12a9e4dceac73f1b18586fc3bb557d73.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 22
 4 -1
4 -1
 Chapter 4 Consumer Markets and Buying Behavior 4 -2 Mc. Graw-Hill/Irwin Copyright © 2004 by The Mc. Graw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved.
Chapter 4 Consumer Markets and Buying Behavior 4 -2 Mc. Graw-Hill/Irwin Copyright © 2004 by The Mc. Graw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved.
 Chapter Goals • • Factors used to explain consumer behavior Consumer demographic changes Consumers decision-making Influences affecting consumers’ decisions 4 -3 Mc. Graw-Hill/Irwin Copyright © 2004 by The Mc. Graw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved.
Chapter Goals • • Factors used to explain consumer behavior Consumer demographic changes Consumers decision-making Influences affecting consumers’ decisions 4 -3 Mc. Graw-Hill/Irwin Copyright © 2004 by The Mc. Graw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved.
 The Consumer Market ULTIMATE CONSUMERS Buy goods and services for their own personal or household use 4 -4
The Consumer Market ULTIMATE CONSUMERS Buy goods and services for their own personal or household use 4 -4
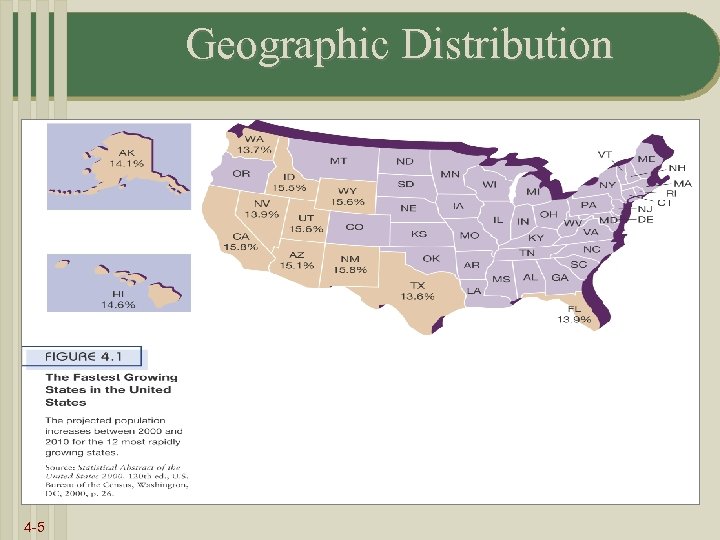 Geographic Distribution 4 -5
Geographic Distribution 4 -5
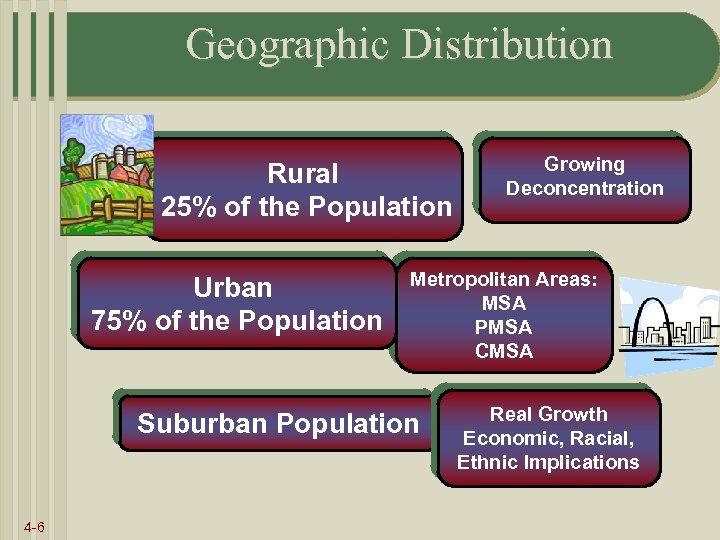 Geographic Distribution Rural 25% of the Population Urban 75% of the Population Metropolitan Areas: MSA PMSA CMSA Suburban Population 4 -6 Growing Deconcentration Real Growth Economic, Racial, Ethnic Implications
Geographic Distribution Rural 25% of the Population Urban 75% of the Population Metropolitan Areas: MSA PMSA CMSA Suburban Population 4 -6 Growing Deconcentration Real Growth Economic, Racial, Ethnic Implications
