95ca54cee0c8e6e64bc291c38beabc47.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 35
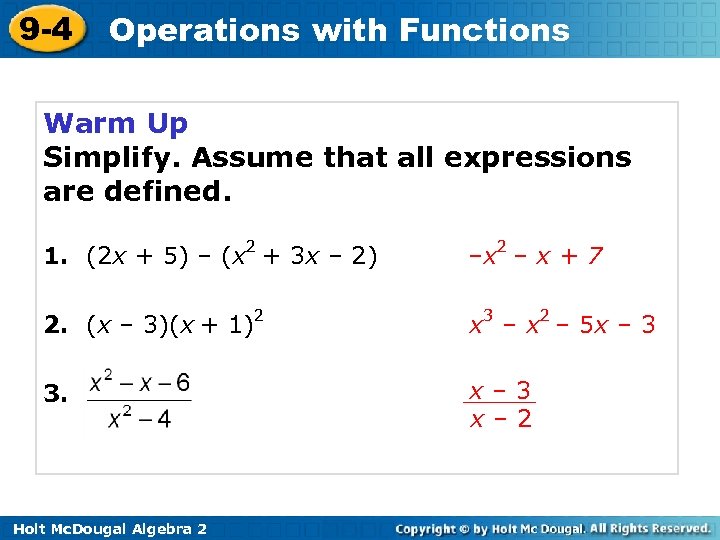 9 -4 Operations with Functions Warm Up Simplify. Assume that all expressions are defined. 1. (2 x + 5) – (x 2 + 3 x – 2) –x 2 – x + 7 2. (x – 3)(x + 1)2 x 3 – x 2 – 5 x – 3 3. x– 3 x– 2 Holt Mc. Dougal Algebra 2
9 -4 Operations with Functions Warm Up Simplify. Assume that all expressions are defined. 1. (2 x + 5) – (x 2 + 3 x – 2) –x 2 – x + 7 2. (x – 3)(x + 1)2 x 3 – x 2 – 5 x – 3 3. x– 3 x– 2 Holt Mc. Dougal Algebra 2
 9 -4 Operations with Functions Objectives Add, subtract, multiply, and divide functions. Write and evaluate composite functions. Holt Mc. Dougal Algebra 2
9 -4 Operations with Functions Objectives Add, subtract, multiply, and divide functions. Write and evaluate composite functions. Holt Mc. Dougal Algebra 2
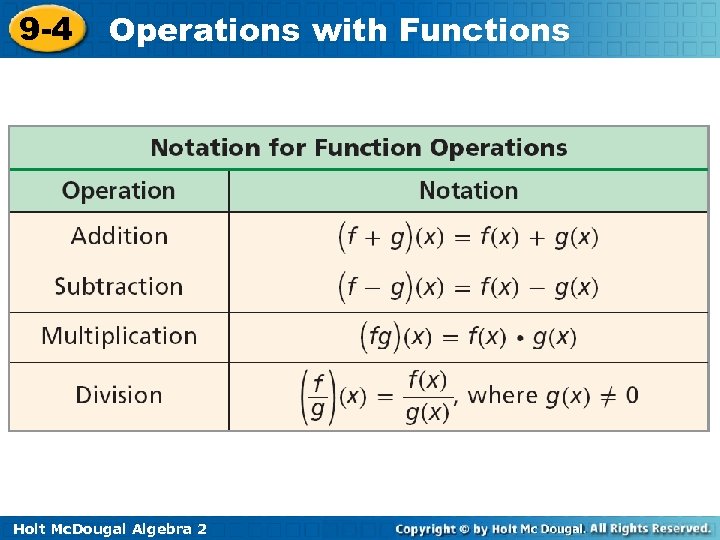
 9 -4 Operations with Functions You can perform operations on functions in much the same way that you perform operations on numbers or expressions. You can add, subtract, multiply, or divide functions by operating on their rules. Holt Mc. Dougal Algebra 2
9 -4 Operations with Functions You can perform operations on functions in much the same way that you perform operations on numbers or expressions. You can add, subtract, multiply, or divide functions by operating on their rules. Holt Mc. Dougal Algebra 2
 9 -4 Operations with Functions Holt Mc. Dougal Algebra 2
9 -4 Operations with Functions Holt Mc. Dougal Algebra 2
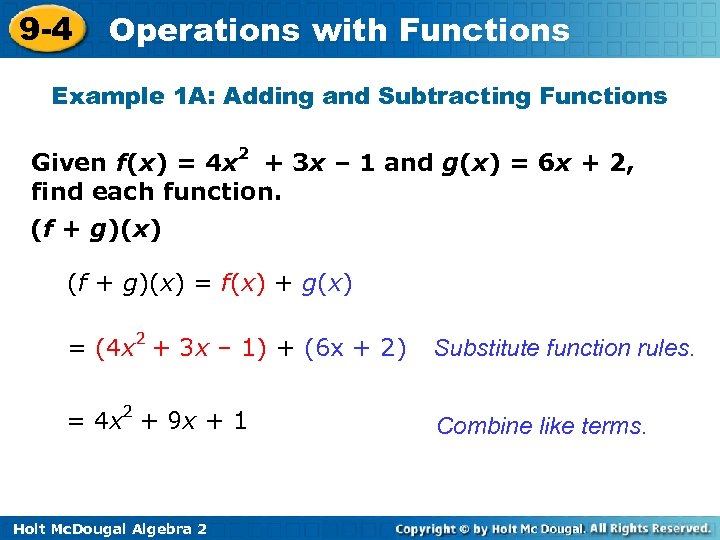 9 -4 Operations with Functions Example 1 A: Adding and Subtracting Functions Given f(x) = 4 x 2 + 3 x – 1 and g(x) = 6 x + 2, find each function. (f + g)(x) = f(x) + g(x) = (4 x 2 + 3 x – 1) + (6 x + 2) Substitute function rules. = 4 x 2 + 9 x + 1 Combine like terms. Holt Mc. Dougal Algebra 2
9 -4 Operations with Functions Example 1 A: Adding and Subtracting Functions Given f(x) = 4 x 2 + 3 x – 1 and g(x) = 6 x + 2, find each function. (f + g)(x) = f(x) + g(x) = (4 x 2 + 3 x – 1) + (6 x + 2) Substitute function rules. = 4 x 2 + 9 x + 1 Combine like terms. Holt Mc. Dougal Algebra 2
