e04c0dcb2038871e7f47c68e37018ab7.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 37

802. 11 Networks Olga Agnew Bryant Likes Daewon Seo
Agenda u Bryant: Olga: u Daewon: u u u 802. 11 Overview 802. 11 b 802. 11 a Comparison - 802. 11 b and 802. 11 a Security

Why wireless? u u u Mobility Flexibility Can be more cost effective

802. 3 Ethernet Networks u u Ethernet networks make up 95% of LANs Ethernet v v v Network Interface Cards (NIC) Network Cables Hubs

802. 11 Wireless Networks u u 802. 11 builds on Ethernet 802. 11 v v v Network Interface Cards (NIC) Air Access Points

802. 11 Components u u Distribution System Access Points Wireless Medium Stations Distribution System Wireless Medium Access Point Station
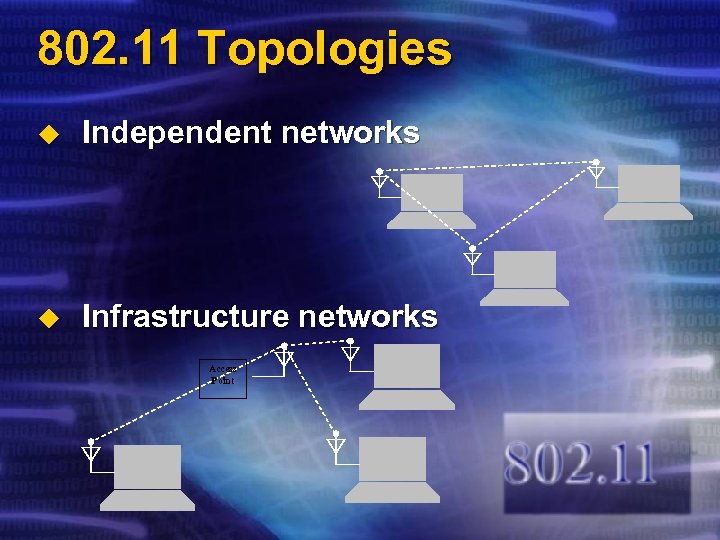
802. 11 Topologies u Independent networks u Infrastructure networks Access Point

Wireless Bridging u Can also be setup as a bridge (Yagi directional antenna) Access Point

802. 11 Media Access Control u u Ethernet uses CSMA/CD 802. 11 uses CSMA/CA v v Distributed Coordination Function (DCF) v Low overhead Point Coordination Function (PCF) v Avoids the hidden node problem

802. 11 Network Operations u Distribution v v u Deliver messages to their destination All messages use this service Integration v Connects the wireless network to the wired network

802. 11 Network Operations u Association v u Reassociation v u “Plugs” stations into the network Switching to another AP with better service Disassociation v Association no longer needed

802. 11 Network Operations u Authentication v u Deauthentication v u Terminates authenticated relationship Privacy v u Prevents unauthorized use Wired Equivalency Privacy (WEP) MAC Service Data Unit (MSDU) Delivery v Destination delivery

802. 11 b

802. 11 b - Data Transmission u u u Transmit 300 to 500 feet Frequency-hopping spread-spectrum (FHSS) v 1 or 2 Mbps Direct-sequence spread-spectrum (DSSS) v 1, 2, 5. 5, or 11 Mbps

802. 11 b – Frequencies and Bandwidth u u 2. 4000 to 2. 4835 GHz frequency 22 MHz bandwidth per channel 3 MHz guardbands Analog radio signal (NIC is modem)

802. 11 b - Transmission u 1 and 2 Mbps speeds v u Use 11 -bit Barker sequence 5. 5 and 11 Mbps speeds v Use complementary code keying (CCK)

802. 11 a

802. 11 a u u Why did ‘a’ come before ‘b’? Is it different? Is it better? Is it faster?

