682cc23eb3fe0bb6826637d551754797.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 52
 318 -595 Safety Product Safety • What consumer product was recently 100% recalled for a safety defect (voluntarily)?
318 -595 Safety Product Safety • What consumer product was recently 100% recalled for a safety defect (voluntarily)?
 318 -595 Safety NEWS from CPSC http: //www. cpsc. gov/ U. S. Consumer Product Safety Commission Office of Information and Public Affairs FOR IMMEDIATE RELEASE September 14, 2006 Release #06 -258 Washington, DC 20207 Segway’s Recall Hotline: (800) 750 -6557 CPSC Recall Hotline: (800) 638 -2772 CPSC Media Contact: (301) 504 -7908 Segway Media Contact: Carla Vallone (866) 473 -4929 Segway Inc. Announces Recall to Repair Segway® Personal Transporters WASHINGTON, D. C. - The U. S. Consumer Product Safety Commission, in cooperation with the firm named below, today announced a voluntary recall of the following consumer product. Consumers should stop using recalled products immediately unless otherwise instructed. Name of Product: Segway Personal Transporter (PT) [also known as the Segway Human Transporter (HT)] Units: About 23, 500 Manufacturer: Segway Inc. , of Bedford, N. H. Hazard: The personal transporter can unexpectedly apply reverse torque to the wheels, which can cause a rider to fall. This can occur when the device is tilted back by the Speed Limiter and the rider comes off and then back onto the device within a short period of time. - (May cause head and wrist injuries to the user)
318 -595 Safety NEWS from CPSC http: //www. cpsc. gov/ U. S. Consumer Product Safety Commission Office of Information and Public Affairs FOR IMMEDIATE RELEASE September 14, 2006 Release #06 -258 Washington, DC 20207 Segway’s Recall Hotline: (800) 750 -6557 CPSC Recall Hotline: (800) 638 -2772 CPSC Media Contact: (301) 504 -7908 Segway Media Contact: Carla Vallone (866) 473 -4929 Segway Inc. Announces Recall to Repair Segway® Personal Transporters WASHINGTON, D. C. - The U. S. Consumer Product Safety Commission, in cooperation with the firm named below, today announced a voluntary recall of the following consumer product. Consumers should stop using recalled products immediately unless otherwise instructed. Name of Product: Segway Personal Transporter (PT) [also known as the Segway Human Transporter (HT)] Units: About 23, 500 Manufacturer: Segway Inc. , of Bedford, N. H. Hazard: The personal transporter can unexpectedly apply reverse torque to the wheels, which can cause a rider to fall. This can occur when the device is tilted back by the Speed Limiter and the rider comes off and then back onto the device within a short period of time. - (May cause head and wrist injuries to the user)
 318 -595 Safety Types of Safety Protections and Mitigations • Protection Against Known Hazards -Common Knowledge Gained from Experience • Protection Against Unsafe Failure Modes -Single Occurrence Failures With No Safety Risk -Double Occurrence Failures With Minimal or No Safety Risk • Protection Against Unwanted or Unsafe Usage -Misuse of Products is Commonly the Root Cause in Safety Issues • Design and Testing to Certify Product to Industry or Government Stds • Failure Modes & Effects Analysis • What If Testing (aka: monkey testing)
318 -595 Safety Types of Safety Protections and Mitigations • Protection Against Known Hazards -Common Knowledge Gained from Experience • Protection Against Unsafe Failure Modes -Single Occurrence Failures With No Safety Risk -Double Occurrence Failures With Minimal or No Safety Risk • Protection Against Unwanted or Unsafe Usage -Misuse of Products is Commonly the Root Cause in Safety Issues • Design and Testing to Certify Product to Industry or Government Stds • Failure Modes & Effects Analysis • What If Testing (aka: monkey testing)
 318 -595 Safety Product Safety • Protection Against Known Hazards – – – – – Electric Shock High or Low Temperatures EMI/EMC Sharp Edges, Pinch Points, Rotating, Shearing, other Explosion, Shattering and other failure modes Chemicals and Substances such as Lead, Mercury, Cadmium, etc Radiation Energy Acoustical Energy Optical Energy Child Safety, Swallowing, Cords, etc
318 -595 Safety Product Safety • Protection Against Known Hazards – – – – – Electric Shock High or Low Temperatures EMI/EMC Sharp Edges, Pinch Points, Rotating, Shearing, other Explosion, Shattering and other failure modes Chemicals and Substances such as Lead, Mercury, Cadmium, etc Radiation Energy Acoustical Energy Optical Energy Child Safety, Swallowing, Cords, etc
 318 -595 Safety Product Safety • Protection Against Unsafe Failure Modes, Operations – – – Current Limiting and Fast Switching Voltage Limiting and Clamping Reverse Voltage Clamping Grounding or Low Potential of all touchable conducting surfaces Ground Fault Current Detection Watchdog Timing and Reset Input Power Filtration and d. I/d. T limiting Insulation of High Voltages Unique external Connectors Max Power Limiting Fault Indications and Operator Warnings Thermal Sensing
318 -595 Safety Product Safety • Protection Against Unsafe Failure Modes, Operations – – – Current Limiting and Fast Switching Voltage Limiting and Clamping Reverse Voltage Clamping Grounding or Low Potential of all touchable conducting surfaces Ground Fault Current Detection Watchdog Timing and Reset Input Power Filtration and d. I/d. T limiting Insulation of High Voltages Unique external Connectors Max Power Limiting Fault Indications and Operator Warnings Thermal Sensing
 318 -595 Safety Product Safety • Mitigation of Unwanted Usage – Improper Power Input – Applications Outside of Product Labeling – Specific Conditions and Environments that could result in product failure or Hazards and Unsafe events – User Limitations such as Age and other Demographics – Improper Disposal Products Must Be Accompanied By Sufficient Clear Instructions, Warnings and Labels to mitigate the possibility to a reasonable level for unsafe occurances
318 -595 Safety Product Safety • Mitigation of Unwanted Usage – Improper Power Input – Applications Outside of Product Labeling – Specific Conditions and Environments that could result in product failure or Hazards and Unsafe events – User Limitations such as Age and other Demographics – Improper Disposal Products Must Be Accompanied By Sufficient Clear Instructions, Warnings and Labels to mitigate the possibility to a reasonable level for unsafe occurances
 318 -595 Safety Test Labs • Test Products to key Safety Standards and authorize a product to be marked with test label as well as key standard label • Labs may need to be certified as part of standards process • Some Test Labs also propose and harmonize Safety Standards (UL, CSA, etc) • Labs Often have their own label or marking that a product shall bear to indicate passing this test labs regime • Examples: – – – UL: Underwriters Labs www. ul. com CSA: Canadian Standards Association www. csa. ca NRTLs: Nationally Recognized Testing Labs (OSHA) Intertek (ETL) http: //www. intertek-etlsemko. com/ TUV http: //www. tuv. com/en/index. php
318 -595 Safety Test Labs • Test Products to key Safety Standards and authorize a product to be marked with test label as well as key standard label • Labs may need to be certified as part of standards process • Some Test Labs also propose and harmonize Safety Standards (UL, CSA, etc) • Labs Often have their own label or marking that a product shall bear to indicate passing this test labs regime • Examples: – – – UL: Underwriters Labs www. ul. com CSA: Canadian Standards Association www. csa. ca NRTLs: Nationally Recognized Testing Labs (OSHA) Intertek (ETL) http: //www. intertek-etlsemko. com/ TUV http: //www. tuv. com/en/index. php
 318 -595 Safety Standards Bodies & Government Agencies • • Create, Harmonize and Adopt Safety Standards – Do NOT Test Some are sanctioned by Governments May be Industry or Product Segment Specific Standards may govern constructions, materials, testing and applications of components and products • Examples of Stds Bodies: – ANSI: American National Standards Institute http: //www. ansi. org/ – CENELEC: European Committee for Electrotechnical Standardization http: //www. cenelec. org/Cenelec/Homepage. htm – IEC: International Electrotechnical Commission http: //www. iec. ch/ – EIA: Electronic Industries Alliance http: //www. eia. org/ – NEMA: National Electric Manufacturers Association http: //www. nema. org/ – ETSI: European Telecommunications Standards Institute http: //www. etsi. org/
318 -595 Safety Standards Bodies & Government Agencies • • Create, Harmonize and Adopt Safety Standards – Do NOT Test Some are sanctioned by Governments May be Industry or Product Segment Specific Standards may govern constructions, materials, testing and applications of components and products • Examples of Stds Bodies: – ANSI: American National Standards Institute http: //www. ansi. org/ – CENELEC: European Committee for Electrotechnical Standardization http: //www. cenelec. org/Cenelec/Homepage. htm – IEC: International Electrotechnical Commission http: //www. iec. ch/ – EIA: Electronic Industries Alliance http: //www. eia. org/ – NEMA: National Electric Manufacturers Association http: //www. nema. org/ – ETSI: European Telecommunications Standards Institute http: //www. etsi. org/