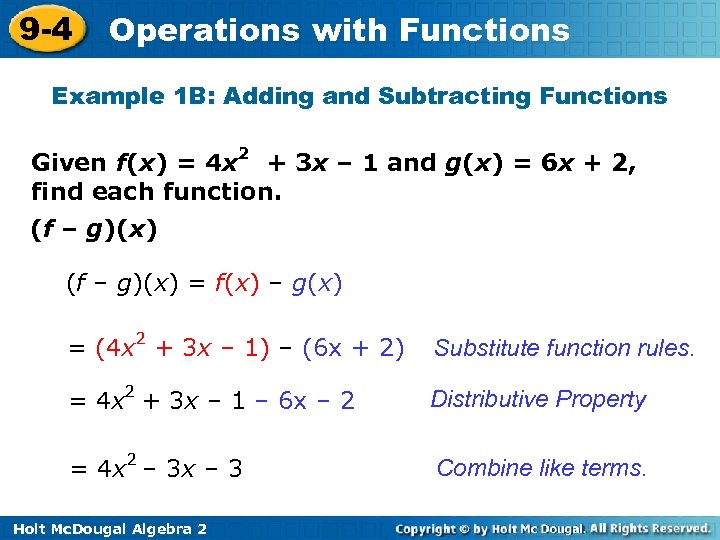 9 -4 Operations with Functions Example 1 B: Adding and Subtracting Functions Given f(x) = 4 x 2 + 3 x – 1 and g(x) = 6 x + 2, find each function. (f – g)(x) = f(x) – g(x) = (4 x 2 + 3 x – 1) – (6 x + 2) Substitute function rules. = 4 x 2 + 3 x – 1 – 6 x – 2 Distributive Property = 4 x 2 – 3 x – 3 Combine like terms. Holt Mc. Dougal Algebra 2
9 -4 Operations with Functions Example 1 B: Adding and Subtracting Functions Given f(x) = 4 x 2 + 3 x – 1 and g(x) = 6 x + 2, find each function. (f – g)(x) = f(x) – g(x) = (4 x 2 + 3 x – 1) – (6 x + 2) Substitute function rules. = 4 x 2 + 3 x – 1 – 6 x – 2 Distributive Property = 4 x 2 – 3 x – 3 Combine like terms. Holt Mc. Dougal Algebra 2
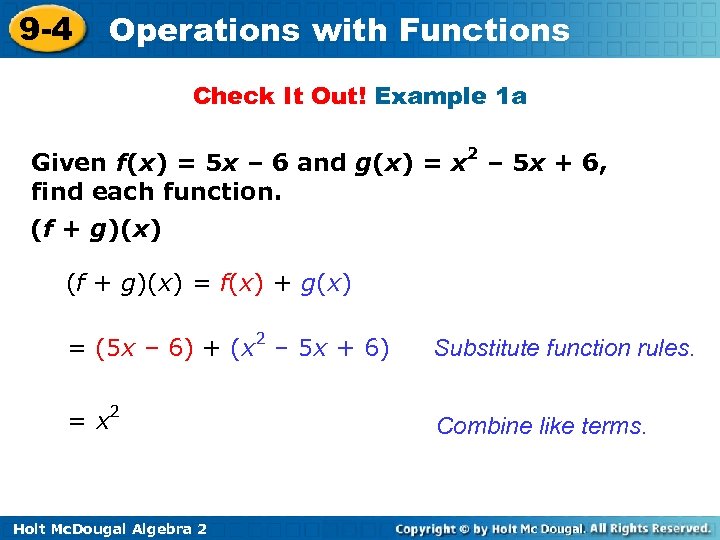 9 -4 Operations with Functions Check It Out! Example 1 a Given f(x) = 5 x – 6 and g(x) = x 2 – 5 x + 6, find each function. (f + g)(x) = f(x) + g(x) = (5 x – 6) + (x 2 – 5 x + 6) Substitute function rules. = x 2 Combine like terms. Holt Mc. Dougal Algebra 2
9 -4 Operations with Functions Check It Out! Example 1 a Given f(x) = 5 x – 6 and g(x) = x 2 – 5 x + 6, find each function. (f + g)(x) = f(x) + g(x) = (5 x – 6) + (x 2 – 5 x + 6) Substitute function rules. = x 2 Combine like terms. Holt Mc. Dougal Algebra 2
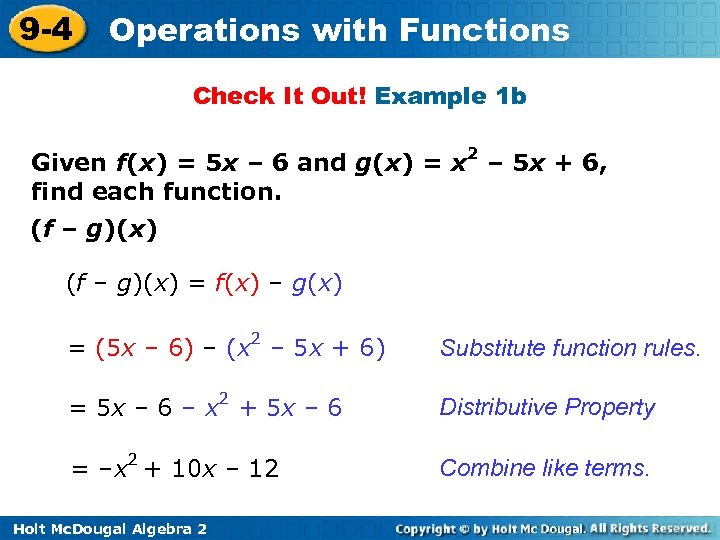 9 -4 Operations with Functions Check It Out! Example 1 b Given f(x) = 5 x – 6 and g(x) = x 2 – 5 x + 6, find each function. (f – g)(x) = f(x) – g(x) = (5 x – 6) – (x 2 – 5 x + 6) Substitute function rules. = 5 x – 6 – x 2 + 5 x – 6 Distributive Property = –x 2 + 10 x – 12 Combine like terms. Holt Mc. Dougal Algebra 2
9 -4 Operations with Functions Check It Out! Example 1 b Given f(x) = 5 x – 6 and g(x) = x 2 – 5 x + 6, find each function. (f – g)(x) = f(x) – g(x) = (5 x – 6) – (x 2 – 5 x + 6) Substitute function rules. = 5 x – 6 – x 2 + 5 x – 6 Distributive Property = –x 2 + 10 x – 12 Combine like terms. Holt Mc. Dougal Algebra 2
 9 -4 Operations with Functions When you divide functions, be sure to note any domain restrictions that may arise. Holt Mc. Dougal Algebra 2
9 -4 Operations with Functions When you divide functions, be sure to note any domain restrictions that may arise. Holt Mc. Dougal Algebra 2
