4be36976eac82ba28988f81a62b4da3a.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 85

 7 Computer-Aided Drafting and Design
7 Computer-Aided Drafting and Design
 • Explain how computer technology is revolutionizing drafting, design, and engineering. • Describe the basic features and operation of a computer-aided drafting program. • Explain the various commands used to create objects in CAD. © Goodheart-Willcox Co. , Inc. Permission granted to reproduce for educational use only.
• Explain how computer technology is revolutionizing drafting, design, and engineering. • Describe the basic features and operation of a computer-aided drafting program. • Explain the various commands used to create objects in CAD. © Goodheart-Willcox Co. , Inc. Permission granted to reproduce for educational use only.
 • Describe the tools used to modify CAD drawings. • Identify the various display functions used in CAD programs. • Describe the typical components in a CAD program Help system. © Goodheart-Willcox Co. , Inc. Permission granted to reproduce for educational use only.
• Describe the tools used to modify CAD drawings. • Identify the various display functions used in CAD programs. • Describe the typical components in a CAD program Help system. © Goodheart-Willcox Co. , Inc. Permission granted to reproduce for educational use only.
 • Explain the importance of CAD file management and identify common storage techniques. • List different types of CAD software and their applications. © Goodheart-Willcox Co. , Inc. Permission granted to reproduce for educational use only.
• Explain the importance of CAD file management and identify common storage techniques. • List different types of CAD software and their applications. © Goodheart-Willcox Co. , Inc. Permission granted to reproduce for educational use only.
 Benefits of CAD • Simplifies traditional drafting tasks – Drawing basic shapes – Lettering – Creating views • Maximizes accuracy and proficiency – Setup tools – Drawing and editing commands – Customization methods © Goodheart-Willcox Co. , Inc. Permission granted to reproduce for educational use only.
Benefits of CAD • Simplifies traditional drafting tasks – Drawing basic shapes – Lettering – Creating views • Maximizes accuracy and proficiency – Setup tools – Drawing and editing commands – Customization methods © Goodheart-Willcox Co. , Inc. Permission granted to reproduce for educational use only.
 Computer Graphics and CAD • First used for aerospace design in 1950 s • Prior to emergence of CAD, design work consisted of 2 D drawing production and modelmaking • CAD introduces many benefits – Eliminates repetitive tasks – Allows more time for creative work – Simplifies process of making 2 D and 3 D designs © Goodheart-Willcox Co. , Inc. Permission granted to reproduce for educational use only.
Computer Graphics and CAD • First used for aerospace design in 1950 s • Prior to emergence of CAD, design work consisted of 2 D drawing production and modelmaking • CAD introduces many benefits – Eliminates repetitive tasks – Allows more time for creative work – Simplifies process of making 2 D and 3 D designs © Goodheart-Willcox Co. , Inc. Permission granted to reproduce for educational use only.
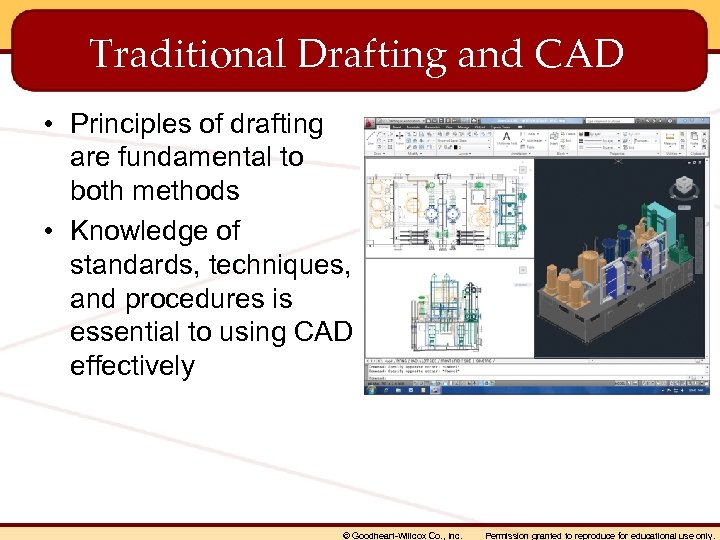 Traditional Drafting and CAD • Principles of drafting are fundamental to both methods • Knowledge of standards, techniques, and procedures is essential to using CAD effectively © Goodheart-Willcox Co. , Inc. Permission granted to reproduce for educational use only.
Traditional Drafting and CAD • Principles of drafting are fundamental to both methods • Knowledge of standards, techniques, and procedures is essential to using CAD effectively © Goodheart-Willcox Co. , Inc. Permission granted to reproduce for educational use only.
 Computer Graphics Programs • Classified according to types of images created – Vector objects – Raster objects © Goodheart-Willcox Co. , Inc. Permission granted to reproduce for educational use only.
Computer Graphics Programs • Classified according to types of images created – Vector objects – Raster objects © Goodheart-Willcox Co. , Inc. Permission granted to reproduce for educational use only.
 Vector Objects • • Created in CAD drawings Made up of lines and arcs Defined with point coordinates in space Hard copy images may be converted to raster format with a scanner © Goodheart-Willcox Co. , Inc. Permission granted to reproduce for educational use only.
Vector Objects • • Created in CAD drawings Made up of lines and arcs Defined with point coordinates in space Hard copy images may be converted to raster format with a scanner © Goodheart-Willcox Co. , Inc. Permission granted to reproduce for educational use only.
 Raster Objects • Also called bitmap graphics • Number of pixels defines resolution • Modified using an image editing program © Goodheart-Willcox Co. , Inc. Permission granted to reproduce for educational use only.
Raster Objects • Also called bitmap graphics • Number of pixels defines resolution • Modified using an image editing program © Goodheart-Willcox Co. , Inc. Permission granted to reproduce for educational use only.
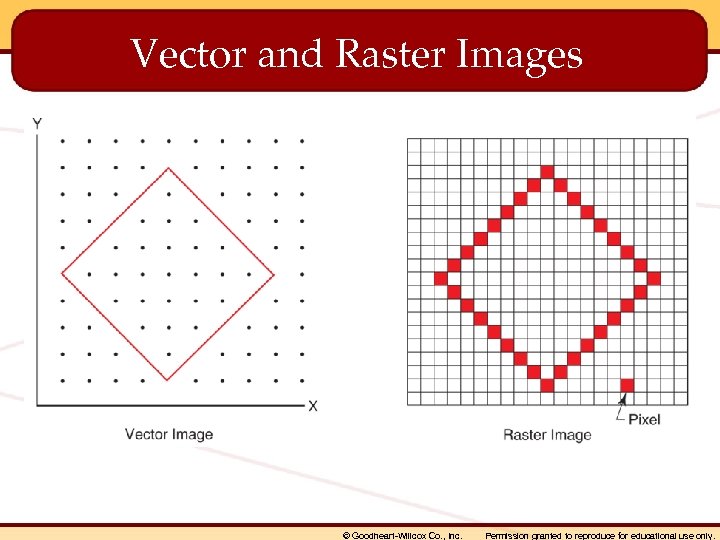 Vector and Raster Images © Goodheart-Willcox Co. , Inc. Permission granted to reproduce for educational use only.
