47e838b405fc9eaaacdacc4774f024c6.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 45
 6 -5 Trapezoids and Kites Warm Up Lesson Presentation Lesson Quiz Holt Geometry
6 -5 Trapezoids and Kites Warm Up Lesson Presentation Lesson Quiz Holt Geometry
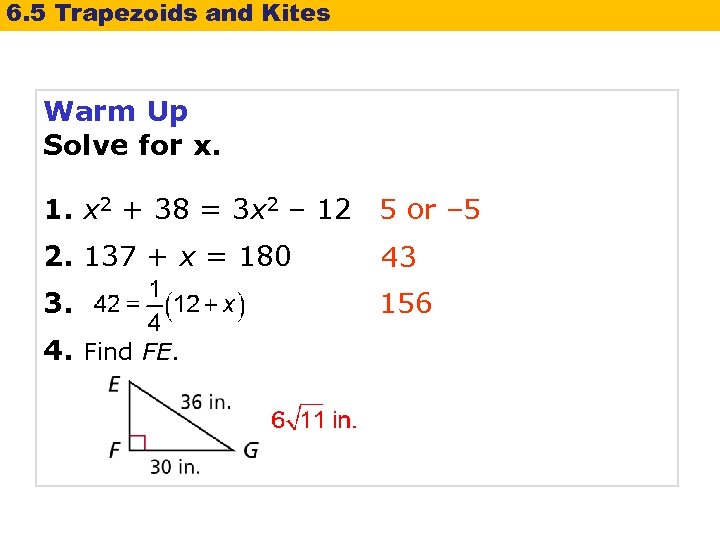 6. 5 Trapezoids and Kites Warm Up Solve for x. 1. x 2 + 38 = 3 x 2 – 12 5 or – 5 2. 137 + x = 180 43 3. 156 4. Find FE.
6. 5 Trapezoids and Kites Warm Up Solve for x. 1. x 2 + 38 = 3 x 2 – 12 5 or – 5 2. 137 + x = 180 43 3. 156 4. Find FE.
 6. 5 Trapezoids and Kites Objectives Use properties of kites to solve problems. Use properties of trapezoids to solve problems.
6. 5 Trapezoids and Kites Objectives Use properties of kites to solve problems. Use properties of trapezoids to solve problems.
 6. 5 Trapezoids and Kites Vocabulary kite trapezoid base of a trapezoid leg of a trapezoid base angle of a trapezoid isosceles trapezoid midsegment of a trapezoid
6. 5 Trapezoids and Kites Vocabulary kite trapezoid base of a trapezoid leg of a trapezoid base angle of a trapezoid isosceles trapezoid midsegment of a trapezoid
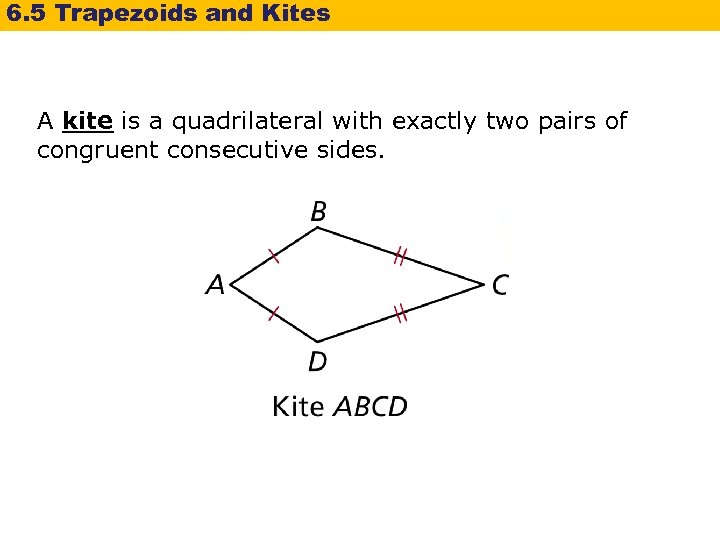 6. 5 Trapezoids and Kites A kite is a quadrilateral with exactly two pairs of congruent consecutive sides.
6. 5 Trapezoids and Kites A kite is a quadrilateral with exactly two pairs of congruent consecutive sides.
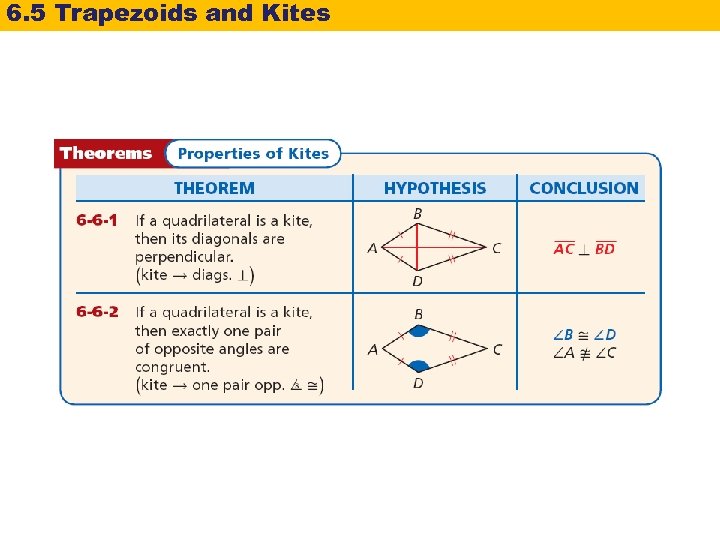 6. 5 Trapezoids and Kites
6. 5 Trapezoids and Kites
 6. 5 Trapezoids and Kites Example 1: Problem-Solving Application Lucy is framing a kite with wooden dowels. She uses two dowels that measure 18 cm, one dowel that measures 30 cm, and two dowels that measure 27 cm. To complete the kite, she needs a dowel to place along. She has a dowel that is 36 cm long. About how much wood will she have left after cutting the last dowel?
6. 5 Trapezoids and Kites Example 1: Problem-Solving Application Lucy is framing a kite with wooden dowels. She uses two dowels that measure 18 cm, one dowel that measures 30 cm, and two dowels that measure 27 cm. To complete the kite, she needs a dowel to place along. She has a dowel that is 36 cm long. About how much wood will she have left after cutting the last dowel?
 6. 5 Trapezoids and Kites Example 1 Continued 1 Understand the Problem The answer will be the amount of wood Lucy has left after cutting the dowel. 2 Make a Plan The diagonals of a kite are perpendicular, so the four triangles are right triangles. Let N represent the intersection of the diagonals. Use the Pythagorean Theorem and the properties of kites to find , and. Add these lengths to find the length of.
6. 5 Trapezoids and Kites Example 1 Continued 1 Understand the Problem The answer will be the amount of wood Lucy has left after cutting the dowel. 2 Make a Plan The diagonals of a kite are perpendicular, so the four triangles are right triangles. Let N represent the intersection of the diagonals. Use the Pythagorean Theorem and the properties of kites to find , and. Add these lengths to find the length of.
