7f7e78e13761d1496e9c16c60ead9d72.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 36
 31. Images & Optical Instruments 1. 2. 3. 4. Images with Mirrors Images with Lens Refraction in Lenses: The Details Optical Instruments
31. Images & Optical Instruments 1. 2. 3. 4. Images with Mirrors Images with Lens Refraction in Lenses: The Details Optical Instruments
 How does laser surgery provide permanent vision correction? Ans: Laser light reshapes cornea to adjust the focal point.
How does laser surgery provide permanent vision correction? Ans: Laser light reshapes cornea to adjust the focal point.
 Light ray = line (or curve) wave front. Geometrical (or ray) optics: Light ray in homegeneous medium = straight line. Valid when L >> . Real image: image location is the point of convergence of actual light rays. Can be shown on screen. Virtual image: some or all of the light rays that converge to form the image are virtual (straight line extension of the actual rays). Can’t be shown on screen.
Light ray = line (or curve) wave front. Geometrical (or ray) optics: Light ray in homegeneous medium = straight line. Valid when L >> . Real image: image location is the point of convergence of actual light rays. Can be shown on screen. Virtual image: some or all of the light rays that converge to form the image are virtual (straight line extension of the actual rays). Can’t be shown on screen.
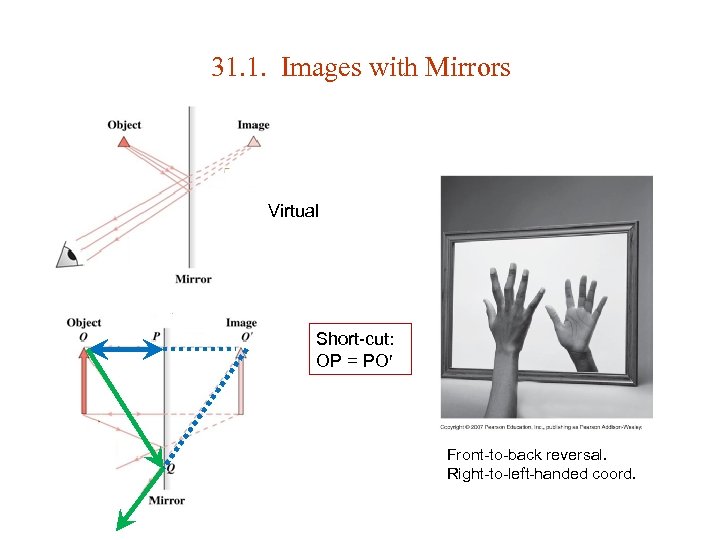 31. 1. Images with Mirrors Virtual Short-cut: OP = PO Front-to-back reversal. Right-to-left-handed coord.
31. 1. Images with Mirrors Virtual Short-cut: OP = PO Front-to-back reversal. Right-to-left-handed coord.
 GOT IT? 31. 1. You stand in front of a plane mirror whose top is at the same height as the top of your head. Approximately how far down must the mirror extend for you to see your full image? Ans. Half your height.
GOT IT? 31. 1. You stand in front of a plane mirror whose top is at the same height as the top of your head. Approximately how far down must the mirror extend for you to see your full image? Ans. Half your height.
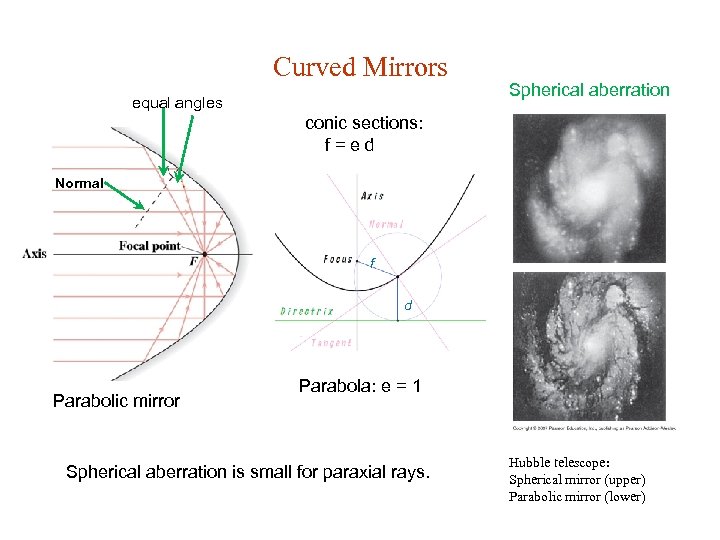 Curved Mirrors equal angles Spherical aberration conic sections: f=ed Normal f d Parabolic mirror Parabola: e = 1 Spherical aberration is small for paraxial rays. Hubble telescope: Spherical mirror (upper) Parabolic mirror (lower)
Curved Mirrors equal angles Spherical aberration conic sections: f=ed Normal f d Parabolic mirror Parabola: e = 1 Spherical aberration is small for paraxial rays. Hubble telescope: Spherical mirror (upper) Parabolic mirror (lower)
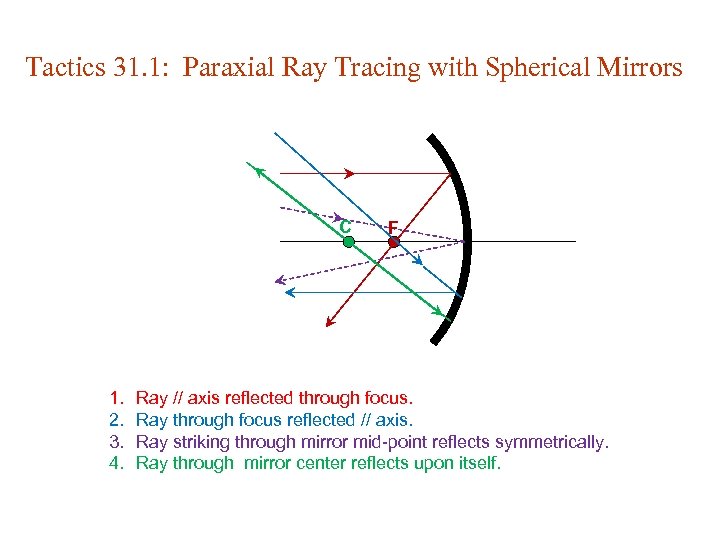 Tactics 31. 1: Paraxial Ray Tracing with Spherical Mirrors C 1. 2. 3. 4. F Ray // axis reflected through focus. Ray through focus reflected // axis. Ray striking through mirror mid-point reflects symmetrically. Ray through mirror center reflects upon itself.
