36b84a3851fb97a12dbddd7c2f0d1955.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 14
 (4) Stacks and Queues ISC 241 Data Structures Dr. Jehad Al Dallal Spring 2017/2018 © 2009 Jehad Al Dallal
(4) Stacks and Queues ISC 241 Data Structures Dr. Jehad Al Dallal Spring 2017/2018 © 2009 Jehad Al Dallal
 Outlines n Stacks n n Example Applications Implementation Queues n n n Example Applications Implementation © 2009 Jehad Al Dallal Stacks and Queues 2
Outlines n Stacks n n Example Applications Implementation Queues n n n Example Applications Implementation © 2009 Jehad Al Dallal Stacks and Queues 2
 Stacks n n Last In First Out It has a top element and the following operations: n n n Push: to add an element to the stack Pop: to delete an element to the stack is. Empty: to check whether the stack is empty size: to get the number of elements in the stack top: to get the top element of the stack © 2009 Jehad Al Dallal Stacks and Queues 3
Stacks n n Last In First Out It has a top element and the following operations: n n n Push: to add an element to the stack Pop: to delete an element to the stack is. Empty: to check whether the stack is empty size: to get the number of elements in the stack top: to get the top element of the stack © 2009 Jehad Al Dallal Stacks and Queues 3
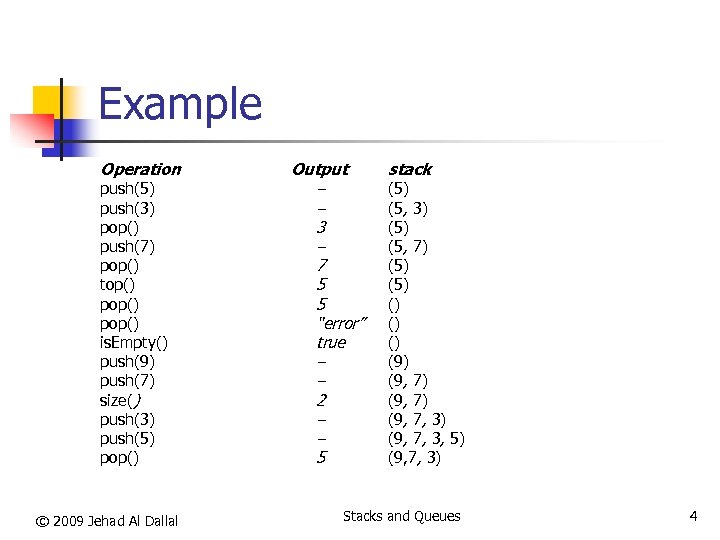 Example Operation push(5) push(3) pop() push(7) pop() top() pop() is. Empty() push(9) push(7) size() push(3) push(5) pop() © 2009 Jehad Al Dallal Output – – 3 – 7 5 5 “error” true – – 2 – – 5 stack (5) (5, 3) (5, 7) (5) () (9) (9, 7) (9, 7, 3, 5) (9, 7, 3) Stacks and Queues 4
Example Operation push(5) push(3) pop() push(7) pop() top() pop() is. Empty() push(9) push(7) size() push(3) push(5) pop() © 2009 Jehad Al Dallal Output – – 3 – 7 5 5 “error” true – – 2 – – 5 stack (5) (5, 3) (5, 7) (5) () (9) (9, 7) (9, 7, 3, 5) (9, 7, 3) Stacks and Queues 4
 Applications of Stacks n n n Page-visited history in a Web browser Undo sequence in a text editor Chain of method calls in the Java Virtual Machine © 2009 Jehad Al Dallal Stacks and Queues 5
Applications of Stacks n n n Page-visited history in a Web browser Undo sequence in a text editor Chain of method calls in the Java Virtual Machine © 2009 Jehad Al Dallal Stacks and Queues 5