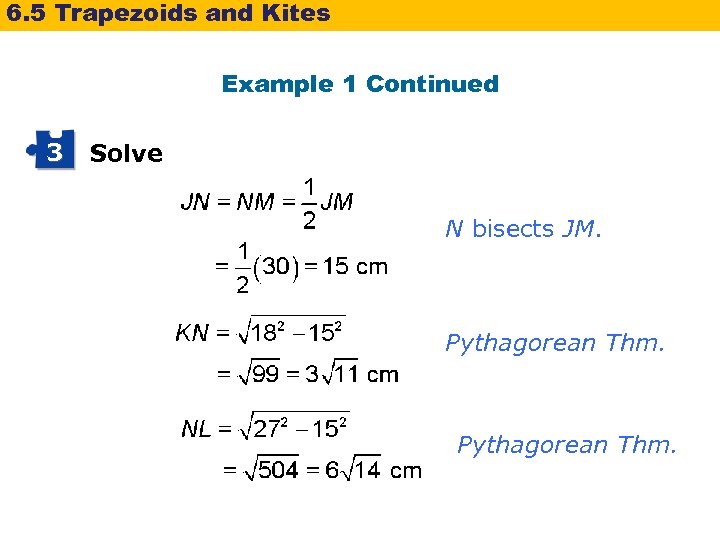 6. 5 Trapezoids and Kites Example 1 Continued 3 Solve N bisects JM. Pythagorean Thm.
6. 5 Trapezoids and Kites Example 1 Continued 3 Solve N bisects JM. Pythagorean Thm.
 6. 5 Trapezoids and Kites Example 1 Continued Lucy needs to cut the dowel to be 32. 4 cm long. The amount of wood that will remain after the cut is, 36 – 32. 4 3. 6 cm Lucy will have 3. 6 cm of wood left over after the cut.
6. 5 Trapezoids and Kites Example 1 Continued Lucy needs to cut the dowel to be 32. 4 cm long. The amount of wood that will remain after the cut is, 36 – 32. 4 3. 6 cm Lucy will have 3. 6 cm of wood left over after the cut.
 6. 5 Trapezoids and Kites Example 1 Continued 4 Look Back To estimate the length of the diagonal, change the side length into decimals and round. , and. The length of the diagonal is approximately 10 + 22 = 32. So the wood remaining is approximately 36 – 32 = 4. So 3. 6 is a reasonable answer.
6. 5 Trapezoids and Kites Example 1 Continued 4 Look Back To estimate the length of the diagonal, change the side length into decimals and round. , and. The length of the diagonal is approximately 10 + 22 = 32. So the wood remaining is approximately 36 – 32 = 4. So 3. 6 is a reasonable answer.
 6. 5 Trapezoids and Kites Check It Out! Example 1 What if. . . ? Daryl is going to make a kite by doubling all the measures in the kite. What is the total amount of binding needed to cover the edges of his kite? How many packages of binding must Daryl buy?
6. 5 Trapezoids and Kites Check It Out! Example 1 What if. . . ? Daryl is going to make a kite by doubling all the measures in the kite. What is the total amount of binding needed to cover the edges of his kite? How many packages of binding must Daryl buy?
 6. 5 Trapezoids and Kites Check It Out! Example 1 Continued 1 Understand the Problem The answer has two parts. • the total length of binding Daryl needs • the number of packages of binding Daryl must buy
6. 5 Trapezoids and Kites Check It Out! Example 1 Continued 1 Understand the Problem The answer has two parts. • the total length of binding Daryl needs • the number of packages of binding Daryl must buy
 6. 5 Trapezoids and Kites Check It Out! Example 1 Continued 2 Make a Plan The diagonals of a kite are perpendicular, so the four triangles are right triangles. Use the Pythagorean Theorem and the properties of kites to find the unknown side lengths. Add these lengths to find the perimeter of the kite.
6. 5 Trapezoids and Kites Check It Out! Example 1 Continued 2 Make a Plan The diagonals of a kite are perpendicular, so the four triangles are right triangles. Use the Pythagorean Theorem and the properties of kites to find the unknown side lengths. Add these lengths to find the perimeter of the kite.
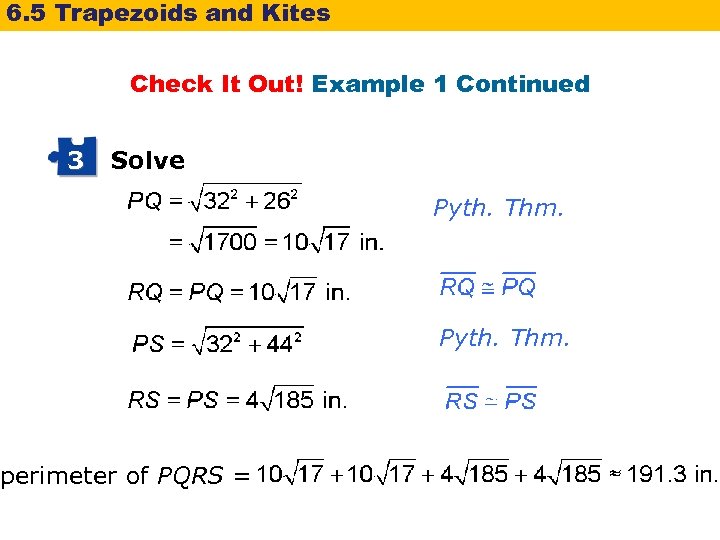 6. 5 Trapezoids and Kites Check It Out! Example 1 Continued 3 Solve perimeter of PQRS = Pyth. Thm.
6. 5 Trapezoids and Kites Check It Out! Example 1 Continued 3 Solve perimeter of PQRS = Pyth. Thm.
 6. 5 Trapezoids and Kites Check It Out! Example 1 Continued Daryl needs approximately 191. 3 inches of binding. One package of binding contains 2 yards, or 72 inches. packages of binding In order to have enough, Daryl must buy 3 packages of binding.
6. 5 Trapezoids and Kites Check It Out! Example 1 Continued Daryl needs approximately 191. 3 inches of binding. One package of binding contains 2 yards, or 72 inches. packages of binding In order to have enough, Daryl must buy 3 packages of binding.
 6. 5 Trapezoids and Kites Check It Out! Example 1 Continued 4 Look Back To estimate the perimeter, change the side lengths into decimals and round. , and kite is approximately . The perimeter of the 2(54) + 2 (41) = 190. So 191. 3 is a reasonable answer.
6. 5 Trapezoids and Kites Check It Out! Example 1 Continued 4 Look Back To estimate the perimeter, change the side lengths into decimals and round. , and kite is approximately . The perimeter of the 2(54) + 2 (41) = 190. So 191. 3 is a reasonable answer.
