 4. 1 Day II: Additive, Multiplicative and Ciphered Systems of Numeration By the end of class you will be able to convert numbers among Hindu-Arabic, Chinese and Greek
4. 1 Day II: Additive, Multiplicative and Ciphered Systems of Numeration By the end of class you will be able to convert numbers among Hindu-Arabic, Chinese and Greek
 Some Chinese Examples: =63 So What Do You Notice? ? =725
Some Chinese Examples: =63 So What Do You Notice? ? =725
 Chinese Numeration System: • Read from bottom up • Group numbers in 2: top number is multiplied by bottom number which is a power of 10 • The bottom number is the units digit (not multiplied by anything • Need to add zeros if they appear consecutively in the middle of the number • 11 -19 not written as powers of 10
Chinese Numeration System: • Read from bottom up • Group numbers in 2: top number is multiplied by bottom number which is a power of 10 • The bottom number is the units digit (not multiplied by anything • Need to add zeros if they appear consecutively in the middle of the number • 11 -19 not written as powers of 10
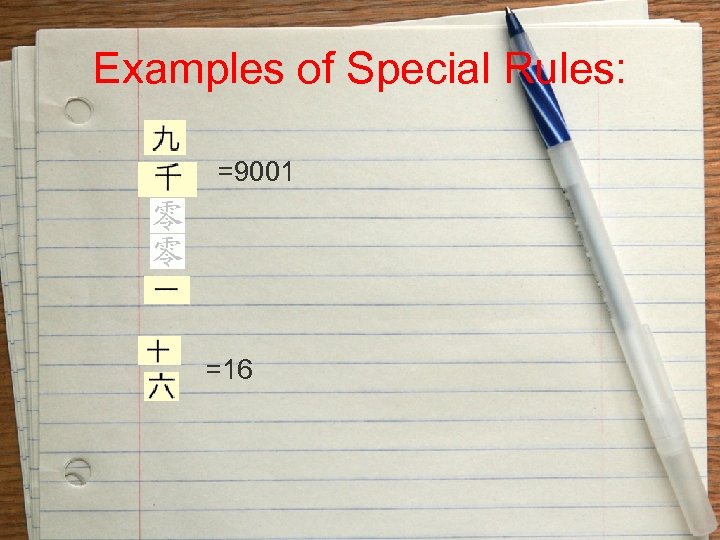 Examples of Special Rules: =9001 =16
Examples of Special Rules: =9001 =16
 Conversions 1) 3) 577 2) 4) 703
Conversions 1) 3) 577 2) 4) 703
 Iconic Greek System • Ciphered System: there are numerals for numbers up to the base, and numerals for multiples of the base (multiples of 10 in this case) • Uses Greek letters of alphabet • Has a multiplicative property: place I as a superscript in front of a number to multiply by 1000
Iconic Greek System • Ciphered System: there are numerals for numbers up to the base, and numerals for multiples of the base (multiples of 10 in this case) • Uses Greek letters of alphabet • Has a multiplicative property: place I as a superscript in front of a number to multiply by 1000
 Write in Hindu Arabic • 1) • 2) • 3) • 4)
Write in Hindu Arabic • 1) • 2) • 3) • 4)
 Write in Greek • 1) 285 • 2) 311 • 3) 1012
Write in Greek • 1) 285 • 2) 311 • 3) 1012
 Summarizer • 1) Create a 4 -foldable with labels “Egyptian”, “Roman”, “Chinese” “Greek” • 2) Write a different numeral in each box • 3) Your partner will convert the numerals to Hindu-Arabic, and write a fact about each numeration system • 4) Check your partner’s work
Summarizer • 1) Create a 4 -foldable with labels “Egyptian”, “Roman”, “Chinese” “Greek” • 2) Write a different numeral in each box • 3) Your partner will convert the numerals to Hindu-Arabic, and write a fact about each numeration system • 4) Check your partner’s work