a5e105f135fcca04b09f18e84cd4aa33.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 65
 5 th Edition PPT 14 -1
5 th Edition PPT 14 -1
 Chapter 14 Buying Merchandise Mc. Graw-Hill/Irwin PPT 14 -2 Retailing Management, 5/e Levy/Weitz: Copyright © 2004 by The Mc. Graw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved.
Chapter 14 Buying Merchandise Mc. Graw-Hill/Irwin PPT 14 -2 Retailing Management, 5/e Levy/Weitz: Copyright © 2004 by The Mc. Graw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved.
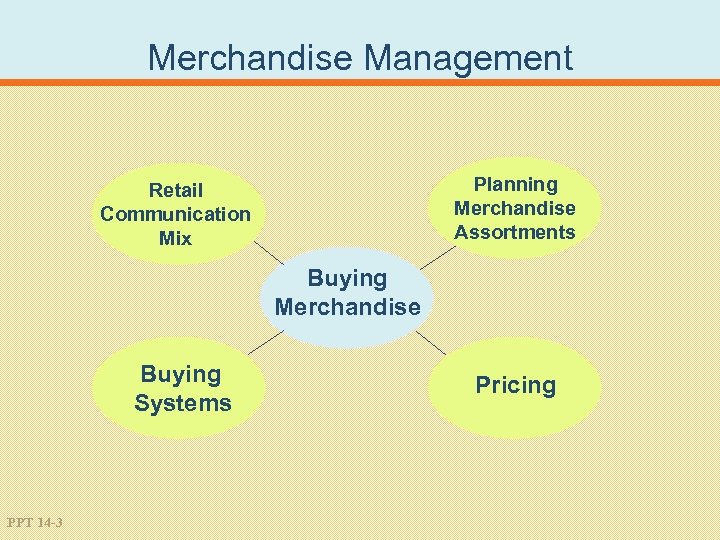 Merchandise Management Planning Merchandise Assortments Retail Communication Mix Buying Merchandise Buying Systems PPT 14 -3 Pricing
Merchandise Management Planning Merchandise Assortments Retail Communication Mix Buying Merchandise Buying Systems PPT 14 -3 Pricing
 Merchandise Branding Strategies • Manufacturer (National) Brands – Designed, produced, and marketed by a vendor and sold by many retailers • Private-Label (Store) Brands – Developed by retailer and only sold in retailer’s outlets • Licensed Brand PPT 14 -4 – Developed by licensee and right sold to either manufacturer or retailer
Merchandise Branding Strategies • Manufacturer (National) Brands – Designed, produced, and marketed by a vendor and sold by many retailers • Private-Label (Store) Brands – Developed by retailer and only sold in retailer’s outlets • Licensed Brand PPT 14 -4 – Developed by licensee and right sold to either manufacturer or retailer
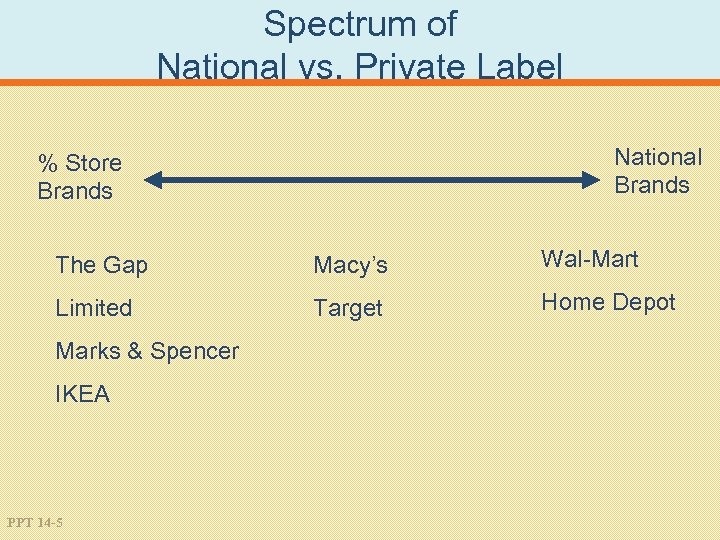 Spectrum of National vs. Private Label National Brands % Store Brands The Gap Macy’s Wal-Mart Limited Target Home Depot Marks & Spencer IKEA PPT 14 -5
Spectrum of National vs. Private Label National Brands % Store Brands The Gap Macy’s Wal-Mart Limited Target Home Depot Marks & Spencer IKEA PPT 14 -5
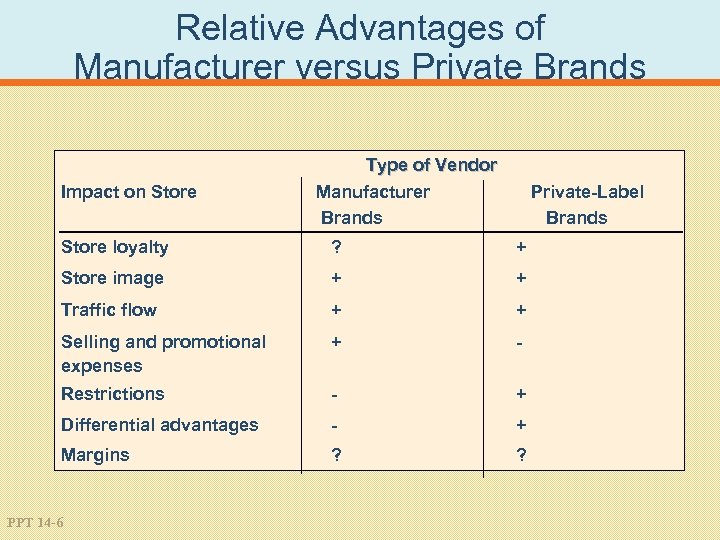 Relative Advantages of Manufacturer versus Private Brands Impact on Store Type of Vendor Manufacturer Brands Private-Label Brands Store loyalty ? + Store image + + Traffic flow + + Selling and promotional expenses + - Restrictions - + Differential advantages - + Margins ? ? PPT 14 -6
Relative Advantages of Manufacturer versus Private Brands Impact on Store Type of Vendor Manufacturer Brands Private-Label Brands Store loyalty ? + Store image + + Traffic flow + + Selling and promotional expenses + - Restrictions - + Differential advantages - + Margins ? ? PPT 14 -6
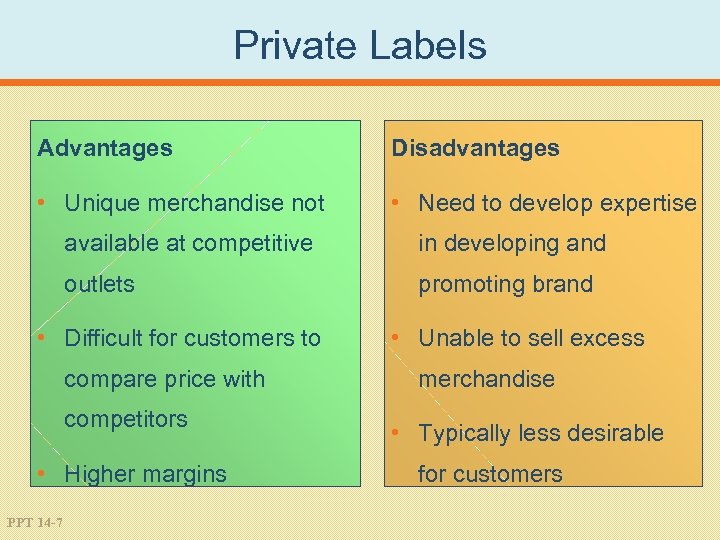 Private Labels Advantages Disadvantages • Unique merchandise not • Need to develop expertise available at competitive in developing and outlets promoting brand • Difficult for customers to compare price with competitors • Higher margins PPT 14 -7 • Unable to sell excess merchandise • Typically less desirable for customers
Private Labels Advantages Disadvantages • Unique merchandise not • Need to develop expertise available at competitive in developing and outlets promoting brand • Difficult for customers to compare price with competitors • Higher margins PPT 14 -7 • Unable to sell excess merchandise • Typically less desirable for customers
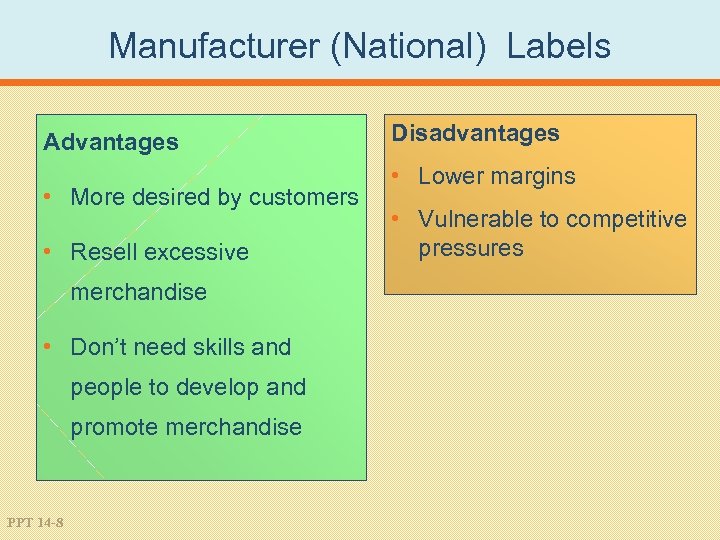 Manufacturer (National) Labels Advantages • More desired by customers • Resell excessive merchandise • Don’t need skills and people to develop and promote merchandise PPT 14 -8 Disadvantages • Lower margins • Vulnerable to competitive pressures
