 4. 6 – Graphs of Composite Trigonometric Functions
4. 6 – Graphs of Composite Trigonometric Functions
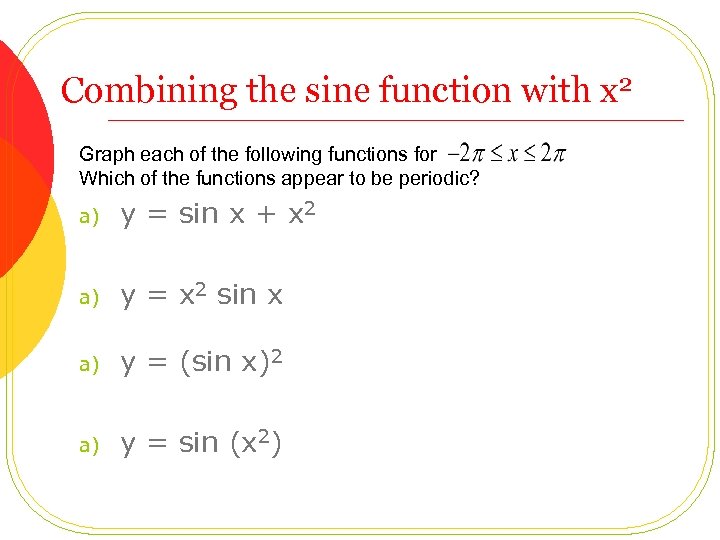 Combining the sine function with x 2 Graph each of the following functions for Which of the functions appear to be periodic? a) y = sin x + x 2 a) y = x 2 sin x a) y = (sin x)2 a) y = sin (x 2)
Combining the sine function with x 2 Graph each of the following functions for Which of the functions appear to be periodic? a) y = sin x + x 2 a) y = x 2 sin x a) y = (sin x)2 a) y = sin (x 2)
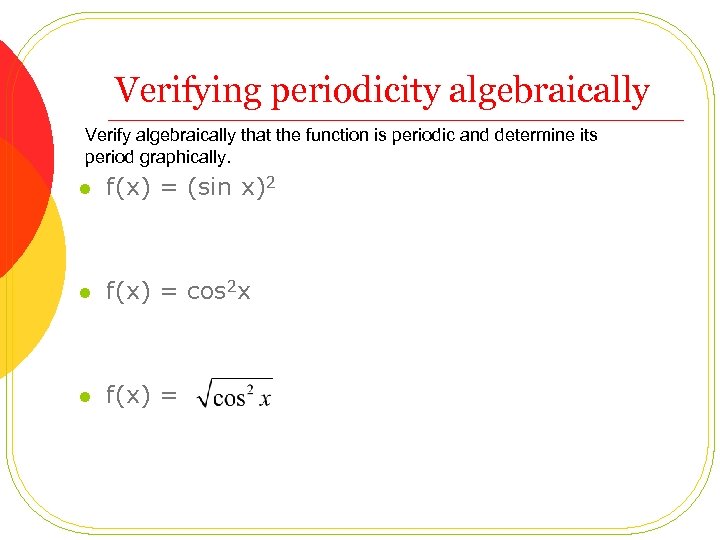 Verifying periodicity algebraically Verify algebraically that the function is periodic and determine its period graphically. l f(x) = (sin x)2 l f(x) = cos 2 x l f(x) =
Verifying periodicity algebraically Verify algebraically that the function is periodic and determine its period graphically. l f(x) = (sin x)2 l f(x) = cos 2 x l f(x) =