 6. 5 Trapezoids and Kites Example 2 A: Using Properties of Kites In kite ABCD, m DAB = 54°, and m CDF = 52°. Find m BCD. Kite cons. sides ∆BCD is isos. 2 sides isos. ∆ CBF CDF isos. ∆ base s m CBF = m CDF Def. of s m BCD + m CBF + m CDF = 180° Polygon Sum Thm.
6. 5 Trapezoids and Kites Example 2 A: Using Properties of Kites In kite ABCD, m DAB = 54°, and m CDF = 52°. Find m BCD. Kite cons. sides ∆BCD is isos. 2 sides isos. ∆ CBF CDF isos. ∆ base s m CBF = m CDF Def. of s m BCD + m CBF + m CDF = 180° Polygon Sum Thm.
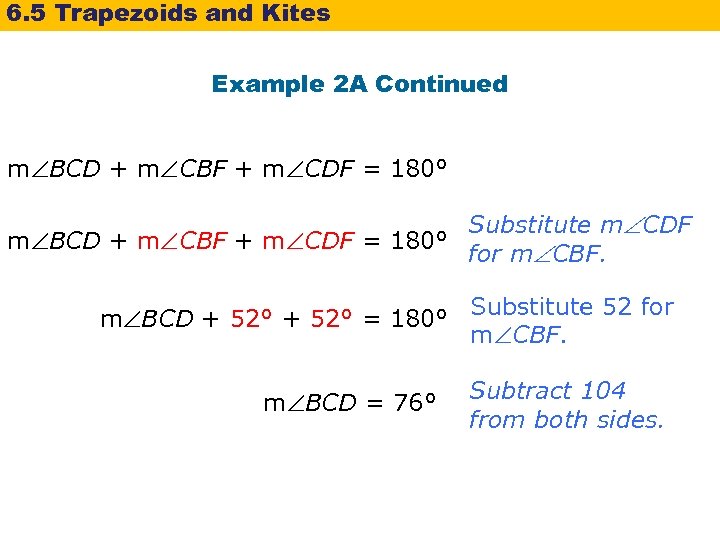 6. 5 Trapezoids and Kites Example 2 A Continued m BCD + m CBF + m CDF = 180° Substitute m CDF m BCD + m CBF + m CDF = 180° for m CBF. m BCD + 52° = 180° m BCD = 76° Substitute 52 for m CBF. Subtract 104 from both sides.
6. 5 Trapezoids and Kites Example 2 A Continued m BCD + m CBF + m CDF = 180° Substitute m CDF m BCD + m CBF + m CDF = 180° for m CBF. m BCD + 52° = 180° m BCD = 76° Substitute 52 for m CBF. Subtract 104 from both sides.
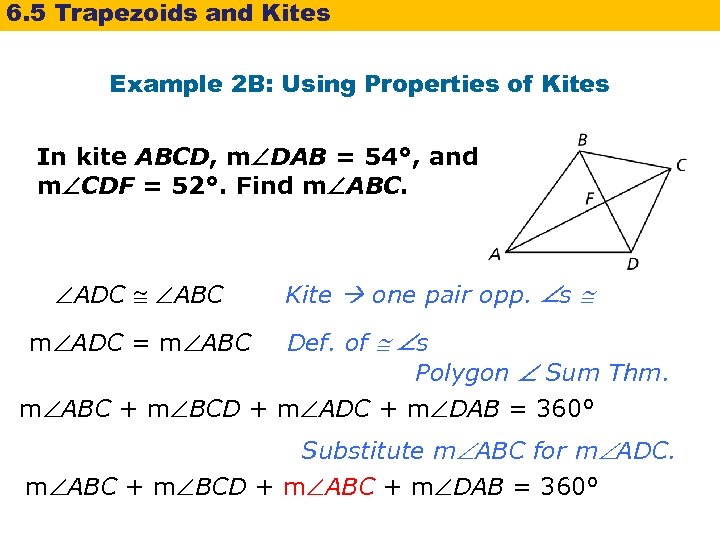 6. 5 Trapezoids and Kites Example 2 B: Using Properties of Kites In kite ABCD, m DAB = 54°, and m CDF = 52°. Find m ABC. ADC ABC Kite one pair opp. s Def. of s Polygon Sum Thm. m ABC + m BCD + m ADC + m DAB = 360° m ADC = m ABC Substitute m ABC for m ADC. m ABC + m BCD + m ABC + m DAB = 360°
6. 5 Trapezoids and Kites Example 2 B: Using Properties of Kites In kite ABCD, m DAB = 54°, and m CDF = 52°. Find m ABC. ADC ABC Kite one pair opp. s Def. of s Polygon Sum Thm. m ABC + m BCD + m ADC + m DAB = 360° m ADC = m ABC Substitute m ABC for m ADC. m ABC + m BCD + m ABC + m DAB = 360°
 6. 5 Trapezoids and Kites Example 2 B Continued m ABC + m BCD + m ABC + m DAB = 360° m ABC + 76° + m ABC + 54° = 360° 2 m ABC = 230° m ABC = 115° Substitute. Simplify. Solve.
6. 5 Trapezoids and Kites Example 2 B Continued m ABC + m BCD + m ABC + m DAB = 360° m ABC + 76° + m ABC + 54° = 360° 2 m ABC = 230° m ABC = 115° Substitute. Simplify. Solve.
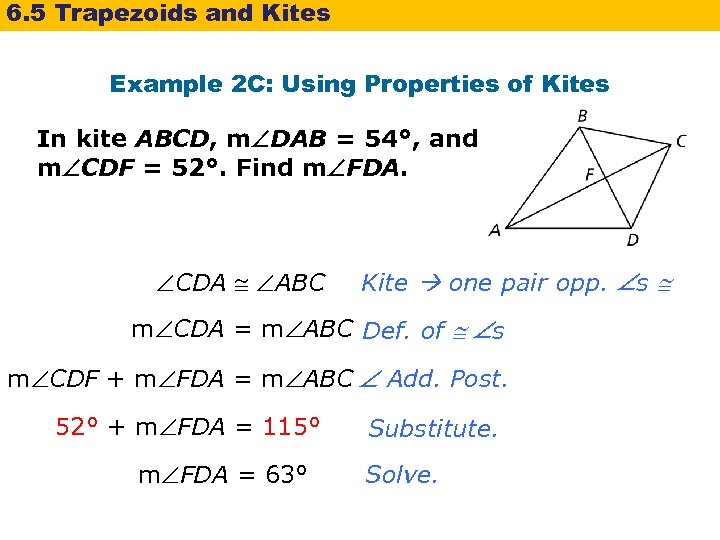 6. 5 Trapezoids and Kites Example 2 C: Using Properties of Kites In kite ABCD, m DAB = 54°, and m CDF = 52°. Find m FDA. CDA ABC Kite one pair opp. s m CDA = m ABC Def. of s m CDF + m FDA = m ABC Add. Post. 52° + m FDA = 115° m FDA = 63° Substitute. Solve.