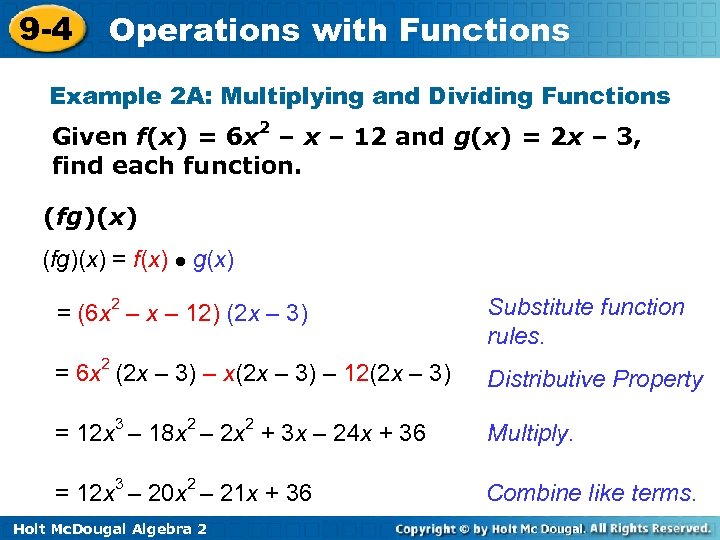 9 -4 Operations with Functions Example 2 A: Multiplying and Dividing Functions Given f(x) = 6 x 2 – x – 12 and g(x) = 2 x – 3, find each function. (fg)(x) = f(x) ● g(x) = (6 x 2 – x – 12) (2 x – 3) Substitute function rules. = 6 x 2 (2 x – 3) – x(2 x – 3) – 12(2 x – 3) Distributive Property = 12 x 3 – 18 x 2 – 2 x 2 + 3 x – 24 x + 36 Multiply. = 12 x 3 – 20 x 2 – 21 x + 36 Combine like terms. Holt Mc. Dougal Algebra 2
9 -4 Operations with Functions Example 2 A: Multiplying and Dividing Functions Given f(x) = 6 x 2 – x – 12 and g(x) = 2 x – 3, find each function. (fg)(x) = f(x) ● g(x) = (6 x 2 – x – 12) (2 x – 3) Substitute function rules. = 6 x 2 (2 x – 3) – x(2 x – 3) – 12(2 x – 3) Distributive Property = 12 x 3 – 18 x 2 – 2 x 2 + 3 x – 24 x + 36 Multiply. = 12 x 3 – 20 x 2 – 21 x + 36 Combine like terms. Holt Mc. Dougal Algebra 2
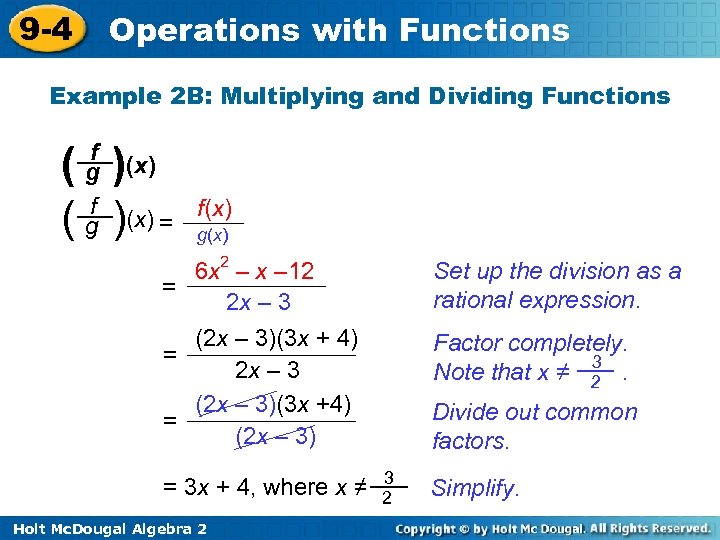 9 -4 Operations with Functions Example 2 B: Multiplying and Dividing Functions f g ( )(x) = f(x) g(x) 6 x 2 – x – 12 = 2 x – 3 (2 x – 3)(3 x + 4) = 2 x – 3 (2 x – 3)(3 x +4) = (2 x – 3) = 3 x + 4, where x ≠ Holt Mc. Dougal Algebra 2 Set up the division as a rational expression. Factor completely. 3 Note that x ≠ 2. Divide out common factors. 3 2 Simplify.
9 -4 Operations with Functions Example 2 B: Multiplying and Dividing Functions f g ( )(x) = f(x) g(x) 6 x 2 – x – 12 = 2 x – 3 (2 x – 3)(3 x + 4) = 2 x – 3 (2 x – 3)(3 x +4) = (2 x – 3) = 3 x + 4, where x ≠ Holt Mc. Dougal Algebra 2 Set up the division as a rational expression. Factor completely. 3 Note that x ≠ 2. Divide out common factors. 3 2 Simplify.
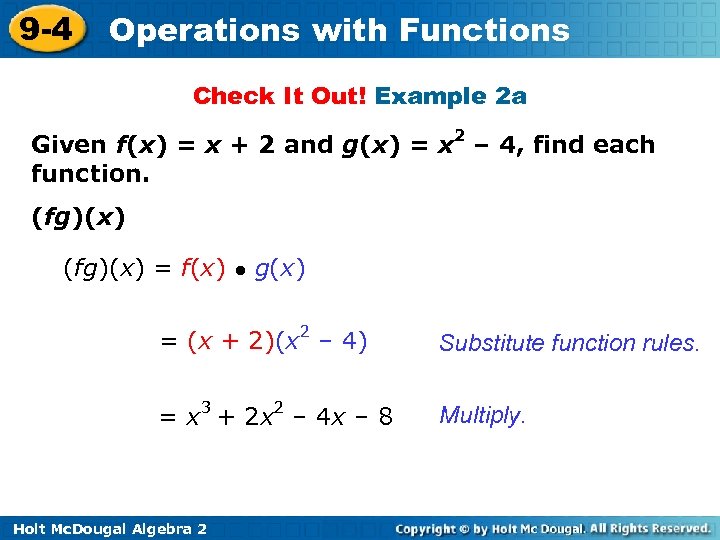 9 -4 Operations with Functions Check It Out! Example 2 a Given f(x) = x + 2 and g(x) = x 2 – 4, find each function. (fg)(x) = f(x) ● g(x) = (x + 2)(x 2 – 4) Substitute function rules. = x 3 + 2 x 2 – 4 x – 8 Multiply. Holt Mc. Dougal Algebra 2
9 -4 Operations with Functions Check It Out! Example 2 a Given f(x) = x + 2 and g(x) = x 2 – 4, find each function. (fg)(x) = f(x) ● g(x) = (x + 2)(x 2 – 4) Substitute function rules. = x 3 + 2 x 2 – 4 x – 8 Multiply. Holt Mc. Dougal Algebra 2
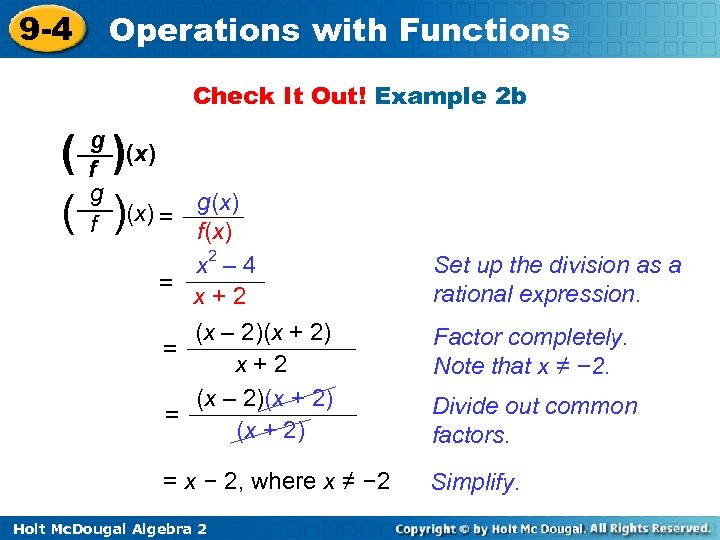 9 -4 Operations with Functions Check It Out! Example 2 b ( ) g (x) f g f (x) = g(x) f(x) x 2 – 4 = x+2 (x – 2)(x + 2) = (x + 2) Divide out common factors. = x – 2, where x ≠ – 2 Simplify. Holt Mc. Dougal Algebra 2 Set up the division as a rational expression. Factor completely. Note that x ≠ – 2.