 318 -595 Safety Government Agencies • Create and Adopt Safety Standards – Do NOT Test • US Government Agencies Fall Under Specific Departments • Standards may govern constructions, materials, testing and applications of components and products • USA Examples: http: //www. firstgov. gov/Agencies/Federal/All_Agencies/index. shtml Ø Ø Ø FDA: USA-Food and Drug Administration (DO-HHS) http: //www. fda. gov/ FAA: USA-Federal Aviation Adminstration (DO-Transportation) http: //www. faa. gov/ OSHA: USA-Occupational & Health Administration (DO-Labor) http: //www. osha. gov/ NIST: USA-National Inst of Standards & Tech (DO-Commerce) http: //www. nist. gov/ NEST: USA-Nuclear Energy Science & Technology (DO-Energy) http: //www. doe. gov/engine/content. do? BT_CODE=OF_PONEST Ø FCC: USA-Federal Communications Comm – Congressional http: //www. fcc. gov/ Ø CSPC: USA-Fed Consumer Product Safety Comm – Congressional http: //www. cpsc. gov/
318 -595 Safety Government Agencies • Create and Adopt Safety Standards – Do NOT Test • US Government Agencies Fall Under Specific Departments • Standards may govern constructions, materials, testing and applications of components and products • USA Examples: http: //www. firstgov. gov/Agencies/Federal/All_Agencies/index. shtml Ø Ø Ø FDA: USA-Food and Drug Administration (DO-HHS) http: //www. fda. gov/ FAA: USA-Federal Aviation Adminstration (DO-Transportation) http: //www. faa. gov/ OSHA: USA-Occupational & Health Administration (DO-Labor) http: //www. osha. gov/ NIST: USA-National Inst of Standards & Tech (DO-Commerce) http: //www. nist. gov/ NEST: USA-Nuclear Energy Science & Technology (DO-Energy) http: //www. doe. gov/engine/content. do? BT_CODE=OF_PONEST Ø FCC: USA-Federal Communications Comm – Congressional http: //www. fcc. gov/ Ø CSPC: USA-Fed Consumer Product Safety Comm – Congressional http: //www. cpsc. gov/
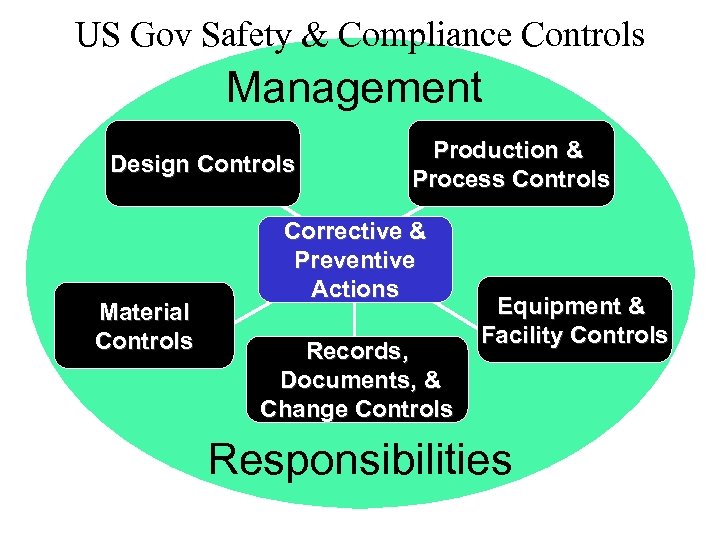 US Gov Safety & Compliance Controls Management Design Controls Material Controls Production & Process Controls Corrective & Preventive Actions Records, Documents, & Change Controls Equipment & Facility Controls Responsibilities
US Gov Safety & Compliance Controls Management Design Controls Material Controls Production & Process Controls Corrective & Preventive Actions Records, Documents, & Change Controls Equipment & Facility Controls Responsibilities
 318 -595 Safety Design Control Terms • Design Inputs • Requirements, Constraints and other information which is needed to formulate a set of design outputs for a given product. • Design Inputs must include customer (user) level requirements as well as product level and flow down to block level requirements • Design Outputs • All drawings, documents, procedures, instructions and other information necessary to describe the constituent parts, assembly, manufacturing process, service and disposal processes for a product. • Design outputs from one team may sometimes become the design inputs to another team.
318 -595 Safety Design Control Terms • Design Inputs • Requirements, Constraints and other information which is needed to formulate a set of design outputs for a given product. • Design Inputs must include customer (user) level requirements as well as product level and flow down to block level requirements • Design Outputs • All drawings, documents, procedures, instructions and other information necessary to describe the constituent parts, assembly, manufacturing process, service and disposal processes for a product. • Design outputs from one team may sometimes become the design inputs to another team.
 318 -595 Safety Design Control Terms • Verification • Design analysis, simulation or prototype testing which provides objective evidence that a design meets all of its block or product level requirements • Is performed at sub-block, block and system levels and usually requires lab testing • Validation • Product field, clinical or customer trial which provides objective evidence that a product meets its customer (user) requirements. • Intended use is an important part of the product labeling. • Must be performed on units which have been constructed using fully verified, released engineering and manufacturing drawings and processes • Is only performed at the system level on completed products
318 -595 Safety Design Control Terms • Verification • Design analysis, simulation or prototype testing which provides objective evidence that a design meets all of its block or product level requirements • Is performed at sub-block, block and system levels and usually requires lab testing • Validation • Product field, clinical or customer trial which provides objective evidence that a product meets its customer (user) requirements. • Intended use is an important part of the product labeling. • Must be performed on units which have been constructed using fully verified, released engineering and manufacturing drawings and processes • Is only performed at the system level on completed products
 318 -595 Safety Design Control Terms • Design Reviews • Peer review of design inputs and design outputs are a mandatory part of many industry product development processes. • Reviews must include objective evidence of attendees, documented issue list with dispensation actions, signatures and dates. • Reviews must include appropriate stake holders (management, customers, other design teams) • Reviews must include at least 1 unbiased, knowledgeable external reviewer Many Companies in Regulated Industries Must Show Objective Evidence of Proper Design Inputs, Outputs, For Example: 21 CFR 820 Reviews, Verification and Validation to Government Agencies
318 -595 Safety Design Control Terms • Design Reviews • Peer review of design inputs and design outputs are a mandatory part of many industry product development processes. • Reviews must include objective evidence of attendees, documented issue list with dispensation actions, signatures and dates. • Reviews must include appropriate stake holders (management, customers, other design teams) • Reviews must include at least 1 unbiased, knowledgeable external reviewer Many Companies in Regulated Industries Must Show Objective Evidence of Proper Design Inputs, Outputs, For Example: 21 CFR 820 Reviews, Verification and Validation to Government Agencies
 318 -595 Safety CPSC Overview: Sanctioned by the US Congress (No direct cabinet level tie) The U. S. Consumer Product Safety Commission is charged with protecting the public from unreasonable risks of serious injury or death from more than 15, 000 types of consumer products under the agency's jurisdiction. Deaths, injuries and property damage from consumer product incidents cost the nation more than $700 billion annually. The CPSC is committed to protecting consumers and families from products that pose a fire, electrical, chemical, or mechanical hazard or can injure children. The CPSC's work to ensure the safety of consumer products - such as toys, cribs, power tools, cigarette lighters, and household chemicals - contributed significantly to the 30 percent decline in the rate of deaths and injuries associated with consumer products over the past 30 years.
318 -595 Safety CPSC Overview: Sanctioned by the US Congress (No direct cabinet level tie) The U. S. Consumer Product Safety Commission is charged with protecting the public from unreasonable risks of serious injury or death from more than 15, 000 types of consumer products under the agency's jurisdiction. Deaths, injuries and property damage from consumer product incidents cost the nation more than $700 billion annually. The CPSC is committed to protecting consumers and families from products that pose a fire, electrical, chemical, or mechanical hazard or can injure children. The CPSC's work to ensure the safety of consumer products - such as toys, cribs, power tools, cigarette lighters, and household chemicals - contributed significantly to the 30 percent decline in the rate of deaths and injuries associated with consumer products over the past 30 years.
 318 -595 Safety Government Agencies may also act as Standards Bodies • Global Examples: Ø SCC: Standards Council of Canada http: //www. scc. ca/ Ø CEN: Comm on European (EU) Normalization http: //www. cenorm. be/cenorm/index. htm Ø SAC: Standard Administration of China http: //www. sac. gov. cn/english/home. asp Ø JSA: Japanese Standards Association http: //www. jsa. or. jp/default_english. asp Ø BIS: Bureau of Indian Standards http: //www. bis. org. in/index_home. htm
318 -595 Safety Government Agencies may also act as Standards Bodies • Global Examples: Ø SCC: Standards Council of Canada http: //www. scc. ca/ Ø CEN: Comm on European (EU) Normalization http: //www. cenorm. be/cenorm/index. htm Ø SAC: Standard Administration of China http: //www. sac. gov. cn/english/home. asp Ø JSA: Japanese Standards Association http: //www. jsa. or. jp/default_english. asp Ø BIS: Bureau of Indian Standards http: //www. bis. org. in/index_home. htm
 318 -595 Safety A brief Tutorial on the Organization of the US Government Departments
318 -595 Safety A brief Tutorial on the Organization of the US Government Departments
 318 -595 Safety US Executive Branch Cabinet Level Departments Headed by Secretary’s Of Special Interest • Vice President • Agriculture • Commerce • Defense • Education • Energy • Health and Human Services • Homeland Security • Housing and Urban Development • Interior • Labor • State • Transportation • Treasury • Veterans Affairs • Justice, Attorney General • Administrator, Environmental Protection Agency • Director, Office of Management and Budget • Director, National Drug Control Policy • U. S. Trade Representative.
318 -595 Safety US Executive Branch Cabinet Level Departments Headed by Secretary’s Of Special Interest • Vice President • Agriculture • Commerce • Defense • Education • Energy • Health and Human Services • Homeland Security • Housing and Urban Development • Interior • Labor • State • Transportation • Treasury • Veterans Affairs • Justice, Attorney General • Administrator, Environmental Protection Agency • Director, Office of Management and Budget • Director, National Drug Control Policy • U. S. Trade Representative.
