e1976ea1020b74bd109e31ea1469407d.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 24
 3100 A Ventilator
3100 A Ventilator
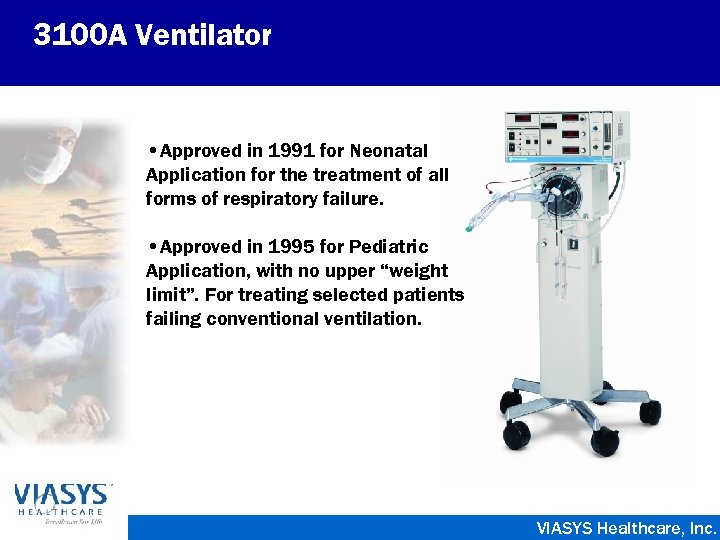 3100 A Ventilator • Approved in 1991 for Neonatal Application for the treatment of all forms of respiratory failure. • Approved in 1995 for Pediatric Application, with no upper “weight limit”. For treating selected patients failing conventional ventilation. VIASYS Healthcare, Inc.
3100 A Ventilator • Approved in 1991 for Neonatal Application for the treatment of all forms of respiratory failure. • Approved in 1995 for Pediatric Application, with no upper “weight limit”. For treating selected patients failing conventional ventilation. VIASYS Healthcare, Inc.
