International Trade.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 16
 37 International Trade Mc. Graw-Hill/Irwin Copyright © 2012 by The Mc. Graw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved.
37 International Trade Mc. Graw-Hill/Irwin Copyright © 2012 by The Mc. Graw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved.
 Some Key Trade Facts Principal U. S. exports include: • Chemicals • Agricultural products • Consumer durables • Semiconductors • Aircraft Principal U. S. imports include: • Petroleum • Automobiles • Metals • Household appliances • Computers U. S. provides about 8. 5% of world’s exports LO 1 37 -2
Some Key Trade Facts Principal U. S. exports include: • Chemicals • Agricultural products • Consumer durables • Semiconductors • Aircraft Principal U. S. imports include: • Petroleum • Automobiles • Metals • Household appliances • Computers U. S. provides about 8. 5% of world’s exports LO 1 37 -2
 Economic Basis for Trade • Nations have different resource • • • LO 2 endowments Labor-intensive goods Land-intensive goods Capital-intensive goods 37 -3
Economic Basis for Trade • Nations have different resource • • • LO 2 endowments Labor-intensive goods Land-intensive goods Capital-intensive goods 37 -3
 Comparative Advantage • Assumptions • Two nations • Same size labor force • Constant costs in each country • Different costs between countries • U. S. absolute advantage in both • Opportunity cost ratio • Slope of the curve • Vegetables sacrificed per ton of beef LO 2 37 -4
Comparative Advantage • Assumptions • Two nations • Same size labor force • Constant costs in each country • Different costs between countries • U. S. absolute advantage in both • Opportunity cost ratio • Slope of the curve • Vegetables sacrificed per ton of beef LO 2 37 -4
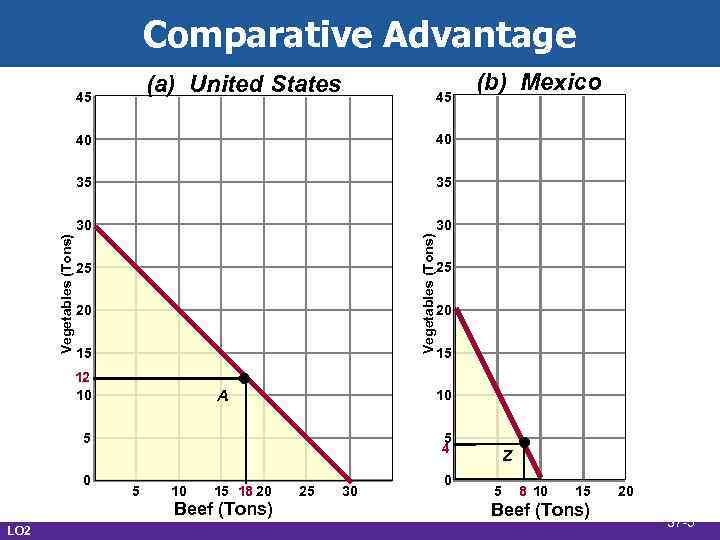 Comparative Advantage (a) United States 45 45 35 30 30 Vegetables (Tons) 40 35 Vegetables (Tons) 40 25 20 15 12 10 A 0 25 20 15 10 5 4 5 5 10 15 18 20 Beef (Tons) LO 2 (b) Mexico 25 30 0 Z 5 8 10 15 Beef (Tons) 20 37 -5
Comparative Advantage (a) United States 45 45 35 30 30 Vegetables (Tons) 40 35 Vegetables (Tons) 40 25 20 15 12 10 A 0 25 20 15 10 5 4 5 5 10 15 18 20 Beef (Tons) LO 2 (b) Mexico 25 30 0 Z 5 8 10 15 Beef (Tons) 20 37 -5
 Comparative Advantage LO 2 37 -6
Comparative Advantage LO 2 37 -6
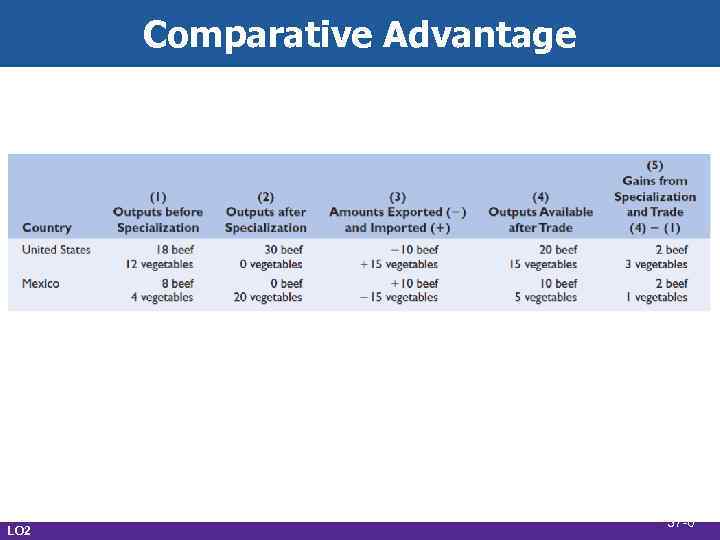
 Comparative Advantage • Terms of trade • U. S. 1 V = 1 B • U. S. will sell 1 B for more than 1 V • Mexico 2 V = 1 B • Mexico will pay less than 2 V for 1 B • Settle between the two • Depends on supply/demand factors • Assume 1 B = 1. 5 V LO 2 37 -7
Comparative Advantage • Terms of trade • U. S. 1 V = 1 B • U. S. will sell 1 B for more than 1 V • Mexico 2 V = 1 B • Mexico will pay less than 2 V for 1 B • Settle between the two • Depends on supply/demand factors • Assume 1 B = 1. 5 V LO 2 37 -7
 Comparative Advantage • Gains from trade • Trading possibilities line • Slope equals terms of trade • Improved options • Complete specialization • More of both goods • More efficient resource allocation LO 2 37 -8
Comparative Advantage • Gains from trade • Trading possibilities line • Slope equals terms of trade • Improved options • Complete specialization • More of both goods • More efficient resource allocation LO 2 37 -8
