34bd3139837a166440ef41cf51fd3aea.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 7

340 b Program Background

General Overview • What is the 340 b program • Recent legislative changes and the impacts • What it means for Indian Tribes • What is means for pharmacies and PBMs Proprietary and Confidential. Do not distribute.
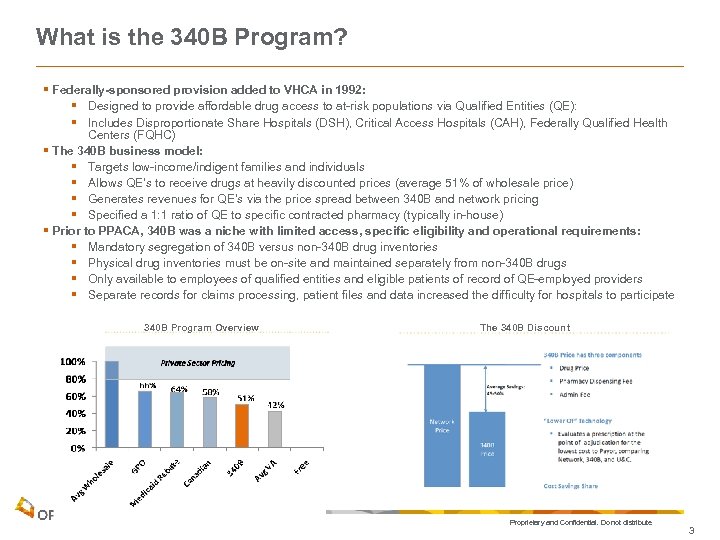
What is the 340 B Program? § Federally-sponsored provision added to VHCA in 1992: § Designed to provide affordable drug access to at-risk populations via Qualified Entities (QE): § Includes Disproportionate Share Hospitals (DSH), Critical Access Hospitals (CAH), Federally Qualified Health Centers (FQHC) § The 340 B business model: § Targets low-income/indigent families and individuals § Allows QE’s to receive drugs at heavily discounted prices (average 51% of wholesale price) § Generates revenues for QE’s via the price spread between 340 B and network pricing § Specified a 1: 1 ratio of QE to specific contracted pharmacy (typically in-house) § Prior to PPACA, 340 B was a niche with limited access, specific eligibility and operational requirements: § Mandatory segregation of 340 B versus non-340 B drug inventories § Physical drug inventories must be on-site and maintained separately from non-340 B drugs § Only available to employees of qualified entities and eligible patients of record of QE-employed providers § Separate records for claims processing, patient files and data increased the difficulty for hospitals to participate 340 B Program Overview The 340 B Discount Proprietary and Confidential. Do not distribute. 3
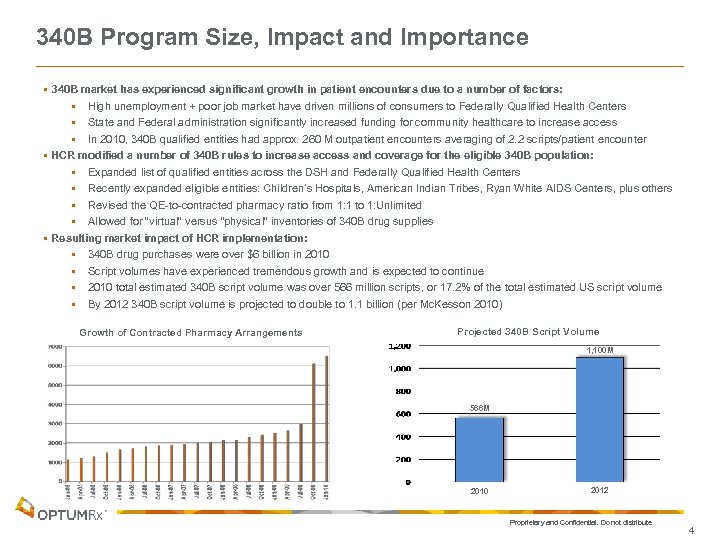
340 B Program Size, Impact and Importance § 340 B market has experienced significant growth in patient encounters due to a number of factors: § High unemployment + poor job market have driven millions of consumers to Federally Qualified Health Centers § State and Federal administration significantly increased funding for community healthcare to increase access § In 2010, 340 B qualified entities had approx. 260 M outpatient encounters averaging of 2. 2 scripts/patient encounter § HCR modified a number of 340 B rules to increase access and coverage for the eligible 340 B population: § Expanded list of qualified entities across the DSH and Federally Qualified Health Centers § Recently expanded eligible entities: Children’s Hospitals, American Indian Tribes, Ryan White AIDS Centers, plus others § Revised the QE-to-contracted pharmacy ratio from 1: 1 to 1: Unlimited § Allowed for “virtual” versus “physical” inventories of 340 B drug supplies § Resulting market impact of HCR implementation: § 340 B drug purchases were over $6 billion in 2010 § Script volumes have experienced tremendous growth and is expected to continue § 2010 total estimated 340 B script volume was over 566 million scripts, or 17. 2% of the total estimated US script volume § By 2012 340 B script volume is projected to double to 1. 1 billion (per Mc. Kesson 2010) Growth of Contracted Pharmacy Arrangements Projected 340 B Script Volume 1, 100 M 566 M 2010 2012 Proprietary and Confidential. Do not distribute. 4

