Chemical Reactions.pptx
- Количество слайдов: 8
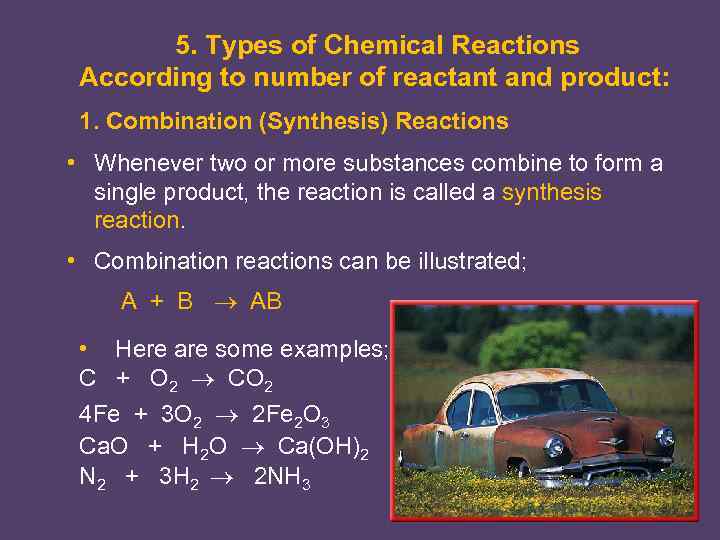
5. Types of Chemical Reactions According to number of reactant and product: 1. Combination (Synthesis) Reactions • Whenever two or more substances combine to form a single product, the reaction is called a synthesis reaction. • Combination reactions can be illustrated; A + B AB • Here are some examples; C + O 2 CO 2 4 Fe + 3 O 2 2 Fe 2 O 3 Ca. O + H 2 O Ca(OH)2 N 2 + 3 H 2 2 NH 3
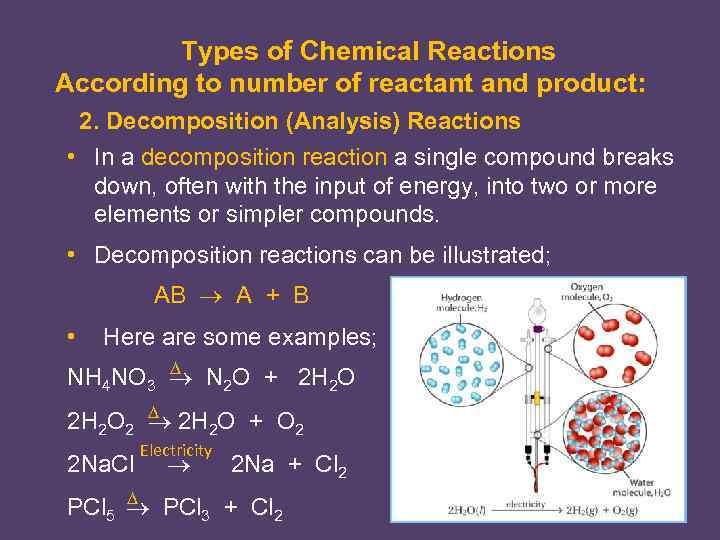
Types of Chemical Reactions According to number of reactant and product: 2. Decomposition (Analysis) Reactions • In a decomposition reaction a single compound breaks down, often with the input of energy, into two or more elements or simpler compounds. • Decomposition reactions can be illustrated; AB A + B • Here are some examples; NH 4 NO 3 N 2 O + 2 H 2 O 2 2 H 2 O + O 2 2 Na. Cl Electricity 2 Na + Cl 2 PCl 5 PCl 3 + Cl 2
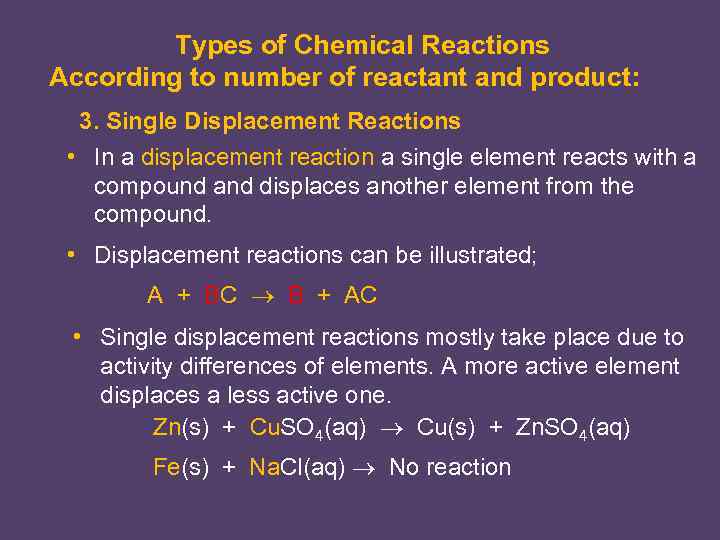
Types of Chemical Reactions According to number of reactant and product: 3. Single Displacement Reactions • In a displacement reaction a single element reacts with a compound and