6. 5 Trapezoids and Kites Example 2 C: Using Properties of Kites In kite ABCD, m DAB = 54°, and m CDF = 52°. Find m FDA. CDA ABC Kite one pair opp. s m CDA = m ABC Def. of s m CDF + m FDA = m ABC Add. Post. 52° + m FDA = 115° m FDA = 63° Substitute. Solve.
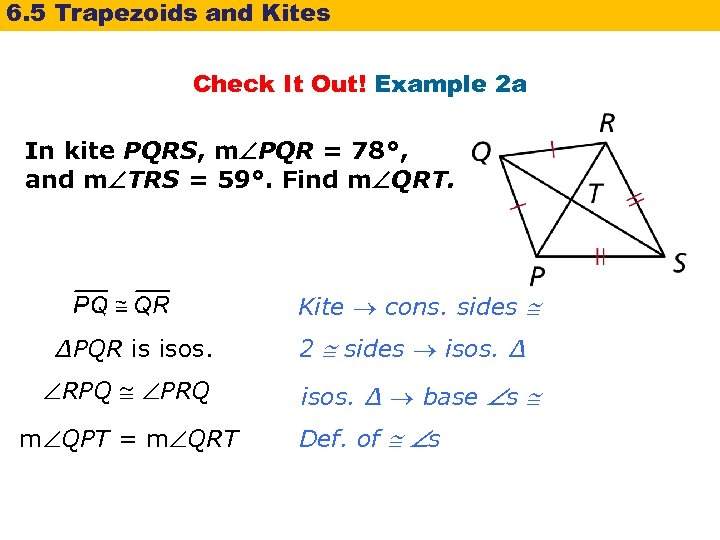 6. 5 Trapezoids and Kites Check It Out! Example 2 a In kite PQRS, m PQR = 78°, and m TRS = 59°. Find m QRT. Kite cons. sides ∆PQR is isos. RPQ PRQ m QPT = m QRT 2 sides isos. ∆ base s Def. of s
6. 5 Trapezoids and Kites Check It Out! Example 2 a In kite PQRS, m PQR = 78°, and m TRS = 59°. Find m QRT. Kite cons. sides ∆PQR is isos. RPQ PRQ m QPT = m QRT 2 sides isos. ∆ base s Def. of s
 6. 5 Trapezoids and Kites Check It Out! Example 2 a Continued m PQR + m QRP + m QPR = 180° Polygon Sum Thm. 78° + m QRT + m QPT = 180° Substitute 78 for m PQR. 78° + m QRT = 180° Substitute. 78° + 2 m QRT = 180° Substitute. 2 m QRT = 102° Subtract 78 from both sides. m QRT = 51° Divide by 2.
6. 5 Trapezoids and Kites Check It Out! Example 2 a Continued m PQR + m QRP + m QPR = 180° Polygon Sum Thm. 78° + m QRT + m QPT = 180° Substitute 78 for m PQR. 78° + m QRT = 180° Substitute. 78° + 2 m QRT = 180° Substitute. 2 m QRT = 102° Subtract 78 from both sides. m QRT = 51° Divide by 2.
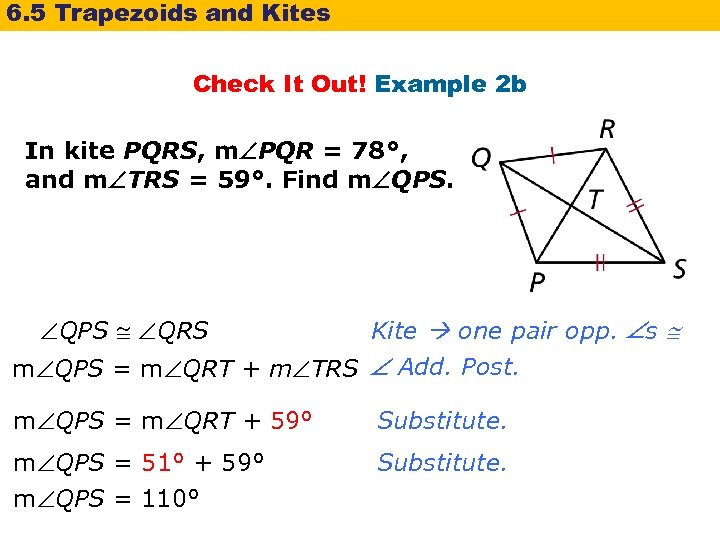 6. 5 Trapezoids and Kites Check It Out! Example 2 b In kite PQRS, m PQR = 78°, and m TRS = 59°. Find m QPS QRS Kite one pair opp. s m QPS = m QRT + m TRS Add. Post. m QPS = m QRT + 59° Substitute. m QPS = 51° + 59° m QPS = 110° Substitute.
6. 5 Trapezoids and Kites Check It Out! Example 2 b In kite PQRS, m PQR = 78°, and m TRS = 59°. Find m QPS QRS Kite one pair opp. s m QPS = m QRT + m TRS Add. Post. m QPS = m QRT + 59° Substitute. m QPS = 51° + 59° m QPS = 110° Substitute.
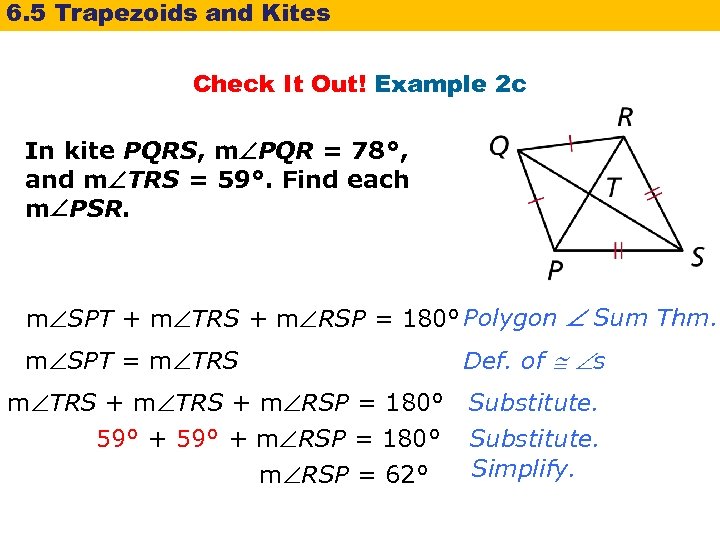 6. 5 Trapezoids and Kites Check It Out! Example 2 c In kite PQRS, m PQR = 78°, and m TRS = 59°. Find each m PSR. m SPT + m TRS + m RSP = 180° Polygon Sum Thm. m SPT = m TRS Def. of s m TRS + m RSP = 180° Substitute. 59° + m RSP = 180° Substitute. Simplify. m RSP = 62°
6. 5 Trapezoids and Kites Check It Out! Example 2 c In kite PQRS, m PQR = 78°, and m TRS = 59°. Find each m PSR. m SPT + m TRS + m RSP = 180° Polygon Sum Thm. m SPT = m TRS Def. of s m TRS + m RSP = 180° Substitute. 59° + m RSP = 180° Substitute. Simplify. m RSP = 62°
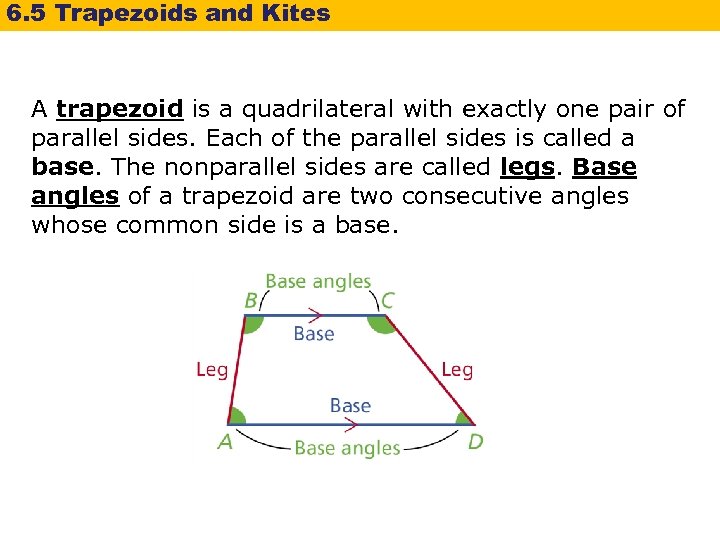 6. 5 Trapezoids and Kites A trapezoid is a quadrilateral with exactly one pair of parallel sides. Each of the parallel sides is called a base. The nonparallel sides are called legs. Base angles of a trapezoid are two consecutive angles whose common side is a base.
