a6562262f7ca656a961fc829d3cc972b.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 48
 6 CHAPTER Consumer Decision Making Chapter 5 Copyright © 2008 by South-Western, a division of Thomson Learning. All rights reserved 1
6 CHAPTER Consumer Decision Making Chapter 5 Copyright © 2008 by South-Western, a division of Thomson Learning. All rights reserved 1
 LO 1 The Importance of Understanding Consumer Behavior Explain why marketing managers should understand consumer behavior Chapter 5 Copyright © 2008 by South-Western, a division of Thomson Learning. All rights reserved 2
LO 1 The Importance of Understanding Consumer Behavior Explain why marketing managers should understand consumer behavior Chapter 5 Copyright © 2008 by South-Western, a division of Thomson Learning. All rights reserved 2
 The Consumer Market “Ultimate” consumers who buy goods and services for their own personal or household use. Chapter 5 Copyright © 2008 by South-Western, a division of Thomson Learning. All rights reserved 3
The Consumer Market “Ultimate” consumers who buy goods and services for their own personal or household use. Chapter 5 Copyright © 2008 by South-Western, a division of Thomson Learning. All rights reserved 3
 Needs vs. Wants (Typical Textbook Def. ) § Needs – Unsatisfactory conditions of the consumer that lead him or her to actions that will make the conditions better § Wants – Desires to obtain more satisfaction than is absolutely necessary to improve unsatisfactory conditions Chapter 5 Copyright © 2008 by South-Western, a division of Thomson Learning. All rights reserved 4
Needs vs. Wants (Typical Textbook Def. ) § Needs – Unsatisfactory conditions of the consumer that lead him or her to actions that will make the conditions better § Wants – Desires to obtain more satisfaction than is absolutely necessary to improve unsatisfactory conditions Chapter 5 Copyright © 2008 by South-Western, a division of Thomson Learning. All rights reserved 4
 Consumer Behavior Processes a consumer uses to make purchase decisions, as well as to use and dispose of purchased goods or services; also includes factors that influence purchase decisions and the product use. LO 1 Chapter 5 Copyright © 2008 by South-Western, a division of Thomson Learning. All rights reserved 5
Consumer Behavior Processes a consumer uses to make purchase decisions, as well as to use and dispose of purchased goods or services; also includes factors that influence purchase decisions and the product use. LO 1 Chapter 5 Copyright © 2008 by South-Western, a division of Thomson Learning. All rights reserved 5
 Consumer Decision-Making Process A five-step process used by consumers when buying goods or services. LO 2 Chapter 5 Copyright © 2008 by South-Western, a division of Thomson Learning. All rights reserved 6
Consumer Decision-Making Process A five-step process used by consumers when buying goods or services. LO 2 Chapter 5 Copyright © 2008 by South-Western, a division of Thomson Learning. All rights reserved 6
