dd64c53f7350f983de719a14414e26b5.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 52
 9 -1
9 -1
 9 -2 What types of long-term capital do firms use?
9 -2 What types of long-term capital do firms use?
 9 -3
9 -3
 9 -4 Should we focus on before-tax or after-tax capital costs?
9 -4 Should we focus on before-tax or after-tax capital costs?
 9 -5 Should we focus on historical (embedded) costs or new (marginal) costs? The cost of capital is used primarily to make decisions which involve raising and investing new capital. So, we should focus on marginal costs.
9 -5 Should we focus on historical (embedded) costs or new (marginal) costs? The cost of capital is used primarily to make decisions which involve raising and investing new capital. So, we should focus on marginal costs.
 9 -6 Cost of Debt
9 -6 Cost of Debt
 9 -7 . . .
9 -7 . . .
 9 -8 Component Cost of Debt
9 -8 Component Cost of Debt
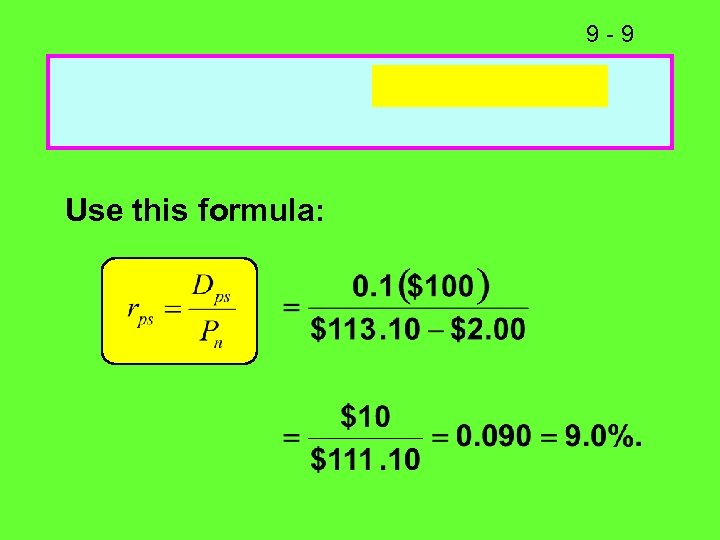 9 -9 Use this formula:
9 -9 Use this formula:
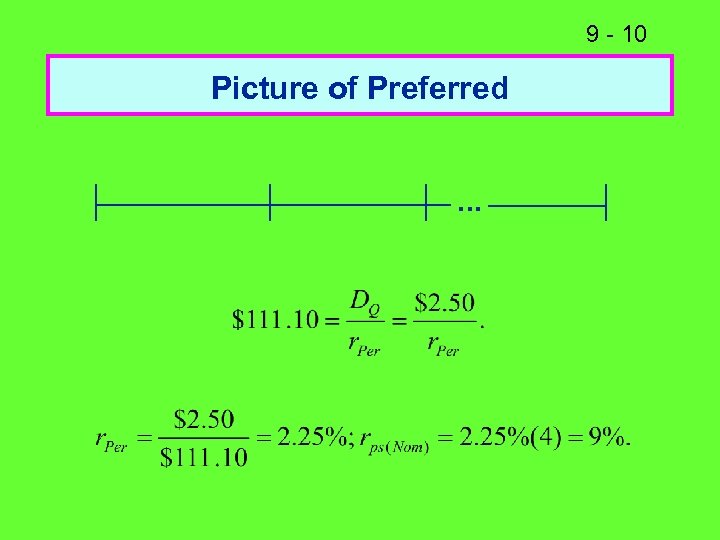 9 - 10 Picture of Preferred. . .
9 - 10 Picture of Preferred. . .
 9 - 11 Note:
9 - 11 Note:
 9 - 12 Is preferred stock more or less risky to investors than debt?
9 - 12 Is preferred stock more or less risky to investors than debt?
 9 - 13
9 - 13
 9 - 14 Example:
9 - 14 Example:
 9 - 15 What are the two ways that companies can raise common equity?