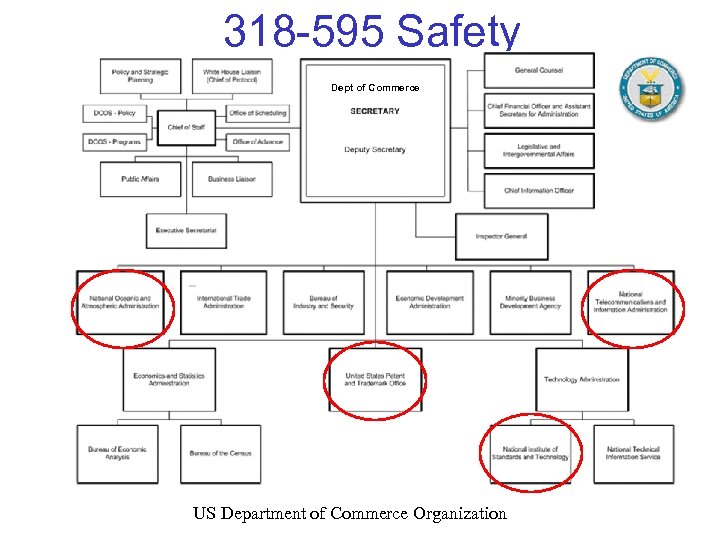 318 -595 Safety Dept of Commerce US Department of Commerce Organization
318 -595 Safety Dept of Commerce US Department of Commerce Organization
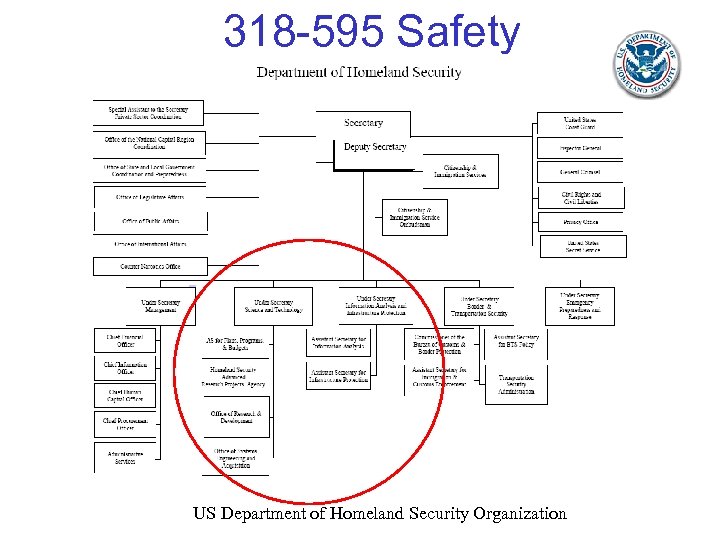 318 -595 Safety US Department of Homeland Security Organization
318 -595 Safety US Department of Homeland Security Organization
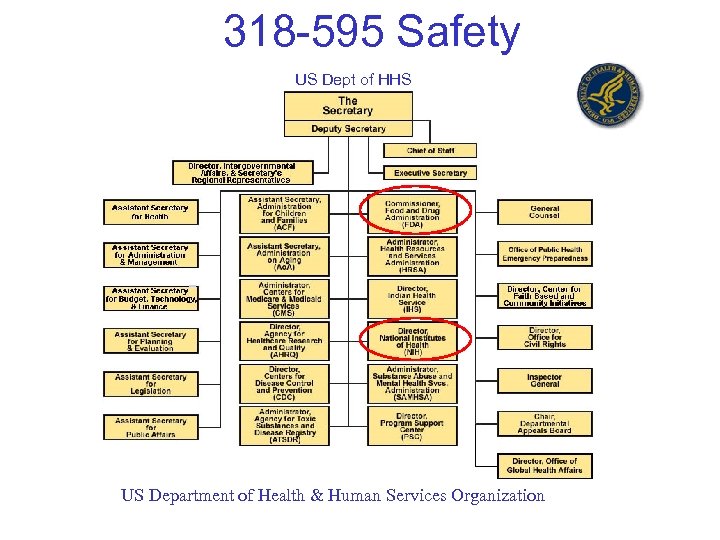 318 -595 Safety US Dept of HHS US Department of Health & Human Services Organization
318 -595 Safety US Dept of HHS US Department of Health & Human Services Organization
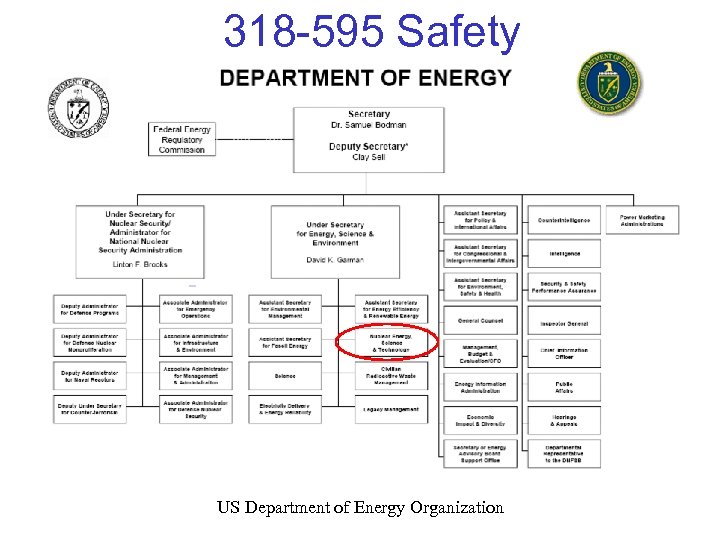 318 -595 Safety US Department of Energy Organization
318 -595 Safety US Department of Energy Organization
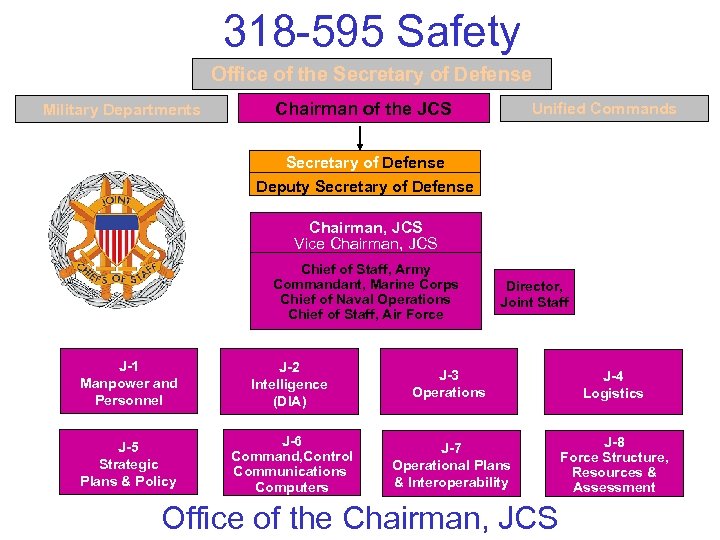
 318 -595 Safety How the US Do. D is organized National • President Command • Secretary of Defense Authority Office of the Secretary of Defense Military Departments • Train & equip Chairman of the JCS Unified Commands • Conduct operations • Plan & coordinate
318 -595 Safety How the US Do. D is organized National • President Command • Secretary of Defense Authority Office of the Secretary of Defense Military Departments • Train & equip Chairman of the JCS Unified Commands • Conduct operations • Plan & coordinate
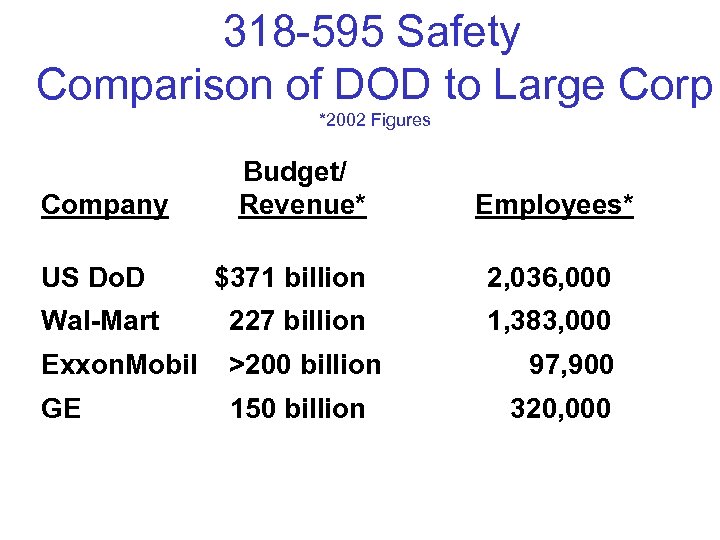 318 -595 Safety Comparison of DOD to Large Corp *2002 Figures Budget/ Company Revenue* Employees* US Do. D $371 billion 2, 036, 000 Wal-Mart 227 billion 1, 383, 000 Exxon. Mobil >200 billion 97, 900 GE 150 billion 320, 000
318 -595 Safety Comparison of DOD to Large Corp *2002 Figures Budget/ Company Revenue* Employees* US Do. D $371 billion 2, 036, 000 Wal-Mart 227 billion 1, 383, 000 Exxon. Mobil >200 billion 97, 900 GE 150 billion 320, 000
 318 -595 Safety Office of the Secretary of Defense Military Departments Chairman of the JCS Unified Commands Secretary of Defense Deputy Secretary of Defense Chairman, JCS Vice Chairman, JCS Chief of Staff, Army Commandant, Marine Corps Chief of Naval Operations Chief of Staff, Air Force J-1 Manpower and Personnel J-2 Intelligence (DIA) J-5 Strategic Plans & Policy J-6 Command, Control Communications Computers Director, Joint Staff J-3 Operations J-7 Operational Plans & Interoperability Office of the Chairman, JCS J-4 Logistics J-8 Force Structure, Resources & Assessment
318 -595 Safety Office of the Secretary of Defense Military Departments Chairman of the JCS Unified Commands Secretary of Defense Deputy Secretary of Defense Chairman, JCS Vice Chairman, JCS Chief of Staff, Army Commandant, Marine Corps Chief of Naval Operations Chief of Staff, Air Force J-1 Manpower and Personnel J-2 Intelligence (DIA) J-5 Strategic Plans & Policy J-6 Command, Control Communications Computers Director, Joint Staff J-3 Operations J-7 Operational Plans & Interoperability Office of the Chairman, JCS J-4 Logistics J-8 Force Structure, Resources & Assessment
 318 -595 Safety Office of the Secretary of Defense Military Departments Unified Commands Chairman of the JCS Secretary of Defense Deputy Secretary of Defense Northern Command European Command Transportation Command Central Command Special Operations Command Southern Command Strategic Command Pacific Command Joint Forces Command • Direct link to President & Secretary of Defense • 5 Commanders have geographic responsibility • 4 Operations Commanders have worldwide responsibility
318 -595 Safety Office of the Secretary of Defense Military Departments Unified Commands Chairman of the JCS Secretary of Defense Deputy Secretary of Defense Northern Command European Command Transportation Command Central Command Special Operations Command Southern Command Strategic Command Pacific Command Joint Forces Command • Direct link to President & Secretary of Defense • 5 Commanders have geographic responsibility • 4 Operations Commanders have worldwide responsibility
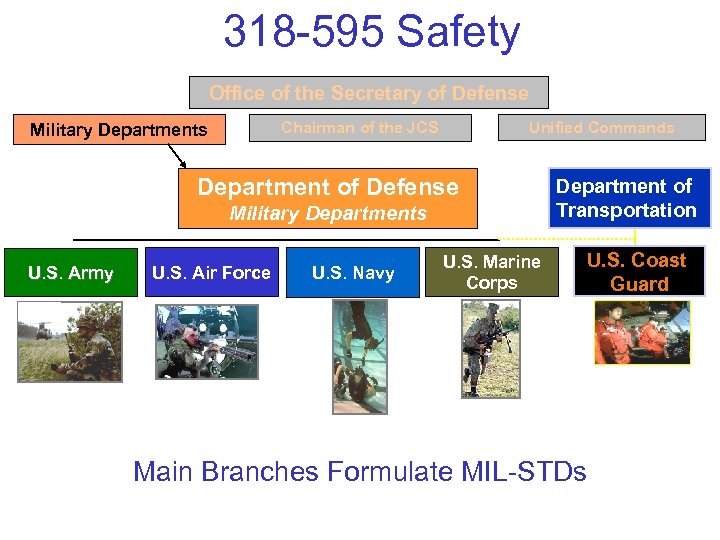 318 -595 Safety Office of the Secretary of Defense Unified Commands Chairman of the JCS Military Departments Department of Defense Military Departments U. S. Army U. S. Air Force U. S. Navy Department of Transportation U. S. Marine Corps Main Branches Formulate MIL-STDs U. S. Coast Guard
318 -595 Safety Office of the Secretary of Defense Unified Commands Chairman of the JCS Military Departments Department of Defense Military Departments U. S. Army U. S. Air Force U. S. Navy Department of Transportation U. S. Marine Corps Main Branches Formulate MIL-STDs U. S. Coast Guard
 318 -595 Safety Office of the Secretary of Defense Military Departments Chairman of the JCS Unified Commands Department of Defense Military Departments U. S. Army U. S. Air Force U. S. Navy Department of Transportation U. S. Marine Corps A Few Key MIL-STDs • MIL-STD-883 Test Method for Microcircuits • MIL-STD-750 Test Method for Semiconductor Devices • MIL-PRF-38534 Perf Spec for Hybrid Microelectronic Devices • MIL-PRF-38535 Perf Spec for Integrated Circuit Mfg • MIL-HDBK-344 Environmental Stress Screening of Elec Equipment • MIL-HDBK-1547 Elec Parts, Materials & Processes for Space Launch Vehicles • MIL-HDBK-2036 Preparation of Electronic Equipment Specifications • MIL-PRF-31032 Perf Spec for Printed Wiring Boards • MIL-STD-202 Test Method Standard for Elec & Electronic Components U. S. Coast Guard
318 -595 Safety Office of the Secretary of Defense Military Departments Chairman of the JCS Unified Commands Department of Defense Military Departments U. S. Army U. S. Air Force U. S. Navy Department of Transportation U. S. Marine Corps A Few Key MIL-STDs • MIL-STD-883 Test Method for Microcircuits • MIL-STD-750 Test Method for Semiconductor Devices • MIL-PRF-38534 Perf Spec for Hybrid Microelectronic Devices • MIL-PRF-38535 Perf Spec for Integrated Circuit Mfg • MIL-HDBK-344 Environmental Stress Screening of Elec Equipment • MIL-HDBK-1547 Elec Parts, Materials & Processes for Space Launch Vehicles • MIL-HDBK-2036 Preparation of Electronic Equipment Specifications • MIL-PRF-31032 Perf Spec for Printed Wiring Boards • MIL-STD-202 Test Method Standard for Elec & Electronic Components U. S. Coast Guard
 318 -595 Safety Standards, Test Labs & Standards Bodies
318 -595 Safety Standards, Test Labs & Standards Bodies
 318 -595 Safety Standards, Test Labs and Agencies • National Electrical Code - Standard – Originally developed in 1897 by the NFPA – Revised every 3 years, Currently 9 chapters, >700 pages – Controls methods, systems and materials used in electrical wiring, and building power distributions – USA Specific but referenced outside US – Also See www. mikeholt. com
318 -595 Safety Standards, Test Labs and Agencies • National Electrical Code - Standard – Originally developed in 1897 by the NFPA – Revised every 3 years, Currently 9 chapters, >700 pages – Controls methods, systems and materials used in electrical wiring, and building power distributions – USA Specific but referenced outside US – Also See www. mikeholt. com
