2618052d11fea45856fa2f124c8cfedc.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 25

7 -1: Buying a Home
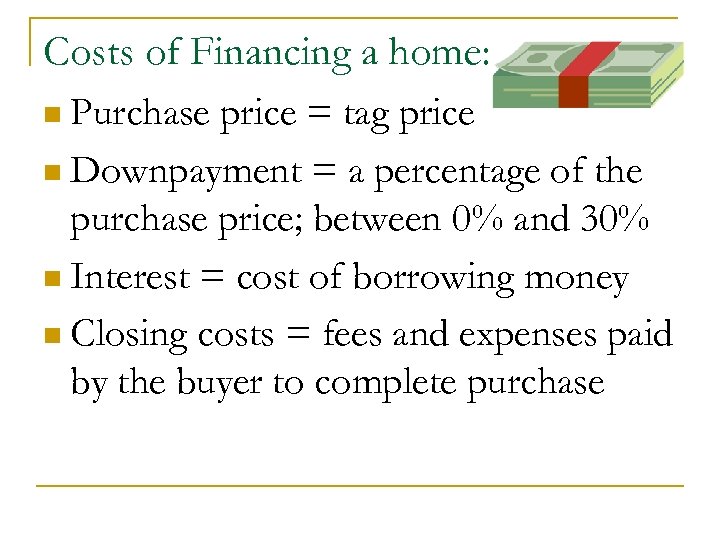
Costs of Financing a home: n Purchase price = tag price n Downpayment = a percentage of the purchase price; between 0% and 30% n Interest = cost of borrowing money n Closing costs = fees and expenses paid by the buyer to complete purchase
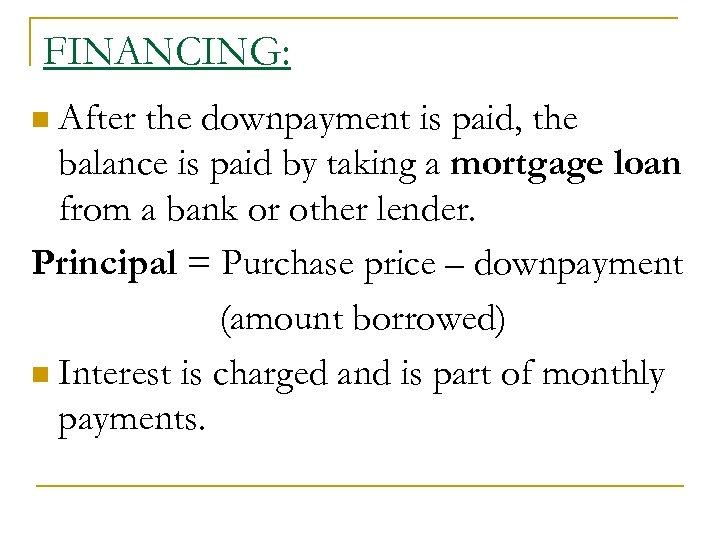
FINANCING: After the downpayment is paid, the balance is paid by taking a mortgage loan from a bank or other lender. Principal = Purchase price – downpayment (amount borrowed) n Interest is charged and is part of monthly payments. n

CLOSING COSTS: Include: legal fees, title insurance, loan origination fees, appraisal and inspection fees, land surveys, and taxes n 1% to 4% of purchase price n http: //c 21 westworld. com/homesearch. htm? scope=ALL&mls=0&hometypes%5 B%5 D=1&minprice=0&maxprice=1500000&bedrooms=0&bathrooms=0&city=long+beach &state=CA&zipcode=&radius=0&street=&county=&subdivision=&development=&garage=0&sqft=&acres=&association_fees=0&listing_status=&email=Enter+Yo ur+Email+Address%21&autosearch_length=279&autosearch_period=7&autosearch_receive=0&autosearch_format=HTML&action=Search
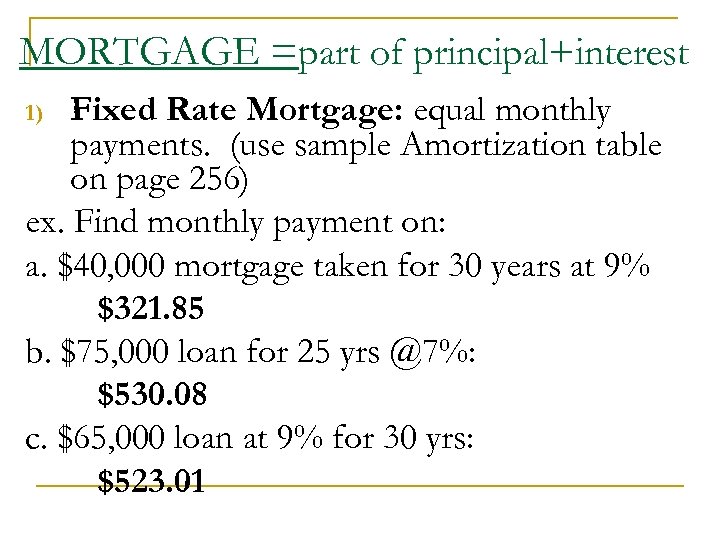
MORTGAGE =part of principal+interest Fixed Rate Mortgage: equal monthly payments. (use sample Amortization table on page 256) ex. Find monthly payment on: a. $40, 000 mortgage taken for 30 years at 9% $321. 85 b. $75, 000 loan for 25 yrs @7%: $530. 08 c. $65, 000 loan at 9% for 30 yrs: $523. 01 1)

