Lection 7_inv_cred_11.pptx
- Количество слайдов: 31
 8. Insurance of international credits and investments
8. Insurance of international credits and investments
 Country risks classification Political risks are related either to the country of a foreign buyer or borrower, or to a third country which can cause the exporter, investor or financier to incur a credit loss. Political risks include: -restrictions on transfer of the credit currency, -rescheduling of debts, -expropriation, and war or insurrection. Commercial risks arise from foreign banks, companies or project companies. Typical commercial risks include Ш buyer's, borrower's or guarantor's insolvency the Ш unwillingness to pay its deb.
Country risks classification Political risks are related either to the country of a foreign buyer or borrower, or to a third country which can cause the exporter, investor or financier to incur a credit loss. Political risks include: -restrictions on transfer of the credit currency, -rescheduling of debts, -expropriation, and war or insurrection. Commercial risks arise from foreign banks, companies or project companies. Typical commercial risks include Ш buyer's, borrower's or guarantor's insolvency the Ш unwillingness to pay its deb.
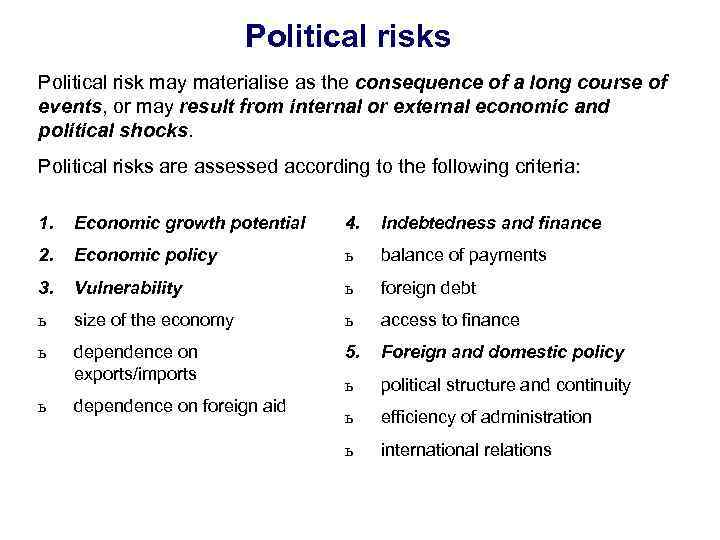 Political risks Political risk may materialise as the consequence of a long course of events, or may result from internal or external economic and political shocks. Political risks are assessed according to the following criteria: 1. Economic growth potential 4. Indebtedness and finance 2. Economic policy ь balance of payments 3. Vulnerability ь foreign debt ь size of the economy ь access to finance ь dependence on exports/imports 5. Foreign and domestic policy ь political structure and continuity ь efficiency of administration ь international relations ь dependence on foreign aid
Political risks Political risk may materialise as the consequence of a long course of events, or may result from internal or external economic and political shocks. Political risks are assessed according to the following criteria: 1. Economic growth potential 4. Indebtedness and finance 2. Economic policy ь balance of payments 3. Vulnerability ь foreign debt ь size of the economy ь access to finance ь dependence on exports/imports 5. Foreign and domestic policy ь political structure and continuity ь efficiency of administration ь international relations ь dependence on foreign aid
 Political risks classification Unforeseen events Political decisions Revolutions 1. Pure political Power change Goods confiscation; trading embargoes; a wrongful response of a guarantee changes in legislation; refusal of the declared intentions; contract cancellation by the private counterparty Change of the government 2. Risks of administrative character Licence withdrawal; an obstacle to carrying out of export or import operations War risks Damage caused to employees of the company abroad 3. Risks of macrolevel An interdiction for converting operations; cardinal changes in economic policy 4. Risks of microlevel Unilateral cancellation of the contract by the counterparty (the state company); non-payment of the state buyer; default of judicial arbitral awards; non-delivery of production because of political views
Political risks classification Unforeseen events Political decisions Revolutions 1. Pure political Power change Goods confiscation; trading embargoes; a wrongful response of a guarantee changes in legislation; refusal of the declared intentions; contract cancellation by the private counterparty Change of the government 2. Risks of administrative character Licence withdrawal; an obstacle to carrying out of export or import operations War risks Damage caused to employees of the company abroad 3. Risks of macrolevel An interdiction for converting operations; cardinal changes in economic policy 4. Risks of microlevel Unilateral cancellation of the contract by the counterparty (the state company); non-payment of the state buyer; default of judicial arbitral awards; non-delivery of production because of political views
 Commercial risks Factors considered assessing of the commercial risks of the transaction include: Ш export transaction/project Ш of business line Ш financing Ш risk-sharing/coverages Ш securities Ш environmental aspects Ш buyer's country Ш other aspects involved, if any The guarantees offered cover risks related to the buyer or the borrower (commercial risks), or to the buyer's or borrower's country (political risks).