6. 5 Trapezoids and Kites A trapezoid is a quadrilateral with exactly one pair of parallel sides. Each of the parallel sides is called a base. The nonparallel sides are called legs. Base angles of a trapezoid are two consecutive angles whose common side is a base.
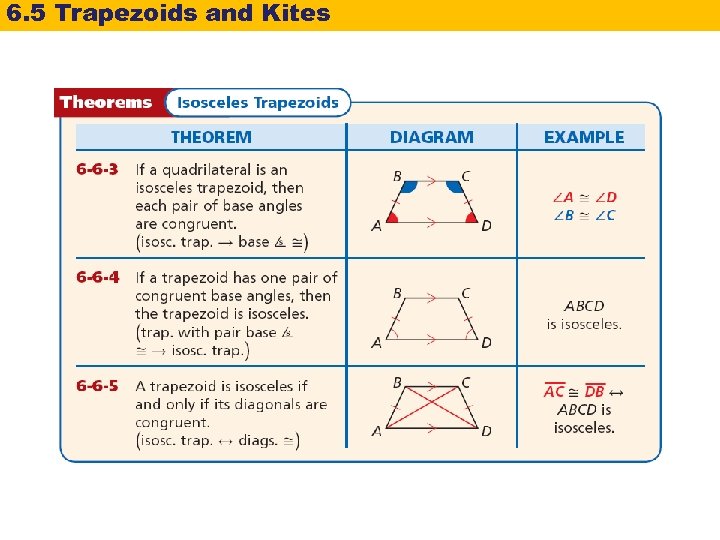
 6. 5 Trapezoids and Kites If the legs of a trapezoid are congruent, the trapezoid is an isosceles trapezoid. The following theorems state the properties of an isosceles trapezoid.
6. 5 Trapezoids and Kites If the legs of a trapezoid are congruent, the trapezoid is an isosceles trapezoid. The following theorems state the properties of an isosceles trapezoid.
 6. 5 Trapezoids and Kites
6. 5 Trapezoids and Kites
 6. 5 Trapezoids and Kites Reading Math Theorem 6 -6 -5 is a biconditional statement. So it is true both “forward” and “backward. ”
6. 5 Trapezoids and Kites Reading Math Theorem 6 -6 -5 is a biconditional statement. So it is true both “forward” and “backward. ”
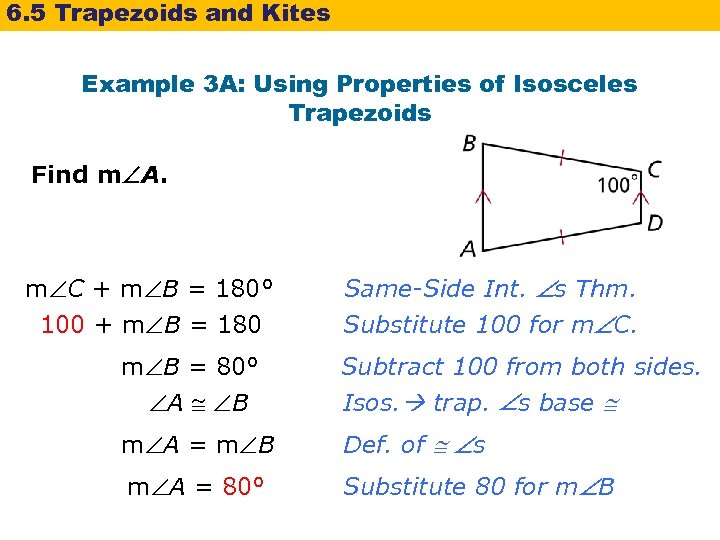 6. 5 Trapezoids and Kites Example 3 A: Using Properties of Isosceles Trapezoids Find m A. m C + m B = 180° 100 + m B = 180 Same-Side Int. s Thm. Substitute 100 for m C. m B = 80° A B Subtract 100 from both sides. Isos. trap. s base m A = m B Def. of s m A = 80° Substitute 80 for m B
6. 5 Trapezoids and Kites Example 3 A: Using Properties of Isosceles Trapezoids Find m A. m C + m B = 180° 100 + m B = 180 Same-Side Int. s Thm. Substitute 100 for m C. m B = 80° A B Subtract 100 from both sides. Isos. trap. s base m A = m B Def. of s m A = 80° Substitute 80 for m B
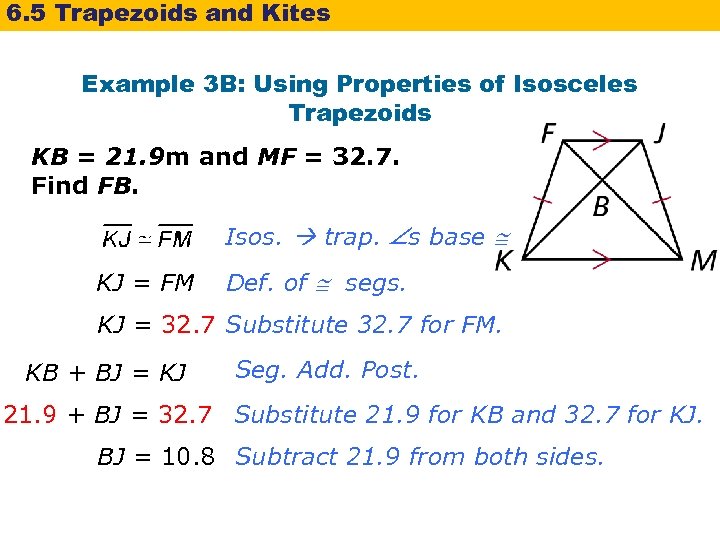 6. 5 Trapezoids and Kites Example 3 B: Using Properties of Isosceles Trapezoids KB = 21. 9 m and MF = 32. 7. Find FB. Isos. trap. s base KJ = FM Def. of segs. KJ = 32. 7 Substitute 32. 7 for FM. KB + BJ = KJ Seg. Add. Post. 21. 9 + BJ = 32. 7 Substitute 21. 9 for KB and 32. 7 for KJ. BJ = 10. 8 Subtract 21. 9 from both sides.