 318 -595 Safety Standards, Test Labs and Agencies • Underwriters Labs – Test Lab (www. ul. com) – Originally developed in 1894 – Mission is to certify the safety of industrial, commercial and consumer products. – Government Independent, Non-for-profit organization – 5 Locations including, Northbrook IL (HQ), Research Triangle NC, Melville NY, Santa Clara CA, Camas WA – Certifications of products, Certifications of Companies – Cross agreement with CSA – Product Certifications C • Listed: Ready to use complete products • Recognized: Certified as a component for use in other products
318 -595 Safety Standards, Test Labs and Agencies • Underwriters Labs – Test Lab (www. ul. com) – Originally developed in 1894 – Mission is to certify the safety of industrial, commercial and consumer products. – Government Independent, Non-for-profit organization – 5 Locations including, Northbrook IL (HQ), Research Triangle NC, Melville NY, Santa Clara CA, Camas WA – Certifications of products, Certifications of Companies – Cross agreement with CSA – Product Certifications C • Listed: Ready to use complete products • Recognized: Certified as a component for use in other products
 318 -595 Safety Example: UL 60950 Safety of Information Technology Equipment This standard is applicable to mains-powered or battery-powered information technology equipment, including electrical business equipment and associated equipment, with a RATED VOLTAGE not exceeding 600 V and designed to be installed in accordance with the Canadian Electrical Code, Part I, CSA C 22. 1; CSA C 22. 2 No. 0 National Electrical Code, NFPA 70 The standard is also applicable to equipment, unless otherwise identified by a marking or instructions, designed to be installed in accordance with Article 645 of the National Electrical Code, NFPA 70 Standard for the Protection of Electronic Computer Data-Processing Equipment, NFPA 75
318 -595 Safety Example: UL 60950 Safety of Information Technology Equipment This standard is applicable to mains-powered or battery-powered information technology equipment, including electrical business equipment and associated equipment, with a RATED VOLTAGE not exceeding 600 V and designed to be installed in accordance with the Canadian Electrical Code, Part I, CSA C 22. 1; CSA C 22. 2 No. 0 National Electrical Code, NFPA 70 The standard is also applicable to equipment, unless otherwise identified by a marking or instructions, designed to be installed in accordance with Article 645 of the National Electrical Code, NFPA 70 Standard for the Protection of Electronic Computer Data-Processing Equipment, NFPA 75
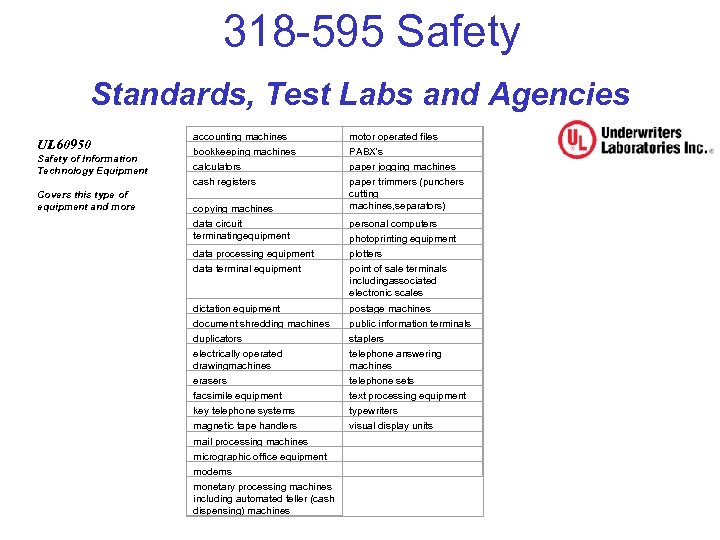 318 -595 Safety Standards, Test Labs and Agencies UL 60950 Safety of Information Technology Equipment Covers this type of equipment and more accounting machines motor operated files bookkeeping machines PABX's calculators paper jogging machines cash registers paper trimmers (punchers cutting machines, separators) copying machines data circuit terminatingequipment personal computers data processing equipment plotters data terminal equipment point of sale terminals includingassociated electronic scales dictation equipment postage machines document shredding machines public information terminals duplicators staplers electrically operated drawingmachines telephone answering machines erasers telephone sets facsimile equipment text processing equipment key telephone systems typewriters magnetic tape handlers visual display units mail processing machines micrographic office equipment modems monetary processing machines including automated teller (cash dispensing) machines photoprinting equipment
318 -595 Safety Standards, Test Labs and Agencies UL 60950 Safety of Information Technology Equipment Covers this type of equipment and more accounting machines motor operated files bookkeeping machines PABX's calculators paper jogging machines cash registers paper trimmers (punchers cutting machines, separators) copying machines data circuit terminatingequipment personal computers data processing equipment plotters data terminal equipment point of sale terminals includingassociated electronic scales dictation equipment postage machines document shredding machines public information terminals duplicators staplers electrically operated drawingmachines telephone answering machines erasers telephone sets facsimile equipment text processing equipment key telephone systems typewriters magnetic tape handlers visual display units mail processing machines micrographic office equipment modems monetary processing machines including automated teller (cash dispensing) machines photoprinting equipment
 318 -595 Safety Example: UL 6500 Audio/Video and Musical Instrument Apparatus for Household, Commercial, and Similar General Use 1. 1 Scope 1. 1. 1 This International Standard applies to electronic apparatus designed to be fed from the MAINS or from a SUPPLY APPARATUS and intended for reception, generation, recording or reproduction respectively of audio, video and associated signals. It also applies to apparatus designed to be used exclusively in combination with the above mentioned apparatus. This standard concerns only safety aspects of the above apparatus; it does not concern other matters, such as style or performance. - receiving apparatus and amplifiers for sound and/or vision; - independent LOAD TRANSDUCERS and SOURCE TRANSDUCERS; - SUPPLY APPARATUS intended to supply other apparatus covered by the scope of this standard; - ELECTRONIC MUSICAL INSTRUMENTS, and electronic accessories such as rhythm generators, tone generators, music tuners and the like for use with electronic or non-electronic musical instruments; - audio and/or video educational apparatus; - video projectors; - video cameras and video monitors; - household video games and flipper games; NOTE 2 - Video and flipper games for commercial use are covered by IEC 60335 -2 -82 [7] UL 22 Figures in square brackets refer to the bibliography given in annex p. - juke boxes; - household electronic gaming and scoring machines; NOTE 3 - Electronic gaming and scoring machines for commercial use are covered by IEC 60335 -2 -82 [7] UL 22 - teletext equipment; - record and optical disc players; - tape and optical disc recorders; - antenna signal converters and amplifiers; - satellite receiver antenna positioners; - Citizen's Band apparatus; - apparatus for IMAGERY; - light effect apparatus; - intercommunication apparatus, using low voltage MAINS as the transmission medium. - video apparatus intended for entertainment purposes in health-care facilities; - cellular phones, wireless modems, and similar transceiving devices; - audio or video apparatus that are used with a battery supply.