Tactics 31. 1: Paraxial Ray Tracing with Spherical Mirrors C 1. 2. 3. 4. F Ray // axis reflected through focus. Ray through focus reflected // axis. Ray striking through mirror mid-point reflects symmetrically. Ray through mirror center reflects upon itself.
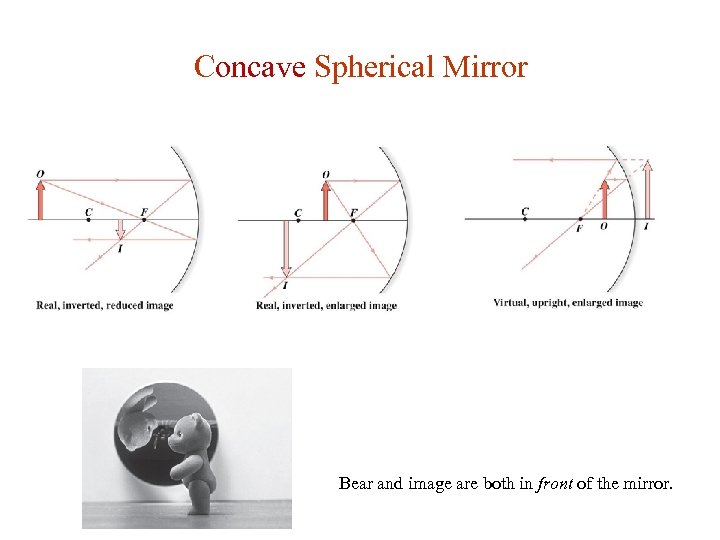 Concave Spherical Mirror Bear and image are both in front of the mirror.
Concave Spherical Mirror Bear and image are both in front of the mirror.
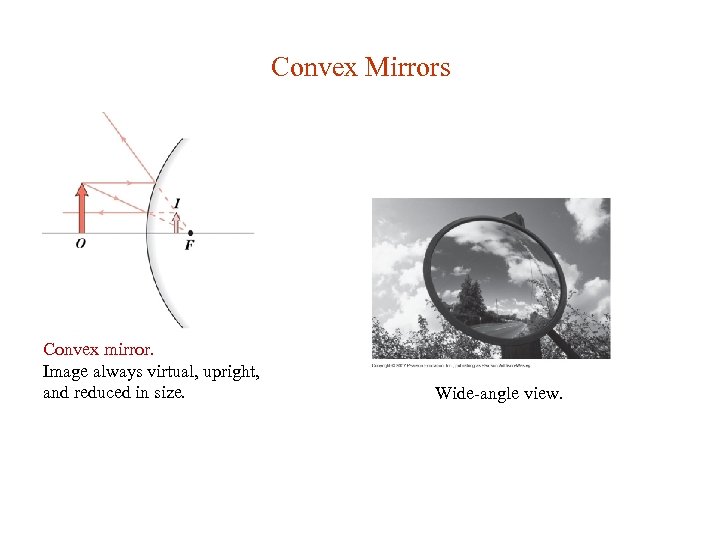 Convex Mirrors Convex mirror. Image always virtual, upright, and reduced in size. Wide-angle view.
Convex Mirrors Convex mirror. Image always virtual, upright, and reduced in size. Wide-angle view.