Commercial risks Factors considered assessing of the commercial risks of the transaction include: Ш export transaction/project Ш of business line Ш financing Ш risk-sharing/coverages Ш securities Ш environmental aspects Ш buyer's country Ш other aspects involved, if any The guarantees offered cover risks related to the buyer or the borrower (commercial risks), or to the buyer's or borrower's country (political risks).
 Country Ratings Rating classification for credit guarantees’ rates: Country classification is determined by: 0 : Advanced economy no minimum premium rate v an assessment of the country's ability to meet its external liabilities 1 : Very low risks v expectations of the country's economic development 2 : Low risks v political stability 3 : Relatively low risks v the legislative environment 4 : Intermediate risks 5 : Relatively high risks 6 : High risks 7 : Very high risks Country classification influences on: q the level of the guarantee premium q the security requirements
Country Ratings Rating classification for credit guarantees’ rates: Country classification is determined by: 0 : Advanced economy no minimum premium rate v an assessment of the country's ability to meet its external liabilities 1 : Very low risks v expectations of the country's economic development 2 : Low risks v political stability 3 : Relatively low risks v the legislative environment 4 : Intermediate risks 5 : Relatively high risks 6 : High risks 7 : Very high risks Country classification influences on: q the level of the guarantee premium q the security requirements
 Guarantees offered to exporter in the export/import operations §Credit Risk Guarantee provides the exporter with cover against credit losses in export trade. §Buyer Credit Guarantee provides lenders with security against credit risks caused by a foreign buyer, buyer's bank or buyer's country. An LCF Guarantee is based on terms and conditions of the Buyer Credit Guarantee supplemented with additional terms. §Letter of Credit Guarantee is an insurance for domestic or foreign confirming bank. §Bank Risk Guarantee - For securing conter-guarantees associated with export trade. §Investment Guarantee can be used by domestic investors to cover foreign investments against political risks. §Bond Guarantee is an insurance for the exporter and/or counter-security for the bond issuer. §Finance Guarantee provides a lender with security for credits received by exporters to finance exports.
Guarantees offered to exporter in the export/import operations §Credit Risk Guarantee provides the exporter with cover against credit losses in export trade. §Buyer Credit Guarantee provides lenders with security against credit risks caused by a foreign buyer, buyer's bank or buyer's country. An LCF Guarantee is based on terms and conditions of the Buyer Credit Guarantee supplemented with additional terms. §Letter of Credit Guarantee is an insurance for domestic or foreign confirming bank. §Bank Risk Guarantee - For securing conter-guarantees associated with export trade. §Investment Guarantee can be used by domestic investors to cover foreign investments against political risks. §Bond Guarantee is an insurance for the exporter and/or counter-security for the bond issuer. §Finance Guarantee provides a lender with security for credits received by exporters to finance exports.
 Guarantee Premiums Short-term (repayment period less than 2 years) Buyer Credit and Credit Risk Guarantees usually cover corporate risk; in consequence, the total premium charged includes both the political base rate and a commercial surcharge. The short-term corporate risk is divided into 4 "premium categories". For country categories 0 and 1 premium category I, for country categories 2 and 3 premium category II, for country categories 4 and 5 premium category III and for country categories 6 and 7 premium category IV.