Vector and Raster Images © Goodheart-Willcox Co. , Inc. Permission granted to reproduce for educational use only.
 How CAD Works • Create CAD model in 2 D or 3 D form • Use commands to give program instructions • Modify objects with editing and modifying commands • Add dimensions and text • Output drawing to plotter or printer © Goodheart-Willcox Co. , Inc. Permission granted to reproduce for educational use only.
How CAD Works • Create CAD model in 2 D or 3 D form • Use commands to give program instructions • Modify objects with editing and modifying commands • Add dimensions and text • Output drawing to plotter or printer © Goodheart-Willcox Co. , Inc. Permission granted to reproduce for educational use only.
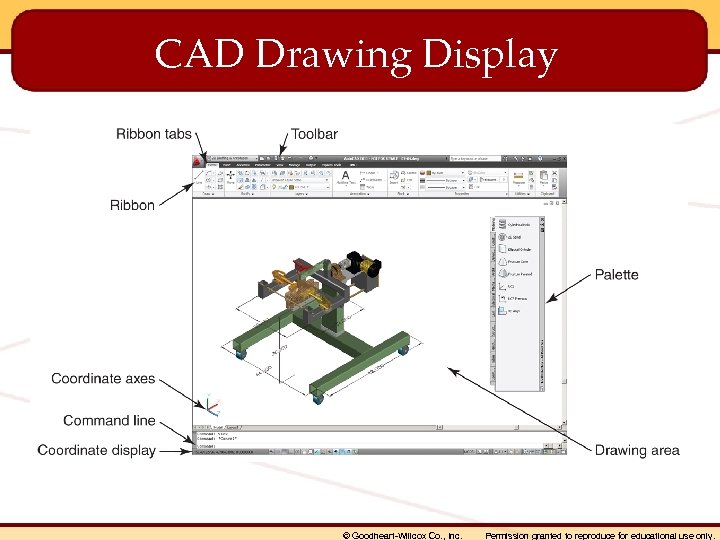 CAD Drawing Display © Goodheart-Willcox Co. , Inc. Permission granted to reproduce for educational use only.
CAD Drawing Display © Goodheart-Willcox Co. , Inc. Permission granted to reproduce for educational use only.
 File Management Commands • • • New Open Close Save as © Goodheart-Willcox Co. , Inc. Permission granted to reproduce for educational use only.
File Management Commands • • • New Open Close Save as © Goodheart-Willcox Co. , Inc. Permission granted to reproduce for educational use only.
 Exporting Files • Typically done with the Export command • Used to create files in a different format – – Windows Metafile (WMF) Bitmap (BMP) Stereolithography (STL) Portable Document Format (PDF) © Goodheart-Willcox Co. , Inc. Permission granted to reproduce for educational use only.
Exporting Files • Typically done with the Export command • Used to create files in a different format – – Windows Metafile (WMF) Bitmap (BMP) Stereolithography (STL) Portable Document Format (PDF) © Goodheart-Willcox Co. , Inc. Permission granted to reproduce for educational use only.
 Plotting and Distribution Commands • Page setup – Used to specify plot device and layout settings • Plot – Used to configure plot device and select type of media • Publish – Used to “publish” multiple-sheet drawing sets © Goodheart-Willcox Co. , Inc. Permission granted to reproduce for educational use only.
Plotting and Distribution Commands • Page setup – Used to specify plot device and layout settings • Plot – Used to configure plot device and select type of media • Publish – Used to “publish” multiple-sheet drawing sets © Goodheart-Willcox Co. , Inc. Permission granted to reproduce for educational use only.
 Basic CAD System Functions • • Coordinate systems Drawing aids Layers and linetypes Blocks © Goodheart-Willcox Co. , Inc. Permission granted to reproduce for educational use only.
Basic CAD System Functions • • Coordinate systems Drawing aids Layers and linetypes Blocks © Goodheart-Willcox Co. , Inc. Permission granted to reproduce for educational use only.
 Coordinate Systems • Used to define coordinates • World coordinate system is most basic system – Based on Cartesian coordinate system © Goodheart-Willcox Co. , Inc. Permission granted to reproduce for educational use only.
Coordinate Systems • Used to define coordinates • World coordinate system is most basic system – Based on Cartesian coordinate system © Goodheart-Willcox Co. , Inc. Permission granted to reproduce for educational use only.
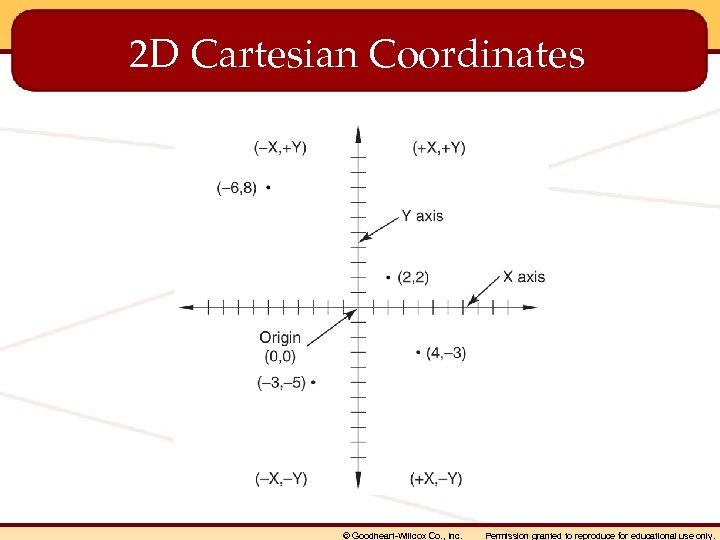 2 D Cartesian Coordinates © Goodheart-Willcox Co. , Inc. Permission granted to reproduce for educational use only.
2 D Cartesian Coordinates © Goodheart-Willcox Co. , Inc. Permission granted to reproduce for educational use only.
 Coordinate Entry Methods • Absolute coordinates • Relative coordinates • Polar coordinates © Goodheart-Willcox Co. , Inc. Permission granted to reproduce for educational use only.
Coordinate Entry Methods • Absolute coordinates • Relative coordinates • Polar coordinates © Goodheart-Willcox Co. , Inc. Permission granted to reproduce for educational use only.
