 6. Logistics Information Systems 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. Introduction Customer order cycle The path of a customer order Definition of electronic data interchange EDI standards Types of EDI systems Benefits of EDI implementation Integrating Order Processing and the Company's Logistics Management Information System
6. Logistics Information Systems 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. Introduction Customer order cycle The path of a customer order Definition of electronic data interchange EDI standards Types of EDI systems Benefits of EDI implementation Integrating Order Processing and the Company's Logistics Management Information System
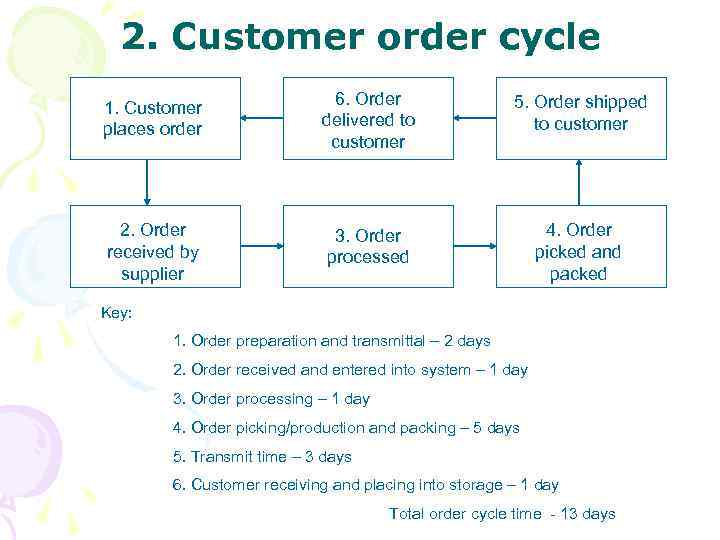 2. Customer order cycle 1. Customer places order 6. Order delivered to customer 5. Order shipped to customer 2. Order received by supplier 3. Order processed 4. Order picked and packed Key: 1. Order preparation and transmittal – 2 days 2. Order received and entered into system – 1 day 3. Order processing – 1 day 4. Order picking/production and packing – 5 days 5. Transmit time – 3 days 6. Customer receiving and placing into storage – 1 day Total order cycle time - 13 days
2. Customer order cycle 1. Customer places order 6. Order delivered to customer 5. Order shipped to customer 2. Order received by supplier 3. Order processed 4. Order picked and packed Key: 1. Order preparation and transmittal – 2 days 2. Order received and entered into system – 1 day 3. Order processing – 1 day 4. Order picking/production and packing – 5 days 5. Transmit time – 3 days 6. Customer receiving and placing into storage – 1 day Total order cycle time - 13 days
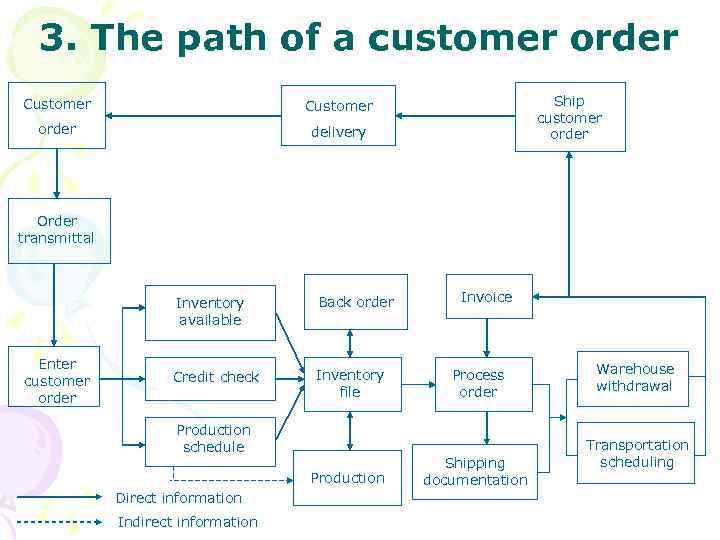 3. The path of a customer order Customer order Ship customer order Customer delivery Order transmittal Inventory available Enter customer order Back order Credit check Inventory file Production schedule Production Direct information Indirect information Invoice Process order Shipping documentation Warehouse withdrawal Transportation scheduling
3. The path of a customer order Customer order Ship customer order Customer delivery Order transmittal Inventory available Enter customer order Back order Credit check Inventory file Production schedule Production Direct information Indirect information Invoice Process order Shipping documentation Warehouse withdrawal Transportation scheduling
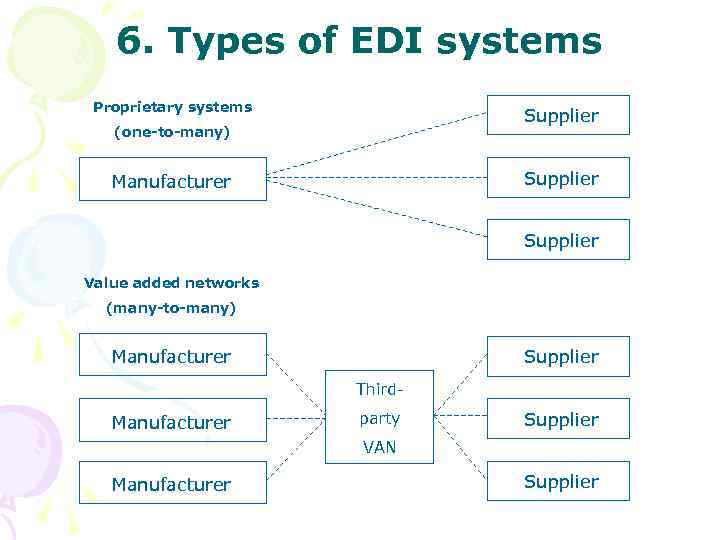 6. Types of EDI systems Proprietary systems Supplier (one-to-many) Supplier Manufacturer Supplier Value added networks (many-to-many) Manufacturer Supplier Third- Manufacturer party Supplier VAN Manufacturer Supplier
6. Types of EDI systems Proprietary systems Supplier (one-to-many) Supplier Manufacturer Supplier Value added networks (many-to-many) Manufacturer Supplier Third- Manufacturer party Supplier VAN Manufacturer Supplier
