782dd04f2a6fc1e6d3dd2ed309cced07.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 18
 60 concepts you’re most apt to hear in a marketing meeting Demographics Psychographics Homogeneous Heterogeneous E- or M-marketing B 2 B B 2 C SCA Risk Transformations Transactions Transvections Marketing Concept Marketing Strategy Marketing Mix Utility Profit Bias Validity Reliability Primary Data Secondary Data TA or TM Segmentation Differentiation Positioning Niche CRM Motivation Knowledge Attitude Needs Wants Brand Equity Feature/Accessory UPC USP NEW Packaging Labeling TWU 5133 Lecture 1 | © 2011 Steve Toms | steve@stevetoms. net | For educational use only Branding Cannibalization Exposure Channels Commercialization Physical Distribution Skimming Penetration BEP IMC Advertising Direct marketing Public Relations Publicity Purpose of this course: Push/Pull ability to sit in marketing POS meeting, understand Rating what is being discussed, and contribute to Reach the discussion. Frequency CPM
60 concepts you’re most apt to hear in a marketing meeting Demographics Psychographics Homogeneous Heterogeneous E- or M-marketing B 2 B B 2 C SCA Risk Transformations Transactions Transvections Marketing Concept Marketing Strategy Marketing Mix Utility Profit Bias Validity Reliability Primary Data Secondary Data TA or TM Segmentation Differentiation Positioning Niche CRM Motivation Knowledge Attitude Needs Wants Brand Equity Feature/Accessory UPC USP NEW Packaging Labeling TWU 5133 Lecture 1 | © 2011 Steve Toms | steve@stevetoms. net | For educational use only Branding Cannibalization Exposure Channels Commercialization Physical Distribution Skimming Penetration BEP IMC Advertising Direct marketing Public Relations Publicity Purpose of this course: Push/Pull ability to sit in marketing POS meeting, understand Rating what is being discussed, and contribute to Reach the discussion. Frequency CPM
 How marketers reduce risk þ Sustainable competitive advantage | SCA (Hallmark’s slogan is…) þ Unique selling proposition | USP (Avis employers tell drivers: ) þ Differentiation (Kellogg’s vs. Post Raisin Bran) þ Positioning (L’Oreal says. . . ? ) TWU 5133 Lecture 1 | © 2011 Steve Toms | steve@stevetoms. net | For educational use only
