PM_Chapter 08_Product.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 71

8 Principles of Marketing Product, Services, and Branding Strategy

Learning Objectives After studying this chapter, you should be able to: 1. Define product and the major classifications of products and services 2. Describe the decisions companies make regarding their individual products and services, product lines, and product mixes 3. Discuss branding strategy—the decisions companies make in building and managing their brands 4. Identify the four characteristics that affect the marketing of a service and the additional marketing considerations that services require 8 -2

Chapter Outline 1. 2. 3. 4. What Is a Product? Product and Service Decisions Branding Strategy: Building Strong Brands Services Marketing 8 -3
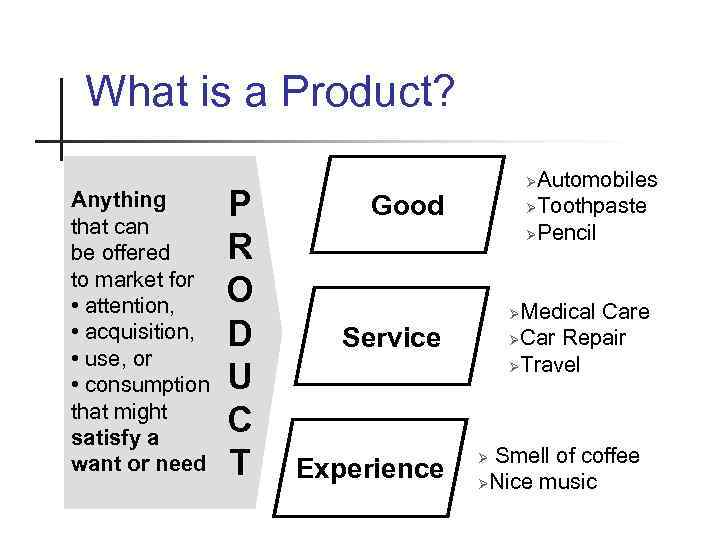
What is a Product? Anything that can be offered to market for • attention, • acquisition, • use, or • consumption that might satisfy а want or need P R O D U C T Automobiles ØToothpaste ØPencil Ø Good Medical Care ØCar Repair ØTravel Ø Service Experience Smell of coffee ØNice music Ø

What is a Product? n Good - tangible n Service – intangible n Experience –memorable n What do you buy when you buy n Lunch at Black and Brown n Perfume at French House n A room in the hotel at Chimbulak

What Is a Product? Products, Services, and Experiences Service is a form of product that consists of activities, benefits, or satisfactions offered for sale that are essentially intangible and do not result in ownership • Doctor’s exam • Legal advice • Postal Service 8 -5

Services Marketing Nature and Characteristics of a Service 8 -57

What Is a Product? Products, Services, and Experiences represent what buying the product or service will do for the customer • Disney • Cream Café • Scuba diving Experiences include zoos and aquariums 8 -6
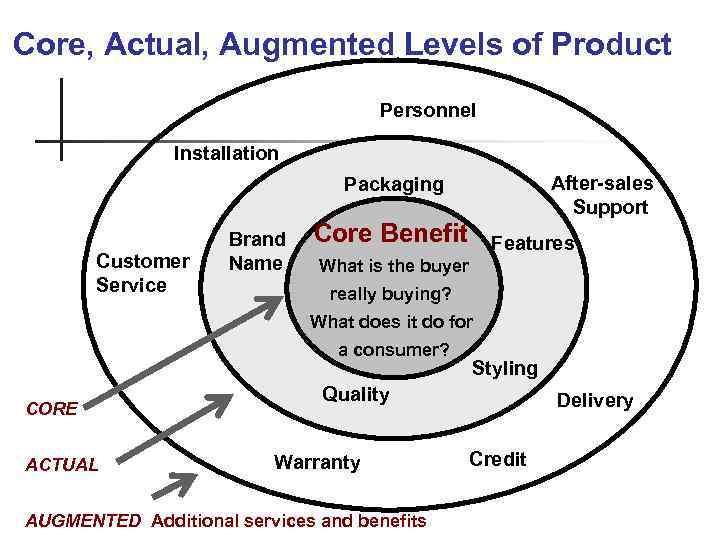
Core, Actual, Augmented Levels of Product Personnel Installation After-sales Support Packaging Customer Service Brand Name Core Benefit Features What is the buyer really buying? What does it do for a consumer? CORE ACTUAL Styling Quality Warranty AUGMENTED Additional services and benefits Delivery Credit

What Is a Product? Levels of Product and Services Core benefits represent what the buyer is really buying Actual product represents the design, brand name, and packaging that delivers the core benefit to the customer Augmented product represents additional services or benefits of the actual product 8 -8
Core, Actual, Augmented Levels of Product n Choose a product n n n Indesit washing machine Hair coloring (dye) at salon i. Pad Corn flakes Identify n n n Core product (core benefit) Actual product Augmented product (additional benefits)