802. 11 a - Data Transmission u u Transmit 100 to 150 feet Orthogonal Frequency-Division Multiplexing (OFDM) v 6 to 54 Mbps
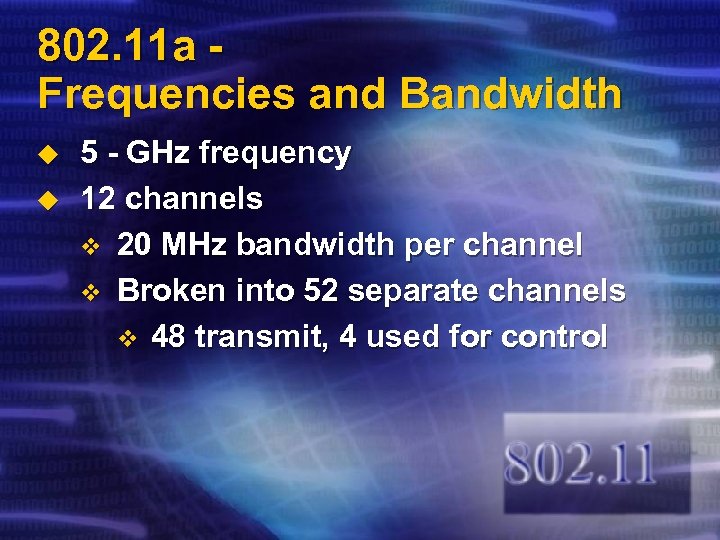
802. 11 a Frequencies and Bandwidth u u 5 - GHz frequency 12 channels v 20 MHz bandwidth per channel v Broken into 52 separate channels v 48 transmit, 4 used for control

802. 11 a - Transmission u u 6 and 9 Mbps speeds v Use 24 -bit Barker sequence v Converted to 1 OFDM symbol of 48 bits 12, 24 and 48 Mbps speeds v Use binary phase shift keying (BPSK)
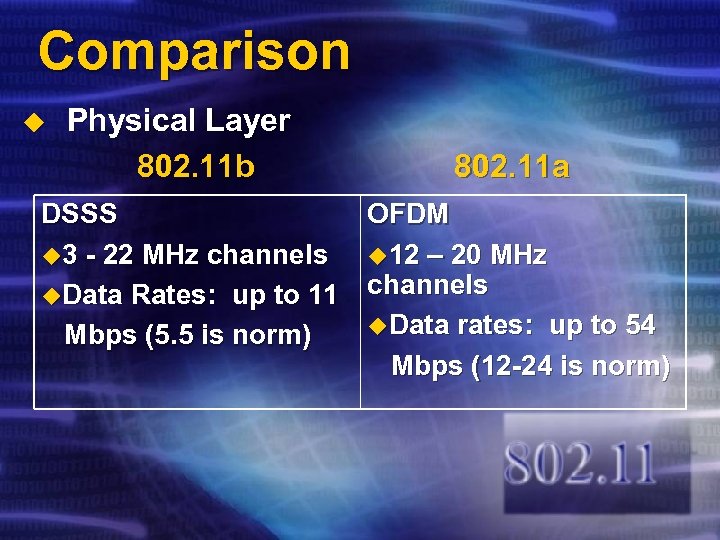
Comparison u Physical Layer 802. 11 b 802. 11 a DSSS OFDM u 3 - 22 MHz channels u 12 – 20 MHz u. Data Rates: up to 11 channels u. Data rates: up to 54 Mbps (5. 5 is norm) Mbps (12 -24 is norm)

Comparison (cont’d) u Physical Layer 802. 11 b DSSS (cont’d) u. Frequency Range up to 300 Feet 802. 11 a OFDM (cont’d) u. Frequency Range: up to 150 Feet

Conclusion u u Is faster really better? What are the application needs? v Better for higher end apps v v u Video, Voice, transmission of large image or large files, etc. Shorter distance Remember…“There’s always a trade-off”

Conclusion (Cont’d) u Additional factors to consider: v v 2. 4 GHz frequency shared by: v wireless phones, microwave ovens v Bluetooth devices, others… Combo-cards now available v Proxim’s

802. 11 Security Overview

Overview of 802. 11 Security u Not long ago v u Wireless security was an afterthought (new and rare) Now v Security issues became more vital (available for anyone and cheap)

Same risks as Wired-LANs? u Threat to physical security of a network v u u Denial of service and sabotage Unauthorized access and eavesdropping Attacks form within the network’s user community v Employees have been known to read, distribute, and alter valuable company data

802. 11 Security Mechanisms u Authentication through… v v u Open system Shared key authentication Data confidentiality through… v Wired Equivalent Privacy (WEP)