Manufacturer (National) Labels Advantages • More desired by customers • Resell excessive merchandise • Don’t need skills and people to develop and promote merchandise PPT 14 -8 Disadvantages • Lower margins • Vulnerable to competitive pressures
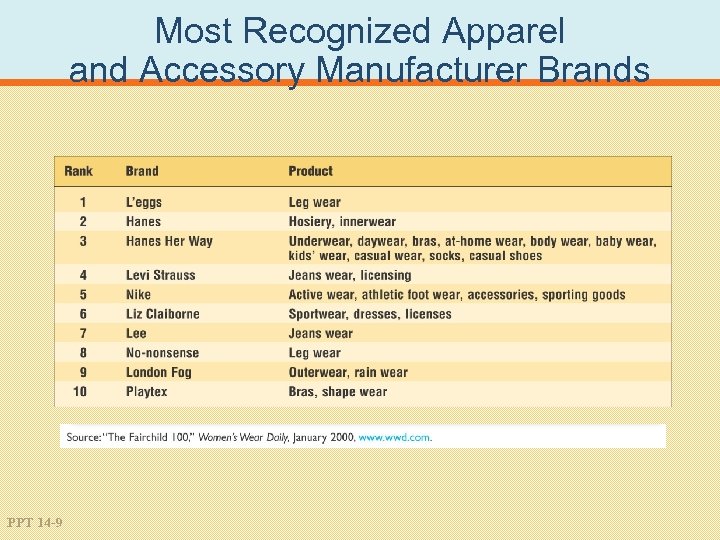 Most Recognized Apparel and Accessory Manufacturer Brands PPT 14 -9
Most Recognized Apparel and Accessory Manufacturer Brands PPT 14 -9
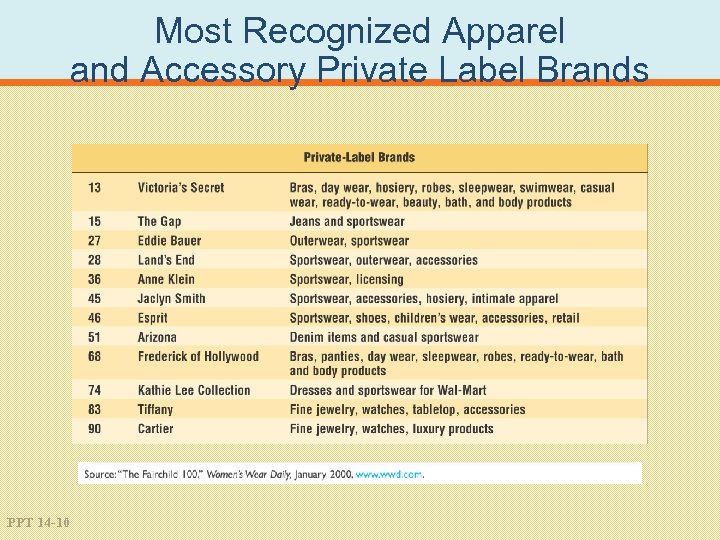 Most Recognized Apparel and Accessory Private Label Brands PPT 14 -10
Most Recognized Apparel and Accessory Private Label Brands PPT 14 -10
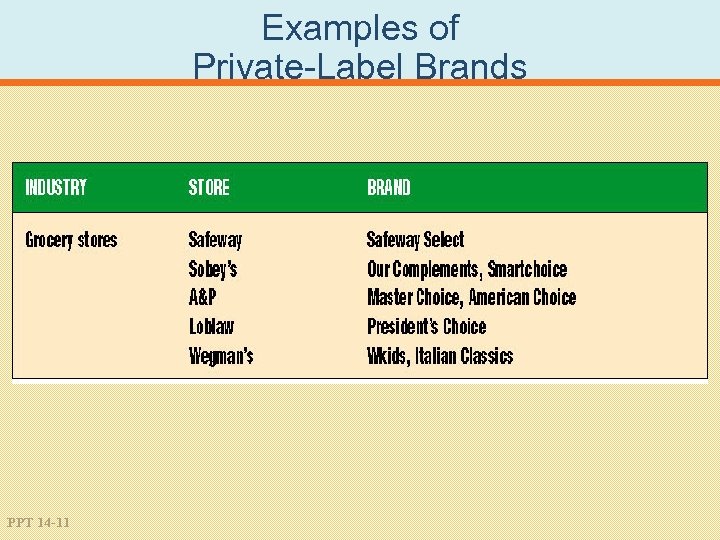 Examples of Private-Label Brands PPT 14 -11
Examples of Private-Label Brands PPT 14 -11
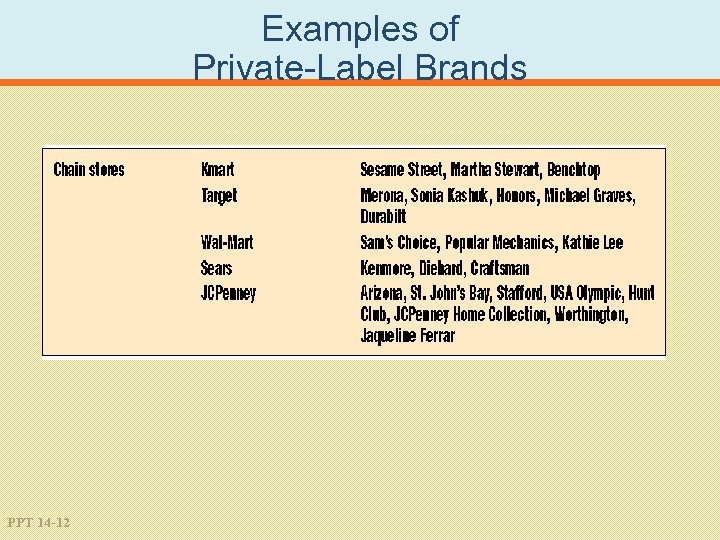 Examples of Private-Label Brands PPT 14 -12
Examples of Private-Label Brands PPT 14 -12
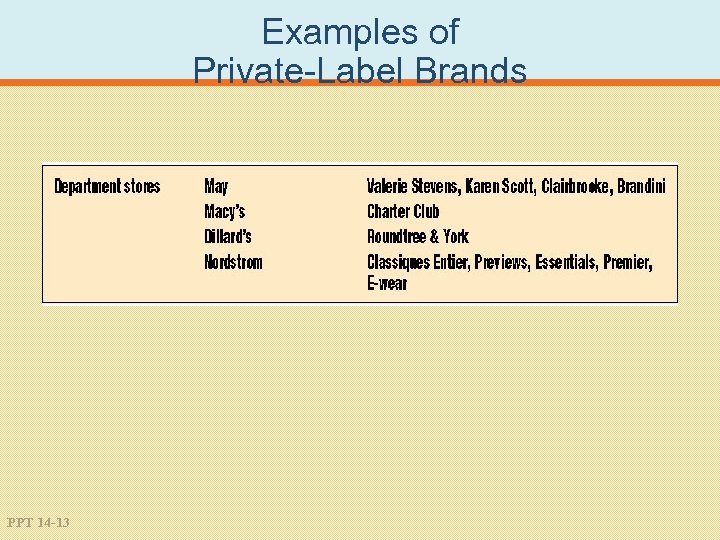 Examples of Private-Label Brands PPT 14 -13
Examples of Private-Label Brands PPT 14 -13
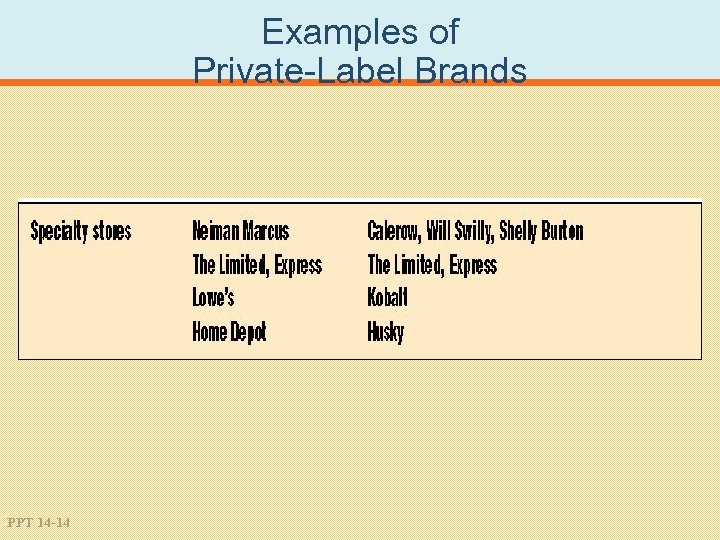 Examples of Private-Label Brands PPT 14 -14
Examples of Private-Label Brands PPT 14 -14
 Private Label Options • Bargain Branding – no-frills product at a discount price. • Copycat Branding – imitates the manufacturer brand in appearance and trade dress • Premium Branding – private label at a comparable manufacturer-brand quality. • Parallel Branding – private labels that closely imitate the trade dress and product attributes of leading manufacturer brands. PPT 14 -15
Private Label Options • Bargain Branding – no-frills product at a discount price. • Copycat Branding – imitates the manufacturer brand in appearance and trade dress • Premium Branding – private label at a comparable manufacturer-brand quality. • Parallel Branding – private labels that closely imitate the trade dress and product attributes of leading manufacturer brands. PPT 14 -15
 Issues in International Sourcing of Private Label Merchandise • Country of Origin Effects • Costs – Foreign Currency Fluctuations – Tariffs – Supply Chain Efficiency and Inventory Carrying Costs – Transportation costs • Quality Control PPT 14 -16
Issues in International Sourcing of Private Label Merchandise • Country of Origin Effects • Costs – Foreign Currency Fluctuations – Tariffs – Supply Chain Efficiency and Inventory Carrying Costs – Transportation costs • Quality Control PPT 14 -16
 Regulations Affecting the Costs of Importing Goods • World Trade Organization • NAFTA • Maquiladores • Free Trade Zones PPT 14 -17
Regulations Affecting the Costs of Importing Goods • World Trade Organization • NAFTA • Maquiladores • Free Trade Zones PPT 14 -17
 Managing International Sources • Quality Control • More difficult to maintain quality standards • Human Right Issues • Need to Build Strategic Partnerships PPT 14 -18
Managing International Sources • Quality Control • More difficult to maintain quality standards • Human Right Issues • Need to Build Strategic Partnerships PPT 14 -18
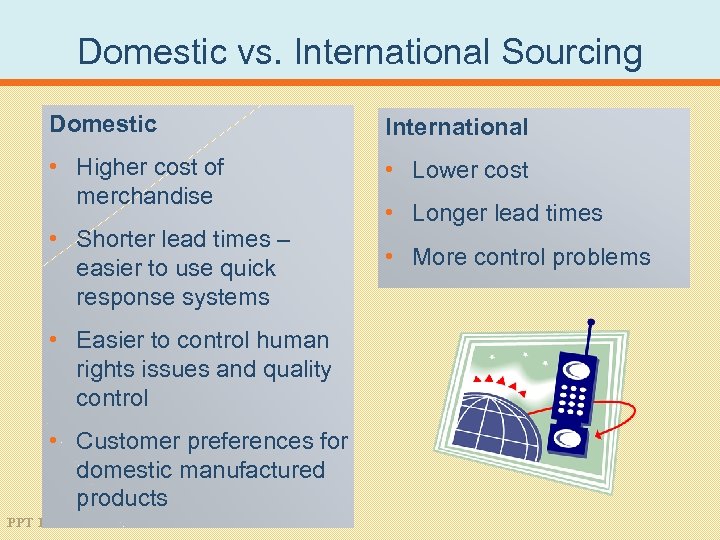 Domestic vs. International Sourcing Domestic International • Higher cost of merchandise • Lower cost • Shorter lead times – easier to use quick response systems • More control problems • Easier to control human rights issues and quality control • Customer preferences for domestic manufactured products PPT 14 -19 • Longer lead times