ex The Smiths are buying a house for $425, 000. They are making a downpayment of 20%. The closing costs will be 3. 5% of the purchase price. 1. How much is their downpayment? 2. How much are closing costs? 3. How much cash do they need to complete the sale? 4. How much are they borrowing?

DISCUSSION: n What are the benefits of buying a home? n What factors need to be considered in making the decision to buy a home?

How much interest do the homeowners end up paying?

7. 1 Day 2 2) Variable or Adjustable Rate Mortgage: • the interest rate is not guaranteed • Usually rate is lower than Fixed R. M. • However, lender can increase or decrease rate at specified intervals 3) Graduated Payment Mortgage (GPM): • Starts with low payments that rise gradually 4) Balloon payment mortgage: • Entire payment for first few years goes to interest only; the last years pay off the principal.

REFINANCING A MORTGAGE Why refinance? n Interest rates go down!!! Refinance = take out a NEW mortgage to pay off an OLD one. n Pay closing costs again, and sometimes prepayment penalty

Ex. The Rowes had a fixed rate mortgage at 16. 25%. The monthly payment on the old mortgage was $845. 86. They got a new mortgage at 13% and their new monthly payment is $585. 79. To get the new mortgage, they had to pay closing costs of $935. They also had to pay a prepayment penalty of $500. a. How much did they save in the first year? b. How much did they save the second year?

7 -2: The Cost of Owning a Home

What are the ongoing expenses? ? ? n Property taxes n Repairs n Maintenance n Insurance n Mortgage interest
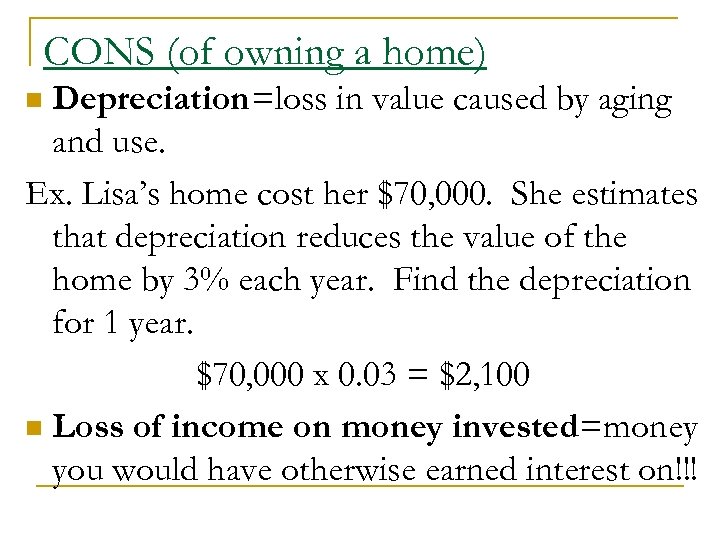
CONS (of owning a home) Depreciation=loss in value caused by aging and use. Ex. Lisa’s home cost her $70, 000. She estimates that depreciation reduces the value of the home by 3% each year. Find the depreciation for 1 year. $70, 000 x 0. 03 = $2, 100 n Loss of income on money invested=money you would have otherwise earned interest on!!! n
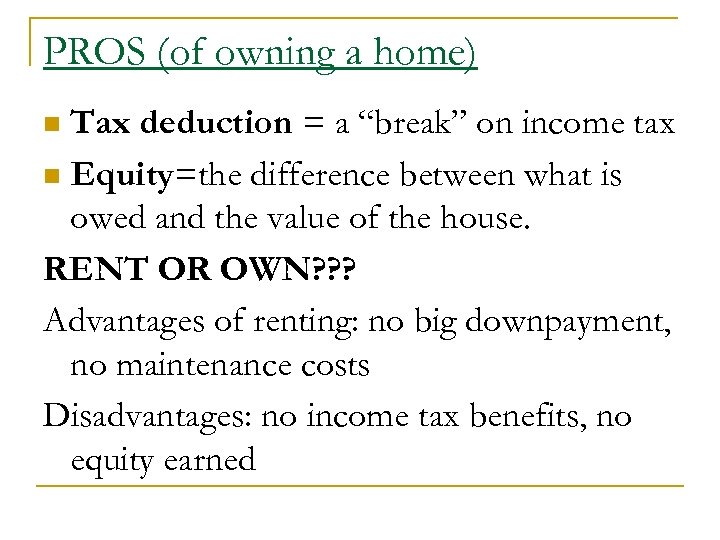
PROS (of owning a home) Tax deduction = a “break” on income tax n Equity=the difference between what is owed and the value of the house. RENT OR OWN? ? ? Advantages of renting: no big downpayment, no maintenance costs Disadvantages: no income tax benefits, no equity earned n

7. 3 Depreciating a Motor Vehicle

DISCUSSION: What do you think has more value: a 3 -year-old car with 18, 000 miles OR a 1 -year-old car of the same make and model with 34, 000 miles?