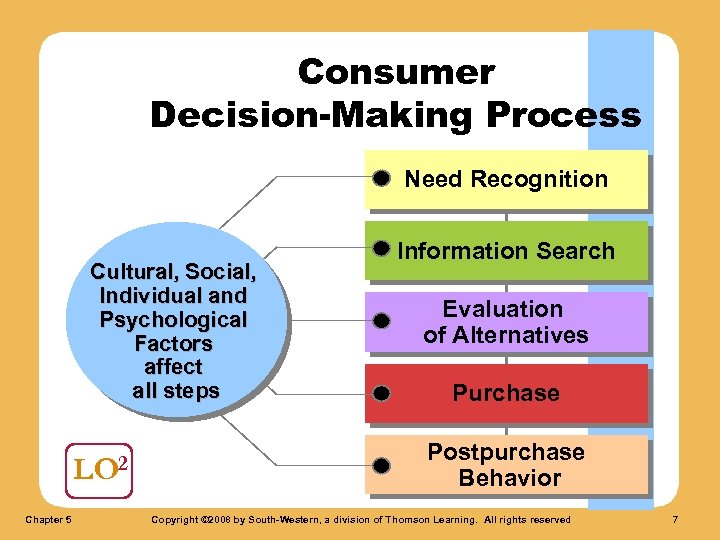 Consumer Decision-Making Process Need Recognition Cultural, Social, Individual and Psychological Factors affect all steps LO 2 Chapter 5 Information Search Evaluation of Alternatives Purchase Postpurchase Behavior Copyright © 2008 by South-Western, a division of Thomson Learning. All rights reserved 7
Consumer Decision-Making Process Need Recognition Cultural, Social, Individual and Psychological Factors affect all steps LO 2 Chapter 5 Information Search Evaluation of Alternatives Purchase Postpurchase Behavior Copyright © 2008 by South-Western, a division of Thomson Learning. All rights reserved 7
 Need Recognition Result of an imbalance between actual and desired states. LO 2 Chapter 5 Copyright © 2008 by South-Western, a division of Thomson Learning. All rights reserved 8
Need Recognition Result of an imbalance between actual and desired states. LO 2 Chapter 5 Copyright © 2008 by South-Western, a division of Thomson Learning. All rights reserved 8
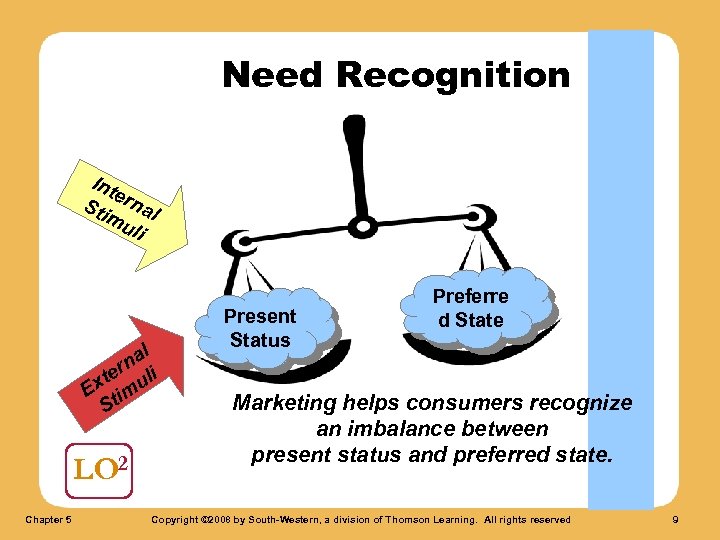 Need Recognition Int e Sti rnal mu li l na ter uli Ex tim S LO 2 Chapter 5 Present Status Preferre d State Marketing helps consumers recognize an imbalance between present status and preferred state. Copyright © 2008 by South-Western, a division of Thomson Learning. All rights reserved 9
Need Recognition Int e Sti rnal mu li l na ter uli Ex tim S LO 2 Chapter 5 Present Status Preferre d State Marketing helps consumers recognize an imbalance between present status and preferred state. Copyright © 2008 by South-Western, a division of Thomson Learning. All rights reserved 9
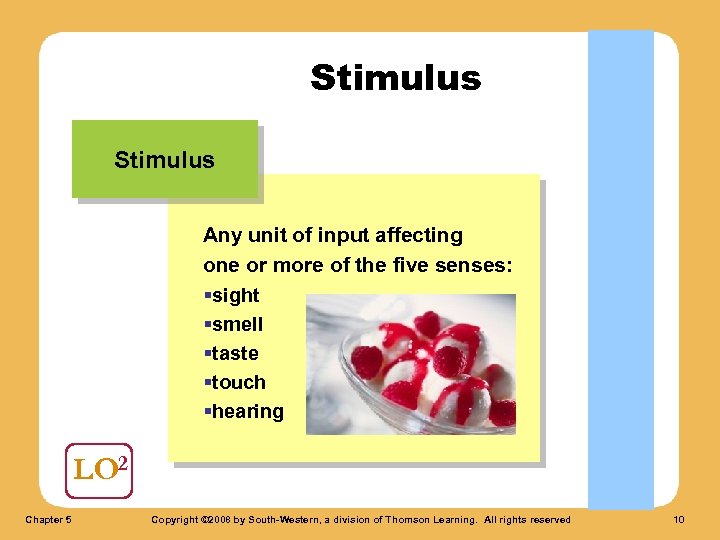 Stimulus Any unit of input affecting one or more of the five senses: §sight §smell §taste §touch §hearing LO 2 Chapter 5 Copyright © 2008 by South-Western, a division of Thomson Learning. All rights reserved 10
Stimulus Any unit of input affecting one or more of the five senses: §sight §smell §taste §touch §hearing LO 2 Chapter 5 Copyright © 2008 by South-Western, a division of Thomson Learning. All rights reserved 10
 Recognition of Unfulfilled Wants u When a current product performing properly isn’t u When the consumer is running out of a product u When another product seems superior to the one currently used LO 2 Chapter 5 Copyright © 2008 by South-Western, a division of Thomson Learning. All rights reserved 11
Recognition of Unfulfilled Wants u When a current product performing properly isn’t u When the consumer is running out of a product u When another product seems superior to the one currently used LO 2 Chapter 5 Copyright © 2008 by South-Western, a division of Thomson Learning. All rights reserved 11
 Information Search Internal Information Search u Recall information in memory External Information search u Seek information in outside environment § § Nonmarketing controlled Marketing controlled LO 2 Chapter 5 Copyright © 2008 by South-Western, a division of Thomson Learning. All rights reserved 12