Domestic vs. International Sourcing Domestic International • Higher cost of merchandise • Lower cost • Shorter lead times – easier to use quick response systems • More control problems • Easier to control human rights issues and quality control • Customer preferences for domestic manufactured products PPT 14 -19 • Longer lead times
 Connecting with Vendors Going to Market • Internet Exchanges • Wholesale Market Centers • Trade Shows • Resident Buying Offices • Meeting Vendors at Your Company PPT 14 -20
Connecting with Vendors Going to Market • Internet Exchanges • Wholesale Market Centers • Trade Shows • Resident Buying Offices • Meeting Vendors at Your Company PPT 14 -20
 Functions Provided by Internet Exchanges • Product Directories • Use of Reverse Auctions • Collaboration in Planning – CPRF Software • General Information about Trends PPT 14 -21
Functions Provided by Internet Exchanges • Product Directories • Use of Reverse Auctions • Collaboration in Planning – CPRF Software • General Information about Trends PPT 14 -21
 Types of Exchanges • Consortium Exchanges – Transora – Worldwide Retail Exchange – Gobal. Net. Xchange • Private Exchanges • Independent Exchanges PPT 14 -22
Types of Exchanges • Consortium Exchanges – Transora – Worldwide Retail Exchange – Gobal. Net. Xchange • Private Exchanges • Independent Exchanges PPT 14 -22
 Online Reverse Auctions • Auction – A market institution with an explicit set of rules determining resource allocation and prices on the basis of bids from market participants. • Why reverse? – Vendors bid for buyer’s business – Price falls • One buyer, multiple vendors • Sealed vs. open bid auctions PPT 14 -23
Online Reverse Auctions • Auction – A market institution with an explicit set of rules determining resource allocation and prices on the basis of bids from market participants. • Why reverse? – Vendors bid for buyer’s business – Price falls • One buyer, multiple vendors • Sealed vs. open bid auctions PPT 14 -23
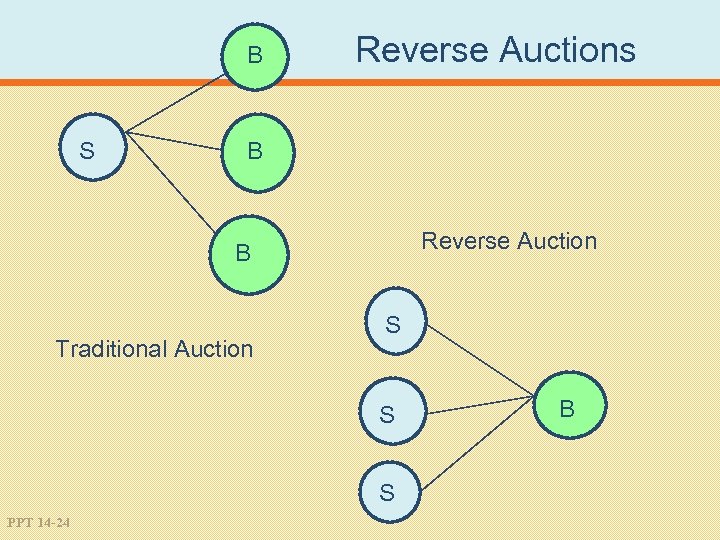 B S Reverse Auctions B Reverse Auction B Traditional Auction S S S PPT 14 -24 B
B S Reverse Auctions B Reverse Auction B Traditional Auction S S S PPT 14 -24 B
 Reverse Auctions in Retail Buying • Online vs. physical differences – Reduced contact cost – Instant feedback – Bidder anonymity • The retailer’s goals – Gain competitive pricing – Open vendor base – Improve negotiation process – Maintain valuable relationships PPT 14 -25
Reverse Auctions in Retail Buying • Online vs. physical differences – Reduced contact cost – Instant feedback – Bidder anonymity • The retailer’s goals – Gain competitive pricing – Open vendor base – Improve negotiation process – Maintain valuable relationships PPT 14 -25
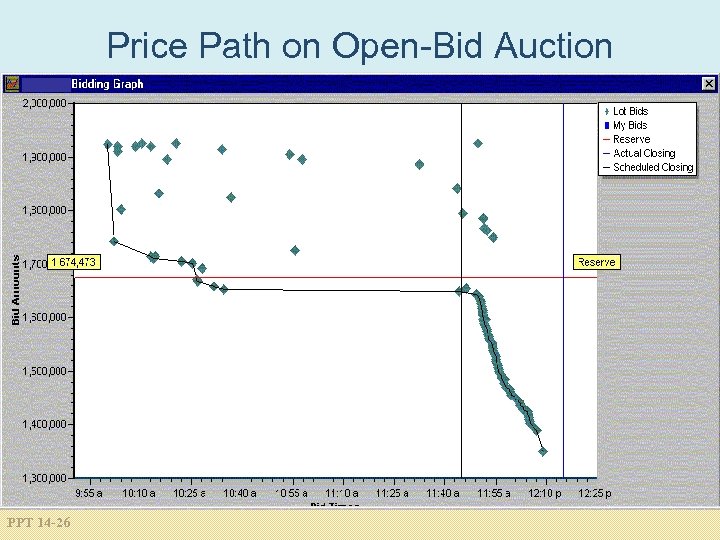 Price Path on Open-Bid Auction PPT 14 -26
Price Path on Open-Bid Auction PPT 14 -26
 Issues in Using Reverse Auctions to Buy Products • Private vs. Collaborative Auctions/Exchanges • Fixed Cost High for Software – Standardized Software Less Need for Collaborative Exchanges • Collusion • Consideration of Quality Differences from Bidders • Impact on Supplier Relationships – Used Primarily for Non-Resale Products – Carpet, Fixtures PPT 14 -27