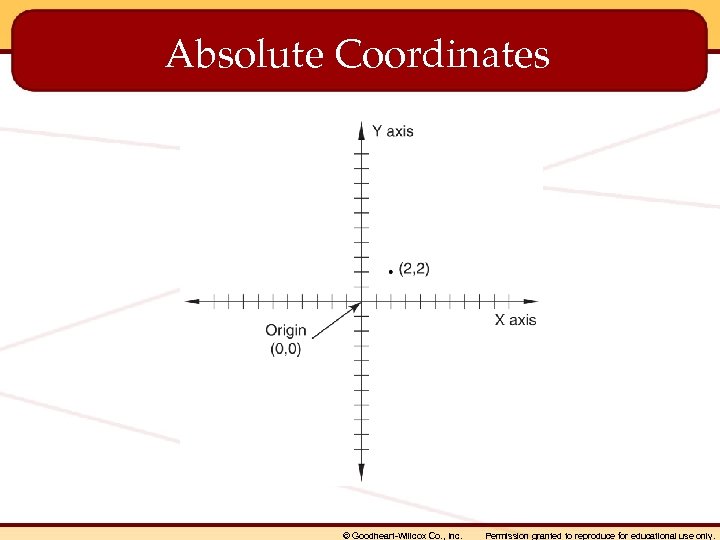 Absolute Coordinates © Goodheart-Willcox Co. , Inc. Permission granted to reproduce for educational use only.
Absolute Coordinates © Goodheart-Willcox Co. , Inc. Permission granted to reproduce for educational use only.
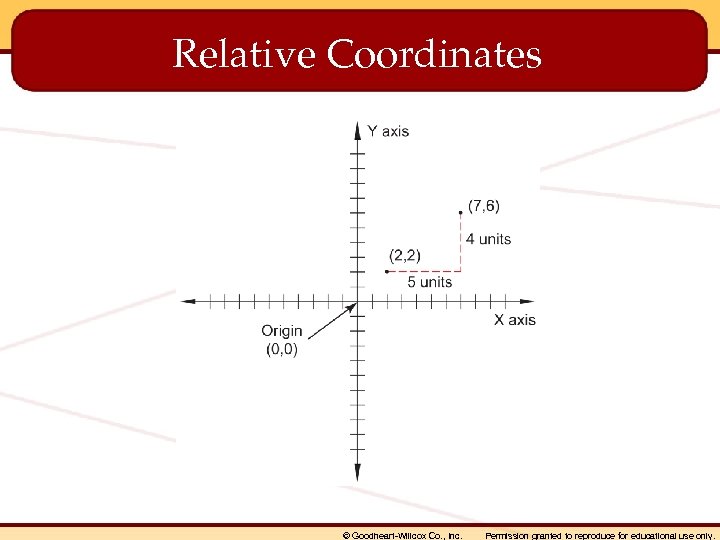 Relative Coordinates © Goodheart-Willcox Co. , Inc. Permission granted to reproduce for educational use only.
Relative Coordinates © Goodheart-Willcox Co. , Inc. Permission granted to reproduce for educational use only.
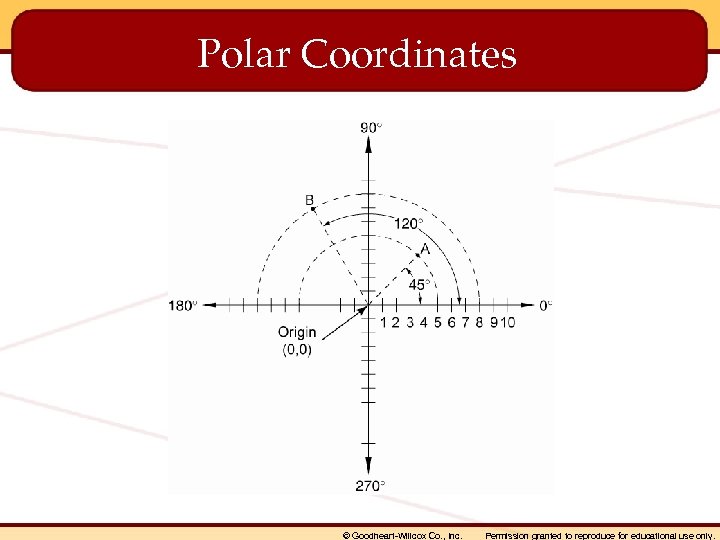 Polar Coordinates © Goodheart-Willcox Co. , Inc. Permission granted to reproduce for educational use only.
Polar Coordinates © Goodheart-Willcox Co. , Inc. Permission granted to reproduce for educational use only.
 User Coordinate System • Useful for creating drawings in 3 D • Orients drawing plane to specific surface • Coordinates are located on drawing plane relative to fixed origin (point on object) • Simplifies 3 D drawing process © Goodheart-Willcox Co. , Inc. Permission granted to reproduce for educational use only.
User Coordinate System • Useful for creating drawings in 3 D • Orients drawing plane to specific surface • Coordinates are located on drawing plane relative to fixed origin (point on object) • Simplifies 3 D drawing process © Goodheart-Willcox Co. , Inc. Permission granted to reproduce for educational use only.
 Drawing Aids • • Grid Snap Object snap Orthogonal mode © Goodheart-Willcox Co. , Inc. Permission granted to reproduce for educational use only.
Drawing Aids • • Grid Snap Object snap Orthogonal mode © Goodheart-Willcox Co. , Inc. Permission granted to reproduce for educational use only.
 Layers • Used to organize drawing content • Named to reflect content – Layer naming conventions observe company or school standards • • Similar to overlays used in manual drafting Assigned colors Assigned linetypes Specified in a drawing template © Goodheart-Willcox Co. , Inc. Permission granted to reproduce for educational use only.
Layers • Used to organize drawing content • Named to reflect content – Layer naming conventions observe company or school standards • • Similar to overlays used in manual drafting Assigned colors Assigned linetypes Specified in a drawing template © Goodheart-Willcox Co. , Inc. Permission granted to reproduce for educational use only.
 Blocks • Typically created for commonly used symbols – Windows and doors on architectural plans • • Used to save drafting time Inserted into drawings as needed Typically stored in a symbol library May be saved with attributes for use in creating a schedule © Goodheart-Willcox Co. , Inc. Permission granted to reproduce for educational use only.
Blocks • Typically created for commonly used symbols – Windows and doors on architectural plans • • Used to save drafting time Inserted into drawings as needed Typically stored in a symbol library May be saved with attributes for use in creating a schedule © Goodheart-Willcox Co. , Inc. Permission granted to reproduce for educational use only.
 Drawing Setup Functions • • Specify drawing unit format Determine drawing scale and sheet size Create layers Save common user settings in a template © Goodheart-Willcox Co. , Inc. Permission granted to reproduce for educational use only.