 Implementation n Can be implemented using n n n An array A linked list A doubly linked list © 2009 Jehad Al Dallal Stacks and Queues 6
Implementation n Can be implemented using n n n An array A linked list A doubly linked list © 2009 Jehad Al Dallal Stacks and Queues 6
 Queues n n First In First Out (FIFO) It has a top element and the following operations: n n n enqueue: to add an element to the queue dequeue: to delete an element to the queue is. Empty: to check whether the queue is empty size: to get the number of elements in the queue front: to get the oldest element in the queue © 2009 Jehad Al Dallal Stacks and Queues 7
Queues n n First In First Out (FIFO) It has a top element and the following operations: n n n enqueue: to add an element to the queue dequeue: to delete an element to the queue is. Empty: to check whether the queue is empty size: to get the number of elements in the queue front: to get the oldest element in the queue © 2009 Jehad Al Dallal Stacks and Queues 7
 Example Operation enqueue(5) enqueue(3) dequeue() enqueue(7) dequeue() front() dequeue() is. Empty() enqueue(9) enqueue(7) size() enqueue(3) enqueue(5) dequeue() © 2009 Jehad Al Dallal Output – – 5 – 3 7 7 “error” true – – 2 – – 9 Q (5) (5, 3) (3, 7) (7) () (9) (9, 7) (9, 7, 3, 5) (7, 3, 5) Stacks and Queues 8
Example Operation enqueue(5) enqueue(3) dequeue() enqueue(7) dequeue() front() dequeue() is. Empty() enqueue(9) enqueue(7) size() enqueue(3) enqueue(5) dequeue() © 2009 Jehad Al Dallal Output – – 5 – 3 7 7 “error” true – – 2 – – 9 Q (5) (5, 3) (3, 7) (7) () (9) (9, 7) (9, 7, 3, 5) (7, 3, 5) Stacks and Queues 8
 Applications of Queues n n n Waiting lists Access to shared resources (e. g. , printer) Multiprogramming © 2009 Jehad Al Dallal Stacks and Queues 9
Applications of Queues n n n Waiting lists Access to shared resources (e. g. , printer) Multiprogramming © 2009 Jehad Al Dallal Stacks and Queues 9
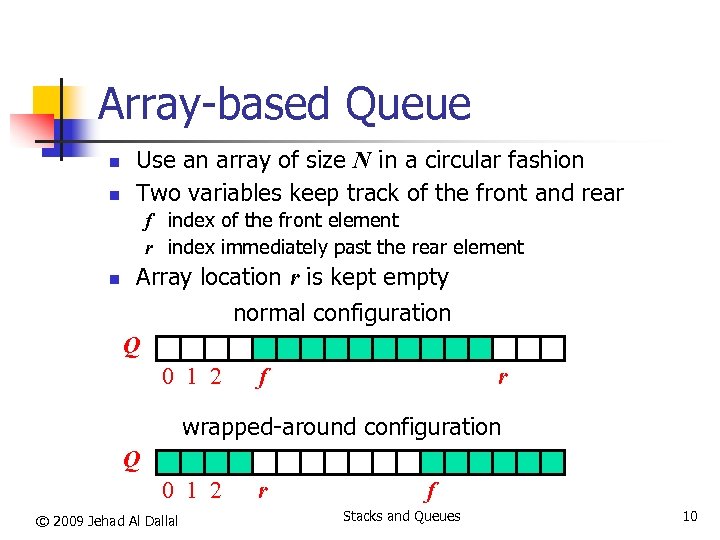 Array-based Queue n n Use an array of size N in a circular fashion Two variables keep track of the front and rear f index of the front element r index immediately past the rear element n Array location r is kept empty normal configuration Q 0 1 2 f r wrapped-around configuration Q 0 1 2 © 2009 Jehad Al Dallal r f Stacks and Queues 10