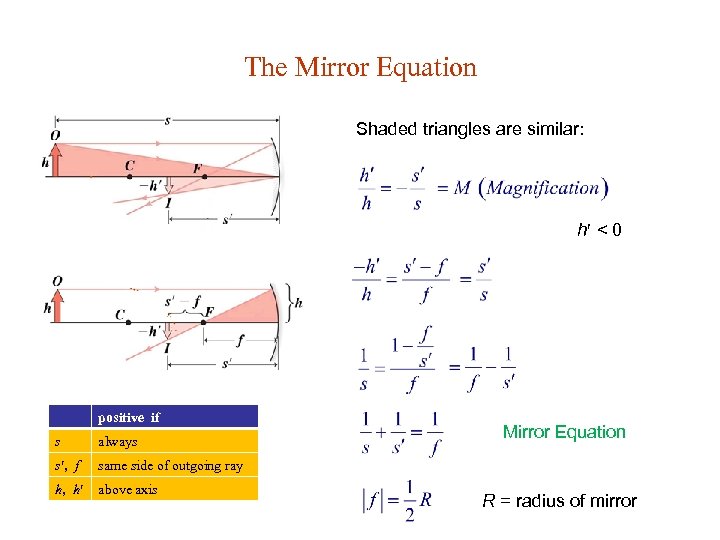 The Mirror Equation Shaded triangles are similar: h < 0 positive if s always s , f same side of outgoing ray h, h above axis Mirror Equation R = radius of mirror
The Mirror Equation Shaded triangles are similar: h < 0 positive if s always s , f same side of outgoing ray h, h above axis Mirror Equation R = radius of mirror
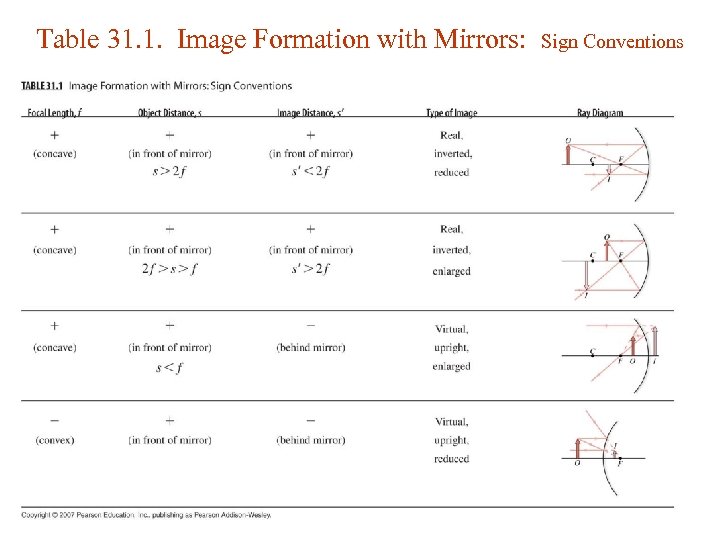 Table 31. 1. Image Formation with Mirrors: Sign Conventions
Table 31. 1. Image Formation with Mirrors: Sign Conventions
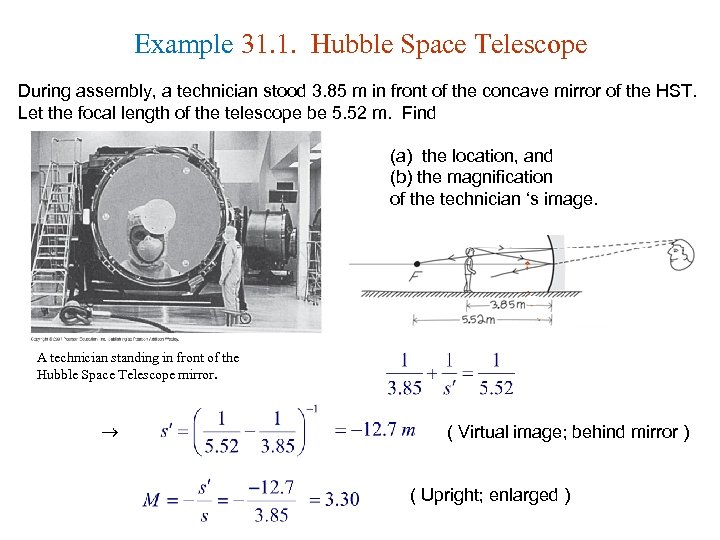 Example 31. 1. Hubble Space Telescope During assembly, a technician stood 3. 85 m in front of the concave mirror of the HST. Let the focal length of the telescope be 5. 52 m. Find (a) the location, and (b) the magnification of the technician ‘s image. A technician standing in front of the Hubble Space Telescope mirror. ( Virtual image; behind mirror ) ( Upright; enlarged )
Example 31. 1. Hubble Space Telescope During assembly, a technician stood 3. 85 m in front of the concave mirror of the HST. Let the focal length of the telescope be 5. 52 m. Find (a) the location, and (b) the magnification of the technician ‘s image. A technician standing in front of the Hubble Space Telescope mirror. ( Virtual image; behind mirror ) ( Upright; enlarged )
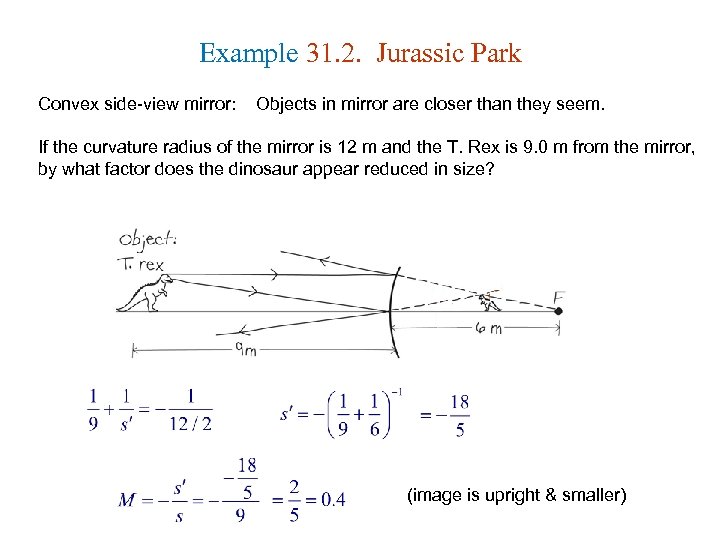 Example 31. 2. Jurassic Park Convex side-view mirror: Objects in mirror are closer than they seem. If the curvature radius of the mirror is 12 m and the T. Rex is 9. 0 m from the mirror, by what factor does the dinosaur appear reduced in size? (image is upright & smaller)
Example 31. 2. Jurassic Park Convex side-view mirror: Objects in mirror are closer than they seem. If the curvature radius of the mirror is 12 m and the T. Rex is 9. 0 m from the mirror, by what factor does the dinosaur appear reduced in size? (image is upright & smaller)