9 - 15 What are the two ways that companies can raise common equity?
 9 - 16 Why is there a cost for reinvested earnings?
9 - 16 Why is there a cost for reinvested earnings?
 9 - 17
9 - 17
 9 - 18
9 - 18
 9 - 19
9 - 19
 9 - 20 Issues in Using CAPM
9 - 20 Issues in Using CAPM
 9 - 21 Issues in Using CAPM (Continued)
9 - 21 Issues in Using CAPM (Continued)
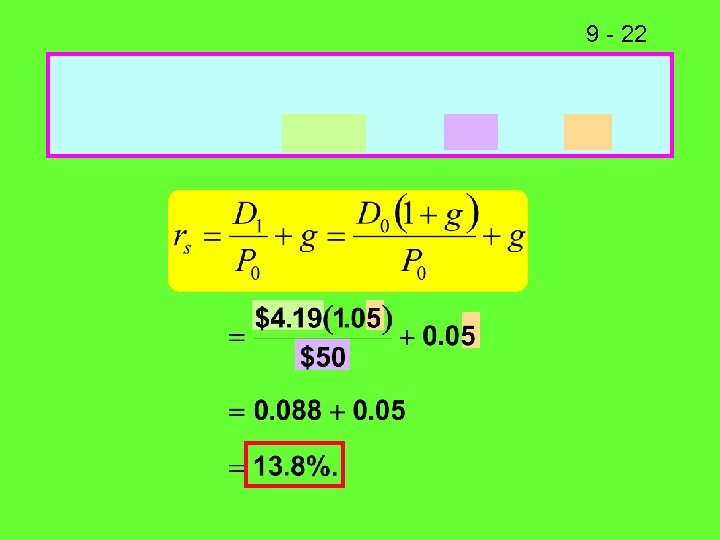 9 - 22
9 - 22
 9 - 23 Estimating the Growth Rate
9 - 23 Estimating the Growth Rate
 9 - 24 Suppose the company has been earning 15% on equity (ROE = 15%) and retaining 35% (dividend payout = 65%), and this situation is expected to continue. What’s the expected future g?
9 - 24 Suppose the company has been earning 15% on equity (ROE = 15%) and retaining 35% (dividend payout = 65%), and this situation is expected to continue. What’s the expected future g?
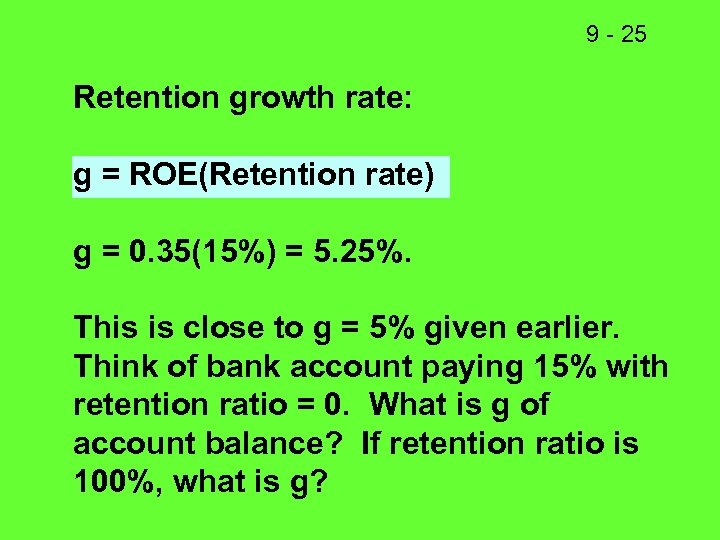 9 - 25 Retention growth rate: g = ROE(Retention rate) g = 0. 35(15%) = 5. 25%. This is close to g = 5% given earlier. Think of bank account paying 15% with retention ratio = 0. What is g of account balance? If retention ratio is 100%, what is g?
