d6af2d4675dd197a2ed89ede65b26e50.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 48
 9. 1 – Similar Right Triangles
9. 1 – Similar Right Triangles
 Theorem 9. 1: If the altitude is drawn to the hypotenuse of a right triangle, then the two triangles formed are similar to the original triangle and to each other. C A N B
Theorem 9. 1: If the altitude is drawn to the hypotenuse of a right triangle, then the two triangles formed are similar to the original triangle and to each other. C A N B
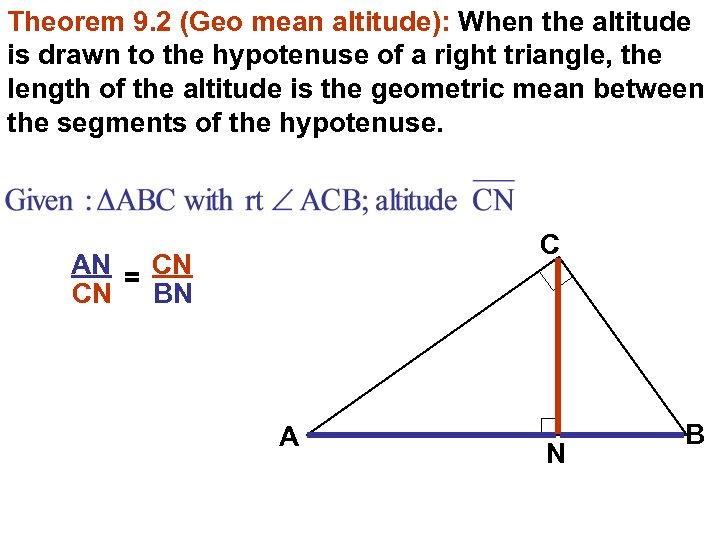 Theorem 9. 2 (Geo mean altitude): When the altitude is drawn to the hypotenuse of a right triangle, the length of the altitude is the geometric mean between the segments of the hypotenuse. C AN = CN CN BN A N B
Theorem 9. 2 (Geo mean altitude): When the altitude is drawn to the hypotenuse of a right triangle, the length of the altitude is the geometric mean between the segments of the hypotenuse. C AN = CN CN BN A N B
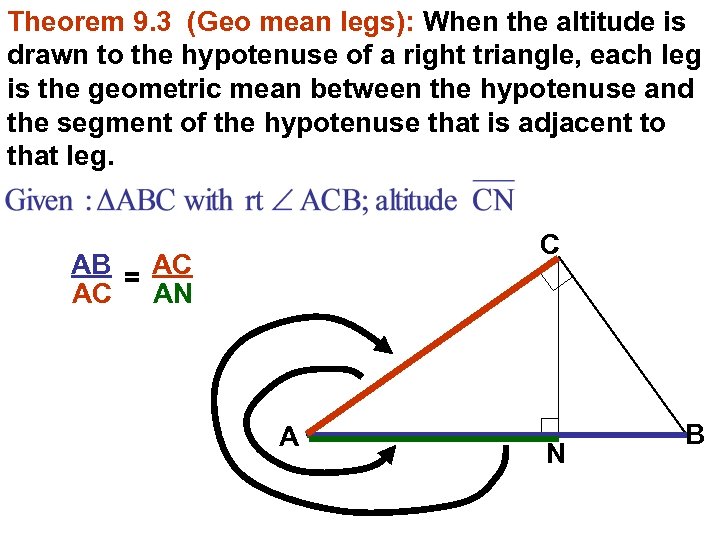 Theorem 9. 3 (Geo mean legs): When the altitude is drawn to the hypotenuse of a right triangle, each leg is the geometric mean between the hypotenuse and the segment of the hypotenuse that is adjacent to that leg. C AB = AC AC AN A N B
Theorem 9. 3 (Geo mean legs): When the altitude is drawn to the hypotenuse of a right triangle, each leg is the geometric mean between the hypotenuse and the segment of the hypotenuse that is adjacent to that leg. C AB = AC AC AN A N B
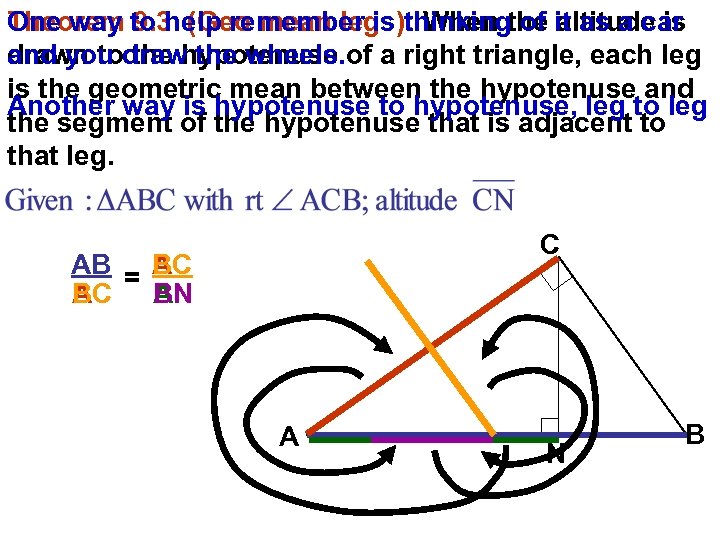 One way 9. 3 (Geo mean legs): When the altitude is Theorem to help remember is thinking of it as a car and you the hypotenuse drawn todraw the wheels. of a right triangle, each leg is the geometric mean between the hypotenuse and Another way is hypotenuse to hypotenuse, leg to leg the segment of the hypotenuse that is adjacent to that leg. C AB = AC BC BC BN AC AN A N B