Issues in Using Reverse Auctions to Buy Products • Private vs. Collaborative Auctions/Exchanges • Fixed Cost High for Software – Standardized Software Less Need for Collaborative Exchanges • Collusion • Consideration of Quality Differences from Bidders • Impact on Supplier Relationships – Used Primarily for Non-Resale Products – Carpet, Fixtures PPT 14 -27
 Negotiating with Vendors Two-way communication designed to reach an agreement when two parties have both shared and conflicting interests. PPT 14 -28
Negotiating with Vendors Two-way communication designed to reach an agreement when two parties have both shared and conflicting interests. PPT 14 -28
 Planning Negotiations • Consider prior history • Assess current situation – General market conditions – Vendor’s position – Power of vendor • Set goals • Be aware of vendor’s goal’s • Number of people involved PPT 14 -29 • Select an advantageous place
Planning Negotiations • Consider prior history • Assess current situation – General market conditions – Vendor’s position – Power of vendor • Set goals • Be aware of vendor’s goal’s • Number of people involved PPT 14 -29 • Select an advantageous place
 Issues to Negotiation • Markup opportunities from excess from vendor’s excess merchandise • Purchase terms • Transportation costs • Delivery times • Exclusivity • Advertising allowances PPT 14 -30
Issues to Negotiation • Markup opportunities from excess from vendor’s excess merchandise • Purchase terms • Transportation costs • Delivery times • Exclusivity • Advertising allowances PPT 14 -30
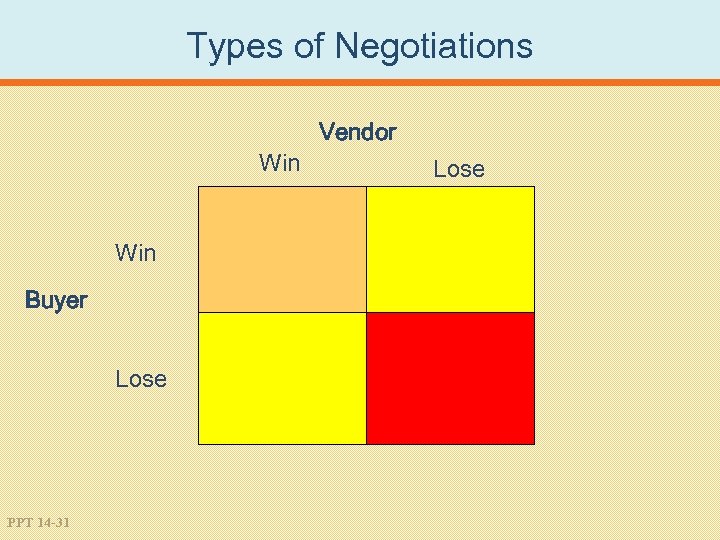 Types of Negotiations Win Buyer Lose PPT 14 -31 Vendor Lose
Types of Negotiations Win Buyer Lose PPT 14 -31 Vendor Lose
 Win - Lose Negotiation • Can be good in the short run and bad in the long-run • Short-term solution-- person you are negotiating with can’t lose all the time • Might degenerate into LOSE - LOSE PPT 14 -32
Win - Lose Negotiation • Can be good in the short run and bad in the long-run • Short-term solution-- person you are negotiating with can’t lose all the time • Might degenerate into LOSE - LOSE PPT 14 -32
 Lose - Lose Negotiation • Wastes time and energy • No relationships established • Objectives not met PPT 14 -33
Lose - Lose Negotiation • Wastes time and energy • No relationships established • Objectives not met PPT 14 -33
 Win - Win Negotiation Collaboration Cooperation Long-term relationship PPT 14 -34 Doesn’t mean “giving-in” Enhances vendor trust
Win - Win Negotiation Collaboration Cooperation Long-term relationship PPT 14 -34 Doesn’t mean “giving-in” Enhances vendor trust
 Guidelines for Negotiations • Separate people from problem • Insist on objective criteria to evaluate performance • Invent options for mutual gain • Let the other party do the talking • Know how far to go PPT 14 -35
Guidelines for Negotiations • Separate people from problem • Insist on objective criteria to evaluate performance • Invent options for mutual gain • Let the other party do the talking • Know how far to go PPT 14 -35
 Negotiating Tips • Be aware of time • Location -- comfortable • Keep negotiating participants even • Be patient • Let him/her mention a figure • Don’t be afraid to say “no” PPT 14 -36
Negotiating Tips • Be aware of time • Location -- comfortable • Keep negotiating participants even • Be patient • Let him/her mention a figure • Don’t be afraid to say “no” PPT 14 -36