Drawing Setup Functions • • Specify drawing unit format Determine drawing scale and sheet size Create layers Save common user settings in a template © Goodheart-Willcox Co. , Inc. Permission granted to reproduce for educational use only.
 Object Drawing Commands • • • Line Circle Arc Ellipse Polygon © Goodheart-Willcox Co. , Inc. Permission granted to reproduce for educational use only.
Object Drawing Commands • • • Line Circle Arc Ellipse Polygon © Goodheart-Willcox Co. , Inc. Permission granted to reproduce for educational use only.
 Drawing Lines • Line command typically used • Requires two coordinates – More coordinates may be added within single command sequence • Use proper linetype – Set appropriate layer current before drawing © Goodheart-Willcox Co. , Inc. Permission granted to reproduce for educational use only.
Drawing Lines • Line command typically used • Requires two coordinates – More coordinates may be added within single command sequence • Use proper linetype – Set appropriate layer current before drawing © Goodheart-Willcox Co. , Inc. Permission granted to reproduce for educational use only.
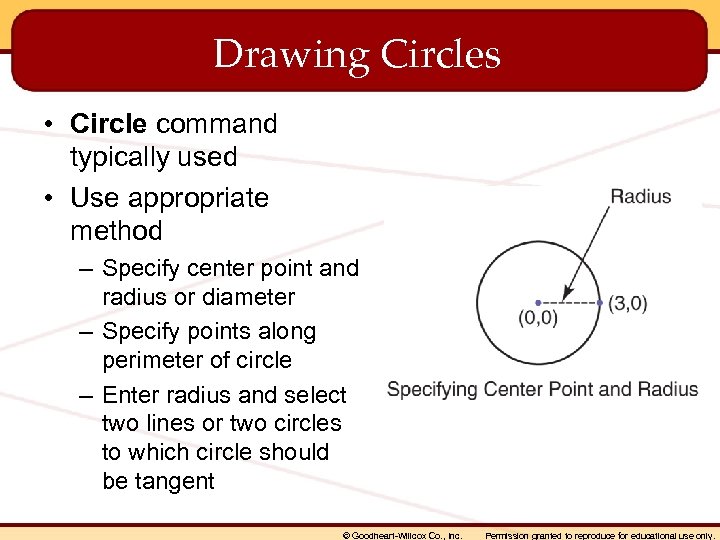 Drawing Circles • Circle command typically used • Use appropriate method – Specify center point and radius or diameter – Specify points along perimeter of circle – Enter radius and select two lines or two circles to which circle should be tangent © Goodheart-Willcox Co. , Inc. Permission granted to reproduce for educational use only.
Drawing Circles • Circle command typically used • Use appropriate method – Specify center point and radius or diameter – Specify points along perimeter of circle – Enter radius and select two lines or two circles to which circle should be tangent © Goodheart-Willcox Co. , Inc. Permission granted to reproduce for educational use only.
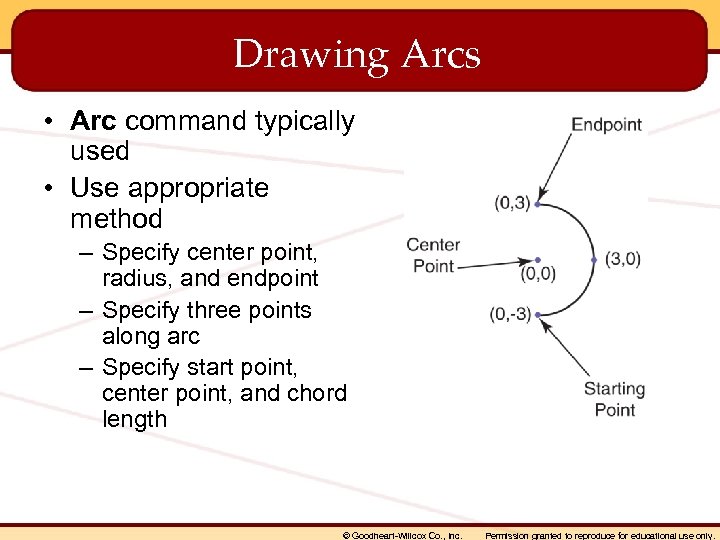 Drawing Arcs • Arc command typically used • Use appropriate method – Specify center point, radius, and endpoint – Specify three points along arc – Specify start point, center point, and chord length © Goodheart-Willcox Co. , Inc. Permission granted to reproduce for educational use only.
Drawing Arcs • Arc command typically used • Use appropriate method – Specify center point, radius, and endpoint – Specify three points along arc – Specify start point, center point, and chord length © Goodheart-Willcox Co. , Inc. Permission granted to reproduce for educational use only.
 Drawing Ellipses • Ellipse command typically used – Specify center point, major axis, and minor axis • Elliptical arcs drawn in similar fashion – Specify axis endpoints and start and end angles © Goodheart-Willcox Co. , Inc. Permission granted to reproduce for educational use only.
Drawing Ellipses • Ellipse command typically used – Specify center point, major axis, and minor axis • Elliptical arcs drawn in similar fashion – Specify axis endpoints and start and end angles © Goodheart-Willcox Co. , Inc. Permission granted to reproduce for educational use only.
 Drawing Polygons • Polygon command typically used – – Enter number of sides Specify center point Inscribe or circumscribe the polygon Enter radius © Goodheart-Willcox Co. , Inc. Permission granted to reproduce for educational use only.
Drawing Polygons • Polygon command typically used – – Enter number of sides Specify center point Inscribe or circumscribe the polygon Enter radius © Goodheart-Willcox Co. , Inc. Permission granted to reproduce for educational use only.
 Editing and Modifying Commands • • • Move Copy Rotate Scale Undo Erase • • • Array Mirror Fillet Trim Extend © Goodheart-Willcox Co. , Inc. Permission granted to reproduce for educational use only.
Editing and Modifying Commands • • • Move Copy Rotate Scale Undo Erase • • • Array Mirror Fillet Trim Extend © Goodheart-Willcox Co. , Inc. Permission granted to reproduce for educational use only.
 Moving Objects • Move command typically used – Select object or objects to move – Specify base point for selection set – Specify displacement point © Goodheart-Willcox Co. , Inc. Permission granted to reproduce for educational use only.
Moving Objects • Move command typically used – Select object or objects to move – Specify base point for selection set – Specify displacement point © Goodheart-Willcox Co. , Inc. Permission granted to reproduce for educational use only.
 Copying Objects • Copy command typically used – – Select object or objects to copy Select base point Specify displacement point Multiple option copies same selection to more than one location © Goodheart-Willcox Co. , Inc. Permission granted to reproduce for educational use only.
