760791aff656857823f4721be52d8d61.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 11
 3. USA, 1918 -1968 5 essays to learn BUT only 1 to write in the exam
3. USA, 1918 -1968 5 essays to learn BUT only 1 to write in the exam
 General Introduction: During the 1920 s there was a prolonged boom in the American economy: Industrial production doubled, the economy grew rapidly and fortunes were made Life had never seemed better for the majority of the American people However on Thursday, 24 th October 1929 share prices on the New York Stock Exchange on Wall Street fell faster and lower than before By the end of the day, $4 billion had been wiped off the value of shares The crisis continued until ‘Black Tuesday’ 29 th October when share prices fell by a further $14 billion WHY? ? ?
General Introduction: During the 1920 s there was a prolonged boom in the American economy: Industrial production doubled, the economy grew rapidly and fortunes were made Life had never seemed better for the majority of the American people However on Thursday, 24 th October 1929 share prices on the New York Stock Exchange on Wall Street fell faster and lower than before By the end of the day, $4 billion had been wiped off the value of shares The crisis continued until ‘Black Tuesday’ 29 th October when share prices fell by a further $14 billion WHY? ? ?
 Issue 3 An Evaluation Of The Reasons For The Economic Crisis 1929 -33: Factor 1: Republican Governments Policies Factor 2: Overproduction & Under -consumption Factor 3: Weaknesses Of The Banking System Factor 4: International Economic Problems Factor 5: Wall Street Crash AIMS OF ESSAY: To Be Able To Discuss the factors which contributed to the economic (financial) crisis in American between 1929 & 1933
Issue 3 An Evaluation Of The Reasons For The Economic Crisis 1929 -33: Factor 1: Republican Governments Policies Factor 2: Overproduction & Under -consumption Factor 3: Weaknesses Of The Banking System Factor 4: International Economic Problems Factor 5: Wall Street Crash AIMS OF ESSAY: To Be Able To Discuss the factors which contributed to the economic (financial) crisis in American between 1929 & 1933
 PAST EXAM QUESTIONS • How far can the Wall Street Crash of 1929 be blamed for the economic crisis of 1929– 1933 in America? (FACTOR 5 – old higher 2015) • To what extent was the saturation of the US market to blame for the economic crisis of 1929– 1933? (FACTOR 2 - 2014) • “The weakness of the US banking system was the main reason for causing the Great Depression of the 1930 s. ” How accurate is this statement? (FACTOR 3 - 2011)
PAST EXAM QUESTIONS • How far can the Wall Street Crash of 1929 be blamed for the economic crisis of 1929– 1933 in America? (FACTOR 5 – old higher 2015) • To what extent was the saturation of the US market to blame for the economic crisis of 1929– 1933? (FACTOR 2 - 2014) • “The weakness of the US banking system was the main reason for causing the Great Depression of the 1930 s. ” How accurate is this statement? (FACTOR 3 - 2011)
 How Bad Was This Crisis? Unemployment Rose From 3. 2% In 1929 To 25. 2% By 1933. This Meant That Nearly 13 Million Were Out Of Work. 20, 000 companies went bankrupt Marchers south on Broadway: typical scene reflecting large population of unemployed in desperate need of work and looking for jobs. (Circa 1935) Other sources say ONE THIRD of the workforce was unemployed
How Bad Was This Crisis? Unemployment Rose From 3. 2% In 1929 To 25. 2% By 1933. This Meant That Nearly 13 Million Were Out Of Work. 20, 000 companies went bankrupt Marchers south on Broadway: typical scene reflecting large population of unemployed in desperate need of work and looking for jobs. (Circa 1935) Other sources say ONE THIRD of the workforce was unemployed
 "Runs on Banks": people milling about outside of bank. (Circa 1933) Banks could not meet depositors’ demands for their money Old people were deprived of their pensions and robbed of their savings 10, 000 banks closed between 1929 and 1933
"Runs on Banks": people milling about outside of bank. (Circa 1933) Banks could not meet depositors’ demands for their money Old people were deprived of their pensions and robbed of their savings 10, 000 banks closed between 1929 and 1933
 Long line of people waiting to be fed in the absence of substantial government relief programs during 1932, free food was distributed with private funds in some urban centres to large numbers of the unemployed Unemployed men eating in Volunteers of America Soup Kitchen in Washington, D. C. (Circa June 1936)
Long line of people waiting to be fed in the absence of substantial government relief programs during 1932, free food was distributed with private funds in some urban centres to large numbers of the unemployed Unemployed men eating in Volunteers of America Soup Kitchen in Washington, D. C. (Circa June 1936)
 Homelessness Arkansas squatter for three years in California near Bakefield, California. (Circa 1935) Many Americans defaulted on mortgages and so their homes were repossessed.