Theodore Levitt pointed out: Competition is not between what companies produce in their factories, but between what they add to their factory output in the form of n packaging, services, n advertising, customer advice, n financing, delivery arrangements, n warehousing, and n other things that people value

Augmenting to Exceed Expectations n n What is total product in the minds of prospective buyers? What is “augmented” for one customer may be “expected” by another What is “augmented” under one circumstance may be “potential” in another Ex. Fruit basket in a hotel room
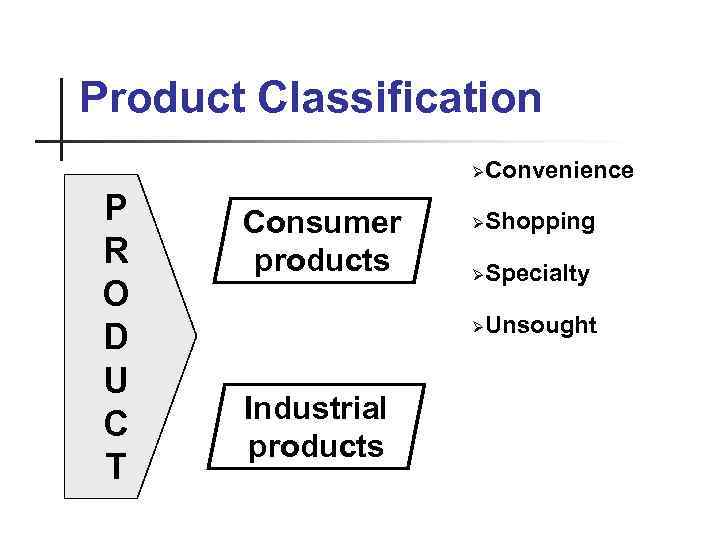
Product Classification ØConvenience P R O D U C T Consumer products ØShopping ØSpecialty ØUnsought Industrial products

Product Classification: Consumer Products - items purchased to satisfy personal or family needs. n Convenience goods are consumer goods and services that the customer n Shopping goods are consumer goods that the customer, in the process of n Specialty goods are consumer goods that have unique characteristics or n Unsought goods are consumer goods that the consumer either does not usually buys frequently, immediately, and with а minimum of comparison and buying effort (tobacco products, soap, and newspapers) selection and purchase, usually compares on such bases as suitability, quality, price, style (furniture, clothing, cars, major appliances) brand identification for which а significant group of buyers is willing to make а special purchase effort (specific brands and types of cars -Jaguar, high-priced photographic equipment) know about or knows about but does not normally think of buying (life insurance and encyclopedias)

Product Classification: Industrial Products Industrial (business-to-business) products items bought by individuals and organizations for use in a company’s operations or to make other products n n The distinction between а consumer good an industrial good is based on the purpose for which the product is purchased. If а consumer buys а lawn mower for use around the home, the lawn mower is а consumer good. If the same consumer buys the same lawn mower for use in а landscaping business, the land mower is an industrial good.

What Is a Product? Product and Service Classifications Industrial products classified by the purpose for which the product is purchased • Materials and parts • Capital • Raw materials 8 -15

What Is a Product? Product and Service Classifications Materials and parts include raw materials and manufactured materials and parts usually sold directly to industrial users • Wheat • Lumber • Iron • Cement 8 -16

What Is a Product? Product and Service Classifications Capital items are industrial products that aid in the buyer’s production or operations • Buildings • Elevators • Computers 8 -17
Product Classification Home task: Marketing Slang n White goods ? n Brown goods ? n Yellow goods ?

What Is a Product? Organizations, Persons, Places, and Ideas Organization marketing consists of activities undertaken to create, maintain, or change attitudes and behavior of target consumers toward an organization 8 -18

What Is a Product? Organizations, Persons, Places, and Ideas Person marketing consists of activities undertaken to create, maintain, or change attitudes and behavior of target consumers toward particular people • President Medvedev 8 -19

What Is a Product? Organizations, Persons, Places, and Ideas Place marketing consists of activities undertaken to create, maintain, or change attitudes and behavior of target consumers toward particular places • Tourism 8 -20

What Is a Product? Organizations, Persons, Places, and Ideas Social marketing is the use of commercial marketing concepts and tools in programs designed to influence individuals’ behavior to improve their well-being and that of society • • Safe driving week Sept 1 smoke free zone 8 -21
Product and Service Decisions Individual Product and Service Decisions 8 -22

Product and Service Decisions Individual Product and Service Decisions Product attributes are the benefits of the product or service • Quality • Features • Style and design 8 -23