9 -4 Operations with Functions Check It Out! Example 2 b ( ) g (x) f g f (x) = g(x) f(x) x 2 – 4 = x+2 (x – 2)(x + 2) = (x + 2) Divide out common factors. = x – 2, where x ≠ – 2 Simplify. Holt Mc. Dougal Algebra 2 Set up the division as a rational expression. Factor completely. Note that x ≠ – 2.
 9 -4 Operations with Functions Another function operation uses the output from one function as the input for a second function. This operation is called the composition of functions. Holt Mc. Dougal Algebra 2
9 -4 Operations with Functions Another function operation uses the output from one function as the input for a second function. This operation is called the composition of functions. Holt Mc. Dougal Algebra 2
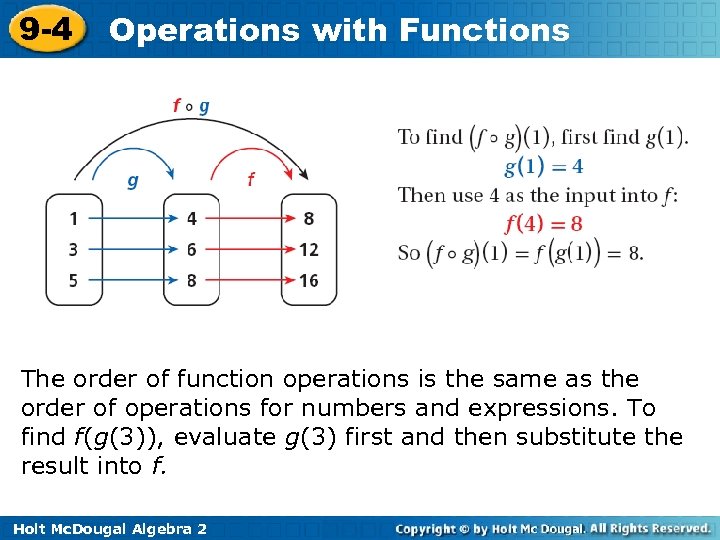 9 -4 Operations with Functions The order of function operations is the same as the order of operations for numbers and expressions. To find f(g(3)), evaluate g(3) first and then substitute the result into f. Holt Mc. Dougal Algebra 2
9 -4 Operations with Functions The order of function operations is the same as the order of operations for numbers and expressions. To find f(g(3)), evaluate g(3) first and then substitute the result into f. Holt Mc. Dougal Algebra 2
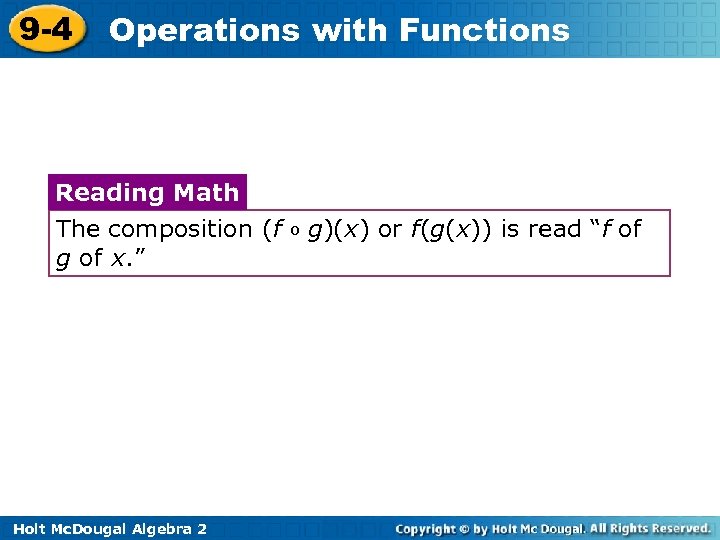 9 -4 Operations with Functions Reading Math The composition (f g of x. ” Holt Mc. Dougal Algebra 2 o g)(x) or f(g(x)) is read “f of
9 -4 Operations with Functions Reading Math The composition (f g of x. ” Holt Mc. Dougal Algebra 2 o g)(x) or f(g(x)) is read “f of
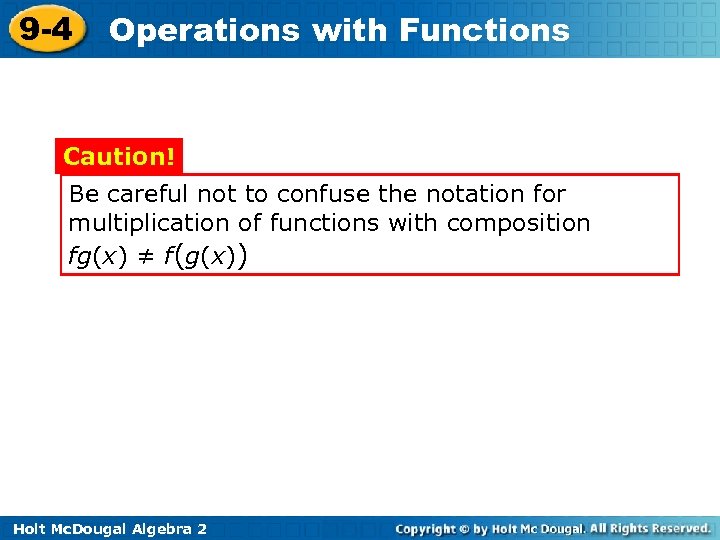 9 -4 Operations with Functions Caution! Be careful not to confuse the notation for multiplication of functions with composition fg(x) ≠ f(g(x)) Holt Mc. Dougal Algebra 2
9 -4 Operations with Functions Caution! Be careful not to confuse the notation for multiplication of functions with composition fg(x) ≠ f(g(x)) Holt Mc. Dougal Algebra 2
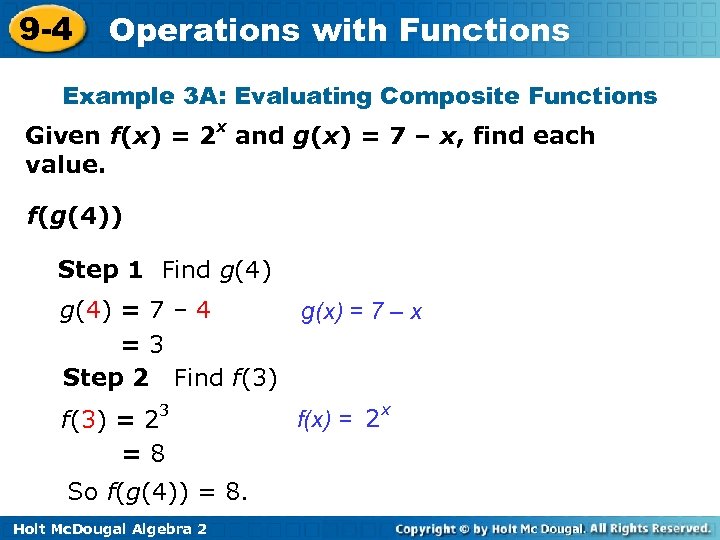 9 -4 Operations with Functions Example 3 A: Evaluating Composite Functions Given f(x) = 2 x and g(x) = 7 – x, find each value. f(g(4)) Step 1 Find g(4) = 7 – 4 g(x) = 7 – x =3 Step 2 Find f(3) = 23 =8 So f(g(4)) = 8. Holt Mc. Dougal Algebra 2 f(x) = 2 x
9 -4 Operations with Functions Example 3 A: Evaluating Composite Functions Given f(x) = 2 x and g(x) = 7 – x, find each value. f(g(4)) Step 1 Find g(4) = 7 – 4 g(x) = 7 – x =3 Step 2 Find f(3) = 23 =8 So f(g(4)) = 8. Holt Mc. Dougal Algebra 2 f(x) = 2 x
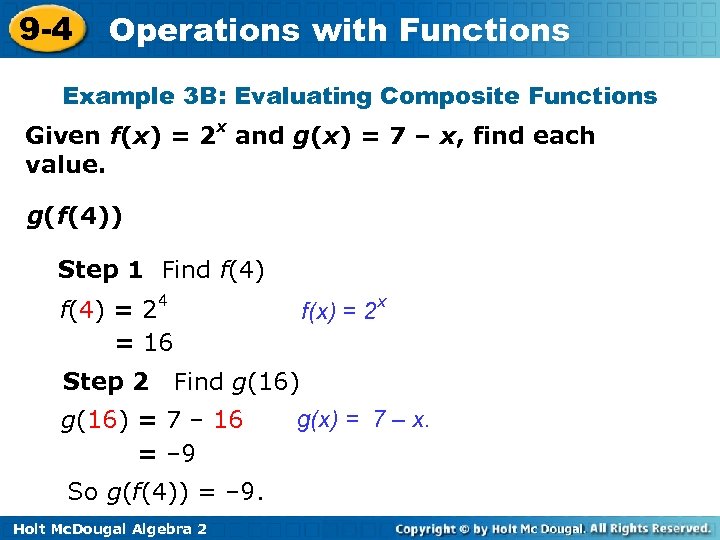 9 -4 Operations with Functions Example 3 B: Evaluating Composite Functions Given f(x) = 2 x and g(x) = 7 – x, find each value. g(f(4)) Step 1 Find f(4) = 24 = 16 Step 2 f(x) = 2 x Find g(16) = 7 – 16 = – 9 So g(f(4)) = – 9. Holt Mc. Dougal Algebra 2 g(x) = 7 – x.