318 -595 Safety Example: UL 6500 Audio/Video and Musical Instrument Apparatus for Household, Commercial, and Similar General Use 1. 1 Scope 1. 1. 1 This International Standard applies to electronic apparatus designed to be fed from the MAINS or from a SUPPLY APPARATUS and intended for reception, generation, recording or reproduction respectively of audio, video and associated signals. It also applies to apparatus designed to be used exclusively in combination with the above mentioned apparatus. This standard concerns only safety aspects of the above apparatus; it does not concern other matters, such as style or performance. - receiving apparatus and amplifiers for sound and/or vision; - independent LOAD TRANSDUCERS and SOURCE TRANSDUCERS; - SUPPLY APPARATUS intended to supply other apparatus covered by the scope of this standard; - ELECTRONIC MUSICAL INSTRUMENTS, and electronic accessories such as rhythm generators, tone generators, music tuners and the like for use with electronic or non-electronic musical instruments; - audio and/or video educational apparatus; - video projectors; - video cameras and video monitors; - household video games and flipper games; NOTE 2 - Video and flipper games for commercial use are covered by IEC 60335 -2 -82 [7] UL 22 Figures in square brackets refer to the bibliography given in annex p. - juke boxes; - household electronic gaming and scoring machines; NOTE 3 - Electronic gaming and scoring machines for commercial use are covered by IEC 60335 -2 -82 [7] UL 22 - teletext equipment; - record and optical disc players; - tape and optical disc recorders; - antenna signal converters and amplifiers; - satellite receiver antenna positioners; - Citizen's Band apparatus; - apparatus for IMAGERY; - light effect apparatus; - intercommunication apparatus, using low voltage MAINS as the transmission medium. - video apparatus intended for entertainment purposes in health-care facilities; - cellular phones, wireless modems, and similar transceiving devices; - audio or video apparatus that are used with a battery supply.
 318 -595 Safety A few UL Standards • UL 60745 -1 • UL 60730 -1 A • UL 60601 -1 • UL 60335 -1 • UL 60065 • UL 2388 • UL 2251 • UL 2231 -1 • UL 2202 • UL 2111 • UL 2054 • UL 1998 • UL 1989 • UL 1981 • UL 1977 • UL 1876 • UL 1778 • UL 1741 • UL 1740 • UL 1703 • UL 1664 • UL 1642 • UL 1641 • UL 1637 • UL 1577 • UL 1559 • UL 1492 • UL 1459 • UL 1449 • UL 1433 Hand-Held Motor-Operated Electric Tools - Safety - Part 1: General Requirements Automatic Electrical Controls for Household and Similar Use, Part 1: General Requirements Medical Electrical Equipment, Part 1: General Requirements for Safety of Household and Similar Electrical Appliances, Part 1: General Requirements Audio, Video and Similar Electronic Apparatus - Safety Requirements Flexible Lighting Products Plugs, Receptacles and Couplers for Electric Vehicles Personnel Protection Systems for Electric Vehicle (EV) Supply Circuits: General Reqs Electric Vehicle (EV) Charging System Equipment Overheating Protection for Motors Household and Commercial Batteries Software in Programmable Components Safety Standard for Standby Batteries Central-Station Automation Systems Component Connectors for Use in Data, Signal, Control and Power Applications Isolating Signal and Feedback Transformers for Use in Electronic Equipment Uninterruptible Power Systems Inverters, Converters, and Controllers for Use in Independent Power Systems Safety Standard for Robots and Robotic Equipment Flat-Plate Photovoltaic Modules and Panels Safety Standard for Immersion Detection Circuit Interrupters Lithium Batteries Installation and Classification of Residential Burglar Alarm Systems Safety Standard for Home Health Care Signaling Equipment Standard for Safety of Optical Isolators Insect-Control Equipment - Electrocution Type Audio-Video Products and Accessories Safety Standard for Telephone Equipment Transient Voltage Surge Suppressors Control Centers for Changing Message Type Electric Signs
318 -595 Safety A few UL Standards • UL 60745 -1 • UL 60730 -1 A • UL 60601 -1 • UL 60335 -1 • UL 60065 • UL 2388 • UL 2251 • UL 2231 -1 • UL 2202 • UL 2111 • UL 2054 • UL 1998 • UL 1989 • UL 1981 • UL 1977 • UL 1876 • UL 1778 • UL 1741 • UL 1740 • UL 1703 • UL 1664 • UL 1642 • UL 1641 • UL 1637 • UL 1577 • UL 1559 • UL 1492 • UL 1459 • UL 1449 • UL 1433 Hand-Held Motor-Operated Electric Tools - Safety - Part 1: General Requirements Automatic Electrical Controls for Household and Similar Use, Part 1: General Requirements Medical Electrical Equipment, Part 1: General Requirements for Safety of Household and Similar Electrical Appliances, Part 1: General Requirements Audio, Video and Similar Electronic Apparatus - Safety Requirements Flexible Lighting Products Plugs, Receptacles and Couplers for Electric Vehicles Personnel Protection Systems for Electric Vehicle (EV) Supply Circuits: General Reqs Electric Vehicle (EV) Charging System Equipment Overheating Protection for Motors Household and Commercial Batteries Software in Programmable Components Safety Standard for Standby Batteries Central-Station Automation Systems Component Connectors for Use in Data, Signal, Control and Power Applications Isolating Signal and Feedback Transformers for Use in Electronic Equipment Uninterruptible Power Systems Inverters, Converters, and Controllers for Use in Independent Power Systems Safety Standard for Robots and Robotic Equipment Flat-Plate Photovoltaic Modules and Panels Safety Standard for Immersion Detection Circuit Interrupters Lithium Batteries Installation and Classification of Residential Burglar Alarm Systems Safety Standard for Home Health Care Signaling Equipment Standard for Safety of Optical Isolators Insect-Control Equipment - Electrocution Type Audio-Video Products and Accessories Safety Standard for Telephone Equipment Transient Voltage Surge Suppressors Control Centers for Changing Message Type Electric Signs
 318 -595 Safety A few more UL Standards • UL 1434 • UL 1419 • UL 1416 • UL 1412 • UL 1411 • UL 1283 • UL 1244 • UL 1236 • UL 1196 • UL 1082 • UL 1077 • UL 1066 • UL 1053 • UL 1047 • UL 1034 • UL 1023 • UL 1020 • UL 1018 • UL 1010 Thermistor-Type Devices Professional Video and Audio Equipment Overcurrent and Overtemperature Protectors for Radio- and Television- Type Appliances Fusing Resistors and Temperature-Limited Resistors for Radio- and TV- Type Appliances Transformers and Motor Transformers for Use in Audio-, Radio-, and TV-Type Appliances Electromagnetic Interference Filters Electrical and Electronic Measuring and Testing Equipment Battery Chargers for Charging Engine-Starter Batteries Standard for Safety for Floating Waterlights Household Electric Coffee Makers and Brewing-Type Appliances Supplementary Protectors for Use in Electrical Equipment Safety Standard for Low Voltage AC and DC Power Circuit Breakers used in Enclosures Standard for Safety for Ground-Fault Sensing and Relaying Equipment Isolated Power Systems Equipment Burglary-Resistant Electric Locking Mechanisms Household Burglar-Alarm System Units Thermal Cutoffs for Use in Electrical Appliances and Components Electric Aquarium Equipment Receptacle-Plug Combinations for Use in Hazardous (Classified) Locations www. ul. com
318 -595 Safety A few more UL Standards • UL 1434 • UL 1419 • UL 1416 • UL 1412 • UL 1411 • UL 1283 • UL 1244 • UL 1236 • UL 1196 • UL 1082 • UL 1077 • UL 1066 • UL 1053 • UL 1047 • UL 1034 • UL 1023 • UL 1020 • UL 1018 • UL 1010 Thermistor-Type Devices Professional Video and Audio Equipment Overcurrent and Overtemperature Protectors for Radio- and Television- Type Appliances Fusing Resistors and Temperature-Limited Resistors for Radio- and TV- Type Appliances Transformers and Motor Transformers for Use in Audio-, Radio-, and TV-Type Appliances Electromagnetic Interference Filters Electrical and Electronic Measuring and Testing Equipment Battery Chargers for Charging Engine-Starter Batteries Standard for Safety for Floating Waterlights Household Electric Coffee Makers and Brewing-Type Appliances Supplementary Protectors for Use in Electrical Equipment Safety Standard for Low Voltage AC and DC Power Circuit Breakers used in Enclosures Standard for Safety for Ground-Fault Sensing and Relaying Equipment Isolated Power Systems Equipment Burglary-Resistant Electric Locking Mechanisms Household Burglar-Alarm System Units Thermal Cutoffs for Use in Electrical Appliances and Components Electric Aquarium Equipment Receptacle-Plug Combinations for Use in Hazardous (Classified) Locations www. ul. com