One way 9. 3 (Geo mean legs): When the altitude is Theorem to help remember is thinking of it as a car and you the hypotenuse drawn todraw the wheels. of a right triangle, each leg is the geometric mean between the hypotenuse and Another way is hypotenuse to hypotenuse, leg to leg the segment of the hypotenuse that is adjacent to that leg. C AB = AC BC BC BN AC AN A N B
 Set up Proportions C A N B
Set up Proportions C A N B
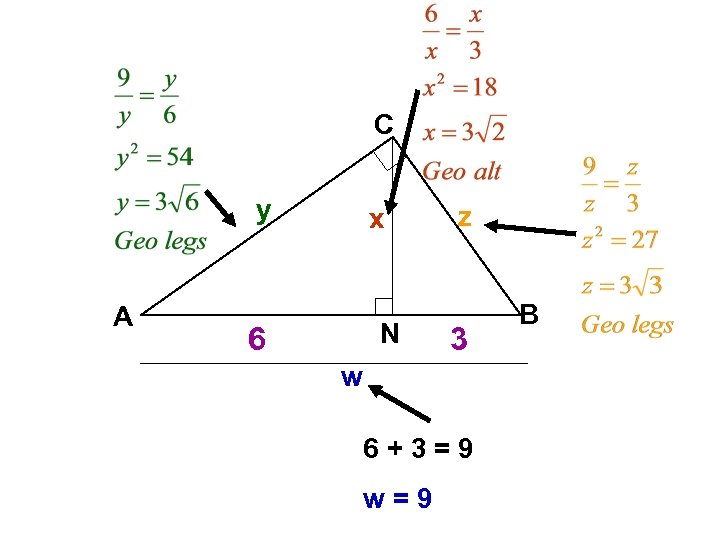 C y A x N 6 z 3 w 6+3=9 w=9 B
C y A x N 6 z 3 w 6+3=9 w=9 B
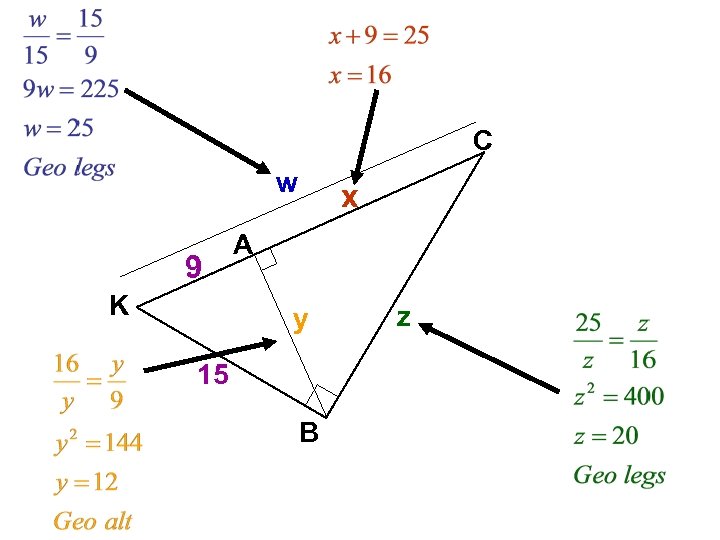 C w 9 K x A y 15 B z
C w 9 K x A y 15 B z
 9. 2 – Pythagorean Theorem
9. 2 – Pythagorean Theorem
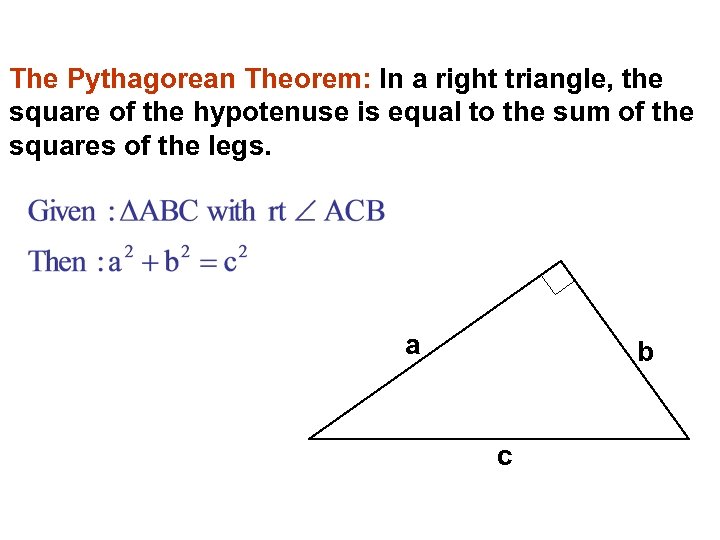 The Pythagorean Theorem: In a right triangle, the square of the hypotenuse is equal to the sum of the squares of the legs. a b c
The Pythagorean Theorem: In a right triangle, the square of the hypotenuse is equal to the sum of the squares of the legs. a b c
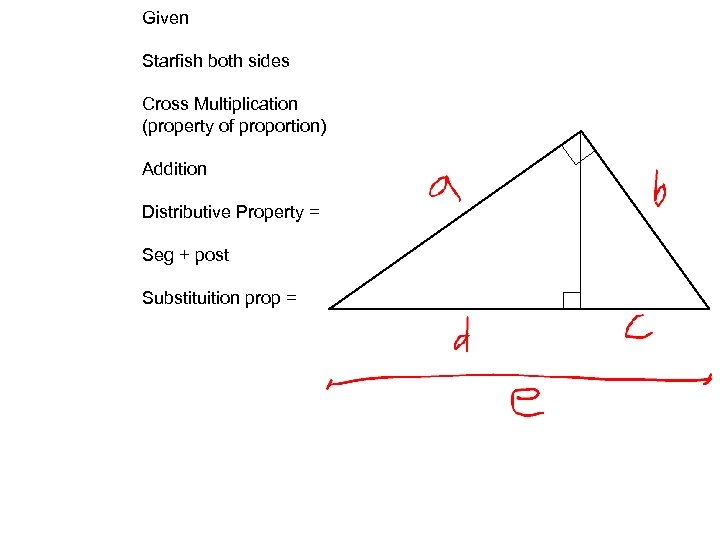 Given Starfish both sides Cross Multiplication (property of proportion) Addition Distributive Property = Seg + post Substituition prop =
Given Starfish both sides Cross Multiplication (property of proportion) Addition Distributive Property = Seg + post Substituition prop =
 • Pythagorean Triple is a set of three positive integers a, b, and c that satisfy the equation a 2 + b 2 = c 2. • Examples: – 3, 4, 5 – 5, 12, 13 – 7, 24, 25 – 8, 15, 17 – Multiples of those.
• Pythagorean Triple is a set of three positive integers a, b, and c that satisfy the equation a 2 + b 2 = c 2. • Examples: – 3, 4, 5 – 5, 12, 13 – 7, 24, 25 – 8, 15, 17 – Multiples of those.