Information Search Internal Information Search u Recall information in memory External Information search u Seek information in outside environment § § Nonmarketing controlled Marketing controlled LO 2 Chapter 5 Copyright © 2008 by South-Western, a division of Thomson Learning. All rights reserved 12
 STAGE 2 – INFORMATION SEARCHIS INFLUENCED BY: § EVOKED SET: § Group of brands that come to mind around time of purchase § CONSIDERATION SET: § Group of brands a consumer will consider buying after search is complete § Car Tire Brands? § Typically 3 -5 Brands in Consideration Set Chapter 5 Copyright © 2008 by South-Western, a division of Thomson Learning. All rights reserved 13
STAGE 2 – INFORMATION SEARCHIS INFLUENCED BY: § EVOKED SET: § Group of brands that come to mind around time of purchase § CONSIDERATION SET: § Group of brands a consumer will consider buying after search is complete § Car Tire Brands? § Typically 3 -5 Brands in Consideration Set Chapter 5 Copyright © 2008 by South-Western, a division of Thomson Learning. All rights reserved 13
 Purchase To buy or not to buy. . . Determines which attributes are most important in influencing a consumer’s choice LO 2 Chapter 5 Copyright © 2008 by South-Western, a division of Thomson Learning. All rights reserved 14
Purchase To buy or not to buy. . . Determines which attributes are most important in influencing a consumer’s choice LO 2 Chapter 5 Copyright © 2008 by South-Western, a division of Thomson Learning. All rights reserved 14
 LO 3 Cognitive Dissonance Chapter 5 Inner tension that a consumer experiences after recognizing an inconsistency between behavior and values 15 or opinions. Copyright © 2008 by South-Western, a division of Thomson Learning. All rights reserved 15
LO 3 Cognitive Dissonance Chapter 5 Inner tension that a consumer experiences after recognizing an inconsistency between behavior and values 15 or opinions. Copyright © 2008 by South-Western, a division of Thomson Learning. All rights reserved 15
 LO 3 Postpurchase Behavior Consumers can reduce dissonance by: u Seeking information that reinforces positive ideas about the purchase u Avoiding information that contradicts the purchase decision u Revoking the original decision by returning the product 16 Marketing can minimize through: Effective Communication Follow-up Guarantees Warranties Chapter 5 Copyright © 2008 by South-Western, a division of Thomson Learning. All rights reserved 16
LO 3 Postpurchase Behavior Consumers can reduce dissonance by: u Seeking information that reinforces positive ideas about the purchase u Avoiding information that contradicts the purchase decision u Revoking the original decision by returning the product 16 Marketing can minimize through: Effective Communication Follow-up Guarantees Warranties Chapter 5 Copyright © 2008 by South-Western, a division of Thomson Learning. All rights reserved 16