 Theory of Operation • Oxygenation is primarily controlled by the Mean Airway Pressure (Paw) and the Fi. O 2 • Ventilation is primarily determined by the stroke volume (Delta-P) and the frequency of the ventilator. VIASYS Healthcare, Inc.
Theory of Operation • Oxygenation is primarily controlled by the Mean Airway Pressure (Paw) and the Fi. O 2 • Ventilation is primarily determined by the stroke volume (Delta-P) and the frequency of the ventilator. VIASYS Healthcare, Inc.
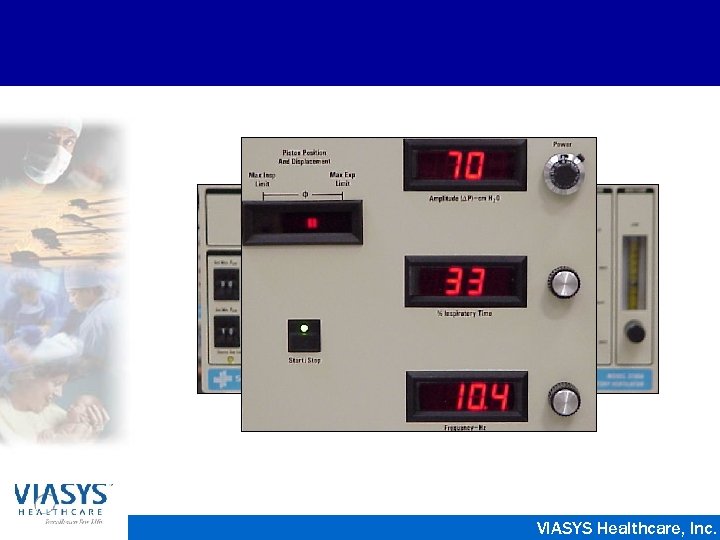
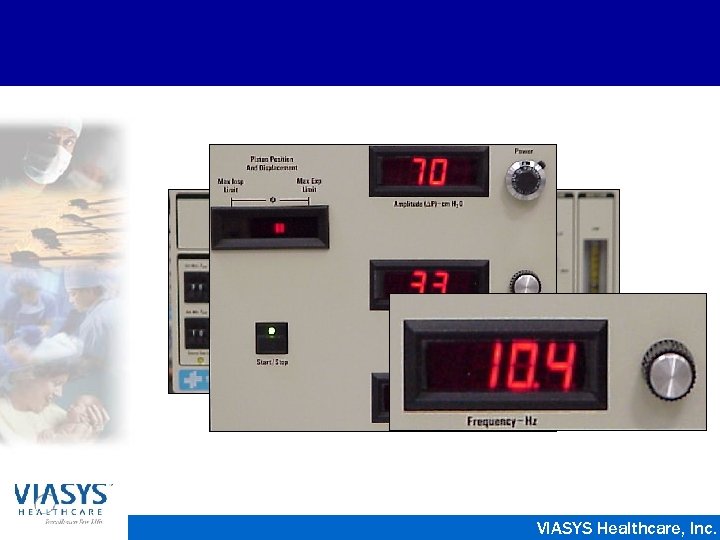
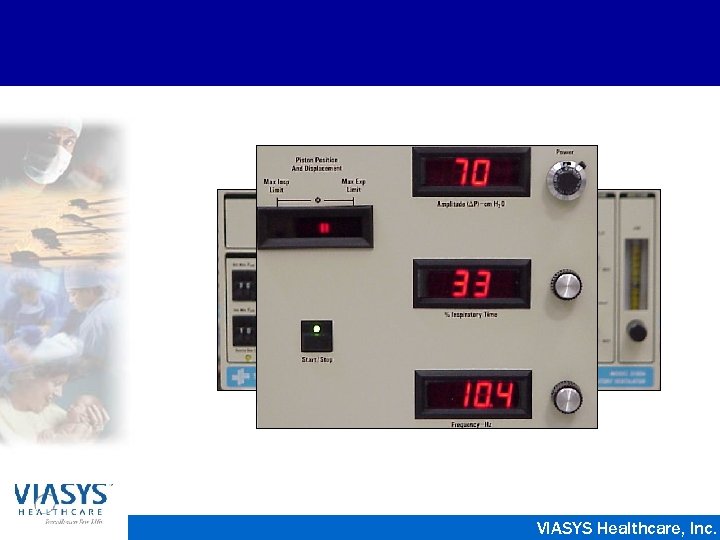
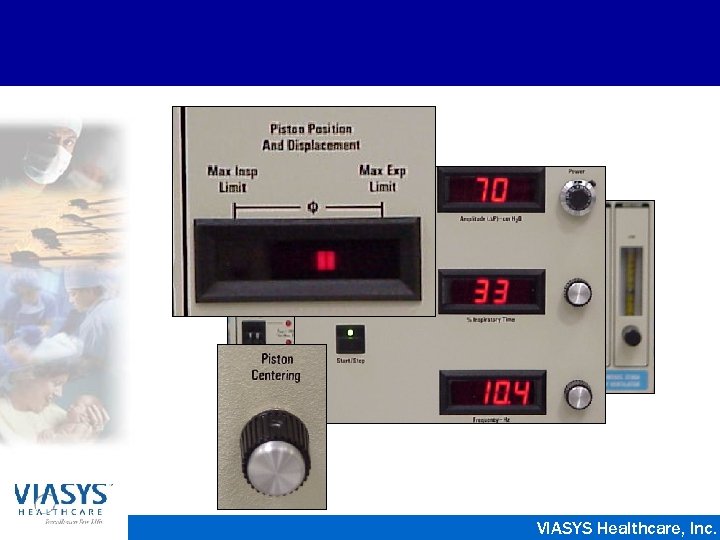
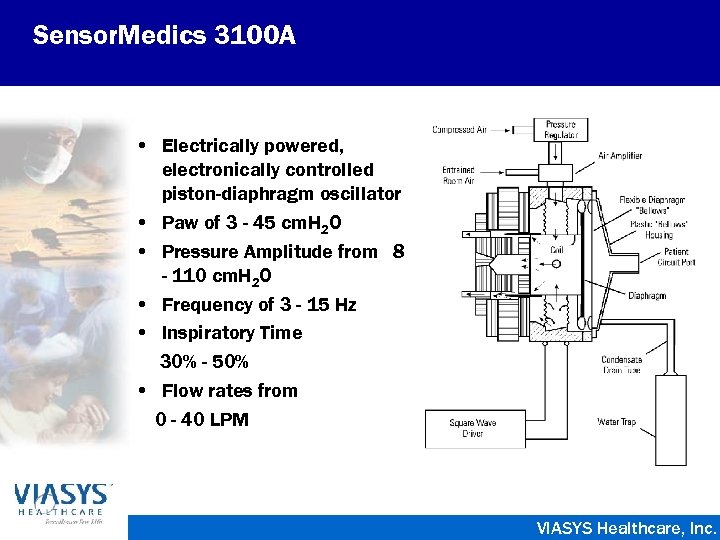 Sensor. Medics 3100 A • Electrically powered, electronically controlled piston-diaphragm oscillator • Paw of 3 - 45 cm. H 2 O • Pressure Amplitude from 8 - 110 cm. H 2 O • Frequency of 3 - 15 Hz • Inspiratory Time 30% - 50% • Flow rates from 0 - 40 LPM VIASYS Healthcare, Inc.
