 8. Warehousing 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. Nature and Importance of Warehousing Types of warehousing Operations: Three Functions Public versus Private warehousing Facility development Location analysis
8. Warehousing 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. Nature and Importance of Warehousing Types of warehousing Operations: Three Functions Public versus Private warehousing Facility development Location analysis
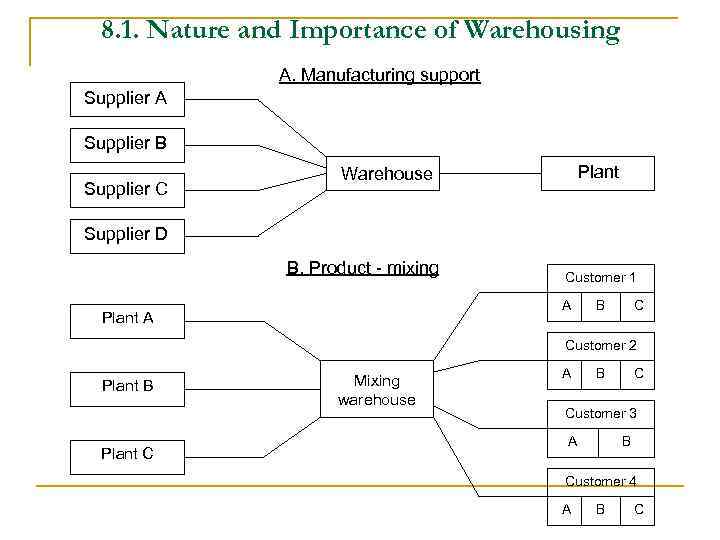 8. 1. Nature and Importance of Warehousing A. Manufacturing support Supplier A Supplier B Supplier C Plant Warehouse Supplier D B. Product - mixing Customer 1 A Plant A B C Customer 2 Plant B Plant C Mixing warehouse A B C Customer 3 A B Customer 4 A B C
8. 1. Nature and Importance of Warehousing A. Manufacturing support Supplier A Supplier B Supplier C Plant Warehouse Supplier D B. Product - mixing Customer 1 A Plant A B C Customer 2 Plant B Plant C Mixing warehouse A B C Customer 3 A B Customer 4 A B C
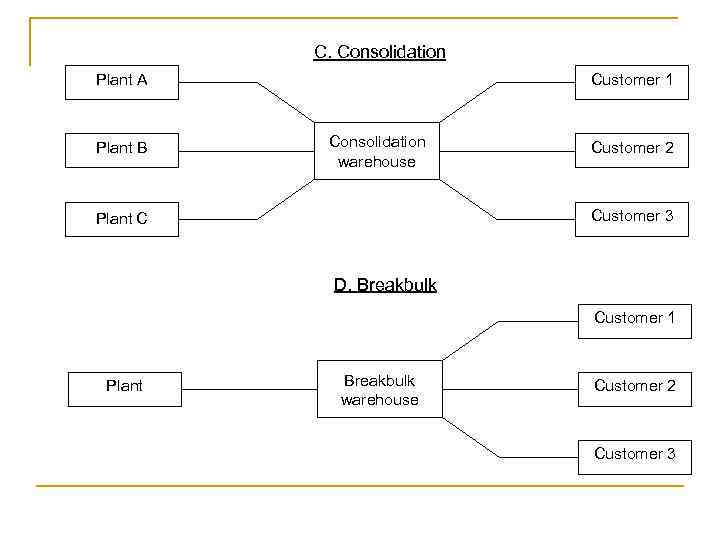 C. Consolidation Plant A Plant B Customer 1 Consolidation warehouse Customer 2 Customer 3 Plant C D. Breakbulk Customer 1 Plant Breakbulk warehouse Customer 2 Customer 3
C. Consolidation Plant A Plant B Customer 1 Consolidation warehouse Customer 2 Customer 3 Plant C D. Breakbulk Customer 1 Plant Breakbulk warehouse Customer 2 Customer 3
 8. 2. Types of warehousing 1. 2. 3. Direct store delivery. Cross-Docking. Contract Warehousing is a long term mutually beneficial arrangement which provides unique and specially tailored warehousing and logistics services exclusively to one client, where vendor and client share the risks associate with the operation. There is the focus on productivity, service and efficiency, no the fee and rate structure itself.