How marketers reduce risk þ Sustainable competitive advantage | SCA (Hallmark’s slogan is…) þ Unique selling proposition | USP (Avis employers tell drivers: ) þ Differentiation (Kellogg’s vs. Post Raisin Bran) þ Positioning (L’Oreal says. . . ? ) TWU 5133 Lecture 1 | © 2011 Steve Toms | steve@stevetoms. net | For educational use only
 “The process of planning and executing the conception, pricing, promotion, and distribution of ideas, goods, and services to create exchanges that satisfy individual and organizational objectives” Difference between marketing and being marketing-oriented TWU 5133 Lecture 1 | © 2011 Steve Toms | steve@stevetoms. net | For educational use only
“The process of planning and executing the conception, pricing, promotion, and distribution of ideas, goods, and services to create exchanges that satisfy individual and organizational objectives” Difference between marketing and being marketing-oriented TWU 5133 Lecture 1 | © 2011 Steve Toms | steve@stevetoms. net | For educational use only
 4 business concepts Assumption: Customer will buy my product if… Production Product TWU 5133 Lecture 1 | © 2011 Steve Toms | steve@stevetoms. net | For educational use only Selling Marketing
4 business concepts Assumption: Customer will buy my product if… Production Product TWU 5133 Lecture 1 | © 2011 Steve Toms | steve@stevetoms. net | For educational use only Selling Marketing
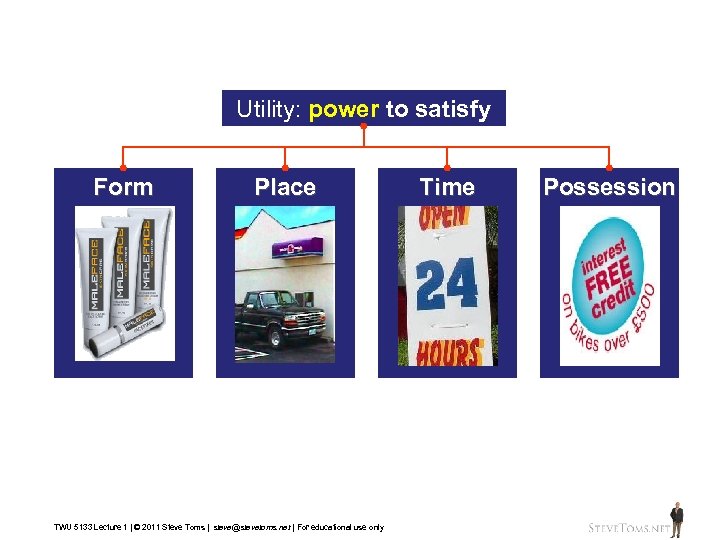 Utility: power to satisfy Form Place TWU 5133 Lecture 1 | © 2011 Steve Toms | steve@stevetoms. net | For educational use only Time Possession
Utility: power to satisfy Form Place TWU 5133 Lecture 1 | © 2011 Steve Toms | steve@stevetoms. net | For educational use only Time Possession
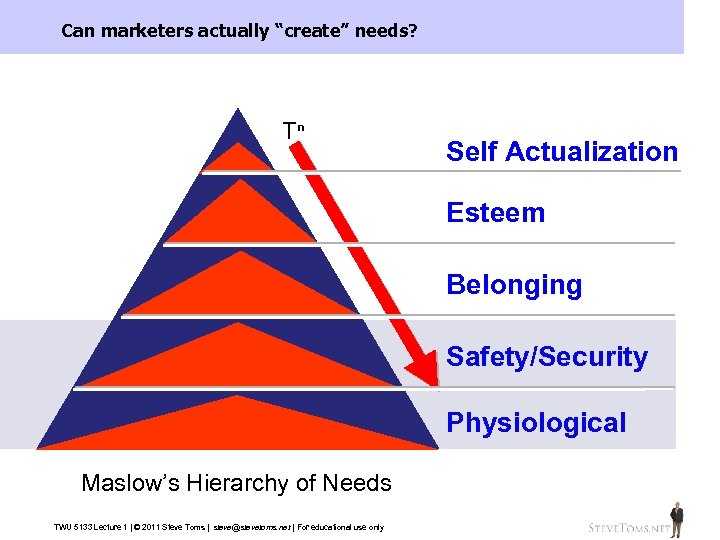 Can marketers actually “create” needs? Tn Self Actualization Esteem Belonging Safety/Security Physiological Maslow’s Hierarchy of Needs TWU 5133 Lecture 1 | © 2011 Steve Toms | steve@stevetoms. net | For educational use only
Can marketers actually “create” needs? Tn Self Actualization Esteem Belonging Safety/Security Physiological Maslow’s Hierarchy of Needs TWU 5133 Lecture 1 | © 2011 Steve Toms | steve@stevetoms. net | For educational use only