 EDI Benefits 1. Reduced paper work to be created and filed. 2. Improved accuracy due to a reduction in manual processing. 3. Increased speed of order transmission and other data. 4. Reduced clerical/administrative effort in data entry, filing, mailing and related tasks. 5. Opportunity of proactive contribution by purchasing because less time is spent on “clerical tasks”. 6. Reduced costs of order placement and related processing and handling.
EDI Benefits 1. Reduced paper work to be created and filed. 2. Improved accuracy due to a reduction in manual processing. 3. Increased speed of order transmission and other data. 4. Reduced clerical/administrative effort in data entry, filing, mailing and related tasks. 5. Opportunity of proactive contribution by purchasing because less time is spent on “clerical tasks”. 6. Reduced costs of order placement and related processing and handling.
 7. Improved information availability due to speed of acknowledgments and shipment advices. 8. Reduced workload and improved accuracy of other departments through linking EDI with other systems, such as bar-coding inventory and electronic funds transfers (EFTs). 9. Reduced inventory due to improved accuracy and reduced order cycle time.
7. Improved information availability due to speed of acknowledgments and shipment advices. 8. Reduced workload and improved accuracy of other departments through linking EDI with other systems, such as bar-coding inventory and electronic funds transfers (EFTs). 9. Reduced inventory due to improved accuracy and reduced order cycle time.
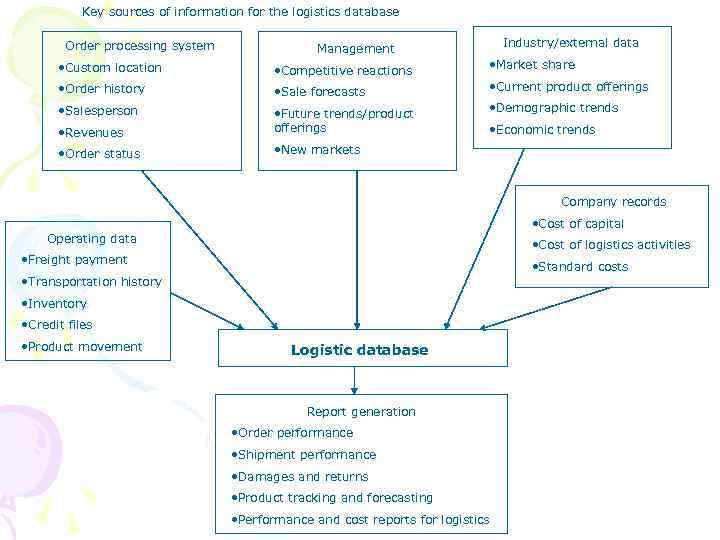 Key sources of information for the logistics database Order processing system Industry/external data Management • Custom location • Competitive reactions • Market share • Order history • Sale forecasts • Current product offerings • Salesperson • Demographic trends • Revenues • Future trends/product offerings • Order status • New markets • Economic trends Company records • Cost of capital Operating data • Cost of logistics activities • Freight payment • Standard costs • Transportation history • Inventory • Credit files • Product movement Logistic database Report generation • Order performance • Shipment performance • Damages and returns • Product tracking and forecasting • Performance and cost reports for logistics
Key sources of information for the logistics database Order processing system Industry/external data Management • Custom location • Competitive reactions • Market share • Order history • Sale forecasts • Current product offerings • Salesperson • Demographic trends • Revenues • Future trends/product offerings • Order status • New markets • Economic trends Company records • Cost of capital Operating data • Cost of logistics activities • Freight payment • Standard costs • Transportation history • Inventory • Credit files • Product movement Logistic database Report generation • Order performance • Shipment performance • Damages and returns • Product tracking and forecasting • Performance and cost reports for logistics