 Negotiating Tips • Don’t over negotiate • Don’t assume • Visualize the negotiation • Timing is everything • Always leave the door open • Maintain self-esteem PPT 14 -37
Negotiating Tips • Don’t over negotiate • Don’t assume • Visualize the negotiation • Timing is everything • Always leave the door open • Maintain self-esteem PPT 14 -37
 SUMMARY • Planning is critical • Knowledge is power • A person will only do what is right for him/her PPT 14 -38
SUMMARY • Planning is critical • Knowledge is power • A person will only do what is right for him/her PPT 14 -38
 Strategic (Partnering) Relationships Retailer and vendor committed to maintaining relationships over the long-term and investing in mutually beneficial opportunities PPT 14 -39
Strategic (Partnering) Relationships Retailer and vendor committed to maintaining relationships over the long-term and investing in mutually beneficial opportunities PPT 14 -39
 Strategic Relationships Win – Win --Concerned about expanding the pie, not how to divide the pie Retailer PPT 14 -40 vs. Vendor
Strategic Relationships Win – Win --Concerned about expanding the pie, not how to divide the pie Retailer PPT 14 -40 vs. Vendor
 Building Blocks for Strategic Partnerships • Mutual Trust • Open Communications • Common Goals • Credible Commitments PPT 14 -41
Building Blocks for Strategic Partnerships • Mutual Trust • Open Communications • Common Goals • Credible Commitments PPT 14 -41
 Developing Trust: Capability or Competence Salespeople demonstrate competence when they can show that they know what they are talking about. Requires knowledge of: The customer The product The industry The competition PPT 14 -42
Developing Trust: Capability or Competence Salespeople demonstrate competence when they can show that they know what they are talking about. Requires knowledge of: The customer The product The industry The competition PPT 14 -42
 Stages in Building Strategic Relationships • Awareness • Exploration • Expansion • Commitment PPT 14 -43
Stages in Building Strategic Relationships • Awareness • Exploration • Expansion • Commitment PPT 14 -43
 Legal and Ethical Issues • Contractual Disputes • Chargebacks • Commercial Bribery • Slotting Allowances • Buybacks • Counterfeit Merchandise • Refusal to Deal • Tying Contracts PPT 14 -44 • Gray Markets and Diverted Merchandise • Exclusive Territories • Exclusive Dealing
Legal and Ethical Issues • Contractual Disputes • Chargebacks • Commercial Bribery • Slotting Allowances • Buybacks • Counterfeit Merchandise • Refusal to Deal • Tying Contracts PPT 14 -44 • Gray Markets and Diverted Merchandise • Exclusive Territories • Exclusive Dealing
 Chargebacks • A practice used by retailers in which they deduct money from the amount they owe a vendor. • Two Reasons: – merchandise isn’t selling – vendor mistakes • Can be a profit center – one senior executive at a large department store chain was told to collect $50 million on chargebacks PPT 14 -45
Chargebacks • A practice used by retailers in which they deduct money from the amount they owe a vendor. • Two Reasons: – merchandise isn’t selling – vendor mistakes • Can be a profit center – one senior executive at a large department store chain was told to collect $50 million on chargebacks PPT 14 -45