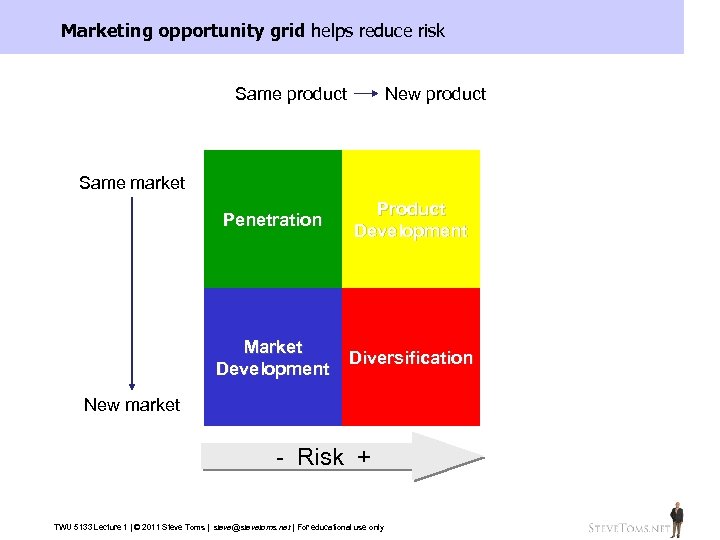 Marketing opportunity grid helps reduce risk Same product Same market Same product Penetration Same market Same product Market New market Development New product Product Same market Development New product Diversification New market - Risk + TWU 5133 Lecture 1 | © 2011 Steve Toms | steve@stevetoms. net | For educational use only
Marketing opportunity grid helps reduce risk Same product Same market Same product Penetration Same market Same product Market New market Development New product Product Same market Development New product Diversification New market - Risk + TWU 5133 Lecture 1 | © 2011 Steve Toms | steve@stevetoms. net | For educational use only
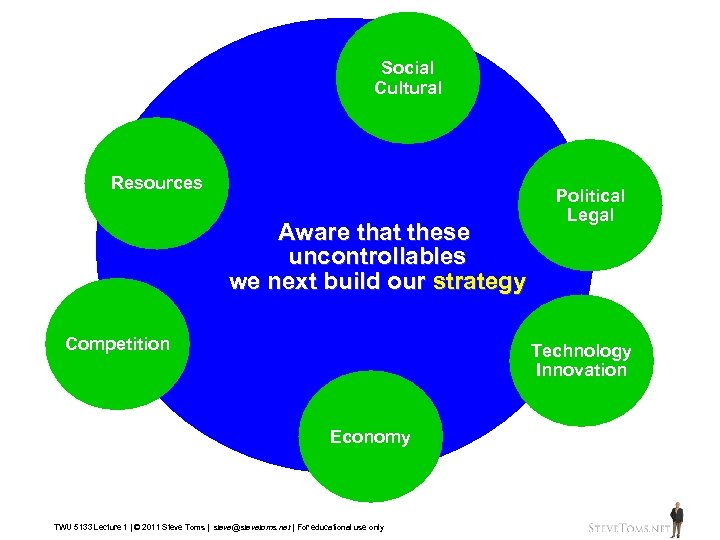 Social Cultural Resources Aware that these uncontrollables we next build our strategy Competition Political Legal Technology Innovation Economy TWU 5133 Lecture 1 | © 2011 Steve Toms | steve@stevetoms. net | For educational use only
Social Cultural Resources Aware that these uncontrollables we next build our strategy Competition Political Legal Technology Innovation Economy TWU 5133 Lecture 1 | © 2011 Steve Toms | steve@stevetoms. net | For educational use only
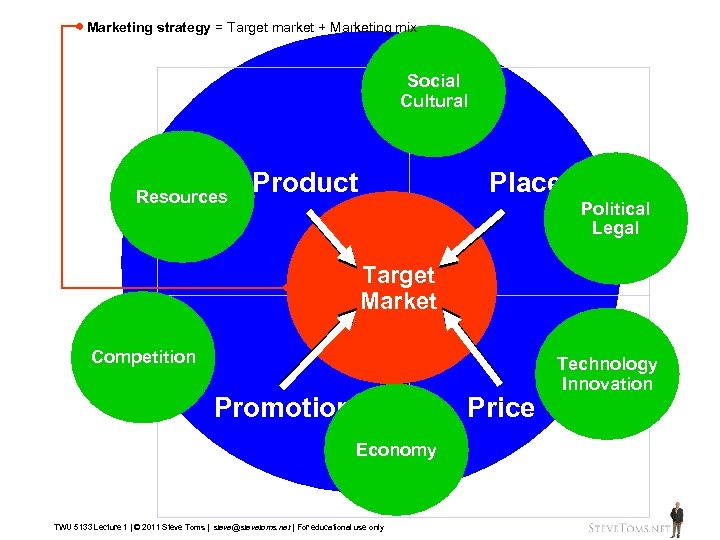 Marketing strategy = Target market + Marketing mix Social Cultural Resources Product Place Uncontrollable Target Marketplace Market Competition Promotion Price Economy TWU 5133 Lecture 1 | © 2011 Steve Toms | steve@stevetoms. net | For educational use only Political Legal Technology Innovation
Marketing strategy = Target market + Marketing mix Social Cultural Resources Product Place Uncontrollable Target Marketplace Market Competition Promotion Price Economy TWU 5133 Lecture 1 | © 2011 Steve Toms | steve@stevetoms. net | For educational use only Political Legal Technology Innovation
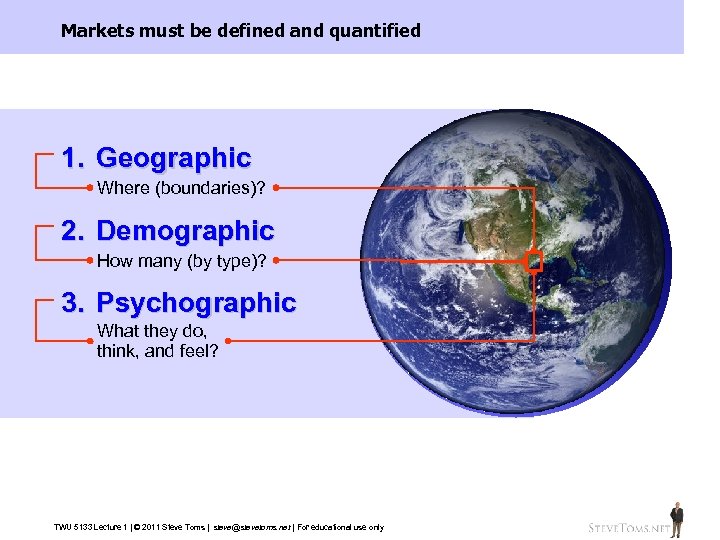 Markets must be defined and quantified 1. Geographic Where (boundaries)? 2. Demographic How many (by type)? 3. Psychographic What they do, think, and feel? TWU 5133 Lecture 1 | © 2011 Steve Toms | steve@stevetoms. net | For educational use only
Markets must be defined and quantified 1. Geographic Where (boundaries)? 2. Demographic How many (by type)? 3. Psychographic What they do, think, and feel? TWU 5133 Lecture 1 | © 2011 Steve Toms | steve@stevetoms. net | For educational use only