Guarantee Premiums Short-term (repayment period less than 2 years) Buyer Credit and Credit Risk Guarantees usually cover corporate risk; in consequence, the total premium charged includes both the political base rate and a commercial surcharge. The short-term corporate risk is divided into 4 "premium categories". For country categories 0 and 1 premium category I, for country categories 2 and 3 premium category II, for country categories 4 and 5 premium category III and for country categories 6 and 7 premium category IV.
 Example of Guarantee Premiums Table SHORT TERM BUYER CREDIT AND CREDIT RISK GUARANTEES CORPORATE RISK PREMIA (%) RISK Premium Category Country category political + commer cial I commercial political + commer cial II IV 0 and 1 2 and 3 4 and 5 6 and 7 3 months 0. 35 0. 45 0. 52 0. 68 0. 90 6 months 0. 40 0. 52 0. 61 0. 81 1. 08 9 months 0. 45 0. 64 0. 77 1. 10 1. 52 1 year 0. 50 0. 76 0. 93 1. 38 1. 96 1 year 3 months 0. 55 0. 88 1. 09 1. 67 2. 46 1 year 6 months 0. 65 1. 04 1. 31 2. 00 3. 00 1 year 9 months 0. 75 1. 21 1. 52 2. 34 3. 54
Example of Guarantee Premiums Table SHORT TERM BUYER CREDIT AND CREDIT RISK GUARANTEES CORPORATE RISK PREMIA (%) RISK Premium Category Country category political + commer cial I commercial political + commer cial II IV 0 and 1 2 and 3 4 and 5 6 and 7 3 months 0. 35 0. 45 0. 52 0. 68 0. 90 6 months 0. 40 0. 52 0. 61 0. 81 1. 08 9 months 0. 45 0. 64 0. 77 1. 10 1. 52 1 year 0. 50 0. 76 0. 93 1. 38 1. 96 1 year 3 months 0. 55 0. 88 1. 09 1. 67 2. 46 1 year 6 months 0. 65 1. 04 1. 31 2. 00 3. 00 1 year 9 months 0. 75 1. 21 1. 52 2. 34 3. 54
 Dynamics of payments’ delays index by branches of economics (Basis - 100) (average on the world ) (chemical industry) (mechanical engineering ) (pharmaceutical ) Source: Sector Analysis, Documentation by Dominique Fruchter - Paris: Coface University, 2007 - с 24
Dynamics of payments’ delays index by branches of economics (Basis - 100) (average on the world ) (chemical industry) (mechanical engineering ) (pharmaceutical ) Source: Sector Analysis, Documentation by Dominique Fruchter - Paris: Coface University, 2007 - с 24
 Dynamics of payments’ delays index by branches of economics (Basis - 100) (average on the world ) (cellulose &paper industry) (metallurgical) (electronic equipment) Source: Sector Analysis, Documentation by Dominique Fruchter - Paris: Coface University, 2007 - с 24
Dynamics of payments’ delays index by branches of economics (Basis - 100) (average on the world ) (cellulose &paper industry) (metallurgical) (electronic equipment) Source: Sector Analysis, Documentation by Dominique Fruchter - Paris: Coface University, 2007 - с 24
 Branch risks by regions and the world countries (according to ratings of Coface) Min risk Max risk C- Source: Sector Analysis, Documentation by Dominique Fruchter - Paris: Coface University, 2007 - с 34
Branch risks by regions and the world countries (according to ratings of Coface) Min risk Max risk C- Source: Sector Analysis, Documentation by Dominique Fruchter - Paris: Coface University, 2007 - с 34
 Risk management for political risks Internal techniques: -Decreasing overall risk exposure (choice of country or trade portfolio structure) -Increasing of operational earnings (contract price regulation) External techniques : -Letter of Credit (Revocable and Irrevocable) -Factoring -Insurance