Homelessness Arkansas squatter for three years in California near Bakefield, California. (Circa 1935) Many Americans defaulted on mortgages and so their homes were repossessed.
 An enduring image of the Great Depression: Destitute pea pickers in California. Mother of seven children. (Circa February 1936) During the Great Depression, people went hungry in one of the richest food producing countries in the world. Ill health due to inadequate healthcare, poor diet and malnutrition became common. Suicide rate rose and families broke up under the pressure of trying to survive.
An enduring image of the Great Depression: Destitute pea pickers in California. Mother of seven children. (Circa February 1936) During the Great Depression, people went hungry in one of the richest food producing countries in the world. Ill health due to inadequate healthcare, poor diet and malnutrition became common. Suicide rate rose and families broke up under the pressure of trying to survive.
 Families on the road with all their possessions packed into their trucks, migrating and looking for work. (Circa 1935)
Families on the road with all their possessions packed into their trucks, migrating and looking for work. (Circa 1935)
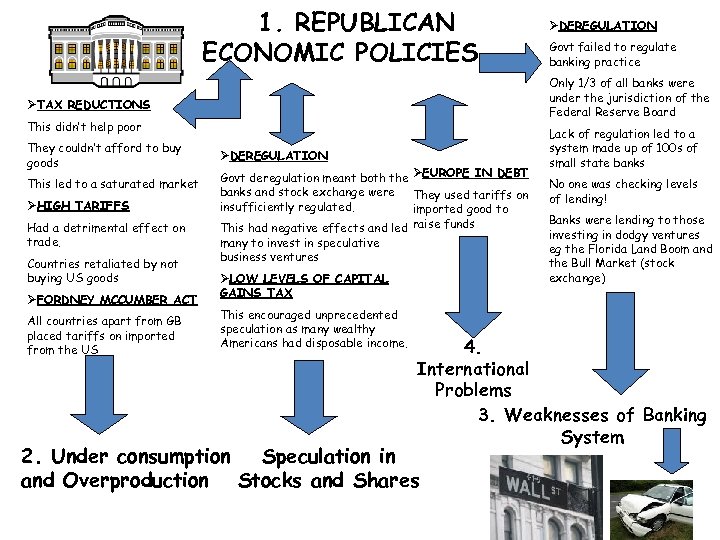 1. REPUBLICAN ECONOMIC POLICIES…… This didn’t help poor This led to a saturated market ØHIGH TARIFFS Had a detrimental effect on trade. Countries retaliated by not buying US goods ØFORDNEY MCCUMBER ACT All countries apart from GB placed tariffs on imported from the US Govt failed to regulate banking practice Only 1/3 of all banks were under the jurisdiction of the Federal Reserve Board ØTAX REDUCTIONS They couldn’t afford to buy goods ØDEREGULATION Govt deregulation meant both the ØEUROPE IN DEBT banks and stock exchange were They used tariffs on insufficiently regulated. imported good to This had negative effects and led raise funds many to invest in speculative business ventures ØLOW LEVELS OF CAPITAL GAINS TAX This encouraged unprecedented speculation as many wealthy Americans had disposable income. Lack of regulation led to a system made up of 100 s of small state banks No one was checking levels of lending! Banks were lending to those investing in dodgy ventures eg the Florida Land Boom and the Bull Market (stock exchange) 4. International Problems 3. Weaknesses of Banking System 2. Under consumption Speculation in and Overproduction Stocks and Shares
1. REPUBLICAN ECONOMIC POLICIES…… This didn’t help poor This led to a saturated market ØHIGH TARIFFS Had a detrimental effect on trade. Countries retaliated by not buying US goods ØFORDNEY MCCUMBER ACT All countries apart from GB placed tariffs on imported from the US Govt failed to regulate banking practice Only 1/3 of all banks were under the jurisdiction of the Federal Reserve Board ØTAX REDUCTIONS They couldn’t afford to buy goods ØDEREGULATION Govt deregulation meant both the ØEUROPE IN DEBT banks and stock exchange were They used tariffs on insufficiently regulated. imported good to This had negative effects and led raise funds many to invest in speculative business ventures ØLOW LEVELS OF CAPITAL GAINS TAX This encouraged unprecedented speculation as many wealthy Americans had disposable income. Lack of regulation led to a system made up of 100 s of small state banks No one was checking levels of lending! Banks were lending to those investing in dodgy ventures eg the Florida Land Boom and the Bull Market (stock exchange) 4. International Problems 3. Weaknesses of Banking System 2. Under consumption Speculation in and Overproduction Stocks and Shares