 318 -595 Safety Standards, Labs and Agencies • CSA International - Test Lab – – – – See www. csa. ca Established in 1919 in Toronto, Canada Similar to UL, Independent, but growing Internationally Controls materials, processes, products, companies Cross certification agreements with UL Does NOT differentiate between products & components Local offices in Canada, US and Asia
318 -595 Safety Standards, Labs and Agencies • CSA International - Test Lab – – – – See www. csa. ca Established in 1919 in Toronto, Canada Similar to UL, Independent, but growing Internationally Controls materials, processes, products, companies Cross certification agreements with UL Does NOT differentiate between products & components Local offices in Canada, US and Asia
 318 -595 Safety IEC – International Electrotechnical Commission www. iec. ch IEC Mission • The International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC) is the leading global organization that prepares and publishes international standards for all electrical, electronic and related technologies. These serve as a basis for national (government) standardization and as references when drafting international tenders and contracts. • Through its members, the IEC promotes international cooperation on all questions of electrotechnical standardization and related matters, such as the assessment of conformity to standards, in the fields of electricity, electronics and related technologies. • The IEC charter embraces all electrotechnologies including electronics, magnetics and electromagnetics, electroacoustics, multimedia, telecommunication, and energy production and distribution, as well as associated general disciplines such as terminology and symbols, electromagnetic compatibility, measurement and performance, dependability, design and development, safety and the environment. The Commission's objectives are to: • Meet the requirements of the global market efficiently • Ensure primacy and maximum world-wide use of its standards and conformity assessment schemes • Assess and improve the quality of products and services covered by its standards • Establish the conditions for the interoperability of complex systems • Increase the efficiency of industrial processes • Contribute to the improvement of human health and safety • Contribute to the protection of the environment.
318 -595 Safety IEC – International Electrotechnical Commission www. iec. ch IEC Mission • The International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC) is the leading global organization that prepares and publishes international standards for all electrical, electronic and related technologies. These serve as a basis for national (government) standardization and as references when drafting international tenders and contracts. • Through its members, the IEC promotes international cooperation on all questions of electrotechnical standardization and related matters, such as the assessment of conformity to standards, in the fields of electricity, electronics and related technologies. • The IEC charter embraces all electrotechnologies including electronics, magnetics and electromagnetics, electroacoustics, multimedia, telecommunication, and energy production and distribution, as well as associated general disciplines such as terminology and symbols, electromagnetic compatibility, measurement and performance, dependability, design and development, safety and the environment. The Commission's objectives are to: • Meet the requirements of the global market efficiently • Ensure primacy and maximum world-wide use of its standards and conformity assessment schemes • Assess and improve the quality of products and services covered by its standards • Establish the conditions for the interoperability of complex systems • Increase the efficiency of industrial processes • Contribute to the improvement of human health and safety • Contribute to the protection of the environment.
 318 -595 Safety IEC – International Electrotechnical Commission Standards Areas • GENERALITIES. TERMINOLOGY. STANDARDIZATION. DOCUMENTATION. • SOCIOLOGY. SERVICES. COMPANY ORGANIZATION AND MANAGEMENT. ADMINISTRATION. TRANSPORT • MATHEMATICS. NATURAL SCIENCES • HEALTH CARE TECHNOLOGY • ENVIRONMENT. HEALTH PROTECTION. SAFETY • METROLOGY AND MEASUREMENT. PHYSICAL PHENOMENA • TESTING • MECHANICAL SYSTEMS AND COMPONENTS FOR GENERAL USE • FLUID SYSTEMS AND COMPONENTS FOR GENERAL USE • MANUFACTURING ENGINEERING • ENERGY AND HEAT TRANSFER ENGINEERING • ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING • ELECTRONICS • TELECOMMUNICATIONS. AUDIO AND VIDEO ENGINEERING • INFORMATION TECHNOLOGY. OFFICE MACHINES • IMAGE TECHNOLOGY • PRECISION MECHANICS. JEWELLERY • ROAD VEHICLE ENGINEERING • RAILWAY ENGINEERING • SHIPBUILDING AND MARINE STRUCTURES • AIRCRAFT AND SPACE VEHICLE ENGINEERING • MATERIALS HANDLING EQUIPMENT • PACKAGING AND DISTRIBUTION OF GOODS • TEXTILE AND LEATHER TECHNOLOGY • CLOTHING INDUSTRY • AGRICULTURE • FOOD TECHNOLOGY • CHEMICAL TECHNOLOGY • MINING AND MINERALS • PETROLEUM AND RELATED TECHNOLOGIES • METALLURGY • WOOD TECHNOLOGY • GLASS AND CERAMICS INDUSTRIES • RUBBER AND PLASTICS INDUSTRIES • PAPER TECHNOLOGY • PAINT AND COLOUR INDUSTRIES • CONSTRUCTION MATERIALS AND BUILDING • CIVIL ENGINEERING • MILITARY ENGINEERING • DOMESTIC AND COMMERCIAL EQUIPMENT. ENTERTAINMENT. SPORTS. • (No title)
318 -595 Safety IEC – International Electrotechnical Commission Standards Areas • GENERALITIES. TERMINOLOGY. STANDARDIZATION. DOCUMENTATION. • SOCIOLOGY. SERVICES. COMPANY ORGANIZATION AND MANAGEMENT. ADMINISTRATION. TRANSPORT • MATHEMATICS. NATURAL SCIENCES • HEALTH CARE TECHNOLOGY • ENVIRONMENT. HEALTH PROTECTION. SAFETY • METROLOGY AND MEASUREMENT. PHYSICAL PHENOMENA • TESTING • MECHANICAL SYSTEMS AND COMPONENTS FOR GENERAL USE • FLUID SYSTEMS AND COMPONENTS FOR GENERAL USE • MANUFACTURING ENGINEERING • ENERGY AND HEAT TRANSFER ENGINEERING • ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING • ELECTRONICS • TELECOMMUNICATIONS. AUDIO AND VIDEO ENGINEERING • INFORMATION TECHNOLOGY. OFFICE MACHINES • IMAGE TECHNOLOGY • PRECISION MECHANICS. JEWELLERY • ROAD VEHICLE ENGINEERING • RAILWAY ENGINEERING • SHIPBUILDING AND MARINE STRUCTURES • AIRCRAFT AND SPACE VEHICLE ENGINEERING • MATERIALS HANDLING EQUIPMENT • PACKAGING AND DISTRIBUTION OF GOODS • TEXTILE AND LEATHER TECHNOLOGY • CLOTHING INDUSTRY • AGRICULTURE • FOOD TECHNOLOGY • CHEMICAL TECHNOLOGY • MINING AND MINERALS • PETROLEUM AND RELATED TECHNOLOGIES • METALLURGY • WOOD TECHNOLOGY • GLASS AND CERAMICS INDUSTRIES • RUBBER AND PLASTICS INDUSTRIES • PAPER TECHNOLOGY • PAINT AND COLOUR INDUSTRIES • CONSTRUCTION MATERIALS AND BUILDING • CIVIL ENGINEERING • MILITARY ENGINEERING • DOMESTIC AND COMMERCIAL EQUIPMENT. ENTERTAINMENT. SPORTS. • (No title)
 318 -595 Safety IEC – International Electrotechnical Commission Example of Standards Area 3316010 Amplifiers (part of Telecom, Audio & Video area) 33. 160. 10 IEC 60268 -3 (2000 -08) Sound system equipment - Part 3: Amplifiers 33. 160. 10 IEC 60268 -3 (2000 -08) Versión Oficial en Español - Equipos para sistemas electroacústicos. Parte 3: Amplificadores. 33. 160. 10 IEC 60268 -8 (1973 -01) Sound system equipment. Part 8: Automatic gain control devices 33. 160. 10 IEC/TR 61292 -1 (1998 -01) Fibre optics - Parameters of amplifier components 33. 160. 10 IEC/TR 61292 -2 (2003 -01) Optical amplifier technical reports - Part 2: Theoretical background for noise figure evaluation using the electrical spectrum analyzer 33. 160. 10 IEC/TR 61292 -3 (2003 -06) Optical amplifiers - Part 3: Classification, characteristics and applications 33. 160. 10 IEC/TR 61292 -4 (2004 -08) Optical amplifiers - Part 4: Maximum permissible optical power for the damage-free and safe use of optical amplifiers, including Raman amplifiers 33. 160. 10 IEC/TR 61292 -5 (2004 -07) Optical amplifiers - Part 5: Polarization mode dispersion parameter - General information 33. 160. 10 IEC 61305 -3 (1995 -05) Household high-fidelity audio equipment and systems - Methods of measuring and specifying the performance - Part 3: Amplifiers 33. 160. 10 IEC 61305 -3 (1995 -05) VERSION OFICIAL EN ESPANOL - Sistemas y equipos domésticos de sonido de alta fidelidad. Métodos de medir y especificar las características de funcionamiento. Parte 3: Amplificadores.