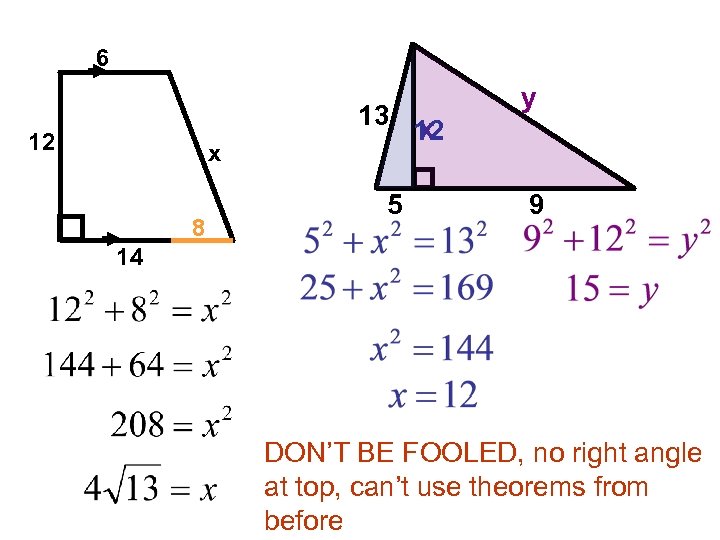 6 13 12 x 8 5 x 12 y 9 14 DON’T BE FOOLED, no right angle at top, can’t use theorems from before
6 13 12 x 8 5 x 12 y 9 14 DON’T BE FOOLED, no right angle at top, can’t use theorems from before
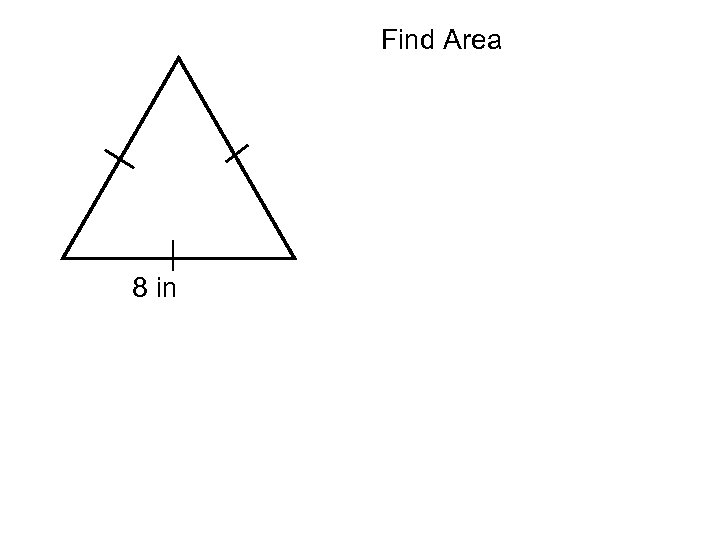 Find Area 8 in
Find Area 8 in
 9. 3 – The Converse of the Pythagorean Theorem
9. 3 – The Converse of the Pythagorean Theorem
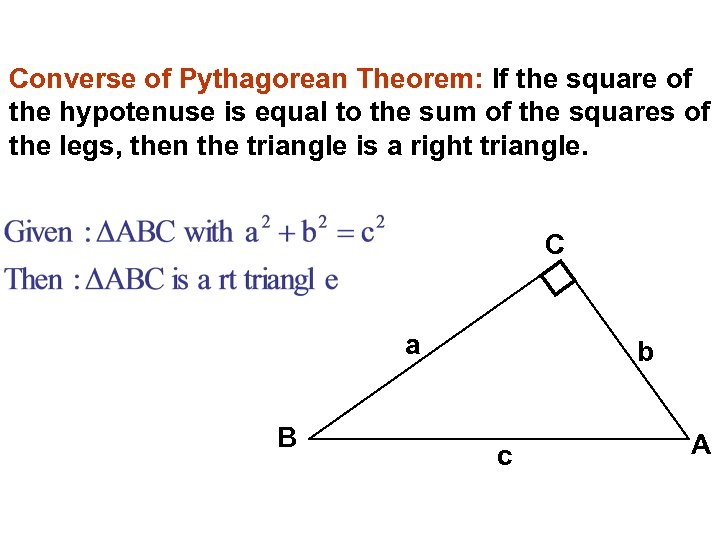 Converse of Pythagorean Theorem: If the square of the hypotenuse is equal to the sum of the squares of the legs, then the triangle is a right triangle. C a B b c A
Converse of Pythagorean Theorem: If the square of the hypotenuse is equal to the sum of the squares of the legs, then the triangle is a right triangle. C a B b c A
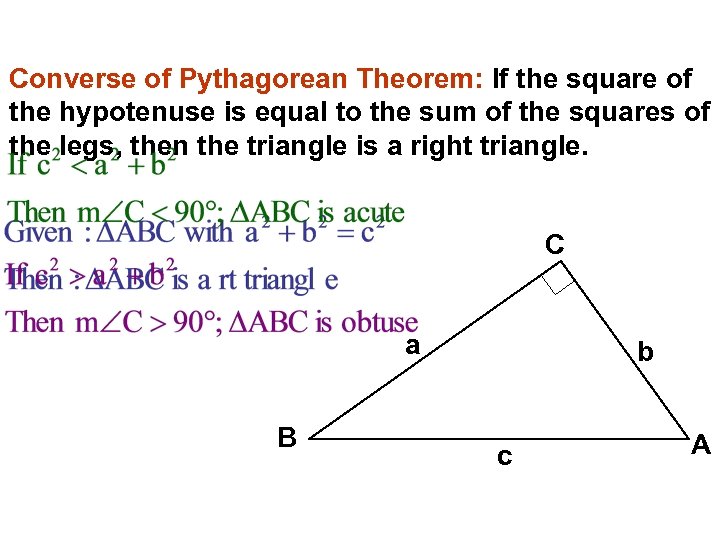 Converse of Pythagorean Theorem: If the square of the hypotenuse is equal to the sum of the squares of the legs, then the triangle is a right triangle. C a B b c A
Converse of Pythagorean Theorem: If the square of the hypotenuse is equal to the sum of the squares of the legs, then the triangle is a right triangle. C a B b c A
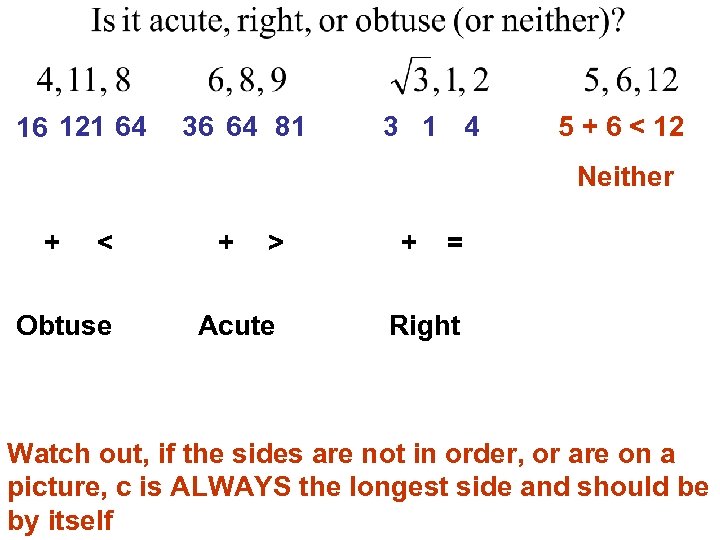 16 121 64 36 64 81 3 1 4 5 + 6 < 12 Neither + < Obtuse + > Acute + = Right Watch out, if the sides are not in order, or are on a picture, c is ALWAYS the longest side and should be by itself