Authentication u Open systems v v Do not provide authentication Only identification using the wireless adapter’s MAC address Access can be based on MAC address of wireless client can be spoofed Overall, the open system is not secure.
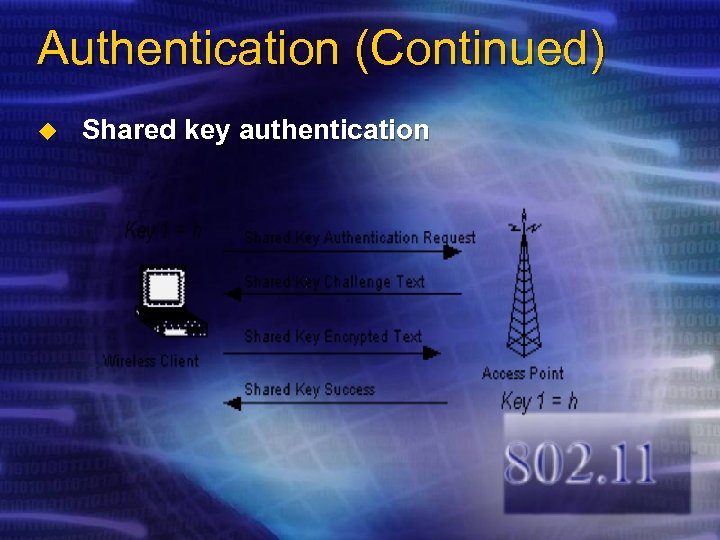
Authentication (Continued) u Shared key authentication
Authentication (Continued) u Shared key authentication… v v u It is delivered to participating station through a secure channel that is independent of IEEE 802. 11 The secret of shared key is manually configured for both the wireless AP and client Securing physical access to the network is difficult Anyone within range of wireless AP can listen other users’ data In the overall, this authentication is not secure and is not recommended for use
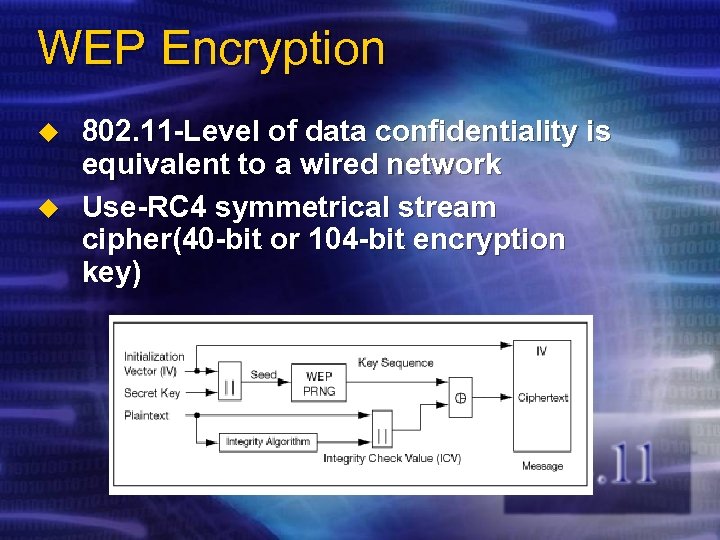
WEP Encryption u u 802. 11 -Level of data confidentiality is equivalent to a wired network Use-RC 4 symmetrical stream cipher(40 -bit or 104 -bit encryption key)

WEP Encryption (Cont) u u u Provide data integrity from random errors (Integrity Check Value) The determination and distribution of WEP keys are not defined text string must be manually configured There is no defined mechanism to change the WEP key

WEP Encryption (Cont) u u All wireless APs and Clients use the same configured WEP key for multiple connection and authentication-it is possible for a malicious users to remotely capture WEP cipher textproblem of security The lack of WEP key management – cause change in WEP key frequently

Security Summary u u The lack of automated authentication and key determination cause problems in shared communication WEP never be totally secure, and 802. 11 security will not be secure either New versions of 802. 11 is focus on new encryption, authentication and key exchange algorithm for better security 802. 11 security is being investigated for better protection from all attacks

Questions?
e04c0dcb2038871e7f47c68e37018ab7.ppt