318 -595 Safety IEC – International Electrotechnical Commission Example of Standards Area 3316010 Amplifiers (part of Telecom, Audio & Video area) 33. 160. 10 IEC 60268 -3 (2000 -08) Sound system equipment - Part 3: Amplifiers 33. 160. 10 IEC 60268 -3 (2000 -08) Versión Oficial en Español - Equipos para sistemas electroacústicos. Parte 3: Amplificadores. 33. 160. 10 IEC 60268 -8 (1973 -01) Sound system equipment. Part 8: Automatic gain control devices 33. 160. 10 IEC/TR 61292 -1 (1998 -01) Fibre optics - Parameters of amplifier components 33. 160. 10 IEC/TR 61292 -2 (2003 -01) Optical amplifier technical reports - Part 2: Theoretical background for noise figure evaluation using the electrical spectrum analyzer 33. 160. 10 IEC/TR 61292 -3 (2003 -06) Optical amplifiers - Part 3: Classification, characteristics and applications 33. 160. 10 IEC/TR 61292 -4 (2004 -08) Optical amplifiers - Part 4: Maximum permissible optical power for the damage-free and safe use of optical amplifiers, including Raman amplifiers 33. 160. 10 IEC/TR 61292 -5 (2004 -07) Optical amplifiers - Part 5: Polarization mode dispersion parameter - General information 33. 160. 10 IEC 61305 -3 (1995 -05) Household high-fidelity audio equipment and systems - Methods of measuring and specifying the performance - Part 3: Amplifiers 33. 160. 10 IEC 61305 -3 (1995 -05) VERSION OFICIAL EN ESPANOL - Sistemas y equipos domésticos de sonido de alta fidelidad. Métodos de medir y especificar las características de funcionamiento. Parte 3: Amplificadores.
 318 -595 Safety What is the “CE” Mark? CE Marking is the symbol “CE” as shown on the top of this page. The letters "CE" are the abbreviation of French phrase "Conformité Européene" which means "European Conformity". The term initially used was "EC Mark" and it was officially replaced by "CE Marking" in the Directive 93/68/EEC in 1993. "CE Marking" is now used in all EU official documents. CE Marking on a product is a manufacturer's declaration that the product complies with the essential requirements of the relevant European health, safety and environmental protection legislations, in practice by many of the so-called Product Directives • “Essential Requirements" are the performance levels contained in harmonized standards to which the products must conform. • “Product Directives” are the legal directives and laws which specify the harmonized standards for certain types and classes of products to conform. Ex; 95/94/EEC: Automotive Products • “Harmonized Standards” are the technical specifications (European Standards or Harmonization Documents) which are established by several European standards agencies (CEN, CENELEC, etc). • CEN is the European Committee for Standardization. • CENELEC is the European Committee for Electrotechnical Standardization.
318 -595 Safety What is the “CE” Mark? CE Marking is the symbol “CE” as shown on the top of this page. The letters "CE" are the abbreviation of French phrase "Conformité Européene" which means "European Conformity". The term initially used was "EC Mark" and it was officially replaced by "CE Marking" in the Directive 93/68/EEC in 1993. "CE Marking" is now used in all EU official documents. CE Marking on a product is a manufacturer's declaration that the product complies with the essential requirements of the relevant European health, safety and environmental protection legislations, in practice by many of the so-called Product Directives • “Essential Requirements" are the performance levels contained in harmonized standards to which the products must conform. • “Product Directives” are the legal directives and laws which specify the harmonized standards for certain types and classes of products to conform. Ex; 95/94/EEC: Automotive Products • “Harmonized Standards” are the technical specifications (European Standards or Harmonization Documents) which are established by several European standards agencies (CEN, CENELEC, etc). • CEN is the European Committee for Standardization. • CENELEC is the European Committee for Electrotechnical Standardization.
 318 -595 Safety Purpose of the CE Mark • The CE Mark is a Manufacturer’s Declaration that the product placed onto the EU market conforms with all the applicable essential requirements in the harmonized standards. ie; The Product is Safe and Complies with all Standards • CE Marking on a product indicates to governmental officials that the product may be legally placed on the market in their country. • CE Marking on a product ensures the free movement of the product within the EFTA & European Union (EU) single market (total 37 countries). • CE Marking on a product permits the withdrawal of any non-conforming products by customs and other enforcement authorities.
318 -595 Safety Purpose of the CE Mark • The CE Mark is a Manufacturer’s Declaration that the product placed onto the EU market conforms with all the applicable essential requirements in the harmonized standards. ie; The Product is Safe and Complies with all Standards • CE Marking on a product indicates to governmental officials that the product may be legally placed on the market in their country. • CE Marking on a product ensures the free movement of the product within the EFTA & European Union (EU) single market (total 37 countries). • CE Marking on a product permits the withdrawal of any non-conforming products by customs and other enforcement authorities.
 318 -595 Safety • CE Mark History CE Mark – 15 countries in original EU (European Union) established harmonized standards – EC/EEC (European Committee/European Economic Community) is the body driving establishment of standards for any product sold in or entering into the EU. – Members may additional more stringent standards but may not contradict existing EC approved standards – Some of the EC Product Directives: • • • 88/106/EEC: Safety of Toys 89/106/EEC: Construction of Products 89/336/EEC, 92/31/EC: EMC 89/392/EEC, 91/368/EC, 3/44/EEC: Machinery 89/686/EEC, 93/95/EEC: Personal Protective Equipment 91/263/EEC, 93/97/EEC, 98/13/EEC: Telecommunications 93/42/EEC: Medical Devices 72/23/EEC: Low Voltage Products 95/94/EEC: Automotive Products 96/57/EC: Energy Efficiency for consumer refrigeration systems
318 -595 Safety • CE Mark History CE Mark – 15 countries in original EU (European Union) established harmonized standards – EC/EEC (European Committee/European Economic Community) is the body driving establishment of standards for any product sold in or entering into the EU. – Members may additional more stringent standards but may not contradict existing EC approved standards – Some of the EC Product Directives: • • • 88/106/EEC: Safety of Toys 89/106/EEC: Construction of Products 89/336/EEC, 92/31/EC: EMC 89/392/EEC, 91/368/EC, 3/44/EEC: Machinery 89/686/EEC, 93/95/EEC: Personal Protective Equipment 91/263/EEC, 93/97/EEC, 98/13/EEC: Telecommunications 93/42/EEC: Medical Devices 72/23/EEC: Low Voltage Products 95/94/EEC: Automotive Products 96/57/EC: Energy Efficiency for consumer refrigeration systems
 318 -595 Safety ISO – International Organization for Standardization Standards Body www. iso. org • ISO is a network of the national standards institutes of 148 countries, on the basis of one member per country. • Central Secretariat in Geneva, Switzerland, coordinates the system • ISO is a non-governmental organization • ISO occupies a special position between the public and private sectors • Many of its member institutes are part of the governmental structure of their countries, or are mandated by their government. • Other members have their roots uniquely in the private sector, having been set up by national partnerships of industry associations.
318 -595 Safety ISO – International Organization for Standardization Standards Body www. iso. org • ISO is a network of the national standards institutes of 148 countries, on the basis of one member per country. • Central Secretariat in Geneva, Switzerland, coordinates the system • ISO is a non-governmental organization • ISO occupies a special position between the public and private sectors • Many of its member institutes are part of the governmental structure of their countries, or are mandated by their government. • Other members have their roots uniquely in the private sector, having been set up by national partnerships of industry associations.
 318 -595 Safety ISO – International Organization for Standardization ISO 9000 Quality The ISO 9000 Family of Standards via ISO web site : http: //www. iso. ch/iso/en/iso 9000 -14000/iso 9000/selection_use/iso 9000 family. html ISO: 9000: 2000, Quality management systems - Fundamentals and vocabulary 9001: 2000, Quality management systems - Requirements (replaces 1994 versions of 9001, 9002 & 9003) 9004: 2000, Quality management systems - Guidelines for performance improvements 10005: 1995, Quality management - Guidelines for quality plans 10006: 1997, Quality management - Guidelines to quality in project management 10007: 1995, Quality management - Guidelines for configuration management
318 -595 Safety ISO – International Organization for Standardization ISO 9000 Quality The ISO 9000 Family of Standards via ISO web site : http: //www. iso. ch/iso/en/iso 9000 -14000/iso 9000/selection_use/iso 9000 family. html ISO: 9000: 2000, Quality management systems - Fundamentals and vocabulary 9001: 2000, Quality management systems - Requirements (replaces 1994 versions of 9001, 9002 & 9003) 9004: 2000, Quality management systems - Guidelines for performance improvements 10005: 1995, Quality management - Guidelines for quality plans 10006: 1997, Quality management - Guidelines to quality in project management 10007: 1995, Quality management - Guidelines for configuration management
 318 -595 Safety ISO 9000 and ISO 14000 Standards • The ISO 9000 and ISO 14000 families are among ISO's most widely known standards ever. • ISO 9000 and ISO 14000 standards are implemented by some 610, 000 organizations (companies & corporations) in 160 countries. • The ISO 9000 family is primarily concerned with "quality management“ • This means what the organization does to fulfill: - the customer's quality requirements, and - applicable regulatory requirements, while aiming to - enhance customer satisfaction, and - achieve continual improvement of its performance in pursuit of these objectives.