9 -4 Operations with Functions Example 3 B: Evaluating Composite Functions Given f(x) = 2 x and g(x) = 7 – x, find each value. g(f(4)) Step 1 Find f(4) = 24 = 16 Step 2 f(x) = 2 x Find g(16) = 7 – 16 = – 9 So g(f(4)) = – 9. Holt Mc. Dougal Algebra 2 g(x) = 7 – x.
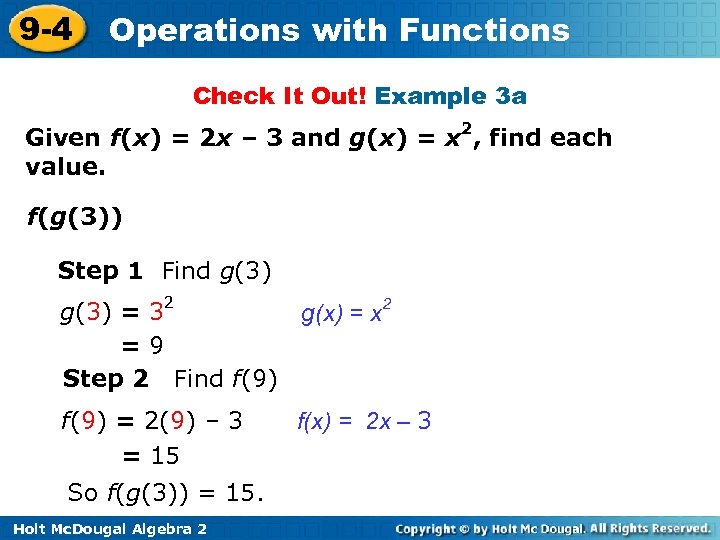 9 -4 Operations with Functions Check It Out! Example 3 a Given f(x) = 2 x – 3 and g(x) = x 2, find each value. f(g(3)) Step 1 Find g(3) = 32 g(x) = x 2 =9 Step 2 Find f(9) = 2(9) – 3 = 15 So f(g(3)) = 15. Holt Mc. Dougal Algebra 2 f(x) = 2 x – 3
9 -4 Operations with Functions Check It Out! Example 3 a Given f(x) = 2 x – 3 and g(x) = x 2, find each value. f(g(3)) Step 1 Find g(3) = 32 g(x) = x 2 =9 Step 2 Find f(9) = 2(9) – 3 = 15 So f(g(3)) = 15. Holt Mc. Dougal Algebra 2 f(x) = 2 x – 3
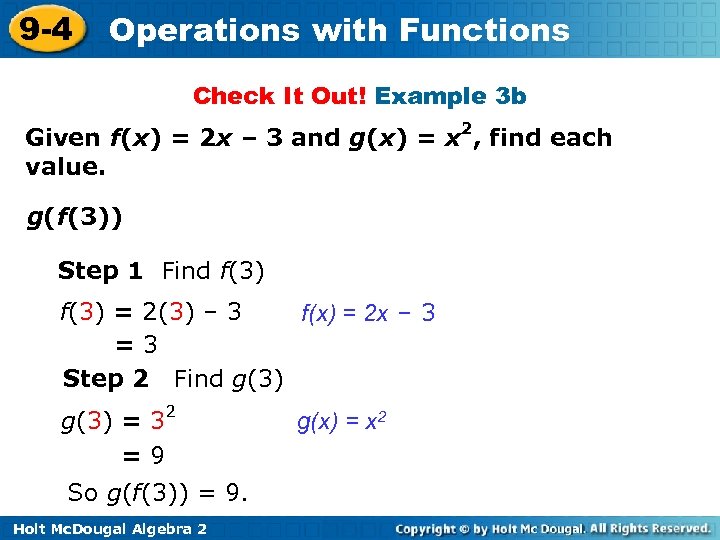 9 -4 Operations with Functions Check It Out! Example 3 b Given f(x) = 2 x – 3 and g(x) = x 2, find each value. g(f(3)) Step 1 Find f(3) = 2(3) – 3 f(x) = 2 x – 3 =3 Step 2 Find g(3) = 32 =9 So g(f(3)) = 9. Holt Mc. Dougal Algebra 2 g(x) = x 2
9 -4 Operations with Functions Check It Out! Example 3 b Given f(x) = 2 x – 3 and g(x) = x 2, find each value. g(f(3)) Step 1 Find f(3) = 2(3) – 3 f(x) = 2 x – 3 =3 Step 2 Find g(3) = 32 =9 So g(f(3)) = 9. Holt Mc. Dougal Algebra 2 g(x) = x 2
 9 -4 Operations with Functions You can use algebraic expressions as well as numbers as inputs into functions. To find a rule for f(g(x)), substitute the rule for g into f. Holt Mc. Dougal Algebra 2
9 -4 Operations with Functions You can use algebraic expressions as well as numbers as inputs into functions. To find a rule for f(g(x)), substitute the rule for g into f. Holt Mc. Dougal Algebra 2
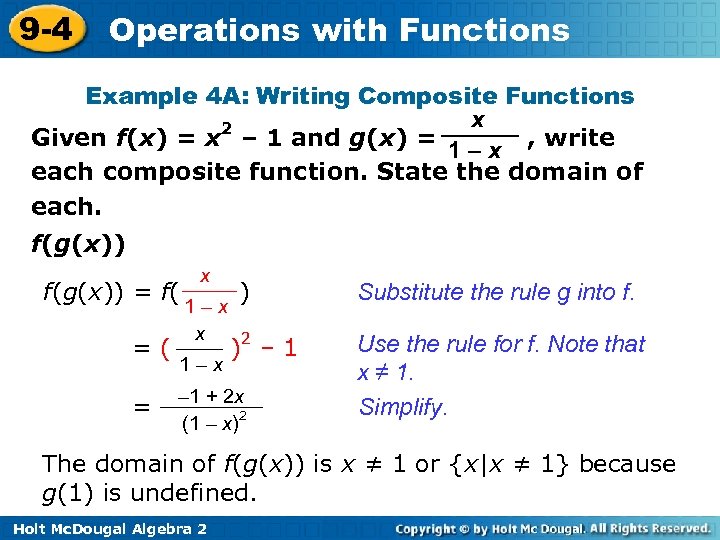 9 -4 Operations with Functions Example 4 A: Writing Composite Functions x 2 Given f(x) = x – 1 and g(x) = , write 1–x each composite function. State the domain of each. f(g(x)) = f( =( = x 1–x ) )2 – 1 + 2 x (1 – x)2 Substitute the rule g into f. Use the rule for f. Note that x ≠ 1. Simplify. The domain of f(g(x)) is x ≠ 1 or {x|x ≠ 1} because g(1) is undefined. Holt Mc. Dougal Algebra 2