Risk management for political risks Internal techniques: -Decreasing overall risk exposure (choice of country or trade portfolio structure) -Increasing of operational earnings (contract price regulation) External techniques : -Letter of Credit (Revocable and Irrevocable) -Factoring -Insurance
 Credit rating agencies ь Business Environmental Risk Intelligence (BERI) ь Frost and Sullivan (Index WPRF – World Political Risk Forecasts) ь Standard & Poor’s Rating Group ь Moody’s Investor Services ь Political Risk Services: International Country Risk Guide
Credit rating agencies ь Business Environmental Risk Intelligence (BERI) ь Frost and Sullivan (Index WPRF – World Political Risk Forecasts) ь Standard & Poor’s Rating Group ь Moody’s Investor Services ь Political Risk Services: International Country Risk Guide
 Biggest credit insurers in Europe Company/ owner Country of origin/ Market for services NCM - Private Netherlands /UK Export Credit Guarantee Department (ECGD) – State UK/UK Euler Hermes - Private Germany/EU Atradius - Private Nitherlands/EU Coface - State France/EU OND - State Belgium/ Belgium SACE - State Italy/Italy NEXI (Nippon Export and Investment Insurance) –State/Private Japan/Japan Eximbank – State, OPIC In cooperation with FCIA (Foreign Credit Insurance Association) USA/USA AIG in cooperation with AIU (American International Underwriters) USA/USA
Biggest credit insurers in Europe Company/ owner Country of origin/ Market for services NCM - Private Netherlands /UK Export Credit Guarantee Department (ECGD) – State UK/UK Euler Hermes - Private Germany/EU Atradius - Private Nitherlands/EU Coface - State France/EU OND - State Belgium/ Belgium SACE - State Italy/Italy NEXI (Nippon Export and Investment Insurance) –State/Private Japan/Japan Eximbank – State, OPIC In cooperation with FCIA (Foreign Credit Insurance Association) USA/USA AIG in cooperation with AIU (American International Underwriters) USA/USA
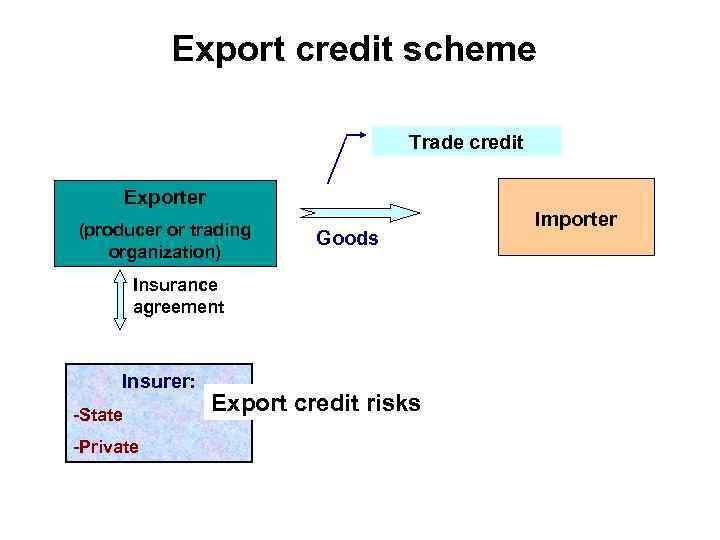 Export credit scheme Trade credit Exporter (producer or trading organization) Goods Insurance agreement Insurer: -State -Private Export credit risks Importer
Export credit scheme Trade credit Exporter (producer or trading organization) Goods Insurance agreement Insurer: -State -Private Export credit risks Importer
 Structure of credit insurance market: international tendencies Private insurers Insurance of commercial credits inside the countries short-term Insurance of short-term exportpolitical risks credits (up to 2 years) State Moderate-terms export credits (2 -5 years) Long-term export credits (more than 5 years) Reinsurance of large risks
Structure of credit insurance market: international tendencies Private insurers Insurance of commercial credits inside the countries short-term Insurance of short-term exportpolitical risks credits (up to 2 years) State Moderate-terms export credits (2 -5 years) Long-term export credits (more than 5 years) Reinsurance of large risks
 Capital concentration in the European credit insurance market Share of market in 2005 Leading insurers: -Euler Hermes -Atradius -Coface Others 87% 13%
Capital concentration in the European credit insurance market Share of market in 2005 Leading insurers: -Euler Hermes -Atradius -Coface Others 87% 13%
 Commercial insurance companies, operating on the export credit insurance market Lloyds of London (Robert and Hiscox syndicate) - UK American international group (AIG) - USA Unistrat Assurances – France Gerling Kreditversicherungs AG – Germany Ingosstrakh - Russia
