7025440c235a2172c487cc3a115b7689.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 11
 5 -Minute Check on Activity 5 -1 1. Determine the growth factor for a 30% increase G-factor = 1 + 0. 3 = 1. 30 2. Determine the growth rate for 1. 53 G-rate = 1 – 1. 53 = 0. 53 or 53% 3. Determine the decay factor for a 16% decrease D-factor = 1 – 0. 16 = 0. 84 4. Determine the decay rate for 0. 81 D-rate = 1 – 0. 81 = 0. 19 or 19% 5. What is the growth factor if gas goes from 3. 25 / gal to 4. 25 / gal? G-factor = 4. 25/3. 25 ≈ 1. 31 6. What is the decay factor if gas goes from 4. 75 / gal to 4. 00 / gal? D-factor = 4. 00/4. 75 ≈ 0. 84 Click the mouse button or press the Space Bar to display the answers.
5 -Minute Check on Activity 5 -1 1. Determine the growth factor for a 30% increase G-factor = 1 + 0. 3 = 1. 30 2. Determine the growth rate for 1. 53 G-rate = 1 – 1. 53 = 0. 53 or 53% 3. Determine the decay factor for a 16% decrease D-factor = 1 – 0. 16 = 0. 84 4. Determine the decay rate for 0. 81 D-rate = 1 – 0. 81 = 0. 19 or 19% 5. What is the growth factor if gas goes from 3. 25 / gal to 4. 25 / gal? G-factor = 4. 25/3. 25 ≈ 1. 31 6. What is the decay factor if gas goes from 4. 75 / gal to 4. 00 / gal? D-factor = 4. 00/4. 75 ≈ 0. 84 Click the mouse button or press the Space Bar to display the answers.
 Activity 5 - 2 Take an Additional 20% Off
Activity 5 - 2 Take an Additional 20% Off
 Objectives • Define consecutive growth and decay factors • Determine a consecutive growth or decay factor from two or more consecutive percent change • Apply consecutive growth or decay factors from to solve problems involving percent changes
Objectives • Define consecutive growth and decay factors • Determine a consecutive growth or decay factor from two or more consecutive percent change • Apply consecutive growth or decay factors from to solve problems involving percent changes
 Vocabulary • Cumulative Factors – the consecutive growth or decay factors from two or more consecutive percent changes
Vocabulary • Cumulative Factors – the consecutive growth or decay factors from two or more consecutive percent changes
 Activity Your friend arrives at you house. Today’s newspaper contains a 20% off coupon at Old Navy. The $100 jacket she had been eyeing all season was already reduced by 40%. She clipped the coupon, drove to the store, selected her jacket and walked up to the register. The cashier brought up a price of $48; your friend insisted that the price should have been only $40. The store manager arrived and re-entered the transaction, and again the registered displayed $48. Your friend left without purchasing the jacket and drove straight to your house to tell you her story. How do you think your friend calculated a price of $40? 20 + 40 = 60% off 100 × (1 – 0. 6) = 40
Activity Your friend arrives at you house. Today’s newspaper contains a 20% off coupon at Old Navy. The $100 jacket she had been eyeing all season was already reduced by 40%. She clipped the coupon, drove to the store, selected her jacket and walked up to the register. The cashier brought up a price of $48; your friend insisted that the price should have been only $40. The store manager arrived and re-entered the transaction, and again the registered displayed $48. Your friend left without purchasing the jacket and drove straight to your house to tell you her story. How do you think your friend calculated a price of $40? 20 + 40 = 60% off 100 × (1 – 0. 6) = 40
 Activity cont You grab a pencil and start your own calculation. First you determine the ticketed price that reflects the 40% reduction. At what price is Old Navy selling the jacket? Explain how you calculated this price. 100 × (1 – 0. 4) = 60 To what price does the 20%-off coupon apply? 60 dollars Apply the 20% discount to determine the final price of the jacket. 60 × (1 – 0. 2) = 48 If you applied the discounts in reverse order, that is, applying the 20% coupon, followed by a 40% reduction, would the final sales price change? No
