f4b999a5ea879393a8e6b802d6adee7d.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 19
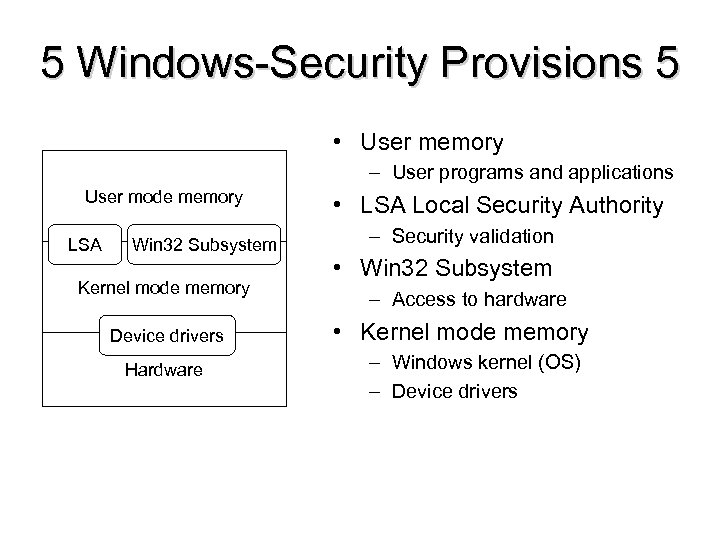 5 Windows-Security Provisions 5 • User memory – User programs and applications User mode memory LSA Win 32 Subsystem Kernel mode memory Device drivers Hardware • LSA Local Security Authority – Security validation • Win 32 Subsystem – Access to hardware • Kernel mode memory – Windows kernel (OS) – Device drivers
5 Windows-Security Provisions 5 • User memory – User programs and applications User mode memory LSA Win 32 Subsystem Kernel mode memory Device drivers Hardware • LSA Local Security Authority – Security validation • Win 32 Subsystem – Access to hardware • Kernel mode memory – Windows kernel (OS) – Device drivers
 Windows Security Features • Internet Connection Firewall ICF – Personal Firewall. Secures a single system. Loggs • Session Initiation Protocol SIP – Provides a secure pathway for real time applications. • • Blank password restrictions Software restriction policies – Software can be isolated using • • Users and Groups as in W 2 K Access Control List as in W 2 K Auditing for all objects User rights GPO ACL SACL – Permission to perform an action. • Group Policy Object – – Are used to control security features There are templates GPMC (Group Policy Management Console from MS) Gpupdate /? GPO
Windows Security Features • Internet Connection Firewall ICF – Personal Firewall. Secures a single system. Loggs • Session Initiation Protocol SIP – Provides a secure pathway for real time applications. • • Blank password restrictions Software restriction policies – Software can be isolated using • • Users and Groups as in W 2 K Access Control List as in W 2 K Auditing for all objects User rights GPO ACL SACL – Permission to perform an action. • Group Policy Object – – Are used to control security features There are templates GPMC (Group Policy Management Console from MS) Gpupdate /? GPO
 Security Features Cont. • • New technology File System as in W 2 K Encrypting File System Kerberos authentication Virtual Private Network NTFS EFS VPN – PPTP, L 2 TP, IPSec • • • Public Key Infrastructure and Certificate service Delegation per OU-basis External Authentication C 2 -security Active Directory Crypto. API PKI & CA • Microsoft Internet Security and Acceleration Server ISA-server – Firewall – Cache AD
Security Features Cont. • • New technology File System as in W 2 K Encrypting File System Kerberos authentication Virtual Private Network NTFS EFS VPN – PPTP, L 2 TP, IPSec • • • Public Key Infrastructure and Certificate service Delegation per OU-basis External Authentication C 2 -security Active Directory Crypto. API PKI & CA • Microsoft Internet Security and Acceleration Server ISA-server – Firewall – Cache AD
 Securing applications IIS ‘problem’ • Web-server (‘Stand-alone’) – HTML – Server-side processing – Scripting Languages – Database connectivity – Other dynamic contents • FTP-server (‘Stand-alone’) – Clear text password
Securing applications IIS ‘problem’ • Web-server (‘Stand-alone’) – HTML – Server-side processing – Scripting Languages – Database connectivity – Other dynamic contents • FTP-server (‘Stand-alone’) – Clear text password
 Securing applications: Web • Use Patches and fixes • Remove the default site • Remove all the extension mappings that you don’t need. • Change the ODBC settings in registry HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINESoftwareMicrosoftJet4. 0enginesSandbox. Mode to a value of 3 (Default is 2) • Move the wwwroot directory to another drive then OS
Securing applications: Web • Use Patches and fixes • Remove the default site • Remove all the extension mappings that you don’t need. • Change the ODBC settings in registry HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINESoftwareMicrosoftJet4. 0enginesSandbox. Mode to a value of 3 (Default is 2) • Move the wwwroot directory to another drive then OS
 Securing applications: FTP • Work as you do with the Web security Mail • Use Cryptography if it’s possibly (SSL, VPN, IPSec, …) • Use SPAM-filter DNS • Use External & Internal DNS if possible. • Lookout for Record poisoning. – Dynamic updates – Cache poisoning • Lookout for Zone transfers. Limit Zone transfer and DNS updates.