6. 5 Trapezoids and Kites Example 3 B: Using Properties of Isosceles Trapezoids KB = 21. 9 m and MF = 32. 7. Find FB. Isos. trap. s base KJ = FM Def. of segs. KJ = 32. 7 Substitute 32. 7 for FM. KB + BJ = KJ Seg. Add. Post. 21. 9 + BJ = 32. 7 Substitute 21. 9 for KB and 32. 7 for KJ. BJ = 10. 8 Subtract 21. 9 from both sides.
 6. 5 Trapezoids and Kites Example 3 B Continued Same line. KFJ MJF Isos. trap. s base Isos. trap. legs ∆FKJ ∆JMF SAS BKF BMJ CPCTC FBK JBM Vert. s
6. 5 Trapezoids and Kites Example 3 B Continued Same line. KFJ MJF Isos. trap. s base Isos. trap. legs ∆FKJ ∆JMF SAS BKF BMJ CPCTC FBK JBM Vert. s
 6. 5 Trapezoids and Kites Example 3 B Continued Isos. trap. legs ∆FBK ∆JBM AAS CPCTC FB = JB Def. of segs. FB = 10. 8 Substitute 10. 8 for JB.
6. 5 Trapezoids and Kites Example 3 B Continued Isos. trap. legs ∆FBK ∆JBM AAS CPCTC FB = JB Def. of segs. FB = 10. 8 Substitute 10. 8 for JB.
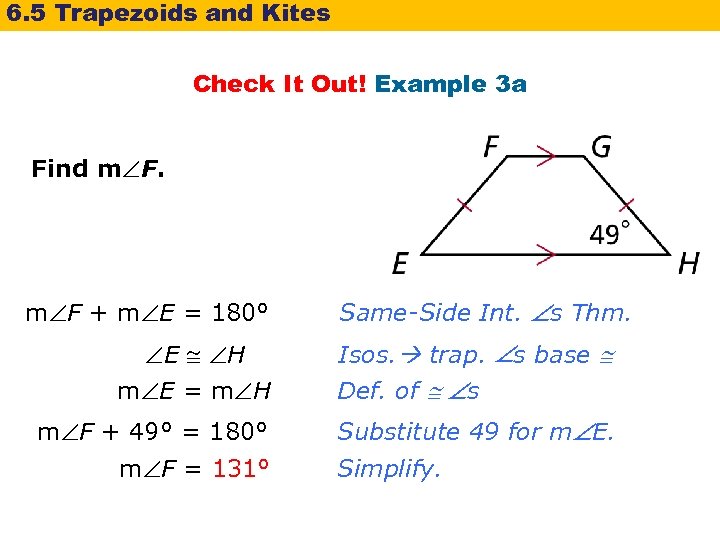 6. 5 Trapezoids and Kites Check It Out! Example 3 a Find m F + m E = 180° E H m E = m H m F + 49° = 180° m F = 131° Same-Side Int. s Thm. Isos. trap. s base Def. of s Substitute 49 for m E. Simplify.
6. 5 Trapezoids and Kites Check It Out! Example 3 a Find m F + m E = 180° E H m E = m H m F + 49° = 180° m F = 131° Same-Side Int. s Thm. Isos. trap. s base Def. of s Substitute 49 for m E. Simplify.
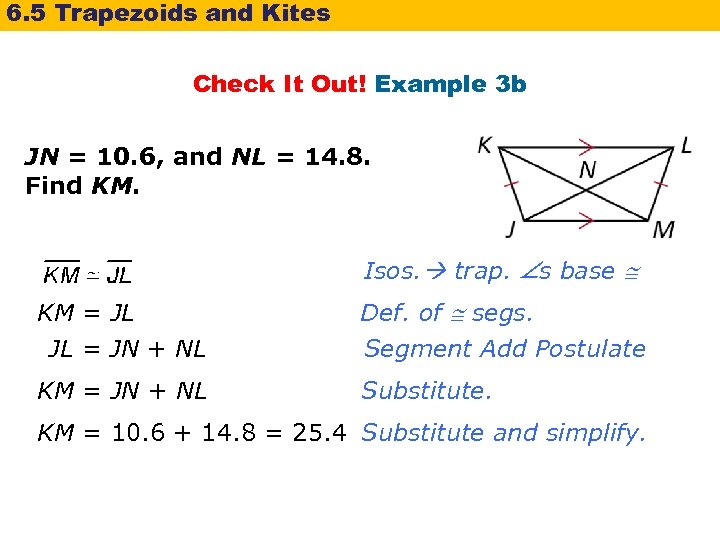 6. 5 Trapezoids and Kites Check It Out! Example 3 b JN = 10. 6, and NL = 14. 8. Find KM. Isos. trap. s base KM = JL JL = JN + NL Def. of segs. KM = JN + NL Substitute. Segment Add Postulate KM = 10. 6 + 14. 8 = 25. 4 Substitute and simplify.
6. 5 Trapezoids and Kites Check It Out! Example 3 b JN = 10. 6, and NL = 14. 8. Find KM. Isos. trap. s base KM = JL JL = JN + NL Def. of segs. KM = JN + NL Substitute. Segment Add Postulate KM = 10. 6 + 14. 8 = 25. 4 Substitute and simplify.