Sensor. Medics 3100 A • Electrically powered, electronically controlled piston-diaphragm oscillator • Paw of 3 - 45 cm. H 2 O • Pressure Amplitude from 8 - 110 cm. H 2 O • Frequency of 3 - 15 Hz • Inspiratory Time 30% - 50% • Flow rates from 0 - 40 LPM VIASYS Healthcare, Inc.
 Paw is created by a continuous bias flow of gas past the resistance (inflation) of the balloon on the mean airway pressure control valve. VIASYS Healthcare, Inc.
Paw is created by a continuous bias flow of gas past the resistance (inflation) of the balloon on the mean airway pressure control valve. VIASYS Healthcare, Inc.
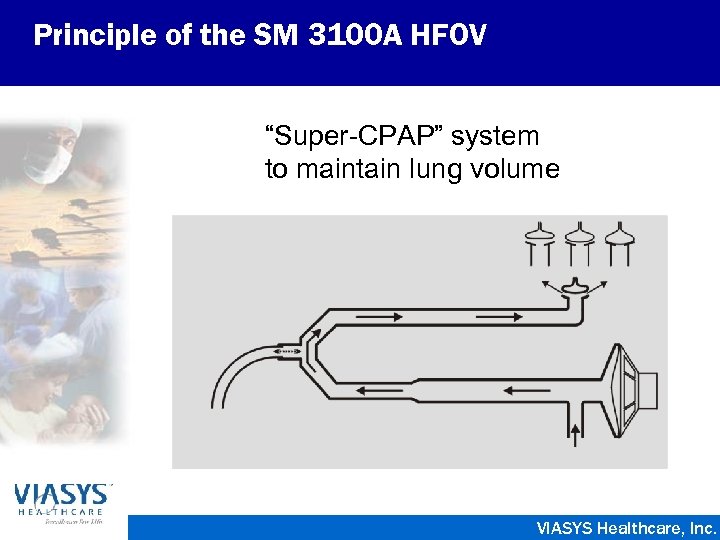 Principle of the SM 3100 A HFOV “Super-CPAP” system to maintain lung volume VIASYS Healthcare, Inc.
Principle of the SM 3100 A HFOV “Super-CPAP” system to maintain lung volume VIASYS Healthcare, Inc.
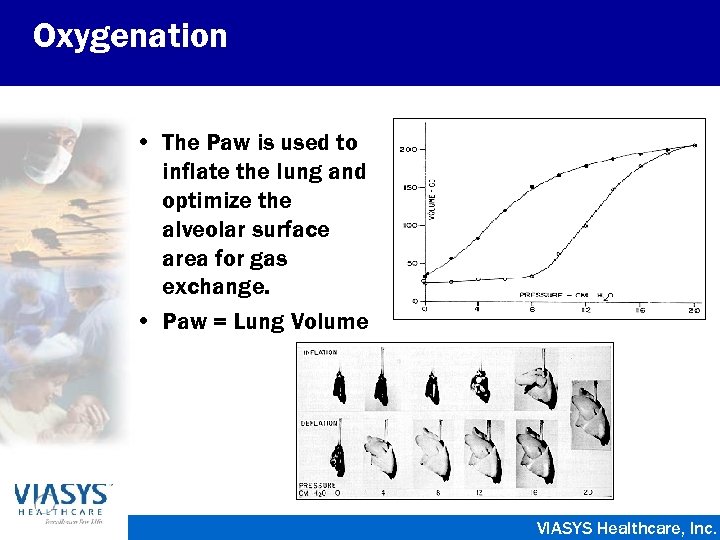 Oxygenation • The Paw is used to inflate the lung and optimize the alveolar surface area for gas exchange. • Paw = Lung Volume VIASYS Healthcare, Inc.
Oxygenation • The Paw is used to inflate the lung and optimize the alveolar surface area for gas exchange. • Paw = Lung Volume VIASYS Healthcare, Inc.