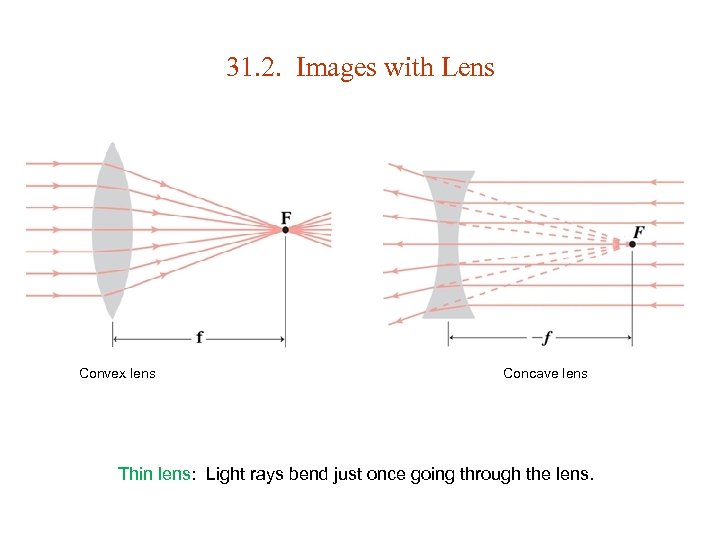 31. 2. Images with Lens Convex lens Concave lens Thin lens: Light rays bend just once going through the lens.
31. 2. Images with Lens Convex lens Concave lens Thin lens: Light rays bend just once going through the lens.
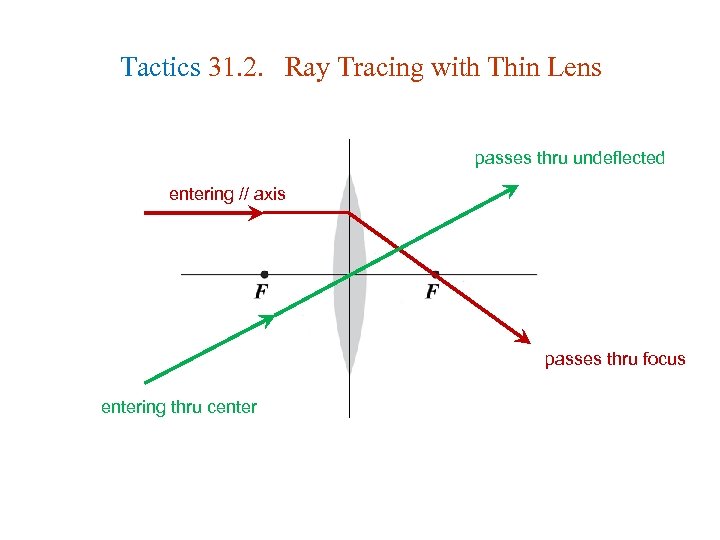 Tactics 31. 2. Ray Tracing with Thin Lens passes thru undeflected entering // axis passes thru focus entering thru center
Tactics 31. 2. Ray Tracing with Thin Lens passes thru undeflected entering // axis passes thru focus entering thru center
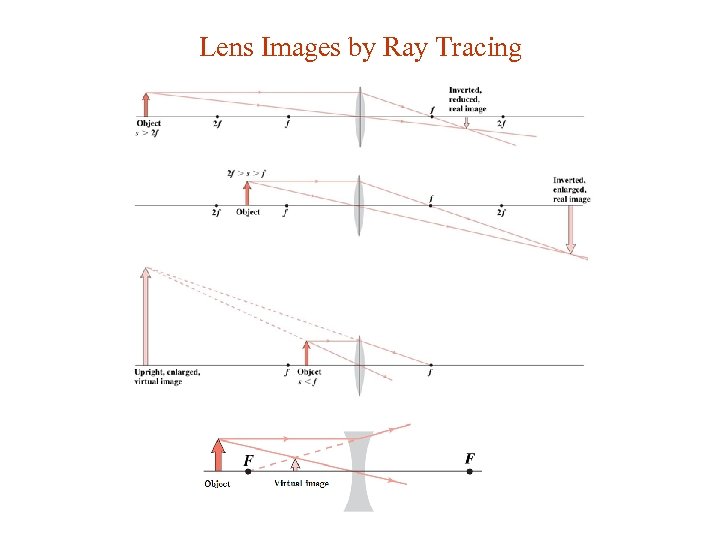 Lens Images by Ray Tracing
Lens Images by Ray Tracing
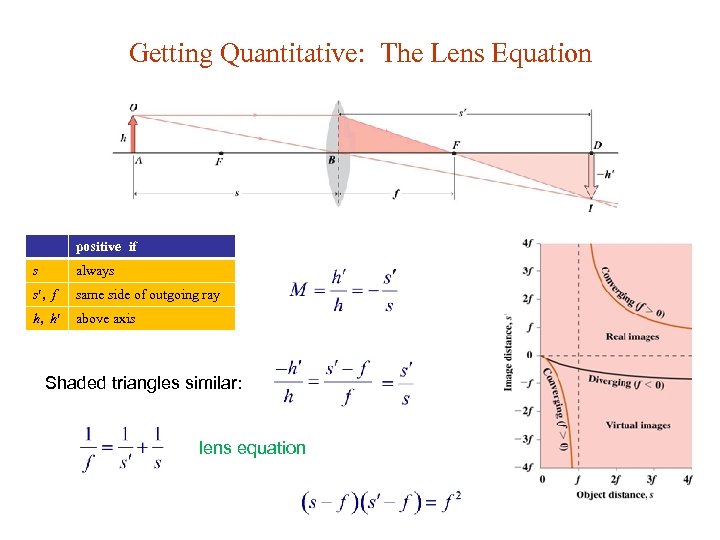 Getting Quantitative: The Lens Equation positive if s always s , f same side of outgoing ray h, h above axis Shaded triangles similar: lens equation
Getting Quantitative: The Lens Equation positive if s always s , f same side of outgoing ray h, h above axis Shaded triangles similar: lens equation
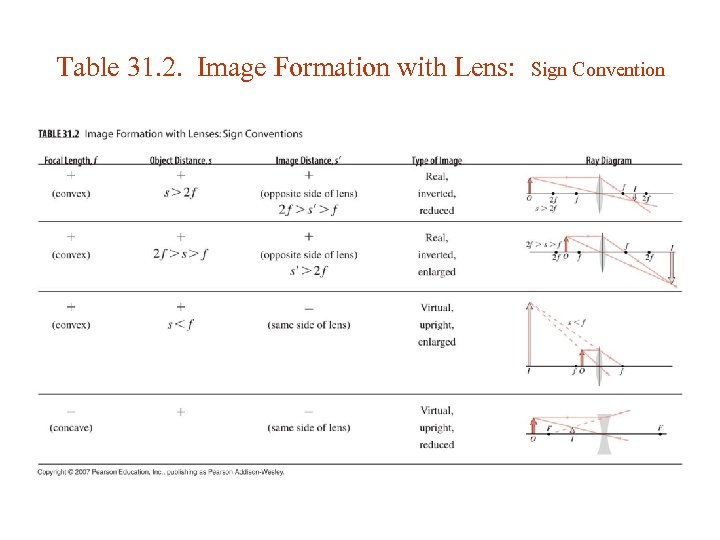 Table 31. 2. Image Formation with Lens: Sign Convention
Table 31. 2. Image Formation with Lens: Sign Convention
 GOT IT? . 31. 3. You look through a lens at this page and see the words enlarged and right-side up. Is the image you observe real or virtual? Is the lens concave or convex?
GOT IT? . 31. 3. You look through a lens at this page and see the words enlarged and right-side up. Is the image you observe real or virtual? Is the lens concave or convex?
 Example 31. 3. Fine Print You ‘re using a magnifying glass (converging lens) with a 30 -cm focal length to read a telephone book. How far from the page should you hold the lens in order to see the print enlarged three times? Image is upright enlarged so it must be virtual. Hence, h > 0, s < 0.