 Commercial Bribery • A vendor or its agent offers to give or pay a retail buyer “something of value” to influence purchasing decisions. • A fine line between the social courtesy of a free lunch and an elaborate free vacation. • Rule of thumb - accept only limited entertainment or token gifts. PPT 14 -46
Commercial Bribery • A vendor or its agent offers to give or pay a retail buyer “something of value” to influence purchasing decisions. • A fine line between the social courtesy of a free lunch and an elaborate free vacation. • Rule of thumb - accept only limited entertainment or token gifts. PPT 14 -46
 Slotting Allowances • Fees paid by a vendor for space in a retail store. • Currently aren’t legal. • Retailers argue that they are a reasonable method for ensuring that their valuable space is used efficiently. • Manufacturers view them as extortion. • $9 billion or 16% of all new product introduction costs in grocery industry. PPT 14 -47
Slotting Allowances • Fees paid by a vendor for space in a retail store. • Currently aren’t legal. • Retailers argue that they are a reasonable method for ensuring that their valuable space is used efficiently. • Manufacturers view them as extortion. • $9 billion or 16% of all new product introduction costs in grocery industry. PPT 14 -47
 Buybacks • Used to get products into retail stores. • Two scenarios: – Retailer allows a vendor to create space for its goods by “buying back” a competitors inventory and removing it from a retailer’s system. – Retailer forces a vendor to buyback slow-moving merchandise. PPT 14 -48
Buybacks • Used to get products into retail stores. • Two scenarios: – Retailer allows a vendor to create space for its goods by “buying back” a competitors inventory and removing it from a retailer’s system. – Retailer forces a vendor to buyback slow-moving merchandise. PPT 14 -48
 Counterfeit Merchandise • Goods made and sold without the permission of the owner of a trademark, a copyright, or a patented invention that is legally protected in the country where it is marketed. • Major problem is counterfeiting intellectual property. PPT 14 -49
Counterfeit Merchandise • Goods made and sold without the permission of the owner of a trademark, a copyright, or a patented invention that is legally protected in the country where it is marketed. • Major problem is counterfeiting intellectual property. PPT 14 -49
 What to do About Counterfeiters • Trademark, copyright, and/or patent products in the countries in which they’re sold. • US government is engaged in bilateral and multicultural negotiations and education to limit counterfeiting. (WTO) • Take steps to protect yourself. PPT 14 -50
What to do About Counterfeiters • Trademark, copyright, and/or patent products in the countries in which they’re sold. • US government is engaged in bilateral and multicultural negotiations and education to limit counterfeiting. (WTO) • Take steps to protect yourself. PPT 14 -50
 Gray-Market and Diverted Merchandise • Gray- Market Merchandise possesses a valid U. S. registered trademark and is made by a foreign manufacturer but is imported into the United States without permission of the U. S. trademark owner. • Not Counterfeit. • Is legal. • Diverted Merchandise is similar to gray-market merchandise except there need not be distribution across international boundaries. PPT 14 -51