 LO 4 Culture Chapter 5 Set of values, norms, attitudes, and other meaningful symbols that shape human behavior and the artifacts, or products, of that behavior as they are transmitted from one generation to the next. Copyright © 2008 by South-Western, a division of Thomson Learning. All rights reserved 17
LO 4 Culture Chapter 5 Set of values, norms, attitudes, and other meaningful symbols that shape human behavior and the artifacts, or products, of that behavior as they are transmitted from one generation to the next. Copyright © 2008 by South-Western, a division of Thomson Learning. All rights reserved 17
 LO 4 Components of Culture Values Language Myths Customs Rituals Laws Material artifacts Chapter 5 Copyright © 2008 by South-Western, a division of Thomson Learning. All rights reserved 18
LO 4 Components of Culture Values Language Myths Customs Rituals Laws Material artifacts Chapter 5 Copyright © 2008 by South-Western, a division of Thomson Learning. All rights reserved 18
 LO 4 Culture is. . . Pervasive Functional Learned Dynamic Chapter 5 Copyright © 2008 by South-Western, a division of Thomson Learning. All rights reserved 19
LO 4 Culture is. . . Pervasive Functional Learned Dynamic Chapter 5 Copyright © 2008 by South-Western, a division of Thomson Learning. All rights reserved 19
 LO 4 Value Chapter 5 Enduring belief that a specific mode of conduct is personally or socially preferable to another mode of conduct. Copyright © 2008 by South-Western, a division of Thomson Learning. All rights reserved 20
LO 4 Value Chapter 5 Enduring belief that a specific mode of conduct is personally or socially preferable to another mode of conduct. Copyright © 2008 by South-Western, a division of Thomson Learning. All rights reserved 20
 LO 4 Core American Values Success Materialism Freedom Progress Youth Capitalism Chapter 5 Copyright © 2008 by South-Western, a division of Thomson Learning. All rights reserved 21
LO 4 Core American Values Success Materialism Freedom Progress Youth Capitalism Chapter 5 Copyright © 2008 by South-Western, a division of Thomson Learning. All rights reserved 21
 LO 4 Subculture Chapter 5 A homogeneous group of people who share elements of the overall culture as well as unique elements of their own group. Copyright © 2008 by South-Western, a division of Thomson Learning. All rights reserved 22
LO 4 Subculture Chapter 5 A homogeneous group of people who share elements of the overall culture as well as unique elements of their own group. Copyright © 2008 by South-Western, a division of Thomson Learning. All rights reserved 22
 LO 4 Social Class Chapter 5 A group of people in a society who are considered nearly equal in status or community esteem, who regularly socialize among themselves both formally and informally, and who share behavioral norms. Copyright © 2008 by South-Western, a division of Thomson Learning. All rights reserved 23