Example 31. 3. Fine Print You ‘re using a magnifying glass (converging lens) with a 30 -cm focal length to read a telephone book. How far from the page should you hold the lens in order to see the print enlarged three times? Image is upright enlarged so it must be virtual. Hence, h > 0, s < 0.
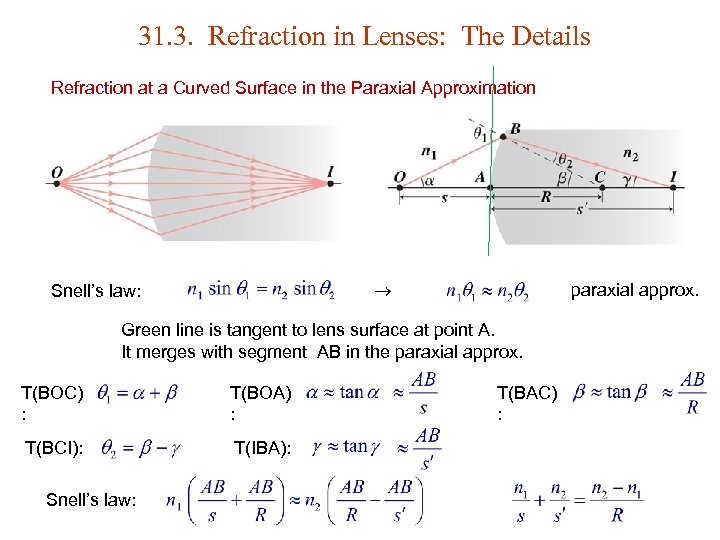 31. 3. Refraction in Lenses: The Details Refraction at a Curved Surface in the Paraxial Approximation Snell’s law: paraxial approx. Green line is tangent to lens surface at point A. It merges with segment AB in the paraxial approx. T(BOC) : T(BOA) : T(BCI): T(IBA): Snell’s law: T(BAC) :
31. 3. Refraction in Lenses: The Details Refraction at a Curved Surface in the Paraxial Approximation Snell’s law: paraxial approx. Green line is tangent to lens surface at point A. It merges with segment AB in the paraxial approx. T(BOC) : T(BOA) : T(BCI): T(IBA): Snell’s law: T(BAC) :
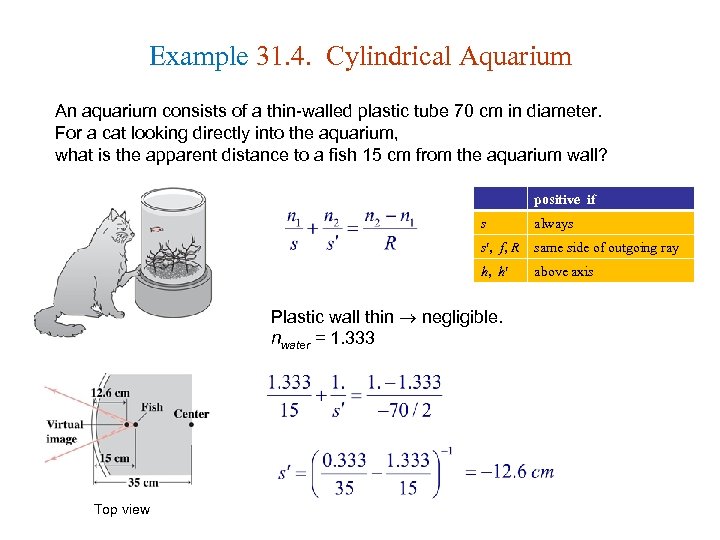 Example 31. 4. Cylindrical Aquarium An aquarium consists of a thin-walled plastic tube 70 cm in diameter. For a cat looking directly into the aquarium, what is the apparent distance to a fish 15 cm from the aquarium wall? positive if s always s , f, R same side of outgoing ray h, h above axis Plastic wall thin negligible. nwater = 1. 333 Top view
Example 31. 4. Cylindrical Aquarium An aquarium consists of a thin-walled plastic tube 70 cm in diameter. For a cat looking directly into the aquarium, what is the apparent distance to a fish 15 cm from the aquarium wall? positive if s always s , f, R same side of outgoing ray h, h above axis Plastic wall thin negligible. nwater = 1. 333 Top view
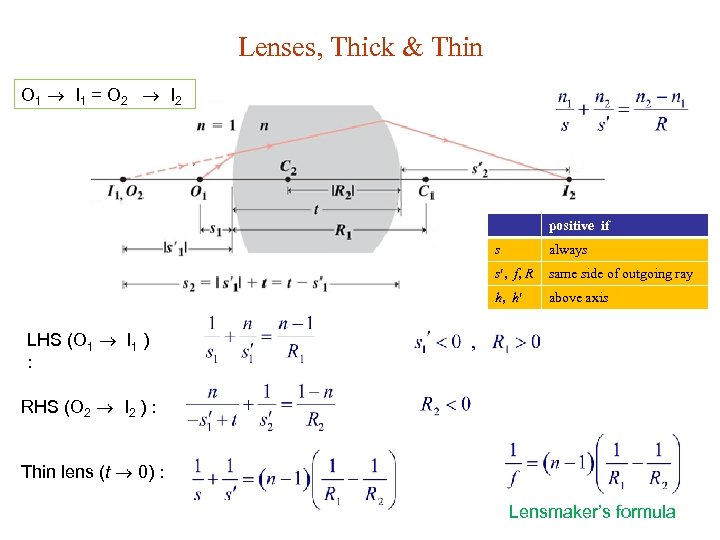 Lenses, Thick & Thin O 1 I 1 = O 2 I 2 positive if s always s , f, R same side of outgoing ray h, h above axis LHS (O 1 I 1 ) : RHS (O 2 I 2 ) : Thin lens (t 0) : Lensmaker’s formula