9 -4 Operations with Functions Example 4 A: Writing Composite Functions x 2 Given f(x) = x – 1 and g(x) = , write 1–x each composite function. State the domain of each. f(g(x)) = f( =( = x 1–x ) )2 – 1 + 2 x (1 – x)2 Substitute the rule g into f. Use the rule for f. Note that x ≠ 1. Simplify. The domain of f(g(x)) is x ≠ 1 or {x|x ≠ 1} because g(1) is undefined. Holt Mc. Dougal Algebra 2
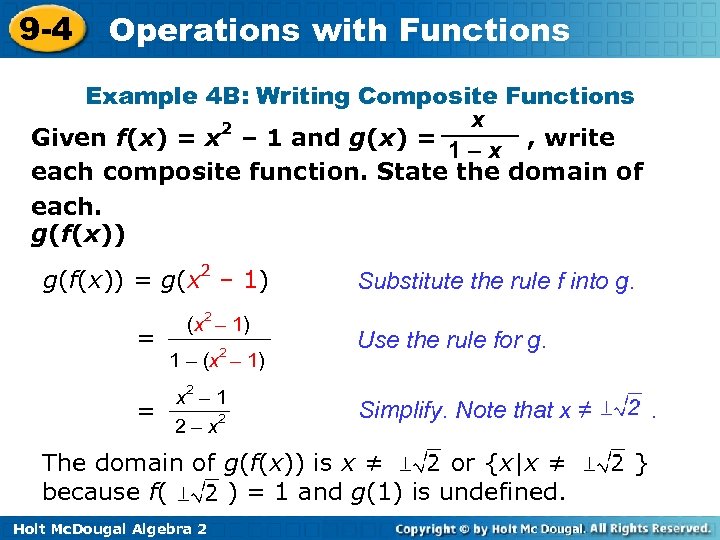 9 -4 Operations with Functions Example 4 B: Writing Composite Functions x 2 Given f(x) = x – 1 and g(x) = , write 1–x each composite function. State the domain of each. g(f(x)) = g(x 2 – 1) = = (x 2 – 1) 2 1 – (x – 1) x 2 – 1 2 – x 2 Substitute the rule f into g. Use the rule for g. Simplify. Note that x ≠ The domain of g(f(x)) is x ≠ or {x|x ≠ because f( ) = 1 and g(1) is undefined. Holt Mc. Dougal Algebra 2 . }
9 -4 Operations with Functions Example 4 B: Writing Composite Functions x 2 Given f(x) = x – 1 and g(x) = , write 1–x each composite function. State the domain of each. g(f(x)) = g(x 2 – 1) = = (x 2 – 1) 2 1 – (x – 1) x 2 – 1 2 – x 2 Substitute the rule f into g. Use the rule for g. Simplify. Note that x ≠ The domain of g(f(x)) is x ≠ or {x|x ≠ because f( ) = 1 and g(1) is undefined. Holt Mc. Dougal Algebra 2 . }
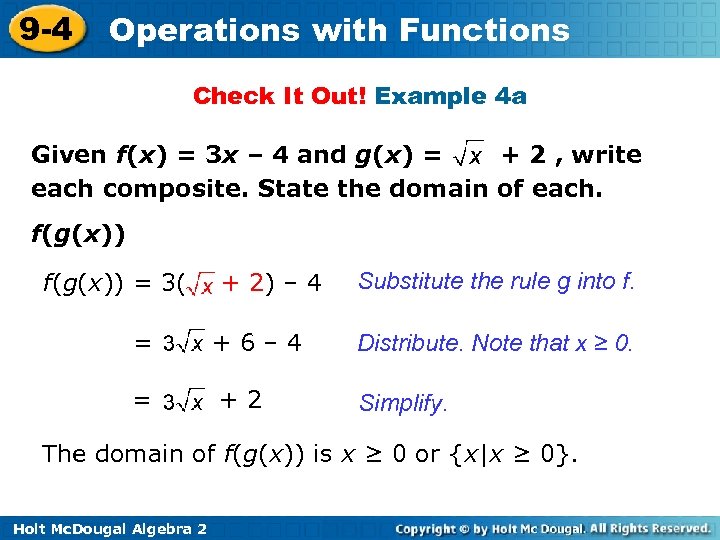 9 -4 Operations with Functions Check It Out! Example 4 a Given f(x) = 3 x – 4 and g(x) = + 2 , write each composite. State the domain of each. f(g(x)) = 3( + 2) – 4 Substitute the rule g into f. = +6– 4 Distribute. Note that x ≥ 0. = +2 Simplify. The domain of f(g(x)) is x ≥ 0 or {x|x ≥ 0}. Holt Mc. Dougal Algebra 2
9 -4 Operations with Functions Check It Out! Example 4 a Given f(x) = 3 x – 4 and g(x) = + 2 , write each composite. State the domain of each. f(g(x)) = 3( + 2) – 4 Substitute the rule g into f. = +6– 4 Distribute. Note that x ≥ 0. = +2 Simplify. The domain of f(g(x)) is x ≥ 0 or {x|x ≥ 0}. Holt Mc. Dougal Algebra 2
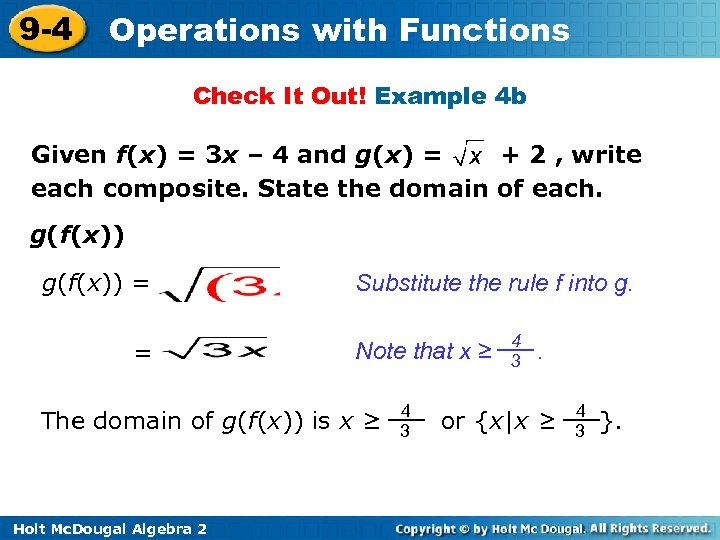 9 -4 Operations with Functions Check It Out! Example 4 b Given f(x) = 3 x – 4 and g(x) = + 2 , write each composite. State the domain of each. g(f(x)) = = Substitute the rule f into g. Note that x ≥ The domain of g(f(x)) is x ≥ Holt Mc. Dougal Algebra 2 4 3 . or {x|x ≥ 4 3 }.