8. 2. Types of warehousing 1. 2. 3. Direct store delivery. Cross-Docking. Contract Warehousing is a long term mutually beneficial arrangement which provides unique and specially tailored warehousing and logistics services exclusively to one client, where vendor and client share the risks associate with the operation. There is the focus on productivity, service and efficiency, no the fee and rate structure itself.
 Public Warehouses 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. General Merchandise Warehouse. Refrigerated Warehouses. Bonded Warehouses. Household Goods Warehouses. Special Commodity Warehouses. Bulk Storage Warehouses.
Public Warehouses 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. General Merchandise Warehouse. Refrigerated Warehouses. Bonded Warehouses. Household Goods Warehouses. Special Commodity Warehouses. Bulk Storage Warehouses.
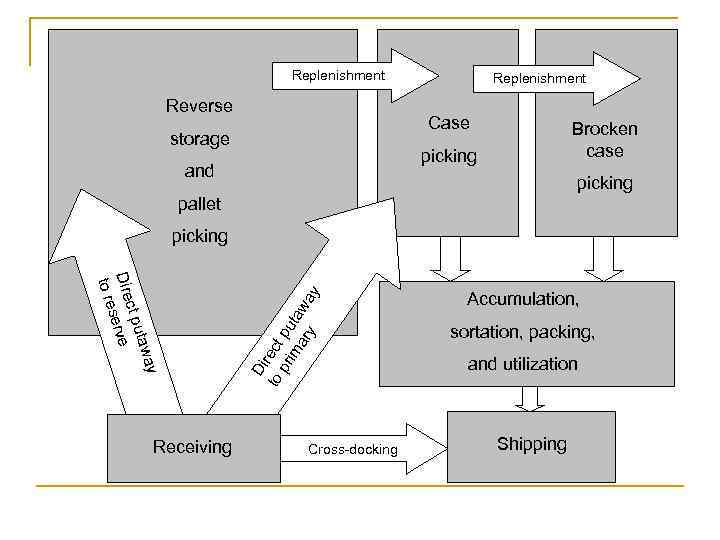 Replenishment Reverse Replenishment Case storage Brocken case picking and picking pallet y tawa ct pu Dire erve s to re Receiving Di to rect pr pu im ta ar wa y y picking Cross-docking Accumulation, sortation, packing, and utilization Shipping
Replenishment Reverse Replenishment Case storage Brocken case picking and picking pallet y tawa ct pu Dire erve s to re Receiving Di to rect pr pu im ta ar wa y y picking Cross-docking Accumulation, sortation, packing, and utilization Shipping
 8. 4. Public vs. Private warehousing 1. Public warehousing 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. Advantages conservation of capital the ability to increase warehouse space to cover peak requirements reduced risk economies of scale flexibility tax advantages specific knowledge of costs for storage and handling potential minimization of labor disputes 1. 2. 3. Disadvantages communications problems lack of the specialized services shortage of space
8. 4. Public vs. Private warehousing 1. Public warehousing 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. Advantages conservation of capital the ability to increase warehouse space to cover peak requirements reduced risk economies of scale flexibility tax advantages specific knowledge of costs for storage and handling potential minimization of labor disputes 1. 2. 3. Disadvantages communications problems lack of the specialized services shortage of space
 2. Private warehousing 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. Advantages degree of control flexibility less costly over the long term better use of human resources tax benefits intangible benefits 1. 2. 3. Disadvantages lack of flexibility financial constraints rate of return
2. Private warehousing 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. Advantages degree of control flexibility less costly over the long term better use of human resources tax benefits intangible benefits 1. 2. 3. Disadvantages lack of flexibility financial constraints rate of return