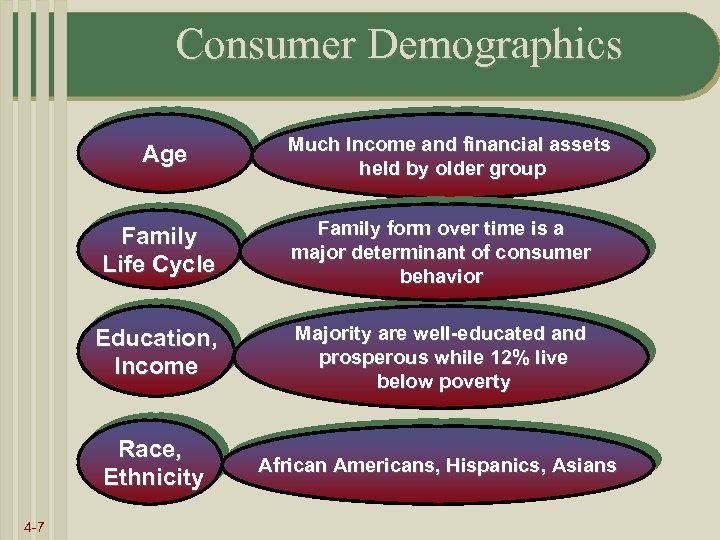 Consumer Demographics Age Much Income and financial assets held by older group Family Life Cycle Education, Income Majority are well-educated and prosperous while 12% live below poverty Race, Ethnicity 4 -7 Family form over time is a major determinant of consumer behavior African Americans, Hispanics, Asians
Consumer Demographics Age Much Income and financial assets held by older group Family Life Cycle Education, Income Majority are well-educated and prosperous while 12% live below poverty Race, Ethnicity 4 -7 Family form over time is a major determinant of consumer behavior African Americans, Hispanics, Asians
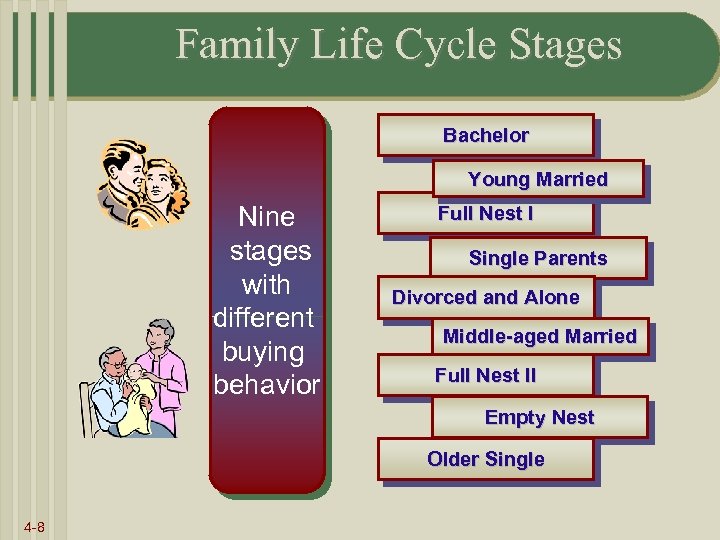 Family Life Cycle Stages Bachelor Young Married Nine stages with different buying behavior Full Nest I Single Parents Divorced and Alone Middle-aged Married Full Nest II Empty Nest Older Single 4 -8
Family Life Cycle Stages Bachelor Young Married Nine stages with different buying behavior Full Nest I Single Parents Divorced and Alone Middle-aged Married Full Nest II Empty Nest Older Single 4 -8
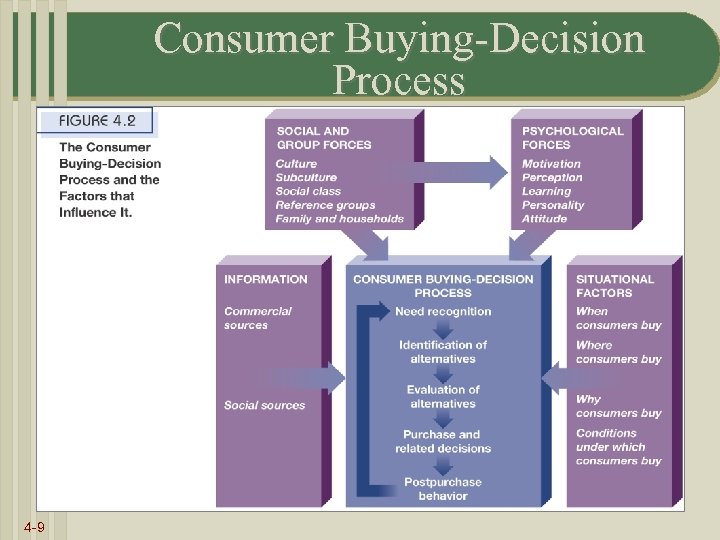 Consumer Buying-Decision Process 4 -9
Consumer Buying-Decision Process 4 -9
 Consumer Buying-Decision Process Loyalty Involvement Impulse Buying 4 -10
Consumer Buying-Decision Process Loyalty Involvement Impulse Buying 4 -10
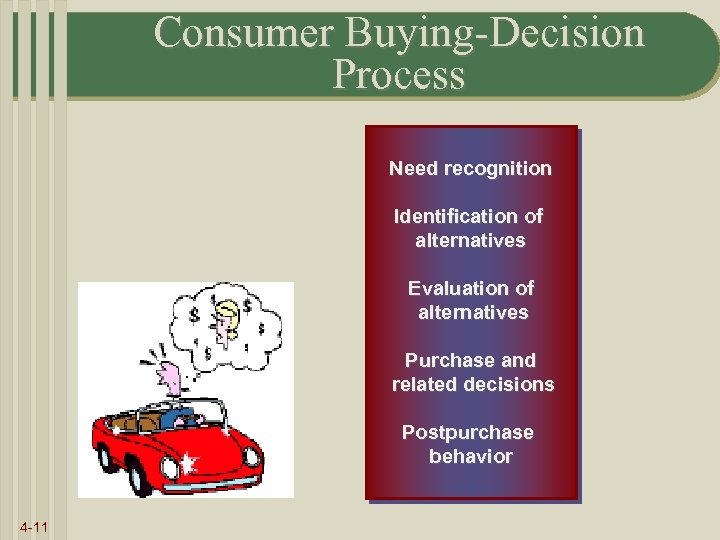 Consumer Buying-Decision Process Need recognition Identification of alternatives Evaluation of alternatives Purchase and related decisions Postpurchase behavior 4 -11
Consumer Buying-Decision Process Need recognition Identification of alternatives Evaluation of alternatives Purchase and related decisions Postpurchase behavior 4 -11
 Information and Purchase Decisions Information Commercial sources Social sources 4 -12
Information and Purchase Decisions Information Commercial sources Social sources 4 -12
 Social Influences Culture Subcultures Social class Reference groups Families and Households 4 -13
Social Influences Culture Subcultures Social class Reference groups Families and Households 4 -13