Lenses, Thick & Thin O 1 I 1 = O 2 I 2 positive if s always s , f, R same side of outgoing ray h, h above axis LHS (O 1 I 1 ) : RHS (O 2 I 2 ) : Thin lens (t 0) : Lensmaker’s formula
 Common Lens Types
Common Lens Types
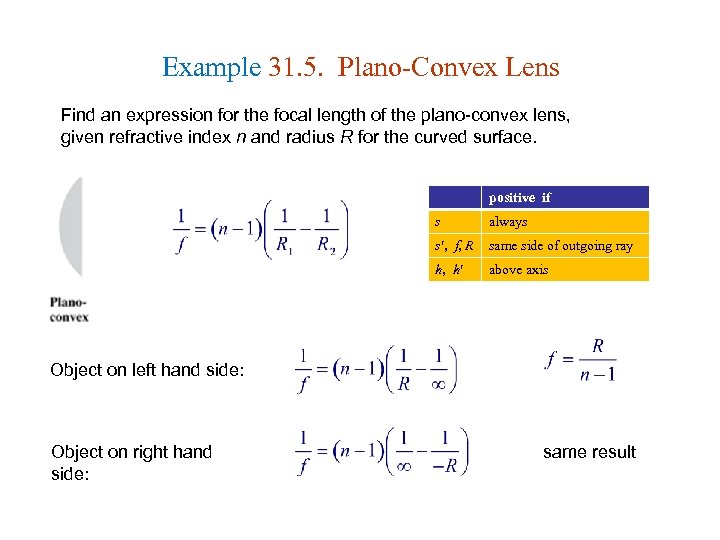 Example 31. 5. Plano-Convex Lens Find an expression for the focal length of the plano-convex lens, given refractive index n and radius R for the curved surface. positive if s always s , f, R same side of outgoing ray h, h above axis Object on left hand side: Object on right hand side: same result
Example 31. 5. Plano-Convex Lens Find an expression for the focal length of the plano-convex lens, given refractive index n and radius R for the curved surface. positive if s always s , f, R same side of outgoing ray h, h above axis Object on left hand side: Object on right hand side: same result
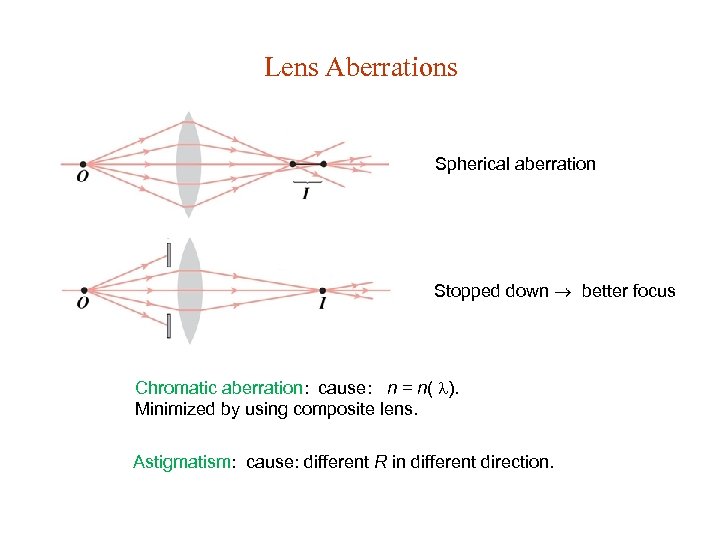 Lens Aberrations Spherical aberration Stopped down better focus Chromatic aberration: cause: n = n( ). Minimized by using composite lens. Astigmatism: cause: different R in different direction.
Lens Aberrations Spherical aberration Stopped down better focus Chromatic aberration: cause: n = n( ). Minimized by using composite lens. Astigmatism: cause: different R in different direction.
![31. 4. Optical Instruments The Eye Corrective power P = 1 / f. [P] 31. 4. Optical Instruments The Eye Corrective power P = 1 / f. [P]](https://present5.com/presentation/7f7e78e13761d1496e9c16c60ead9d72/image-27.jpg) 31. 4. Optical Instruments The Eye Corrective power P = 1 / f. [P] = diopter = m 1 Myopic (nearsighted) Corrective: Divergent lens. Hyperopic (farsighted) Corrective: Convergent lens.
