42014a980a564fec745cf9072b4a00a0.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 41
 332 - Unit 2 1 D Vectors & Newton’s Laws of Motion
332 - Unit 2 1 D Vectors & Newton’s Laws of Motion
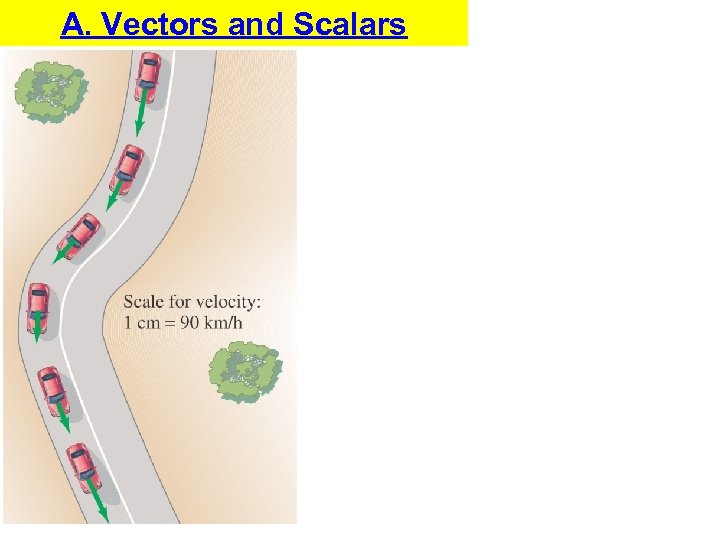 A. Vectors and Scalars
A. Vectors and Scalars
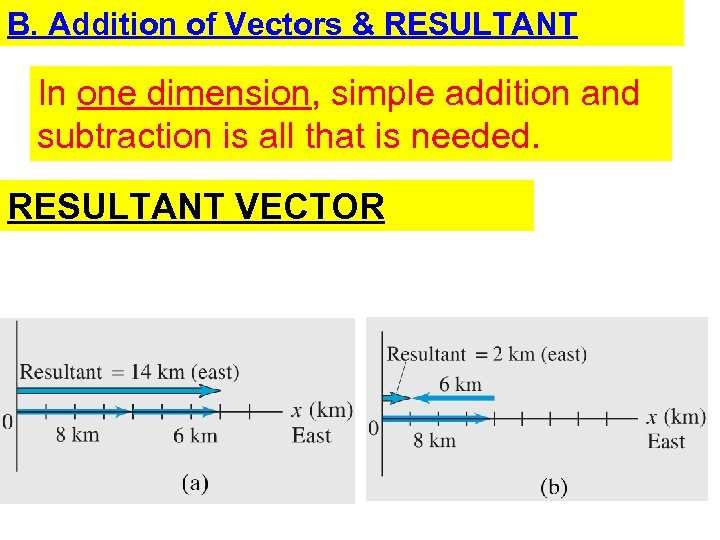 B. Addition of Vectors & RESULTANT In one dimension, simple addition and subtraction is all that is needed. RESULTANT VECTOR
B. Addition of Vectors & RESULTANT In one dimension, simple addition and subtraction is all that is needed. RESULTANT VECTOR
 Aristotle vs Galileo • 2000 yrs of Greek influence on motion • What enables an object to move? • Galileo…What enables an object to continue moving? • Reason out ‘resistance’ or ‘friction’
Aristotle vs Galileo • 2000 yrs of Greek influence on motion • What enables an object to move? • Galileo…What enables an object to continue moving? • Reason out ‘resistance’ or ‘friction’
 C. FORCES NET FORCE
C. FORCES NET FORCE
 D. TYPES OF FORCES
D. TYPES OF FORCES
 1) Force of Gravity (Weight) - Without gravity, how can we distinguish between a 1 kg and a 2 kg mass?
1) Force of Gravity (Weight) - Without gravity, how can we distinguish between a 1 kg and a 2 kg mass?
 An astronaut’s weight on Earth is 950 N. He lands on Mars and stands on a scale where it reads 359 N. A) Determine the acceleration due to gravity on Mars. B) He drops a rock from a height of 1. 8 m. Calculate the time it takes to fall to ground below.
An astronaut’s weight on Earth is 950 N. He lands on Mars and stands on a scale where it reads 359 N. A) Determine the acceleration due to gravity on Mars. B) He drops a rock from a height of 1. 8 m. Calculate the time it takes to fall to ground below.
 *Since gold is sold by weight, should you buy it in Philadelphia, Pa or Denver, Colorado? *If you want to fit into a smaller size prom dress…should you zip up in the Poconos or here in Philly?
*Since gold is sold by weight, should you buy it in Philadelphia, Pa or Denver, Colorado? *If you want to fit into a smaller size prom dress…should you zip up in the Poconos or here in Philly?
 2) Normal Force (Support Force) If the box weighed less, what would happen to the normal force acting on the box?
2) Normal Force (Support Force) If the box weighed less, what would happen to the normal force acting on the box?