Array-based Queue n n Use an array of size N in a circular fashion Two variables keep track of the front and rear f index of the front element r index immediately past the rear element n Array location r is kept empty normal configuration Q 0 1 2 f r wrapped-around configuration Q 0 1 2 © 2009 Jehad Al Dallal r f Stacks and Queues 10
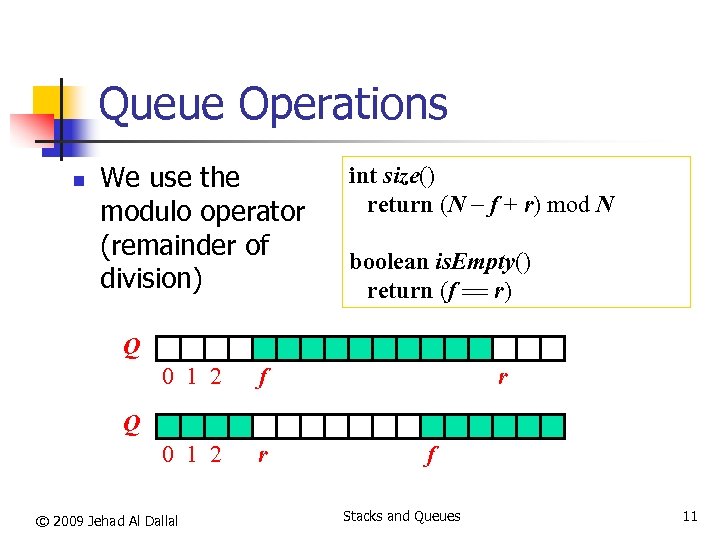 Queue Operations n We use the modulo operator (remainder of division) int size() return (N f + r) mod N boolean is. Empty() return (f == r) Q 0 1 2 f 0 1 2 r r Q © 2009 Jehad Al Dallal f Stacks and Queues 11
Queue Operations n We use the modulo operator (remainder of division) int size() return (N f + r) mod N boolean is. Empty() return (f == r) Q 0 1 2 f 0 1 2 r r Q © 2009 Jehad Al Dallal f Stacks and Queues 11
![Queue Operations (cont. ) void enqueue(o) if (size() == N 1) error else Q[r] Queue Operations (cont. ) void enqueue(o) if (size() == N 1) error else Q[r]](https://present5.com/presentation/36b84a3851fb97a12dbddd7c2f0d1955/image-12.jpg) Queue Operations (cont. ) void enqueue(o) if (size() == N 1) error else Q[r] = o r = (r + 1) mod N Q 0 1 2 f 0 1 2 r r Q © 2009 Jehad Al Dallal f Stacks and Queues 12
Queue Operations (cont. ) void enqueue(o) if (size() == N 1) error else Q[r] = o r = (r + 1) mod N Q 0 1 2 f 0 1 2 r r Q © 2009 Jehad Al Dallal f Stacks and Queues 12
![Queue Operations (cont. ) object dequeue() if (is. Empty()) error else o = Q[f] Queue Operations (cont. ) object dequeue() if (is. Empty()) error else o = Q[f]](https://present5.com/presentation/36b84a3851fb97a12dbddd7c2f0d1955/image-13.jpg) Queue Operations (cont. ) object dequeue() if (is. Empty()) error else o = Q[f] f = (f + 1) mod N return o Q 0 1 2 f 0 1 2 r r Q © 2009 Jehad Al Dallal f Stacks and Queues 13
Queue Operations (cont. ) object dequeue() if (is. Empty()) error else o = Q[f] f = (f + 1) mod N return o Q 0 1 2 f 0 1 2 r r Q © 2009 Jehad Al Dallal f Stacks and Queues 13
 Reference n Data Structures and Algorithms in Java, Michael T. Goodrich and Roberto Tamassia, John Wiley & Sons, Inc, 6 th Edition, 2015 © 2009 Jehad Al Dallal Stacks and Queues 14
Reference n Data Structures and Algorithms in Java, Michael T. Goodrich and Roberto Tamassia, John Wiley & Sons, Inc, 6 th Edition, 2015 © 2009 Jehad Al Dallal Stacks and Queues 14