31. 4. Optical Instruments The Eye Corrective power P = 1 / f. [P] = diopter = m 1 Myopic (nearsighted) Corrective: Divergent lens. Hyperopic (farsighted) Corrective: Convergent lens.
 Application: Laser Vision Correction LASIK procedure
Application: Laser Vision Correction LASIK procedure
 Conceptual Example 31. 6. Contact Lens Mix-Up You and your roommate have gotten your boxes of disposable contact lenses mixed up. One box is marked “ 1. 75 diopter”, the other “+2. 5 diopter”. You are farsighted and your roommate is nearsighted. Which lenses are yours? Converging lens correct far-sightedness. f >0 P=1/f >0
Conceptual Example 31. 6. Contact Lens Mix-Up You and your roommate have gotten your boxes of disposable contact lenses mixed up. One box is marked “ 1. 75 diopter”, the other “+2. 5 diopter”. You are farsighted and your roommate is nearsighted. Which lenses are yours? Converging lens correct far-sightedness. f >0 P=1/f >0
 Making the Connection What’s the focal length of your contact?
Making the Connection What’s the focal length of your contact?
 Example 31. 6. Lost Your Glasses! You’ve lost your reading glasses; without them, your eyes can’t focus closer than 70 cm. Nonprescription reading glasses come in 0. 25 -diopter increments. Which glasses should you buy so you can focus at the standard 25 -cm near point? Aim: make object at 25 cm appears to be at 70 cm. i. e. , s = 25 cm , s = 70 cm. Ans: buy glasses with P = 2. 5 diopters
Example 31. 6. Lost Your Glasses! You’ve lost your reading glasses; without them, your eyes can’t focus closer than 70 cm. Nonprescription reading glasses come in 0. 25 -diopter increments. Which glasses should you buy so you can focus at the standard 25 -cm near point? Aim: make object at 25 cm appears to be at 70 cm. i. e. , s = 25 cm , s = 70 cm. Ans: buy glasses with P = 2. 5 diopters
 Cameras Works like the eye.
Cameras Works like the eye.