 3) Tension Force - A force that exists within ropes, cables, wires, string, etc
3) Tension Force - A force that exists within ropes, cables, wires, string, etc
 4) Friction Force
4) Friction Force
 E. NEWTON’S LAWS
E. NEWTON’S LAWS
 Newton’s st 1 Law (law of inertia)
Newton’s st 1 Law (law of inertia)
 MASS
MASS
 Why do all objects fall at the same rate? (|a|=g=9. 8 m/s 2) • Aristotle felt heavy fell faster than light • Without air resistance, a light object falls the same as a heavy object… Explain.
Why do all objects fall at the same rate? (|a|=g=9. 8 m/s 2) • Aristotle felt heavy fell faster than light • Without air resistance, a light object falls the same as a heavy object… Explain.
 Newton’s 3 rd Law
Newton’s 3 rd Law
 A/R pairs • You punch wall… • You pull a rope… • You press against floor…
A/R pairs • You punch wall… • You pull a rope… • You press against floor…
 Locomotion… • Describe the action/reaction process in order to walk forward. • Describe the action/reaction process in order to swim forward?
Locomotion… • Describe the action/reaction process in order to walk forward. • Describe the action/reaction process in order to swim forward?
 Use 3 rd law to describe the motion of: A Rocket taking off A helicopter hovering over the ground
Use 3 rd law to describe the motion of: A Rocket taking off A helicopter hovering over the ground
 Bug vs Bus • A loaded school bus hits a bug. Which body receives the greater force of impact, bug or bus?
Bug vs Bus • A loaded school bus hits a bug. Which body receives the greater force of impact, bug or bus?
 Who pulls harder on the rope? What determines who wins the tug of war?
Who pulls harder on the rope? What determines who wins the tug of war?
 Fan for boat with no wind?
Fan for boat with no wind?
 Newton’s 2 nd Law -What does Fnet mean? -If Fnet = 0, what implications does that have on object’s motion?
Newton’s 2 nd Law -What does Fnet mean? -If Fnet = 0, what implications does that have on object’s motion?
 Force Body Diagrams FBD’s • Drawing forces on object helps to solve problem. If you can draw FBD, you can setup equation. • Specific forces are: – Tension (FT) – Normal (FN) – Gravity (Fg) – Friction (Ff)
Force Body Diagrams FBD’s • Drawing forces on object helps to solve problem. If you can draw FBD, you can setup equation. • Specific forces are: – Tension (FT) – Normal (FN) – Gravity (Fg) – Friction (Ff)
 2 nd Law with force diagrams • A 5. 0 kg box is pulled to the right by a rope parallel to surface. The tension is 30 N. If the box accelerates from rest to 3. 6 m/s in 2. 0 s, determine the frictional force between the box and surface.
2 nd Law with force diagrams • A 5. 0 kg box is pulled to the right by a rope parallel to surface. The tension is 30 N. If the box accelerates from rest to 3. 6 m/s in 2. 0 s, determine the frictional force between the box and surface.
 • A 900 kg elevator accelerates upward at 3. 0 m/s 2. Determine the tension in the cable that supports the elevator.
• A 900 kg elevator accelerates upward at 3. 0 m/s 2. Determine the tension in the cable that supports the elevator.
 • A 17 kg shopping cart is pushed down an aisle where there is a friction force of 12 N on the cart. If the cart accelerates from 0. 75 m/s to 1. 2 m/s over 3. 7 m, determine force applied to the cart.
• A 17 kg shopping cart is pushed down an aisle where there is a friction force of 12 N on the cart. If the cart accelerates from 0. 75 m/s to 1. 2 m/s over 3. 7 m, determine force applied to the cart.
 • A 0. 75 kg krimpet is launched straight upwards with a speed of 16 m/s. It takes 1. 1 s to reach its apex. Air friction is present. • A) Draw FBD • B) Calculate the acceleration of the krimpet • C) Calculate the force of air friction on krimpet. • D) Will it take the same time to fall as it did on way up? JUSTIFY.
• A 0. 75 kg krimpet is launched straight upwards with a speed of 16 m/s. It takes 1. 1 s to reach its apex. Air friction is present. • A) Draw FBD • B) Calculate the acceleration of the krimpet • C) Calculate the force of air friction on krimpet. • D) Will it take the same time to fall as it did on way up? JUSTIFY.
 Air Resistance during a fall
Air Resistance during a fall
 What force(s) act on an 833 N skydiver at instant he steps off helicopter if it is hovering? What happens to speed of skydiver after t = 0? Therefore, what happens to force of air friction as skydiver continues to fall?
What force(s) act on an 833 N skydiver at instant he steps off helicopter if it is hovering? What happens to speed of skydiver after t = 0? Therefore, what happens to force of air friction as skydiver continues to fall?