 Psychological Influences Motivation Perception Learning Personality Attitude 4 -14
Psychological Influences Motivation Perception Learning Personality Attitude 4 -14
 Maslow’s Hierarchy of Needs 4 -15
Maslow’s Hierarchy of Needs 4 -15
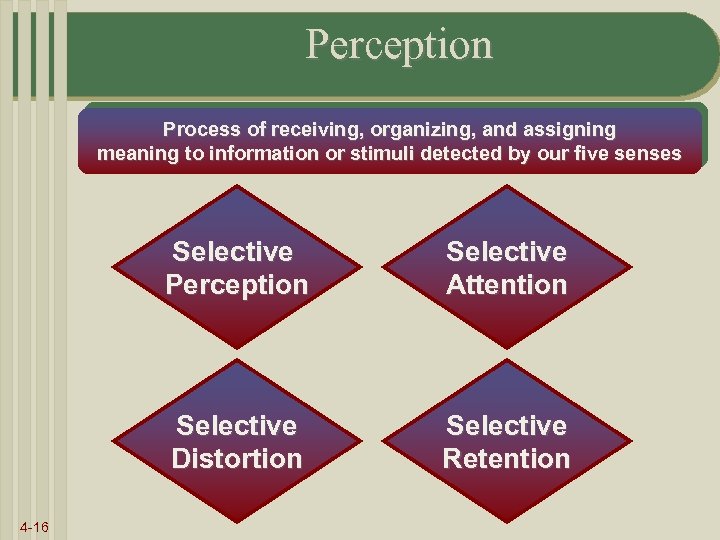 Perception Process of receiving, organizing, and assigning meaning to information or stimuli detected by our five senses Selective Perception Selective Distortion 4 -16 Selective Attention Selective Retention
Perception Process of receiving, organizing, and assigning meaning to information or stimuli detected by our five senses Selective Perception Selective Distortion 4 -16 Selective Attention Selective Retention
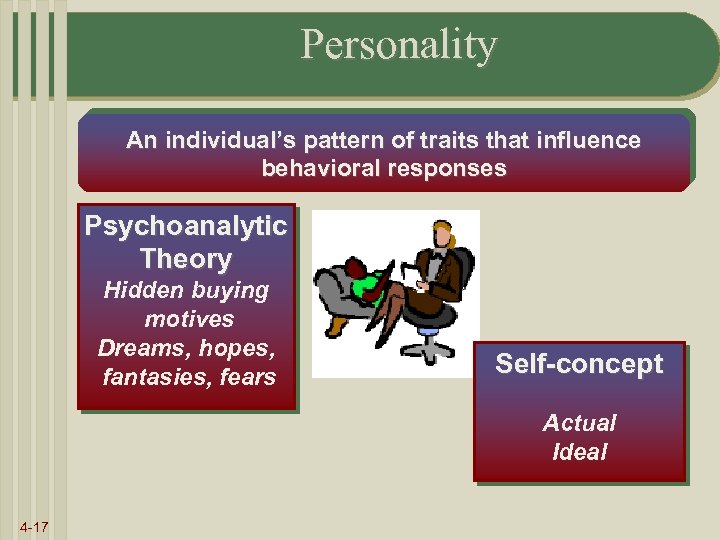 Personality An individual’s pattern of traits that influence behavioral responses Psychoanalytic Theory Hidden buying motives Dreams, hopes, fantasies, fears Self-concept Actual Ideal 4 -17
Personality An individual’s pattern of traits that influence behavioral responses Psychoanalytic Theory Hidden buying motives Dreams, hopes, fantasies, fears Self-concept Actual Ideal 4 -17
 Attitudes Learned predisposition to respond to an object in a consistently favorable or unfavorable way Characteristics Learned Object Direction Intensity Stable Generalizable 4 -18
Attitudes Learned predisposition to respond to an object in a consistently favorable or unfavorable way Characteristics Learned Object Direction Intensity Stable Generalizable 4 -18
 Situational Factors When consumers buy Where consumers buy Why consumers buy Conditions under which consumers buy 4 -19
Situational Factors When consumers buy Where consumers buy Why consumers buy Conditions under which consumers buy 4 -19
 Situational Influences Surroundings Time Consumer Moods and Motives 4 -20 Terms
Situational Influences Surroundings Time Consumer Moods and Motives 4 -20 Terms