 Composing y = sin x and y = x 3 Prove algebraically that f(x) = sin 3 x is periodic and find the period graphically:
Composing y = sin x and y = x 3 Prove algebraically that f(x) = sin 3 x is periodic and find the period graphically:
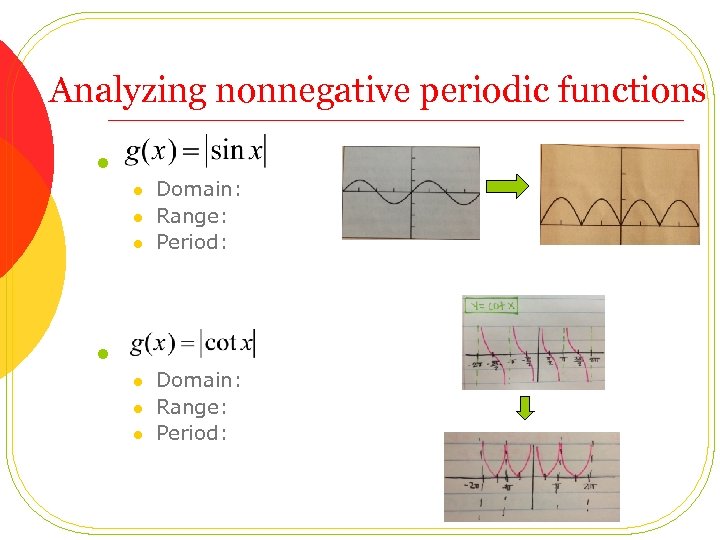 Analyzing nonnegative periodic functions l l l l Domain: Range: Period:
Analyzing nonnegative periodic functions l l l l Domain: Range: Period:
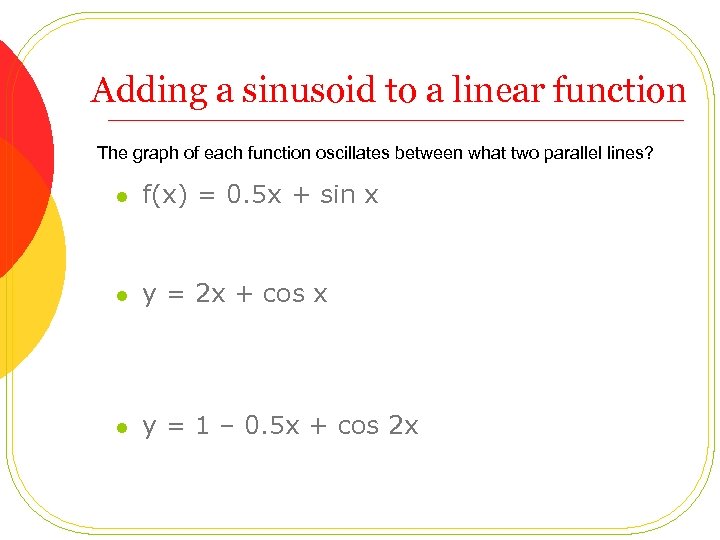 Adding a sinusoid to a linear function The graph of each function oscillates between what two parallel lines? l f(x) = 0. 5 x + sin x l y = 2 x + cos x l y = 1 – 0. 5 x + cos 2 x
Adding a sinusoid to a linear function The graph of each function oscillates between what two parallel lines? l f(x) = 0. 5 x + sin x l y = 2 x + cos x l y = 1 – 0. 5 x + cos 2 x