LO 4 Social Class Chapter 5 A group of people in a society who are considered nearly equal in status or community esteem, who regularly socialize among themselves both formally and informally, and who share behavioral norms. Copyright © 2008 by South-Western, a division of Thomson Learning. All rights reserved 23
 LO 4 Social Class Measurements Occupation Income Education Wealth Other Variables Chapter 5 Copyright © 2008 by South-Western, a division of Thomson Learning. All rights reserved 24
LO 4 Social Class Measurements Occupation Income Education Wealth Other Variables Chapter 5 Copyright © 2008 by South-Western, a division of Thomson Learning. All rights reserved 24
 LO 5 Social Influences Reference Groups Opinion Leaders 25 Family Members Chapter 5 Copyright © 2008 by South-Western, a division of Thomson Learning. All rights reserved 25
LO 5 Social Influences Reference Groups Opinion Leaders 25 Family Members Chapter 5 Copyright © 2008 by South-Western, a division of Thomson Learning. All rights reserved 25
 LO 5 Reference Group A group in society that influences an individual’s 26 purchasing behavior. Chapter 5 Copyright © 2008 by South-Western, a division of Thomson Learning. All rights reserved 26
LO 5 Reference Group A group in society that influences an individual’s 26 purchasing behavior. Chapter 5 Copyright © 2008 by South-Western, a division of Thomson Learning. All rights reserved 26
 LO 5 Influences of Reference Groups u They serve as information sources and influence perceptions. u They affect an individual’s aspiration levels. u Their norms either constrain or stimulate consumer behavior. Chapter 5 27 Copyright © 2008 by South-Western, a division of Thomson Learning. All rights reserved 27
LO 5 Influences of Reference Groups u They serve as information sources and influence perceptions. u They affect an individual’s aspiration levels. u Their norms either constrain or stimulate consumer behavior. Chapter 5 27 Copyright © 2008 by South-Western, a division of Thomson Learning. All rights reserved 27
 LO 5 Opinion Leaders An individual who influences the opinion of others. 28 Chapter 5 Copyright © 2008 by South-Western, a division of Thomson Learning. All rights reserved 28
LO 5 Opinion Leaders An individual who influences the opinion of others. 28 Chapter 5 Copyright © 2008 by South-Western, a division of Thomson Learning. All rights reserved 28
 Reference Group Impact Example § Social Environment usually much more influential § Opinion Leaders Important – Rich’s runners’ group example. . . 29 Chapter 5 Copyright © 2008 by South-Western, a division of Thomson Learning. All rights reserved 29
Reference Group Impact Example § Social Environment usually much more influential § Opinion Leaders Important – Rich’s runners’ group example. . . 29 Chapter 5 Copyright © 2008 by South-Western, a division of Thomson Learning. All rights reserved 29
 LO 5 Family Purchase Process Roles in the Family u Initiators u Influencers u Decision Makers 30 u Purchasers u Consumers Chapter 5 Copyright © 2008 by South-Western, a division of Thomson Learning. All rights reserved 30