9 - 25 Retention growth rate: g = ROE(Retention rate) g = 0. 35(15%) = 5. 25%. This is close to g = 5% given earlier. Think of bank account paying 15% with retention ratio = 0. What is g of account balance? If retention ratio is 100%, what is g?
 9 - 26 Could DCF methodology be applied if g is not constant?
9 - 26 Could DCF methodology be applied if g is not constant?
 9 - 27
9 - 27
 9 - 28
9 - 28
 9 - 29 Determining the Weights for the WACC
9 - 29 Determining the Weights for the WACC
 9 - 30 Estimating Weights for the Capital Structure
9 - 30 Estimating Weights for the Capital Structure
 9 - 31 Estimating Weights (Continued)
9 - 31 Estimating Weights (Continued)
 9 - 32
9 - 32
 9 - 33 What’s the WACC?
9 - 33 What’s the WACC?
 9 - 34 What factors influence a company’s WACC?
9 - 34 What factors influence a company’s WACC?
 9 - 35 Should the company use the composite WACC as the hurdle rate for each of its divisions?
9 - 35 Should the company use the composite WACC as the hurdle rate for each of its divisions?
 9 - 36 What procedures are used to determine the risk-adjusted cost of capital for a particular division?
9 - 36 What procedures are used to determine the risk-adjusted cost of capital for a particular division?
 9 - 37 Methods for Estimating Beta for a Division or a Project 1. Pure play. Find several publicly traded companies exclusively in project’s business. Use average of their betas as proxy for project’s beta. Hard to find such companies.
9 - 37 Methods for Estimating Beta for a Division or a Project 1. Pure play. Find several publicly traded companies exclusively in project’s business. Use average of their betas as proxy for project’s beta. Hard to find such companies.
 9 - 38 2. Accounting beta. Run regression between project’s ROA and S&P index ROA. Accounting betas are correlated (0. 5 – 0. 6) with market betas. But normally can’t get data on new projects’ ROAs before the capital budgeting decision has been made.
9 - 38 2. Accounting beta. Run regression between project’s ROA and S&P index ROA. Accounting betas are correlated (0. 5 – 0. 6) with market betas. But normally can’t get data on new projects’ ROAs before the capital budgeting decision has been made.
 9 - 39 Find the division’s market risk and cost of capital based on the CAPM, given these inputs:
9 - 39 Find the division’s market risk and cost of capital based on the CAPM, given these inputs:
 9 - 40
9 - 40
 9 - 41 How does the division’s WACC compare with the firm’s overall WACC?
9 - 41 How does the division’s WACC compare with the firm’s overall WACC?
 9 - 42 What are three types of project risk?
9 - 42 What are three types of project risk?
 9 - 43 How is each type of risk used?
9 - 43 How is each type of risk used?
 9 - 44 A Project-Specific, Risk-Adjusted Cost of Capital
9 - 44 A Project-Specific, Risk-Adjusted Cost of Capital
 9 - 45 Why is the cost of internal equity from reinvested earnings cheaper than the cost of issuing new common stock? 1. When a company issues new common stock they also have to pay flotation costs to the underwriter. 2. Issuing new common stock may send a negative signal to the capital markets, which may depress stock price.
9 - 45 Why is the cost of internal equity from reinvested earnings cheaper than the cost of issuing new common stock? 1. When a company issues new common stock they also have to pay flotation costs to the underwriter. 2. Issuing new common stock may send a negative signal to the capital markets, which may depress stock price.
 9 - 46
9 - 46
 9 - 47 Estimate the cost of new 30 -year debt: Par=$1, 000, Coupon=10%paid annually, and F=2%.
9 - 47 Estimate the cost of new 30 -year debt: Par=$1, 000, Coupon=10%paid annually, and F=2%.
 9 - 48 Comments about flotation costs:
9 - 48 Comments about flotation costs:
 9 - 49 Four Mistakes to Avoid
9 - 49 Four Mistakes to Avoid
 9 - 50
9 - 50
 9 - 51
9 - 51
 9 - 52
9 - 52