Product and Service Decisions Individual Product and Service Decisions Quality in terms of the product or service is the lack of defects Quality in terms of the customer is the value and satisfaction provided by the product or service What is the best quality? 8 -24

Product and Service Decisions Individual Product and Service Decisions Product quality includes level and consistency • • • Quality level is the level of quality that supports the product’s positioning Performance quality is the ability of a product to perform its functions Quality consistency is the freedom from defects and the delivering of a targeted level of performance 8 -25

Product and Service Decisions Individual Product and Service Decisions Product features are a competitive tool for differentiating a product from competitors’ products Samsung 2 View 8 -27

Product and Service Decisions Individual Product and Service Decisions Product features are assessed based on the value to the customer versus the cost to the company 8 -27

Product and Service Decisions Individual Product and Service Decisions Product style and design add value to customer value Style describes the appearance of the product Design contributes to a product’s usefulness as well as to its looks 8 -28

Product and Service Decisions Individual Product and Service Decisions Packaging involves designing and producing the container or wrapper for a product 8 -31

Product and Service Decisions Individual Product and Service Decisions Label identifies the product or brand, describes attributes, and provides promotion 8 -31

Product and Service Decisions Individual Product and Service Decisions Product support services augment actual products Companies must continually: • Assess the value of current services to obtain ideas for new ones • Assess the costs of providing these services • Develop a package of services to satisfy customers and provide profit to the company 8 -32
Product and Service Decisions Product Line Decisions Product line is a group of products that are closely related because they function in a similar manner, are sold to the same customer groups, are marketed through the same types of outlets, or fall within given price ranges 8 -33

Product and Service Decisions Product Line Decisions Product line length is the number of items in the product line • Line stretching • Line filling 8 -34

Product and Service Decisions Product Line Decisions Product line stretching is when a company lengthens its product line beyond its current price range Product line filling occurs when companies add more items within the present price range of the line • • • Downward Upward Combination • • More profits Satisfying dealers Excess capacity Plugging holes to fend off competitors 8 -35

Product and Service Decisions Product Line Decisions Downward product line stretching is used by companies at the upper end of the market to plug a market hole or respond to a competitor’s attack Upward product line stretching is by companies at the lower end of the market to add prestige to their current products Combination line stretching is used by companies in the middle range of the market to achieve both goals of upward and downward line stretching 8 -36

Product and Service Decisions Product Mix Decisions Product mix consists of all the products and items that a particular seller offers for sale • Width • Depth • Length • Consistency 8 -39

Product and Service Decisions Product Mix Decisions Product mix width is the number of different product lines the company carries Product mix length is the total number of items the company carries within its product lines Product line depth is the number of versions offered of each product in the line Consistency is how closely the various product lines are in end use, production requirements, or distribution channels 8 -40

Branding

Branding n Brand - n Brand Name - a part of a brand that can be spoken, including letters, n Brand Mark - n Trademark - а brand or part of а brand that is given legal protection — n Brand Recognition - is the extend to which consumers are aware of name, term, sign, symbol, or design, or combination of them, intended to identify the goods or services of one sellers and to differentiate them from those of competitors words, and numbers that part of а brand which can be recognized as а symbol, design, or distinctive coloring or lettering. it protects the seller' s exclusive rights to use the brand name or brand mark. a brand

Benefits of Branding n Brand names help buyers in a number of ways: · tell the buyer something about product quality increase the shopper’s efficiency help call consumers’ attention to new products n Branding also gives the supplier several advantages: · · · · makes it easier for the supplier to process orders and track down problems provides legal protection for unique production features that otherwise might be copied by competitors helps supplier attract a loyal and profitable set of customers helps the supplier to segment markets helps build the corporate image, making it easier to launch new brands & gain acceptance by distributors & consumers

Benefits of Branding n n n n n Branding also gives the seller several advantages. easier to process orders and track down problems to provide legal protection for unique product features that might otherwise be copied by competitors to attract a loyal and profitable set of customers to help segment markets Branding also benefits society as а whole. leads to higher and more consistent product quality increases innovation by giving producers an incentive to look for new features that can be protected against imitating competitors more product variety and choice for consumers increases shopper efficiency because it provides much more information about products and where to find them

Branding Strategy: Building Strong Brands Brand represents the consumer’s perceptions and feelings about a product and its performance. It is the company’s promise to deliver a specific set of features, benefits, services, and experiences consistently to the buyers 8 -42

Branding Strategy: Building Strong Brands Brand equity is the positive differential effect that knowing the brand name has on customer response to the product or service Brand equity provides competitive advantage • Consumer awareness and loyalty • Benefits • Beliefs and value 8 -44

Branding Strategy: Building Strong Brands Customer equity is the value of the customer relationships that the brand creates Brand valuation is the process of estimating the total financial value of the brand 8 -45