9 -4 Operations with Functions Check It Out! Example 4 b Given f(x) = 3 x – 4 and g(x) = + 2 , write each composite. State the domain of each. g(f(x)) = = Substitute the rule f into g. Note that x ≥ The domain of g(f(x)) is x ≥ Holt Mc. Dougal Algebra 2 4 3 . or {x|x ≥ 4 3 }.
 9 -4 Operations with Functions Composite functions can be used to simplify a series of functions. Holt Mc. Dougal Algebra 2
9 -4 Operations with Functions Composite functions can be used to simplify a series of functions. Holt Mc. Dougal Algebra 2
 9 -4 Operations with Functions Example 5: Business Application Jake imports furniture from Mexico. The exchange rate is 11. 30 pesos per U. S. dollar. The cost of each piece of furniture is given in pesos. The total cost of each piece of furniture includes a 15% service charge. A. Write a composite function to represent the total cost of a piece of furniture in dollars if the cost of the item is c pesos. Holt Mc. Dougal Algebra 2
9 -4 Operations with Functions Example 5: Business Application Jake imports furniture from Mexico. The exchange rate is 11. 30 pesos per U. S. dollar. The cost of each piece of furniture is given in pesos. The total cost of each piece of furniture includes a 15% service charge. A. Write a composite function to represent the total cost of a piece of furniture in dollars if the cost of the item is c pesos. Holt Mc. Dougal Algebra 2
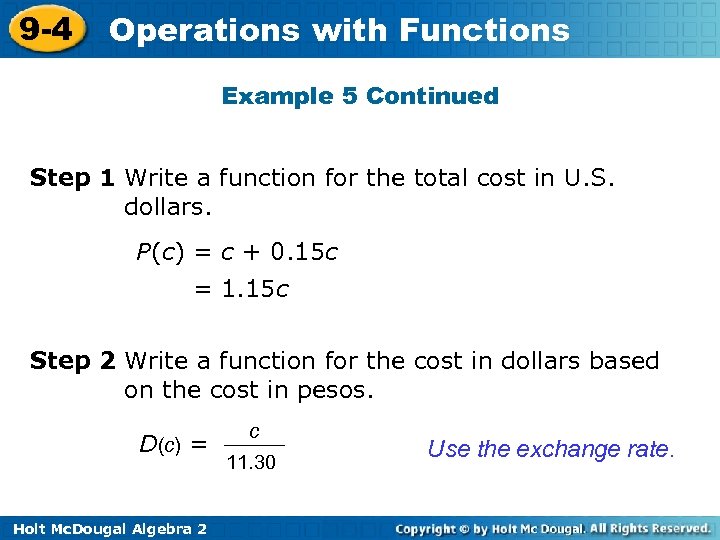 9 -4 Operations with Functions Example 5 Continued Step 1 Write a function for the total cost in U. S. dollars. P(c) = c + 0. 15 c = 1. 15 c Step 2 Write a function for the cost in dollars based on the cost in pesos. D(c) = Holt Mc. Dougal Algebra 2 c 11. 30 Use the exchange rate.
9 -4 Operations with Functions Example 5 Continued Step 1 Write a function for the total cost in U. S. dollars. P(c) = c + 0. 15 c = 1. 15 c Step 2 Write a function for the cost in dollars based on the cost in pesos. D(c) = Holt Mc. Dougal Algebra 2 c 11. 30 Use the exchange rate.
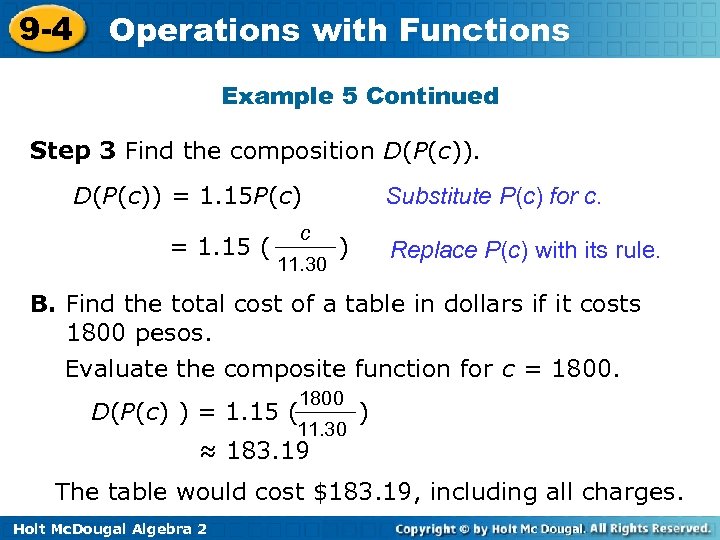 9 -4 Operations with Functions Example 5 Continued Step 3 Find the composition D(P(c)) = 1. 15 P(c) = 1. 15 ( c 11. 30 Substitute P(c) for c. ) Replace P(c) with its rule. B. Find the total cost of a table in dollars if it costs 1800 pesos. Evaluate the composite function for c = 1800. D(P(c) ) = 1. 15 ( 1800 11. 30 ) ≈ 183. 19 The table would cost $183. 19, including all charges. Holt Mc. Dougal Algebra 2
9 -4 Operations with Functions Example 5 Continued Step 3 Find the composition D(P(c)) = 1. 15 P(c) = 1. 15 ( c 11. 30 Substitute P(c) for c. ) Replace P(c) with its rule. B. Find the total cost of a table in dollars if it costs 1800 pesos. Evaluate the composite function for c = 1800. D(P(c) ) = 1. 15 ( 1800 11. 30 ) ≈ 183. 19 The table would cost $183. 19, including all charges. Holt Mc. Dougal Algebra 2
 9 -4 Operations with Functions Check It Out! Example 5 During a sale, a music store is selling all drum kits for 20% off. Preferred customers also receive an additional 15% off. a. Write a composite function to represent the final cost of a kit for a preferred customer that originally cost c dollars. Step 1 Write a function for the final cost of a kit that originally cost c dollars. f(c) = 0. 80 c Holt Mc. Dougal Algebra 2 Drum kits are sold at 80% of their cost.