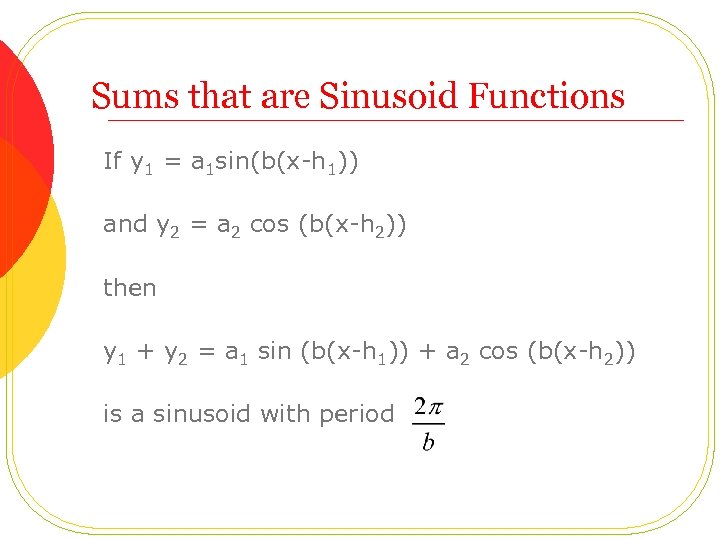 Sums that are Sinusoid Functions If y 1 = a 1 sin(b(x-h 1)) and y 2 = a 2 cos (b(x-h 2)) then y 1 + y 2 = a 1 sin (b(x-h 1)) + a 2 cos (b(x-h 2)) is a sinusoid with period
Sums that are Sinusoid Functions If y 1 = a 1 sin(b(x-h 1)) and y 2 = a 2 cos (b(x-h 2)) then y 1 + y 2 = a 1 sin (b(x-h 1)) + a 2 cos (b(x-h 2)) is a sinusoid with period
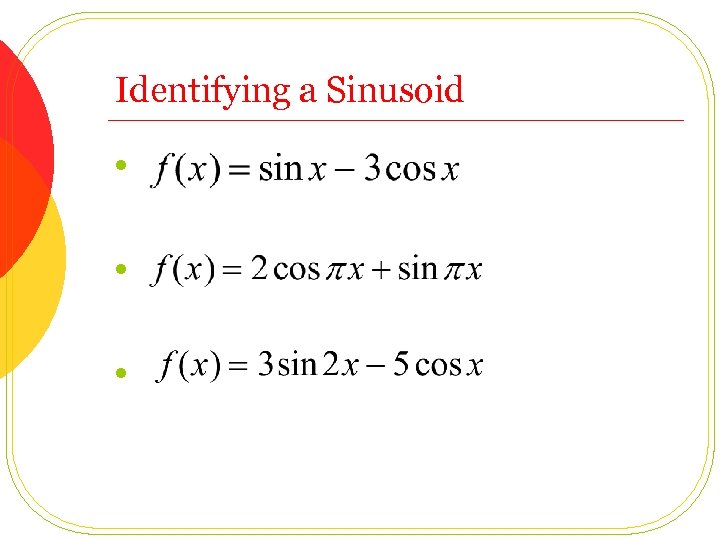 Identifying a Sinusoid l l l
Identifying a Sinusoid l l l
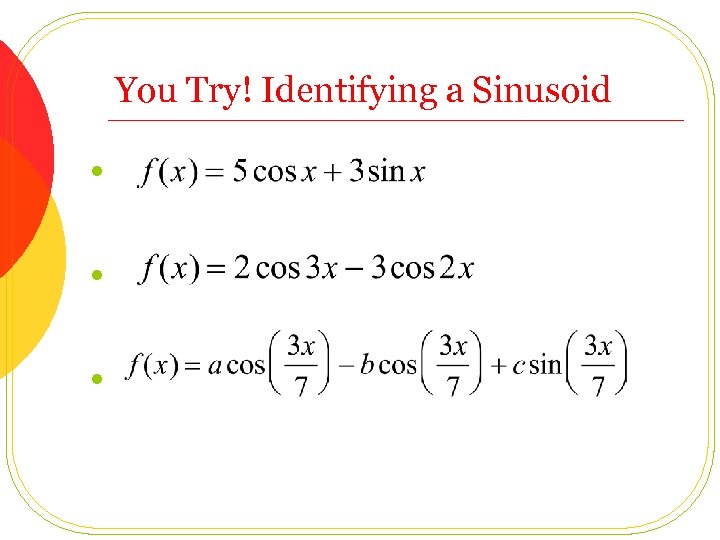 You Try! Identifying a Sinusoid l l l
You Try! Identifying a Sinusoid l l l
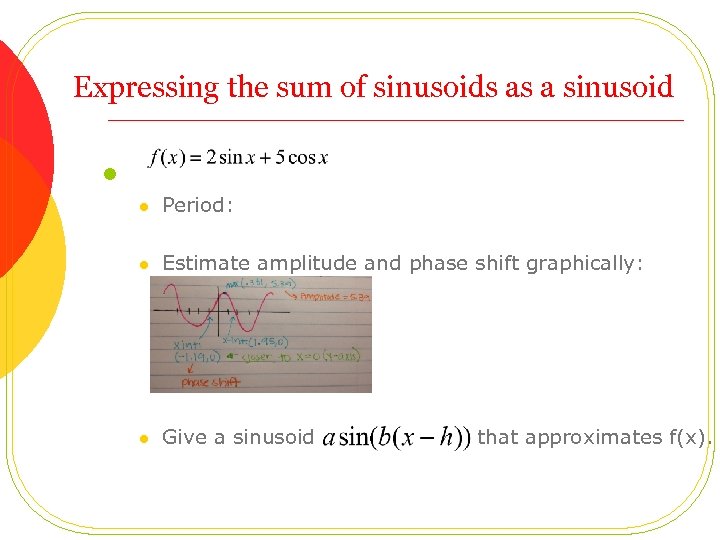 Expressing the sum of sinusoids as a sinusoid l l Period: l Estimate amplitude and phase shift graphically: l Give a sinusoid that approximates f(x).
Expressing the sum of sinusoids as a sinusoid l l Period: l Estimate amplitude and phase shift graphically: l Give a sinusoid that approximates f(x).