LO 5 Family Purchase Process Roles in the Family u Initiators u Influencers u Decision Makers 30 u Purchasers u Consumers Chapter 5 Copyright © 2008 by South-Western, a division of Thomson Learning. All rights reserved 30
 Individual Influences Gender Age Life Cycle Personality Self-Concept Lifestyle LO 6 Chapter 5 Copyright © 2008 by South-Western, a division of Thomson Learning. All rights reserved 31
Individual Influences Gender Age Life Cycle Personality Self-Concept Lifestyle LO 6 Chapter 5 Copyright © 2008 by South-Western, a division of Thomson Learning. All rights reserved 31
 Psychological Influences Perception Motivation Learning Beliefs & Attitudes LO 7 Chapter 5 Copyright © 2008 by South-Western, a division of Thomson Learning. All rights reserved 32
Psychological Influences Perception Motivation Learning Beliefs & Attitudes LO 7 Chapter 5 Copyright © 2008 by South-Western, a division of Thomson Learning. All rights reserved 32
 Perception Process by which people select, organize, and interpret stimuli into a meaningful and coherent picture. LO 7 Chapter 5 Copyright © 2008 by South-Western, a division of Thomson Learning. All rights reserved 33
Perception Process by which people select, organize, and interpret stimuli into a meaningful and coherent picture. LO 7 Chapter 5 Copyright © 2008 by South-Western, a division of Thomson Learning. All rights reserved 33
 Perception Selective Exposure Selective Distortion Selective Retention LO 7 Chapter 5 Copyright © 2008 by South-Western, a division of Thomson Learning. All rights reserved 34
Perception Selective Exposure Selective Distortion Selective Retention LO 7 Chapter 5 Copyright © 2008 by South-Western, a division of Thomson Learning. All rights reserved 34
 Perception Selective Exposure Consumer notices certain stimuli and ignores others Selective Distortion Consumer changes or distorts information that conflicts with feelings or beliefs Selective Retention Consumer remembers only that information that supports personal beliefs LO 7 Chapter 5 Copyright © 2008 by South-Western, a division of Thomson Learning. All rights reserved 35
Perception Selective Exposure Consumer notices certain stimuli and ignores others Selective Distortion Consumer changes or distorts information that conflicts with feelings or beliefs Selective Retention Consumer remembers only that information that supports personal beliefs LO 7 Chapter 5 Copyright © 2008 by South-Western, a division of Thomson Learning. All rights reserved 35
 Marketing Implications of Perception u u u u Important attributes Price Brand names Quality and reliability Threshold level of perception Product or repositioning changes Foreign consumer perception LO 7 Chapter 5 Copyright © 2008 by South-Western, a division of Thomson Learning. All rights reserved 36
Marketing Implications of Perception u u u u Important attributes Price Brand names Quality and reliability Threshold level of perception Product or repositioning changes Foreign consumer perception LO 7 Chapter 5 Copyright © 2008 by South-Western, a division of Thomson Learning. All rights reserved 36