9 -4 Operations with Functions Check It Out! Example 5 During a sale, a music store is selling all drum kits for 20% off. Preferred customers also receive an additional 15% off. a. Write a composite function to represent the final cost of a kit for a preferred customer that originally cost c dollars. Step 1 Write a function for the final cost of a kit that originally cost c dollars. f(c) = 0. 80 c Holt Mc. Dougal Algebra 2 Drum kits are sold at 80% of their cost.
 9 -4 Operations with Functions Check It Out! Example 5 Continued Step 2 Write a function for the final cost if the customer is a preferred customer. g(c) = 0. 85 c Holt Mc. Dougal Algebra 2 Preferred customers receive 15% off.
9 -4 Operations with Functions Check It Out! Example 5 Continued Step 2 Write a function for the final cost if the customer is a preferred customer. g(c) = 0. 85 c Holt Mc. Dougal Algebra 2 Preferred customers receive 15% off.
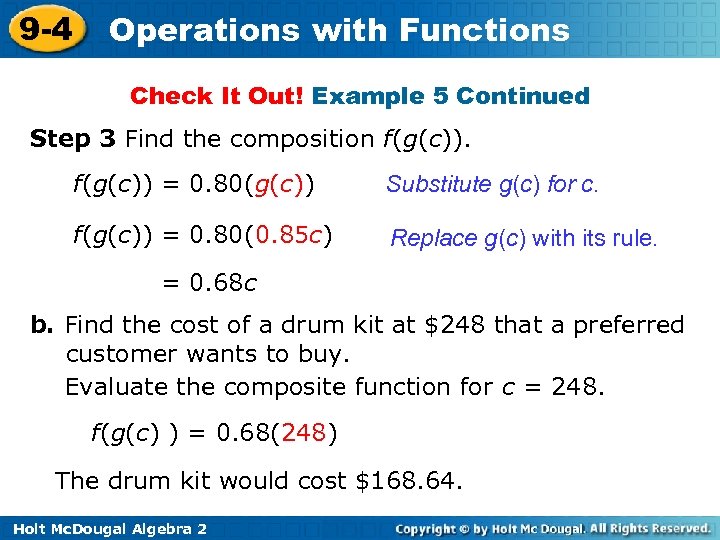 9 -4 Operations with Functions Check It Out! Example 5 Continued Step 3 Find the composition f(g(c)) = 0. 80(g(c)) Substitute g(c) for c. f(g(c)) = 0. 80(0. 85 c) Replace g(c) with its rule. = 0. 68 c b. Find the cost of a drum kit at $248 that a preferred customer wants to buy. Evaluate the composite function for c = 248. f(g(c) ) = 0. 68(248) The drum kit would cost $168. 64. Holt Mc. Dougal Algebra 2
9 -4 Operations with Functions Check It Out! Example 5 Continued Step 3 Find the composition f(g(c)) = 0. 80(g(c)) Substitute g(c) for c. f(g(c)) = 0. 80(0. 85 c) Replace g(c) with its rule. = 0. 68 c b. Find the cost of a drum kit at $248 that a preferred customer wants to buy. Evaluate the composite function for c = 248. f(g(c) ) = 0. 68(248) The drum kit would cost $168. 64. Holt Mc. Dougal Algebra 2
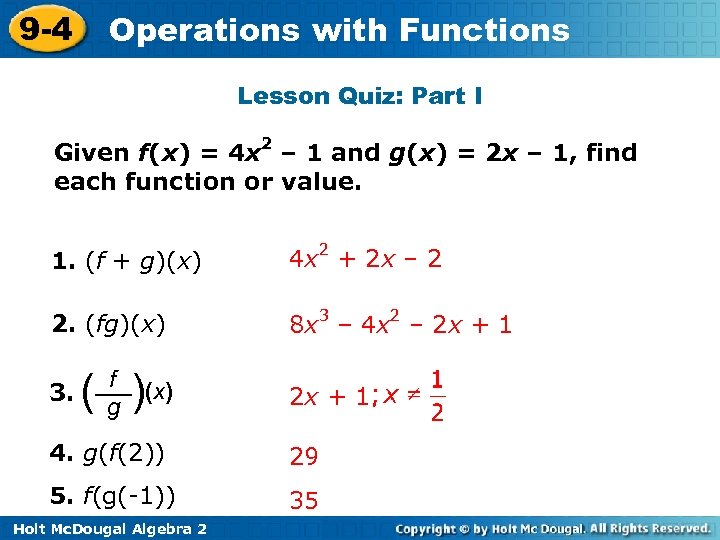 9 -4 Operations with Functions Lesson Quiz: Part I Given f(x) = 4 x 2 – 1 and g(x) = 2 x – 1, find each function or value. 1. (f + g)(x) 4 x 2 + 2 x – 2 2. (fg)(x) 8 x 3 – 4 x 2 – 2 x + 1 3. ( )(x) f g 2 x + 1 4. g(f(2)) 29 5. f(g(-1)) 35 Holt Mc. Dougal Algebra 2
9 -4 Operations with Functions Lesson Quiz: Part I Given f(x) = 4 x 2 – 1 and g(x) = 2 x – 1, find each function or value. 1. (f + g)(x) 4 x 2 + 2 x – 2 2. (fg)(x) 8 x 3 – 4 x 2 – 2 x + 1 3. ( )(x) f g 2 x + 1 4. g(f(2)) 29 5. f(g(-1)) 35 Holt Mc. Dougal Algebra 2
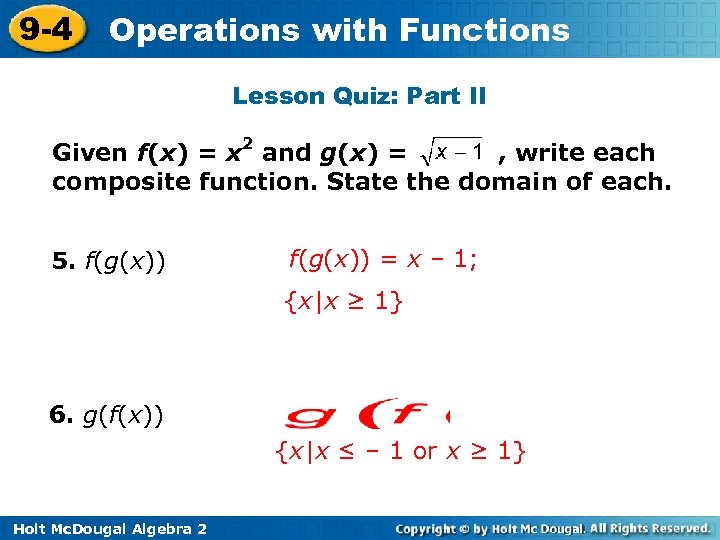 9 -4 Operations with Functions Lesson Quiz: Part II Given f(x) = x 2 and g(x) = , write each composite function. State the domain of each. 5. f(g(x)) = x – 1; {x|x ≥ 1} 6. g(f(x)) {x|x ≤ – 1 or x ≥ 1} Holt Mc. Dougal Algebra 2
9 -4 Operations with Functions Lesson Quiz: Part II Given f(x) = x 2 and g(x) = , write each composite function. State the domain of each. 5. f(g(x)) = x – 1; {x|x ≥ 1} 6. g(f(x)) {x|x ≤ – 1 or x ≥ 1} Holt Mc. Dougal Algebra 2


