grass roots support such as mentorships © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall 29

Labor and Union Issues • Historically, labor unions were developed to protect workers from horrible working conditions • Today, unions act as bargaining units to negotiate specific employment issues for groups of workers o Locals are created for specific industry, company, region, or business sector © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall 30

AFL-CIO • American Federation of Labor (AFL) founded in 1886 to protect skilled workers • Congress of Industrial Organization (CIO) formed in 1935 to represent entire industries • Combined in 1955 and has 56 member unions today © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall 31

Management/Labor Relations • Collective bargaining process • If no agreement is reached: o Mediation o Arbitration • If negotiation breaks down: o Management may hire strikebreakers or lockout union members o Union members may boycott, strike (and picket), or stage sick-outs © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall 32

The State of Labor Unions • The role of unions is declining in the U. S. because of: o Their success in improving working conditions. o Decline in traditional union industries. • Unions are looking at international coordination to protect their interests © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall 33
Trends in Employee Benefits • Domestic-partner benefits • Paternity benefits • Adoption benefits © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall 34

Chapter Summary 1. What processes are involved in human resource management? 2. Why is the performance management process proven to be more effective than performance appraisals? 3. What are the main components of compensating and scheduling employees? 4. How does employee status change through promotions, transfers, retirement, and termination? 5. How does incorporating diversity affect the workforce? 6. What are the objectives, structures, and future of labor unions in the global business environment? © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall 35

Beyond the Book © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall 36

External Recruiting Advantages: Disadvantages: • Provides new ideas and fresh perspectives • May be more able to initiate a turnaround • Brings in experienced employees • May be less upsetting to present organizational hierarchy • Allows rapid growth • Can increase diversity • Takes longer and costs more • Risk of candidate’s ability to fit with rest of organization • Demoralizing for existing employees • Outsider takes time to become familiar with current systems • Current organization members may fight new ideas © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall 37

“Eighty Is the New Fifty” • More executives are in their 70 s, 80 s, and even 90 s • There is still bias toward older workers in general • Organizations have to learn to manage the older workforce • Perceptions should change as the baby boomers age past the traditional retirement age and want to keep working © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall 38

Rethinking Retirement • Charles Schwab Corporation surveyed nearly 4, 000 across four generations: o Silent Generation (age 63– 83) o Boomers (age 44– 62) o Generation X (age 32– 43) o Generation Y (age 21– 31) • Survey conducted in March and April 2008 Some of the findings: o “Old age” doesn’t begin until 75 or older o Median net worth of retires today is $250, 000, but respondents believe they need at least $500, 000 o Gen Y expects to provide 61% of retirement funds themselves vs. the Silent Generation at 32% o Staying mentally active is the biggest reason for working after retirement o 45% view retirement as a time to “give back” © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall 39

Monster. com and Workforce Diversity • Many companies look at managing a diverse workforce as a competitive advantage. • Hiring workers that represent and understand emerging groups makes sense. o Hispanic Americans account for 15% of the country’s total population. o The Hispanic population accounted for $489 billion in 2000 and is expected to be $1. 2 trillion in 2012. • Monster has created a “diversity database” to help job candidates highlight their cultural understanding, experiences, and knowledge. © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. 40

The State of U. S. Workers • The number receiving unemployment benefits in June 2008 rose to 3. 1 million, the highest since 2004 • Labor is business’ biggest cost o Wage growth has decelerated o Average weekly earnings of production workers were up 3. 2% from June 2007 to June 2008 (4. 6% in August 2006) • In recent decades, labor unions have most power, companies have outsourced offshore and automated • U. S. workers are getting squeezed with sharply rising prices for food and energy, but wages growing more slowly © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. 41

Human Resources and the Green Movement: Work Less • The U. S. leads the world in work and waste • U. S. workers work 100+ more hours per year than in 1976 o This has increased our productivity but also our energy consumption and greenhouse gas emissions • To help the Green Movement, companies should reinvent the work week © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall 42
96ecd7467d34ba8653701f37824e1bde.ppt