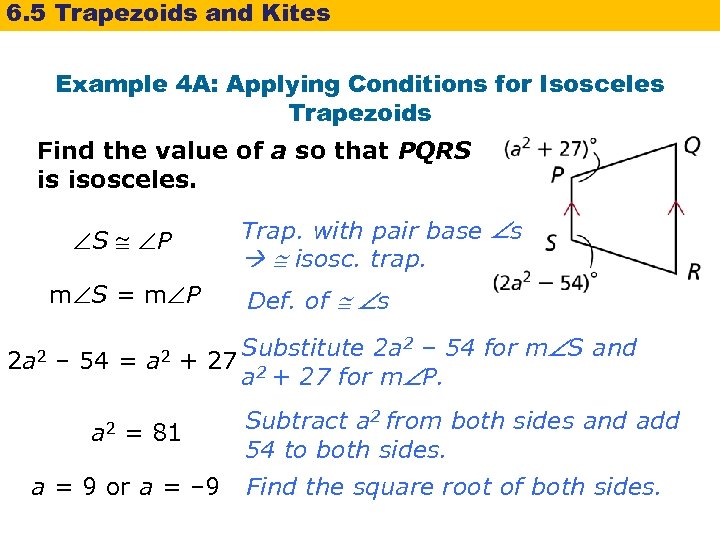 6. 5 Trapezoids and Kites Example 4 A: Applying Conditions for Isosceles Trapezoids Find the value of a so that PQRS is isosceles. Trap. with pair base s isosc. trap. S P m S = m P 2 a 2 – 54 = a 2 Def. of s Substitute 2 a 2 – 54 for m S and + 27 2 a + 27 for m P. = 81 a = 9 or a = – 9 Subtract a 2 from both sides and add 54 to both sides. Find the square root of both sides.
6. 5 Trapezoids and Kites Example 4 A: Applying Conditions for Isosceles Trapezoids Find the value of a so that PQRS is isosceles. Trap. with pair base s isosc. trap. S P m S = m P 2 a 2 – 54 = a 2 Def. of s Substitute 2 a 2 – 54 for m S and + 27 2 a + 27 for m P. = 81 a = 9 or a = – 9 Subtract a 2 from both sides and add 54 to both sides. Find the square root of both sides.
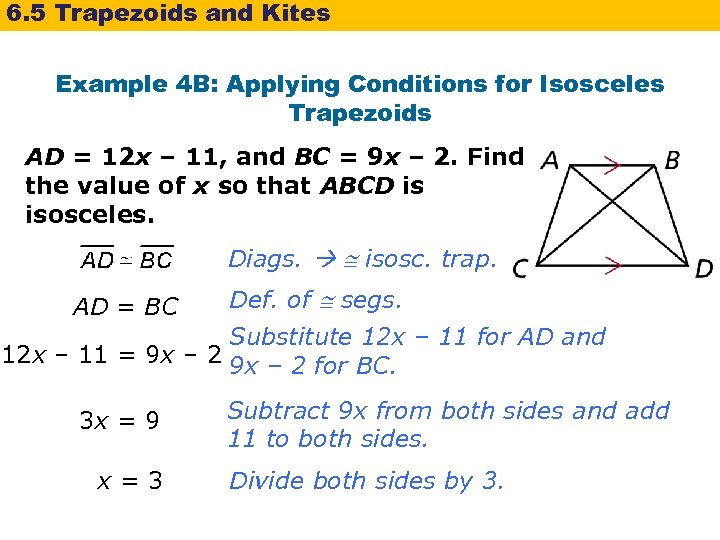 6. 5 Trapezoids and Kites Example 4 B: Applying Conditions for Isosceles Trapezoids AD = 12 x – 11, and BC = 9 x – 2. Find the value of x so that ABCD is isosceles. Diags. isosc. trap. AD = BC Def. of segs. Substitute 12 x – 11 for AD and 12 x – 11 = 9 x – 2 for BC. 3 x = 9 x=3 Subtract 9 x from both sides and add 11 to both sides. Divide both sides by 3.
6. 5 Trapezoids and Kites Example 4 B: Applying Conditions for Isosceles Trapezoids AD = 12 x – 11, and BC = 9 x – 2. Find the value of x so that ABCD is isosceles. Diags. isosc. trap. AD = BC Def. of segs. Substitute 12 x – 11 for AD and 12 x – 11 = 9 x – 2 for BC. 3 x = 9 x=3 Subtract 9 x from both sides and add 11 to both sides. Divide both sides by 3.
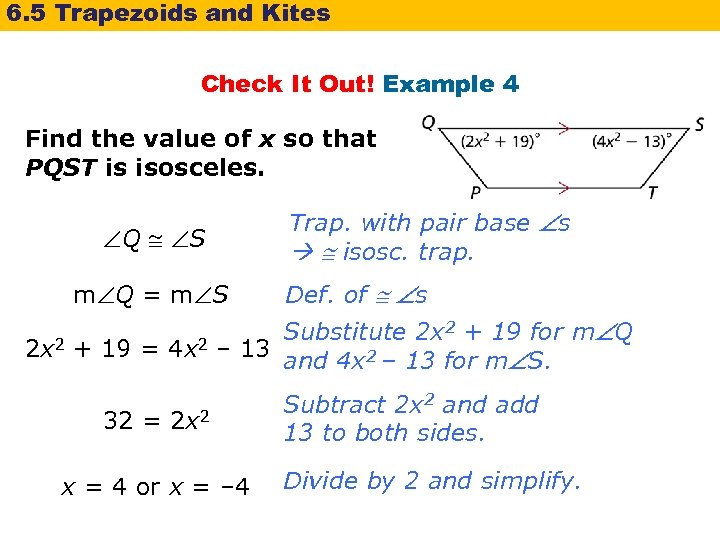 6. 5 Trapezoids and Kites Check It Out! Example 4 Find the value of x so that PQST is isosceles. Q S m Q = m S Trap. with pair base s isosc. trap. Def. of s Substitute 2 x 2 + 19 for m Q 2 x 2 + 19 = 4 x 2 – 13 and 4 x 2 – 13 for m S. 32 = 2 x 2 x = 4 or x = – 4 Subtract 2 x 2 and add 13 to both sides. Divide by 2 and simplify.
6. 5 Trapezoids and Kites Check It Out! Example 4 Find the value of x so that PQST is isosceles. Q S m Q = m S Trap. with pair base s isosc. trap. Def. of s Substitute 2 x 2 + 19 for m Q 2 x 2 + 19 = 4 x 2 – 13 and 4 x 2 – 13 for m S. 32 = 2 x 2 x = 4 or x = – 4 Subtract 2 x 2 and add 13 to both sides. Divide by 2 and simplify.
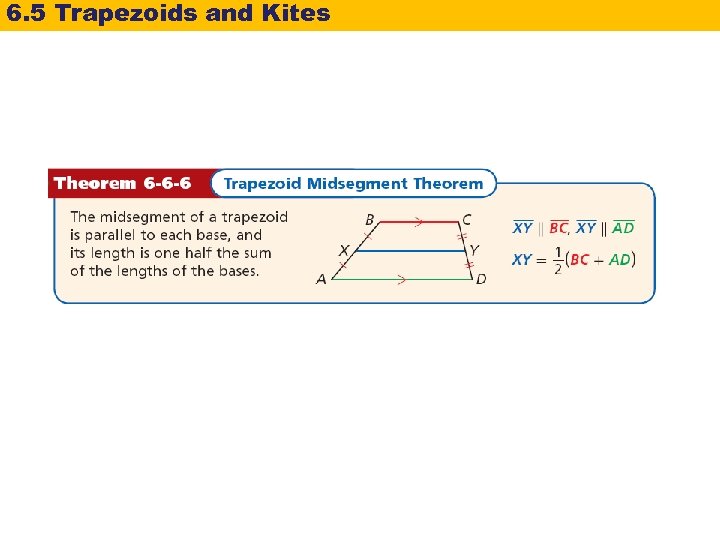
 6. 5 Trapezoids and Kites The midsegment of a trapezoid is the segment whose endpoints are the midpoints of the legs. In Lesson 5 -1, you studied the Triangle Midsegment Theorem. The Trapezoid Midsegment Theorem is similar to it.