displaces another element from the compound. • Displacement reactions can be illustrated; A + BC B + AC • Single displacement reactions mostly take place due to activity differences of elements. A more active element displaces a less active one. Zn(s) + Cu. SO 4(aq) Cu(s) + Zn. SO 4(aq) Fe(s) + Na. Cl(aq) No reaction
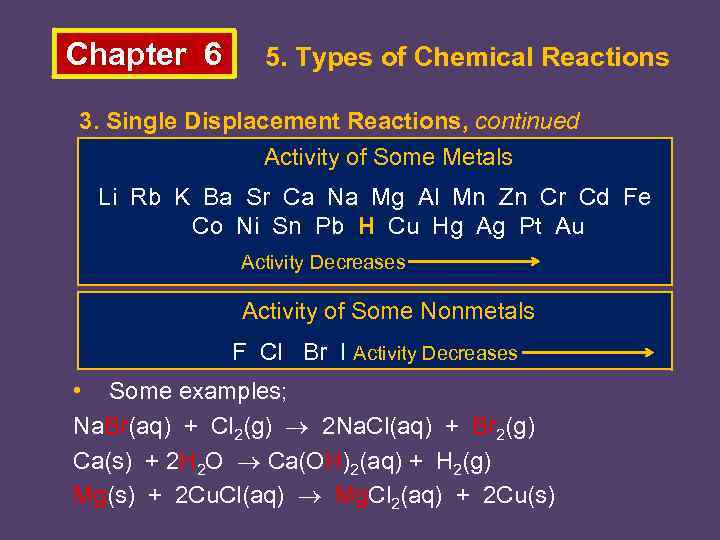
Chapter 6 5. Types of Chemical Reactions 3. Single Displacement Reactions, continued Activity of Some Metals Li Rb K Ba Sr Ca Na Mg Al Mn Zn Cr Cd Fe Co Ni Sn Pb H Cu Hg Ag Pt Au Activity Decreases Activity of Some Nonmetals F Cl Br I Activity Decreases • Some examples; Na. Br(aq) + Cl 2(g) 2 Na. Cl(aq) + Br 2(g) Ca(s) + 2 H 2 O Ca(OH)2(aq) + H 2(g) Mg(s) + 2 Cu. Cl(aq) Mg. Cl 2(aq) + 2 Cu(s)
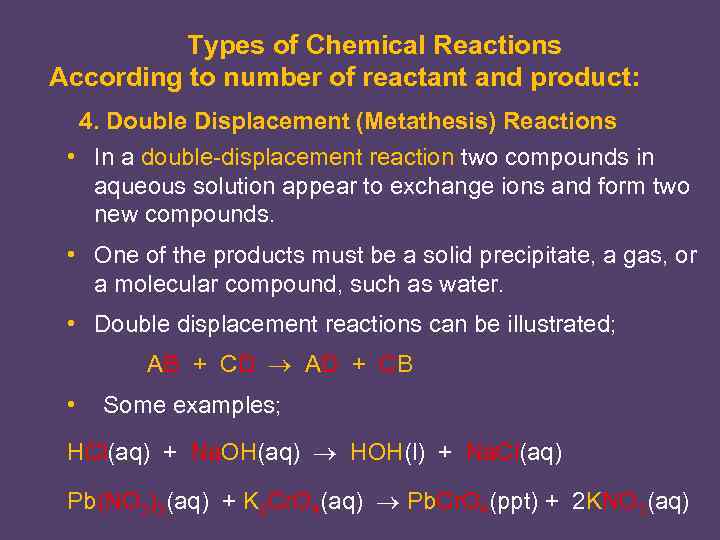
Types of Chemical Reactions According to number of reactant and product: 4. Double Displacement (Metathesis) Reactions • In a double-displacement reaction two compounds in aqueous solution appear to exchange ions and form two new compounds. • One of the products must be a solid precipitate, a gas, or a molecular compound, such as water. • Double displacement reactions can be illustrated; AB + CD AD + CB • Some examples; HCl(aq) + Na. OH(aq) HOH(l) + Na. Cl(aq) Pb(NO 3)2(aq) + K 2 Cr. O 4(aq) Pb. Cr. O 4(ppt) + 2 KNO 3(aq)