Copying Objects • Copy command typically used – – Select object or objects to copy Select base point Specify displacement point Multiple option copies same selection to more than one location © Goodheart-Willcox Co. , Inc. Permission granted to reproduce for educational use only.
 Rotating Objects • Rotate command typically used – – Used to change angular position of object Select object or objects to rotate Specify base point Specify angle (clockwise or counterclockwise) © Goodheart-Willcox Co. , Inc. Permission granted to reproduce for educational use only.
Rotating Objects • Rotate command typically used – – Used to change angular position of object Select object or objects to rotate Specify base point Specify angle (clockwise or counterclockwise) © Goodheart-Willcox Co. , Inc. Permission granted to reproduce for educational use only.
 Scaling Objects • Scale command typically used – Used to reduce or enlarge objects by specified scale factor – Select object to scale – Select base point – Specify scale factor © Goodheart-Willcox Co. , Inc. Permission granted to reproduce for educational use only.
Scaling Objects • Scale command typically used – Used to reduce or enlarge objects by specified scale factor – Select object to scale – Select base point – Specify scale factor © Goodheart-Willcox Co. , Inc. Permission granted to reproduce for educational use only.
 Undoing Operations • Undo command typically used – Used to “undo” previous action – Allows for undoing multiple actions in reverse sequence © Goodheart-Willcox Co. , Inc. Permission granted to reproduce for educational use only.
Undoing Operations • Undo command typically used – Used to “undo” previous action – Allows for undoing multiple actions in reverse sequence © Goodheart-Willcox Co. , Inc. Permission granted to reproduce for educational use only.
 Erasing Objects • Erase command typically used – Used to remove unwanted objects quickly – Select objects to erase – Use Undo command to restore erased object © Goodheart-Willcox Co. , Inc. Permission granted to reproduce for educational use only.
Erasing Objects • Erase command typically used – Used to remove unwanted objects quickly – Select objects to erase – Use Undo command to restore erased object © Goodheart-Willcox Co. , Inc. Permission granted to reproduce for educational use only.
 Arraying Objects • Array command typically used – Used to copy and orient multiple objects in a pattern • Use rectangular array for rectangular orientation – Enter base point, number of rows, number of columns, and spacing • Use polar array for polar orientation – Specify center point, number of objects, and angular value determining amount of rotation © Goodheart-Willcox Co. , Inc. Permission granted to reproduce for educational use only.
Arraying Objects • Array command typically used – Used to copy and orient multiple objects in a pattern • Use rectangular array for rectangular orientation – Enter base point, number of rows, number of columns, and spacing • Use polar array for polar orientation – Specify center point, number of objects, and angular value determining amount of rotation © Goodheart-Willcox Co. , Inc. Permission granted to reproduce for educational use only.
 Mirroring Objects • Mirror command typically used – Used to create symmetrical objects by creating mirrored copy of object – Select object to mirror – Specify mirror axis – Keep or delete original object © Goodheart-Willcox Co. , Inc. Permission granted to reproduce for educational use only.
Mirroring Objects • Mirror command typically used – Used to create symmetrical objects by creating mirrored copy of object – Select object to mirror – Specify mirror axis – Keep or delete original object © Goodheart-Willcox Co. , Inc. Permission granted to reproduce for educational use only.
 Creating Rounded Corners • Fillet command typically used – Used to create round or fillet – Set radius – Select entities forming intersection © Goodheart-Willcox Co. , Inc. Permission granted to reproduce for educational use only.
Creating Rounded Corners • Fillet command typically used – Used to create round or fillet – Set radius – Select entities forming intersection © Goodheart-Willcox Co. , Inc. Permission granted to reproduce for educational use only.
 Creating Angled Corners • Chamfer command typically used – Used to create chamfer – Set chamfer distance – Select two lines © Goodheart-Willcox Co. , Inc. Permission granted to reproduce for educational use only.
Creating Angled Corners • Chamfer command typically used – Used to create chamfer – Set chamfer distance – Select two lines © Goodheart-Willcox Co. , Inc. Permission granted to reproduce for educational use only.
 Trimming Lines • Trim command typically used – Used to clean up line overlaps – Specify cutting edge – Select object to trim © Goodheart-Willcox Co. , Inc. Permission granted to reproduce for educational use only.
Trimming Lines • Trim command typically used – Used to clean up line overlaps – Specify cutting edge – Select object to trim © Goodheart-Willcox Co. , Inc. Permission granted to reproduce for educational use only.
 Extending Lines • Extend command typically used – Used to lengthen object to meet edge – Specify boundary – Select object to extend © Goodheart-Willcox Co. , Inc. Permission granted to reproduce for educational use only.
Extending Lines • Extend command typically used – Used to lengthen object to meet edge – Specify boundary – Select object to extend © Goodheart-Willcox Co. , Inc. Permission granted to reproduce for educational use only.
 Display Commands • Zoom command – Used to zoom in (to view drawing details) or zoom out (to reduce the view) • Pan command – Used to adjust view in real time without changing magnification • More advanced commands available in 3 D drawing programs © Goodheart-Willcox Co. , Inc. Permission granted to reproduce for educational use only.
Display Commands • Zoom command – Used to zoom in (to view drawing details) or zoom out (to reduce the view) • Pan command – Used to adjust view in real time without changing magnification • More advanced commands available in 3 D drawing programs © Goodheart-Willcox Co. , Inc. Permission granted to reproduce for educational use only.
 Making Measurements • Measure Geometry command typically used to calculate common measurements – Linear distances • Select two points – Area and perimeter calculations • Select object or pick points defining the area © Goodheart-Willcox Co. , Inc. Permission granted to reproduce for educational use only.
Making Measurements • Measure Geometry command typically used to calculate common measurements – Linear distances • Select two points – Area and perimeter calculations • Select object or pick points defining the area © Goodheart-Willcox Co. , Inc. Permission granted to reproduce for educational use only.
 Object Property and Drawing Status Commands • Properties command – Used to identify object coordinates and settings assigned to object • List command – Used to list information from drawing database • Status command – Used to identify drawing statistics • Time command – Used to identify current time and drawing time in current session © Goodheart-Willcox Co. , Inc. Permission granted to reproduce for educational use only.
Object Property and Drawing Status Commands • Properties command – Used to identify object coordinates and settings assigned to object • List command – Used to list information from drawing database • Status command – Used to identify drawing statistics • Time command – Used to identify current time and drawing time in current session © Goodheart-Willcox Co. , Inc. Permission granted to reproduce for educational use only.
 Help System • • Provides user help Accessed with Help command Organized into documents and references Includes search functions and question-andanswer tools © Goodheart-Willcox Co. , Inc. Permission granted to reproduce for educational use only.