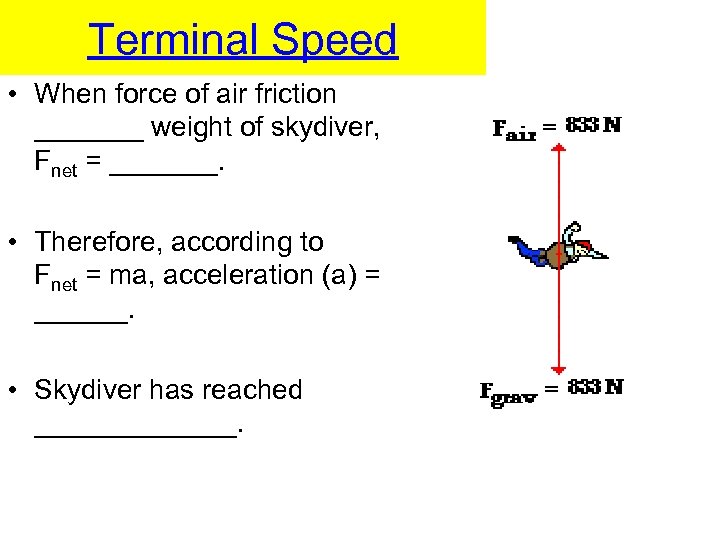 Terminal Speed • When force of air friction _______ weight of skydiver, Fnet = _______. • Therefore, according to Fnet = ma, acceleration (a) = ______. • Skydiver has reached _______.
Terminal Speed • When force of air friction _______ weight of skydiver, Fnet = _______. • Therefore, according to Fnet = ma, acceleration (a) = ______. • Skydiver has reached _______.
 Velocity vs Acceleration • BEFORE reaching terminal speed, the speed of skydiver _____ as he falls. • BEFORE reaching terminal speed, the acceleration of skydiver ____ as he falls.
Velocity vs Acceleration • BEFORE reaching terminal speed, the speed of skydiver _____ as he falls. • BEFORE reaching terminal speed, the acceleration of skydiver ____ as he falls.
 Pulling Parachute? • After pulling parachute, what happens to force of air friction on skydiver? • What does parachute change about skydiver? • What happens to speed of skydiver after pulling chute? • What is direction of acceleration after pulling chute? • Which way does skydiver move after pulling chute relative to ground?
Pulling Parachute? • After pulling parachute, what happens to force of air friction on skydiver? • What does parachute change about skydiver? • What happens to speed of skydiver after pulling chute? • What is direction of acceleration after pulling chute? • Which way does skydiver move after pulling chute relative to ground?
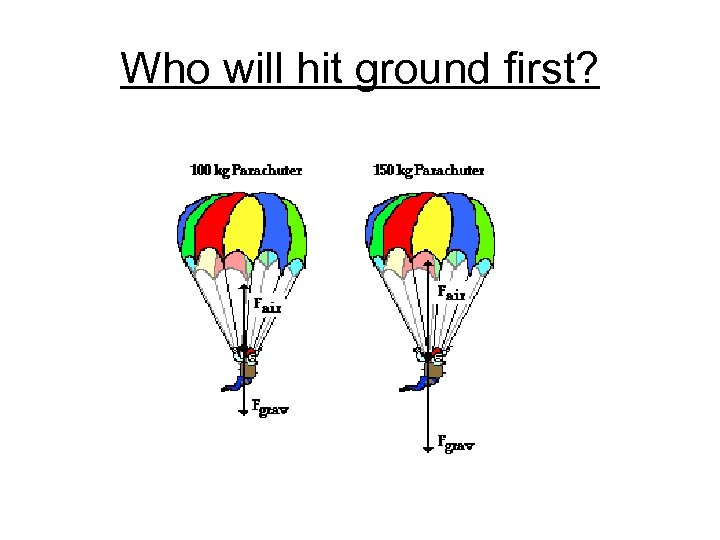 Who will hit ground first?
Who will hit ground first?
 Friction
Friction
 2 Types of Friction • Static (Ffs) • Kinetic (Ffk) or sliding
2 Types of Friction • Static (Ffs) • Kinetic (Ffk) or sliding
 Static Ff
Static Ff
 Example 1 A 10 kg crate is pushed along floor with a force of 60 N. If coefficient of kinetic friction is 0. 35, find acceleration of crate.
Example 1 A 10 kg crate is pushed along floor with a force of 60 N. If coefficient of kinetic friction is 0. 35, find acceleration of crate.
 Example 2 It requires a force of 175 N to push a 50 kg box across the floor at constant speed. Determine the coefficient of kinetic friction.
Example 2 It requires a force of 175 N to push a 50 kg box across the floor at constant speed. Determine the coefficient of kinetic friction.
 Example 3 The coefficient of static friction is 0. 85. A refrigerator weighs 1000 N. a) What minimum force is needed to move the refrigerator? b) What if it is pushed with 700 N to the right? Describe the motion.
Example 3 The coefficient of static friction is 0. 85. A refrigerator weighs 1000 N. a) What minimum force is needed to move the refrigerator? b) What if it is pushed with 700 N to the right? Describe the motion.