16 121 64 36 64 81 3 1 4 5 + 6 < 12 Neither + < Obtuse + > Acute + = Right Watch out, if the sides are not in order, or are on a picture, c is ALWAYS the longest side and should be by itself

 Reminders of the past. Properties of: Parallelograms Rectangles 1) 1) 2) 2) 3) Rhombus 4) 1) 5) 2) 6) 3)
Reminders of the past. Properties of: Parallelograms Rectangles 1) 1) 2) 2) 3) Rhombus 4) 1) 5) 2) 6) 3)
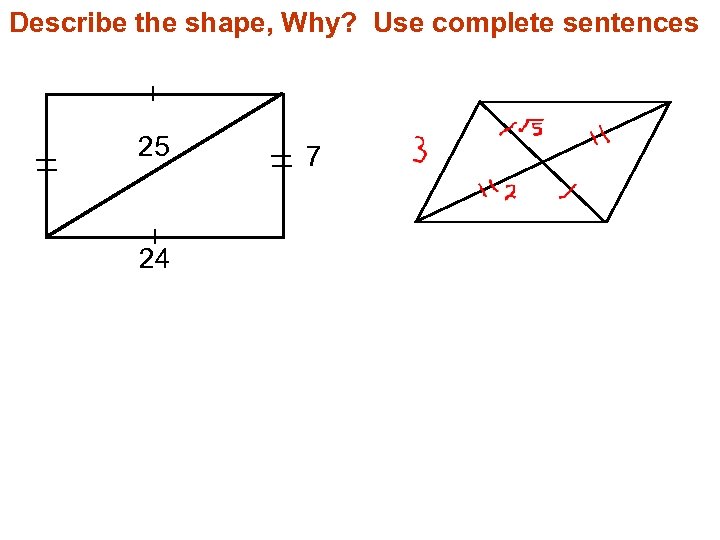 Describe the shape, Why? Use complete sentences 25 24 7
Describe the shape, Why? Use complete sentences 25 24 7
 9. 4 – Special Right Triangles
9. 4 – Special Right Triangles
 • Rationalize practice
• Rationalize practice
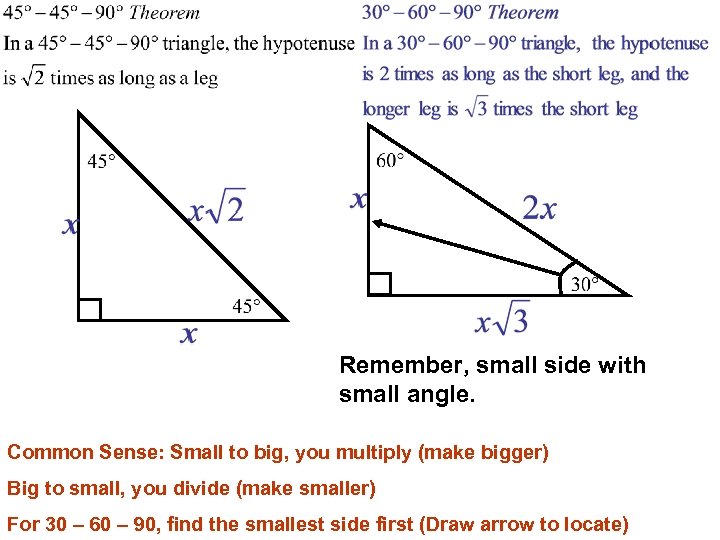 Remember, small side with small angle. Common Sense: Small to big, you multiply (make bigger) Big to small, you divide (make smaller) For 30 – 60 – 90, find the smallest side first (Draw arrow to locate)
Remember, small side with small angle. Common Sense: Small to big, you multiply (make bigger) Big to small, you divide (make smaller) For 30 – 60 – 90, find the smallest side first (Draw arrow to locate)
 Lots of examples
Lots of examples
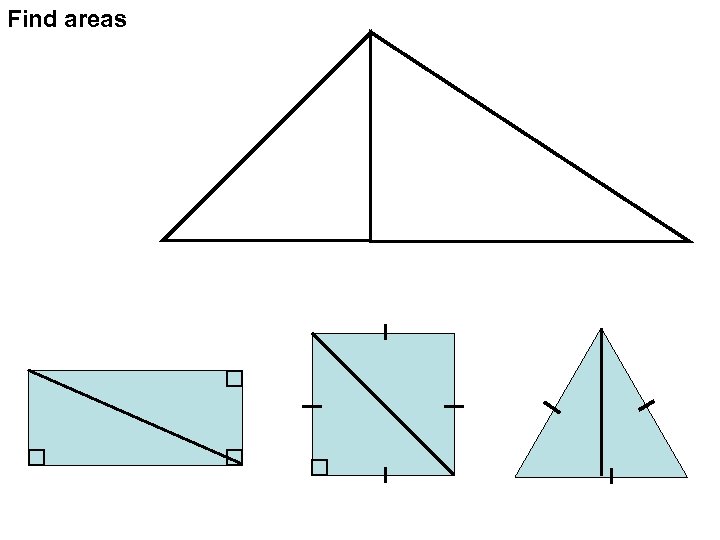 Find areas
Find areas
 9. 5 – Trigonometric Ratios
9. 5 – Trigonometric Ratios
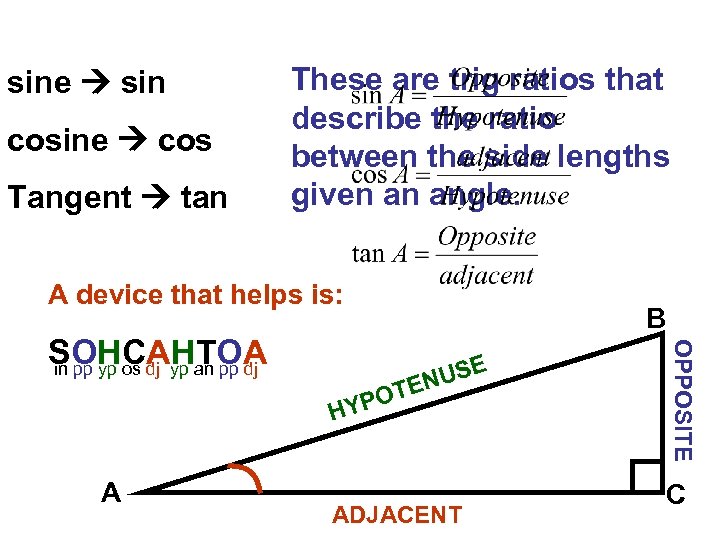 sine sin cosine cos Tangent tan These are trig ratios that describe the ratio between the side lengths given an angle. A device that helps is: A USE EN POT HY ADJACENT OPPOSITE SOHCAHTOA in pp yp os dj yp an pp dj B C