Help System • • Provides user help Accessed with Help command Organized into documents and references Includes search functions and question-andanswer tools © Goodheart-Willcox Co. , Inc. Permission granted to reproduce for educational use only.
 File Management and Storage • Establish a logical system of folders to organize files in a project • Use established file naming conventions – Use prefixes to identify project and drawing information • Follow school or company practice © Goodheart-Willcox Co. , Inc. Permission granted to reproduce for educational use only.
File Management and Storage • Establish a logical system of folders to organize files in a project • Use established file naming conventions – Use prefixes to identify project and drawing information • Follow school or company practice © Goodheart-Willcox Co. , Inc. Permission granted to reproduce for educational use only.
 Backing Up and Archiving Files • Save and back up work at regular intervals • Follow established protocol – Save work every 15 minutes – Save to a network server – Back up files on a weekly basis • Create file archive during project wrapup – Ensure that files can be accessed in future – Use standard naming, organization, and backup practices © Goodheart-Willcox Co. , Inc. Permission granted to reproduce for educational use only.
Backing Up and Archiving Files • Save and back up work at regular intervals • Follow established protocol – Save work every 15 minutes – Save to a network server – Back up files on a weekly basis • Create file archive during project wrapup – Ensure that files can be accessed in future – Use standard naming, organization, and backup practices © Goodheart-Willcox Co. , Inc. Permission granted to reproduce for educational use only.
 CAD System Components • • • Computer Monitor Keyboard Pointing device Output device Software © Goodheart-Willcox Co. , Inc. Permission granted to reproduce for educational use only.
CAD System Components • • • Computer Monitor Keyboard Pointing device Output device Software © Goodheart-Willcox Co. , Inc. Permission granted to reproduce for educational use only.
 CAD Software • Type used depends on specific application – – 2 D drawing 3 D modeling Mechanical drafting and manufacturing Advanced rendering and animation © Goodheart-Willcox Co. , Inc. Permission granted to reproduce for educational use only.
CAD Software • Type used depends on specific application – – 2 D drawing 3 D modeling Mechanical drafting and manufacturing Advanced rendering and animation © Goodheart-Willcox Co. , Inc. Permission granted to reproduce for educational use only.
 CAD Modeling Programs • Used to construct 3 D models • Classified by modeling method – Solid modeling – Surface modeling – Parametric modeling • Often provide rendering capability © Goodheart-Willcox Co. , Inc. Permission granted to reproduce for educational use only.
CAD Modeling Programs • Used to construct 3 D models • Classified by modeling method – Solid modeling – Surface modeling – Parametric modeling • Often provide rendering capability © Goodheart-Willcox Co. , Inc. Permission granted to reproduce for educational use only.
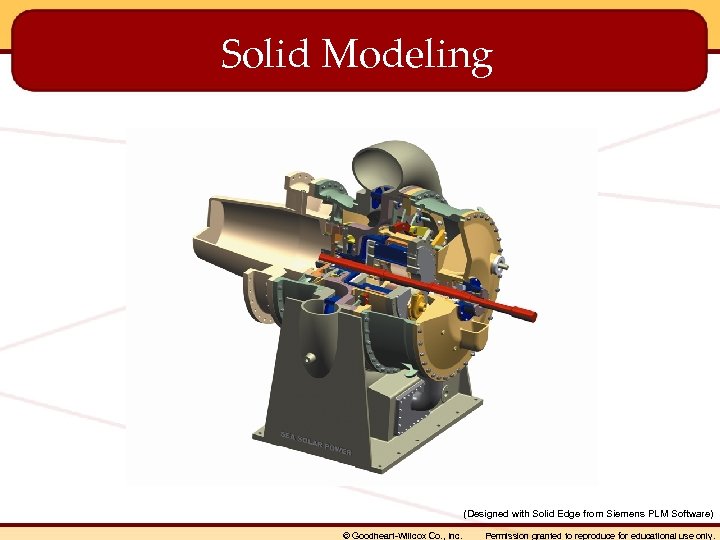 Solid Modeling (Designed with Solid Edge from Siemens PLM Software) © Goodheart-Willcox Co. , Inc. Permission granted to reproduce for educational use only.
Solid Modeling (Designed with Solid Edge from Siemens PLM Software) © Goodheart-Willcox Co. , Inc. Permission granted to reproduce for educational use only.
 Surface Modeling (Discreet, a division of Autodesk) © Goodheart-Willcox Co. , Inc. Permission granted to reproduce for educational use only.
Surface Modeling (Discreet, a division of Autodesk) © Goodheart-Willcox Co. , Inc. Permission granted to reproduce for educational use only.
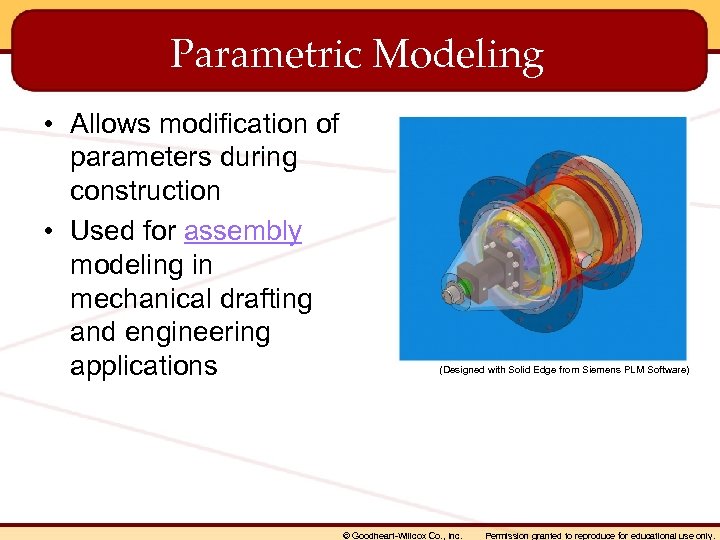 Parametric Modeling • Allows modification of parameters during construction • Used for assembly modeling in mechanical drafting and engineering applications (Designed with Solid Edge from Siemens PLM Software) © Goodheart-Willcox Co. , Inc. Permission granted to reproduce for educational use only.
Parametric Modeling • Allows modification of parameters during construction • Used for assembly modeling in mechanical drafting and engineering applications (Designed with Solid Edge from Siemens PLM Software) © Goodheart-Willcox Co. , Inc. Permission granted to reproduce for educational use only.
 Computer-Aided Design/Computer. Aided Manufacturing (CAD/CAM) • Computer numerical control (CNC) machines control manufacturing processes • Computer data input to machine controls movement of machine tools • CAD-generated drawings supply tool data © Goodheart-Willcox Co. , Inc. Permission granted to reproduce for educational use only.