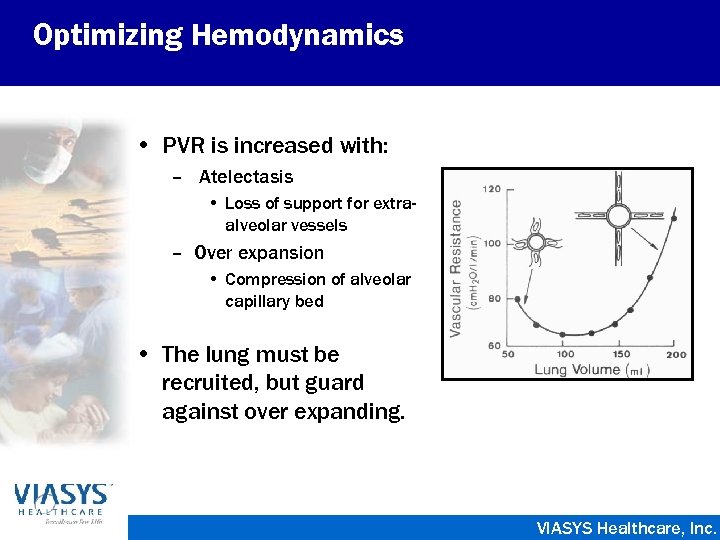 Optimizing Hemodynamics • PVR is increased with: – Atelectasis • Loss of support for extraalveolar vessels – Over expansion • Compression of alveolar capillary bed • The lung must be recruited, but guard against over expanding. VIASYS Healthcare, Inc.
Optimizing Hemodynamics • PVR is increased with: – Atelectasis • Loss of support for extraalveolar vessels – Over expansion • Compression of alveolar capillary bed • The lung must be recruited, but guard against over expanding. VIASYS Healthcare, Inc.
 Ventilation VIASYS Healthcare, Inc.
Ventilation VIASYS Healthcare, Inc.
 Primary control of CO 2 is by the stroke volume produced by the Power Setting. VIASYS Healthcare, Inc.
Primary control of CO 2 is by the stroke volume produced by the Power Setting. VIASYS Healthcare, Inc.
 Alveolar ventilation during CMV is defined as F x Vt Alveolar Ventilation during HFV is defined as F x Vt 2 Therefore, changes in volume delivery (as a function of Delta-P, Freq. , or % Insp. Time) have the most significant affect on CO 2 elimination VIASYS Healthcare, Inc.
Alveolar ventilation during CMV is defined as F x Vt Alveolar Ventilation during HFV is defined as F x Vt 2 Therefore, changes in volume delivery (as a function of Delta-P, Freq. , or % Insp. Time) have the most significant affect on CO 2 elimination VIASYS Healthcare, Inc.
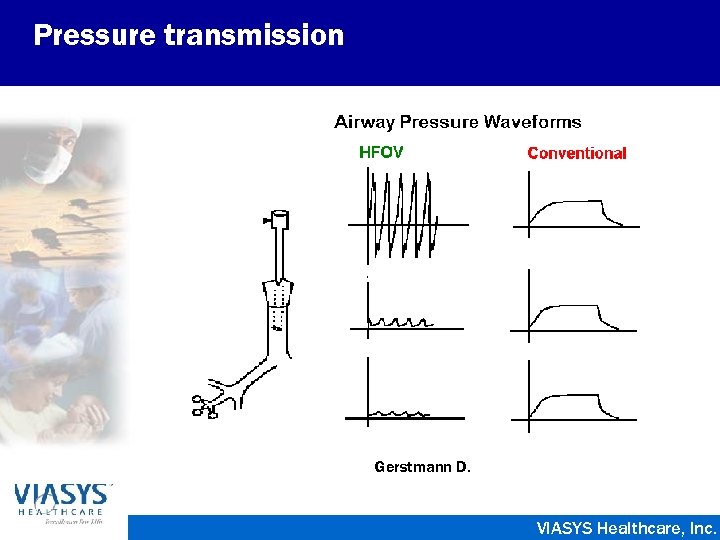 Pressure transmission Gerstmann D. VIASYS Healthcare, Inc.
Pressure transmission Gerstmann D. VIASYS Healthcare, Inc.