Activity cont You grab a pencil and start your own calculation. First you determine the ticketed price that reflects the 40% reduction. At what price is Old Navy selling the jacket? Explain how you calculated this price. 100 × (1 – 0. 4) = 60 To what price does the 20%-off coupon apply? 60 dollars Apply the 20% discount to determine the final price of the jacket. 60 × (1 – 0. 2) = 48 If you applied the discounts in reverse order, that is, applying the 20% coupon, followed by a 40% reduction, would the final sales price change? No
 Cumulative Factors You can form a single decay (or growth) factor that represents the cumulative effect of applying the consecutive factors; the single decay factor is the product of the three decay factors. For example: a 10% off coupon on top of 25% off all Holiday items yields (1 – 0. 10)(1 – 0. 25) = (0. 9)(0. 75) = (0. 675)
Cumulative Factors You can form a single decay (or growth) factor that represents the cumulative effect of applying the consecutive factors; the single decay factor is the product of the three decay factors. For example: a 10% off coupon on top of 25% off all Holiday items yields (1 – 0. 10)(1 – 0. 25) = (0. 9)(0. 75) = (0. 675)
 Cumulative Factors Example 1 A stunning $2000 gold and diamond necklace you saw was far too expensive to even consider. However, over several weeks you tracked the following successive discounts: 20% off list; 30% off marked price; and an additional 40% off every item. Determine the selling price after each of the discounts is taken. 2000 × (1 – 0. 2) = 1600 × (1 – 0. 3) = 1120 × (1 – 0. 4) = 672
Cumulative Factors Example 1 A stunning $2000 gold and diamond necklace you saw was far too expensive to even consider. However, over several weeks you tracked the following successive discounts: 20% off list; 30% off marked price; and an additional 40% off every item. Determine the selling price after each of the discounts is taken. 2000 × (1 – 0. 2) = 1600 × (1 – 0. 3) = 1120 × (1 – 0. 4) = 672
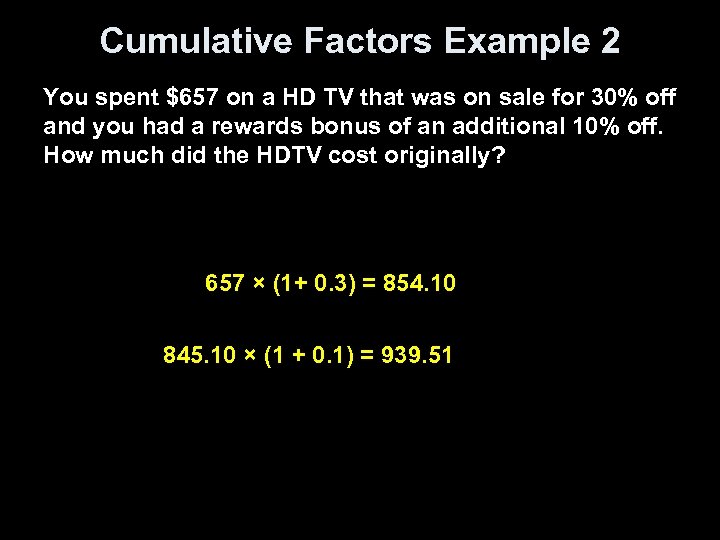 Cumulative Factors Example 2 You spent $657 on a HD TV that was on sale for 30% off and you had a rewards bonus of an additional 10% off. How much did the HDTV cost originally? 657 × (1+ 0. 3) = 854. 10 845. 10 × (1 + 0. 1) = 939. 51
Cumulative Factors Example 2 You spent $657 on a HD TV that was on sale for 30% off and you had a rewards bonus of an additional 10% off. How much did the HDTV cost originally? 657 × (1+ 0. 3) = 854. 10 845. 10 × (1 + 0. 1) = 939. 51
 Cumulative Factors Example 3 You purchased $1000 of a recommended stock last year and watched gleefully as it rose quickly by 30%. Unfortunately, the economy turned downward, and your stock recently fell 30% from last year’s high. Have you made or lost money on your investment? 1000 × (1+ 0. 3) = 1300 × (1 – 0. 3) = 910 1000 – 910 = 90 dollar loss
Cumulative Factors Example 3 You purchased $1000 of a recommended stock last year and watched gleefully as it rose quickly by 30%. Unfortunately, the economy turned downward, and your stock recently fell 30% from last year’s high. Have you made or lost money on your investment? 1000 × (1+ 0. 3) = 1300 × (1 – 0. 3) = 910 1000 – 910 = 90 dollar loss
 Summary and Homework • Summary – Cumulative effect of a sequence of percent changes is the product of the associated growth or decay factors – Cumulative effect of a sequence of percent changes is the same regardless of the order the changes are applied • Homework – pg 542; problems 1 – 6
Summary and Homework • Summary – Cumulative effect of a sequence of percent changes is the product of the associated growth or decay factors – Cumulative effect of a sequence of percent changes is the same regardless of the order the changes are applied • Homework – pg 542; problems 1 – 6