sine sin cosine cos Tangent tan These are trig ratios that describe the ratio between the side lengths given an angle. A device that helps is: A USE EN POT HY ADJACENT OPPOSITE SOHCAHTOA in pp yp os dj yp an pp dj B C
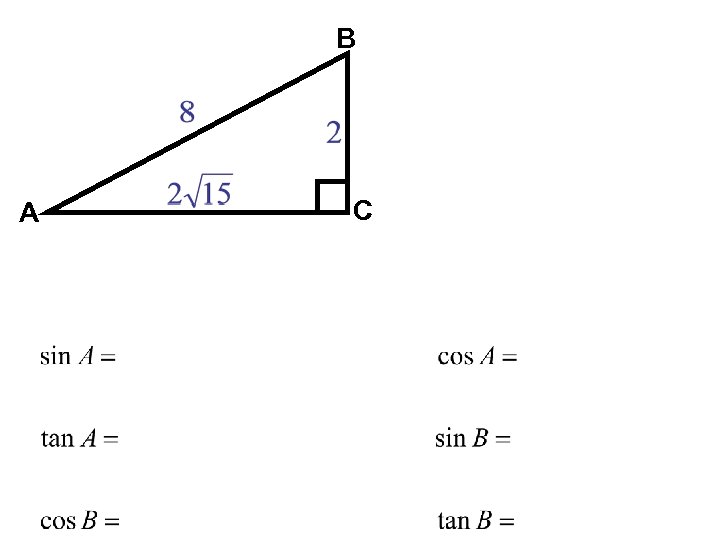 B A C
B A C
 • Calculator CHECK – MODE!!!!!! Should be in degrees – sin(30 o) Test, should give you. 5
• Calculator CHECK – MODE!!!!!! Should be in degrees – sin(30 o) Test, should give you. 5
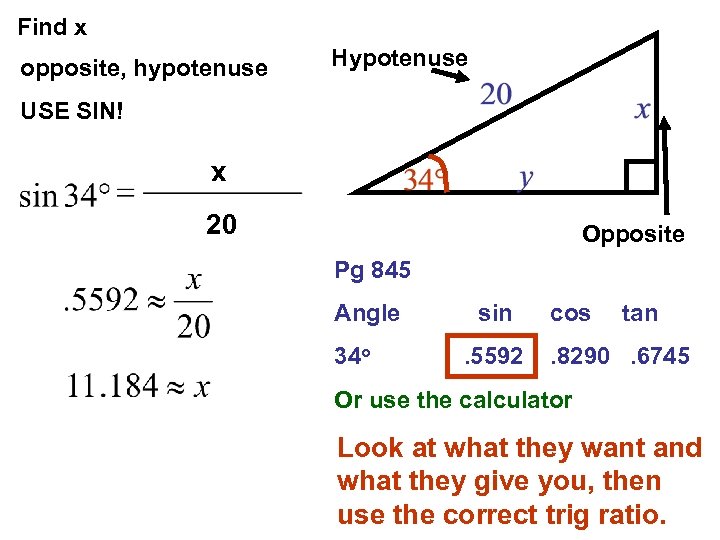 Find x opposite, hypotenuse Hypotenuse USE SIN! x 20 Opposite Pg 845 Angle 34 o sin. 5592 cos tan . 8290. 6745 Or use the calculator Look at what they want and what they give you, then use the correct trig ratio.
Find x opposite, hypotenuse Hypotenuse USE SIN! x 20 Opposite Pg 845 Angle 34 o sin. 5592 cos tan . 8290. 6745 Or use the calculator Look at what they want and what they give you, then use the correct trig ratio.
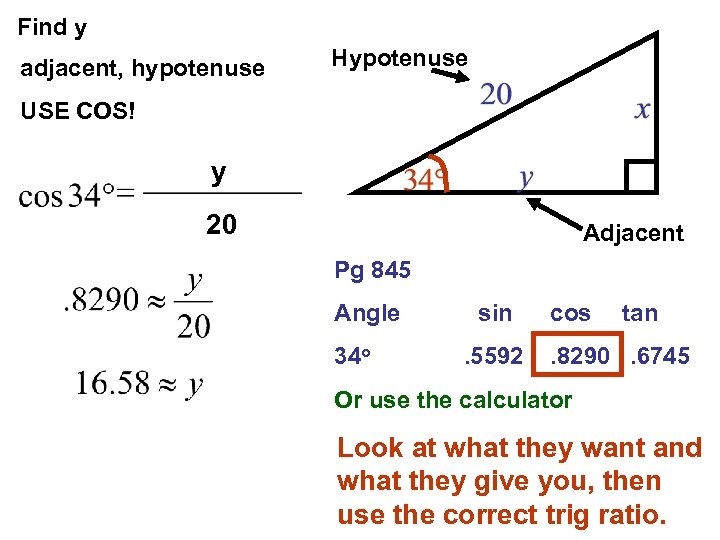 Find y adjacent, hypotenuse Hypotenuse USE COS! y 20 Adjacent Pg 845 Angle 34 o sin. 5592 cos tan . 8290. 6745 Or use the calculator Look at what they want and what they give you, then use the correct trig ratio.
Find y adjacent, hypotenuse Hypotenuse USE COS! y 20 Adjacent Pg 845 Angle 34 o sin. 5592 cos tan . 8290. 6745 Or use the calculator Look at what they want and what they give you, then use the correct trig ratio.