Types of Chemical Reactions According to heat: Endothermic and Exothermic Reactions • A reaction which absorbs energy is endothermic reaction and which release energy is exothermic reaction. • Some examples; Ca(s) + 2 H 2 O(l) Ca(OH)2(aq) + H 2(g) + Energy Exothermic Reaction H 2 O(l) + Energy H 2(g) + O 2(g) Endothermic Reaction
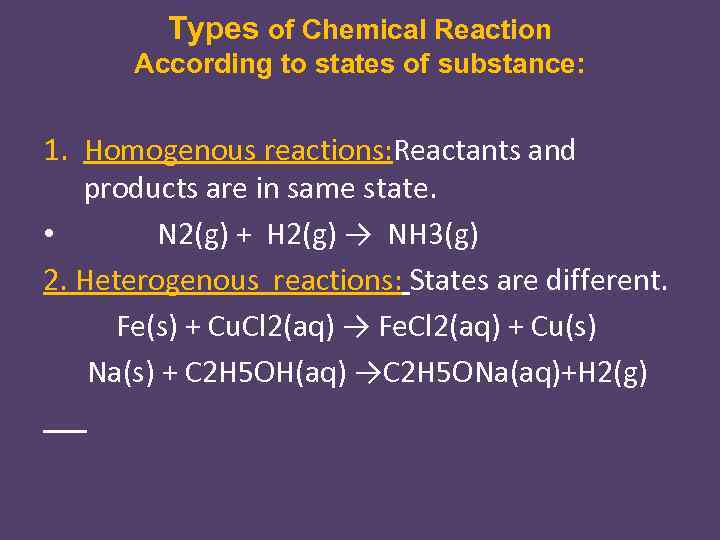
Types of Chemical Reaction According to states of substance: 1. Homogenous reactions: Reactants and products are in same state. • N 2(g) + H 2(g) → NH 3(g) 2. Heterogenous reactions: States are different. Fe(s) + Cu. Cl 2(aq) → Fe. Cl 2(aq) + Cu(s) Na(s) + C 2 H 5 OH(aq) →C 2 H 5 ONa(aq)+H 2(g)
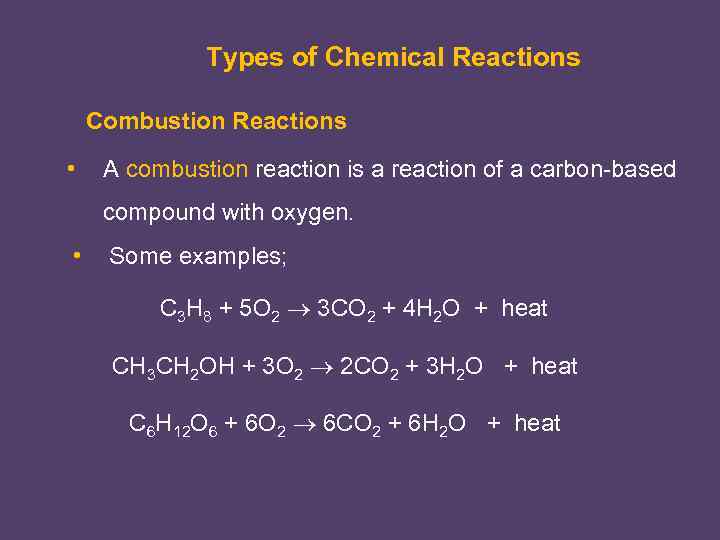
Types of Chemical Reactions Combustion Reactions • A combustion reaction is a reaction of a carbon-based compound with oxygen. • Some examples; C 3 H 8 + 5 O 2 3 CO 2 + 4 H 2 O + heat CH 3 CH 2 OH + 3 O 2 2 CO 2 + 3 H 2 O + heat C 6 H 12 O 6 + 6 O 2 6 CO 2 + 6 H 2 O + heat
Chemical Reactions.pptx