Computer-Aided Design/Computer. Aided Manufacturing (CAD/CAM) • Computer numerical control (CNC) machines control manufacturing processes • Computer data input to machine controls movement of machine tools • CAD-generated drawings supply tool data © Goodheart-Willcox Co. , Inc. Permission granted to reproduce for educational use only.
 Rendering Program • Used to create realistic displays of models with special effects – Lighting – Materials – Environmental settings • Requires greater computing power to perform necessary calculations © Goodheart-Willcox Co. , Inc. Permission granted to reproduce for educational use only.
Rendering Program • Used to create realistic displays of models with special effects – Lighting – Materials – Environmental settings • Requires greater computing power to perform necessary calculations © Goodheart-Willcox Co. , Inc. Permission granted to reproduce for educational use only.
 Animation Program • Used to assign movement parameters for frameby-frame animations • Used for higher-end applications – Architectural building tours – Film special effects – Medical imaging © Goodheart-Willcox Co. , Inc. Permission granted to reproduce for educational use only.
Animation Program • Used to assign movement parameters for frameby-frame animations • Used for higher-end applications – Architectural building tours – Film special effects – Medical imaging © Goodheart-Willcox Co. , Inc. Permission granted to reproduce for educational use only.
 What are coordinates? Points representing units of real measurement from a fixed point. © Goodheart-Willcox Co. , Inc. Permission granted to reproduce for educational use only.
What are coordinates? Points representing units of real measurement from a fixed point. © Goodheart-Willcox Co. , Inc. Permission granted to reproduce for educational use only.
 When using relative coordinates, objects are drawn using coordinates in relation to the _____. last coordinate specified © Goodheart-Willcox Co. , Inc. Permission granted to reproduce for educational use only.
When using relative coordinates, objects are drawn using coordinates in relation to the _____. last coordinate specified © Goodheart-Willcox Co. , Inc. Permission granted to reproduce for educational use only.
 How does orthogonal mode simplify the task of drawing horizontal and vertical lines? The movement of the cursor is confined to horizontal and vertical movement in relation to the drawing plane. © Goodheart-Willcox Co. , Inc. Permission granted to reproduce for educational use only.
How does orthogonal mode simplify the task of drawing horizontal and vertical lines? The movement of the cursor is confined to horizontal and vertical movement in relation to the drawing plane. © Goodheart-Willcox Co. , Inc. Permission granted to reproduce for educational use only.
 What are layers? Layers are user-defined object settings that can be displayed or “turned off” to distinguish the different types of content in a drawing. © Goodheart-Willcox Co. , Inc. Permission granted to reproduce for educational use only.
What are layers? Layers are user-defined object settings that can be displayed or “turned off” to distinguish the different types of content in a drawing. © Goodheart-Willcox Co. , Inc. Permission granted to reproduce for educational use only.
 An ellipse has a center point, a(n) _____ axis, and a(n) _____ axis. major, minor © Goodheart-Willcox Co. , Inc. Permission granted to reproduce for educational use only.
An ellipse has a center point, a(n) _____ axis, and a(n) _____ axis. major, minor © Goodheart-Willcox Co. , Inc. Permission granted to reproduce for educational use only.
 What two types of arrays can be created with the Array command? Rectangular and polar arrays © Goodheart-Willcox Co. , Inc. Permission granted to reproduce for educational use only.
What two types of arrays can be created with the Array command? Rectangular and polar arrays © Goodheart-Willcox Co. , Inc. Permission granted to reproduce for educational use only.
 The Mirror command is useful when drawing _____ objects. symmetrical © Goodheart-Willcox Co. , Inc. Permission granted to reproduce for educational use only.
The Mirror command is useful when drawing _____ objects. symmetrical © Goodheart-Willcox Co. , Inc. Permission granted to reproduce for educational use only.
 The _____ command can be used to restore an object that has been erased unintentionally. Undo © Goodheart-Willcox Co. , Inc. Permission granted to reproduce for educational use only.
The _____ command can be used to restore an object that has been erased unintentionally. Undo © Goodheart-Willcox Co. , Inc. Permission granted to reproduce for educational use only.
 Which of the following is not an object drawing command? A. Line B. Properties C. Circle D. Arc B. Properties © Goodheart-Willcox Co. , Inc. Permission granted to reproduce for educational use only.
Which of the following is not an object drawing command? A. Line B. Properties C. Circle D. Arc B. Properties © Goodheart-Willcox Co. , Inc. Permission granted to reproduce for educational use only.
 Name three most common types of CAD modeling. Solid modeling, surface modeling, and parametric modeling © Goodheart-Willcox Co. , Inc. Permission granted to reproduce for educational use only.
Name three most common types of CAD modeling. Solid modeling, surface modeling, and parametric modeling © Goodheart-Willcox Co. , Inc. Permission granted to reproduce for educational use only.
 What is parametric modeling? An advanced form of modeling that allows object dimensions, or parameters, to be modified during the construction of a model. © Goodheart-Willcox Co. , Inc. Permission granted to reproduce for educational use only.
What is parametric modeling? An advanced form of modeling that allows object dimensions, or parameters, to be modified during the construction of a model. © Goodheart-Willcox Co. , Inc. Permission granted to reproduce for educational use only.
 How does CAD/CAM combine CAD with automated manufacturing operations? After a part is drawn in a CAD program, the design data is calculated by the program. The computer data is input to the CNC machine to control the movement of machine tools. © Goodheart-Willcox Co. , Inc. Permission granted to reproduce for educational use only.
How does CAD/CAM combine CAD with automated manufacturing operations? After a part is drawn in a CAD program, the design data is calculated by the program. The computer data is input to the CNC machine to control the movement of machine tools. © Goodheart-Willcox Co. , Inc. Permission granted to reproduce for educational use only.
 • Absolute coordinates – Coordinates located in relation to the coordinate system origin (0, 0, 0). • Array – An orientation of copied objects in a rectangular or polar pattern. • Assembly – A functional mechanism made up of multiple components, referred to as parts. • Attributes – Text strings of information about related block symbols, such as product numbers, sizes, or materials. © Goodheart-Willcox Co. , Inc. Permission granted to reproduce for educational use only.
• Absolute coordinates – Coordinates located in relation to the coordinate system origin (0, 0, 0). • Array – An orientation of copied objects in a rectangular or polar pattern. • Assembly – A functional mechanism made up of multiple components, referred to as parts. • Attributes – Text strings of information about related block symbols, such as product numbers, sizes, or materials. © Goodheart-Willcox Co. , Inc. Permission granted to reproduce for educational use only.