Depreciation= loss of value The difference between a car’s original cost and its resale or trade-in value. n Resale value= market value n q n Find in Kelley Blue Book Trade-in value = amount you get for your old car when you trade it in for a new car.

Ex. Alfonzo buys a car for $16, 500 and 4 years later trades it in for $7, 500. Find the total depreciation. $16, 500 – 7, 500 = $9, 000

Finding Average Annual Depreciation Ex. A car that cost $14, 800 has an estimated tradein value of $5, 900 at the end of 4 years. Find the average annual depreciation. ($14, 800 – 5, 900) = $8, 900 ÷ 4 = $2, 225
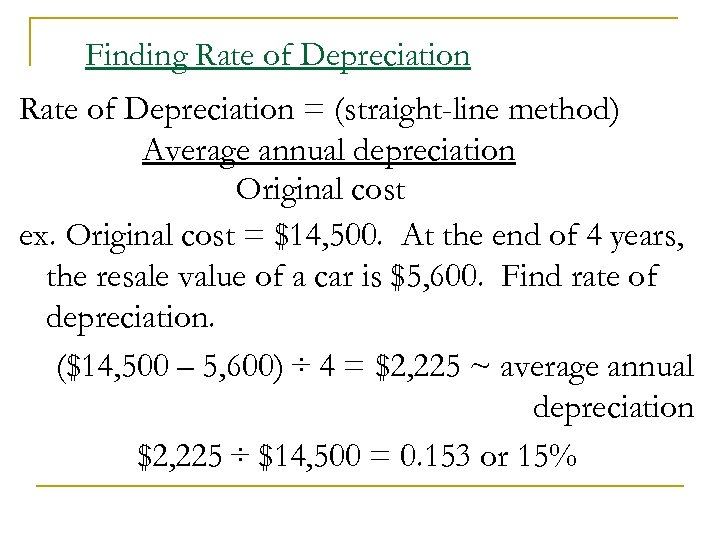
Finding Rate of Depreciation = (straight-line method) Average annual depreciation Original cost ex. Original cost = $14, 500. At the end of 4 years, the resale value of a car is $5, 600. Find rate of depreciation. ($14, 500 – 5, 600) ÷ 4 = $2, 225 ~ average annual depreciation $2, 225 ÷ $14, 500 = 0. 153 or 15%

7 -4 Cost of Operating a Motor Vehicle

Operating costs = sum of all the annual expenses: Insurance n Gas, Oil, Inspection fees, tires, repairs n License n Garage rent, parking fees n Toll, taxes n General upkeep n Depreciation n Loss of interest on investment n
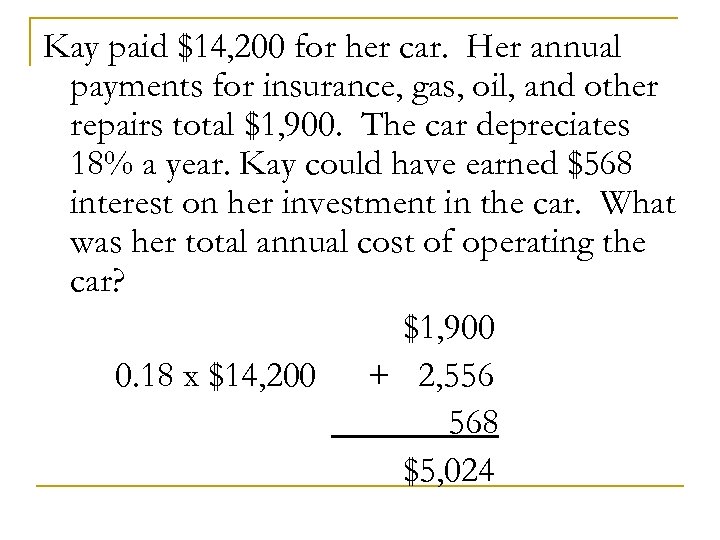
Kay paid $14, 200 for her car. Her annual payments for insurance, gas, oil, and other repairs total $1, 900. The car depreciates 18% a year. Kay could have earned $568 interest on her investment in the car. What was her total annual cost of operating the car? $1, 900 0. 18 x $14, 200 + 2, 556 568 $5, 024

Leasing a Motor Vehicle Leasing = renting a car for a fixed amount of time n Leases usually run for 24, 36, or 48 months n The number of miles a car or truck can be driven is LIMITED. n There is a fee for excess mileage. n
2618052d11fea45856fa2f124c8cfedc.ppt