Gray-Market and Diverted Merchandise • Gray- Market Merchandise possesses a valid U. S. registered trademark and is made by a foreign manufacturer but is imported into the United States without permission of the U. S. trademark owner. • Not Counterfeit. • Is legal. • Diverted Merchandise is similar to gray-market merchandise except there need not be distribution across international boundaries. PPT 14 -51
 Gray-market and Diverted Merchandise: Taking Sides • Discount stores argue customers benefit because it lowers prices. • Traditional retailers claim important service after sale will be unavailable • May hurt the trademark’s image. PPT 14 -52
Gray-market and Diverted Merchandise: Taking Sides • Discount stores argue customers benefit because it lowers prices. • Traditional retailers claim important service after sale will be unavailable • May hurt the trademark’s image. PPT 14 -52
 Avoiding the Gray-Market Problem • Require customers to sign a contract stipulating that they will not engage in gray marketing. • Produce different versions of products for different markets. PPT 14 -53
Avoiding the Gray-Market Problem • Require customers to sign a contract stipulating that they will not engage in gray marketing. • Produce different versions of products for different markets. PPT 14 -53
 Exclusive Territories • Granted to retailers so no other retailer in the territory can sell a particular brand. • Benefits vendors by assuring them that “quality” retailers represent their products. • Assure retailers adequate supply. • Grants retailers a monopoly. • Illegal when they restrict competition. PPT 14 -54
Exclusive Territories • Granted to retailers so no other retailer in the territory can sell a particular brand. • Benefits vendors by assuring them that “quality” retailers represent their products. • Assure retailers adequate supply. • Grants retailers a monopoly. • Illegal when they restrict competition. PPT 14 -54
 Exclusive Dealing Agreements • Occur when a manufacturer or wholesaler restricts a retailer into carrying only its products and nothing from competing vendors. • Illegal when they restrict competition. PPT 14 -55
Exclusive Dealing Agreements • Occur when a manufacturer or wholesaler restricts a retailer into carrying only its products and nothing from competing vendors. • Illegal when they restrict competition. PPT 14 -55
 Tying Contracts • An agreement that requires the retailer to take a product it doesn’t necessarily desire to ensure that it can buy a product it does desire. • Illegal when they lessen competition. • Ok to protect goodwill and quality reputation of vendor. PPT 14 -56
Tying Contracts • An agreement that requires the retailer to take a product it doesn’t necessarily desire to ensure that it can buy a product it does desire. • Illegal when they lessen competition. • Ok to protect goodwill and quality reputation of vendor. PPT 14 -56
 Refusals to Deal • Suppliers and retailers have the right to deal or refuse to deal with anyone they choose. • Except when it lessens competition. PPT 14 -57
Refusals to Deal • Suppliers and retailers have the right to deal or refuse to deal with anyone they choose. • Except when it lessens competition. PPT 14 -57
 Terms of Purchase • Discounts – Trade (Functional) Discounts – Chain Discounts – Quantity Discounts – Seasonal discounts – Cash discounts • ROG and EOM dating – Anticipation discounts • Shipping Terms and Conditions PPT 14 -58