 The “F” Test Count the number of Fs in the following sentence: FINISHED FILES ARE THE RESULT OF YEARS OF SCIENTIFIC STUDY COMBINED WITH THE EXPERIENCE OF MANY YEARS. Chapter 5 Copyright © 2008 by South-Western, a division of Thomson Learning. All rights reserved 37
The “F” Test Count the number of Fs in the following sentence: FINISHED FILES ARE THE RESULT OF YEARS OF SCIENTIFIC STUDY COMBINED WITH THE EXPERIENCE OF MANY YEARS. Chapter 5 Copyright © 2008 by South-Western, a division of Thomson Learning. All rights reserved 37
 Stimulus Discrimination vs. Stimulus Generalization Chapter 5 Copyright © 2008 by South-Western, a division of Thomson Learning. All rights reserved 38
Stimulus Discrimination vs. Stimulus Generalization Chapter 5 Copyright © 2008 by South-Western, a division of Thomson Learning. All rights reserved 38
 Interpretation: Meaning consumer attaches to a stimulus § NAMES § Signal Power /Quality (Toro Snow Pup/Master) § Cars: Mustang / Barracuda / Viper § Donkey / Weasel? § NUMBERS – 350 Z / WD-40 / Acura CL? § COLORS – Different for different cultures Chapter 5 Copyright © 2008 by South-Western, a division of Thomson Learning. All rights reserved 39
Interpretation: Meaning consumer attaches to a stimulus § NAMES § Signal Power /Quality (Toro Snow Pup/Master) § Cars: Mustang / Barracuda / Viper § Donkey / Weasel? § NUMBERS – 350 Z / WD-40 / Acura CL? § COLORS – Different for different cultures Chapter 5 Copyright © 2008 by South-Western, a division of Thomson Learning. All rights reserved 39
 Interpretation: Meaning consumer attaches to a stimulus § COLOR – Signal Newness or Quality (Black Label) – Signal Product Contents (Sodas) Chapter 5 Copyright © 2008 by South-Western, a division of Thomson Learning. All rights reserved 40
Interpretation: Meaning consumer attaches to a stimulus § COLOR – Signal Newness or Quality (Black Label) – Signal Product Contents (Sodas) Chapter 5 Copyright © 2008 by South-Western, a division of Thomson Learning. All rights reserved 40
 Motivation Maslow’s Hierarchy of Needs A method of classifying human needs and motivations into five categories in ascending order of importance. LO 7 Chapter 5 Copyright © 2008 by South-Western, a division of Thomson Learning. All rights reserved 41
Motivation Maslow’s Hierarchy of Needs A method of classifying human needs and motivations into five categories in ascending order of importance. LO 7 Chapter 5 Copyright © 2008 by South-Western, a division of Thomson Learning. All rights reserved 41
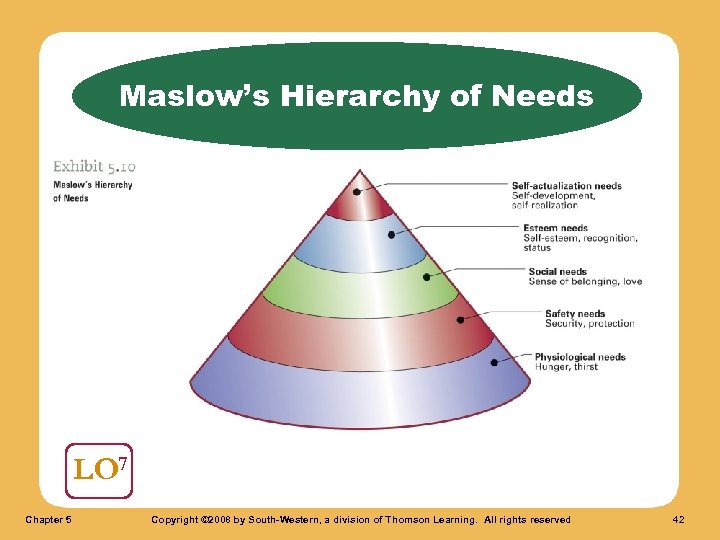 Maslow’s Hierarchy of Needs LO 7 Chapter 5 Copyright © 2008 by South-Western, a division of Thomson Learning. All rights reserved 42
Maslow’s Hierarchy of Needs LO 7 Chapter 5 Copyright © 2008 by South-Western, a division of Thomson Learning. All rights reserved 42