 Showing a function is periodic but not a sinusoid l f(x) = sin 2 x + cos 3 x l f(x) = 2 cos x + cos 3 x
Showing a function is periodic but not a sinusoid l f(x) = sin 2 x + cos 3 x l f(x) = 2 cos x + cos 3 x
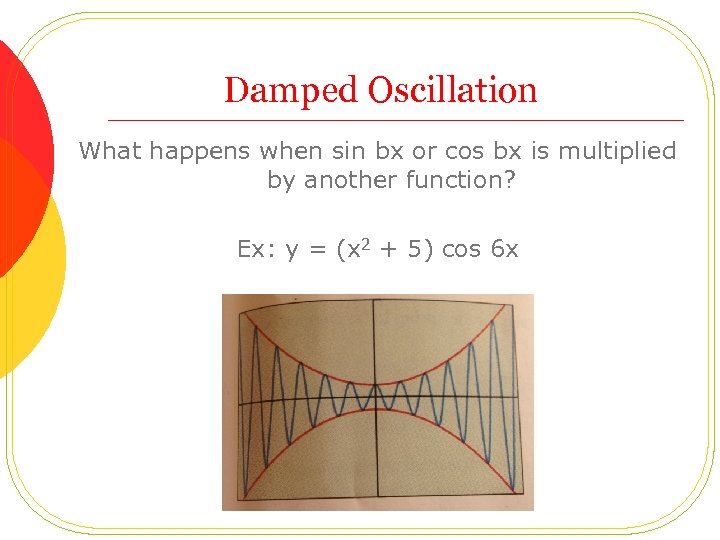 Damped Oscillation What happens when sin bx or cos bx is multiplied by another function? Ex: y = (x 2 + 5) cos 6 x
Damped Oscillation What happens when sin bx or cos bx is multiplied by another function? Ex: y = (x 2 + 5) cos 6 x
 Damped Oscillation The graph of y = f(x) cos bx or y = f(x) sin bx oscillates between the graphs of y = f(x) and y = -f(x). When this reduces the amplitude of the wave, it is called damped oscillation. The factor of f(x) is called the damping factor.
Damped Oscillation The graph of y = f(x) cos bx or y = f(x) sin bx oscillates between the graphs of y = f(x) and y = -f(x). When this reduces the amplitude of the wave, it is called damped oscillation. The factor of f(x) is called the damping factor.
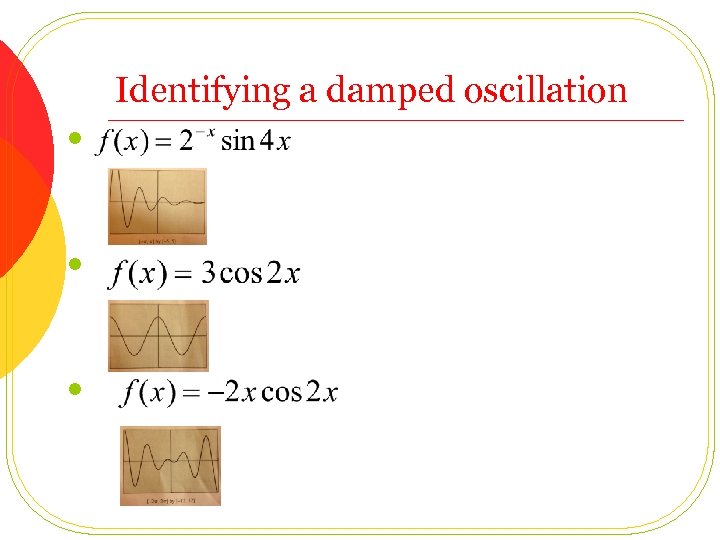 Identifying a damped oscillation l l l
Identifying a damped oscillation l l l
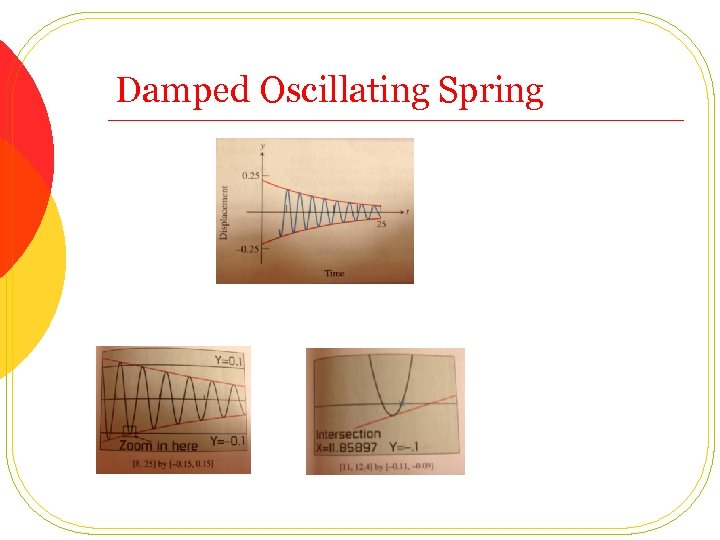
 A damped oscillation spring Ms. Samara’s Precalculus class collected data for an air table glider that oscillated between two springs. The class determined from the data that the equation : Modeled the displacement y of the spring from its original position as a function of time t. a) Identify the damping factor and tell where the damping occurs b) Approximately how long does it take for the spring to be damped so that ?
A damped oscillation spring Ms. Samara’s Precalculus class collected data for an air table glider that oscillated between two springs. The class determined from the data that the equation : Modeled the displacement y of the spring from its original position as a function of time t. a) Identify the damping factor and tell where the damping occurs b) Approximately how long does it take for the spring to be damped so that ?
 Damped Oscillating Spring
Damped Oscillating Spring