Securing applications: FTP • Work as you do with the Web security Mail • Use Cryptography if it’s possibly (SSL, VPN, IPSec, …) • Use SPAM-filter DNS • Use External & Internal DNS if possible. • Lookout for Record poisoning. – Dynamic updates – Cache poisoning • Lookout for Zone transfers. Limit Zone transfer and DNS updates.
 Securing Web & E-mail Using SSL & TSL • SSL (Secure Sockets Layer) – CPU-intensive (2 -100 times slower) – Only TCP • TSL (Transport Layer Security) – Makes a tunnel for communication • HTTPS (port 443) – MS IIS (Web-server) with SSL • Windows SMTP service with SSL
Securing Web & E-mail Using SSL & TSL • SSL (Secure Sockets Layer) – CPU-intensive (2 -100 times slower) – Only TCP • TSL (Transport Layer Security) – Makes a tunnel for communication • HTTPS (port 443) – MS IIS (Web-server) with SSL • Windows SMTP service with SSL
 Certificate Service Windows • Two types: 1. Enterprise (require AD) Computers in the AD will trust the root CA 2. Stand-alone (basic type) Does not support logon certificates. Certificate requests are set to pending and admin has to issue the certificate. For use in a Stand-alone server.
Certificate Service Windows • Two types: 1. Enterprise (require AD) Computers in the AD will trust the root CA 2. Stand-alone (basic type) Does not support logon certificates. Certificate requests are set to pending and admin has to issue the certificate. For use in a Stand-alone server.
 Certificate Service Windows 1. Install Certificate service. 2. Configurate CA (Certificate Authority). 3. Set up the policy (CRL and so on). 4. Create Certificate templates. 5. Enable Certificate templates. 6. Certificate enrollment.
Certificate Service Windows 1. Install Certificate service. 2. Configurate CA (Certificate Authority). 3. Set up the policy (CRL and so on). 4. Create Certificate templates. 5. Enable Certificate templates. 6. Certificate enrollment.
 IPSec ’works’ on layer 3. => under TCP, UDP, ICMP, … => Transparent for applications! => Will protect every application as: Remote login, Client/server, email, FTP, Web and so on. There is special hardware from Intel, 3 com, Cisco, and other, just to unload the IPSec processing from the CPU.
IPSec ’works’ on layer 3. => under TCP, UDP, ICMP, … => Transparent for applications! => Will protect every application as: Remote login, Client/server, email, FTP, Web and so on. There is special hardware from Intel, 3 com, Cisco, and other, just to unload the IPSec processing from the CPU.
 IPSec Two protocols: – AH – ESP Authentication Header Encapsulated Security Payload Two modes: – Transport mode – Tunnel mode IKE – Protocol for connecting Creates SA Security Association (Key, Used protocol, Destination IP…) If you want duplex you need two SA’s SPI – Holds used SA (SPI=32 bit value in every IP-header) Anti-replay service 0 -(32 bitar-1) window=64
IPSec Two protocols: – AH – ESP Authentication Header Encapsulated Security Payload Two modes: – Transport mode – Tunnel mode IKE – Protocol for connecting Creates SA Security Association (Key, Used protocol, Destination IP…) If you want duplex you need two SA’s SPI – Holds used SA (SPI=32 bit value in every IP-header) Anti-replay service 0 -(32 bitar-1) window=64
 Intrusion Detecting System IDS Tar vid där FW slutar på “insidan” och övervakar trafiken innanför. • I samma dator som känsliga data • Nätverksbaserat – Ett antal agenter som samlar data till en central som analyserar. IP Två Principer: 1. Anomali-detektion. 2. Missbruks-detektion. (IDS kan fungera enligt båda men vanligast bara som en av principerna) http: //www. snort. org/
Intrusion Detecting System IDS Tar vid där FW slutar på “insidan” och övervakar trafiken innanför. • I samma dator som känsliga data • Nätverksbaserat – Ett antal agenter som samlar data till en central som analyserar. IP Två Principer: 1. Anomali-detektion. 2. Missbruks-detektion. (IDS kan fungera enligt båda men vanligast bara som en av principerna) http: //www. snort. org/
 Intrusion Detecting System IDS 1. Noggrann statistik över “normalt” beteende. • Larm om något ovanligt inträffar. • • Sällan använda anrop. Extremt mycket trafik. - Risk för falsklarm + Angreppsmetod behöver inte var känd. 2. Larmar på kända typer av attacker - Stor ‘databas’ krävs, måste uppdateras ofta. + Falsklarm ovanligt.