 Safety Appeal toward Women. . . Safe-T-Man Chapter 5 Copyright © 2008 by South-Western, a division of Thomson Learning. All rights reserved 43
Safety Appeal toward Women. . . Safe-T-Man Chapter 5 Copyright © 2008 by South-Western, a division of Thomson Learning. All rights reserved 43
 Safety Appeal toward Children. . . Chapter 5 Copyright © 2008 by South-Western, a division of Thomson Learning. All rights reserved 44
Safety Appeal toward Children. . . Chapter 5 Copyright © 2008 by South-Western, a division of Thomson Learning. All rights reserved 44
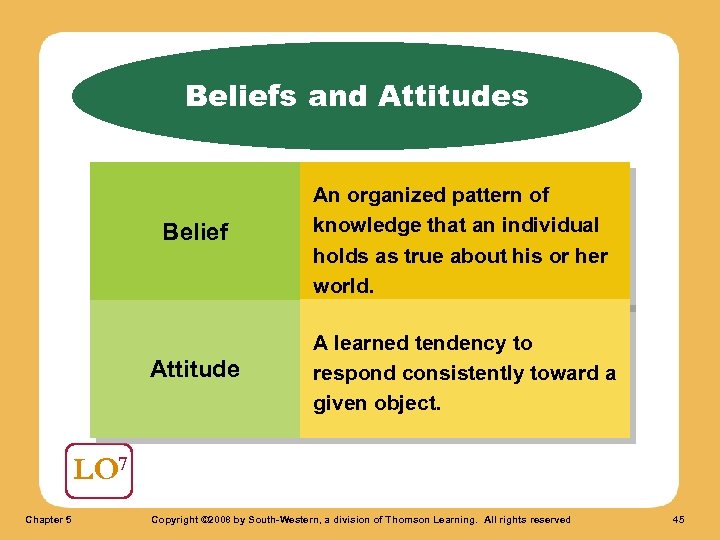 Beliefs and Attitudes Belief An organized pattern of knowledge that an individual holds as true about his or her world. Attitude A learned tendency to respond consistently toward a given object. LO 7 Chapter 5 Copyright © 2008 by South-Western, a division of Thomson Learning. All rights reserved 45
Beliefs and Attitudes Belief An organized pattern of knowledge that an individual holds as true about his or her world. Attitude A learned tendency to respond consistently toward a given object. LO 7 Chapter 5 Copyright © 2008 by South-Western, a division of Thomson Learning. All rights reserved 45
 Changing Attitudes u Change beliefs about the brand’s attributes u Change the relative importance of these beliefs u Add new beliefs LO 7 Chapter 5 Copyright © 2008 by South-Western, a division of Thomson Learning. All rights reserved 46
Changing Attitudes u Change beliefs about the brand’s attributes u Change the relative importance of these beliefs u Add new beliefs LO 7 Chapter 5 Copyright © 2008 by South-Western, a division of Thomson Learning. All rights reserved 46
 Chapter 3 Consumer Markets and Buying Behavior COMPENSATORY VS. NON-COMPENSAGTORY CHOICE MODELS Chapter 1 Copyright © 2008 by South-Western, a division of Thomson Learning. All rights reserved 47
Chapter 3 Consumer Markets and Buying Behavior COMPENSATORY VS. NON-COMPENSAGTORY CHOICE MODELS Chapter 1 Copyright © 2008 by South-Western, a division of Thomson Learning. All rights reserved 47
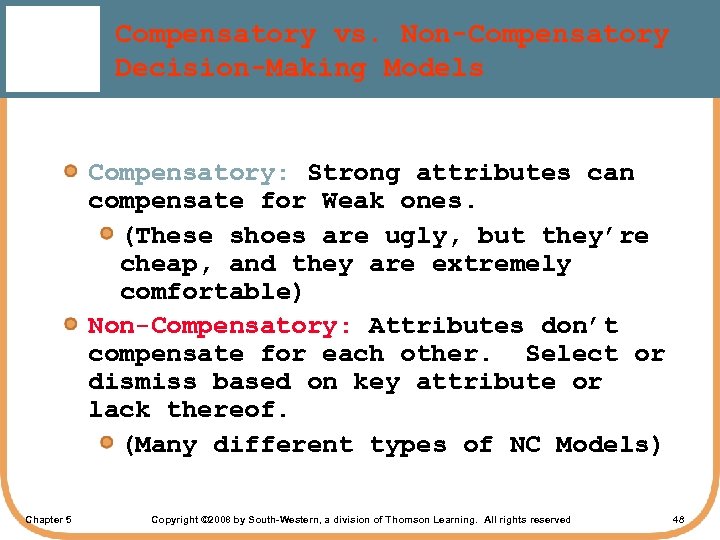 Compensatory vs. Non-Compensatory Decision-Making Models Compensatory: Strong attributes can compensate for Weak ones. (These shoes are ugly, but they’re cheap, and they are extremely comfortable) Non-Compensatory: Attributes don’t compensate for each other. Select or dismiss based on key attribute or lack thereof. (Many different types of NC Models) Chapter 5 Copyright © 2008 by South-Western, a division of Thomson Learning. All rights reserved 48
Compensatory vs. Non-Compensatory Decision-Making Models Compensatory: Strong attributes can compensate for Weak ones. (These shoes are ugly, but they’re cheap, and they are extremely comfortable) Non-Compensatory: Attributes don’t compensate for each other. Select or dismiss based on key attribute or lack thereof. (Many different types of NC Models) Chapter 5 Copyright © 2008 by South-Western, a division of Thomson Learning. All rights reserved 48