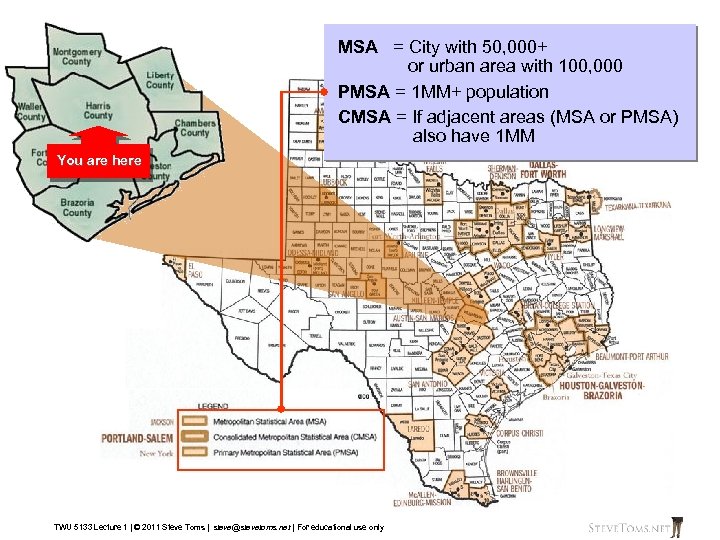 MSA = City with 50, 000+ or urban area with 100, 000 PMSA = 1 MM+ population CMSA = If adjacent areas (MSA or PMSA) also have 1 MM You are here TWU 5133 Lecture 1 | © 2011 Steve Toms | steve@stevetoms. net | For educational use only
MSA = City with 50, 000+ or urban area with 100, 000 PMSA = 1 MM+ population CMSA = If adjacent areas (MSA or PMSA) also have 1 MM You are here TWU 5133 Lecture 1 | © 2011 Steve Toms | steve@stevetoms. net | For educational use only
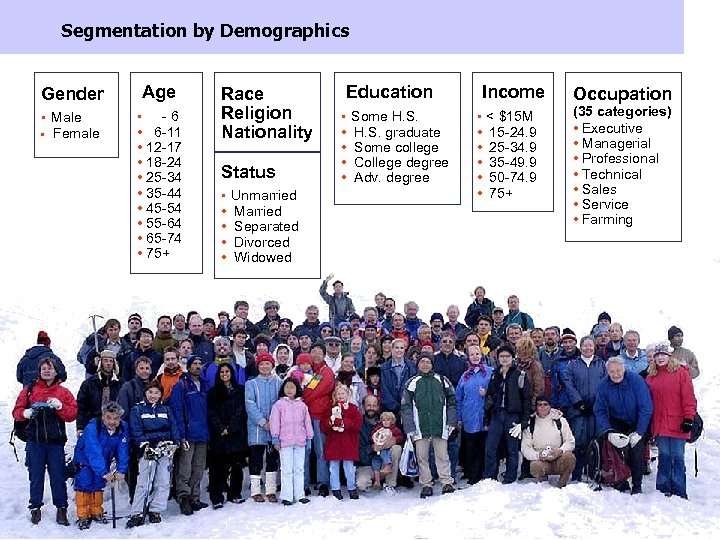 Segmentation by Demographics Gender • Male • Female Age • - 6 • 6 -11 • 12 -17 • 18 -24 • 25 -34 • 35 -44 • 45 -54 • 55 -64 • 65 -74 • 75+ Race Religion Nationality Status • Unmarried • • Education • Some H. S. • • H. S. graduate Some college College degree Adv. degree Married Separated Divorced Widowed TWU 5133 Lecture 1 | © 2011 Steve Toms | steve@stevetoms. net | For educational use only Income • < $15 M • • • 15 -24. 9 25 -34. 9 35 -49. 9 50 -74. 9 75+ Occupation (35 categories) • Executive • Managerial • Professional • Technical • Sales • Service • Farming
Segmentation by Demographics Gender • Male • Female Age • - 6 • 6 -11 • 12 -17 • 18 -24 • 25 -34 • 35 -44 • 45 -54 • 55 -64 • 65 -74 • 75+ Race Religion Nationality Status • Unmarried • • Education • Some H. S. • • H. S. graduate Some college College degree Adv. degree Married Separated Divorced Widowed TWU 5133 Lecture 1 | © 2011 Steve Toms | steve@stevetoms. net | For educational use only Income • < $15 M • • • 15 -24. 9 25 -34. 9 35 -49. 9 50 -74. 9 75+ Occupation (35 categories) • Executive • Managerial • Professional • Technical • Sales • Service • Farming
 Segmentation by Psychographics (behavior) þ Activities (do, go, read, watch) þ Interests (hobbies, þ Opinions (feel recreation, lifestyle) about various issues) Nielsen, Simmons, TGI, Dun and Bradstreet, Standard and Poor, etc. TWU 5133 Lecture 1 | © 2011 Steve Toms | steve@stevetoms. net | For educational use only