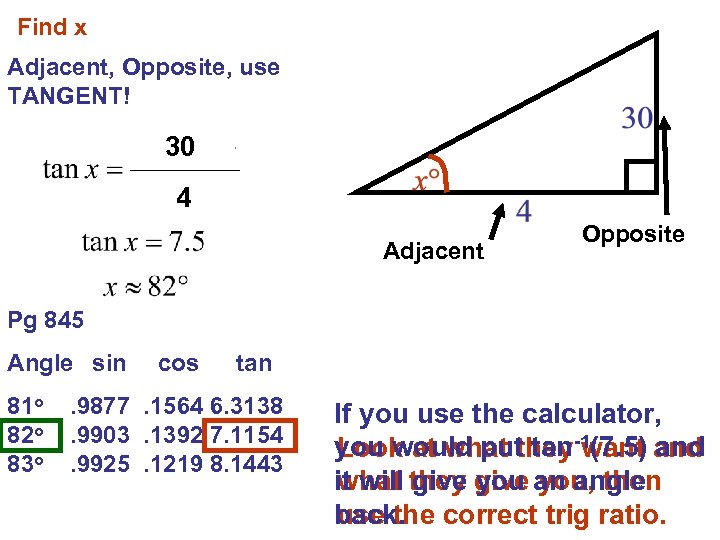 Find x Adjacent, Opposite, use TANGENT! 30 4 Adjacent Opposite Pg 845 Angle sin 81 o 82 o 83 o cos tan . 9877. 1564 6. 3138. 9903. 1392 7. 1154. 9925. 1219 8. 1443 If you use the calculator, you would put tan-1(7. 5) and Look at what they want it will they give an angle what give you, then back. correct trig ratio. use the
Find x Adjacent, Opposite, use TANGENT! 30 4 Adjacent Opposite Pg 845 Angle sin 81 o 82 o 83 o cos tan . 9877. 1564 6. 3138. 9903. 1392 7. 1154. 9925. 1219 8. 1443 If you use the calculator, you would put tan-1(7. 5) and Look at what they want it will they give an angle what give you, then back. correct trig ratio. use the
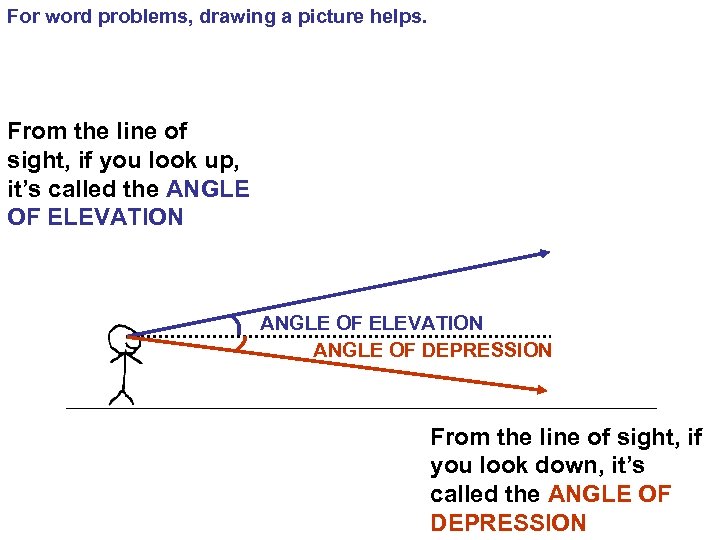 For word problems, drawing a picture helps. From the line of sight, if you look up, it’s called the ANGLE OF ELEVATION ANGLE OF DEPRESSION From the line of sight, if you look down, it’s called the ANGLE OF DEPRESSION
For word problems, drawing a picture helps. From the line of sight, if you look up, it’s called the ANGLE OF ELEVATION ANGLE OF DEPRESSION From the line of sight, if you look down, it’s called the ANGLE OF DEPRESSION
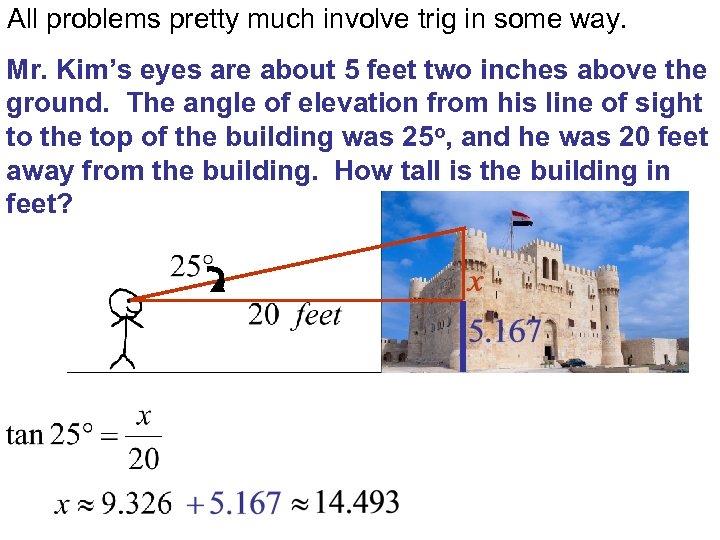 All problems pretty much involve trig in some way. Mr. Kim’s eyes are about 5 feet two inches above the ground. The angle of elevation from his line of sight to the top of the building was 25 o, and he was 20 feet away from the building. How tall is the building in feet?
All problems pretty much involve trig in some way. Mr. Kim’s eyes are about 5 feet two inches above the ground. The angle of elevation from his line of sight to the top of the building was 25 o, and he was 20 feet away from the building. How tall is the building in feet?