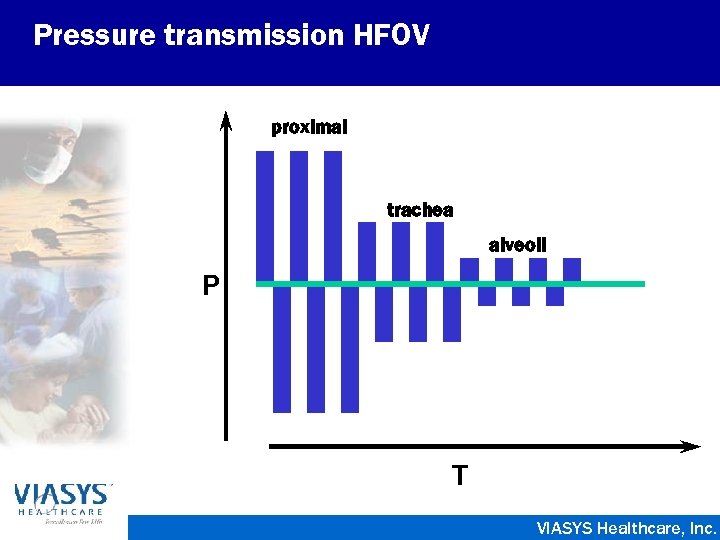 Pressure transmission HFOV proximal trachea alveoli P T VIASYS Healthcare, Inc.
Pressure transmission HFOV proximal trachea alveoli P T VIASYS Healthcare, Inc.
 Secondary control of Pa. CO 2 is the set Frequency. VIASYS Healthcare, Inc.
Secondary control of Pa. CO 2 is the set Frequency. VIASYS Healthcare, Inc.
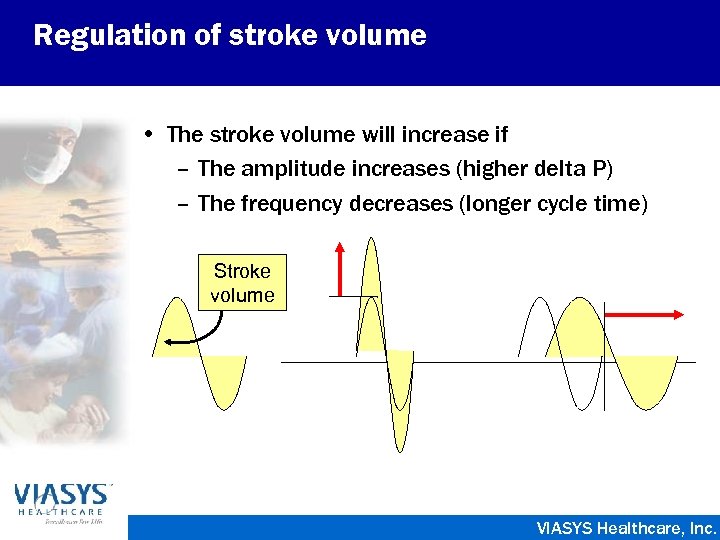 Regulation of stroke volume • The stroke volume will increase if – The amplitude increases (higher delta P) – The frequency decreases (longer cycle time) Stroke volume VIASYS Healthcare, Inc.
Regulation of stroke volume • The stroke volume will increase if – The amplitude increases (higher delta P) – The frequency decreases (longer cycle time) Stroke volume VIASYS Healthcare, Inc.
 • The % Inspiratory Time controls the time for piston displacement, controlling CO 2 elimination. • Increasing % Inspiratory Time will also affect lung recruitment by increasing delivered Paw. VIASYS Healthcare, Inc.
• The % Inspiratory Time controls the time for piston displacement, controlling CO 2 elimination. • Increasing % Inspiratory Time will also affect lung recruitment by increasing delivered Paw. VIASYS Healthcare, Inc.
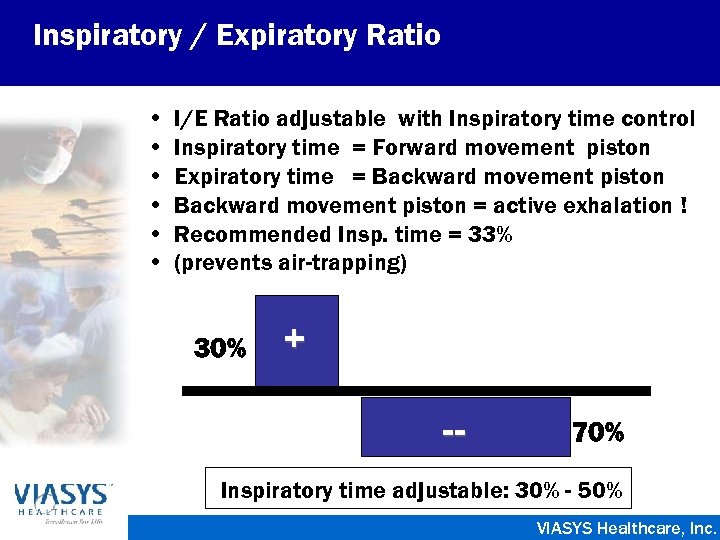 Inspiratory / Expiratory Ratio • • • I/E Ratio adjustable with Inspiratory time control Inspiratory time = Forward movement piston Expiratory time = Backward movement piston = active exhalation ! Recommended Insp. time = 33% (prevents air-trapping) 30% + -- 70% Inspiratory time adjustable: 30% - 50% VIASYS Healthcare, Inc.