318 -595 Safety ISO 9000 and ISO 14000 Standards • The ISO 9000 and ISO 14000 families are among ISO's most widely known standards ever. • ISO 9000 and ISO 14000 standards are implemented by some 610, 000 organizations (companies & corporations) in 160 countries. • The ISO 9000 family is primarily concerned with "quality management“ • This means what the organization does to fulfill: - the customer's quality requirements, and - applicable regulatory requirements, while aiming to - enhance customer satisfaction, and - achieve continual improvement of its performance in pursuit of these objectives.
 318 -595 Safety ISO 9000 and ISO 14000 Standards • Similar to the US EPS, the ISO 14000 family of standards is primarily concerned with “Environmental Management" • Specifies what an organization must do to: - minimize harmful effects on the environment caused by its activities - achieve continual improvement of its environmental performance
318 -595 Safety ISO 9000 and ISO 14000 Standards • Similar to the US EPS, the ISO 14000 family of standards is primarily concerned with “Environmental Management" • Specifies what an organization must do to: - minimize harmful effects on the environment caused by its activities - achieve continual improvement of its environmental performance
 318 -595 Safety Other Safety Standards Organizations • AAMI - American Association of Medical Instrumentation • ANSI - American National Standards Institute • ASTM - American Society for Testing and Materials • NFPA - National Fire Protection Association • SCC - Standards Council of Canada See: http: //ulstandardsinfonet. ul. com/catalog/stdscatframe. html For an exhaustive list of potentially applicable safety standards (> 200 stds)
318 -595 Safety Other Safety Standards Organizations • AAMI - American Association of Medical Instrumentation • ANSI - American National Standards Institute • ASTM - American Society for Testing and Materials • NFPA - National Fire Protection Association • SCC - Standards Council of Canada See: http: //ulstandardsinfonet. ul. com/catalog/stdscatframe. html For an exhaustive list of potentially applicable safety standards (> 200 stds)
 318 -595 Safety UL Std Example: UL 1236 Battery Chargers for Charging Engine-Starter Batteries UL 1236 Scope 1. 1 These requirements cover battery chargers rated 600 volts or less and intended for household or commercial use to charge engine-starter batteries, in accordance with the National Electrical Code, ANSI/NFPA 70. 1. 2 A battery charger for use with an internal combustion engine is to be investigated under the requirements of this standard and the applicable requirements for the end product. 1. 3 These requirements do not cover a battery charger for use in a marina or boatyard, or other marine application excepting a battery charger intended to be permanently installed on a boat; for fire protection signaling service; or an appliance or system in which a battery charger is used. UL Standards. Info. Net | Underwriters Laboratories Inc. Copyright © 2003 Underwriters Laboratories Inc.
318 -595 Safety UL Std Example: UL 1236 Battery Chargers for Charging Engine-Starter Batteries UL 1236 Scope 1. 1 These requirements cover battery chargers rated 600 volts or less and intended for household or commercial use to charge engine-starter batteries, in accordance with the National Electrical Code, ANSI/NFPA 70. 1. 2 A battery charger for use with an internal combustion engine is to be investigated under the requirements of this standard and the applicable requirements for the end product. 1. 3 These requirements do not cover a battery charger for use in a marina or boatyard, or other marine application excepting a battery charger intended to be permanently installed on a boat; for fire protection signaling service; or an appliance or system in which a battery charger is used. UL Standards. Info. Net | Underwriters Laboratories Inc. Copyright © 2003 Underwriters Laboratories Inc.
 318 -595 Safety Project Safety Std Examples Lasers and Products Containing Lasers US/FDA: IEC: 21 CFR 1040. 10 - Laser Products 60820 - Electrical Safety of Laser Equipment and Installations 60825 - Radiation Safety of Laser Products, Equipment Classification, Requirements and User's Guide 60601 -2 -22 Diagnostic and Therapeutic Laser Equipment Other: ANSI Z 136. 3 - Safe use of lasers in health care facilities Imaging and Display Including CRT Type Video Monitors US/FDA: Other: 21 CFR 1020. 10 - Television Receivers (x-ray emissions) SMPTE Standards and Publications (test paterns) Broadcast TV Standards by Country (NTSC, PAL, SECAM etc. ) Video Recording Formats & Standards (VHS, Beta, Hi 8 etc. ) Imaging Systems: Range of Factors Affecting Image Quality Telephone Terminal and Communications Equipment US/FCC: 47 CFR 68 Connection of terminal equipment to the telephone network IEC: 60617 -9 Graphical symbols for diagrams part 9: telecommunications: switching and peripheral equipment EC: 1999/5/EC R&TTE - Radio & Telecommunications Terminal Equipment Directive
318 -595 Safety Project Safety Std Examples Lasers and Products Containing Lasers US/FDA: IEC: 21 CFR 1040. 10 - Laser Products 60820 - Electrical Safety of Laser Equipment and Installations 60825 - Radiation Safety of Laser Products, Equipment Classification, Requirements and User's Guide 60601 -2 -22 Diagnostic and Therapeutic Laser Equipment Other: ANSI Z 136. 3 - Safe use of lasers in health care facilities Imaging and Display Including CRT Type Video Monitors US/FDA: Other: 21 CFR 1020. 10 - Television Receivers (x-ray emissions) SMPTE Standards and Publications (test paterns) Broadcast TV Standards by Country (NTSC, PAL, SECAM etc. ) Video Recording Formats & Standards (VHS, Beta, Hi 8 etc. ) Imaging Systems: Range of Factors Affecting Image Quality Telephone Terminal and Communications Equipment US/FCC: 47 CFR 68 Connection of terminal equipment to the telephone network IEC: 60617 -9 Graphical symbols for diagrams part 9: telecommunications: switching and peripheral equipment EC: 1999/5/EC R&TTE - Radio & Telecommunications Terminal Equipment Directive
 318 -595 Safety Project Health and Safety Aspects • Key Safety Requirements Checklist - Electrical ü Over current or short circuit protection on power inputs ü Over current or short circuit protection on power outputs and higher energy signal outputs ü Internal over current protection on all power supplies ü XFMR Isolation from AC power line to electronic circuits ü Low leakage (<1 m. A) to earth ground return ü Proper wire gauges and trace widths vs. max application current ü Insulation and creepage distance versus voltage between conductors ü Min 50% derating of wattage components ü Worst case ambient thermal rise internal to product accounted for ü Diagnostic Tests or Failure Mode Indicators for Operator/Service ü Failure Modes & Effects Analysis (what happens if any one component fails, ie; shorts inputs to outputs or opens? ) ü Electromagnetic Compliance
318 -595 Safety Project Health and Safety Aspects • Key Safety Requirements Checklist - Electrical ü Over current or short circuit protection on power inputs ü Over current or short circuit protection on power outputs and higher energy signal outputs ü Internal over current protection on all power supplies ü XFMR Isolation from AC power line to electronic circuits ü Low leakage (<1 m. A) to earth ground return ü Proper wire gauges and trace widths vs. max application current ü Insulation and creepage distance versus voltage between conductors ü Min 50% derating of wattage components ü Worst case ambient thermal rise internal to product accounted for ü Diagnostic Tests or Failure Mode Indicators for Operator/Service ü Failure Modes & Effects Analysis (what happens if any one component fails, ie; shorts inputs to outputs or opens? ) ü Electromagnetic Compliance
 318 -595 Safety Project Health and Safety Aspects • Key Safety Requirements Checklist - Mechanical ü Product is free from pinch points and sharp or rough edges ü Electronics/mechanics susceptible to dirt, fluids, are reasonably sealed from environment? (thru packaging or potting) ü Consideration for handles, carrying, ergonomics, etc ü If the product is > 40 lbs, must provide considered handles, fixtures, etc for the user including OSHA mfg issues? ü Maximum surface temperature of product must not exceed 40 o. C on any surface that can be touched by a user ü Does the product emit other energy output such light, sound, heat, etc and is there a safe level which can be related to a Safety Standard? ü Does the product have sufficient stand-up stability with no reasonable tip hazard or sliding hazards ü Has the product been designed and assembled to withstand designated lifetime of mechanical stresses including shipping
318 -595 Safety Project Health and Safety Aspects • Key Safety Requirements Checklist - Mechanical ü Product is free from pinch points and sharp or rough edges ü Electronics/mechanics susceptible to dirt, fluids, are reasonably sealed from environment? (thru packaging or potting) ü Consideration for handles, carrying, ergonomics, etc ü If the product is > 40 lbs, must provide considered handles, fixtures, etc for the user including OSHA mfg issues? ü Maximum surface temperature of product must not exceed 40 o. C on any surface that can be touched by a user ü Does the product emit other energy output such light, sound, heat, etc and is there a safe level which can be related to a Safety Standard? ü Does the product have sufficient stand-up stability with no reasonable tip hazard or sliding hazards ü Has the product been designed and assembled to withstand designated lifetime of mechanical stresses including shipping
 318 -595 Safety Project Health and Safety Aspects • Key Safety Requirements Checklist – Materials and Usage ü Does the Operator Manual include specific labeling of usage ü Does the Operator/Service Manuals include proper warnings for typical hazardous misuses ü Has the product been labeled adequately for misuse by children or other demographic groups ü Are there any hazardous materials including Pb, Cd, Cr+6, Hg, Polybrominated Biphenals (PBB) and Diphenal Ethers (PBDE) used in the product. If so, where are they and in what concentrations. ü What chemicals and raw materials are used in the product and have the Material Safety Data Sheets (MSDS) been reviewed for these materials?
318 -595 Safety Project Health and Safety Aspects • Key Safety Requirements Checklist – Materials and Usage ü Does the Operator Manual include specific labeling of usage ü Does the Operator/Service Manuals include proper warnings for typical hazardous misuses ü Has the product been labeled adequately for misuse by children or other demographic groups ü Are there any hazardous materials including Pb, Cd, Cr+6, Hg, Polybrominated Biphenals (PBB) and Diphenal Ethers (PBDE) used in the product. If so, where are they and in what concentrations. ü What chemicals and raw materials are used in the product and have the Material Safety Data Sheets (MSDS) been reviewed for these materials?