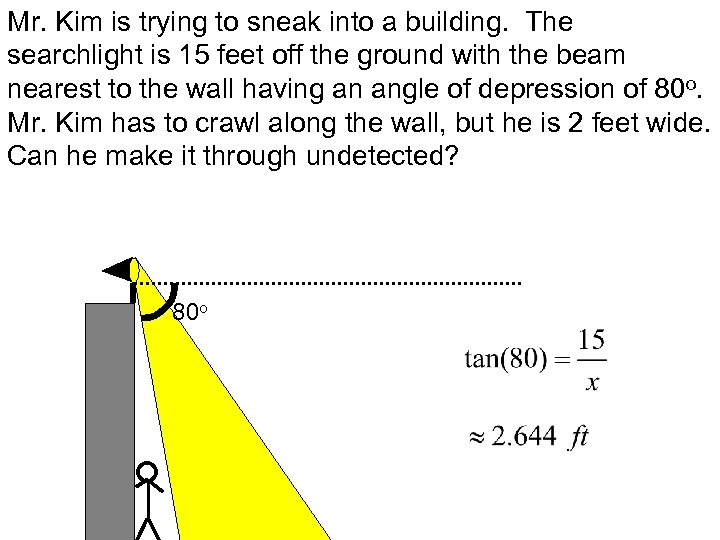 Mr. Kim is trying to sneak into a building. The searchlight is 15 feet off the ground with the beam nearest to the wall having an angle of depression of 80 o. Mr. Kim has to crawl along the wall, but he is 2 feet wide. Can he make it through undetected? 80 o
Mr. Kim is trying to sneak into a building. The searchlight is 15 feet off the ground with the beam nearest to the wall having an angle of depression of 80 o. Mr. Kim has to crawl along the wall, but he is 2 feet wide. Can he make it through undetected? 80 o
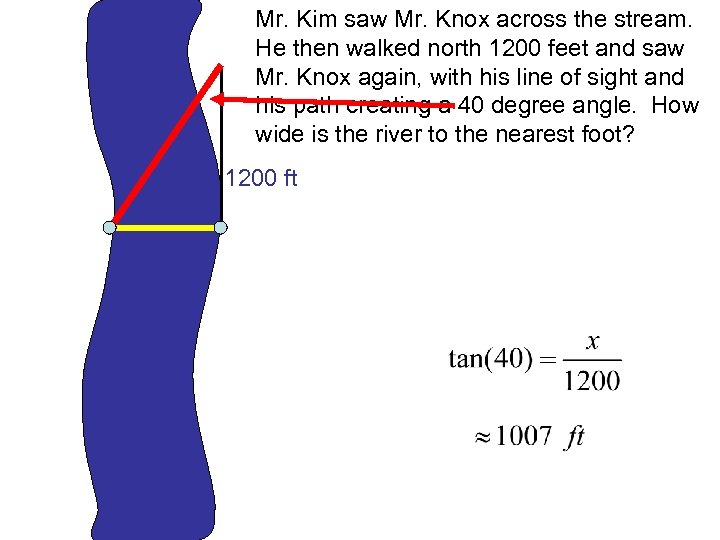 Mr. Kim saw Mr. Knox across the stream. He then walked north 1200 feet and saw Mr. Knox again, with his line of sight and his path creating a 40 degree angle. How wide is the river to the nearest foot? 1200 ft
Mr. Kim saw Mr. Knox across the stream. He then walked north 1200 feet and saw Mr. Knox again, with his line of sight and his path creating a 40 degree angle. How wide is the river to the nearest foot? 1200 ft
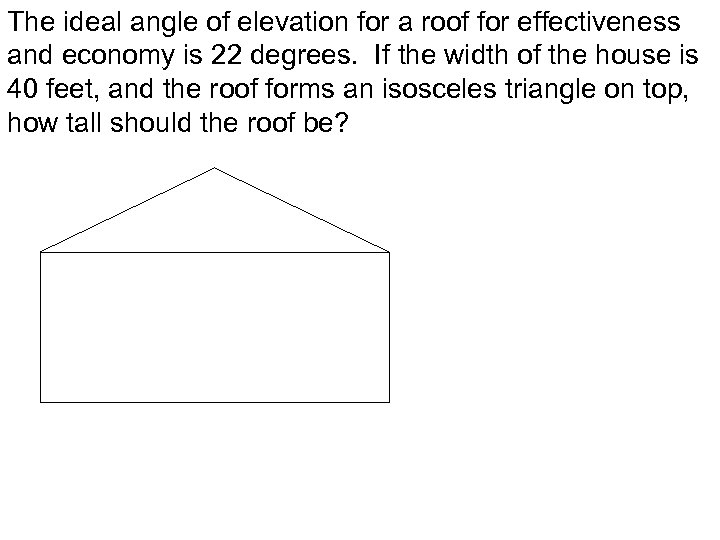 The ideal angle of elevation for a roof for effectiveness and economy is 22 degrees. If the width of the house is 40 feet, and the roof forms an isosceles triangle on top, how tall should the roof be?
The ideal angle of elevation for a roof for effectiveness and economy is 22 degrees. If the width of the house is 40 feet, and the roof forms an isosceles triangle on top, how tall should the roof be?