Branding Strategy: Building Strong Brands Brand strategy decisions include: • Brand positioning • Brand name selection • Brand sponsorship • Brand development 8 -46

Branding Strategy: Building Strong Brands Brand Positioning Brand strategy decisions include: • Product attributes • Product benefits • Product beliefs and values 8 -47

Selecting а Brand Name n It should suggest something about the product’s benefits n n It should suggest product qualities n n (3 M, Puma) It should be distinctive n n (Concrete Products, Элитстрой) It should be easy to pronounce, recognise, and remember n n (Trans. Systema, Lazy Holidays) (Giorgio Armani) It should not carry poor meanings in other countries and languages n (Exxon, Bluewater, Khaki)

Branding Strategy: Building Strong Brands Brand Sponsorship • • Manufacturer’s brand Private brand Licensed brand Co-brand 8 -49

Branding Strategy: Building Strong Brands Brand Sponsorship Private brands (Store Brand, Private label) provide retailers with advantages • • Product mix control Slotting fees for manufacturers’ brands Higher margins Exclusivity n n Ramstore shampoo Mango, Zara, Gap 8 -50

Branding Strategy: Building Strong Brands Brand Sponsorship • Licensed brand n Name and character licensing has grown 8 -49

Branding Strategy: Building Strong Brands Brand Sponsorship • • • Co-branding – practice of using the established brand names of two different companies on the same product Dell Computers with Intel Processors Haagen Dazs launched a Bailey’s flavored ice cream n Advantages n n Broader consumer appeal Greater brand equity Efficient means of expansion into new product categories Limitations n n n Complex legal contracts Requires careful coordination of marketing efforts Requires that partners trust one another 8 -49

Branding Strategy: Building Strong Brands Brand Development • • Line extensions Brand extensions Multibrands New brands 8 -51

Branding Strategy: Building Strong Brands Brand Development Line extensions occur when a company extends existing brand names to new forms, colors, sizes, ingredients, or flavors of an existing product category Coca cola, Cola light, Cola cherry Brand extensions extend a brand name to a new or modified product in a new category Panasonic TV set, Panasonic digital camera 8 -52

Branding Strategy: Building Strong Brands Brand Development Multibranding - is the marketing strategy of giving each product in a portfolio its own unique brand name. Ariel, Tide, Mif New brands are used when existing brands are inappropriate for new products in new product categories or markets General Motors Chevrolet Nova. In South America "no va" means "it won't go". GM renamed the car in its Spanish markets to the Caribe. 8 -53

Branding Strategy: Building Strong Brands Brand Development 8 -53

Branding Strategy: Building Strong Brands Managing Brands Requires: • Continuous brand communication • Customer-centered training • Brand audits 8 -54

Services Marketing Types of Service Industries • • • Government Private not-for-profit organizations Business services 8 -55

Services Marketing Nature and Characteristics of a Service • • Intangibility Inseparability Variability Perishability 8 -56

Services Marketing Nature and Characteristics of a Service 8 -57

Services Marketing Strategies for Service Firms In addition to traditional marketing strategies, service firms often require additional strategies • Service-profit chain • Internal marketing • Interactive marketing 8 -59

Services Marketing Strategies for Service Firms Service-profit chain links service firm profits with employee and customer satisfaction • Internal service quality • Satisfied and productive service employees • Greater service value • Satisfied and loyal customers • Healthy service profits and growth 8 -60

Services Marketing Strategies for Service Firms Internal marketing means that the service firm must orient and motivate its customer contact employees and supporting service people to work as a team to provide customer satisfaction Internal marketing must precede external marketing 8 -61

Services Marketing Strategies for Service Firms Interactive marketing means that service quality depends heavily on the quality of the buyerseller interaction during the service encounter • Service differentiation • Service quality • Service productivity 8 -62

Services Marketing Strategies for Service Firms 8 -62

Services Marketing Strategies for Service Firms Managing service differentiation creates a competitive advantage from the offer, delivery, and image of the service • Offer can include distinctive features • Delivery can include more able and reliable customer contact people, environment, or process • Image can include symbols and branding 8 -63

Services Marketing Strategies for Service Firms Managing service quality provides a competitive advantage by delivering consistently higher quality than its competitors Service quality always varies depending on interactions between employees and customers 8 -64

Services Marketing Strategies for Service Firms Service recovery can turn disappointed customers into loyal customers • Empower employees • • • Responsibility Authority Incentive 8 -65

Services Marketing Strategies for Service Firms Managing service productivity refers to the cost side of marketing strategies for service firms • Employee recruiting, hiring, and training strategies • Service quantity and quality strategies 8 -66
PM_Chapter 08_Product.ppt