 Key Terms and Concepts • Ultimate consumer • Metropolitan Statistical Area (MSA) • Primary Metropolitan Statistical Area (PMSA) • Consolidated Metropolitan Statistical Area (CMSA) • Demographics • Family life-cycle stage • Consumer buying decision process • Level of Involvement • Loyalty 4 -21 Mc. Graw-Hill/Irwin • Impulse buying • Patronage buying motives • Postpurchase cognitive dissonance • Commercial information environment • Social information environment • Culture • Subculture • Social class • Reference groups Copyright © 2004 by The Mc. Graw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved.
Key Terms and Concepts • Ultimate consumer • Metropolitan Statistical Area (MSA) • Primary Metropolitan Statistical Area (PMSA) • Consolidated Metropolitan Statistical Area (CMSA) • Demographics • Family life-cycle stage • Consumer buying decision process • Level of Involvement • Loyalty 4 -21 Mc. Graw-Hill/Irwin • Impulse buying • Patronage buying motives • Postpurchase cognitive dissonance • Commercial information environment • Social information environment • Culture • Subculture • Social class • Reference groups Copyright © 2004 by The Mc. Graw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved.
 Key Terms and Concepts • • Family Household Motive Maslow’s need hierarchy Perception Selective perception Learning 4 -22 Mc. Graw-Hill/Irwin • • • Stimulus-response theory Personality Psychoanalytic theory Self-concept Attitude Situational influence Copyright © 2004 by The Mc. Graw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved.
Key Terms and Concepts • • Family Household Motive Maslow’s need hierarchy Perception Selective perception Learning 4 -22 Mc. Graw-Hill/Irwin • • • Stimulus-response theory Personality Psychoanalytic theory Self-concept Attitude Situational influence Copyright © 2004 by The Mc. Graw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved.