Intrusion Detecting System IDS 1. Noggrann statistik över “normalt” beteende. • Larm om något ovanligt inträffar. • • Sällan använda anrop. Extremt mycket trafik. - Risk för falsklarm + Angreppsmetod behöver inte var känd. 2. Larmar på kända typer av attacker - Stor ‘databas’ krävs, måste uppdateras ofta. + Falsklarm ovanligt.
 Time • W 2 K*, W 2 K, XP uses Windows Time Service, the time comes from the ADserver and the KDC (Kerberos Key Distribution Center) there. (KDC also includes Authentication Server and Ticket Granting Server) • Kerberos uses SNTP (Simple Network Time Protocol) for synchronization.
Time • W 2 K*, W 2 K, XP uses Windows Time Service, the time comes from the ADserver and the KDC (Kerberos Key Distribution Center) there. (KDC also includes Authentication Server and Ticket Granting Server) • Kerberos uses SNTP (Simple Network Time Protocol) for synchronization.
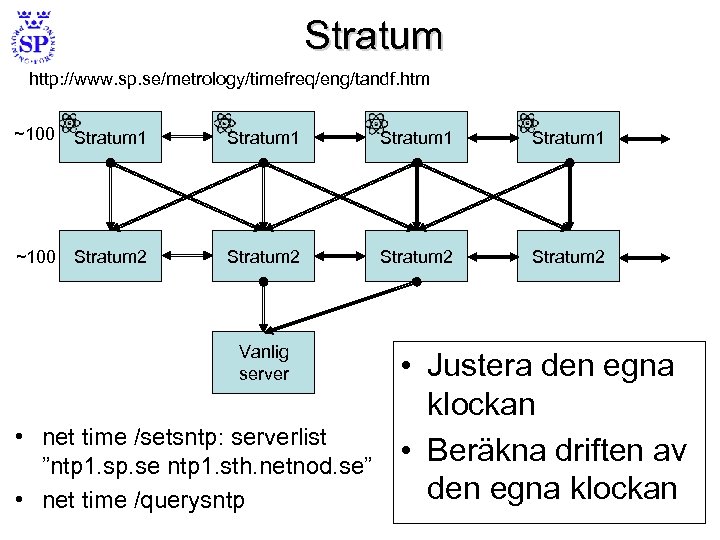 Stratum http: //www. sp. se/metrology/timefreq/eng/tandf. htm ~100 Stratum 1 ~100 Stratum 2 Vanlig server • net time /setsntp: serverlist ”ntp 1. sp. se ntp 1. sth. netnod. se” • net time /querysntp • Justera den egna klockan • Beräkna driften av den egna klockan
Stratum http: //www. sp. se/metrology/timefreq/eng/tandf. htm ~100 Stratum 1 ~100 Stratum 2 Vanlig server • net time /setsntp: serverlist ”ntp 1. sp. se ntp 1. sth. netnod. se” • net time /querysntp • Justera den egna klockan • Beräkna driften av den egna klockan
 The end !
The end !
 *VPN Virtual Private Network L 2 TP, PPTP
*VPN Virtual Private Network L 2 TP, PPTP
 *Microsoft ISA (Internet Security and Acceleration Server) Firewall/Cache
*Microsoft ISA (Internet Security and Acceleration Server) Firewall/Cache
 Mer • Vulnerability (Sårbarheter, säkerhetshål/Svagheter)?
Mer • Vulnerability (Sårbarheter, säkerhetshål/Svagheter)?