 Trade Barriers and Export Subsidies • Tariffs • Revenue tariff • Protective tariff • Import quota • Nontariff barrier (NTB) • Voluntary export restriction • LO 4 (VER) Export subsidy 37 -9
Trade Barriers and Export Subsidies • Tariffs • Revenue tariff • Protective tariff • Import quota • Nontariff barrier (NTB) • Voluntary export restriction • LO 4 (VER) Export subsidy 37 -9
 Economic Impact of Tariffs • Direct effects • Decline in consumption • Increase in domestic production • Decline in imports • Tariff revenue • Indirect effects LO 4 37 -10
Economic Impact of Tariffs • Direct effects • Decline in consumption • Increase in domestic production • Decline in imports • Tariff revenue • Indirect effects LO 4 37 -10
 Economic Impact of Quotas • Decline in consumption • Increase in domestic production • Decline in imports • Quotas do not provide for any government revenue but instead transfer it to foreign producers LO 4 37 -11
Economic Impact of Quotas • Decline in consumption • Increase in domestic production • Decline in imports • Quotas do not provide for any government revenue but instead transfer it to foreign producers LO 4 37 -11
 The Case for Protection • Military self-sufficiency • Diversification for stability • Infant industry • Protection against dumping • Increased domestic employment • Cheap foreign labor LO 5 37 -12
The Case for Protection • Military self-sufficiency • Diversification for stability • Infant industry • Protection against dumping • Increased domestic employment • Cheap foreign labor LO 5 37 -12
 GATT • Three principles: • Equal, nondiscriminatory trade between member nations • Reduction in tariffs • Elimination of import quotas LO 5 37 -13
GATT • Three principles: • Equal, nondiscriminatory trade between member nations • Reduction in tariffs • Elimination of import quotas LO 5 37 -13
 WTO • Established by Uruguay Round of • • • LO 5 GATT 153 member nations in 2010 Oversees trade agreements and rules on disputes Critics argue that it may allow nations to circumvent environmental and worker-protection laws 37 -14
WTO • Established by Uruguay Round of • • • LO 5 GATT 153 member nations in 2010 Oversees trade agreements and rules on disputes Critics argue that it may allow nations to circumvent environmental and worker-protection laws 37 -14
 European Union • Initiated in 1958 as Common Market • Abolished tariffs and import quotas • • LO 5 between member nations Established common tariff with nations outside the EU Created Euro Zone with one currency 37 -15
European Union • Initiated in 1958 as Common Market • Abolished tariffs and import quotas • • LO 5 between member nations Established common tariff with nations outside the EU Created Euro Zone with one currency 37 -15
 NAFTA • Agreement between U. S. , Canada, • • • LO 5 and Mexico Established a free trade zone between the countries Trade has increased in all countries Enhanced standard of living 37 -16
NAFTA • Agreement between U. S. , Canada, • • • LO 5 and Mexico Established a free trade zone between the countries Trade has increased in all countries Enhanced standard of living 37 -16