Segmentation by Psychographics (behavior) þ Activities (do, go, read, watch) þ Interests (hobbies, þ Opinions (feel recreation, lifestyle) about various issues) Nielsen, Simmons, TGI, Dun and Bradstreet, Standard and Poor, etc. TWU 5133 Lecture 1 | © 2011 Steve Toms | steve@stevetoms. net | For educational use only
 3 important research terms 1. Reliability: study can be replicated and get same basic results (free of errors) 2. Validity: data reflects what it was designed to measure 3. Bias: insert opinions, or skewing data to mean other than what they say TWU 5133 Lecture 1 | © 2011 Steve Toms | steve@stevetoms. net | For educational use only
3 important research terms 1. Reliability: study can be replicated and get same basic results (free of errors) 2. Validity: data reflects what it was designed to measure 3. Bias: insert opinions, or skewing data to mean other than what they say TWU 5133 Lecture 1 | © 2011 Steve Toms | steve@stevetoms. net | For educational use only
 How can research reduce risk? ? Find an unmet need Allocate resources Make a profit Define target market Right product Right place Right price Right promotion Marketing concept Marketing strategy TWU 5133 Lecture 1 | © 2011 Steve Toms | steve@stevetoms. net | For educational use only
How can research reduce risk? ? Find an unmet need Allocate resources Make a profit Define target market Right product Right place Right price Right promotion Marketing concept Marketing strategy TWU 5133 Lecture 1 | © 2011 Steve Toms | steve@stevetoms. net | For educational use only
 2 types of marketing data Primary data are facts and figures newly-collected for the project at hand Data are the facts and figures pertinent to the problem Secondary data are facts and figures already collected before current project Data are the facts and figures that might be or can be applied to the problem It’s about getting a truer picture of the potential. TWU 5133 Lecture 1 | © 2011 Steve Toms | steve@stevetoms. net | For educational use only
2 types of marketing data Primary data are facts and figures newly-collected for the project at hand Data are the facts and figures pertinent to the problem Secondary data are facts and figures already collected before current project Data are the facts and figures that might be or can be applied to the problem It’s about getting a truer picture of the potential. TWU 5133 Lecture 1 | © 2011 Steve Toms | steve@stevetoms. net | For educational use only