Inspiratory / Expiratory Ratio • • • I/E Ratio adjustable with Inspiratory time control Inspiratory time = Forward movement piston Expiratory time = Backward movement piston = active exhalation ! Recommended Insp. time = 33% (prevents air-trapping) 30% + -- 70% Inspiratory time adjustable: 30% - 50% VIASYS Healthcare, Inc.
 VIASYS Healthcare, Inc.
VIASYS Healthcare, Inc.
 VIASYS Healthcare, Inc.
VIASYS Healthcare, Inc.
 VIASYS Healthcare, Inc.
VIASYS Healthcare, Inc.
 VIASYS Healthcare, Inc.
VIASYS Healthcare, Inc.
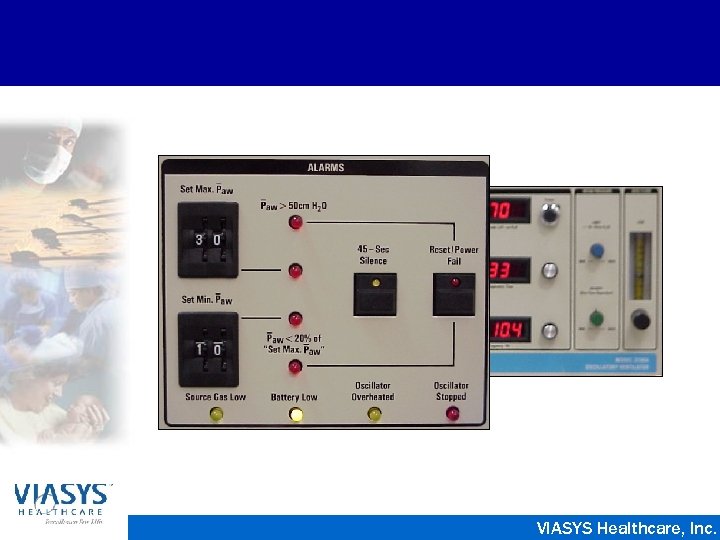 VIASYS Healthcare, Inc.
VIASYS Healthcare, Inc.
 Patient Circuit Calibration VIASYS Healthcare, Inc.
Patient Circuit Calibration VIASYS Healthcare, Inc.
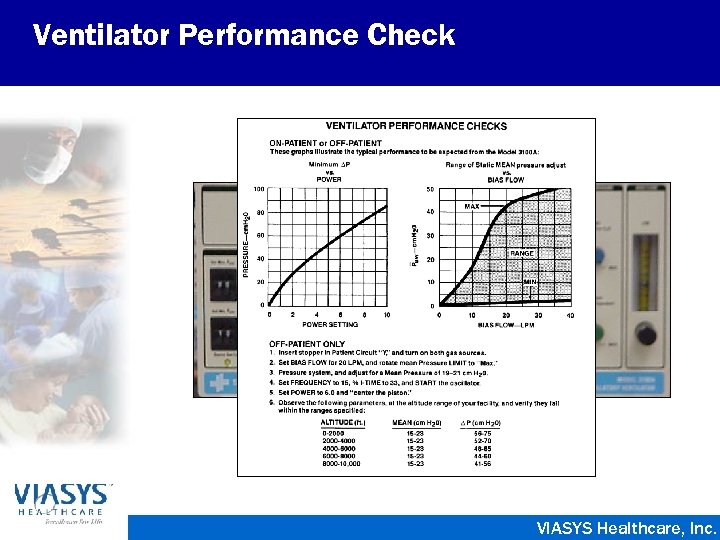 Ventilator Performance Check VIASYS Healthcare, Inc.
Ventilator Performance Check VIASYS Healthcare, Inc.