6. 5 Trapezoids and Kites The midsegment of a trapezoid is the segment whose endpoints are the midpoints of the legs. In Lesson 5 -1, you studied the Triangle Midsegment Theorem. The Trapezoid Midsegment Theorem is similar to it.
 6. 5 Trapezoids and Kites
6. 5 Trapezoids and Kites
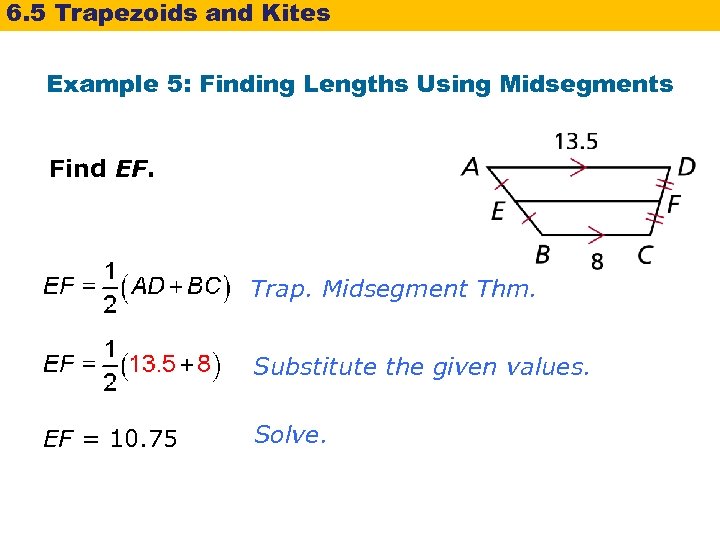 6. 5 Trapezoids and Kites Example 5: Finding Lengths Using Midsegments Find EF. Trap. Midsegment Thm. Substitute the given values. EF = 10. 75 Solve.
6. 5 Trapezoids and Kites Example 5: Finding Lengths Using Midsegments Find EF. Trap. Midsegment Thm. Substitute the given values. EF = 10. 75 Solve.
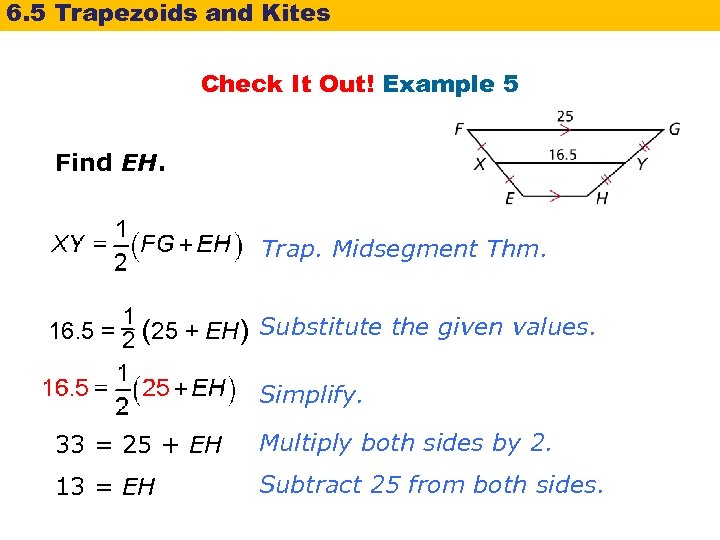 6. 5 Trapezoids and Kites Check It Out! Example 5 Find EH. Trap. Midsegment Thm. 1 16. 5 = 2 (25 + EH) Substitute the given values. Simplify. 33 = 25 + EH Multiply both sides by 2. 13 = EH Subtract 25 from both sides.
6. 5 Trapezoids and Kites Check It Out! Example 5 Find EH. Trap. Midsegment Thm. 1 16. 5 = 2 (25 + EH) Substitute the given values. Simplify. 33 = 25 + EH Multiply both sides by 2. 13 = EH Subtract 25 from both sides.
 6. 5 Trapezoids and Kites Lesson Quiz: Part I 1. Erin is making a kite based on the pattern below. About how much binding does Erin need to cover the edges of the kite? about 191. 2 in. In kite HJKL, m KLP = 72°, and m HJP = 49. 5°. Find each measure. 2. m LHJ 81° 3. m PKL 18°
6. 5 Trapezoids and Kites Lesson Quiz: Part I 1. Erin is making a kite based on the pattern below. About how much binding does Erin need to cover the edges of the kite? about 191. 2 in. In kite HJKL, m KLP = 72°, and m HJP = 49. 5°. Find each measure. 2. m LHJ 81° 3. m PKL 18°
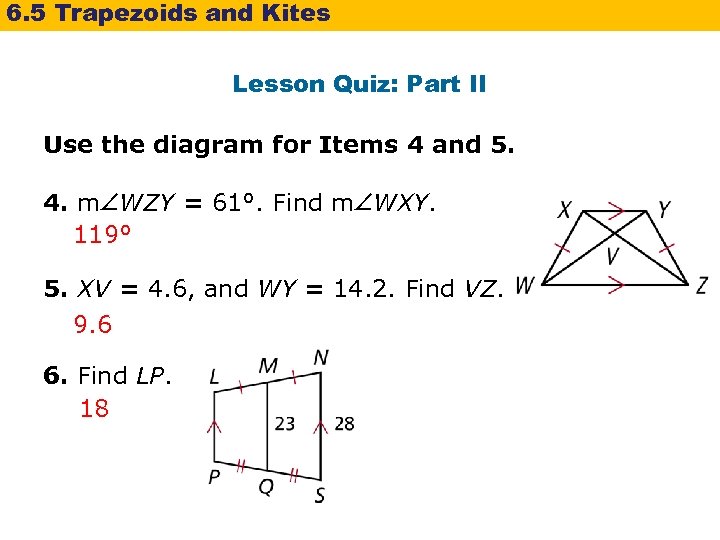 6. 5 Trapezoids and Kites Lesson Quiz: Part II Use the diagram for Items 4 and 5. 4. m WZY = 61°. Find m WXY. 119° 5. XV = 4. 6, and WY = 14. 2. Find VZ. 9. 6 6. Find LP. 18
6. 5 Trapezoids and Kites Lesson Quiz: Part II Use the diagram for Items 4 and 5. 4. m WZY = 61°. Find m WXY. 119° 5. XV = 4. 6, and WY = 14. 2. Find VZ. 9. 6 6. Find LP. 18