Commercial insurance companies, operating on the export credit insurance market Lloyds of London (Robert and Hiscox syndicate) - UK American international group (AIG) - USA Unistrat Assurances – France Gerling Kreditversicherungs AG – Germany Ingosstrakh - Russia
 International investments’ insurance agencies Multilateral Investments Guaranteeing Agency (MIGA) - a member of the World Bank Group MIGA Member Countries (168): Ø Industrialized Countries (23) - Australia, Austria, Belgium, Canada, Denmark, Finland, France, Germany, Greece, Iceland, Ireland, Italy, Japan, Luxembourg, Netherlands, Norway, Portugal, Slovenia, Spain, Sweden, Switzerland, United Kingdom, United States Ø Developing Countries (145) Source: http: //www. miga. org
International investments’ insurance agencies Multilateral Investments Guaranteeing Agency (MIGA) - a member of the World Bank Group MIGA Member Countries (168): Ø Industrialized Countries (23) - Australia, Austria, Belgium, Canada, Denmark, Finland, France, Germany, Greece, Iceland, Ireland, Italy, Japan, Luxembourg, Netherlands, Norway, Portugal, Slovenia, Spain, Sweden, Switzerland, United Kingdom, United States Ø Developing Countries (145) Source: http: //www. miga. org
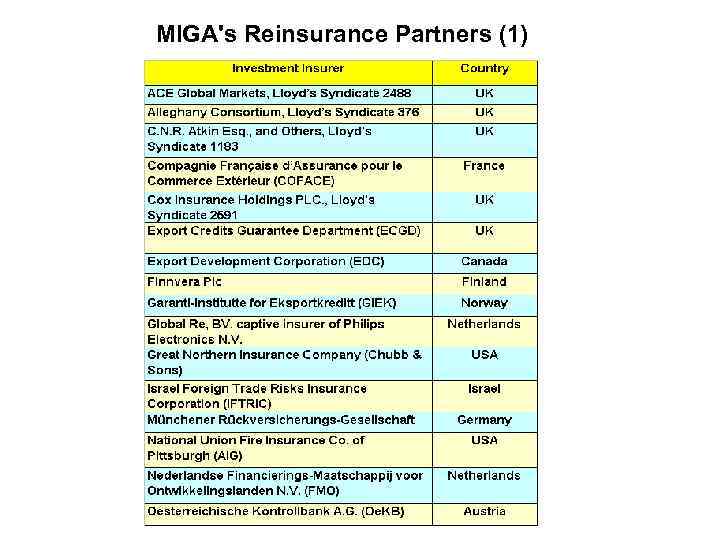 MIGA's Reinsurance Partners (1)
MIGA's Reinsurance Partners (1)
 MIGA's Reinsurance Partners (2)
MIGA's Reinsurance Partners (2)
 Functions of MIGA is a multilateral risk mitigator, promoting foreign direct investment into developing countries by: INSURING investors against political or noncommercial risks Political risks insured: insured ü Currency transfer restriction ü Expropriation ü War and civil disturbance ü Breach of contract
Functions of MIGA is a multilateral risk mitigator, promoting foreign direct investment into developing countries by: INSURING investors against political or noncommercial risks Political risks insured: insured ü Currency transfer restriction ü Expropriation ü War and civil disturbance ü Breach of contract
 Who eligible for MIGA’s Guarantee Coverage? Ø New cross-border investments originating in any MIGA member country, destined for any developing member country Ø New investment contributions associated with the expansion, modernization, or financial restructuring of existing projects Investment projects must be financially and economically viable, environmentally sound, and consistent with the labor standards and other development objectives of the country hosting the investment
Who eligible for MIGA’s Guarantee Coverage? Ø New cross-border investments originating in any MIGA member country, destined for any developing member country Ø New investment contributions associated with the expansion, modernization, or financial restructuring of existing projects Investment projects must be financially and economically viable, environmentally sound, and consistent with the labor standards and other development objectives of the country hosting the investment
 Currency transfer restriction Coverage protects against: v losses arising from an investor's inability to convert local currency (capital, interest, principal, profits, royalties, or other monetary benefits) into foreign exchange for transfer outside the host country. v insures against excessive delays in acquiring foreign exchange caused by the host government's actions or failure to act. Currency devaluation is not covered.