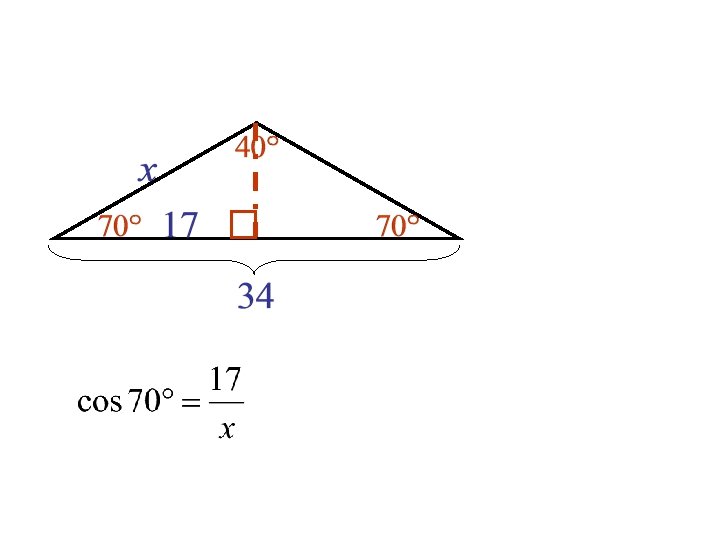
 • DJ is at the top of a right triangular block of stone. The face of the stone is 50 paces long. The angle of depression from the top of the stone to the ground is 40 degrees (assume DJ’s eyes are at his feet). How tall is the triangular block?
• DJ is at the top of a right triangular block of stone. The face of the stone is 50 paces long. The angle of depression from the top of the stone to the ground is 40 degrees (assume DJ’s eyes are at his feet). How tall is the triangular block?
 9. 6 – Solving Right Triangles
9. 6 – Solving Right Triangles
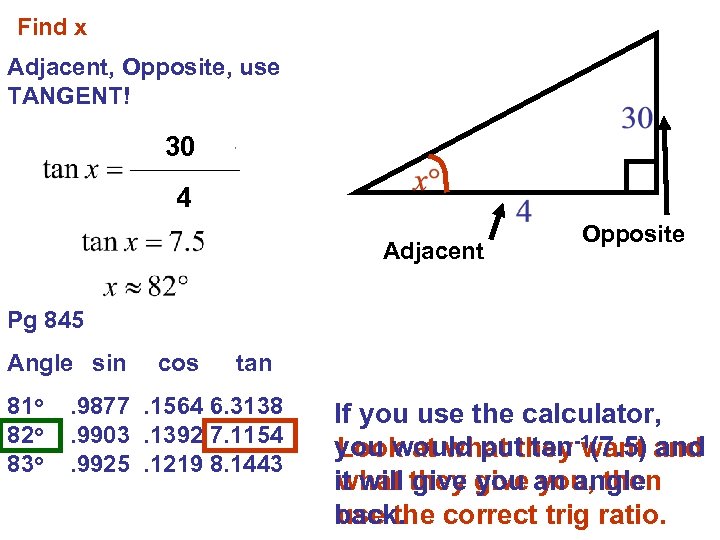 Find x Adjacent, Opposite, use TANGENT! 30 4 Adjacent Opposite Pg 845 Angle sin 81 o 82 o 83 o cos tan . 9877. 1564 6. 3138. 9903. 1392 7. 1154. 9925. 1219 8. 1443 If you use the calculator, you would put tan-1(7. 5) and Look at what they want it will they give an angle what give you, then back. correct trig ratio. use the
Find x Adjacent, Opposite, use TANGENT! 30 4 Adjacent Opposite Pg 845 Angle sin 81 o 82 o 83 o cos tan . 9877. 1564 6. 3138. 9903. 1392 7. 1154. 9925. 1219 8. 1443 If you use the calculator, you would put tan-1(7. 5) and Look at what they want it will they give an angle what give you, then back. correct trig ratio. use the
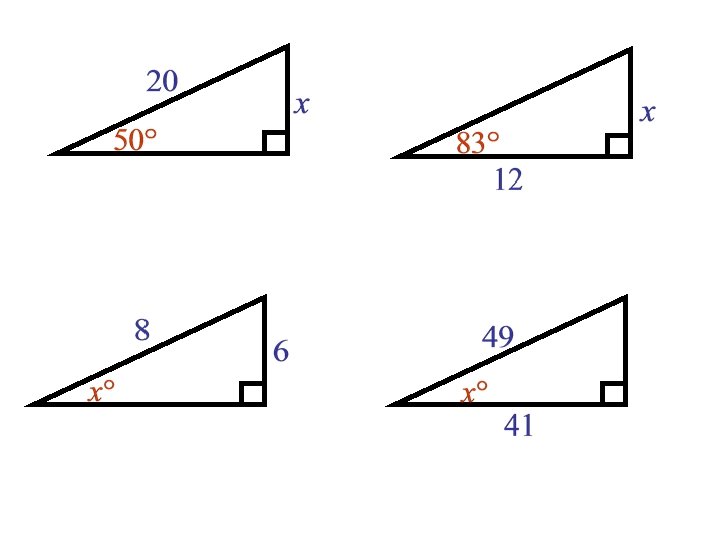
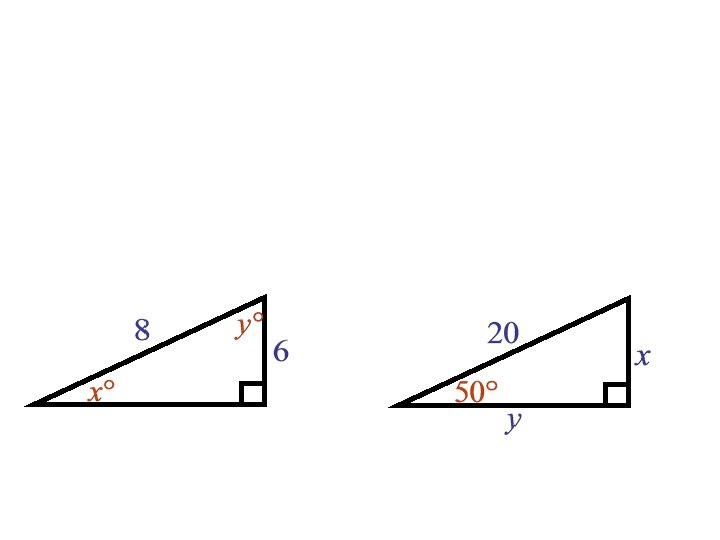
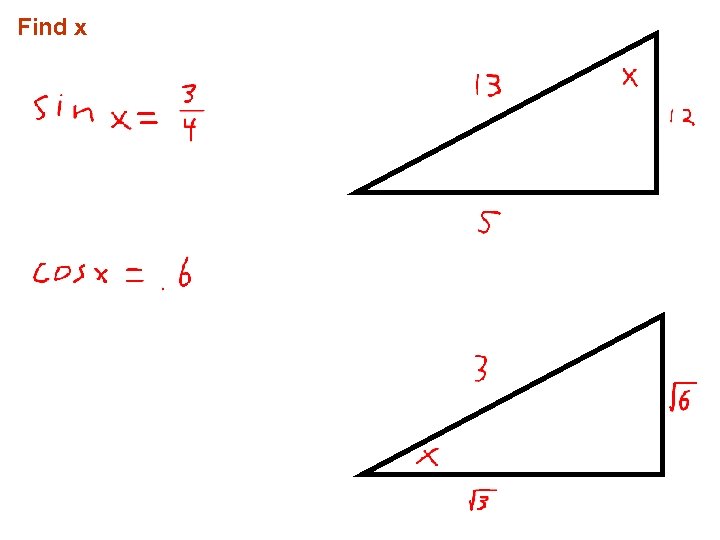 Find x
Find x
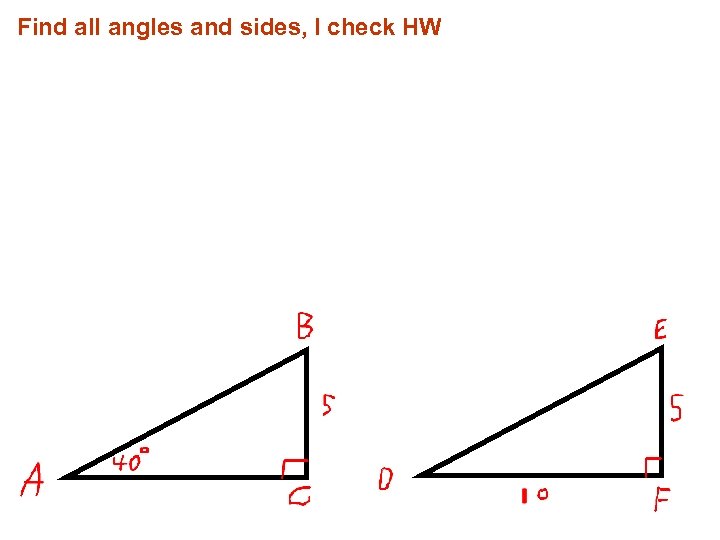 Find all angles and sides, I check HW
Find all angles and sides, I check HW
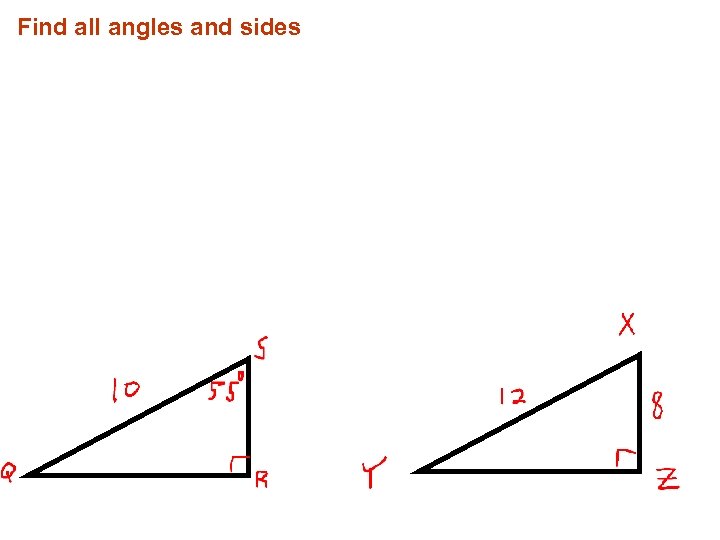 Find all angles and sides
Find all angles and sides