Terms of Purchase • Discounts – Trade (Functional) Discounts – Chain Discounts – Quantity Discounts – Seasonal discounts – Cash discounts • ROG and EOM dating – Anticipation discounts • Shipping Terms and Conditions PPT 14 -58
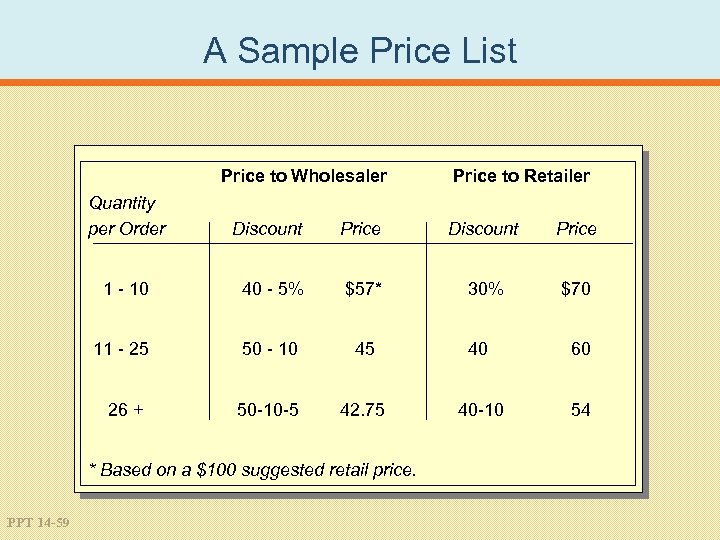 A Sample Price List Price to Wholesaler Quantity per Order Price to Retailer Discount Price 1 - 10 40 - 5% $57* 30% $70 11 - 25 50 - 10 45 40 60 26 + 50 -10 -5 42. 75 40 -10 54 * Based on a $100 suggested retail price. PPT 14 -59
A Sample Price List Price to Wholesaler Quantity per Order Price to Retailer Discount Price 1 - 10 40 - 5% $57* 30% $70 11 - 25 50 - 10 45 40 60 26 + 50 -10 -5 42. 75 40 -10 54 * Based on a $100 suggested retail price. PPT 14 -59
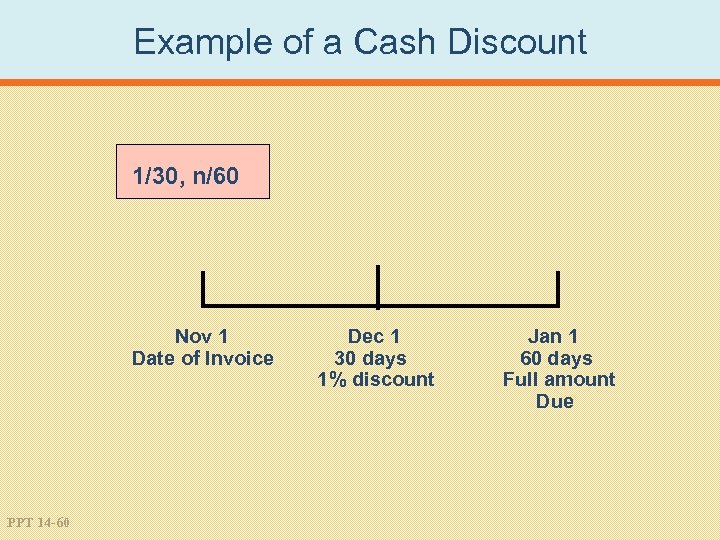 Example of a Cash Discount 1/30, n/60 Nov 1 Date of Invoice PPT 14 -60 Dec 1 30 days 1% discount Jan 1 60 days Full amount Due
Example of a Cash Discount 1/30, n/60 Nov 1 Date of Invoice PPT 14 -60 Dec 1 30 days 1% discount Jan 1 60 days Full amount Due
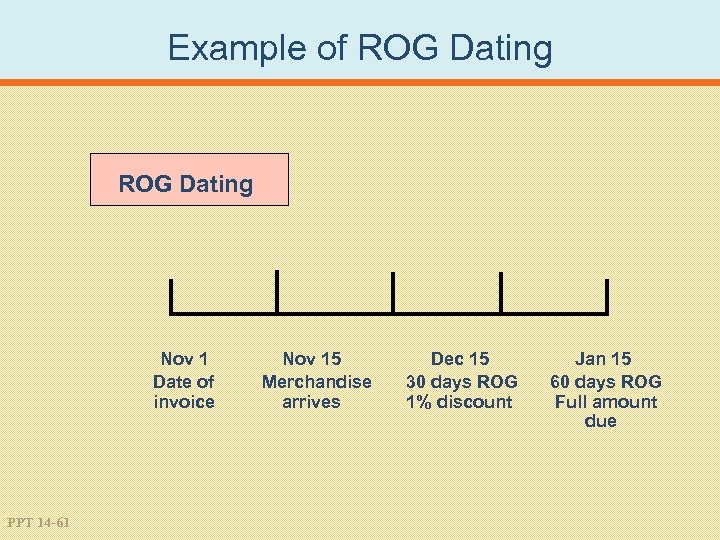 Example of ROG Dating Nov 1 Date of invoice PPT 14 -61 Nov 15 Merchandise arrives Dec 15 30 days ROG 1% discount Jan 15 60 days ROG Full amount due
Example of ROG Dating Nov 1 Date of invoice PPT 14 -61 Nov 15 Merchandise arrives Dec 15 30 days ROG 1% discount Jan 15 60 days ROG Full amount due
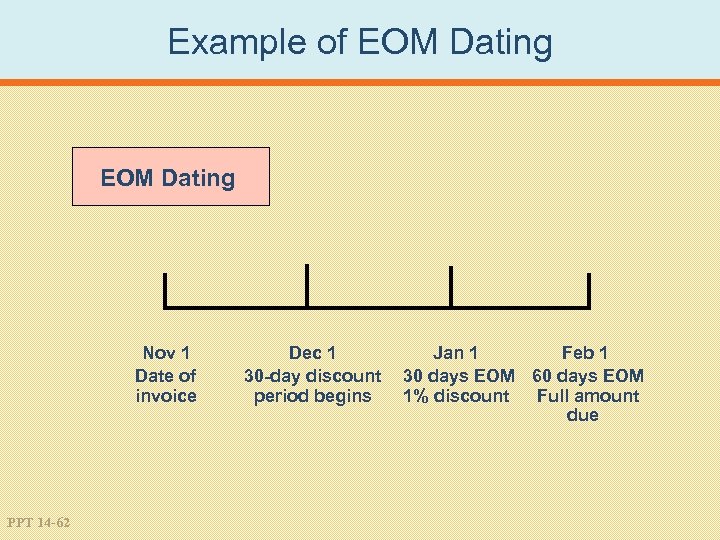 Example of EOM Dating Nov 1 Date of invoice PPT 14 -62 Dec 1 30 -day discount period begins Jan 1 Feb 1 30 days EOM 60 days EOM 1% discount Full amount due
Example of EOM Dating Nov 1 Date of invoice PPT 14 -62 Dec 1 30 -day discount period begins Jan 1 Feb 1 30 days EOM 60 days EOM 1% discount Full amount due
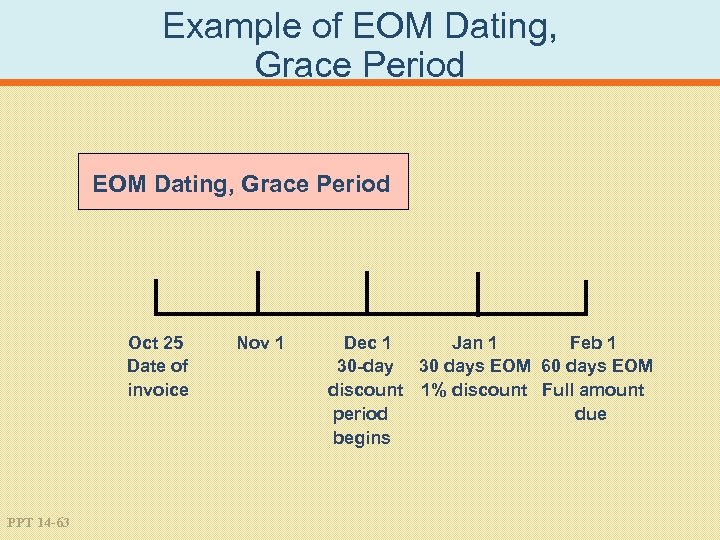 Example of EOM Dating, Grace Period Oct 25 Date of invoice PPT 14 -63 Nov 1 Dec 1 Jan 1 Feb 1 30 -day 30 days EOM 60 days EOM discount 1% discount Full amount period due begins
Example of EOM Dating, Grace Period Oct 25 Date of invoice PPT 14 -63 Nov 1 Dec 1 Jan 1 Feb 1 30 -day 30 days EOM 60 days EOM discount 1% discount Full amount period due begins
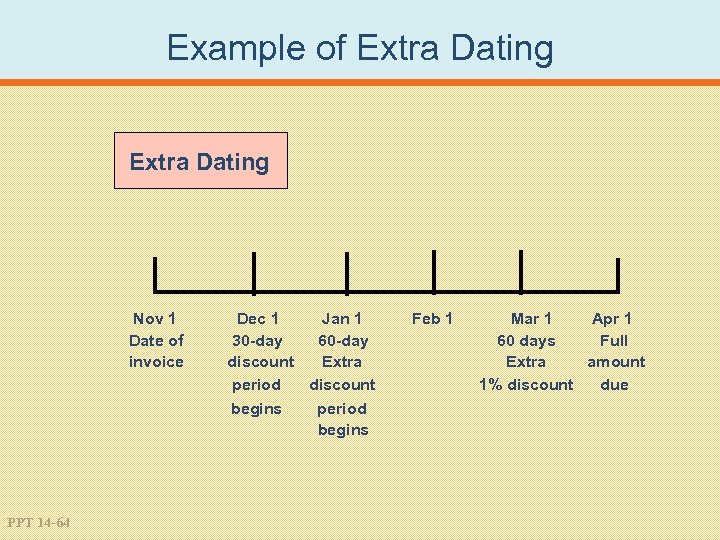 Example of Extra Dating Nov 1 Date of invoice PPT 14 -64 Dec 1 Jan 1 30 -day 60 -day discount Extra period discount begins period begins Feb 1 Mar 1 Apr 1 60 days Full Extra amount 1% discount due
Example of Extra Dating Nov 1 Date of invoice PPT 14 -64 Dec 1 Jan 1 30 -day 60 -day discount Extra period discount begins period begins Feb 1 Mar 1 Apr 1 60 days Full Extra amount 1% discount due
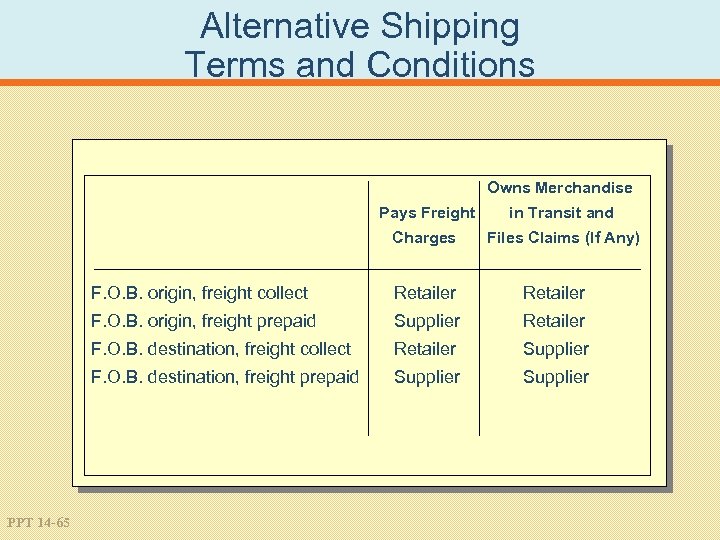 Alternative Shipping Terms and Conditions Owns Merchandise Pays Freight in Transit and Charges Files Claims (If Any) F. O. B. origin, freight collect Retailer F. O. B. origin, freight prepaid Supplier Retailer F. O. B. destination, freight collect Retailer Supplier F. O. B. destination, freight prepaid PPT 14 -65 Retailer Supplier
Alternative Shipping Terms and Conditions Owns Merchandise Pays Freight in Transit and Charges Files Claims (If Any) F. O. B. origin, freight collect Retailer F. O. B. origin, freight prepaid Supplier Retailer F. O. B. destination, freight collect Retailer Supplier F. O. B. destination, freight prepaid PPT 14 -65 Retailer Supplier