Currency transfer restriction Coverage protects against: v losses arising from an investor's inability to convert local currency (capital, interest, principal, profits, royalties, or other monetary benefits) into foreign exchange for transfer outside the host country. v insures against excessive delays in acquiring foreign exchange caused by the host government's actions or failure to act. Currency devaluation is not covered.
 Expropriation Coverage offers protection against: q loss of the insured investment as a result of acts by the host government that may reduce or eliminate ownership of, control over, or rights to the insured investment. q also covers partial losses, as well as "creeping expropriation, " a series of acts that over time have an expropriatory effect. Bona fide, non-discriminatory measures taken by the host government in the exercise of its legitimate regulatory authority are not considered expropriatory.
Expropriation Coverage offers protection against: q loss of the insured investment as a result of acts by the host government that may reduce or eliminate ownership of, control over, or rights to the insured investment. q also covers partial losses, as well as "creeping expropriation, " a series of acts that over time have an expropriatory effect. Bona fide, non-discriminatory measures taken by the host government in the exercise of its legitimate regulatory authority are not considered expropriatory.
 Breach of contract Coverage protects against: Losses arising from the host government's breach or repudiation of a contractual agreement with the investor. In the event of such an alleged breach or repudiation, the investor must be able to invoke a dispute resolution mechanism (e. g. , arbitration) set out in the underlying contract and obtain an award for damages. The investor may file for a claim if, after a specified period of time, payment is not received.
Breach of contract Coverage protects against: Losses arising from the host government's breach or repudiation of a contractual agreement with the investor. In the event of such an alleged breach or repudiation, the investor must be able to invoke a dispute resolution mechanism (e. g. , arbitration) set out in the underlying contract and obtain an award for damages. The investor may file for a claim if, after a specified period of time, payment is not received.
 War and civil disturbance Coverage protects against: § Loss due to the destruction, disappearance, or physical damage to tangible assets caused by politically motivated acts of war or civil disturbance, including revolution, insurrection, and coups d'état. § Terrorism and sabotage are also covered. § War and civil disturbance coverage also extends to events that result in the total inability of the project enterprise to conduct operations essential to its overall financial viability.
War and civil disturbance Coverage protects against: § Loss due to the destruction, disappearance, or physical damage to tangible assets caused by politically motivated acts of war or civil disturbance, including revolution, insurrection, and coups d'état. § Terrorism and sabotage are also covered. § War and civil disturbance coverage also extends to events that result in the total inability of the project enterprise to conduct operations essential to its overall financial viability.
 Commercial insurance companies in the foreign trade credits’ market
Commercial insurance companies in the foreign trade credits’ market
 Stages of insurance 1 Stage: Application to insurance Insurer Client (exporter) 2 Stage: Rate making Insurer Risk analysis Decision about taking for insurance the risk Declining application Accepting application
Stages of insurance 1 Stage: Application to insurance Insurer Client (exporter) 2 Stage: Rate making Insurer Risk analysis Decision about taking for insurance the risk Declining application Accepting application
 Factors, influencing on the decision about insurance Insurance rate Defining of credit limits and credit ratings for insured contracts * Satisfactory credit rating Positive decision Unsatisfactory credit ratings Negative decision
Factors, influencing on the decision about insurance Insurance rate Defining of credit limits and credit ratings for insured contracts * Satisfactory credit rating Positive decision Unsatisfactory credit ratings Negative decision