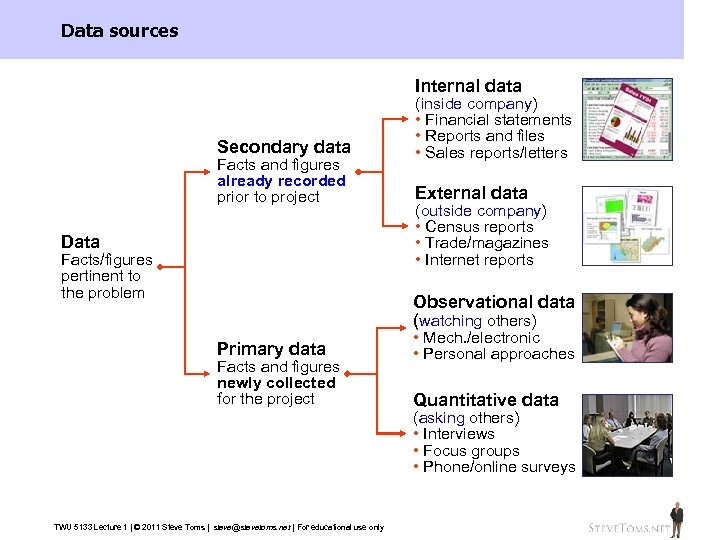 Data sources Internal data Secondary data Facts and figures already recorded prior to project Data Facts/figures pertinent to the problem (inside company) • Financial statements • Reports and files • Sales reports/letters External data (outside company) • Census reports • Trade/magazines • Internet reports Observational data (watching others) Primary data Facts and figures newly collected for the project • Mech. /electronic • Personal approaches Quantitative data (asking others) • Interviews • Focus groups • Phone/online surveys TWU 5133 Lecture 1 | © 2011 Steve Toms | steve@stevetoms. net | For educational use only
Data sources Internal data Secondary data Facts and figures already recorded prior to project Data Facts/figures pertinent to the problem (inside company) • Financial statements • Reports and files • Sales reports/letters External data (outside company) • Census reports • Trade/magazines • Internet reports Observational data (watching others) Primary data Facts and figures newly collected for the project • Mech. /electronic • Personal approaches Quantitative data (asking others) • Interviews • Focus groups • Phone/online surveys TWU 5133 Lecture 1 | © 2011 Steve Toms | steve@stevetoms. net | For educational use only
 How to find data on the Internet Where to find data þ 1930 s: SIC codes set uniform method for collecting data (up to 4 digits) þ 1997: NAICS replaces SIC; reflects new businesses in U. S. , Canada, and Mexico (6 digits) þ Google: Input NAICS+zip code+Enter (or other U. S. Census segment) www. census. gov/epcd/www/naics. html TWU 5133 Lecture 1 | © 2011 Steve Toms | steve@stevetoms. net | For educational use only
How to find data on the Internet Where to find data þ 1930 s: SIC codes set uniform method for collecting data (up to 4 digits) þ 1997: NAICS replaces SIC; reflects new businesses in U. S. , Canada, and Mexico (6 digits) þ Google: Input NAICS+zip code+Enter (or other U. S. Census segment) www. census. gov/epcd/www/naics. html TWU 5133 Lecture 1 | © 2011 Steve Toms | steve@stevetoms. net | For educational use only