340 B Market – What’s the Attraction? § § Continued growth of Qualified Entities (QE): § Currently over 15, 000 QE’s across the US and US territories, up from 14, 000 QE’s in 2010 § California alone has over 10% (1, 500) of all QE’s § DSH, Critical Access Hospitals and Federally Qualified Health Centers facilities represent over 80% of all qualified entities § 340 B program does not discriminate; anyone who meets eligibility requirements can access 340 B drug prices Program is difficult to understand even harder to administer, manage: § Competition is fragmented and no large competitors currently in this space § A number of companies provide consulting services and/or program administration, management § 340 B may not be compatible with standard PBM business models § Growth in this market would likely increase attraction by various companies Significant increase reported in RFP’s containing 340 B requirements: § Entities are looking for ways to increase their revenue § RFP’s are being received from 340 B QE’s plus prospective clients looking for added capabilities § Majority of Public Sector and Medicaid RFP’s (80 -100%) include 340 B requirements § Many RFP’s show lack of knowledge on 340 B specifics and qualifications; many RFP requestors do not qualify for 340 B Potential market risks for future considerations: § Changes in legislation may impact 340 B program and discounts: § Optum. Rx believes there is no current legislative activity significantly impacting the 340 B market § Increased access and participation may drive Pharma to reconsider participation and/or pricing: § This is a Federally sponsored program; unsure whether Pharma will object to small % of their overall sales § Trend shifts towards Specialty drug development may cause shift in program design Proprietary and Confidential. Do not distribute. 5

340 B Market – Implications for Tribes? • Ability to take advantage of 340 b pricing without a tribal pharmacy • No rebates paid on 340 b drugs • Tribes need contract with wholesaler and have agreements with each pharmacy they intend to fill 340 b scripts with • May want to consider a 340 b-facilitation vendor to handle: – Patient eligibility verification – Virtual inventory control – Automated reporting and auditing requirements • Even though eligible by Tribal status, still need to register with Health Resources and Services Administration (HRSA): Office of Pharmacy Affairs (OPA) – http: //opanet. hrsa. gov/opa/default. aspx Proprietary and Confidential. Do not distribute. 6

340 B Market – Implication to Pharmacies/PBMs? • Limited or no “spread” revenue on 340 b drugs • Pharmacies may charge a large dispense fee • PBMs may require an administration fee (for full pass-through of the 340 b discount) • Few, if any, PBMs currently engaged in “ 340 b verification” processes Proprietary and Confidential. Do not distribute. 7
34bd3139837a166440ef41cf51fd3aea.ppt