 • Blocks – Predrawn objects designed for multiple use in drawing projects. • Cartesian coordinate system – A system in which coordinate points are located using the X, Y, and Z axes. • Chamfer – An angled cut made to remove the “corner” of two perpendicular surfaces. © Goodheart-Willcox Co. , Inc. Permission granted to reproduce for educational use only.
• Blocks – Predrawn objects designed for multiple use in drawing projects. • Cartesian coordinate system – A system in which coordinate points are located using the X, Y, and Z axes. • Chamfer – An angled cut made to remove the “corner” of two perpendicular surfaces. © Goodheart-Willcox Co. , Inc. Permission granted to reproduce for educational use only.
 • Computer-aided design/computer-aided manufacturing (CAD/CAM) – A type of manufacturing in which machining data is generated from CAD drawings and used by computer numerical control (CNC) machines. • Coordinates – The positions or locations of points along the X, Y, and Z axes. In a CAD system, the points represent units of real measurement from a fixed point. • Fillet – An arc representing an inside rounded corner. © Goodheart-Willcox Co. , Inc. Permission granted to reproduce for educational use only.
• Computer-aided design/computer-aided manufacturing (CAD/CAM) – A type of manufacturing in which machining data is generated from CAD drawings and used by computer numerical control (CNC) machines. • Coordinates – The positions or locations of points along the X, Y, and Z axes. In a CAD system, the points represent units of real measurement from a fixed point. • Fillet – An arc representing an inside rounded corner. © Goodheart-Willcox Co. , Inc. Permission granted to reproduce for educational use only.
 • Grid – A network of uniformly spaced points used to determine distances. • Layers – User-defined object settings that can be displayed or “turned off” to distinguish the different types of content in a drawing. • Linetype – A user-defined object setting used to describe a line definition in the Alphabet of Lines. • Object snap – A function that allows the cursor to be “snapped” to specific locations on an object. © Goodheart-Willcox Co. , Inc. Permission granted to reproduce for educational use only.
• Grid – A network of uniformly spaced points used to determine distances. • Layers – User-defined object settings that can be displayed or “turned off” to distinguish the different types of content in a drawing. • Linetype – A user-defined object setting used to describe a line definition in the Alphabet of Lines. • Object snap – A function that allows the cursor to be “snapped” to specific locations on an object. © Goodheart-Willcox Co. , Inc. Permission granted to reproduce for educational use only.
 • Orthogonal mode – A drawing mode used to draw horizontal and vertical lines by confining the cursor to horizontal and vertical movement. • Parametric modeling – A type of 3 D-based drawing in which changes to object parameters during the modeling process affect the entire model. • Pixels – Tiny shapes of data making up a raster image. Also called picture elements. • Polar coordinates – Coordinates located at a given distance and angle. © Goodheart-Willcox Co. , Inc. Permission granted to reproduce for educational use only.
• Orthogonal mode – A drawing mode used to draw horizontal and vertical lines by confining the cursor to horizontal and vertical movement. • Parametric modeling – A type of 3 D-based drawing in which changes to object parameters during the modeling process affect the entire model. • Pixels – Tiny shapes of data making up a raster image. Also called picture elements. • Polar coordinates – Coordinates located at a given distance and angle. © Goodheart-Willcox Co. , Inc. Permission granted to reproduce for educational use only.
 • Raster objects – Objects made up of pixels. Also known as bitmap graphics. • Relative coordinates – Coordinates located in relation to the last point specified (or the origin, if a previous point has not been specified). • Rendering – A highly realistic representation of a model with lighting, shadows, and other visual effects applied. © Goodheart-Willcox Co. , Inc. Permission granted to reproduce for educational use only.
• Raster objects – Objects made up of pixels. Also known as bitmap graphics. • Relative coordinates – Coordinates located in relation to the last point specified (or the origin, if a previous point has not been specified). • Rendering – A highly realistic representation of a model with lighting, shadows, and other visual effects applied. © Goodheart-Willcox Co. , Inc. Permission granted to reproduce for educational use only.
 • Resolution – A term used to describe the visual quality of a raster image, determined by the number of pixels making up the image. • Round – An arc representing an outside rounded corner. See also Fillet. • Scanner – A computer hardware device used to convert a hard copy image into digital form. © Goodheart-Willcox Co. , Inc. Permission granted to reproduce for educational use only.
• Resolution – A term used to describe the visual quality of a raster image, determined by the number of pixels making up the image. • Round – An arc representing an outside rounded corner. See also Fillet. • Scanner – A computer hardware device used to convert a hard copy image into digital form. © Goodheart-Willcox Co. , Inc. Permission granted to reproduce for educational use only.
 • Schedule – A chart or table used to list manufacturing and purchasing information about parts and products on a drawing. • Snap – A function that allows the user to align or “snap” the cursor to specific increments in an invisible grid. • Solid modeling – A type of 3 D-based drawing used to create solids (objects that represent the entire mass of an object). © Goodheart-Willcox Co. , Inc. Permission granted to reproduce for educational use only.
• Schedule – A chart or table used to list manufacturing and purchasing information about parts and products on a drawing. • Snap – A function that allows the user to align or “snap” the cursor to specific increments in an invisible grid. • Solid modeling – A type of 3 D-based drawing used to create solids (objects that represent the entire mass of an object). © Goodheart-Willcox Co. , Inc. Permission granted to reproduce for educational use only.
 • Surface modeling – A type of 3 D-based drawing used to create surface models (objects that have an outer “skin” to represent exterior surfaces). • Symbol library – A collection of related drawing symbols. • Template – A saved set of configurations used to start a drawing file. © Goodheart-Willcox Co. , Inc. Permission granted to reproduce for educational use only.
• Surface modeling – A type of 3 D-based drawing used to create surface models (objects that have an outer “skin” to represent exterior surfaces). • Symbol library – A collection of related drawing symbols. • Template – A saved set of configurations used to start a drawing file. © Goodheart-Willcox Co. , Inc. Permission granted to reproduce for educational use only.
 • User coordinate system – A relative drawing configuration enabling the user to orient a drawing plane to a specific surface, typically used in 3 D drawing. • Vector objects – Objects made up of lines and arcs, defined with point coordinates in space. • World coordinate system – A system for locating points using Cartesian coordinates on the XYZ axes in relation to the 0, 0, 0 origin. © Goodheart-Willcox Co. , Inc. Permission granted to reproduce for educational use only.
• User coordinate system – A relative drawing configuration enabling the user to orient a drawing plane to a specific surface, typically used in 3 D drawing. • Vector objects – Objects made up of lines and arcs, defined with point coordinates in space. • World coordinate system – A system for locating points using Cartesian coordinates on the XYZ axes in relation to the 0, 0, 0 origin. © Goodheart-Willcox Co. , Inc. Permission granted to reproduce for educational use only.