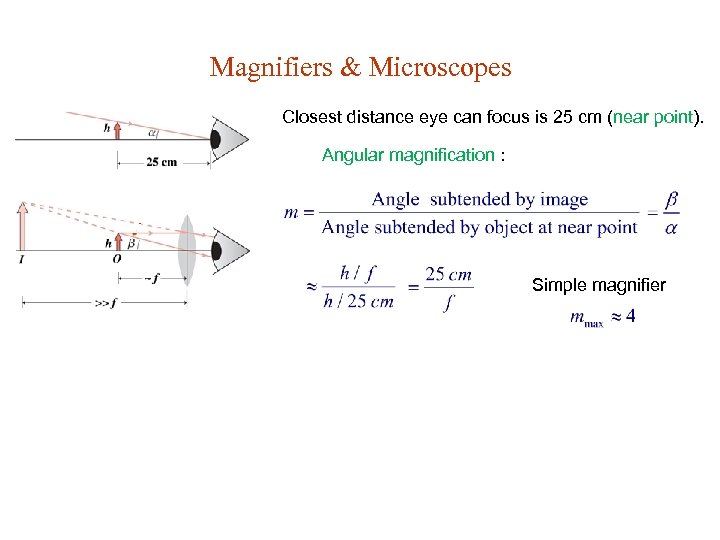 Magnifiers & Microscopes Closest distance eye can focus is 25 cm (near point). Angular magnification : Simple magnifier
Magnifiers & Microscopes Closest distance eye can focus is 25 cm (near point). Angular magnification : Simple magnifier
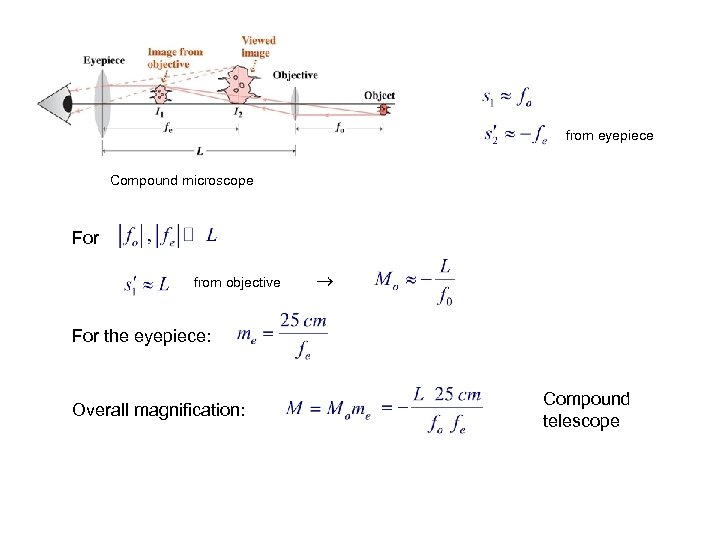 from eyepiece Compound microscope For from objective For the eyepiece: Overall magnification: Compound telescope
from eyepiece Compound microscope For from objective For the eyepiece: Overall magnification: Compound telescope
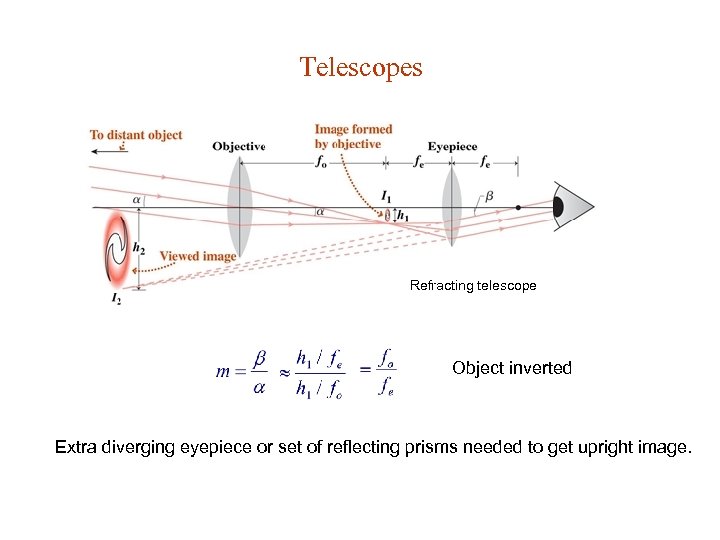 Telescopes Refracting telescope Object inverted Extra diverging eyepiece or set of reflecting prisms needed to get upright image.
Telescopes Refracting telescope Object inverted Extra diverging eyepiece or set of reflecting prisms needed to get upright image.
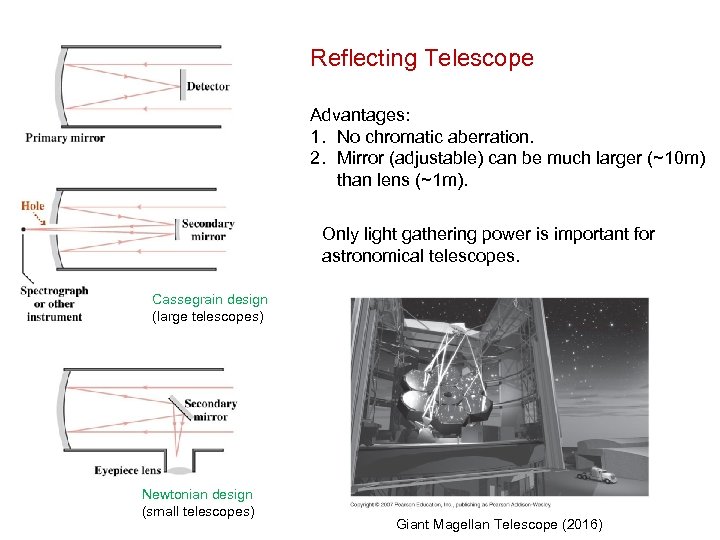 Reflecting Telescope Advantages: 1. No chromatic aberration. 2. Mirror (adjustable) can be much larger (~10 m) than lens (~1 m). Only light gathering power is important for astronomical telescopes. Cassegrain design (large telescopes) Newtonian design (small telescopes) Giant Magellan Telescope (2016)
Reflecting Telescope Advantages: 1. No chromatic aberration. 2. Mirror (adjustable) can be much larger (~10 m) than lens (~1 m). Only light gathering power is important for astronomical telescopes. Cassegrain design (large telescopes) Newtonian design (small telescopes) Giant Magellan Telescope (2016)


